Effects of Red Ginseng on Neural Injuries with Reference to the Molecular Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Main Active Ingredients of Red Ginseng (RG)
3. Effects of RG on Brain Ischemia
4. Effects of RG on Neurotrauma
5. Effect of RG on Neurodegeneration
6. Conclusion and Perspectives of RG Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RG | red ginseng |
| WG | white ginseng |
| PPD | protopanaxadiol |
| PPT | protopanaxatriol |
| HPLC | high performance liquid chromatography |
| r-tPA | recombinant tissue plasminogen activator |
| gRb1 | ginsenoside Rb1 |
| STAT5 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 |
| MCAO | middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| dgRb1 | dihydroginsenoside Rb1 |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| GDNF | glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor |
| ARE | antioxidant response element |
| SCI | spinal cord injury |
| TBI | traumatic brain injury |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| HD | Huntington’s disease |
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| EEG | electroencephalogram |
References
- Cheng, Y.; Shen, L.H.; Zhang, J.T. Anti-amnestic and anti-aging effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and Rb1 and its mechanism of action. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.Y.; Yang, W.M. Panax ginseng ameliorates airway inflammation in an ovalbumin-sensitized mouse allergic asthma model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 136, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-P.; Liu, I.-M.; Cheng, J.-T. Improvement of Insulin Resistance by Panax Ginseng in Fructose-rich Chow-fed Rats. Horm Metab Res. 2005, 37, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purves, D.; Augustine, G.J.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Katz, L.C.; LaMantia, A.-S.; McNamara, J.O.; Williams, S.M. Neuroscience, 2nd ed.; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Radad, K.; Moldzio, R.; Rausch, W.-D. Ginsenosides and Their CNS Targets. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2011, 17, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, L.P. Chapter 1 Ginsenosides: Chemistry, Biosynthesis, Analysis, and Potential Health Effects. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; Volume 55, pp. 1–99. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.-H.; Bae, O.-N.; Park, J.H. Recent Methodology in Ginseng Analysis. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, C.-Y.; Moon, J.-M.; Kim, B.-Y.; Lim, S.-H.; Lee, G.-S.; Yu, H.-S.; Cho, S.-I. Comparative study of Korean White Ginseng and Korean Red Ginseng on efficacies of OVA-induced asthma model in mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, S.-H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, Y.-S.; Hyun, S.H.; Han, C.-K. Red ginseng monograph. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ki-Yeul, N. The Comparative Understanding between Red Ginseng and White Ginsengs, Processed Ginsengs (Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer). J. Ginseng Res. 2005, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.M.; Bae, B.-S.; Park, H.-W.; Ahn, N.-G.; Cho, B.-G.; Cho, Y.-L.; Kwak, Y.-S. Characterization of Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer): History, preparation method, and chemical composition. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, P.; Samukawa, K.; Fujita, H.; Kato, H.; Sakanaka, M. Oral Administration of Red Ginseng Extract Promotes Neurorestoration after Compressive Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. J. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 1265464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhao, Y. Current Evaluation of the Millennium Phytomedicine-Ginseng (I): Etymology, Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry, Market and Regulations. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2475–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, J.; Siesjö, B.K.; Symon, L. Thresholds in cerebral ischemia–the ischemic penumbra. Stroke 1981, 12, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahan, R.; Vinuela, F. Treatment of acute ischemic stroke: Intravenous and endovascular therapies. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2009, 7, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.C.; Yoshimura, H.; Matsuda, S.; Lim, J.