On Underdispersed Count Kernels for Smoothing Probability Mass Functions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Some Properties of Underdispersed Count Distributions
- The double Poisson pmf is defined bywithand where is the dispersion parameter and . The mean and variance do not have closed-form expressions but they can be approximated, respectively, by
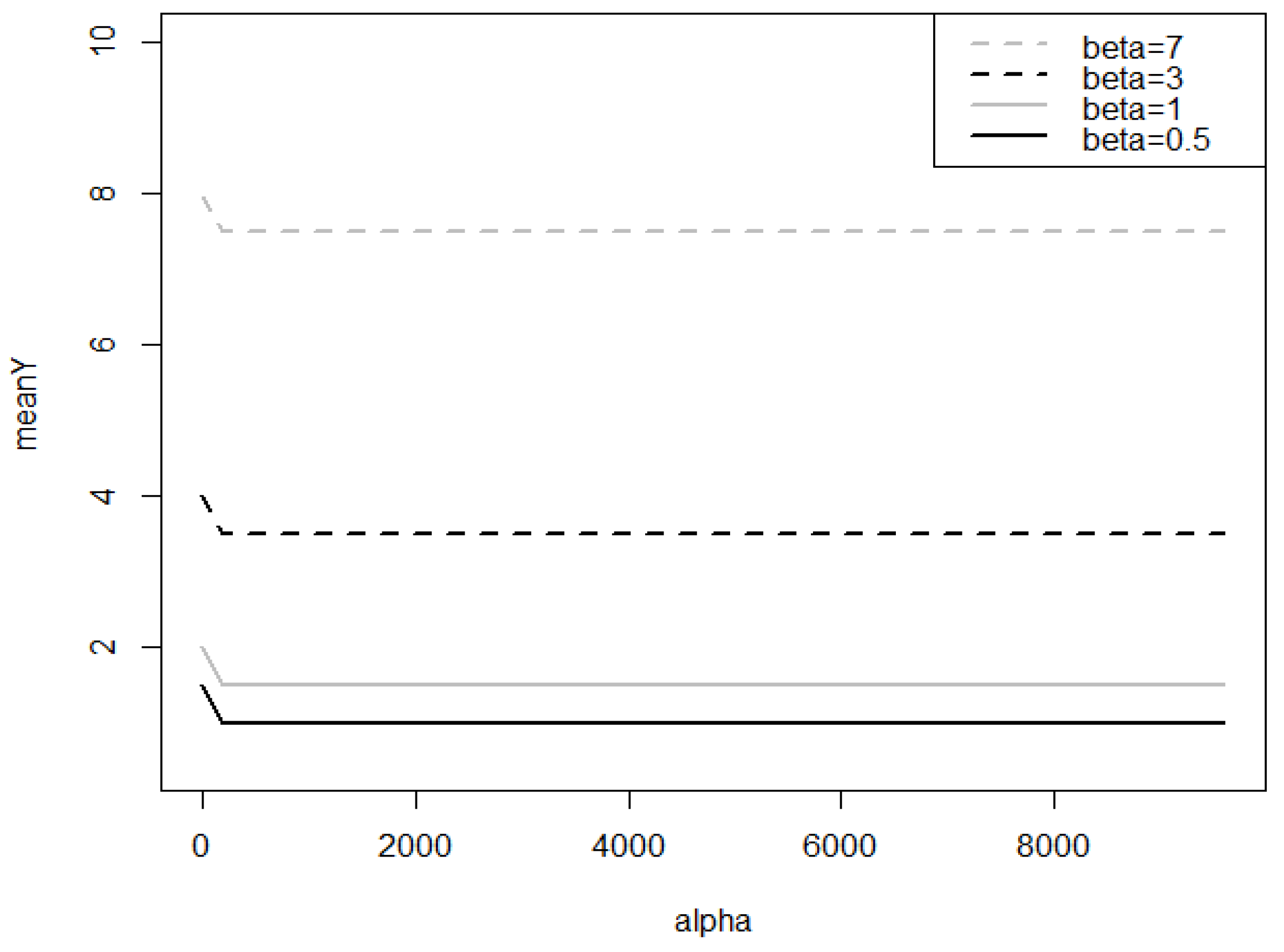
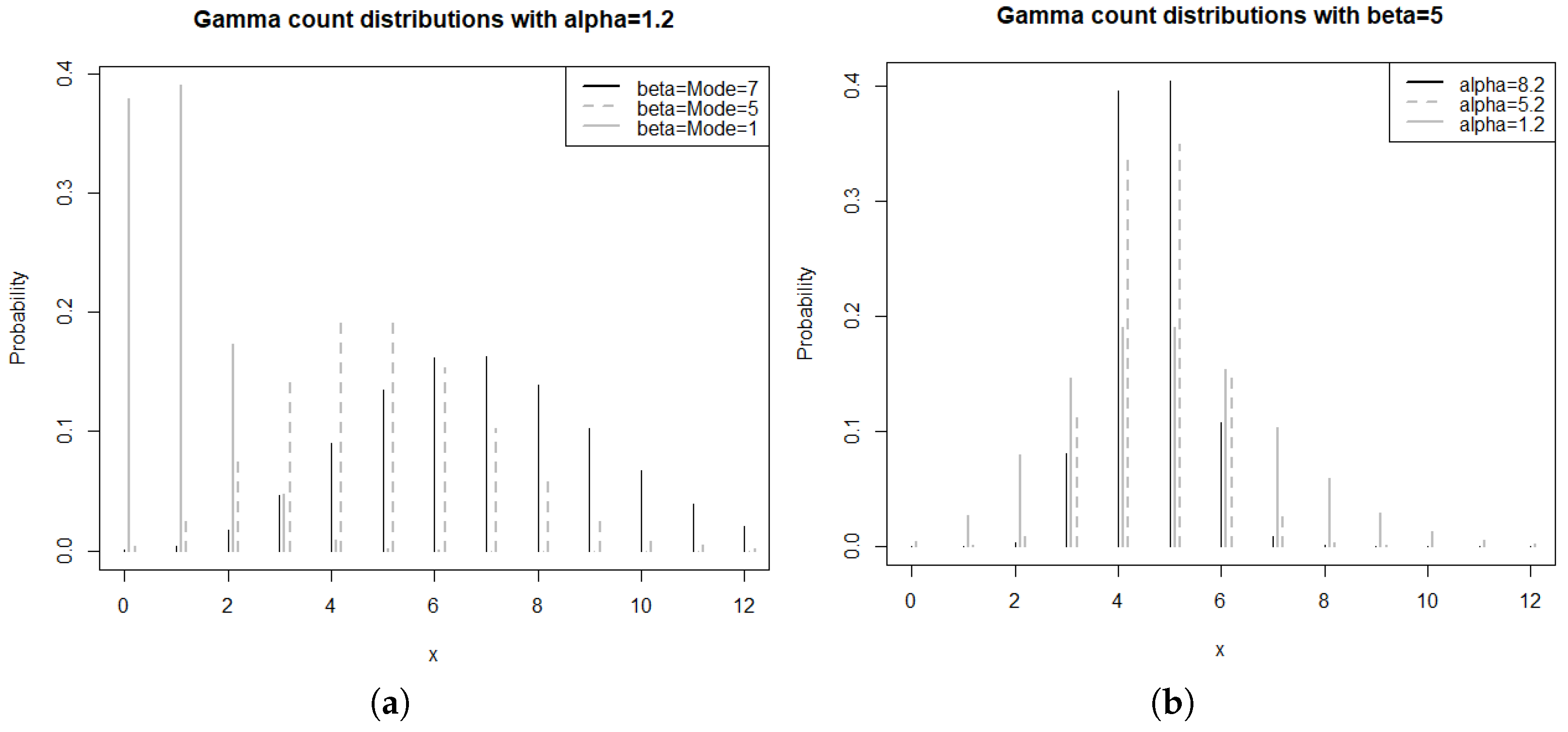
- The gamma-count pmf for the number of events within the time interval is given, with , throughwith the cumulative distribution functionand for and T can be set to one, without loss of generality. The parameter is such that and refer to underdispersion or overdispersion, respectively. Here, the mean and variance are not available in closed form but they can be computed throughSee Winkelmann [16] for further details, Zeviani et al. [17] for an application to regression model, and also [15].Numerically and from Figure 1, we can observe that the mean of the gamma-count distribution is almost always a constant around ; specifically, by zooming in, we notice that the shape of the curve is logarithmic or approximately linear in for fixed . The same fact is observed for its mode, as shown in Figure 2. We also note that Figure 2 highlights the role of as a shape or location parameter and as a scale or dispersion parameter of the gamma-count distribution. Hence, the variance of the gamma-count distribution can be seen as a function of .
