Environmental Pressures at Dirre Sheikh Hussein Sanctuary
Abstract
:1. Introduction
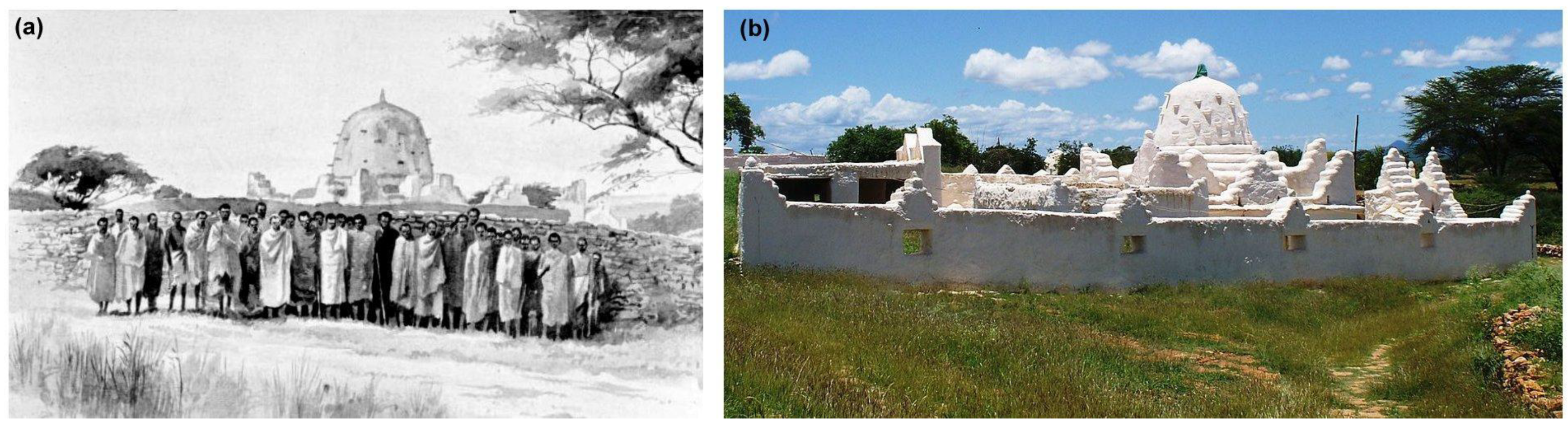
1.1. Cultural Site
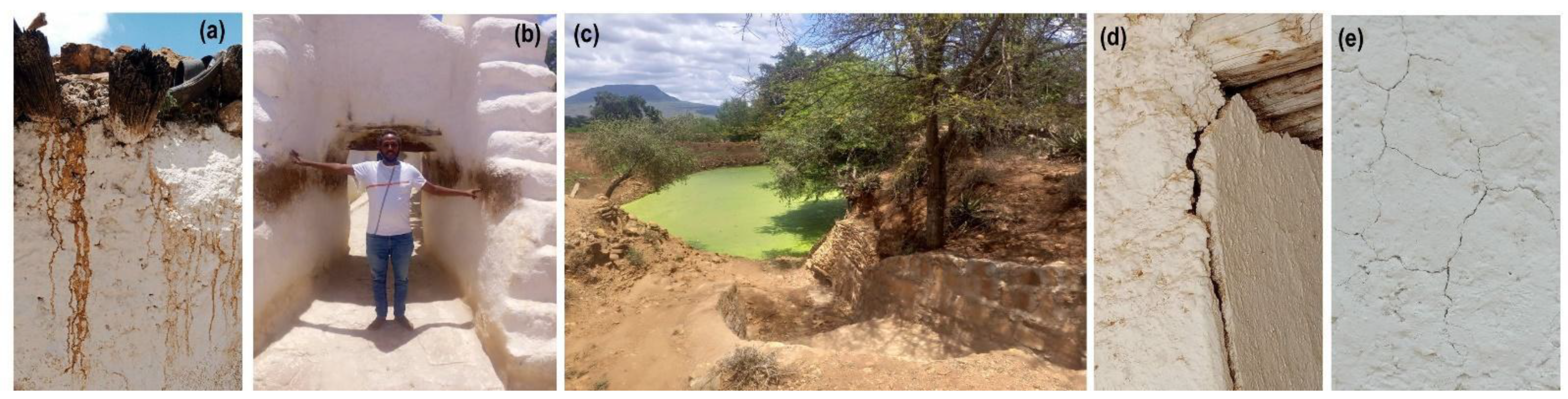
1.2. Structure and Condition
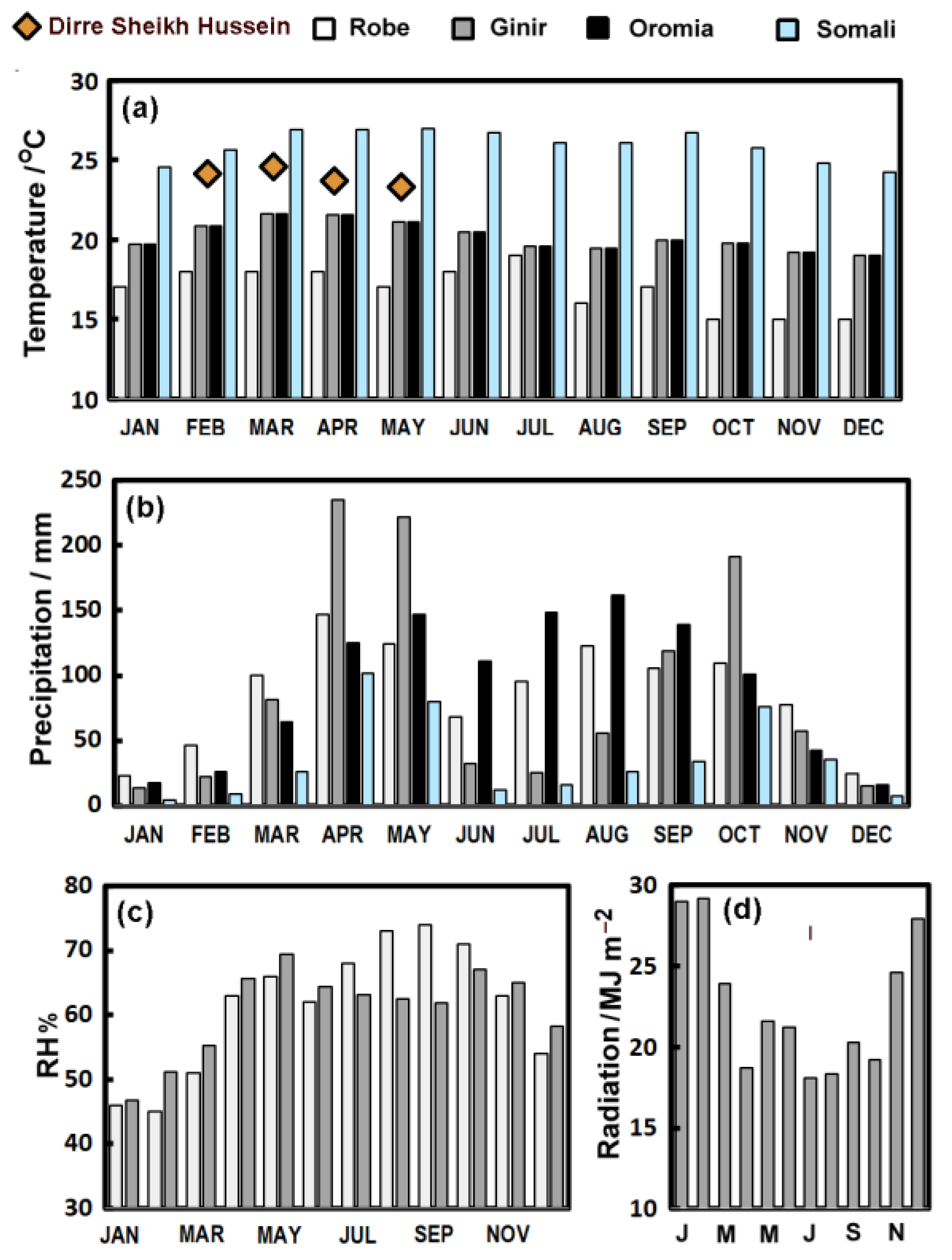
1.3. Environment and Climate
2. Materials and Methods
- Climate Research Unit (accessed on 27 August 2022)
