Abstract
This paper studies a subclass of the class of generalized hyperbolic distribution called the semi-hyperbolic distribution. We obtain analytical expressions for the cumulative distribution function and, specifically, their first and second lower partial moments. Using the received formulas, we compute the value at risk, the expected shortfall, and the semivariance in the semi-hyperbolic model of the financial market. The formulas depend on the values of generalized hypergeometric functions and modified Bessel functions of the second kind. The research illustrates the possibility of analysis of generalized hyperbolic models using the same methodology as is employed for the well-established variance-gamma model.
1. Introduction
In this paper, we explore a subclass of the generalized hyperbolic (GH) distribution, which we term the semi-hyperbolic distribution. The class of GH distribution was primarily introduced by Barndorff-Nielsen [1] for the investigation of the physics of dune movements. This distribution is infinitely divisible, and therefore, it originates from corresponding Lévy processes. The widely discussed subclasses of the GH distribution are the normal–inverse Gaussian (NIG) and the hyperbolic distribution. We call the considered subclass of distributions semi-hyperbolic because their probability density functions are close to the densities of the hyperbolic distribution. Presently, an important area of the applications of GH distribution is financial index modeling; see the work by Eberlein [2]. Next, we introduce the family of GH distribution in more detail. Specifically, we start from the discussion of the two most prominent members of the class of GH distribution: the NIG and hyperbolic distributions. We consider below several research papers in which the theoretical properties of these distributions are investigated, and the financial data are calibrated in the related market models.
The NIG distribution was first discussed in terms of financial applications by Barndorff-Nielsen [3] and Rydberg [4]. The properties of the NIG distribution are summarized in Barndorff-Nielsen [5]. Different approximations of the NIG Lévy processes are provided by Pacheco-González [6] and by Chapter 3 of Rasmus [7] and Benth et al. [8]. Computational methods in the NIG model for various problems of mathematical finance have been developed by Aguilar [9], Ivanov and Temnov [10], and Venter and de Jongh [11]. It has been shown by Mabitsela et al. [12] that the NIG distribution fits well with the equity behavior at the Johannesburg Stock Exchange.
The hyperbolic distribution was examined as a pattern for daily German stock index returns, primarily by Eberlein and Keller [13]. Eberlein et al. [14] confirmed the use of the hyperbolic model for the simulation of the NYSE composite. Küchler et al. [15] presented an empirical study that affirmed that the hyperbolic distribution fitted well to the stock returns of German companies listed on the DAX and the FAZ indices. Bauer [16] showed that the symmetric hyperbolic distribution estimates the 1% value-at-risk substantially better than the normal distribution. Dorić and Nikolić-Dorić [17] investigated how accurately the hyperbolic distribution described BELEX15 index returns.
Furthermore, we consider the two distributions that are very close to GH ones. They are the variance-gamma and skewed Student’s t distributions. As is revealed in Eberlein and von Hammerstein [18], the gamma and the inverse gamma distributions can be understood as limiting cases of the generalized inverse Gaussian (GIG) distribution. Therefore, since the GIG probability densities are the mixing densities for the GH distribution, the variance-gamma distribution and the skewed Student’s t distribution can be referred to as the limiting cases of the GH ones. The variance-gamma and skewed Student’s t distributions are very popular in financial applications. Madan and Seneta [19] modeled the indices of the Sydney Stock Exchange using the symmetric variance-gamma distribution and introduced a compound Poisson approximation for this distribution. Daal and Madan [20] showed that the variance-gamma model fitted well for the exchange rate dynamics of German financial markets. Rathgeber et al. [21] evaluated the parameters of the variance-gamma distribution gauging Dow Jones index returns. Employing the variance-gamma model, Wallmeier and Diethelm [22] calibrated the Swiss market for structured financial products. Alvarez and Baixauli [23] showed that the Student’s t model for index returns provides better results in value-at-risk estimation than the normal, the logistic, and the Edgeworth–Sargan models for several market variables. Using maximum likelihood estimation, Aas and Haff [24] calibrated the parameters of the skewed Student’s t distribution for international bonds and Norwegian indices. The theoretical properties of the skewed Student’s t distribution were investigated by Finlay and Seneta [25]. Müller and Righi [26] confirmed that the skewed Student’s t model has good performance for value-at-risk prediction based on the Ibovespa index statistics.
