Abstract
This research investigated how detergent type and concentration, solution temperature, and flow rate affect ultrasonic cleaning efficiency in jewelry manufacturing. A silver bracelet without gemstones served as the test sample, and the study combined harmonic response analysis to assess acoustic pressure distribution with computational fluid dynamics to examine fluid flow patterns inside an ultrasonic cleaning machine. Cleaning tests were performed under real factory conditions to verify the simulations. Results showed that cleaning efficiency depends on the combined chemical and ultrasonic effects. Adding detergent lowered surface tension, encouraging cavitation bubble formation; higher temperatures (up to 60 °C) softened dirt, making removal easier; and moderate solution flow improved the cleaning, helping to carry dirt away from jewelry surfaces. Too much flow, however, decreased cavitation activity. The highest cleaning efficiency (93.890%) was achieved with 3% U-type detergent at 60 °C and a flow rate of 5 L/min, while pure water at room temperature (30 °C) without flow had the lowest efficiency (0.815%), confirmed by weighing and scanning electron microscope measurements. Interestingly, maximum ultrasonic power concentration did not always match the highest cleaning efficiency. The study supports sustainable practices by limiting detergent use to 3%, in line with Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure).
1. Introduction
Thailand is a leader in jewelry manufacturing, recognized for its exceptional craftsmanship, skilled labor, and robust industry infrastructure. Silver jewelry is a key export product, one of its many strengths. In 2024, Thailand was the world’s third-largest exporter of silver jewelry, with exports valued at approximately $9609.10 million, a 6.11% increase from the previous year, underscoring the country’s expertise and competitiveness in manufacturing this product [1,2]. One of the key areas that keeps Thailand a leader in this field is its ability to develop its own manufacturing processes, particularly the ultrasonic cleaning process.
Ultrasonic cleaning is a critical process in manufacturing, offering several key advantages. The high-frequency sound waves create tiny bubbles that gently yet effectively remove dirt, oils, and grime from even the most intricate and hard-to-reach areas, such as behind gemstones and within detailed settings. This method restores the jewelry’s original shine and brilliance without damaging delicate stones or metals. Ultrasonic cleaning also helps prevent tarnish and buildup, prolonging the life of the jewelry. It provides a hygienic clean by eliminating bacteria and contaminants, making it a safe and thorough cleaning option for maintaining the beauty and durability of jewelry. This process enables the simultaneous cleaning of multiple items quickly, reduces reliance on harsh chemicals and excessive water, minimizes the risk of surface damage compared to mechanical scrubbing, eliminates bacteria and fine particles, supports mass production, and requires minimal maintenance. Additionally, it is compatible with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, and ceramics.
However, the efficiency of ultrasonic cleaning depends on both the operating conditions and the design of the ultrasonic cleaner. The operating conditions include the type of cleaning solution, sonication time, surfactant, temperature, fluid flow rate, object shape, frequency, cleaning position, and the type of cleaning detergent [3,4,5,6,7]. The design of ultrasonic cleaners is closely related to the design of their components, such as the transducer [8,9,10] and the ultrasonic cleaner [11,12]. The transducer and ultrasonic cleaner must be designed to suit the object to be cleaned and the type of dirt present. Proper operating conditions and optimal design of ultrasonic cleaners will ensure the highest ultrasonic cleaning efficiency.
Generally, the favored method for increasing ultrasonic cleaning efficiency in jewelry factories involves introducing cleaning detergents into a non-flowing solution during operation at an appropriate temperature, since some jewelry factories have found that the cleaning efficiency is low when applying a flowing solution, as evidenced in [11,12]. Hence, using the flowing solution may affect the fluid properties of the solution, reducing cavitation and disadvantages for ultrasonic cleaning. However, some factories argue that a flowing solution provides higher cleaning efficiency than a non-flowing solution. The solution with the optimal flow rate enhances cleaning efficiency through acoustic streaming, which transfers momentum to help clean the product and remove dirt and contaminants from the surface. Hence, this solution flow helps remove dirt and contaminants easily [13,14,15]. Consequently, solution flow in ultrasonic cleaning may be suitable for certain types of jewelry products. Regarding cleaning detergents, they enhance ultrasonic cleaning by lowering surface tension, which increases cavitation bubble formation. Additionally, temperature enhances ultrasonic cleaning by improving cavitation and increasing the effectiveness of cleaning solutions. The appropriate temperature softens dirt and reduces adhesion between the dirt and the surface, allowing for better dirt removal. Excessive heat from excessively high temperatures can reduce cavitation efficiency and damage products, so optimal temperature control is crucial for effective and safe cleaning. In short, cleaning detergents, temperatures, and solution flow settings in operating conditions are crucial for achieving high cleaning efficiency.
