Natural Stones Used in the Orsi-Marconi Palace Façade (Bologna): A Petro-Mineralogical Characterization
Abstract
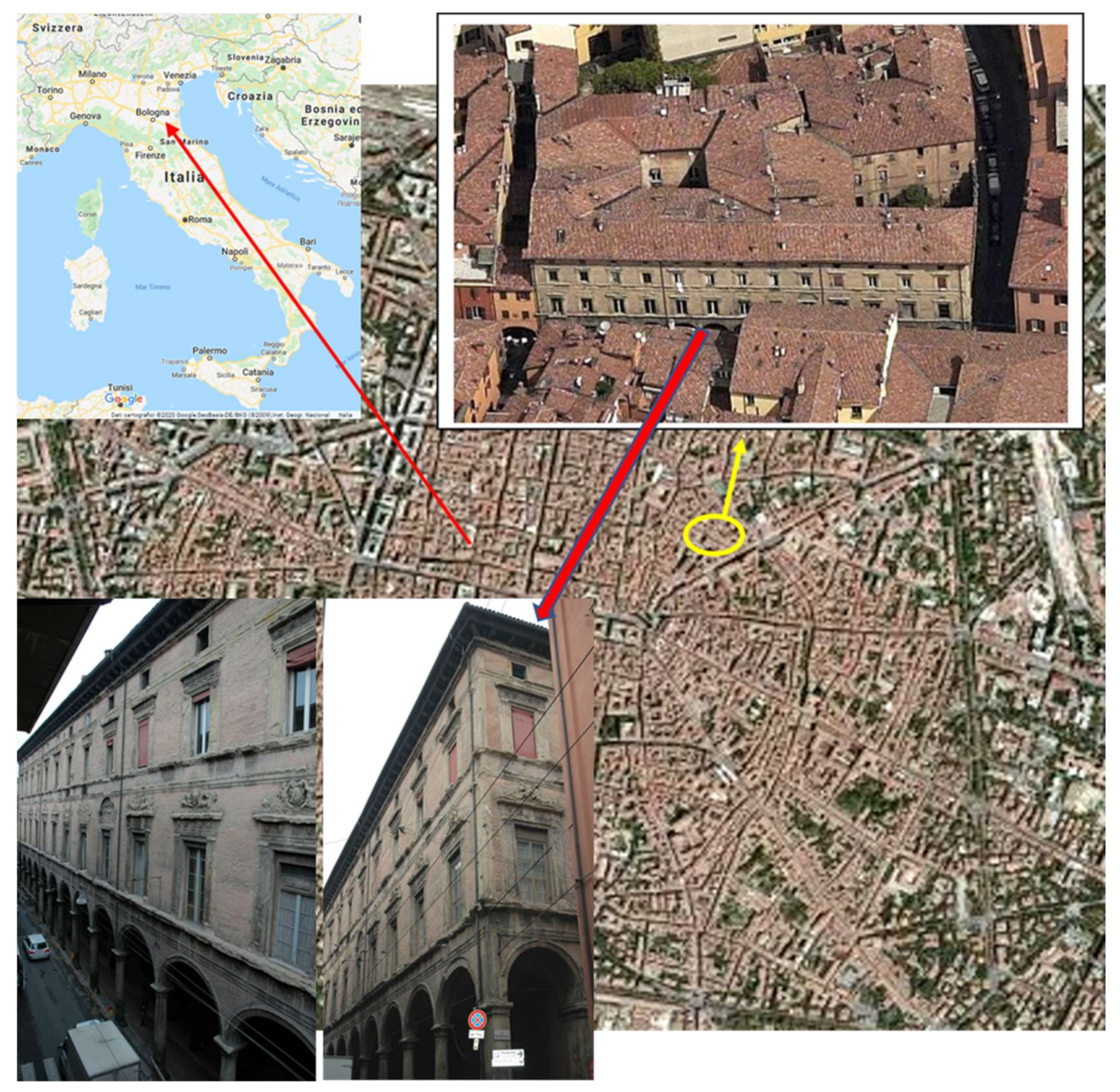
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
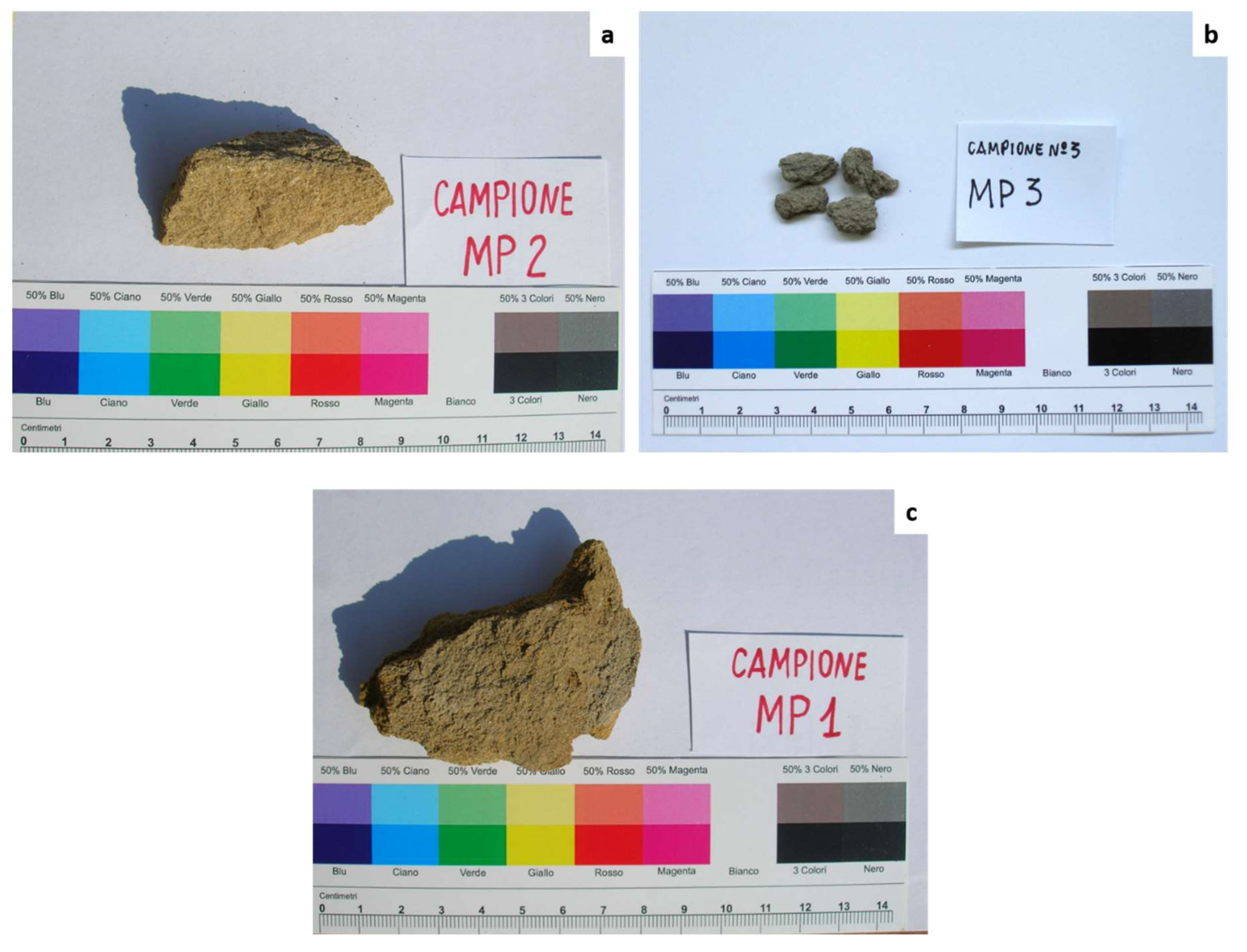
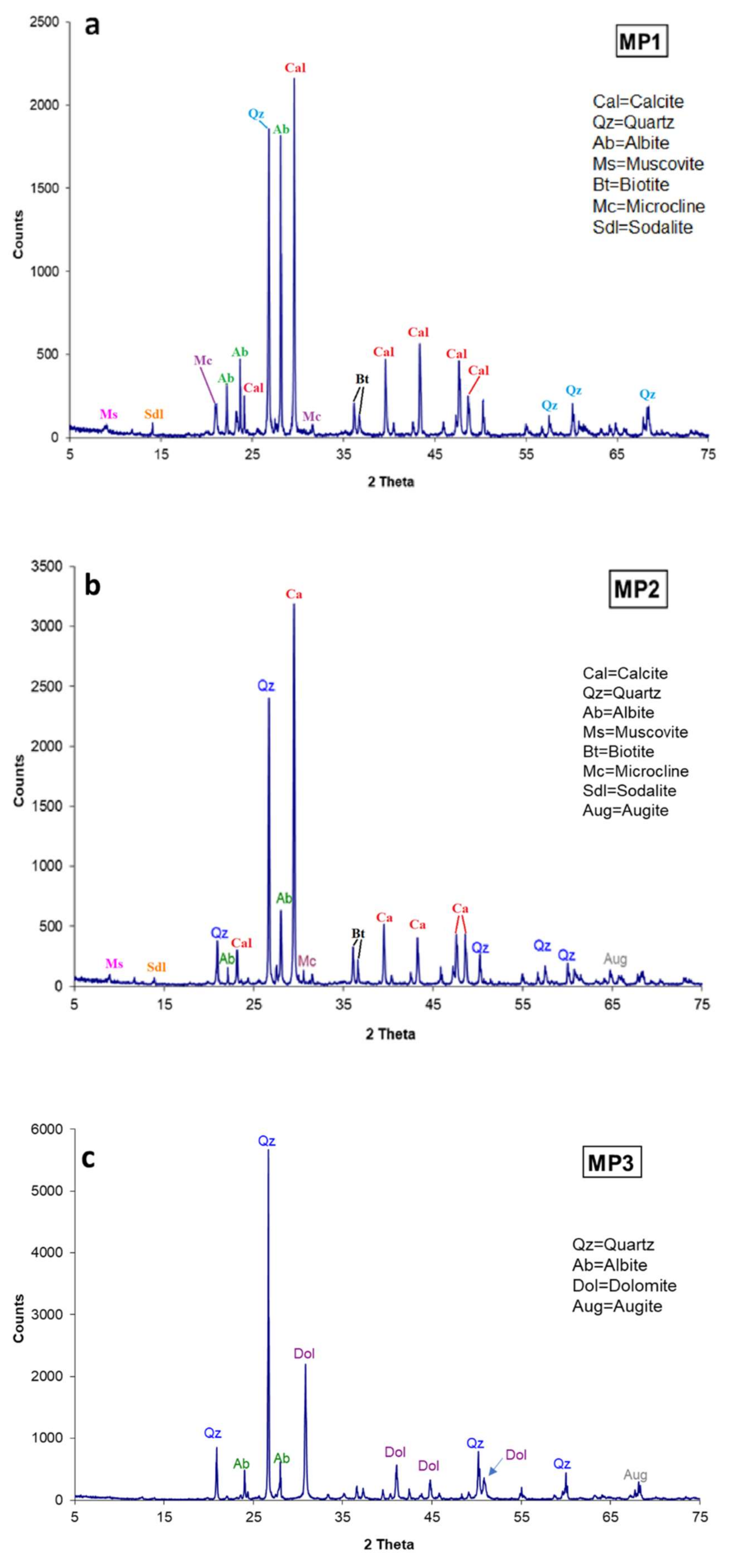
- C.MP2: A small sample of yellow sandstone already detached during demolition and belonging to the horizontal sandstone mouldings (Figure 4a);