Analytical results for distribution functions, risk measures, and option prices are obtained in the mentioned models using generalized hypergeometric functions, which are computed very fast. For their properties and connections with other special functions, see Rathie and de Sena Monteiro Ozelim [27], Choi et al. [28], and Srivastava [29]. We refer to Madan et al. [30], Ano and Ivanov [31], and Ivanov [32] regarding the variance-gamma model, to Ivanov [33] regarding the skew Student’s t model, and to Ano and Ivanov [31] and Ivanov and Temnov [10] regarding the NIG one. At the same time, modern research papers that analyze data from financial markets often recommend the simulation of index returns with GH distribution as well as the above-mentioned ones.
The following works study the class of GH distribution without the suggestion that one of the parameters of the distribution is fixed. In particular, all parameters of the GH distribution are estimated in those papers about financial market data. Daskalaki and Katris [34] reported that the GH distribution is the most successful choice for European stock market modeling. Baciu [35] showed that the GH model is the best fit for Bucharest Stock Exchange returns. Rathgeber et al. [36] extended the simplified method of moments for the problem of the estimation of the parameters of the GH process. Balter and McNeil [37] calibrated symmetric GH distribution based on S&P500 index statistics. An extension of the family of GH distributions was introduced in Klebanov and Rachev [38]. Mixtures of the GH distribution have been studied by Han and Yin [39].
Semi-hyperbolic distribution is a subclass of GH distribution, which is determined by the parameter for this subclass (see Section 2 in this paper for details). In particular, as is shown in Table 12 of Daskalaki and Katris [34], this value of conforms to the movements of the OMXH25 and SAX indices. The aim of this paper is to obtain analytical results for the theoretical characteristics of the semi-hyperbolic distribution and to apply them to the computation of the basic monetary risk measures in the semi-hyperbolic model.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 describes the class of GIG distribution, including the semi-hyperbolic inverse Gaussian (SHIG) one, which is the mixing distribution for the semi-hyperbolic distribution. In Section 3, we present the probability density function and the moments of the semi-hyperbolic distribution, and formulate the main theoretical results of the work. The values of the monetary risk measures are given in Section 4. Examples of the calculation of the obtained formulas are presented in Section 5.
2. Materials and Methods
As mentioned in the previous section, the semi-hyperbolic distribution is a normal mean-variance mixture, where the mixing density is the semi-hyperbolic inverse Gaussian (SHIG) distribution. The SHIG distribution is a member of the class of generalized inverse Gaussian (GIG) distributions. This class introduced in Good [40], Sichel [41] and Barndorff-Nielsen [1] for the aim of statistical modeling in variety of scientific areas. Properties of the family of GIG distributions are summarized in Eberlein and von Hammerstein [18]. Methods of the parameter estimation for these distributions were discussed by Tsai et al. [42] and Lee and Whitmore [43].
A generalized inverse Gaussian distribution has the probability density function
where
is the modified Bessel function of the second kind (on its properties, see Chapters 9 and 10 of Abramowitz and Stegun [44]). The restrictions on the parameters in (1) are and .
Next, we consider important examples of the GIG distributions and their limiting cases (see Eberlein and von Hammerstein [18] for details), which are mentioned in the Introduction.
Example 1.
Inverse Gaussian distribution. Since
with respect to formula 8.469.3 of Gradshteyn and Ryzhik [45], we have in the case of that
where has the inverse Gaussian distribution, that is
for a Wiener process (see Subsection 2.2.1 of Rasmus [7] or Chapter III.1d.3 of Shiryaev [46]).
Example 2.
Hyperbolic inverse Gaussian distribution. If , then
where has the hyperbolic inverse Gaussian distribution with parameters and , see (10) in Eberlein and Keller [13].
Example 3.
Gamma distribution. The modified Bessel function of the second kind has the asymptotics (see 9.6.9 of Abramowitz and Stegun [44]) for
where is the gamma function. It follows immediately from (4) that if , then
Therefore, we have from (1) and (5) that
where Y has the gamma distribution with the parameters λ and .
Example 4.