The literature review, for example, as presented in [4,6,7,16,17,18], provides essential knowledge that is applied to various cleaning tasks, such as electronic devices, medical apparatus, and food production equipment. Unfortunately, no studies have been found on the effects of factors such as cleaning detergents, temperatures, and fluid flows practically used in jewelry factories. Importantly, the jewelry cleaning process utilizes dubbing, a wax made from animal fat, to aid in cleaning, which is not used on the mentioned cleaning tasks. Because ultrasonic cleaning of jewelry differs from that studied in [4,6,7,16,17,18] and is more challenging, the novelty of this research lies in the findings on how detergent type, concentration, temperature, and solution flow rate influence cleaning efficiency. The research findings help improve the jewelry cleaning process and address a knowledge gap not covered in those references. The knowledge reports in those references are not suitable for the jewelry cleaning process. Thus, understanding the effect of those factors is essential and requires further study to achieve high cleaning efficiency, which this research aims to investigate.
This article presents collaborative research with a jewelry factory to examine operating conditions, including detergent types, temperatures, and solution flow rates, and their impact on the ultrasonic cleaning process. The aim is to improve cleaning efficiency and identify optimal operating conditions that support Industry 5.0 and the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Three cleaning detergents commonly employed in the actual cleaning process were considered. The cleaning process was imitated using an ultrasonic cleaning machine (UCM) and jewelry samples under actual operating conditions from the jewelry factory. This UCM can adjust solution temperature and flow rate, making it suitable for this research. The cleaning results were analyzed using computer simulation and experiments. The computer simulations include harmonic response analysis and computational fluid dynamics, while the experiments involve fluid property measurements and an ultrasonic cleaning test.
2. Background and Tools
This section describes the background and tools applied to design a research methodology.
2.1. Jewelry Cleaning Process
This process depends on product types, shapes, and jewelry manufacturers; however, it can be concluded in Figure 1 for jewelry pieces with intricate shapes and no gemstones, such as necklaces and bracelets. If jewelry pieces have gemstones, ultrasonic cleaning requires caution to avoid damage to gemstones.
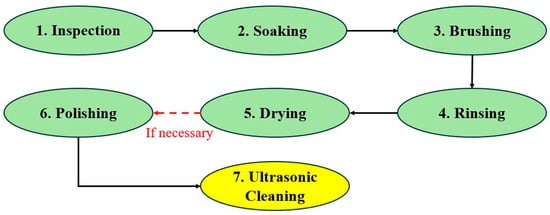
Figure 1.
Jewelry cleaning process.
First, inspection, the jewelry pieces assembled by the automatic machine are inspected for completeness. Remanufacturing may be necessary if the jewelry pieces have missing stones, damaged clasps, or incompleteness. Second, soaking, the jewelry pieces are soaked for 3–30 min in warm water and mild soap. Third, brushing, they are scrubbed with a gentle brush. Hard-to-reach areas are focused on by avoiding excessive pressure. Fourth, rinsing, the jewelry pieces are cleaned with warm, flowing water. Fifth, wipe them completely dry using a soft, lint-free cloth. If necessary, to ensure that the jewelry pieces are clean, durable, shiny, and attractive to customers, the process may require additional steps, as follows. Sixth, polishing, dubbing, a wax derived from animal fat, is commonly used to polish metals, enhancing their appearance by making them bright, shiny, and aesthetically appealing. Jewelry pieces are polished with dubbing until they achieve a reflective finish. However, this process presents a significant drawback: dubbing often becomes lodged in the microscopic pores of the jewelry, where it cannot be effectively removed through manual wiping or polishing. Consequently, ultrasonic cleaning is required to eliminate the residual dubbing and restore the jewelry’s shine. Lastly, they are cleaned using ultrasonics to ensure that the jewelry pieces are of high quality. This research is helpful at this step.