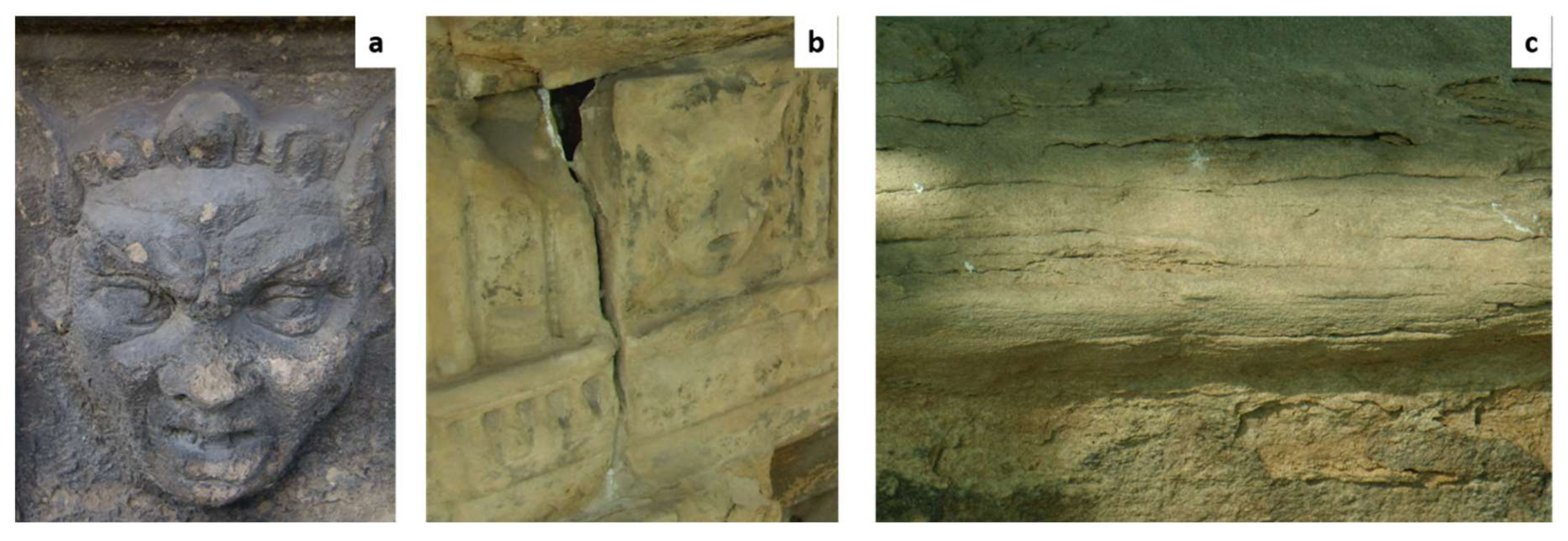
- C.MP3: A small sample of grey sandstone belonging to the top of a capital on which an arch rests (Figure 4b); a sample of consolidated yellow sandstone was collected following the restoration treatments;
- C.MP1: A sample of consolidated yellow sandstone (Figure 4c) which came off during a grouting operation on a part of the horizontal moulding with an organic consolidating agent (Ethyl Silicate), near the sampling area of the C.MP2 sample. The consolidation treatment was part of previous preservations: the sample was collected after one week from the treatment. The decision to take a consolidated sample with yellow sandstone was due to the fact that this type of material prevailed on the building compared to the grey one.