- Timeanddate for current meteorological observations (accessed on 24 August 2022)
- Weatherbase averages of longer term observatios (last accessed on 24 August 2022)
- World Climate Change Knowledge Portal: CRU, ERA5 and CMIP6 (accessed on 27 August 2022)
3. Results
3.1. Recent Climate
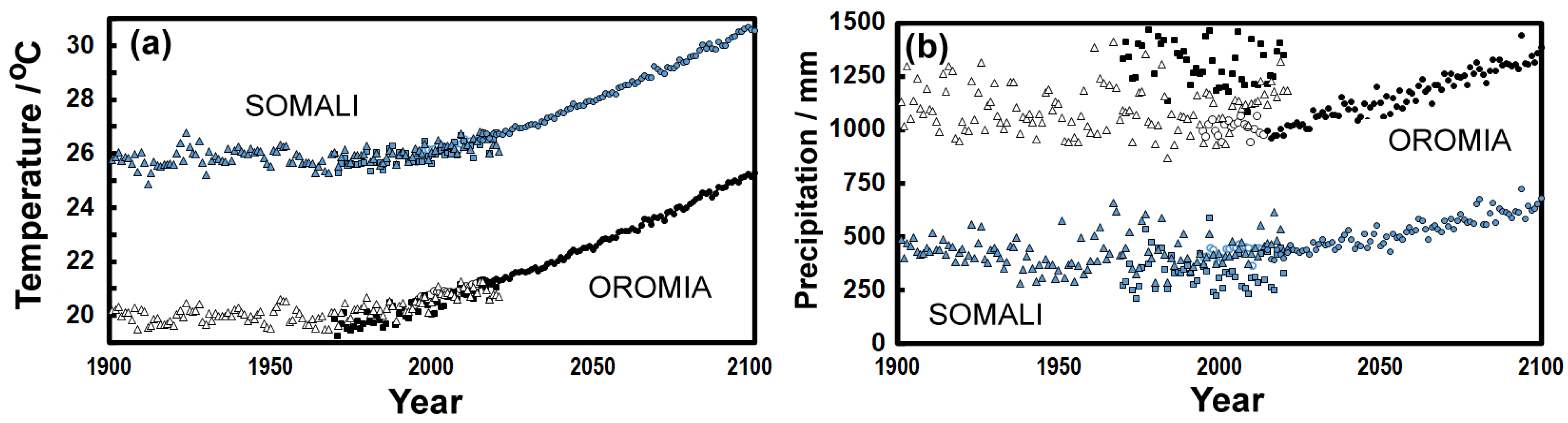