- The CoM-Poisson distribution with location parameter and dispersion parameter ( for underdispersion) such that its pmf is defined bywhere function is the solution to equationand it is used to define the normalizing constant . Then,when as . See, for example, ref. [8] for some references.
3. Associated Kernel Versions
- (i)
- the mode m of always belongs to ;
- (ii)
- if μ is the mean of , then , where denotes the integer part.
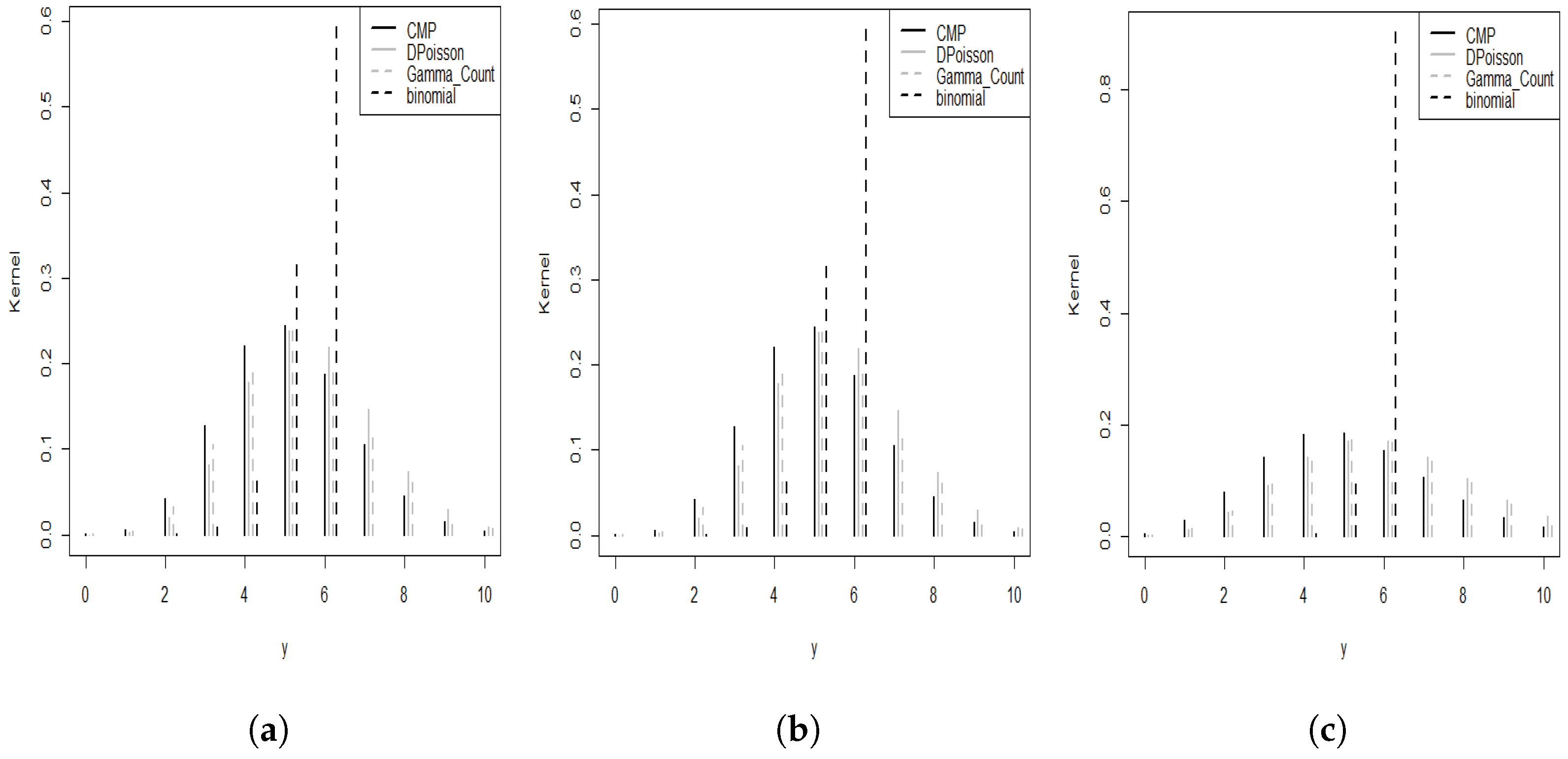
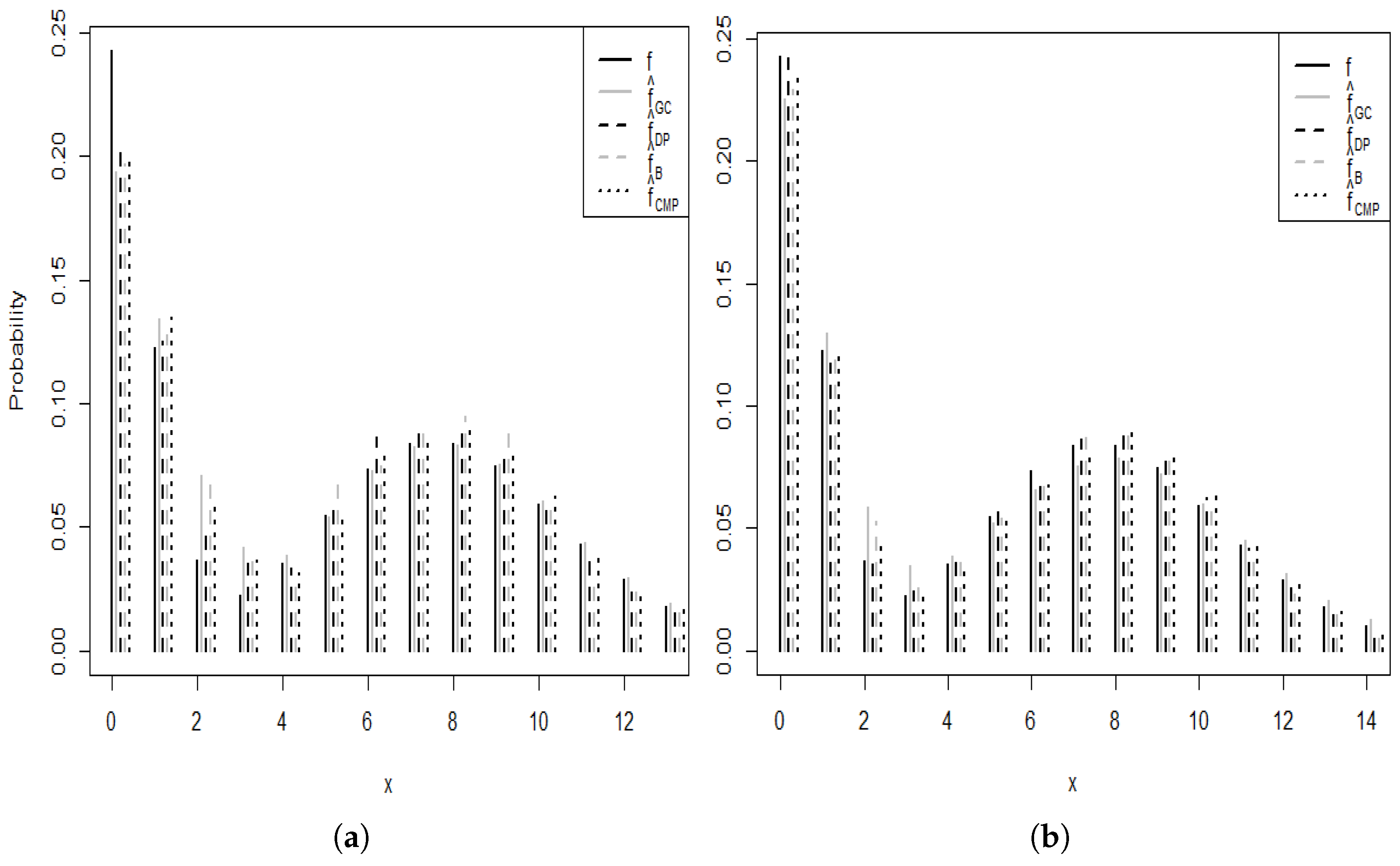
4. Simulation Studies and an Application to Real Data
- Scenario A is generated by using the Poisson distribution
- Scenario B comes from the zero-inflated Poisson distribution
- Scenario C is from a mixture of two Poisson distributions
- Scenario D comes from a mixture of three Poisson distributions
5. Summary and Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cmp | CoM-Poisson |
| dp | Double Poisson |
| gc | gamma-count |
| iid | Independent and identically distributed |
| ISE | Integrated squared error |
| pmf | Probability mass functions |
Appendix A. Some Other Underdispersed Count Distributions for Kernels Attempts
- The BerPoi distribution has its pmf,with and . Its mean and variance are, respectively,
- The generalized Poisson (GP) is defined through its pmf aswith and ; see Harris et al. [26]. The corresponding mean and variance are given byWe thus obtain underdispersion for .
- The pmf of the so-called Underdispersed Poisson distribution of Singh et al. [27] is given, for and , bywith
- The BerG distribution is defined bywith parameters and . Its mean and variance are, successively,This model presents overdispersion, equidispersion and underdispersion for , and , respectively. See Bourguignon and de Medeiros [28] for further details.
- The hyper-Poisson distribution, initially proposed by Bardwell and Crow [29], is defined as follows:with , for , r a positive integer, andas the confluent hypergeometric series. The mean and variance are
Appendix B. Local Bayesian Bandwidths of Discrete Kernels
References