2.2. Chemical and Mineralogical Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Macroscopic Characterization: Colors and Shape
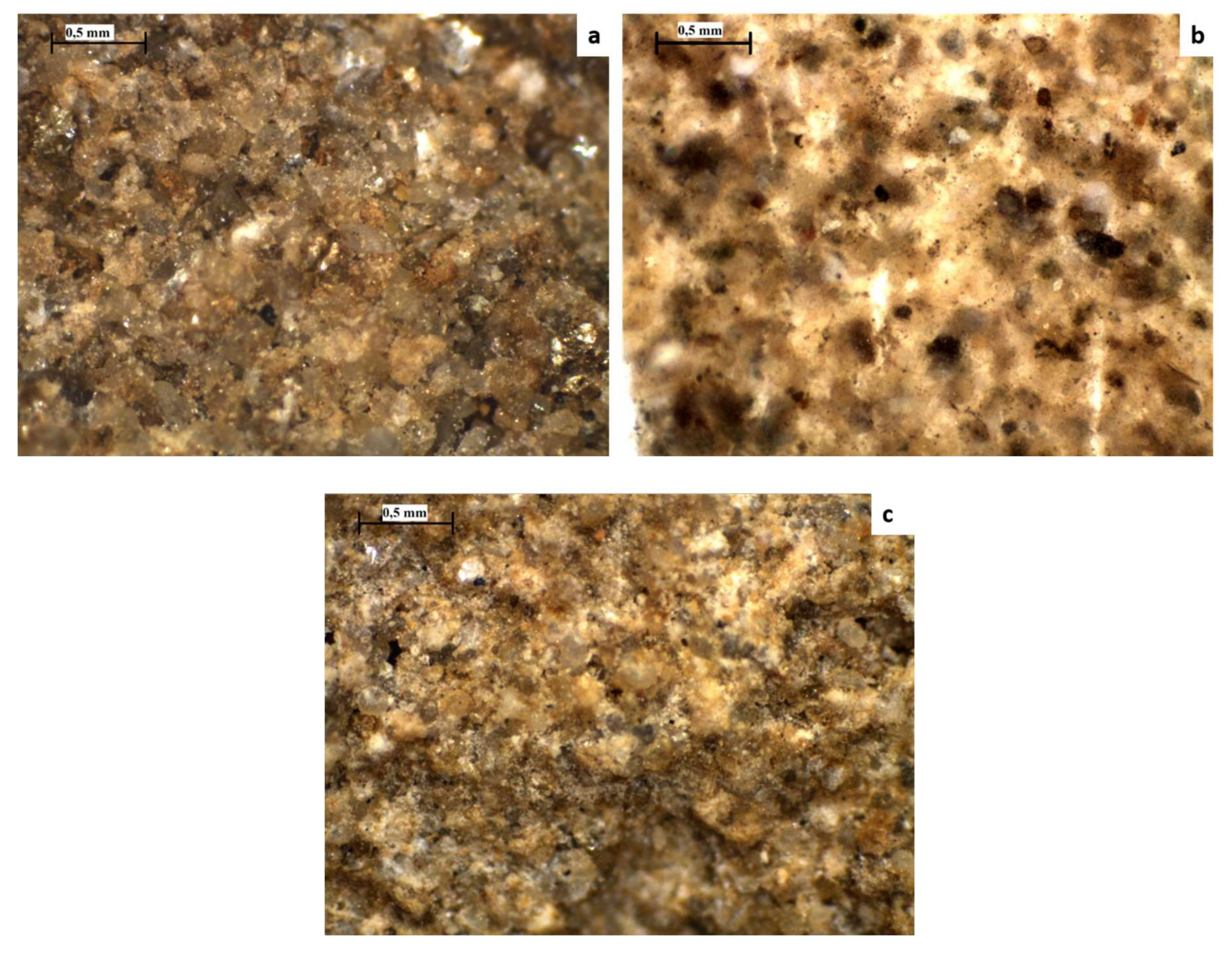
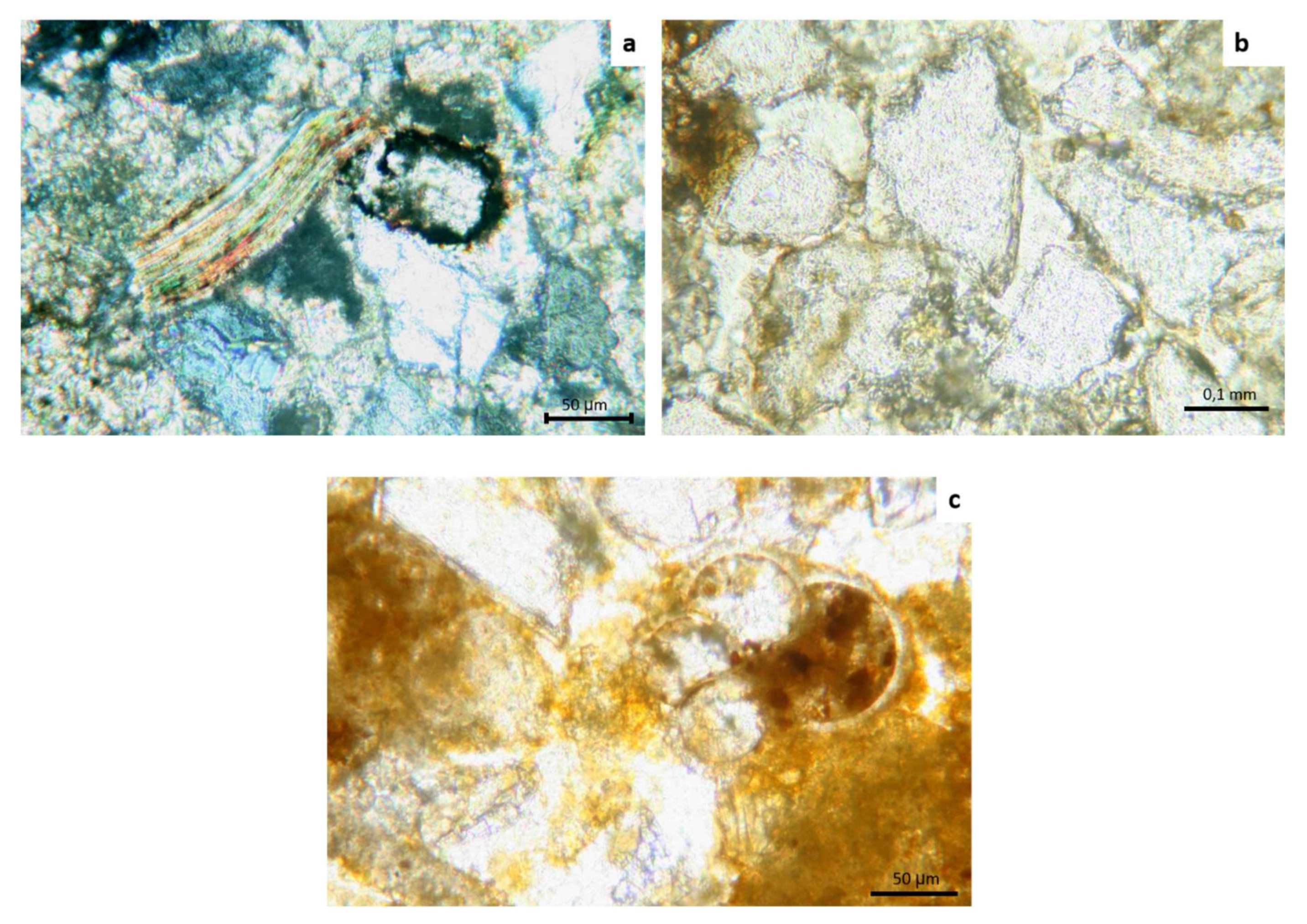
3.2. Optical Microscopic Characterization
3.3. XRPD Data Analysis
3.4. XRF Data Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- -
- evaluate the impact on the stone conservation of air pollution and meteoric water;
- -
- determine that the concentration of specific elements (such as Ba, Zn, Zr, etc.) was higher in the yellow sandstone samples, evidencing the fingerprint of air pollution due to vehicular emissions;
- -
- consider the evolution of the conservation state of the rock substrate. The abundance of some elements, such as Zn, Cu, Ni, etc., were usually higher in the substrate, coupled with the presence of a network of microcracks, that could also lead to the formation of new crusts contributing to the acceleration of weathering damage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guidicini, G. Cose Notabili Della Città di Bologna: Ossia Storia Cronologica de’ Suoi Stabili Sacri, Pubblici e Private; Forni, A., Ed.; Arnaldo Forni: Bologna, Italy, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Manzini, G. Antonio Morandi, “il Terribilia”, nell’architettura bolognese del ’500. Il Carrobbio. Rivista di Studi Bolognesi 1983, 9, 243–255. [Google Scholar]
- Bacci, P.; Del Monte, M.; Sabbioni, C.; Zappia, G. Black Crusts as Air Pollution Indicators. In Proceedings of the European Symposium, Bologna, Italy, 13–16 June 1991; pp. 462–464. [Google Scholar]
- Violante, F.S.; Barbieri, A.; Curti, S.; Sanguinetti, G.; Graziosi, F.; Mattioli, S. Urban atmospheric pollution: Personal exposure versus fixed monitoring station measurements. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarti, E.; Pasti, L.; Rossi, M.; Ascanelli, M.; Pagnoni, A.; Trombini, M.; Remelli, M. The composition of PM 1 and PM 2.5 samples, metals and their water soluble fractions in the Bologna area (Italy). Atmospheric Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comite, V.; De Buergo, M.A.; Barca, D.; Belfiore, C.; Bonazza, A.; La Russa, M.; Pezzino, A.; Randazzo, L.; Ruffolo, S. Damage monitoring on carbonate stones: Field exposure tests contributing to pollution impact evaluation in two Italian sites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortíz, R.; Ortiz, P.; Vázquez, M.; Martín, J. Integration of georeferenced informed system and digital image analysis to asses the effect of cars pollution on historical buildings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graue, B. Environmental Impact on Stone Decay: Crust Formation at the Cologne Cathedral. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Deterioration and Conservation of Stone, New York, NY, USA, 21–25 October 2012; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Balog, A.A.; Corbizan, N.; Mosonyi, E. Analysis of Limestones from Heritage Buildings as Damage Diagnostics. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2016, 68, 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Farkas, O.; Siegesmund, S.; Licha, T.; Török, Á. Geochemical and mineralogical composition of black weathering crusts on limestones from seven different European countries. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, M.Y.; Kaçmaz, A.U. The investigation of static and dynamic capillary by water absorption in porous building stones under normal and salty water conditions. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Dong, Z.; Jia, H. Decay of sandstone subjected to a combined action of repeated freezing–thawing and salt crystallization. Bull. Int. Assoc. Eng. Geol. 2019, 78, 5951–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, D.; Martínez-Martínez, J.; Cueto, N.; Ordóñez, S.; Garcia-Del-Cura, M.A. Impact of salt and frost weathering on the physical and durability properties of travertines and carbonate tufas used as building material. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubelli, B.; Cnudde, V.; Diaz-Goncalves, T.; Franzoni, E.; Van Hees, R.P.J.; Ioannou, I.; Menéndez, B.; Nunes, C.; Siedel, H.; Stefanidou, M.; et al. Towards a more effective and reliable salt crystallization test for porous building materials: State of the art. Mater. Struct. 2018, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosoarca, M.; Keller, A.I.; Petruş, C.; Racolta, A. Failure analysis of historical buildings due to climate change. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 82, 666–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalagli, N.; Kita, A.; Castaldo, V.; Pisello, A.L.; Ubertini, F. Hierarchical environmental risk mapping of material degradation in historic masonry buildings: An integrated approach considering climate change and structural damage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 215, 998–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gohary, M.A. Environmental impacts: Weathering factors, mechanism and forms affected the stone decaying in Petra. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 135, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Turo, F.; Proietti, C.; Screpanti, A.; Fornasier, M.F.; Cionni, I.; Favero, G.; De Marco, A. Impacts of air pollution on cultural heritage corrosion at European level: What has been achieved and what are the future scenarios. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooers, H.; Carlson, M.; Harrison, R.M.; Inkpen, R.; Loeffler, S. Correlation of gravestone decay and air quality 1960–2010. Atmospheric Environ. 2017, 152, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Janvier-Badosa, S.; Beck, K.; Brunetaud, X.; Al-Mukhtar, M. The SACRE Project: A Diagnosis Tool of Built Heritage. Computer Vision 2016, 10058, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.; Mateus, R.; Silvestre, J.D. Comparative Analysis of Inspection and Diagnosis Tools for Ancient Buildings; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Cantisani, E.; De Luca, D.; Frediani, P.; Garzonio, C.A.; Ricci, M.; Stori, F. Restoration of a Sandstone Facade: From the Project to the Monitoring. Int. J. Arch. Heritage 2012, 6, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Briceño, C.; Gonzales, M.; Yaya, C.; Moreira, S.; Aguilar, R. Preliminary Structural Diagnosis of the Sacsamarca Church in Peru Using Photogrammetry and IR Thermography; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; Volume 18, pp. 2431–2438. [Google Scholar]
- Sabbioni, C. Characterization of Atmospheric Particles on Monuments by Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy Dispersive X-ray Analyses. Electron Microsc. 1992, 2, 773–777. [Google Scholar]