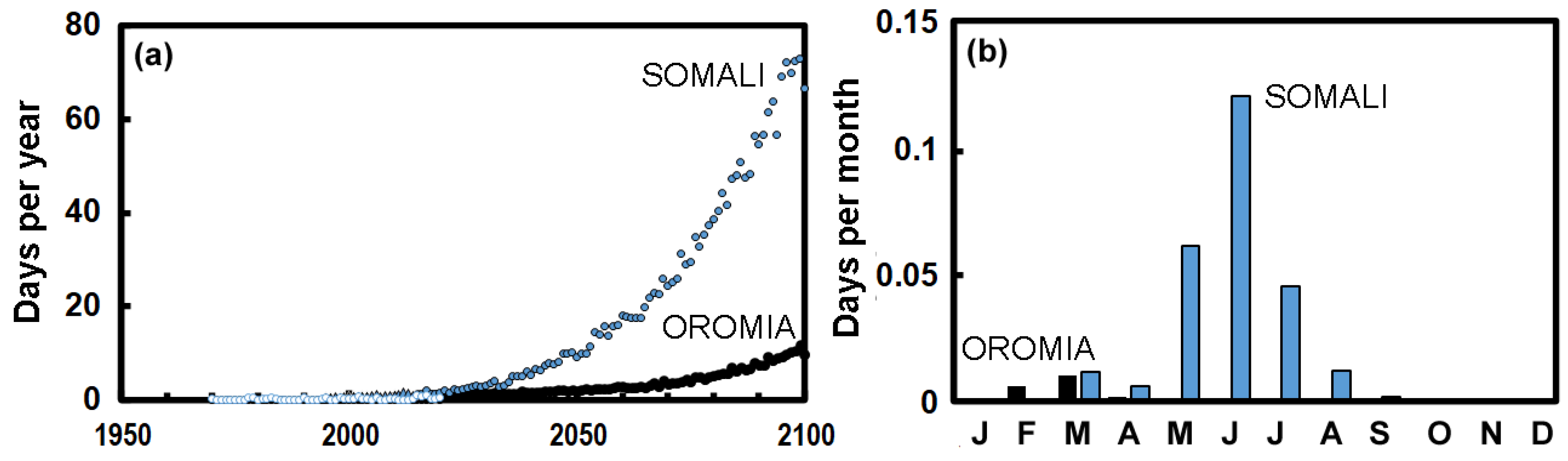
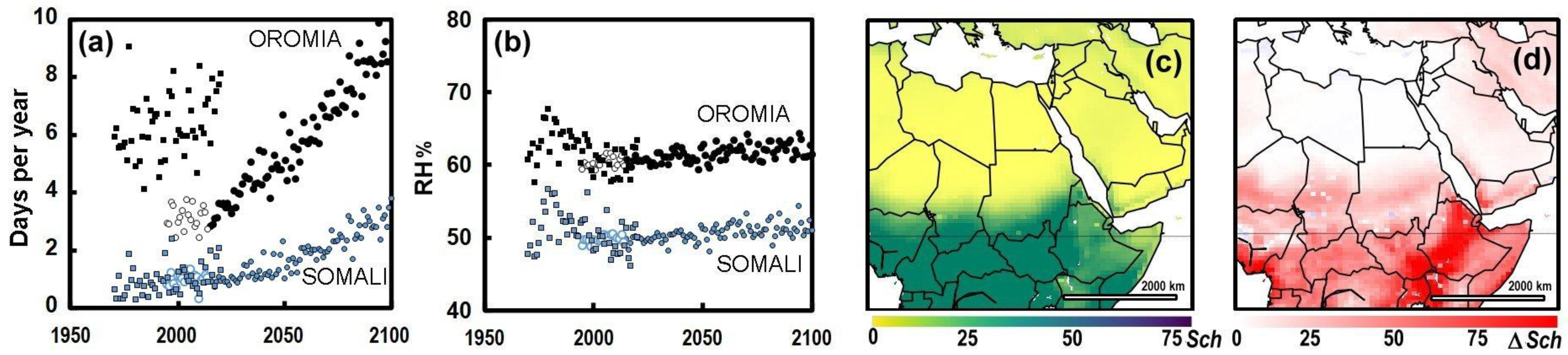
3.2. Climate Change
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tola, S. The conservation of Dirre Sheikh Hussein Heritage Site, Oromia Culture and Tourism Bureau, Ethiopia. 2009. Available online: https://www.hdm.lth.se/fileadmin/hdm/alumni/papers/CMHB_2008b/10_ETH_Sintayehu_Tola_Kenea_Sheikh_Hussein_Heritage_Site.pdf (accessed on 29 August 2022).
- UNESCO. Dirre Sheik Hussein Religious, Cultural and Historical Site. 2011. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5649/#:~:text=Description,East%20countries%2C%20twice%20a%20year (accessed on 29 August 2022).