-H.; Sakanaka, M. Ginseng root prevents learning disability and neuronal loss in gerbils with 5-minute forebrain ischemia. Acta Neuropathol. 1995, 91, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-H.; Wen, T.-C.; Matsuda, S.; Tanaka, J.; Maeda, N.; Peng, H.; Aburaya, J.; Ishihara, K.; Sakanaka, M. Protection of ischemic hippocampal neurons by ginsenoside Rb1, a main ingredient of ginseng root. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 28, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Matsuda, S.; Tanaka, J.; Tateishi, N.; Maeda, N.; Wen, T.-C.; Peng, H.; Sakanaka, M. Ginsenoside Rb1 prevents image navigation disability, cortical infarction, and thalamic degeneration in rats with focal cerebral ischemia. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 1998, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.-A.; Hyun, Y.-J.; Choo, M.-K.; Oh, J.K.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, D.-H. Protective effect of fermented Red ginseng on a transient focal ischemic rats. Arch. Pharm Res. 2004, 27, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovich, D.G.; Kitts, D.D. Generation of ginsenosides Rg3 and Rh2 from North American ginseng. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
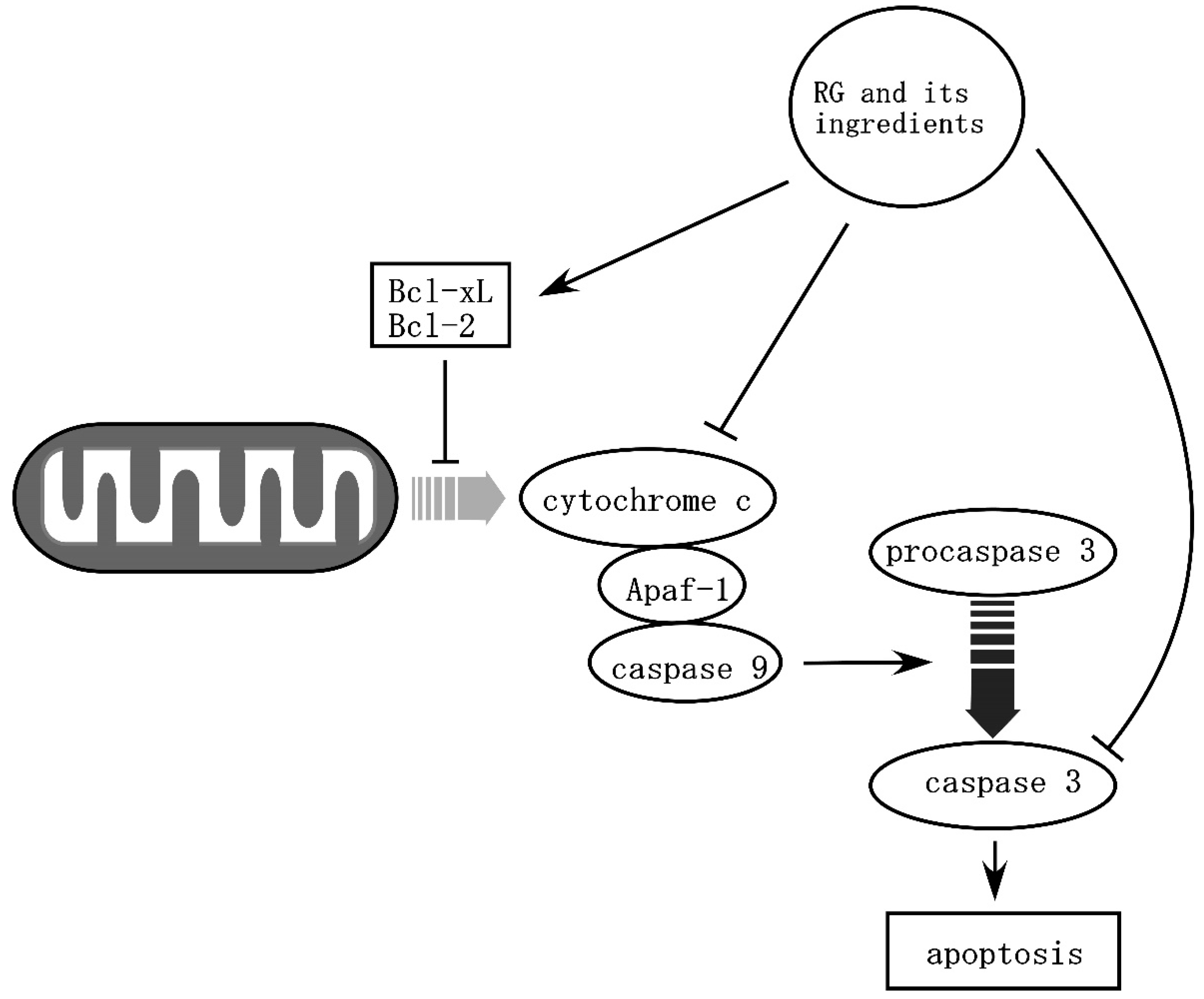
- Zhang, B.; Hata, R.; Zhu, P.; Sato, K.; Wen, T.-C.; Yang, L.; Fujita, H.; Mitsuda, N.; Tanaka, J.; Samukawa, K.; et al. Prevention of Ischemic Neuronal Death by Intravenous Infusion of a Ginseng Saponin, Ginsenoside Rb1, That Upregulates Bcl-xL Expression. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2006, 26, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, D.T.; Korsmeyer, S.J. BCL-2 FAMILY: Regulators of Cell Death. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 395–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenmann, S.; Stoll, G.; Schroeter, M.; Krajewski, S.; Reed, J.C.; Bähr, M. Differential Regulation of Bax, Bcl-2, and Bcl-X Proteins in Focal Cortical Ischemia in the Rat. Brain Pathol. 1998, 8, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiessner, C.; Allegrini, P.R.; Rupalla, K.; Sauer, D.; Oltersdorf, T.; McGregor, A.L.; Bischoff, S.; Böttiger, B.W.; van der Putten, H. Neuron-specific transgene expression of Bcl-XL but not Bcl-2 genes reduced lesion size after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 268, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakanaka, M.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, B.; Wen, T.-C.; Cao, F.; Ma, Y.-J.; Samukawa, K.; Mitsuda, N.; Tanaka, J.; Kuramoto, M.; et al. Intravenous Infusion of Dihydroginsenoside Rb1 Prevents Compressive Spinal Cord Injury and Ischemic Brain Damage through Upregulation of VEGF and Bcl-xL. J. Neurotrauma 2007, 24, 1037–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, A.; Zhou, Y.; San, X.; Jin, T.; Jin, Y. Panax ginseng ginsenoside-Rg2 protects memory impairment via anti-apoptosis in a rat model with vascular dementia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 115, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.-L.; Yang, C.-X.; Xu, P.; Gao, X.-Q.; Deng, L.; Chen, P.; Sun, Z.-L.; Chen, Q.-Y. Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on transient cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2007, 1167, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Bhalla, K.; Kim, C.N.; Ibrado, A.M.; Cai, J.; Peng, T.-I.; Jones, D.P.; Wang, X. Prevention of Apoptosis by Bcl-2: Release of Cytochrome c from Mitochondria Blocked. Science 1997, 275, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, B.; Lu, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Ge, P. Ginsenoside Rb1 Attenuates Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation-Induced Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells via Protection of Mitochondria and Inhibition of AIF and Cytochrome c Release. Molecules 2013, 18, 12777–12792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.-Q.; Yang, C.-X.; Chen, G.-J.; Wang, G.-Y.; Chen, B.; Tan, S.-K.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Q.-L. Ginsenoside Rb1 regulates the expressions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and caspase-3 and induces neurogenesis in rats with experimental cerebral ischemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 132, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davalos, D.; Grutzendler, J.; Yang, G.; Kim, J.V.; Zuo, Y.; Jung, S.; Littman, D.R.; Dustin, M.L.; Gan, W.