- Sabbioni, C. Contribution of atmospheric deposition to the formation of damage layers. Sci. Total. Environ. 1995, 167, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkington, A.; Martin, E.; Viles, H.; Smith, B. Surface change and decay of sandstone samples exposed to a polluted urban atmosphere over a six-year period: Belfast, Northern Ireland. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkanç, M. Deterioration of different stones used in historical buildings within Nigde province, Cappadocia. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonazza, A.; Sabbioni, C.; Ghedini, N. Quantitative data on carbon fractions in interpretation of black crusts and soiling on European built heritage. Atmospheric Environ. 2005, 39, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, M.F.; Belfiore, C.M.; Comite, V.; Barca, D.; Bonazza, A.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Crisci, G.M.; Pezzino, A. Geochemical study of black crusts as a diagnostic tool in cultural heritage. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 113, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barca, D.; Comite, V.; Belfiore, C.M.; Bonazza, A.; La Russa, M.F.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Crisci, G.M.; Pezzino, A.; Sabbioni, C. Impact of air pollution in deterioration of carbonate building materials in Italian urban environments. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 48, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, M.F.; Fermo, P.; Comite, V.; Belfiore, C.M.; Barca, D.; Cerioni, A.; De Santis, M.; Barbagallo, L.F.; Ricca, M.; Ruffolo, S.A. The Oceanus statue of the Fontana di Trevi (Rome): The analysis of black crust as a tool to investigate the urban air pollution and its impact on the stone degradation. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 593–594, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barca, D.; Belfiore, C.M.; Crisci, G.M.; La Russa, M.F.; Pezzino, A.; Ruffolo, S.A. A new methodological approach for the chemical characterization of black crusts on building stones: A case study from the Catania city centre (Sicily, Italy). J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocchino, E.; Fried, A.; Koulouris, A.; Vaccaro, C. Micro-chemical/structural characterisation of thin layer masonry: A correlation with engineering performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocchino, E.; Telloli, C.; Caraccio, S.; Guarnieri, C.; Vaccaro, C. Medieval Glassworks in the City of Ferrara (North Eastern Italy): The Case Study of Piazza Municipale. Heritage 2020, 3, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocchino, E.; Rapti-Caputo, D.; Vaccaro, C. Chemical–mineralogical characterisation as useful tool in the assessment of the decay of the Mesola Castle (Ferrara, Italy). Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2672–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzini, M.; Randazzo, L.; Saitta, M. Revisione di una Metodologia Analitica per Fluorescenza-x, Basata sulla Correzione Completa degli Effetti di Matrice. Soc. It. Mineral. E Petrol. Rendiconti 1975, 31, 365–378. [Google Scholar]