- Semu, K.T. The culture of accommodating diversity embedded in the sufi saint cult of Bale, Ethiopia: A historical overview. J. Equity Sci. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 5, 29–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ta’a, T. Religious beliefs among the Oromo: Waaqeffannaa, Christianity and Islam in the context of ethnic identity, citizenship and integration. Ethiop. J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2012, 8, 87–111. [Google Scholar]
- Semu, K.T. Dynamics of the cult of Sheik Hussein of Bale, Ethiopia: Its course and curse of the extremists, a historical perspective. Ethiop. J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2016, 12, 63–101. [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson Smith, A. Through Unknown African Countries: The First Expedition from Somaliland to Lake Rudolf; India Office: London, UK, 1897. [Google Scholar]
- Oyst1. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Sheikh_Hussein.jpg (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Akbaba, A.; Ahmed, M.J. Identifying and mapping of halal tourism resources and routes in Ethiopia. Int. J. Contemp. Tour. Res. 2021, 5, 13–34. [Google Scholar]
- Aseres, S.A. Key stakeholders roles and tourism development in Bale Zone, Ethiopia. Int. J. Bus. Manag. Adm. 2016, 1, 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Esubalew, B.; Solomon, N.; Akele, B. Religious tourism practices, potentials, and challenges: The case of Dire Sheikh Hussein Area, South East Ethiopia. J. Soc. Sci. 2020, 48, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Østebø, T. Local reforms and the search for change: The emergence of Salafism in Bale, Ethiopia. Africa 2011, 81, 628–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østebø, T. Localising Salafism. Religious Change among Oromo Muslims in Bale, Ethiopia; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tadese, M.; Kumar, L.; Koech, R. Long-term variability in potential evapotranspiration, water availability and drought under climate change scenarios in the Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Atmos 2020, 11, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizaw, M.S.; Gan, T.Y. Impact of climate change and El Niño episodes on droughts in sub-Saharan Africa. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, K.; Warren, R. Quantifying the impact of climate change on drought regimes using the standardised precipitation index. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 120, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muluneh, A. Impact of climate change on soil water balance, maize production, and potential adaptation measures in the Rift Valley drylands of Ethiopia. J. Arid. Environ. 2020, 179, 104195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demie, G.; Negash, M.; Awas, T. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used by indigenous people in and around Dirre Sheikh Hussein heritage site of South-eastern Ethiopia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 220, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, S.A.; Richards, J.; Fatorić, S. Climate change and cultural heritage: A systematic literature review (2016–2020). Hist. Environ. Policy Pract. 2021, 12, 434–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, N.P.; Clarke, J.; Orr, S.A.; Cundill, G.; Orlove, B.; Fatorić, S.; Sabour, S.; Khalaf, N.; Rockman, M.; Pinho, P.; et al. Decolonizing climate change–heritage research. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.; Mould, C.; Bewket, W. Over one century of rainfall and temperature observations in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.; Osborn, T.J.; Jones, P.; Lister, D. Version 4 of the CRU TS monthly high-resolution gridded multivariate climate dataset. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lisø, K.R.; Hygen, H.O.; Kvande, T.; Thue, J.V. Decay potential in wood structures using climate data. Build. Res. Inf. 2006, 34, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, T.C. A climate index for estimating potential for decay in wood structures above ground. Prod. J. 1971, 21, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gwynn, C.W. A journey in Southern Abyssinia. Geogr. J. 1911, 38, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, N.; Insoll, T. Monitoring Islamic archaeological landscapes in Ethiopia using open source satellite imagery. J. Field Archaeol. 2019, 44, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolossa, T.T.; Abebe, F.B.; Girma, A.A. Rainwater harvesting technology practices and implication of climate change characteristics in Eastern Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1724354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbioni, C.; Brimblecombe, P.; Cassar, M. (Eds.) The Atlas of Climate Change Impact on European Cultural Heritage: Scientific Analysis and Management Strategies; Anthem Press: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brimblecombe, P. Refining climate change threats to heritage. J. Inst. Conserv. 2014, 37, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.; Brimblecombe, P. Moisture as a driver of long-term threats to timber heritage. Part I: Changing heritage climatology. Heritage 2022, 5, 1929–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajet, H.T.T.; Hygen, H.O. Potential risk of wood decay. 2017. Available online: https://www.met.no/publikasjoner/met-report/met-report-2017/_/attachment/download/c7df823f-5c98-4968-81fc-694e6fb6c49b:f495ddf4c9d7358398f610f0ed735c8382dad535/MET-report-08-2017.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Abdelhamid, M.M.A.; Li, D.; Ren, G.; Zhang, C. Estimating deterioration rate of some carbonate rocks used as building materials under repeated frost damage process, China. Adv. Mater. 2020, 2020, 3826128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, C.M.; Brimblecombe, P.; Harris, I. Predicting long term freez—Thaw risks on Europe built heritage and archaeological sites in a changing climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 377, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godts, S.; Orr, S.A.; Desarnaud, J.; Steiger, M.; Wilhelm, K.; De Clercq, H.; Cnudde, V.; De Kock, T. NaCl-related weathering of stone: The importance of kinetics and salt mixtures in environmental risk assessment. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, C.M.; Brimblecombe, P.; Menéndez, B.; Benavente, D.; Harris, I.; Déqué, M. Climatology of salt transitions and implications for stone weathering. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2577–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimblecombe, P.; Hayashi, M. Pressures from long term environmental change at the shrines and temples of Nikkō. Herit. Sci. 2018, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branysova, T.; Demnerova, K.; Durovic, M.; Stiborova, H. Microbial biodeterioration of cultural heritage and identification of the active agents over the last two decades. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 55, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappitelli, F.; Cattò, C.; Villa, F. The control of cultural heritage microbial deterioration. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimblecombe, P. Visitor responses and climate change. In Cultural Heritage from Pollution to Climate Change; Lefevre, R., Sabbioni, C., Eds.; Edipuglia: Bari, Italy, 2016; pp. 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Aynalem, S.; Akele, B.; Alemayehu, H.; Molla, G. Assessment and identification of the tourism resources of Bale Zone, Ethiopia. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2015, 4, 1000176. [Google Scholar]
- Bayih, B.E.; Tola, M.W. Practices and challenges of promoting major tourism destinations of Bale Zone for sustainable tourism development in Ethiopia. Afr. J. Hosp. Tour. Leis. 2017, 6, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Dagnachew, S.E. Interfaith tourism in Ethiopia: An opportunity for socio-economic development and peace-building? In Peace Journeys: A New Direction in Religious Tourism and Pilgrimage Research; McIntosh, I.S., Haddah, N.F., Munro, D., Eds.; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Newcastle-on-Tyne, UK.