In this paper, we consider the case of in (1). The semi-hyperbolic inverse Gaussian distribution has the three parameters , and the probability density function
The semi-hyperbolic distribution is defined as the normal mean-variance mixture (see Barndorff-Nielsen [1], Section 3.2 of McNeil et al. [47] and Chapter III.1d of Shiryaev [46] on the theory of mean-variance mixtures) with the SHIG mixing density, that is
where , and is the standard normal random variable independent with the SHIG one. Further, we study the SH distribution based on the definition (8).
3. Preliminary Formulas
In this section, we specify formulas that have been first received in general forms by Barndorff-Nielsen and Stelzer [48], Scott et al. [49] and given in Chapters 9.4 and 9.5 of Paolella [50] for the GIG and GH distributions. These identities are also required since the GH distribution was defined in those works with in the mixtures of type (8).
Let
The characteristic function of the SHIG distribution is computed as
Formula (3.471.9) of Gradshteyn and Ryzhik [45] includes the identity
for and . Using (10), we find that
Similarly to (11), it is easy to find that the moments for of the SHIG distribution are determined by the equality
Next, let us discuss the characteristic function of the SH distribution. Since
and
we find that
Applying (8), we find that the moments for of the SH distribution can be derived as
where is the integer part of and the moments of the SHIG distribution are determined by (12).
Set
and
Then we can rewrite as
The identity (16) is used onwards for the computation of the characteristics of the SH distribution.
4. Main Results
The main results of this paper give us the formulas for the cumulative semi-hyperbolic distribution functions and the first and second lower partial moments of the semi-hyperbolic distribution. To formulate the results, we should introduce extra notations.
We set
Together with it, we employ a designation (see (16) at p.25 of Srivastava and Karlsson [51])
for the degenerate generalized hypergeometric function (the confluent Appell function or the Humbert series), which is the double sum
for , where , , is the Pochhammer’s symbol. For more information on the generalized hypergeometric functions and their integral representations, we refer to Sections 1.2 and 1.3 of Srivastava and Karlsson [51], Section 4.22 of Erdélyi et al. [52] and Srivastava et al. [53]. Hypergeometric functions on the complex plane are considered in Sadykov [54,55]. Generalized hypergeometric series of matrix variables are discussed by Cuchta et al. [56,57].
The next theorem yields an analytical expression for the cumulative semi-hyperbolic distribution function.
Theorem 1.
Proof Sketch.
The proof of Theorem 1 can be divided into three steps.
Step 1. We show that the computation of the required probability can be cut to the calculation of the integral
Step 2. For , the integral is transformed so that formula 3.383.8 of Gradshteyn and Ryzhik [45] can be applied to it.
Step 3. For , we convert to a special form so that formula 4.3.24 of Erdélyi et al. [52] can be used to it.
□
The complete proof is set in Appendix A (see Proof of Theorem 1 therein).
The following example illustrates how Theorem 1 works for the simplest case .
Example 5.
The lower partial moments of the semi-hyperbolic distribution are defined by the identity
The theorem below provides explicit formulas for the first and second lower partial moments of the SH distribution.
Theorem 2.
For , the lower partial moments
and
with , and
where .
Proof Sketch.
The proof of Theorem 2 can be divided into four steps.
Step 1. The general formula for the nth lower partial moment is received.
Step 2. The value of the first lower partial moment is obtained using the result of Theorem 1.
Step 3. It is shown that the computation of the second lower partial moment can be reduced to the calculation of the integral
Step 4. The integral is transformed so that formula 4.3.24 of Erdélyi et al. [52] can be employed to it. □
The full proof is given in Appendix A (see Proof of Theorem 2 therein).
5. Applications
The standards of Basel III regulations order the use of monetary risk measures to control the market risk to banks. The main risk measure is called the value-at-risk (VaR). Informally, the p-VaR can be defined as the maximum possible loss of the final net worth after excluding all worse outcomes whose combined probability is at most p. In an appropriate probabilistic model, the p-VaR is defined as the upper p-quantile of the loss distribution with the minus sign. That is, if the loss is modeled by a random variable , the p-VaR of is
see Definition 3.3 in Artzner et al. [58] or Definition 4.40 in Föllmer and Schied [59]. Let us note that this definition of the VaR implies small values of the parameter p. An alternative definition, with a large p, is given in McNeil et al. [47], see Definition 2.10 therein.