- Lachance, G.R.; Traill, R.J. Practical Solution to the Matrix Problem in X-ray Analysis. Can. Spetrosc. 1966, 11, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau, R.M. Corrections for matrix effects in X-ray fluorescence analysis—A tutorial. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2006, 61, 759–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, K.; Lu, C. Experimental Study and Matrix Effect Correction of Pseudobinary Samples in XRF Analysis. IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamaschi, B.; Marzola, L.; Radice, M.; Manfredini, S.; Baldini, E.; Vicentini, C.B.; Marrocchino, E.; Molesini, S.; Ziosi, P.; Vaccaro, C.; et al. Comparative Study of SPA Mud from “Bacino Idrominerario Omogeneo dei Colli Euganei (B.I.O.C.E.)–Italy” and Industrially Optimized Mud for Skin Applications. Life 2020, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Li, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Z.; Wei, N.; Zhang, X. Late Quaternary Paleoenvironmental Reconstruction, Using Benthic Foraminifera and Ostracoda, of Marine Sedimentary Beds On the Southern Coast of Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China. J. Foraminifer. Res. 2018, 48, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scerri, S. Sedimentary Evolution and Resultant Geological Landscapes; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, G.A. Age Determination of Young Rocks and Artifacts; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Jang, M. Heterogeneous photooxidation of sulfur dioxide in the presence of airborne mineral dust particles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 58617–58627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Conceição, F.T.; Fernandes, A.M.; Hissler, C.; Lupinacci, C.M.; Menegário, A.A.; Moruzzi, R.B. Multi-tracer analysis to estimate the historical evolution of pollution in riverbed sediment of subtropical watershed, the lower course of the Piracicaba River, São Paulo, Brazil. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonska, M.; Rietmeijer, F.; Janeczek, J. Fine-grained barite in coal fly ash from the Upper Silesian Industrial Region. Environ. Geol. 2001, 40, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczyńska-Michalik, W. Influence of Atmospheric Pollution on the Weathering of Stones in Cracow Monuments and Rock Outcrops in Cracow, Cracow-Częstochowa Upland and the Carpathians; Editor Wydawnictwo Naukowe Akademii Pedagogicznej: Krakow, Poland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo, L.; Zerbi, C.M.; Bugini, R. Black layers on historical architecture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2008, 16, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlister, J.J.; Smith, B.; Török, Á. Transition metals and water-soluble ions in deposits on a building and their potential catalysis of stone decay. Atmospheric Environ. 2008, 42, 7657–7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comite, V.; Ricca, M.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Graziano, S.F.; Rovella, N.; Rispoli, C.; Gallo, C.; Randazzo, L.; Barca, D.; Cappelletti, P.; et al. Multidisciplinary Approach for Evaluating the Geochemical Degradation of Building Stone Related to Pollution Sources in the Historical Center of Naples (Italy). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargossi, G.M.; Gamberini, F.; Gasparotto, G.; Grillini, G.C.; Marocchi, M. Dimension and Ornamental Stones from the Tosco-Romagnolo and Bolognese Apennine. Periodico di Mineralogia 2004, 73, 171–195. [Google Scholar]