- Harfouche, L.; Adjabi, S.; Zougab, N.; Funke, B. Multiplicative bias correction for discrete kernels. Stat. Methods Appl. 2018, 27, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somé, S.M.; Kokonendji, C.C.; Belaid, N.; Adjabi, S.; Abid, R. Bayesian local bandwidths in a flexible semiparametric kernel estimation for multivariate count data with diagnostics. Stat. Methods Appl. 2023, 32, 843–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, J.S.; Li, Q. Nomparametric estimation of regression functions with both categorical and continuous data. J. Econom. 2004, 119, 99–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokonendji, C.C.; Senga Kiessé, T. Discrete associated kernels method and extensions. Stat. Methodol. 2011, 8, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitchison, J.; Aitken, C.G.G. Multivariate binary discrimination by the kernel method. Biometrika 1976, 63, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Van Ryzin, J. A class of smooth estimators for discrete distributions. Biometrika 1981, 68, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Sippel, L.; Fung, T. Consistent second-order discrete kernel smoothing using dispersed Conway-Maxwell-Poisson kernels. Comput. Stat. 2022, 37, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esstafa, Y.; Kokonendji, C.C.; Somé, S.M. Asymptotic properties of the normalised discrete associated-kernel estimator for probability mass function. J. Nonparametric Stat. 2023, 35, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Borrego, I.; Opsomer, J.D.; Rueda, M.; Arcos, A. Nonparametric estimation with mixed data types in survey sampling. Rev. Mat. Complut. 2014, 27, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.; Li, Q.; Racine, J.S. A consistent model specification test with mixed discrete and continuous data. J. Econ. 2007, 140, 802–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Racine, J.S. Nonparametric Econometrics: Theory and Practice; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kokonendji, C.C.; Somé, S.M. On multivariate associated kernels to estimate general density functions. J. Korean Stat. Soc. 2018, 47, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.Y.; Henderson, D.J.; Parmeter, C.F. Plug-in bandwidth selection for kernel density estimation with discrete data. Econometrics 2015, 3, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B. Double exponential families and their use in generalized linear regression. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1986, 81, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, D.; Umetsu, C.A.; Camargo, A.F.M.; Rodrigues De Lara, I.A. Flexible models for non-equidispersed count data: Comparative performance of parametric models to deal with underdispersion. AStA Adv. Stat. Anal. 2022, 106, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmann, R. Duration dependence and dispersion in count-data models. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 1995, 3, 467–474. [Google Scholar]
- Zeviani, W.M.; Ribeiro, P.J., Jr.; Bonat, W.H.; Shimakura, S.E.; Muniz, J.A. The Gamma-count distribution in the analysis of experimental underdispersed data. J. Appl. Stat. 2014, 41, 2616–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jin, X.; Kawczak, J. Birnbaum-Saunder and lognormal kernel estimators for modelling durations in high frequency financial data. Ann. Econom. Financ. 2003, 4, 103–1024. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: http://cran.r-project.org/ (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Swihart, B.; Lindsey, J. Rmutil: Utilities for Nonlinear Regression and Repeated Measurements Models, R Package Version 1.1.0. 2017. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rmutil (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Wansouwé, W.E.; Somé, S.M.; Kokonendji, C.C. Ake: An R package for discrete and continuous associated kernel estimations. R J. 2016, 8, 258–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.; Alwan, A.; Wishart, J.; Huang, A. Mpcmp: Mean-Parametrized Conway-Maxwell Poisson (COM-Poisson) Regression, R Package Version 0.3.6. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/mpcmp/index.html (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Cahoy, D.; Di Nardo, E.; Polito, F. Flexible models for overdispersed and underdispersed count data. Stat. Pap. 2021, 62, 2969–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louzayadio, C.G.; Malouata, R.O.; Koukouatikissa, M.D. A weighted Poisson distribution for underdispersed count data. Int. J. Stat. Probab. 