Modeling and Forecasting Medium-Term Electricity Consumption Using Component Estimation Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. An Overview of Pakistan Electricity Sector
3. Proposed Forecasting Model
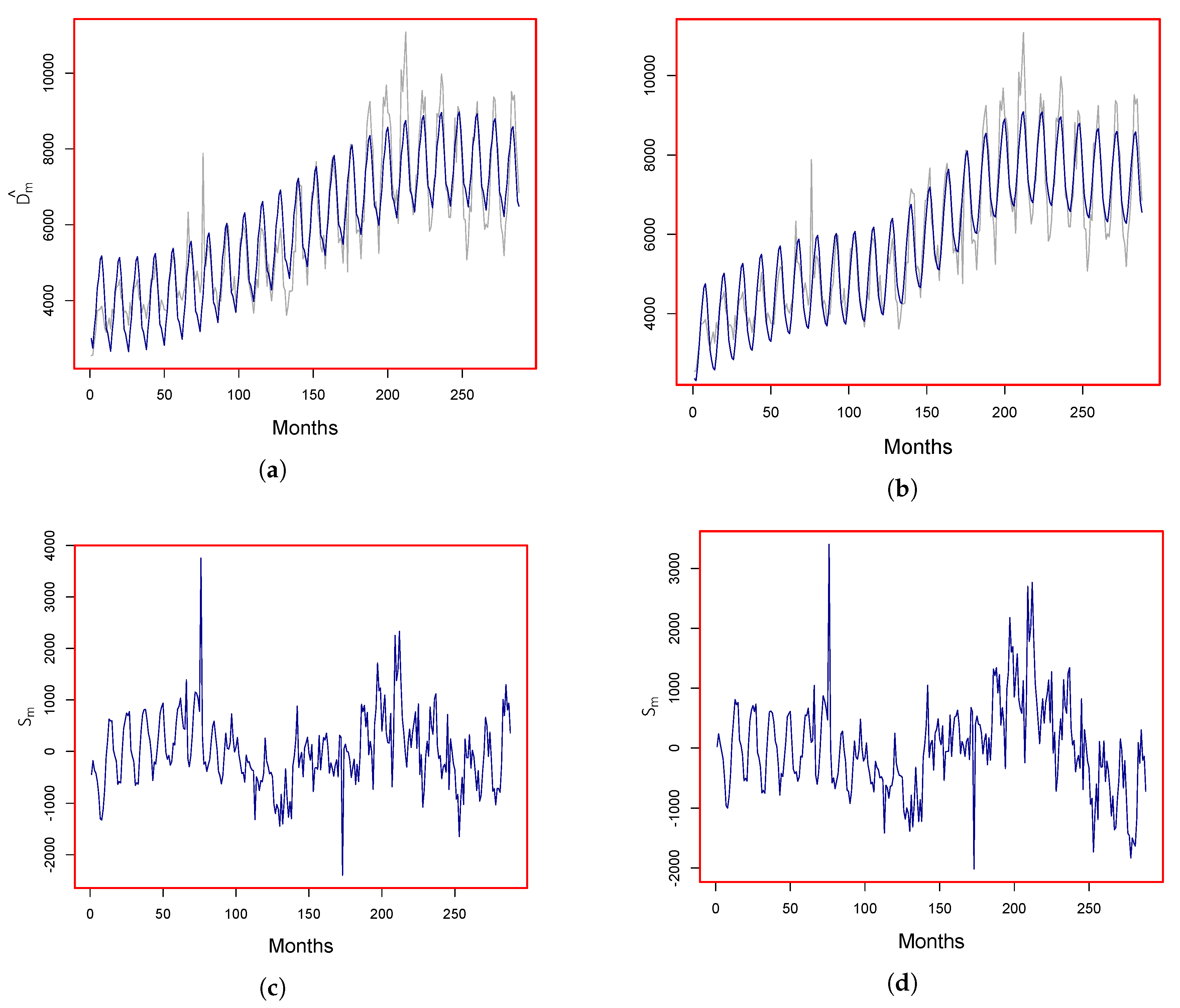
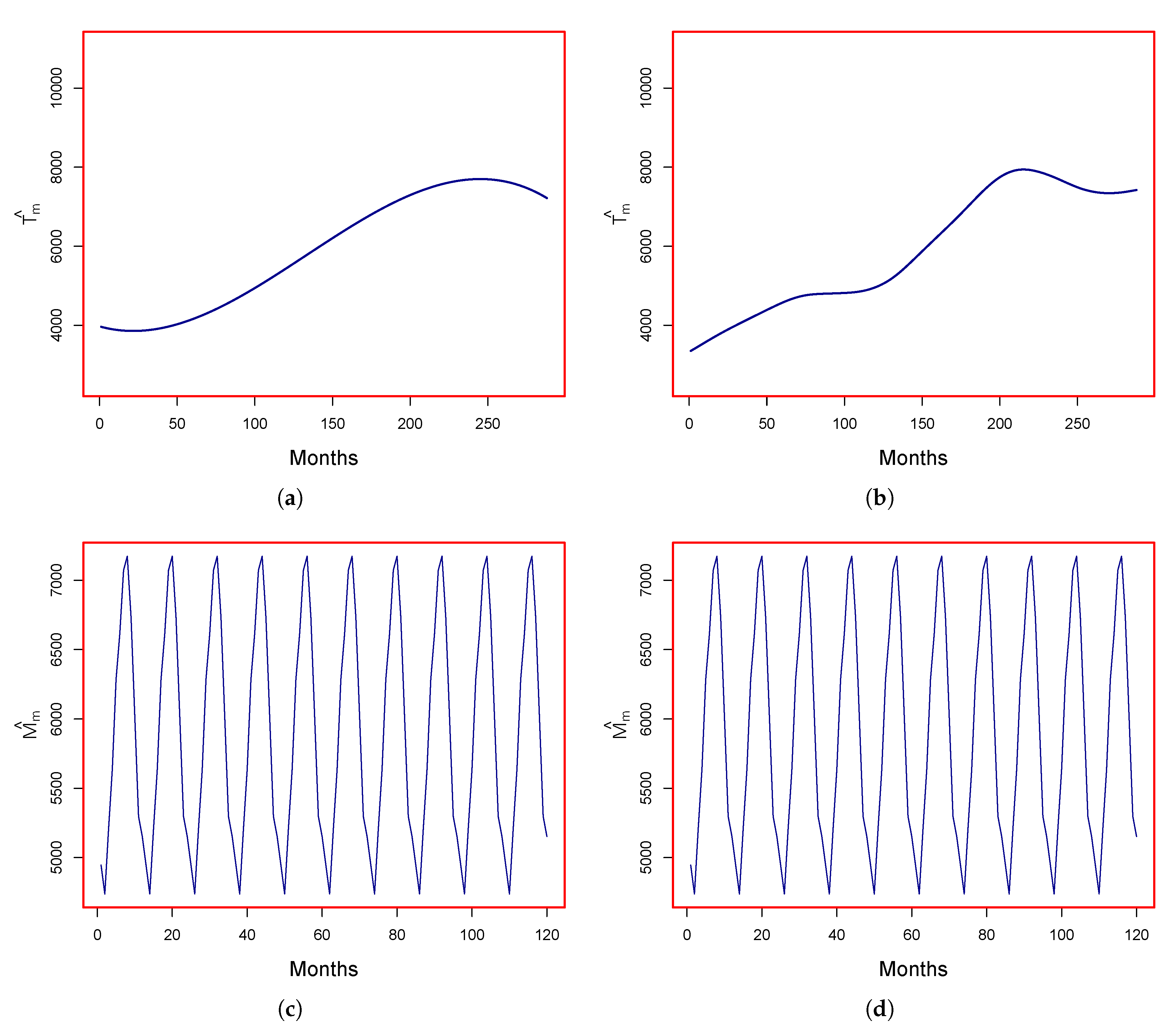
3.1. Modeling the Deterministic Component
3.1.1. Parametric Case
3.1.2. Nonparametric Case
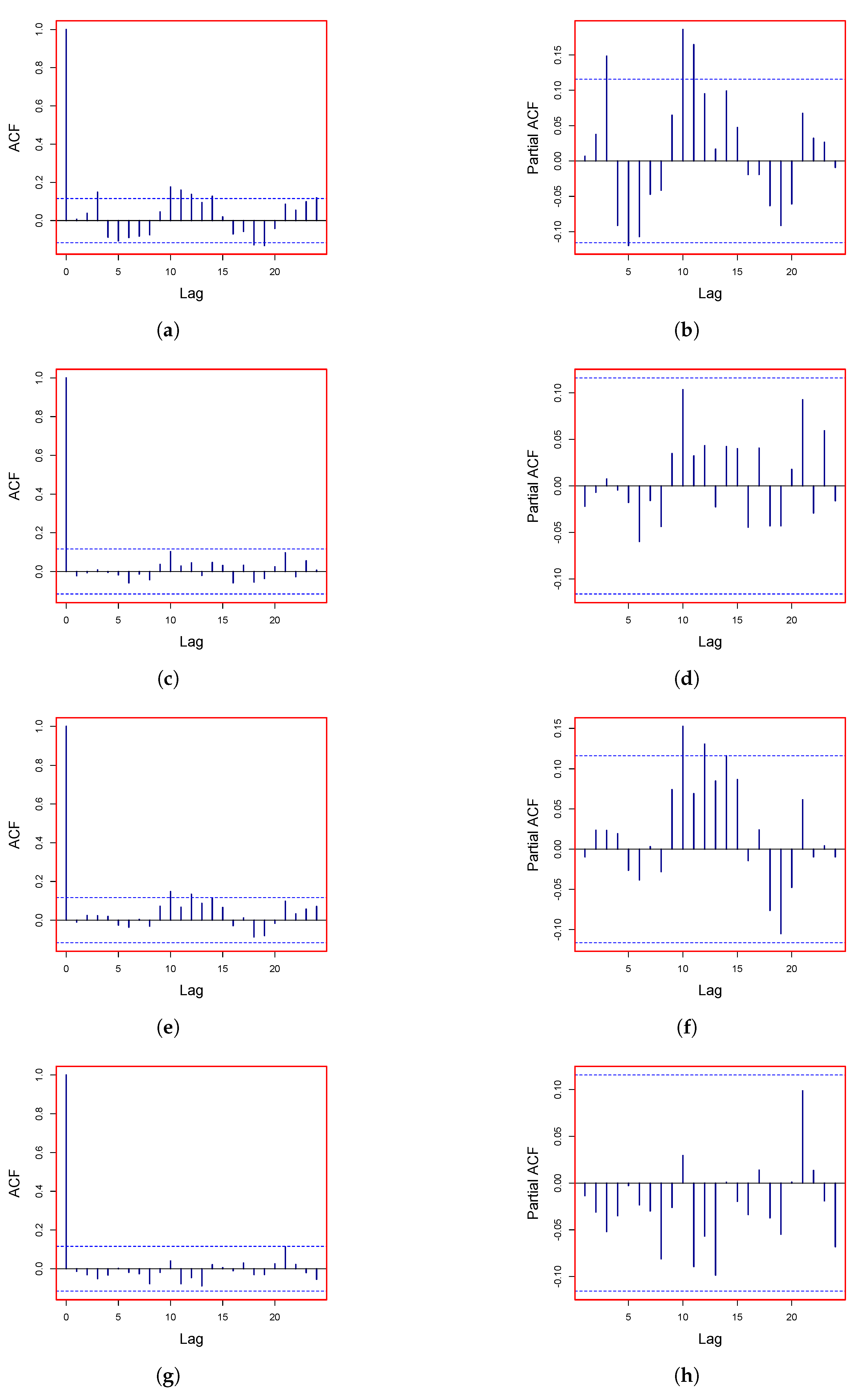
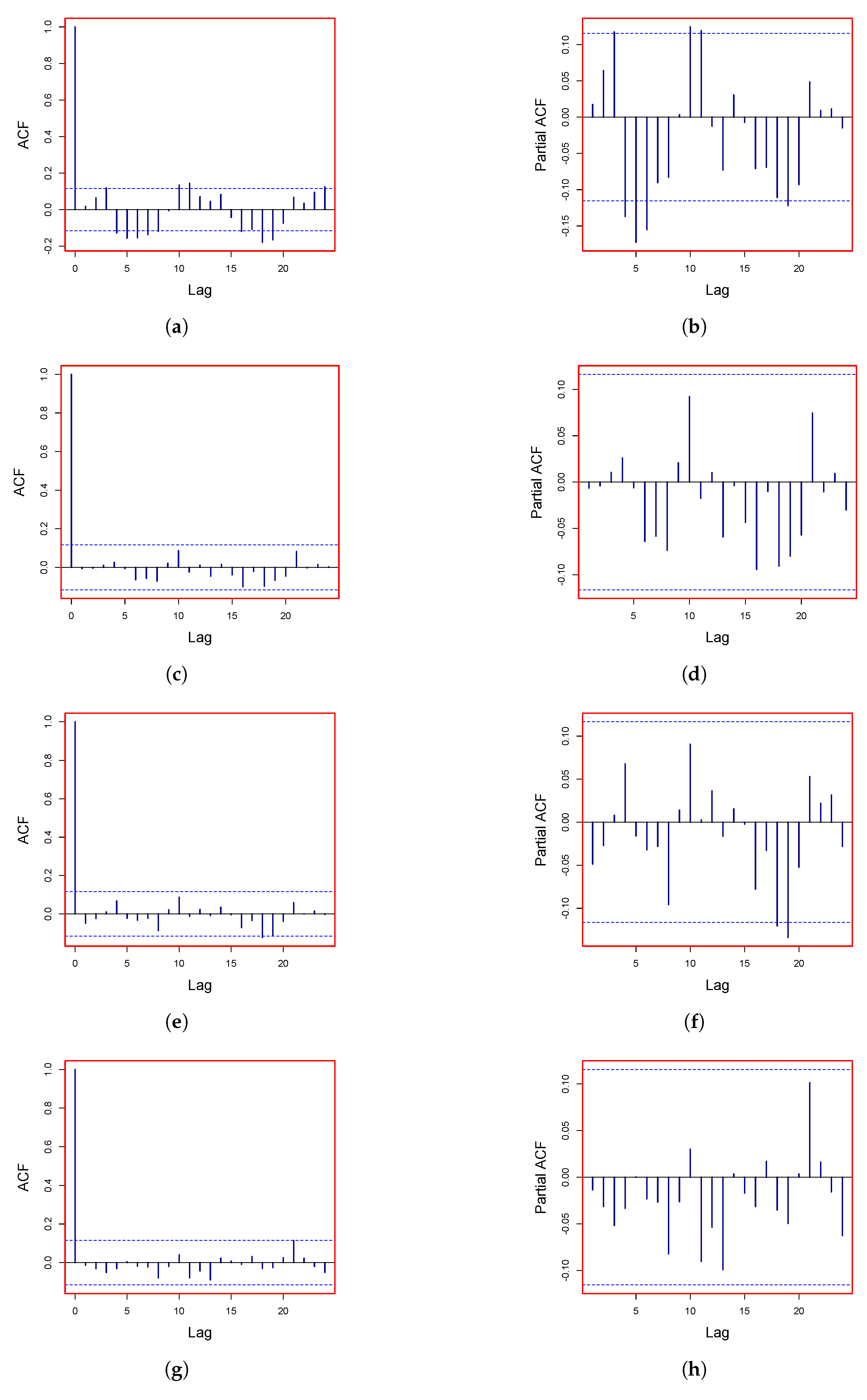
3.2. Modeling the Stochastic Component
3.2.1. AutoRegressive Model
3.2.2. Nonparametric AutoRegressive Model
3.2.3. Smooth Transition AutoRegressive (STAR) Model
3.2.4. AutoRegressive Moving Average Model
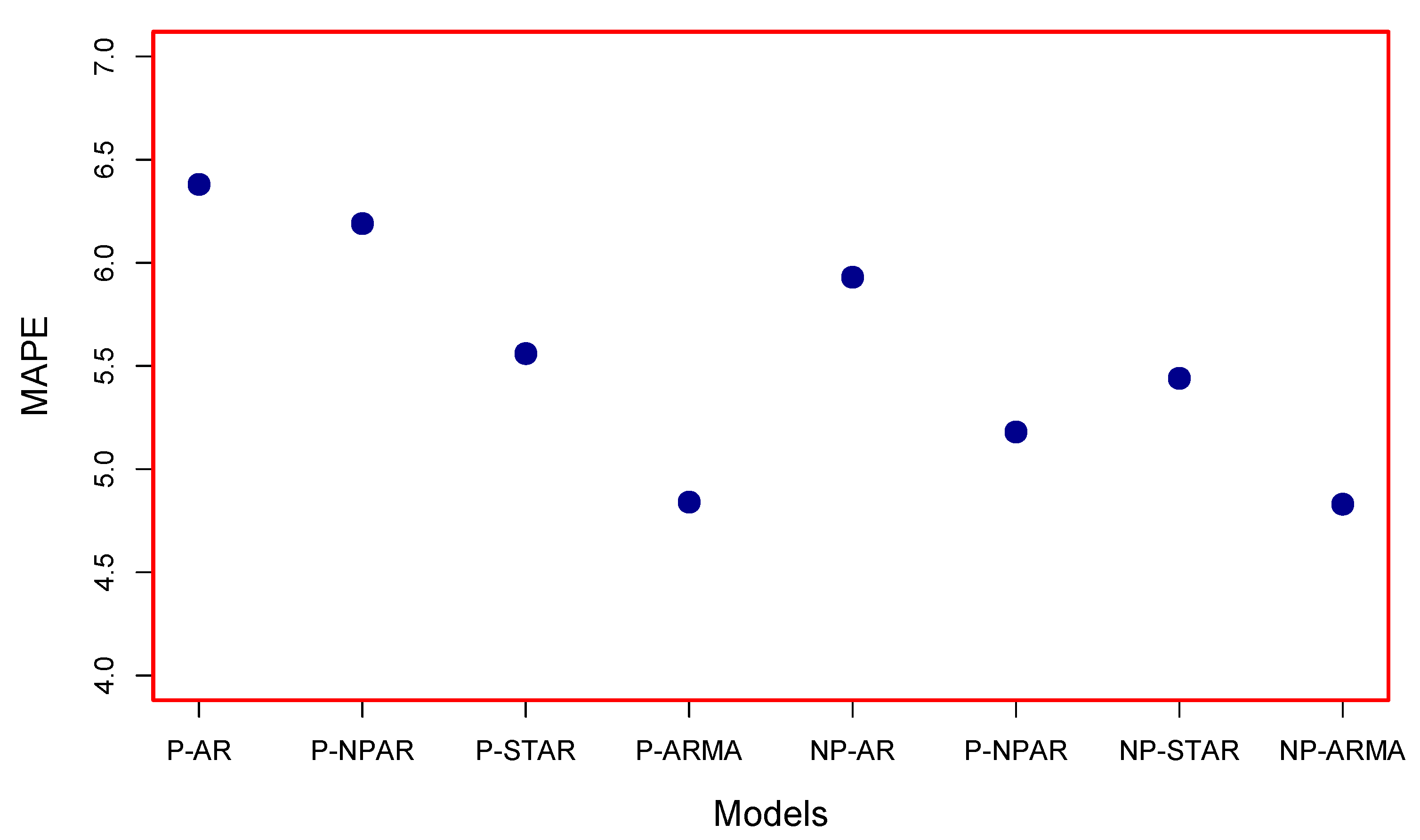
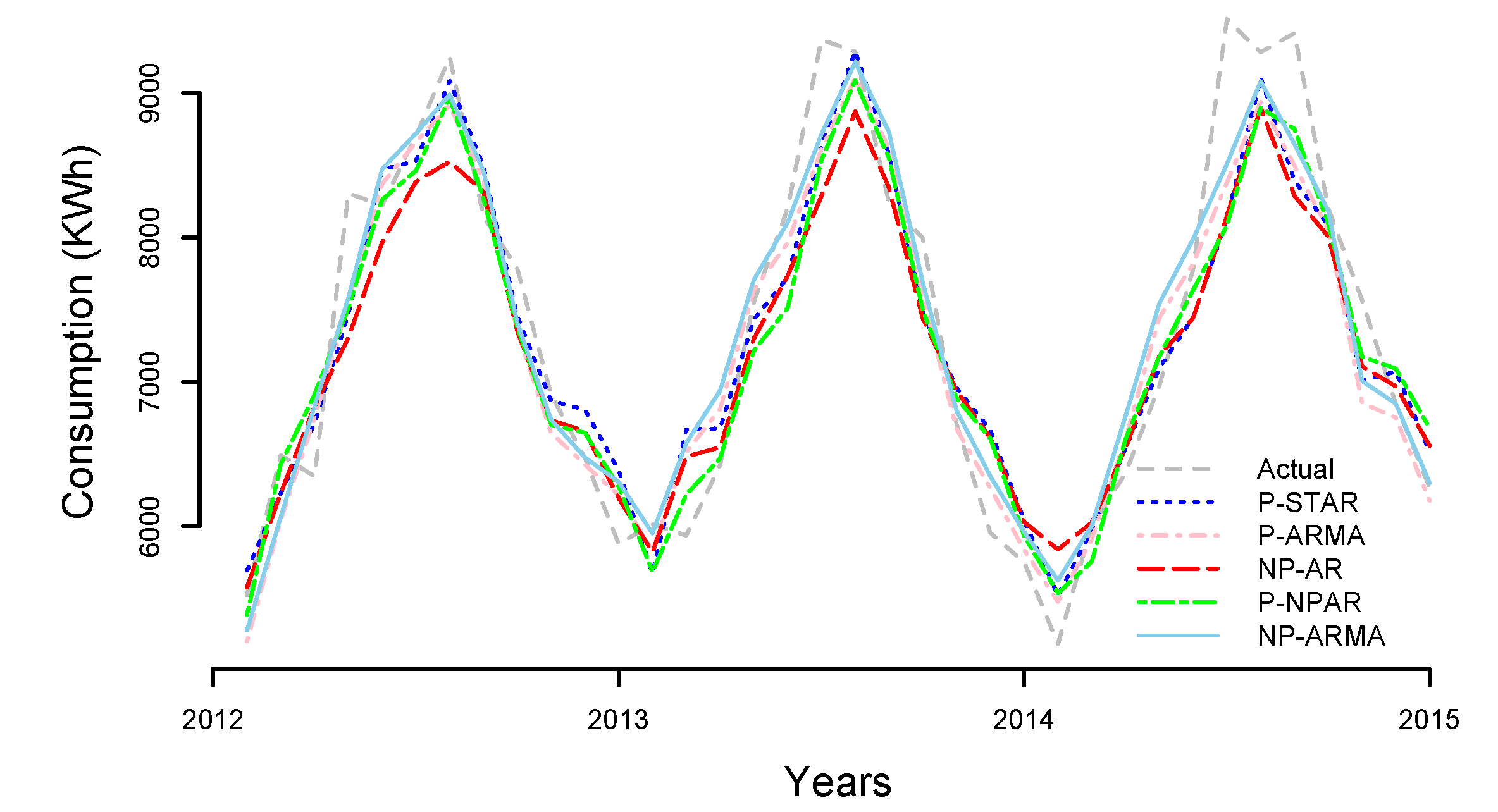
4. Out-of-Sample Forecasting
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hahn, H.; Meyer-Nieberg, S.; Pickl, S. Electric load forecasting methods: Tools for decision making. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 199, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S. Climate Change 2007—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fourth Assessment Report of the IPCC; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, V.; Manca, O.; Nardini, S. Electricity consumption forecasting in Italy using linear regression models. Energy 2009, 34, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.; Bodger, P. Forecasting electricity consumption in New Zealand using economic and demographic variables. Energy 2005, 30, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, D.; Tan, S.S.; Cheng, C.; Chan, E.K. Parallel neural network-fuzzy expert system strategy for short-term load forecasting: System implementation and performance evaluation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1999, 14, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakides, E.; Polycarpou, M. Short Term Electric Load Forecasting: A Tutorial. In Trends in Neural Computation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 391–418. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Romera, E.; Jaramillo-Moran, M.A.; Carmona-Fernandez, D. Monthly electric energy demand forecasting based on trend extraction. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringwood, J.V.; Bofelli, D.; Murray, F.J. Forecasting electricity demand on short, medium and long time scales using neural networks. Intel Robot Syst. 2001, 21, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, N.; Yokoyama, R.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, Z. A flexible long-term load forecasting approach based on new dynamic simulation theory—GSIM. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2001, 23, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSharry, P.E.; Bouwman, S.; Bloemhof, G. Probabilistic forecasts of the magnitude and timing of peak electricity demand. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2005, 20, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalexopoulos, A.D.; Hesterberg, T.C. A regression-based approach to short-term system load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1990, 5, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, R. Univariate modeling and forecasting of monthly energy demand time series using abductive and neural networks. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2008, 54, 903–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamaniotis, M.; Bargiotas, D.; Tsoukalas, L.H. Towards smart energy systems: Application of kernel machine regression for medium term electricity load forecasting. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González-Romera, E.; Jaramillo-Morán, M.Á.; Carmona-Fernández, D. Forecasting of the electric energy demand trend and monthly fluctuation with neural networks. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2007, 52, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucenic, C.; George, A. A Neuro-fuzzy Approach to Forecast the Electricity Demand. In Proceedings of the 2006 IASME/WSEAS International Conference on Energy & Environmental Systems, Chalkida, Greece, 8–10 May 2006; pp. 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, P.C.; Fan, C.Y.; Lin, J.J. Monthly electricity demand forecasting based on a weighted evolving fuzzy neural network approach. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2011, 33, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, D.; Atak, M. Grey prediction with rolling mechanism for electricity demand forecasting of Turkey. Energy 2007, 32, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Xia, F. Integration of Grey Model and Multiple Regression Model to Predict Energy Consumption. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Energy and Environment Technology, Guilin, China, 16–18 October 2009; Volume 1, pp. 194–197. [Google Scholar]
- Yanjun, L.; Yuliang, Z. Energy Demand Forecast of Henan Province by Using Gray Models GM (1, 1). Henan Sci. 2009, 12, 010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, G.; Dong, Y. Application of residual modification approach in seasonal ARIMA for electricity demand forecasting: A case study of China. Energy Policy 2012, 48, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, S.; Iqbal, N.; Anwar, S. Modelling electricity demand using the STAR (Smooth Transition Auto-Regressive) model in Pakistan. Energy 2014, 78, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, Y.; Oga, T.; Kakamu, K. Forecasting electricity demand in Japan: A Bayesian spatial autoregressive ARMA approach. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2010, 54, 2721–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, F.H.; Crone, S.F. Multivariate k-nearest NeighbourRegression forTime Series Data—A Novel Algorithm for Forecasting UK Electricity Demand. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Dallas, TX, USA, 4–9 August 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, D.H.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Agalgaonkar, A. A variance inflation factor and backward elimination based robust regression model for forecasting monthly electricity demand using climatic variables. Appl. Energy 2015, 140, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, W.; Sun, D. A trend fixed on firstly and seasonal adjustment model combined with the ε-SVR for short-term forecasting of electricity demand. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 4901–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.C.; Dong, Y.; Lai, C.Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Wei, S.Y. SVR with hybrid chaotic immune algorithm for seasonal load demand forecasting. Energies 2011, 4, 960–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.W. An artificial chromosomes embedded genetic algorithms for smart grid power demand forecast. J. Ind. Intell. Inf. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, T. Back propagation neural network with adaptive differential evolution algorithm for time series forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Ren, Y.; Suganthan, P.N.; Amaratunga, G.A. Empirical mode decomposition based ensemble deep learning for load demand time series forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 54, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Lo, S.K.; Do, Q.H. Forecasting monthly electricity demands: An application of neural networks trained by heuristic algorithms. Information 2017, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, I.; Lisi, F. Forecasting of electricity price through a functional prediction of sale and purchase curves. J. Forecast. 2020, 39, 242–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, F.; Sharif, M. Forecasting electricity consumption for Pakistan. Int. J. of Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2014, 4, 496–503. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Saba, T.; El-Amin, I. Artificial neural networks as applied to long-term demand forecasting. Artif. Intell. Eng. 1999, 13, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, R.; Al-Garni, A. Forecasting monthly electric energy consumption in eastern Saudi Arabia using univariate time-series analysis. Energy 1997, 22, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Iqbal, M.J.; Sharif, M. Relationship between extreme temperature and electricity demand in Pakistan. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2013, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mostafapour, E.; Panahi, M.; Farsadi, M. A Hybrid “k-means, VSS LMS” Learning Method for RBF Network in Short-term Load Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2015 9th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkey, 26–28 November 2015; pp. 961–965. [Google Scholar]
- Elattar, E.E.; Goulermas, J.; Wu, Q.H. Electric load forecasting based on locally weighted support vector regression. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybernet. Part C (Appl. Rev.) 2010, 40, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiassi, M.; Zimbra, D.K.; Saidane, H. Medium term system load forecasting with a dynamic artificial neural network model. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2006, 76, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, M.; Campbell, A.; Sangamwar, S.; Li, C.; Hong, T. Combining weather stations for electric load forecasting. Energies 2019, 12, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lisi, F.; Shah, I. Forecasting next-day electricity demand and prices based on functional models. Energy Syst. 2019, 1–30, In Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulakov, S. X-model: Further development and possible modifications. Forecasting 2020, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, I.; Lisi, F. Day-ahead Electricity Demand Forecasting with Non-parametric Functional Models. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM), Lisbon, Portugal, 19–22 May 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, I.; Iftikhar, H.; Ali, S.; Wang, D. Short-Term Electricity Demand Forecasting Using ComponentsEstimation Technique. Energies 2019, 12, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamil, F. On the electricity shortage, price and electricity theft nexus. Energy Policy 2013, 54, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A. Power Crisis in Pakistan: A Crisis in Governance? Technical report; Pakistan Institute of Development Economics: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, A.; Khan, K.; Akhtar, M. Energy intensity: A decomposition exercise for Pakistan. Pak. Dev. Rev. 2014, 53, 531–549. [Google Scholar]
- National Electric Power Regulatory Authority. (2011a); Report. 2011, Volume 46, pp. 1583–1599. Available online: https://nepra.org.pk/tariff/Tariff/KESC/2012/TRF-133%20KESC20Dec-2011%2028-05-2012%204778-82.PDF (accessed on 30 April 2020).
- Kessides, I.N. Chaos in power: Pakistan’s electricity crisis. Energy Policy 2013, 55, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Power Policy of Pakistan; Report. 2013, pp. 1–26. Available online: https://policy.asiapacificenergy.org/sites/default/files/National%20Power%20Policy%202013.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2020).
- An Overview of Electricity Sector In Pakistan; Islamabad Chamber of Commerce and Industry: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2015; Technical Report.
- Pakistan Economic Survey 2015–16; Report. 2016; pp. 1–10. Available online: http://www.finance.gov.pk/survey/chapters_16/highlights_2015_16.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2020).