-B. ATP mediates rapid microglial response to local brain injury in vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, L.; Lu, T.; Xu, G.; Liu, X. Suppression of local inflammation contributes to the neuroprotective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 in rats with cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 2012, 202, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhapurapu, S.; Karin, M. Regulation and Function of NF-κB Transcription Factors in the Immune System. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 693–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A.; Martin-Villalba, A.; Weih, F.; Vogel, J.; Wirth, T.; Schwaninger, M. NF-κB is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. Nature Medicine 1999, 5, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z. Ischemia-reperfusion Injury in the Brain: Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Biochem. Pharmacol. Open Access 2016, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q. Role of Nrf2 in Oxidative Stress and Toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol Toxicol 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Xu, M.; Jeong, S.; Qian, Y.; Wu, H.; Xia, Q.; Kong, X. The Role of Nrf2 in Liver Disease: Novel Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.P.; Jeong, H.G. Ginsenoside Rb1 protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress by increasing heme oxygenase-1 expression through an estrogen receptor-related PI3K/Akt/Nrf2-dependent pathway in human dopaminergic cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 242, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Moriano, C.; González-Burgos, E.; Iglesias, I.; Lozano, R.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Evaluation of the adaptogenic potential exerted by ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 against oxidative stress-mediated neurotoxicity in an in vitro neuronal model. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, N.; Liu, Q.; Ren, H.; Wu, D.; Luo, C.; Li, P.; Wan, J.-B.; Su, H. Ginsenoside Rb1 Protects Rat Neural Progenitor Cells against Oxidative Injury. Molecules 2014, 19, 3012–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Miao, W.; Teng, J.; Zhang, L. Ginsenoside Rb1 Protects the Brain from Damage Induced by Epileptic Seizure via Nrf2/ARE Signaling. CPB 2018, 45, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Gu, X.; Yu, M.; Zi, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xiang, L. Effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on oxidative stress injury in rat spinal cords by regulating the eNOS/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusart, I.; Schwab, M.E. Secondary Cell Death and the Inflammatory Reaction After Dorsal Hemisection of the Rat Spinal Cord. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1994, 6, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyinbo, C.A. Secondary injury mechanisms in traumatic spinal cord injury: A nugget of this multiply cascade. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2011, 71, 281–299. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P. Intravenous Infusion of Ginsenoside Rb1 Ameliorates Compressive Spinal Cord Injury through Upregulation of Bcl-xL and VEGF. Int. J. Neurol. Neurother. 2015, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz de Almodovar, C.; Lambrechts, D.; Mazzone, M.; Carmeliet, P. Role and Therapeutic Potential of VEGF in the Nervous System. Phys. Rev. 2009, 89, 607–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.O.; Kim, Y.; Lee, K.; Na, S.W.; Hong, S.P.; Valan Arasu, M.; Yoon, Y.W.; Kim, J. Panax ginseng Improves Functional Recovery after Contusive Spinal Cord Injury by Regulating the Inflammatory Response in Rats: An In Vivo Study. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2015/817096/ (accessed on 26 February 2019).