The ultrasonic cleaning used in this research is suitable for jewelry without gemstones. This type of jewelry, which is mass-produced, requires dubbing to assist with cleaning. Because of the high volume of mass production, this research is both necessary and worthwhile. In contrast, jewelry with gemstones is often expensive and may be custom-made, so ultrasonic cleaning can damage it. Therefore, it is usually better to use handcrafted cleaning and other alternative methods.
Before cleaning, the solution (cleaning fluid) comes into contact with the dirt. Figure 2 presents the ultrasonic cleaning mechanism with solution flow. The cavitation and acoustic streaming from incoming ultrasonics and solution flow cause the cleaning at the interface between the dirt and the jewelry surface (see Figure 2a). Generally, during cleaning, when ultrasonic cleaning is operated without the solution flow, the outside dirt is removed, but it remains attached to the surface of the jewelry. Consequently, the cavitation bubble cleaning is unable to clean the inside dirt (see Figure 2b). Suppose the ultrasonic cleaning is operated with the solution flow. In that case, the solution flow helps remove dirt from the outside, allowing cavitation bubbles to reach the dirt inside and increase cleaning efficiency easily. Moreover, after cleaning, the solution flow also helps carry away the removed dirt from the jewelry surface and also from the UCM to the outer (see Figure 2c), thereby preventing recontamination issues [15]. Without a solution flow, the removed dirt may remain on the jewelry surface and freely float inside the UCM, risking reattachment to the jewelry surface and obstructing the ultrasonic cleaning. The disadvantage of the major solution flow is that it may reduce the intensity of the ultrasonic effect, leading to debate among jewelry manufacturers about whether the solution flow is effective; therefore, this research helps to clarify the debate.
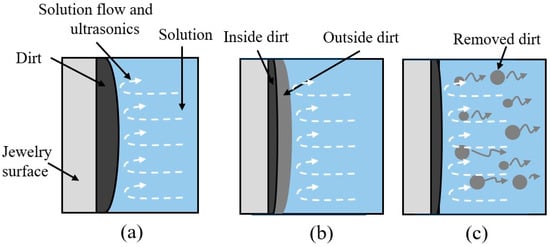
Figure 2.
The ultrasonic cleaning mechanism with solution flow: (a) before cleaning, (b) during cleaning, and (c) after cleaning.
To illustrate the surface cleaning, Fuchs [4] proposed that it consists of three effects: the ultrasonic effect, the chemical effect, and the combined effect. All depend on time to clean and temperature, as concluded in Figure 3. Accordingly, the combined effect encompasses detergent usage, solution flow rate, and temperature, all of which impact the cleaning efficiency. Suitable operating conditions will enable the achievement of a high cleaning efficiency.
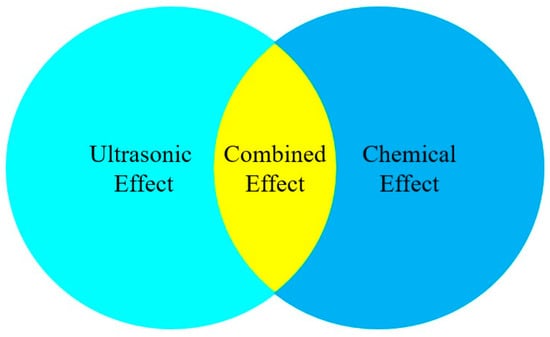
Figure 3.
The surface cleaning and its related effects.
2.2. Computer Simulation Principle
It consists of harmonic response analysis and computational fluid dynamics, employed to investigate cavitation and solution flow in the cleaning process due to the UCM and operating conditions.