2021, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguignon, M.; Gallardo, D.I.; Medeiros, R.M. A simple and useful regression model for underdispersed count data based on Bernoulli–Poisson convolution. Stat. Pap. 2022, 63, 821–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.; Yang, Z.; Hardin, J.W. Model. Underdispersed Count Data Gen. Poisson Regression. Stata J. 2012, 12, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.P.; Singh, G.; Das, U.D.; Maurya, D.K. An Under-Dispersed Discrete Distribution and Its Application. J. Stat. Appl. Probab. Lett. 2021, 8, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon, M.; de Medeiros, R.M. A simple and useful regression model for fitting count data. Test 2022, 31, 790–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardwell, G.E.; Crow, E.L. A two-parameter family of hyper-Poisson distributions. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1964, 9, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez-Castillo, A.J.; Conde-Sánchez, A. A hyper-Poisson regression model for overdispersed and underdispersed count data. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2013, 61, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 20 | 0.14757 | 1.37290 | 0.07343 | 51.82259 |
| 50 | 0.22256 | 4.63862 | 0.14665 | 126.42510 |
| 100 | 0.42298 | 10.53522 | 0.16610 | 263.30720 |
| 250 | 0.79673 | 17.08182 | 0.25914 | 467.66510 |
| 500 | 1.82560 | 32.71456 | 0.49030 | 945.52740 |
| A | 10 | 9.2240 (7.9708) | 8.2596 (6.9910) | 24.5732 (19.0226) | 17.7012 (23.1386) |
| 25 | 3.4346 (2.2426) | 4.0327 (2.5589) | 8.5250 (5.8778) | 9.3622 (11.2054) | |
| 50 | 2.9191 (2.0443) | 3.5842 (2.7603) | 4.5986 (3.0472) | 5.4105 (4.0815) | |
| 100 | 1.8657 (1.2710) | 2.0070 (1.6637) | 2.2286 (1.3852) | 2.7595 (2.2578) | |
| 250 | 0.9299 (0.7017) | 0.9670 (0.7401) | 1.2736 (0.8046) | 1.2511 (0.9823) | |
| 500 | 0.5621 (0.3472) | 0.5906 (0.3923) | 1.2451 (0.6987) | 0.3669 (0.3047) | |
| B | 10 | 9.9963 (8.2902) | 10.4663 (8.8282) | 25.3129 (13.1625) | 26.0588 (26.1514) |
| 25 | 4.9811 (3.2787) | 5.4373 (4.2802) | 11.1561 (5.4033) | 10.5811 (8.4023) | |
| 50 | 3.1851 (2.2039) | 3.2929 (2.6541) | 5.0259 (3.1212) | 5.7034 (3.4369) | |