- Wang, W.; Shen, H.; Xie, J.-J.; Ling, J.; Lu, H. Neuroprotective effect of ginseng against spinal cord injury induced oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 3514–3521. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Lin, C.; Wu, S.; Huang, K.; Wang, Y.; Bao, X.; Zhang, F.; Huang, Z.; Teng, H. Inhibition of Autophagy is Involved in the Protective Effects of Ginsenoside Rb1 on Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.C.; Kim, Y.B.; Park, S.W.; Hwang, S.N.; Min, B.K.; Hong, H.J.; Kwon, J.T.; Suk, J.S. Neuroprotective Effect of Ginseng Total Saponins in Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2005, 20, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, L.; Jiang, Z.-L.; Wang, G.-H.; Hu, B.-Y.; Ke, K.-F. Treatment with ginseng total saponins reduces the secondary brain injury in rat after cortical impact. J. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 90, 1424–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rinwa, P.; Dhar, H. Microglial inhibitory effect of ginseng ameliorates cognitive deficits and neuroinflammation following traumatic head injury in rats. Inflammopharmacol 2014, 22, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; Chen, X.; Huang, T.; Lue, L.-F.; Luddy, J.S.; Yan, S.S. Multi-faced neuroprotective effects of Ginsenoside Rg1 in an Alzheimer mouse model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kan, H.; Yin, Y.; Wu, W.; Hu, W.; Li, W.; Li, W. Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on chronic restraint stress induced learning and memory impairments in male mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 120, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Kang, T.; Qi, B.; Kong, L.; Jiao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J. Neuroprotective effects of ginseng protein on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the hippocampus of D-galactose/AlCl3 inducing rats model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 179, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Yan, Y.; Tao, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Kang, T.; Yang, J. Ginseng Protein Reverses Amyloid Beta Peptide and H2O2 Cytotoxicity in Neurons, and Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in AD Rats Induced by a Combination of D-Galactose and AlCl3. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.-H.; Lee, S.-T.; Chu, K.; Oh, M.J.; Park, H.-J.; Shim, J.-Y.; Kim, M. An open-label trial of Korean red ginseng as an adjuvant treatment for cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2008, 15, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.-H.; Park, M.-H.; Lee, J.-H. Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on Cognitive Function and Quantitative EEG in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Preliminary Study. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2016, 22, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Yang, E.J.; Kim, J.I.; Ernst, E. Ginseng for Cognitive Function in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review; Centre for Reviews and Dissemination: Heslington, York, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Van Kampen, J.; Robertson, H.; Hagg, T.; Drobitch, R. Neuroprotective actions of the ginseng extract G115 in two rodent models of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 184, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kampen, J.M.; Baranowski, D.B.; Shaw, C.A.; Kay, D.G. Panax ginseng is neuroprotective in a novel progressive model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 50, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.; Yoon, I.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Jang, B.-J.; Jeong, S.M.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, B.-H.; Han, J.-S.; Oh, S.; et al. Protective effects of ginseng saponins on 3-nitropropionic acid-induced striatal degeneration in rats. Neuropharmacology 2005, 48, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Hoang-Gia, T.; Wu, H.; Lee, M.-R.; Gu, L.; Wang, C.; Yun, B.-S.; Wang, Q.; Ye, S.; Sung, C.-K. Ginsenoside Rb1 improves spatial learning and memory by regulation of cell genesis in the hippocampal subregions of rats. Brain Res. 2011, 1382, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, K.; Shen, H.; Chen, X. Long-term Ginsenoside Rg1 Supplementation Improves Age-Related Cognitive Decline by Promoting Synaptic Plasticity Associated Protein Expression in C57BL/6J Mice. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2013, 69A, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokot, N.T.; Kairupan, T.S.; Cheng, K.-C.; Runtuwene, J.; Kapantow, N.H.; Amitani, M.; Morinaga, A.; Amitani, H.; Asakawa, A.; Inui, A. A Role of Ginseng and Its Constituents in the Treatment of Central Nervous System Disorders. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2016/2614742/ (accessed on 25 February 2019).