2.2.1. Harmonic Response Analysis
Harmonic response analysis (HRA) is a technique used in engineering to determine how a structure responds to sinusoidal (harmonic) loads [19,20]. It helps predict steady-state vibrations, identify resonant frequencies, assess potential fatigue or failure risks, and especially investigate acoustic pressure in a single-frequency ultrasonic cleaning tank [8,10,11,12]. In ANSYS software version 2022R1, a governing equation for the HRA is given by Equation (1) [10,11,12].
where ω is the ultrasonic-driven frequency (rad/s), [M] is the mass matrix (N s2/Pa), [C] is the damping matrix (N s/m), [K] is the stiffness matrix (N/Pa), {F} is the acoustic load vector (N), and {p} is the nodal acoustic pressure vector (Pa). The subscript f refers to the fluid as a solution in this case.
HRA results yield the {p}, which relates to cavitation intensity and distribution.
2.2.2. Computational Fluid Dynamics
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and algorithms to solve and simulate fluid flow problems. By solving equations like Navier–Stokes and turbulence equations, CFD enables engineers and scientists to model airflow, heat transfer, and fluid behavior in various systems using computer-based simulations.
The shear stress transport (SST) k-ω turbulence model in ANSYS Fluent 2022R1 was employed in this research due to its reliability and widespread application in academia and industry. It can be expressed as follows [21,22]:
where μt is the eddy viscosity, μ is the dynamic viscosity, Pk is the shear production of turbulence, ω is the specific dissipation rate, and k is the turbulent kinetic energy. F1 is a blending function, α, β, β*, σω, and σω2 are coefficients of the SST k-ω turbulence model, while ui, uj, and uk are Cartesian velocities.
CFD results yield fluid velocities and vectors by solving the Navier-Stokes equations and Equations (2) and (3) to analyze the solution flow.
2.3. Measurement
The measurements used to determine key results that help assess the effect of operating conditions on detergents, temperature, and fluid flow in ultrasonic cleaning include fluid property measurements, ultrasonic power concentration, weighing, and scanning electron microscope measurements.
2.3.1. Viscosity, Surface Tension, and Density
Focusing on ultrasonics, since the cavitation intensity depends on the fluid properties of the solution, such as viscosity, surface tension, and density, three measurements were established. The HAAKETM MARSTM 60 Rheometer by Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (Massachusetts, MA, USA) [23] was used to determine the dynamic viscosity, the OCA 25 Optical Contact Angle by Dataphysics Instruments (Filderstadt, Germany) [24] was used to determine the surface tension, and the direct method was used to determine the density. In the solution density (ρ) measurement, the solution was filled in the beaker of volume V, and then it was weighed by a digital scale, AND GR-200, with a 0.0001 g resolution. The ρ was calculated by Equation (4):
where m is the solution mass (kg/m3) and V is the solution volume (m3).
2.3.2. Ultrasonic Power Concentration
Ultrasonic power concentration measurement in ultrasonic cleaning assesses the distribution and intensity of ultrasonic energy within a cleaner. It ensures effective and uniform cavitation for optimal cleaning. Results are typically expressed in watts per liter (W/L). This measurement helps identify weak zones, optimize equipment settings, and ensure consistent cleaning performance across the entire cleaner. In this research, the UPC3000 (NGL Cleaning Technology, Nyon, Switzerland), a device that measures ultrasonic power concentration using NGL cleaning technology [25], was employed. This device is widely used in many factories, and some research [8,11,12] has been conducted on ultrasonic cleaning.
2.3.3. Weighting
The digital scale AND GR-200 model by A&D Company Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan) [26], with a 0.0001 g resolution, was used to weigh the jewelry samples before and after ultrasonic cleaning. Dirt attached to the jewelry’s surface will make it heavier. Ultrasonic cleaning will remove this dirt, making the jewelry lighter and more appealing. The weighing results were used to calculate the cleaning efficiency as a percentage, which helped with the analysis.