- Weron, R.; Bierbrauer, M.; Trück, S. Modeling electricity prices: Jump diffusion and regime switching. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2004, 336, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Jong, C. The nature of power spikes: A regime-switch approach. Stud. Nonlinear Dyn. Econ. 2006, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosater, P.; Mosler, K. Can Markov regime-switching models improve power-price forecasts? Evidence from German daily power prices. Appl. Energy 2006, 83, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagbe, K.; Cugliari, J.; Jacques, J. Short-term electricity demand forecasting using a functional state space model. Energies 2018, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dordonnat, V.; Koopman, S.J.; Ooms, M. Intra-daily smoothing splines for time-varying regression models of hourly electricity load. J. Energy Mark. 2010, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, I. Modeling and Forecasting Electricity Market Variables. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Padova, Padova, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pilipovic, D. Energy Risk: Valuing and Managing Energy Derivatives; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 300. [Google Scholar]
- Escribano, A.; Ignacio Pe na, J.; Villaplana, P. Modelling electricity prices: International evidence. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2011, 73, 622–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veraart, A.E.; Veraart, L.A. Modelling Electricity Day-ahead Prices by Multivariate Lévy Semistationary Processes. In Quantitative Energy Finance; Springer: New York, USA, 2014; pp. 157–188. [Google Scholar]
- Lucia, J.J.; Schwartz, E.S. Electricity prices and power derivatives: Evidence from the nordic power exchange. Rev. Derivat. Res. 2002, 5, 5–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.M.; Chen, R.; Liu, L.M.; Harris, J.L. A semi-parametric time series approach in modeling hourly electricity loads. J. Forecast. 2006, 25, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, D.A.; Fuller, W.A. Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, P.C.; Perron, P. Testing for a unit root in time series regression. Biometrika 1988, 75, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Lean, H.H. The dynamics of electricity consumption and economic growth: A revisit study of their causality in Pakistan. Energy 2012, 39, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavaliere, G. Unit root tests under time-varying variances. Econ. Rev. 2005, 23, 259–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, B.; Parisio, L.; Pelagatti, M.; Baldi, F. Long-run relations in European electricity prices. J. Appl. Econ. 2010, 25, 805–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, L.A. All of Nonparametric Statistics; Springer: New York, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Teräsvirta, T. Specification, estimation, and evaluation of smooth transition autoregressive models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1994, 89, 208–218. [Google Scholar]
- Diebold, F.; Mariano, R. Comparing predictive accuracy. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 1995, 13, 253–263. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Rahman, M.; Memon, J.A. Forecasting electricity consumption in Pakistan: The way forward. Energy Policy 2016, 90, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SOURCE | PRODUCER | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WAPDA Hydel | 6516 | 6516 | 6733 | 6902 | 6902 | |
| HYDEL | IPPs Hydel | 129 | 214 | 214 | 214 | 214 |