The expected shortfall (ES) monetary risk measure can be suggested as a substitution of the VaR since the ES takes into account the tail risk. Because of it, the ES is recommended to banks by the Basel III regulations instead of the VaR, which had been ordered by Basel II. Mathematically, the ES of level p is defined for a random outcome as
A number of research papers were set to calculate the basic risk measures in various models. The computations of the measures in semi-analytical forms by the Fourier transform technique are given in Armenti et al. [60] and Drapeu et al. [61]. Analytical formulas for some specific models are provided by Ivanov [62,63] and Rockafellar and Uryasev [64]. Monte Carlo simulations of the VAR and ES were made by Chun et al. [65] and Mafusalov and Uryasev [66]. Nonparametric methods for the estimation of these basic monetary risk measures were developed in Cai and Wang [67], Chen and Tang [68] and Scailett [69].
An advanced risk measurement can be used by banks for the aim of the management and control. Although the variance is often employed for the portfolio optimization problems (see, for example, Fontana and Schweizer [70] and Schweizer et al. [71]), it is not the appropriate choice if the underlying distribution is asymmetric. Because of it, the target semivariance risk measure is applied. The target u semivariance of is defined as
A summary of early studies about the semivariance is given in Nawrocki [72]. Performance risk measures based on the semivariance were introduced by van der Meer and Sortino [73] and van der Meer et al. [74]. The realized semivariance was studied in Barndorff-Nielsen et al. [75]. An empirical analysis was produced by Ang et al. [76]. Computations for non-Gaussian cases were made by Jarrow and Zhao [77] and Ivanov [78].
In this section, we assume that there are n assets in the investment portfolio whose dynamics are determined as
where , , is the semi-hyperbolic inverse Gaussian variable and , are the standard normal random variables with correlation coefficients between and . It is supposed that the normal distributions are independent with the semi-hyperbolic inverse Gaussian one. Also, we propose that a non-risk asset is included in the portfolio. Namely, with the dynamic
As mentioned in the Introduction, Daskalaki and Katris [34] have made a detailed calibration of the GH distribution for different market indices. It is found by them that the estimations of the parameter are and for the OMXH25 and SAX indices, respectively (see Table 12 therein). We assume that the considered portfolio consists of stocks from the indices with . Such portfolios should be modeled by the semi-hyperbolic distribution.
To assess the risks of portfolio at the time , it is enough to discuss the random variable
Set
Because of
where is again the standard normal distribution, we have that
To compute the p-VaR of , we have to find the quantile solving an equation
with one of the zero-finding algorithms, see Brent [79] for details. Once again, since has a continuous distribution, we have that
It issues immediately from (22) that
Implementing (23), we obtain the following corollary of Theorems 1 and 2.
Corollary 1.
The value-at-risk is determined as the solution of the equation
with the minus sign. The expected shortfall is calculated with respect to the formula
The target u semivariance is computed as
6. Numerical Analysis
In this section, we compare the normal and semi-hyperbolic distributions. The idea is to adjust the parameters of the SH distribution so that the second moments of the distributions match each other.
Set . Then, the sought should solve the equation
The tables of the values of the modified Bessel function of the second kind give us the solution
Therefore, we compare the distributions
Set . Then, the probability density functions of these normal and semi-hyperbolic distributions are
respectively. The density functions are plotted at Figure 1.
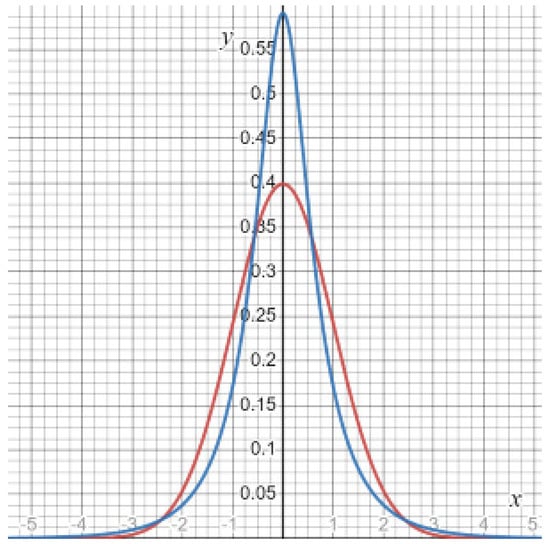
Figure 1.