2.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscope
A scanning electron microscope (SEM) reveals fine surface details by detecting secondary or backscattered electrons emitted from the sample, making it essential for analyzing the microstructures of jewelry surfaces, particularly after ultrasonic cleaning. This research employed a SEM model, ZEISS EVO MA10 by ZEISS Microscopy (Jena, Germany), with a resolution up to 100 nm. The surface images of the jewelry samples, both before and after ultrasonic cleaning, were captured using the SEM for analysis.
3. Methodology
Figure 4 illustrates the methodology employed in this research, which is described as follows:
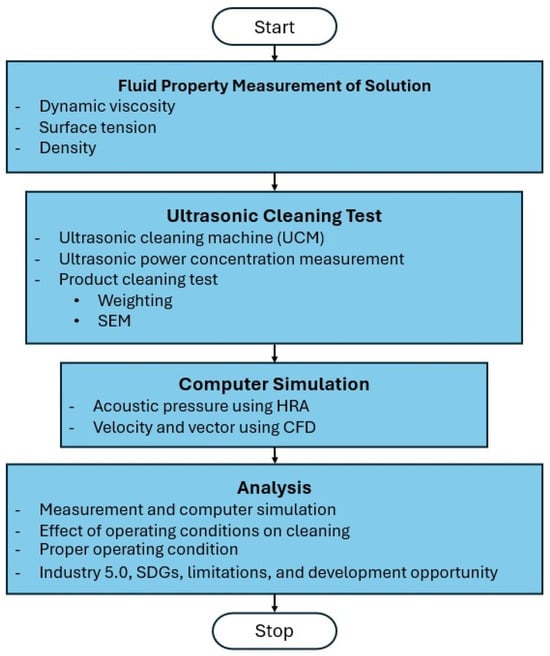
Figure 4.
Research methodology.
3.1. Fluid Property Measurement of Solution
Since the fluid properties: dynamic viscosity (μ), surface tension (γ), and density (ρ) change with temperature, which affects the cleaning due to cavitation and acoustic streaming, measurements of the mentioned fluid properties were established under specific operating conditions. In the measurements, the solutions are mixtures of water and detergents, which have specific types and concentrations used in the jewelry cleaning process, presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
The conditions for measuring the fluid properties.
The solution W is pure water without any added detergent. It was measured μ, γ, and ρ at temperatures of 30 °C and 60 °C as described in Section 2.3. The 30 °C is the room temperature at the jewelry factory, and 60 °C is the maximum temperature that the heater of the UCM can safely operate, as recommended by the factory’s operators. The solution S is a mixture of 97% water and detergent S (Pathumthani, Thailand) of 3% by volume. The solution preparation process was repeated for detergents N (Lopburi, Thailand) and U (China). A total of eight conditions were investigated for the fluid properties. Figure 5 illustrates the detergents (a) S, (b) N, and (c) U employed in this research. All are frequently used in many jewelry factories. They were named by S, N, and U to avoid a conflict of interest. Table 2 reports the detergent properties at a reference temperature of 20 °C, which is employed to facilitate analysis.

Figure 5.
Detergents: (a) S, (b) N, and (c) U.

Table 2.
The detergent properties at a temperature of 20 °C.
To measure the density, the solutions at 30 °C and 60 °C were filled into 100 mL beakers. Then, the ρ for various conditions were calculated using Equation (4). The results of fluid properties of solutions for various conditions are reported in Section 4.1.
3.2. Ultrasonic Cleaning Test
This section describes the ultrasonic cleaning test, which includes the tools and methods to assess the cleaning efficiency.
3.2.1. Ultrasonic Cleaning Machine
Figure 6 shows the automatic cleaning machine (UCM): (a) overview and (b) 40 kHz tank that was used for the cleaning test. The UCM has five tanks, each corresponding to a different frequency, such as 28 kHz, 40 kHz, 80 kHz, 120 kHz, and 170 kHz. However, the 40 kHz tank, 50 L, marked as a red arrow in (a), was used for the ultrasonic cleaning test, as this frequency is suitable for many jewelry designs suggested by the jewelry manufacturer. The UCM has a circulation system and heater that can adjust the solution flow rate up to 25 L/min and the temperature up to 60 °C, making it suitable for this research. In (b), when the circulation system is on, the solution flows from the bottom to the top and overflows around the rim, as indicated by the yellow arrows. In the concept design of UCM (ACE Ultimate Co. Ltd., Nonthaburi, Thailand), the circulation system generates a solution flow that collides with the jewelry pieces to help ultrasonic cleaning, as described in Figure 2. Moreover, the solution flow carries dirt to the filter and wastewater treatment system installed outside the UCM, thereby preventing recontamination [15] and supporting environmental friendliness.