| Sub-Total | 6645 | 6730 | 6947 | 7116 | 7116 | |
| % Share Generation | 28.47 | 28.65 | 29.28 | 29.99 | 28.67 | |
| GENCOs with PEPCO | 4785 | 4785 | 4785 | 4590 | 5762 | |
| KESC Own | 1821 | 2381 | 2359 | 1951 | 1874 | |
| IPPs | 4288.5 | 4282 | 4297 | 4489 | 201.5 | |
| THERMAL | RPPs | 201.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CPPs/SPPs (KESC) | 324 | 239 | 203 | 200 | 200 | |
| Sub-Total | 15,910 | 15,969 | 15,941 | 15,719 | 16,814 | |
| % Share Generation | %68.16 | 67.99 | 67.19 | 66.25 | 67.74 | |
| CHASNUPP I-II (NTDC) | 650 | 650 | 650 | 650 | 650 | |
| NUCLEAR | KANUPP (NTDC) | 137 | 137 | 137 | 137 | 137 |
| Sub-Total | 787 | 787 | 787 | 787 | 787 | |
| % Share Generation | 3.37 | 3.35 | 3.32 | 3.32 | 3.17 | |
| Wind P-P (PEPCO) | 0 | 1 | 50 | 106 | 106 | |
| WIND | Sub-Total | 0 | 1 | 50 | 106 | 106 |
| % Share Genration | 0 | 0 | 0.21 | 0.45 | 0.43 | |
| Total Installed Cap | 23,342 | 23,487 | 23,725 | 23,728 | 24,823 |
| Model | MAPE | MAE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| P-STAR | 5.56 | 397.99 | 513.22 |
| P-AR | 6.38 | 454.49 | 569.74 |
| P-NPAR | 6.19 | 439.79 | 563.21 |
| P-ARMA | 4.84 | 355.24 | 467.42 |
| NP-STAR | 5.44 | 402.78 | 526.67 |
| NP-AR | 5.93 | 435.63 | 550.41 |
| NP-NPAR | 5.18 | 379.98 | 492.81 |
| NP-ARMA | 4.83 | 348.31 | 460.80 |
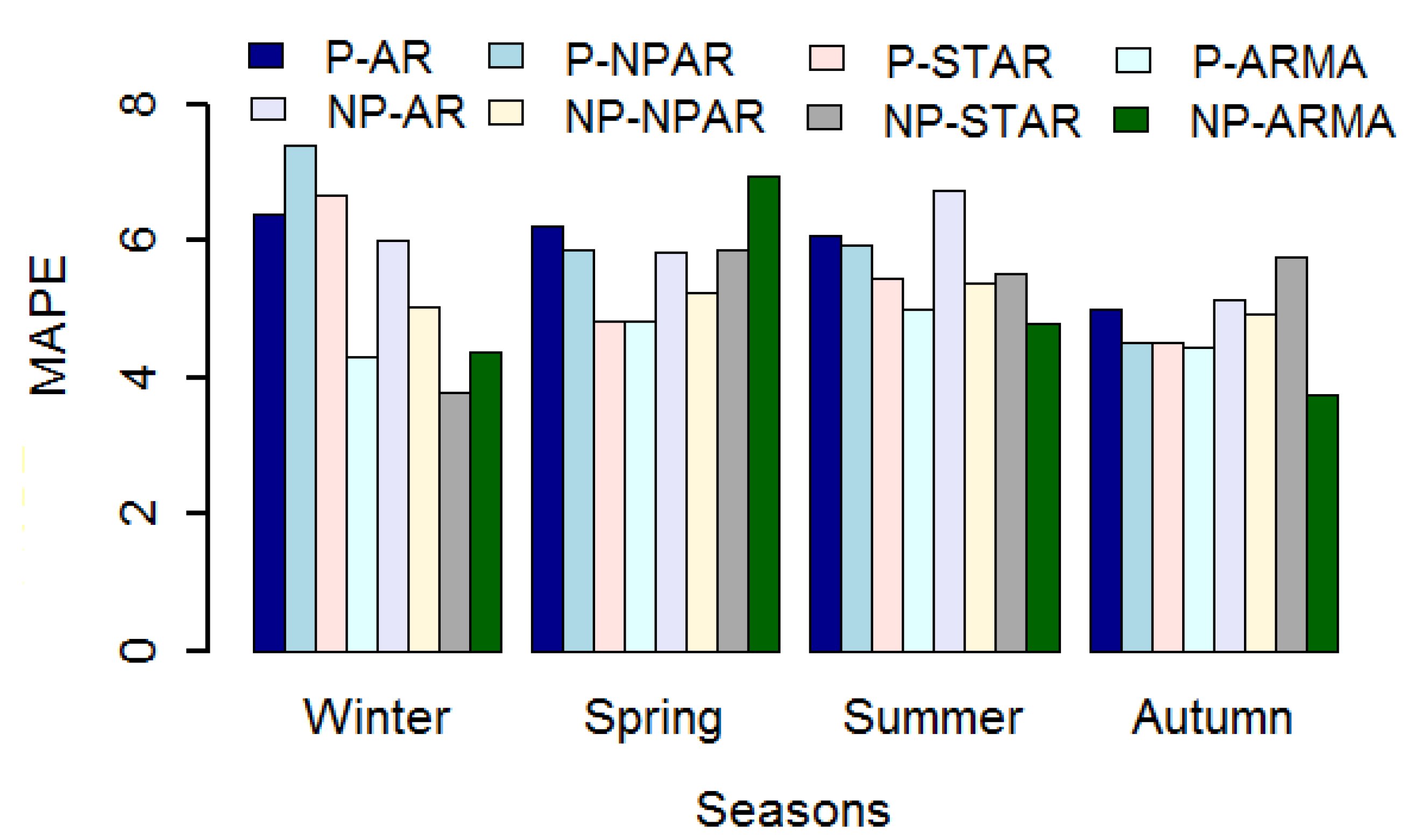
| Models | Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-AR | 6.38 | 6.21 | 6.09 | 5.00 |
| P-NPAR | 7.40 | 5.86 | 5.96 | 4.53 |
| P-STAR | 6.66 | 4.84 | 5.47 | 4.50 |
| P-ARMA | 4.31 | 4.84 | 5.02 | 4.45 |
| NP-AR | 6.03 | 5.83 | 6.75 | 5.14 |
| NP-NPAR | 5.05 | 5.26 | 5.39 | 4.92 |
| NP-STAR | 3.78 | 5.86 | 5.53 | 5.77 |
| NP-ARMA | 4.36 | 6.96 | 4.79 | 3.74 |
| MODELS | P-AR | P-NPAR | P-STAR | P-ARMA | NP-AR | NP-NPAR | NP-STAR | NP-ARMA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-AR | - | 0.41 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.09 | <0.01 |
| P-NPAR | 0.59 | - | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.01 |
| P-STAR | 0.98 | 0.94 | - | 0.02 | 0.82 | 0.16 | 0.66 | 0.03 |
| P-ARMA | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | - | 0.97 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 0.30 |
| NP-AR | 0.75 | 0.61 | 0.18 | 0.03 | - | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.03 |
| NP-NPAR | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 0.24 | 0.98 | - | 0.92 | 0.21 |
| NP-STAR | 0.91 | 0.77 | 0.34 | 0.03 | 0.87 | 0.08 | - | 0.04 |
| NP-ARMA | >0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.70 | 0.97 | 0.79 | 0.96 | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shah, I.; Iftikhar, H.; Ali, S. Modeling and Forecasting Medium-Term Electricity Consumption Using Component Estimation Technique. Forecasting 2020, 2, 163-179. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast2020009
Shah I, Iftikhar H, Ali S. Modeling and Forecasting Medium-Term Electricity Consumption Using Component Estimation Technique. Forecasting. 2020; 2(2):163-179. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast2020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleShah, Ismail, Hasnain Iftikhar, and Sajid Ali. 2020. "Modeling and Forecasting Medium-Term Electricity Consumption Using Component Estimation Technique" Forecasting 2, no. 2: 163-179. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast2020009
APA StyleShah, I., Iftikhar, H., & Ali, S. (2020). Modeling and Forecasting Medium-Term Electricity Consumption Using Component Estimation Technique. Forecasting, 2(2), 163-179. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast2020009