- Gummadi, S.; Rao, K.P.; Seid, J.; Legesse, G.; Kadiyala, M.D.; Takele, R.; Amede, T.; Whitbread, A. Spatio-temporal variability and trends of precipitation and extreme rainfall events in Ethiopia in 1980–2010. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 134, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleshi, Y.; Zanke, U. Recent changes in rainfall and rainy days in Ethiopia. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimblecombe, P.; Richards, J. Moisture as a driver of long-term threats to timber heritage. Part II: Risks imposed at local sites. Heritage 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Insoll, T.; Khalaf, N.; MacLean, R.; Parsons-Morgan, H.; Tait, N.; Gaastra, J.; Beldados, A.; Pryor, A.J.; Evis, L.; Dussubieux, L. Material cosmopoitanism: The entrepot of Harlaa as an Islamic gateway to eastern Ethiopia. Antiquity 2021, 95, 487–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wubneh, M. Urban resilience and sustainability of the city of Gondar (Ethiopia) in the face of adverse historical changes. Plan Perspect. 2021, 36, 363–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woredekal, S. Restoration of historical monuments of Gondar. Ann. D’éthiopie 1985, 13, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, B. Community engagement in cultural heritage management—Case studies of museums in Harar and Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. 2008. Available online: https://repository.kulib.kyoto-u.ac.jp/dspace/bitstream/2433/137081/1/ytiik00063.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Tarsitani, B.A. Merging past and present in the Museums of Harar, Ethiopia. Nilo-Ethiop. Stud. 2009, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Woldeyes, Y.G. Preliminary Report: Conservation Concerns for the Lalibela Rock Hewn Churches. IIEE Ethiopia. 2018. Available online: https://espace.curtin.edu.au/bitstream/handle/20.500.11937/75855/76057.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Delmonaco, G.; Margottini, C.; Spizzichinom, D. Analysis of rock weathering and conservation strategies for rock-hewn churches of Lalibela (Ethiopia). Prot. Hist. Build. PROHITECH 2009, 9, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Negussie, E. Conserving the rock-hewn churches of lalibela as a world heritage site: A case for international support and local participation. In Proceedings of the Changing World, Changing Views of Heritage: Heritage and Social Change, ICOMOS Scientific Symposium, Dublin, Ireland, 30 October 2010; Theme 3. pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tola, H.G.; Brimblecombe, P. Environmental Pressures at Dirre Sheikh Hussein Sanctuary. Heritage 2022, 5, 2661-2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030139
Tola HG, Brimblecombe P. Environmental Pressures at Dirre Sheikh Hussein Sanctuary. Heritage. 2022; 5(3):2661-2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030139
Chicago/Turabian StyleTola, Habtamu Gizawu, and Peter Brimblecombe. 2022. "Environmental Pressures at Dirre Sheikh Hussein Sanctuary" Heritage 5, no. 3: 2661-2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030139
APA StyleTola, H. G., & Brimblecombe, P. (2022). Environmental Pressures at Dirre Sheikh Hussein Sanctuary. Heritage, 5(3), 2661-2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030139