- Radad, K.; Gille, G.; Moldzio, R.; Saito, H.; Ishige, K.; Rausch, W.-D. Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 effects on survival and neurite growth of MPP+-affected mesencephalic dopaminergic cells. J. Neural. Transm. 2004, 111, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
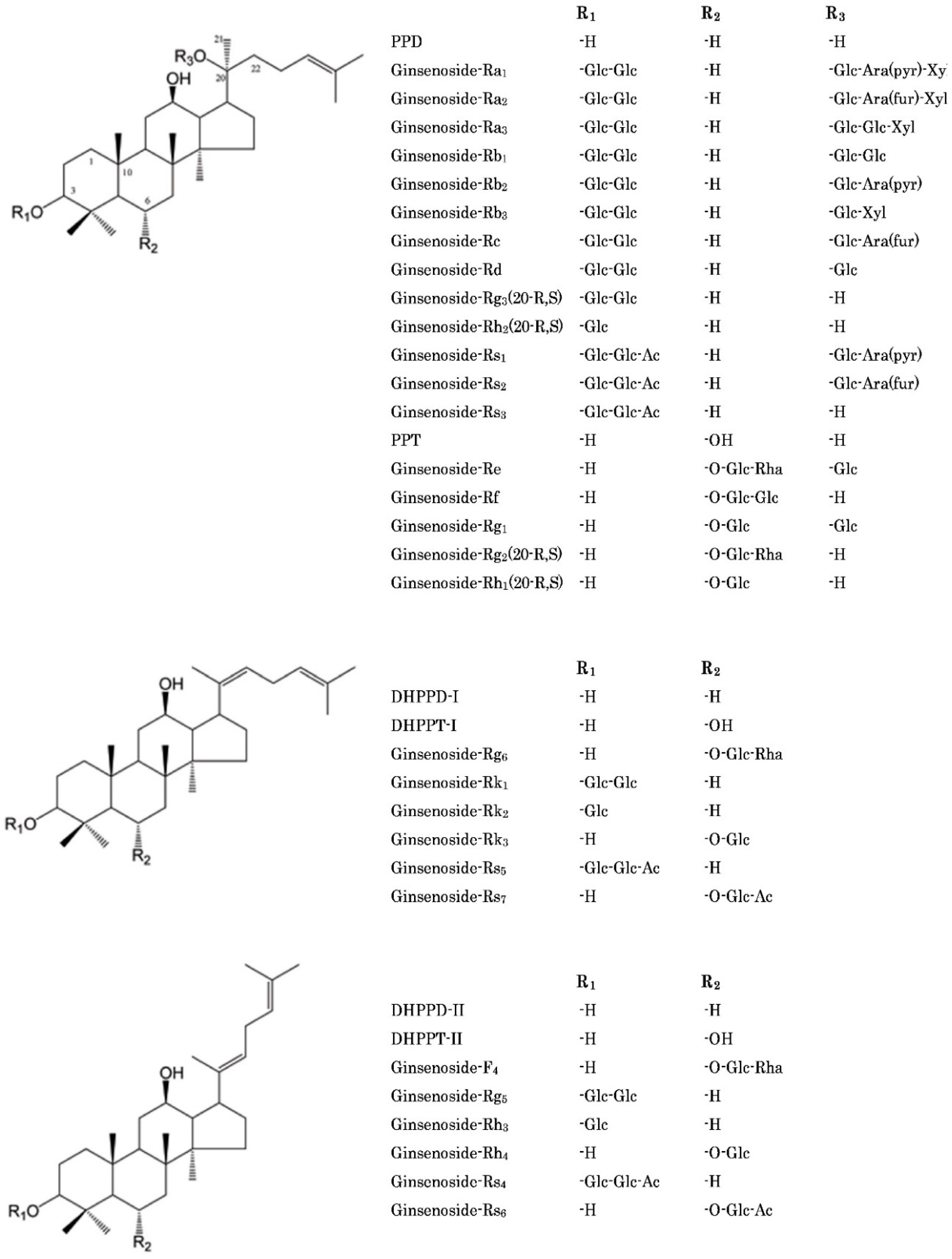
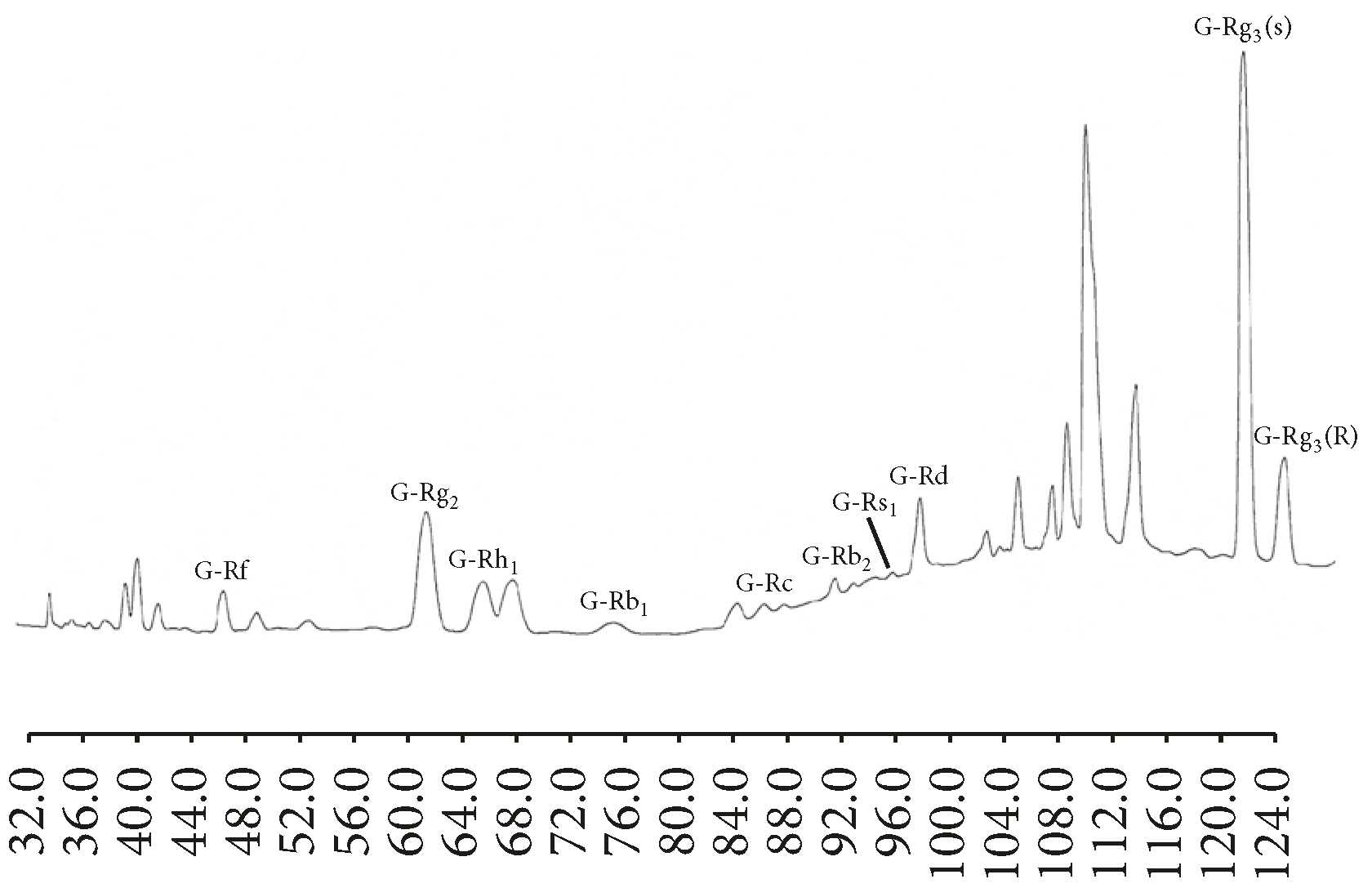
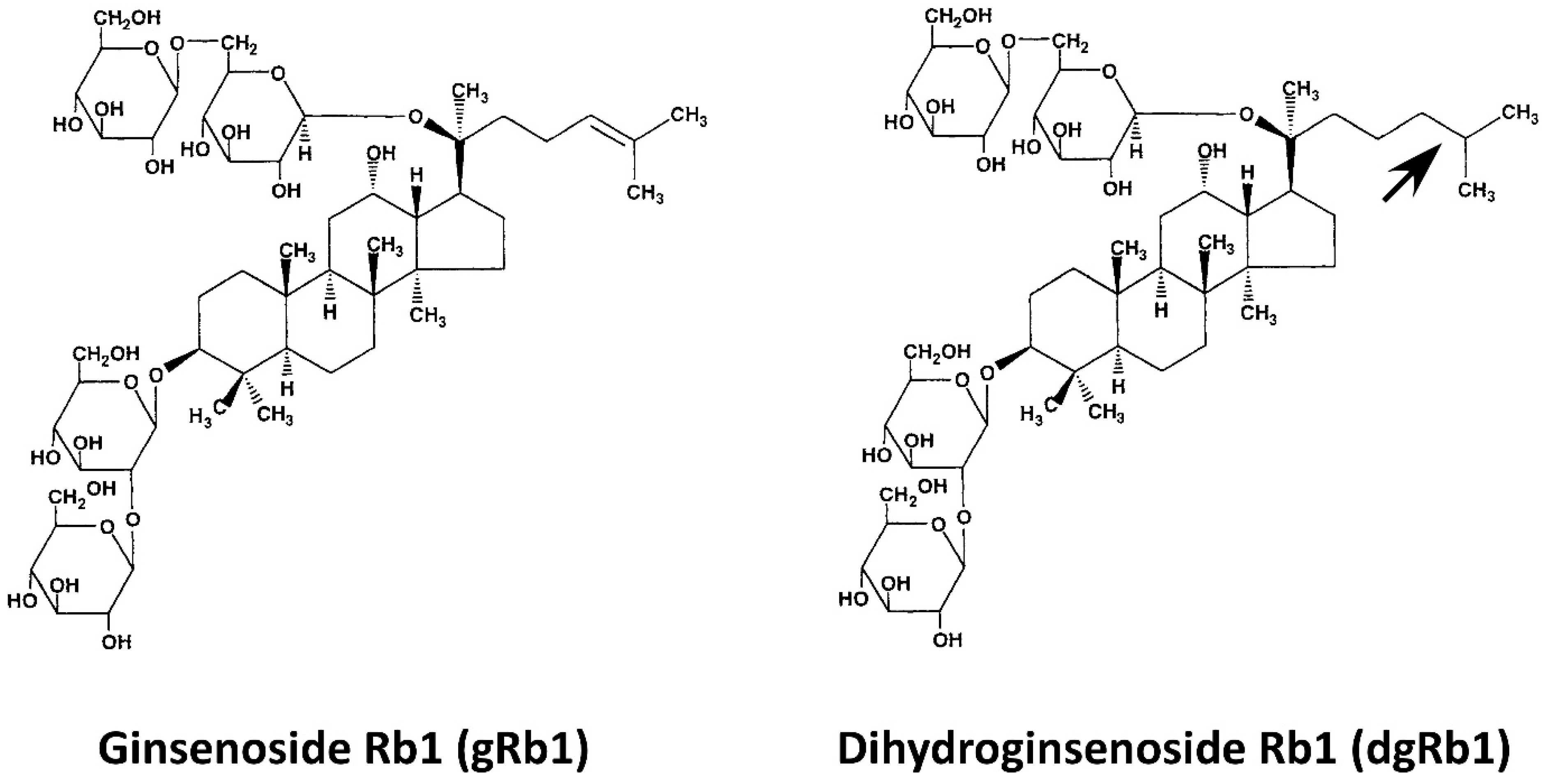
| Steaming Time (Hours) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Total | 35.439 | 42.113↑ | 57.974↑ | 50.332↑ |
| Diol | 21.768 | 28.488↑ | 43.063↑ | 36.974↑ |
| Triol | 11.569 | 11.505 | 12.533↑ | 11.237 |
| Diol/Triol | 1.867 | 2.476↑ | 3.436↑ | 3.29↑ |
| Ginsenoside-Ro | 2.012 | 2.12↑ | 2.378↑ | 2.121↑ |
| Rb1 | 8.097 | 10.88↑ | 16.016↑ | 14.316↑ |
| Rb2 | 5.531 | 7.23↑ | 11.352↑ | 9.282↑ |
| Rc | 4.989 | 6.495↑ | 9.943↑ | 8.119↑ |
| Rd | 1.251 | 1.629↑ | 2.31↑ | 1.864↑ |
| Re | 4.779 | 4.105 | 5.223↑ | 3.72 |
| Rf | 2.54 | 2.533 | 2.669↑ | 2.413 |
| Rg1 | 3.859 | 4.335↑ | 3.723 | 3.971↑ |