- Marszałek, M.; Alexandrowicz, Z.; Rzepa, G. Composition of weathering crusts on sandstones from natural outcrops and architectonic elements in an urban environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 14023–14036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, C.M.; Brimblecombe, P. The effect of atmospheric pollution on building materials. Le J. de Phys. Colloq. 2002, 12, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Arkarazo, I.; Angulo, M.; Bartolomé, L.; Etxebarria, N.; Olazabal, M.Á.; Madariaga, J.M. An integrated analytical approach to diagnose the conservation state of building materials of a palace house in the metropolitan Bilbao (Basque Country, North of Spain). Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 584, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, P. Environmental Surfaces and Interfaces from the Nanoscale to the Global Scale; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]



| Oxides | C.MP2 | C.MP3 | C.MP1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 38.06 | 41.53 | 42.06 |
| TiO2 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.22 |
| Al2O3 | 4.53 | 4.71 | 5.53 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.64 | 2.71 | 2.96 |
| MnO | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| MgO | 1.10 | 10.41 | 1.07 |
| CaO | 31.10 | 16.97 | 26.74 |
| Na2O | 0.70 | 0.62 | 0.70 |
| K2O | 0.73 | 0.85 | 0.93 |
| P2O5 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.07 |
| LOI | 21.81 | 21.82 | 19.58 |
| TOT | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Trace Elements | C.MP2 | C.MP3 | C.MP1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | 119.5 | 172.6 | 156.3 |
| Ce | n.d. | n.d. | 0.5 |
| Co | 0.5 | 3.4 | 3.0 |
| Cr | 16.8 | 29.4 | 27.3 |
| La | 2.6 | 3.7 | 5.7 |
| Nb | n.d. | n.d. | 0.3 |
| Ni | 10.8 | 12.7 | 31.7 |
| Pb | 10.9 | 9.1 | 13.8 |
| Rb | 22.0 | 30.6 | 27.9 |
| Sr | 248.0 | 225.4 | 258.8 |
| Th | 0.8 | 2.2 | 1.2 |
| V | 18.5 | 18.8 | 26.6 |
| Y | 9.6 | 7.7 | 10.8 |
| Zn | 13.3 | 1096.0 | 21.7 |
| Zr | 140.9 | 224.2 | 145.4 |
| Cu | 14.8 | 28.2 | 12.5 |
| Ga | 6.4 | 5.6 | 6.9 |
| Nd | 6.5 | 4.2 | 5.2 |
| S | 3796.1 | 448.9 | 5544.4 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marrocchino, E.; Telloli, C.; Pedrini, M.; Vaccaro, C. Natural Stones Used in the Orsi-Marconi Palace Façade (Bologna): A Petro-Mineralogical Characterization. Heritage 2020, 3, 1109-1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage3040062
Marrocchino E, Telloli C, Pedrini M, Vaccaro C. Natural Stones Used in the Orsi-Marconi Palace Façade (Bologna): A Petro-Mineralogical Characterization. Heritage. 2020; 3(4):1109-1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage3040062
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarrocchino, Elena, Chiara Telloli, Martina Pedrini, and Carmela Vaccaro. 2020. "Natural Stones Used in the Orsi-Marconi Palace Façade (Bologna): A Petro-Mineralogical Characterization" Heritage 3, no. 4: 1109-1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage3040062
APA StyleMarrocchino, E., Telloli, C., Pedrini, M., & Vaccaro, C. (2020). Natural Stones Used in the Orsi-Marconi Palace Façade (Bologna): A Petro-Mineralogical Characterization. Heritage, 3(4), 1109-1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage3040062