The normal (red) and semi-hyperbolic (blue) probability density functions.
Furthermore, it follows from (18) that
with
Formula (4.3.24) of Erdélyi et al. [52] includes the identity
for , and . We have from (25) that
where
Hence, we find that for
where
Based on the calculations above, Table 1 provides the comparison of the symmetric normal and semi-hyperbolic distributions (24) with the same mean and variance for variant arguments.

Table 1.
The comparison of the cumulative distribution functions.
7. Discussion
The obtained results show that the analytical expressions based on values of generalized hypergeometric functions (Sections 1.2 and 1.3 of Srivastava and Karlsson [51]) are approachable for the GH models besides the NIG one (Ivanov and Temnov [10]). The derived formulas use the modified Bessel function of the second kind, the Appell function, and can be computed under one second with the modern software. As in the VG model (Madan et al. [30], Ivanov [63]), the explicit solutions are obtained for the cumulative distribution function, the first and second lower partial moments of the SH distribution, and the received formulas are applied to the problem of computation of the VAR, the ES, and the semivariance in the related investment portfolio model with dependent asset returns.
Numerical computations, which are provided for the symmetric normal and SH distributions with the same mean and variance have discovered that the cumulative distribution functions significantly differ at the tails and mid part. The SH distribution has the tails for the arguments and 3, which are six times larger than the idem tails of the normal one. And at the same time, the mid part (between and ) of the SH distribution relates to the similar part of the normal one as 5 to 4. Therefore, we deduce that the SH model distinguishes better phenomena with a larger number of extreme events and events close to the mean value.
A future study should yield the computation of the nth lower partial moments of SH distribution together with the calculation of the prices of option contracts in the SH model since such results are available in the VG model, see Madan et al. [30] and Ivanov [78]. The SH Lévy process with drift switching (Ivanov [63]) can be studied. Together with it, the next investigations should relate to the obtaining of analytical solutions for the GH hyperbolic distributions with integer including the hyperbolic one of Eberlein and Keller [13]. Although the standard stochastic simulation methods (Chapter XII of Asmussen and Glynn [80]) can be applied to the semi-hyperbolic distribution, it is necessary to notice that their speed is often insufficient. Because of this, an interesting problem is to develop fast quasi-Monte Carlo procedures for the SH distribution similarly to the methods that are developed for the variance-gamma distribution (Avramidis et al. [81], Avaramidis and L’Ecuyer [82] and Chapter 6.2 of Lemieux [83]).
8. Conclusions
Taking into account the review of the related literature, the results of this paper, including the applications and the numerical analysis, and the discussion of the results, we can make the following conclusions.
- –
- The review of the literature about the class of GH distribution confirms the necessity of the development of the mathematical methods of its analysis.
- –
- The subclass of the family of GH distributions, the semi-hyperbolic distributions, is analytically tractable similarly to the VG distributions.
- –
- The obtained formulas depend on the values of degenerate generalized hypergeometric functions and can be computed very fast.
- –
- The numerical analysis shows that the SH distribution discerns better than the normal data with heavy tails and a central part.
- –
- Keeping in mind the amount of work, we look forward to the future studies of the whole class of GH distribution.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank the anonymous referees whose remarks have significantly improved the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| GH | Generalized Hyperbolic |
| SH | Semi-Hyperbolic |
| GIG | Generalized Inverse Gaussian |
| NIG | Normal-Inverse Gaussian |
| SHIG | Semi-Hyperbolic Inverse Gaussian |
| VaR | Value-at-Risk |
| ES | Expected Shortfall |
Appendix A
Proof of Theorem 1.
Next, we compute for variant values of v.
Case 1. . Set
Then,
where
with . Therefore,
when .
Put . Thereat
and therefore
Case 1.1. . Then,
Formula (3.383.8) of Gradshteyn and Ryzhik [45] includes the identity
for , , . Applying (A6) to (A5), we find that
According to (A6), we find that
Next, we find that
Formula (4.3.24) of Erdélyi et al. [52] comprises the identity
for , and . Employing (A11) to (A10), we find that
Case 2. . Then,
and we can use Case 1 herein. Then,
if .