| 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg1 | 0.481 | 0.468 | 0.7↑ | 0.589↑ |
| 20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg2 | - | - | 0.042 * | 0.125 * |
| 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 | - | 0.093 * | 0.221 * | 0.408 * |
| 20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg3 | - | 0.054 * | 0.14 * | 0.262 * |
| 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh1 | - | 0.064 * | 0.134 * | 0.277 * |
| 20(R)-Ginsenoside Rh1 | - | - | 0.042 * | 0.142 * |
| Ginsenoside-Rs1 | 1.143 | 1.105 | 1.577↑ | 1.233↑ |
| quinquenoside-R1 | 0.757 | 1.002↑ | 1.504↑ | 1.49↑ |
| Types of Neural Injury | Ischemia | Trauma | Neurodegeneration |
| Types of study | In vivo and in vitro studies. | In vivo and in vitro studies. | In vivo and in vitro studies, clinical studies. |
| Active components | RG powder, RG extract, gRb1, gRh2, dgRb1 | RG extract, ginseng total saponin, gRb1, dgRb1 | RG powder, gRb1, gRg1 |
| Effect | Prevention of learning disability and neuron loss; reduction of infarct volume. | Prevention of neuron loss and promotion of restoration of white matter after SCI; amelioration of cognitive deficits; decrement of contusion damage after TBI. | Amelioration of cognitive disorders; improvement of cognitive function; increment of relative ratio of alpha waves; reduction of Aβ and phosphorylated-tau; inhibition of α-synuclein aggregation. |
| Proposed mechanisms | Anti-apoptosis: up-regulation of Bcl-xL and Bcl-2; inhibition of cytochrome-c and caspase-3. Neurotrophic action: up-regulation of BDNF and GDNF. Anti-inflammation: inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines; inhibition of microglia activation; inhibition of NF-κB activation. Anti-oxidation: activation of Nrf2/ARE pathway. | Anti-apoptosis: up-regulation of Bcl-xL Neurotrophic action: up-regulation of VEGF. Anti-inflammation: inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines; inhibition of microglia activation; inhibition of autophagy. Anti-oxidation. | Anti-apoptosis: upregulation of Bcl-xL. Anti-inflammation: inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines; inhibition of microglia activation. |
| Reference | [16,17,18,19,20,21,25,26,27,29,30,32,38,39,40,41,42] | [12,25,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52] | [53,54,55,56,57,58,60,61,62,63,64,65,66] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, P.; Sakanaka, M. Effects of Red Ginseng on Neural Injuries with Reference to the Molecular Mechanisms. J 2019, 2, 116-127. https://doi.org/10.3390/j2020009
Zhu P, Sakanaka M. Effects of Red Ginseng on Neural Injuries with Reference to the Molecular Mechanisms. J. 2019; 2(2):116-127. https://doi.org/10.3390/j2020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Pengxiang, and Masahiro Sakanaka. 2019. "Effects of Red Ginseng on Neural Injuries with Reference to the Molecular Mechanisms" J 2, no. 2: 116-127. https://doi.org/10.3390/j2020009
APA StyleZhu, P., & Sakanaka, M. (2019). Effects of Red Ginseng on Neural Injuries with Reference to the Molecular Mechanisms. J, 2(2), 116-127. https://doi.org/10.3390/j2020009