| 100 | 2.2802 (1.2304) | 1.8941 (1.3242) | 2.8072 (1.4701) | 3.3802 (2.0909) | |
| 250 | 1.7360 (0.7059) | 1.0332 (0.6626) | 1.3826 (0.6745) | 1.0374 (0.7745) | |
| 500 | 1.5323 (0.5410) | 0.6010 (0.6010) | 0.8543 (0.3585) | 0.6245 (0.4315) | |
| C | 10 | 10.1931 (7.5874) | 11.2862 (7.3767) | 20.3614 (10.5060) | 23.3991 (20.7747) |
| 25 | 5.3461 (3.8926) | 5.3975 (3.5143) | 8.1700 (4.1344) | 10.5258 (8.6422) | |
| 50 | 4.1610 (2.9936) | 4.0950 (2.6204) | 4.8990 (3.1218) | 5.0903 (4.2856) | |
| 100 | 2.9958 (2.0992) | 2.1094 (1.7659) | 2.8961 (2.6908) | 3.0479 (2.1213) | |
| 250 | 2.6143 (1.7647) | 1.5706 (1.2562) | 2.0777 (2.4729) | 0.8465 (0.5463) | |
| 500 | 2.3825 (1.4641) | 1.0457 (1.1703) | 1.6664 (2.4254) | 0.4847 (0.2213) | |
| D | 10 | 4.8289 (2.9155) | 4.9263 (2.9017) | 27.3001 (10.7675) | 10.7178 (20.0109) |
| 25 | 2.3274 (1.5628) | 2.5004 (1.5756) | 9.4341 (3.6559) | 9.8068 (9.6282) | |
| 50 | 1.6284 (1.0325) | 1.8046 (1.2067) | 4.8759 (1.9313) | 2.1646 (1.8732) | |
| 100 | 0.9935 (0.4916) | 1.0355 (0.6685) | 2.4179 (0.9076) | 1.1866 (0.7682) | |
| 250 | 0.5522 (0.5522) | 0.5493 (0.3678) | 0.9362 (0.4277) | 0.4444 (0.3726) | |
| 500 | 0.4297 (0.2286) | 0.3738 (0.2110) | 0.5068 (0.1881) | 0.3746 (0.2075) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kokonendji, C.C.; Somé, S.M.; Esstafa, Y.; Bourguignon, M. On Underdispersed Count Kernels for Smoothing Probability Mass Functions. Stats 2023, 6, 1226-1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats6040076
Kokonendji CC, Somé SM, Esstafa Y, Bourguignon M. On Underdispersed Count Kernels for Smoothing Probability Mass Functions. Stats. 2023; 6(4):1226-1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats6040076
Chicago/Turabian StyleKokonendji, Célestin C., Sobom M. Somé, Youssef Esstafa, and Marcelo Bourguignon. 2023. "On Underdispersed Count Kernels for Smoothing Probability Mass Functions" Stats 6, no. 4: 1226-1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats6040076
APA StyleKokonendji, C. C., Somé, S. M., Esstafa, Y., & Bourguignon, M. (2023). On Underdispersed Count Kernels for Smoothing Probability Mass Functions. Stats, 6(4), 1226-1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats6040076