Proof of Theorem 2.
At first, let us discuss the nth lower partial moment of the semi-hyperbolic distribution for . We have from (16) that
where
.
Next, we pass to the computation of the first lower partial moment. We find that
Since
it is easy to notice that
Therefore, we find that
and obtain (20).
Furthermore, we calculate the second lower partial moment of the semi-hyperbolic distribution. We find that
with
Integrating by parts, we find that
with
where .
Let . Then,
and hence
Set . Then,
where
and
with
Put for . Thereat
and
References
- Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E. Exponentially decreasing distributions for the logarithm of particle size. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1977, 353, 401–419. [Google Scholar]
- Eberlein, E. Application of generalized hyperbolic Lévy motions to finance. In Lévy Processes: Theory and Applications; Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E., Mikosch, T., Resnick, S., Eds.; Birkhäuser Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 319–337. [Google Scholar]
- Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E. Normal inverse Gaussian distributions and stochastic volatility modelling. Scand. J. Stat. 1997, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydberg, T.H. The normal-inverse Gaussian process: Simulation and approximation. Stoch. Model. 1997, 13, 887–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E. Processes of normal inverse Gaussian type. Financ. Stoch. 1998, 2, 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-González, C.G. Approximation for the normal inverse Gaussian process using random sums. Stoch. Anal. Appl. 2009, 27, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmus, S. Pricing Exotic Derivatives Using Lévy Process Input; Media-Tryck: Lund, Sweden, 2004; pp. 31–49. [Google Scholar]
- Benth, F.E.; Di Persio, L.; Lavagnini, S. Stochastic modeling of wind derivatives in energy markets. Risks 2018, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, J.-P. Explicit option valuation in the exponential NIG model. Quant. Financ. 2021, 21, 1281–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, R.V.; Temnov, G. Truncated moment-generating functions of the NIG process and their applications. Stoch. Dyn. 2017, 17, 1750039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, J.; de Jongh, R. Risk estimation using the normal inverse Gaussian distribution. J. Risks 2002, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabitsela, L.; Maré, E.; Kufakunesu, R. Quantification of VaR: A note on VaR valuation in the South African equity market. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2015, 8, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberlein, E.; Keller, U. Hyperbolic distributions in finance. Bernoulli 1995, 1, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberlein, E.; Keller, U.; Prause, K. New Insights into smile, mispricing, and value at risk: The hyperbolic model. J. Bus. 1998, 71, 371–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küchler, U.; Neumann, K.; Sorensen, M.; Streller, A. Stock returns and hyperbolic distributions. Math. Comput. Model. 1999, 29, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C. Value at risk using hyperbolic distributions. J. Econ. Bus. 2000, 52, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorić, D.; Nikolić-Dorić, E. Return distribution and value at risk estimation for BELEX15. Yugosl. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 21, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberlein, E.; von Hammerstein, E.A. Generalized hyperbolic and inverse Gaussian distributions: Limiting cases and approximation of processes. In Seminar on Stochastic Analysis, Random Fields and Applications IV, Progress in Probability; Dalang, R.C., Dozzi, M., Russo, F., Eds.; Birkhäuser Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2004; Volume 58, pp. 221–264. [Google Scholar]
- Madan, D.B.; Seneta, E. The variance gamma (V.G.) model for share market returns. J. Bus. 1990, 63, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daal, E.A.; Madan, D.B. An empirical examination of the variance-gamma model for foreign currency options. J. Bus. 2005, 78, 2121–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathgeber, A.W.; Stadler, J.; Stöckl, S. Modeling share returns—An empirical study on the variance gamma model. J. Econom. Financ. 2016, 40, 653–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallmeier, M.; Diethelm, M. Multivariate downside risk: Normal versus variance gamma. J. Futur. Mark. 2012, 32, 431–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.; Baixauli, J.S. Evaluating effects of excess kurtosis on VaR estimates: Evidence for international stock indices. Rev. Quant. Financ. Account. 2006, 27, 27–46. [Google Scholar]