Figure 6.
The ultrasonic cleaning machine (UCM) for ultrasonic cleaning test: (a) overview and (b) a circulation flow.
3.2.2. Ultrasonic Power Concentration Measurement
This process aims to measure the cavitation intensity level for various conditions. First, pure water was used as a solution. It was filled in the 40 kHz tank of UCM, and then the UPC3000 device measured the ultrasonic power concentration at the tank center for 10 s at room temperature (30 °C). The measurement was repeated five times to determine the average value of the ultrasonic power concentration. Then, the measurement was repeated at water temperatures of 40 °C, 50 °C, and 60 °C, and the solution flow rate of 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, and 25 L/min. Lastly, the UCM was filled with solutions of detergent at varying percentages by volume (1%, 2%, and 3%) for the specified temperatures, and the UPC3000 device measured the ultrasonic power concentrations at various temperatures, flow rates, and detergent concentrations. There were 96 conditions to measure in total.
3.2.3. Product Cleaning Test
This process, which includes ultrasonic cleaning, weighing, and SEM, aims to evaluate cleaning efficiency under selected operating conditions from 96 options using the UPC3000. Figure 7 shows a diagram of the product cleaning test. Figure 8 presents a jewelry sample used in the ultrasonic cleaning test. It is a popular style yet challenging bracelet to clean; therefore, it is suitable for use as a sample.
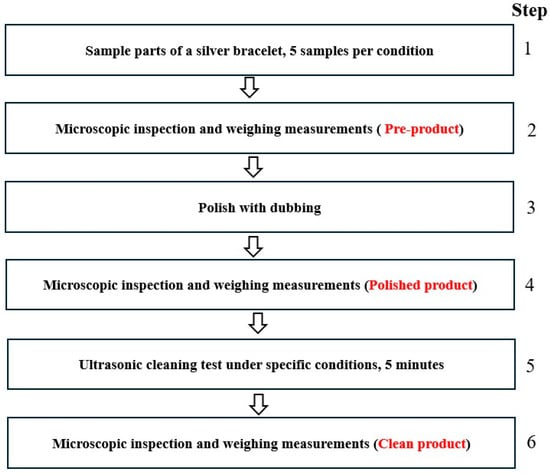
Figure 7.
The jewelry sample cleaning test diagram.

Figure 8.
The sample of the product for the cleaning test.
In Figure 7, first, parts of the silver bracelet were prepared as samples, five samples per condition. Each sample had the same shape and similar weight. Second, all samples were forwarded to the SEM for microscopic inspection to examine their surface and then weighed using a digital scale, as mentioned in Section 2.3.3 and Section 2.3.4. The results were recorded as pre-product results. Third, all samples were polished with dubbing. Fourth, the samples were returned to the SEM and digital scale again to record the polished product results. Fifth, all samples were positioned in the center of the UCM under specific conditions for 5 min of ultrasonic cleaning. Last, when the samples were dried, they were sent to the SEM and the digital scale again for recording as clean product results.
After the product weighing was completed, the cleaning efficiency was determined by Equation (5):
where η is the percentage of cleaning efficiency, and W is the product’s weight. The subscripts ’po’, ‘cl’, and ‘pr’ refer to the polished, clean, and pre-product stages, respectively.