- Aas, K.; Haff, I.H. The generalized hyperbolic skew Student’s t-distribution. J. Financ. Econom. 2006, 4, 275–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, R.; Seneta, E. Stationary-increment student and variance-gamma processes. J. Appl. Probab. 2006, 43, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.M.; Righi, M. Comparison of value at risk (VaR) multivariate forecast models. Comput. Econ. 2022, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathie, P.N.; de Sena Monteiro Ozelim, L.C. On the relation between Lambert w-function and generalized hypergeometric functions. Stats 2022, 5, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Hasanov, A.; Srivastava, H.M.; Turaev, M. Integral representations for Srivastava’s triple hypergeometric functions. Taiwan. J. Math. 2011, 15, 2751–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, H.M. A survey of some recent developments on higher transcendental functions of analytic number theory and applied mathematics. Symmetry 2021, 13, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, D.B.; Carr, P.; Chang, E.C. The variance gamma process and option pricing. Rev. Financ. 1998, 2, 79–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ano, K.; Ivanov, R.V. On exact pricing of FX options in multivariate time-changed Lévy models. Rev. Deriv. Res. 2016, 19, 201–216. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, R.V. The downside and upside beta valuation in the variance-gamma model. Int. J. Anal. Appl. 2021, 19, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, R.V. On the stochastic volatility in the generalized Black-Scholes-Merton model. Risks 2023, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalaki, S.; Katris, C. Marginal distribution modeling and value at risk estimation for stock index returns. J. Appl. Oper. Res. 2014, 6, 207–221. [Google Scholar]
- Baciu, O.A. Generalized hyperbolic distributions: Empirical evidence on Bucharest stock exchange. Rev. Financ. Bank. 2015, 7, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Rathgeber, A.W.; Stadler, J.; Stöckl, S. Fitting generalized hyperbolic processes—New insights for generating initial values. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 2017, 46, 5752–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balter, J.; McNeil, A.J. On the Basel liquidity formula for elliptical distributions. Risks 2018, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebanov, L.; Rachev, S.T. ν-Generalized hyperbolic distributions. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2023, 16, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Yin, C. Tail conditional moments for location-scale mixture of elliptical distributions. Mathematics 2022, 10, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, I.J. On the population frequencies of species and the estimation of population parameters. Biometrika 1953, 40, 237–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichel, H. Statistical valuation of diamondiferous deposits. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 1973, 73, 235–243. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, T.-R.; Xin, H.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Lio, Y. Bias-corrected maximum likelihood estimation and Bayesian inference for the process performance index using inverse Gaussian distribution. Stats 2022, 5, 1079–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-L.T.; Whitmore, G.A. Multivariate threshold regression models with cure rates: Identification and estimation in the presence of the Esscher property. Stats 2022, 5, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions, 10th ed.; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1972; pp. 355–456. [Google Scholar]
- Gradshteyn, I.S.; Ryzhik, I.M. Table of Integrals, Series and Products, 7th ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shiryaev, A.N. Essentials of Stochastic Finance; World Scientific: Singapore, 1999; pp. 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- McNeil, A.J.; Frey, R.; Embrechts, P. Quantitative Risk Management; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 38, 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E.; Stelzer, R. Absolute moments of generalized hyperbolic distributions and approximate scaling of normal inverse Gaussian Lévy processes. Scand. Stat. 2005, 32, 617–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.J.; Würtz, D.; Dong, C.; Tran, T.T. Moments of the generalized hyperbolic distribution. Comput. Stat. 2011, 26, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolella, M.S. Intermediate Probability: A Computational Approach; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2007; pp. 306–328. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, H.M.; Karlsson, P.W. Multiple Gaussian Hypergeometric Series; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 15–33. [Google Scholar]
- Erdélyi, A.; Magnus, W.; Oberhettinger, F.; Tricomi, F.G. Tables of Integral Transforms; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1954; pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, H.M.; Qureshi, M.I.; Quraishi, K.A.; Singh, R. Applications of some hypergeometric summation theorems involving double series. J. Appl. Math. Stat. Inform. 2012, 8, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sadykov, T.M. On the analytic complexity of hypergeometric functions. Proc. Steklov Inst. Math. 2017, 298, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadykov, T.M. Computational problems of multivariate hypergeometric theory. Program. Comput. Softw. 2018, 44, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuchta, T.; Grow, D.; Wintz, N. Divergence criteria for matrix generalized hypergeometric series. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 2022, 150, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuchta, T.; Grow, D.; Wintz, N. Discrete matrix hypergeometric functions. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2023, 518, 126716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artzner, P.; Delbaen, F.; Eber, J.-M.; Heath, D. Coherent measures of risk. Math. Financ. 1999, 9, 203–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Föllmer, H.; Schied, A. Stochastic Finance: An Introduction in Discrete Time, 2nd ed.; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2004; p. 177. [Google Scholar]
- Armenti, Y.; Crépey, S.; Drapeau, S.; Papapantoleon, A. Multivariate shortfall risk allocation and systemic risk. SIAM J. Financ. Math. 2018, 9, 90–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapeau, S.; Kupper, M.; Papapantoleon, A. A Fourier approach to the computation of CVaR and optimized certainty equivalents. J. Risk 2014, 16, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, R.V. A credit-risk valuation under the variance-gamma asset return. Risks 2018, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, R.V. The risk measurement under the variance-gamma process with drift switching. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2022, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockafellar, R.T.; Uryasev, S. Conditional value-at-risk for general loss distributions. J. Bank. Financ. 2002, 26, 1443–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.Y.; Shapiro, A.; Uryasev, S. Conditional value-at-risk and average value-at-risk: Estimation and asymptotics. Oper. Res. 2012, 60, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafusalov, A.; Uryasev, S. CVaR (superquantile) norm: Stochastic case. Europ. J. Operat. Res. 2016, 249, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, X. Nonparametric estimation of conditional var and expected shortfall. J. Econom. 2008, 147, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.X.; Tang, C.Y. Nonparametric inference of value-at-risk for dependent financial returns. J. Financ. Econom. 2005, 3, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaillet, O. Nonparametric estimation of conditional expected shortfall. Insur. Risk Manag. J. 2005, 74, 639–660. [Google Scholar]
- Fontana, C.; Schweizer, M. Simplified mean-variance portfolio optimisation. Math. Financ. Econ. 2012, 6, 125–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, M.; Zivoi, D.; Šikić, M. Dynamic mean-variance optimization problems with deterministic information. Int. J. Theor. Appl. Financ. 2018, 21, 1850011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocki, D.N. A brief history of downside risk measures. J. Investig. 1999, 8, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meer, R.; Sortino, F.A. Downside risk: Capturing what’s at stake in investment situations. J. Portf. Manag. 1991, 17, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer, R.; Plantinga, A.; Sortino, F.A. The Dutch triangle. J. Portf. Manag. 1999, 26, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E.; Kinnebrouk, S.; Shephard, N. Measuring downside risk: Realised semivariance. In Volatility and Time Series Econometrics: Essays in Honor of Robert F. Engle; Bollerslev, T., Russell, J., Watson, M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 117–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, A.; Chen, J.; Xing, Y. Downside risk. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2006, 19, 1191–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrow, R.A.; Zhao, F. Downside loss aversion and portfolio management. Manag. Sci. 2006, 52, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, R.V. On lower partial moments for the investment portfolio with variance-gamma distributed returns. Lith. Math. J. 2022, 62, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brent, R.P. Multiple-precision zero-finding methods and the complexity of elementary function evaluation. In Analytic Computational Complexity; Traub, J.F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1976; pp. 151–176. [Google Scholar]
- Asmussen, S.; Glynn, P.W. Stochastic Simulation: Algorithms and Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 325–344. [Google Scholar]
- Avramidis, A.N.; L’Ecuyer, P.; Tremblay, P.-A. Efficient simulation of gamma and variance-gamma processes. In Proceedings of the 2003 Winter Simulation Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 7–10 December 2003; Chick, S., Sánchez, P.J., Ferrin, D., Morrice, D.J., Hung, Y.-C., Eds.; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Avramidis, A.N.; L’Ecuyer, P. Efficient Monte Carlo and quasi–Monte Carlo option pricing under the variance gamma model. Manag. Sci. 2006, 52, 1930–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lemieux, C. Monte Carlo and Quasi-Monte Carlo Sampling; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 234–238. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).