3.3. Computer Simulation Approach
3.3.1. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Model and Boundary Conditions
A computer simulation combining HRA and CFD was employed to investigate the acoustic pressure, solution velocity, and vectors during ultrasonic cleaning, thereby analyzing the effect of operating conditions on the cleaning process. To ease analysis, the computer-aided design (CAD) model of UCM was simplified by ignoring irrelevant components and samples, as shown in Figure 9, for the computer simulation process. The solution was released from a small hole as an inlet to the UCM marked as red and then overflowed from the top edge as an outlet marked as yellow, as shown in Figure 9a. Simultaneously, 18 transducers with a frequency of 40 kHz in the box located at the bottom vibrate, sending ultrasonic waves into the solution and creating cavitation bubbles for ultrasonic cleaning. Focusing on the transducer (Guangdong, China) in Figure 9b includes a piezoelectric type 4 (PZT4) (Guangdong, China) that converts electricity to vibration, a front mass made from aluminum alloy (Samutprakarn, Thailand) to help transmit ultrasonic waves from vibration to the solution, and stainless steel type 304 (SUS304) (Samutprakarn, Thailand) as the back mass to enhance the vibration intensity and reflect ultrasonic waves to the front [10].
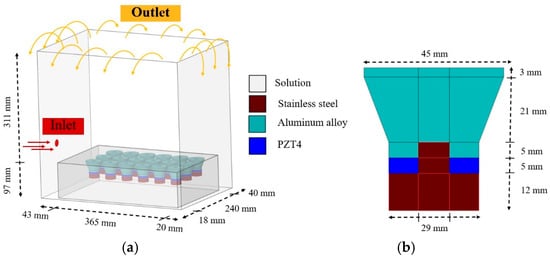
Figure 9.
The CAD model of UCM for computer simulation: (a) overview and (b) transducer.
In the HRA, the material and analysis settings were assigned in the same way as [11,15]. Both works have a different design of UCM from this research, but have similar settings.
In the CFD, the velocity inlet was assigned to water (solution) at 30 °C, with a velocity range of 0–1.47 m/s, corresponding to a flow rate of 0–25 L/min, consistent with the UCM’s operation. The gauge pressure of 0 Pa was assigned to the pressure outlet. The SST k-ω was employed as a turbulence model.
3.3.2. Mesh-Independent Analysis
Moreover, the fluid properties set in the HRA and CFD, the μ and ρ were assigned following the measured results in Section 3.1. Figure 10 shows the mesh-independent analysis: (a) graph and (b) the optimum mesh model. Six mesh models, depending on the number of elements per wavelength, were assigned to be hex-dominant for creating hexahedra. It was found that the more elements per wavelength, the smaller the element size, and the greater the element count, as expected. The solution flow rate of 5 L/min at 30 °C was set in CFD, and 40 kHz was assigned to HRA to investigate a trial case for mesh-independent analysis. In (a), focusing on the maximum acoustic pressure from the HRA and the velocity at the UCM’s center of the CFD, the 10 elements per wavelength provided the optimal mesh model with an average orthogonal quality of 0.92 and a maximum skewness of 0.83, making it suitable for the HRA and CFD processes. In (b) is the optimal mesh model consisting of 828,731 nodes and 827,683 elements, which had an element size of 2–3.5 mm with y+ of 5.1. The set of 10 is better than at least 6 elements per wavelength suggested by [18] to get accurate results. The automatic wall treatment (AWT) was employed. In ANSYS Fluent 2021R1, it is a near-wall treatment method where Fluent automatically chooses between wall function or low-Re treatment based on the value of y+ and the mesh structure of the wall area, yielding consistent and accurate results [21].
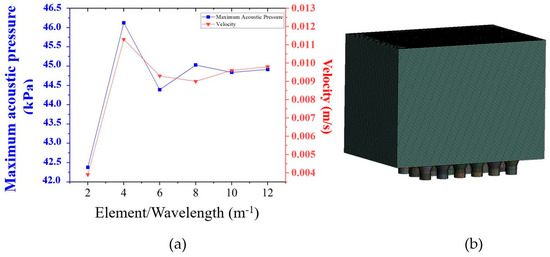
Figure 10.
Mesh-independent analysis: (a) graph and (b) the optimal mesh model for HRA and CFD.
4. Results and Discussion
This is divided into four parts: measurement and computer simulation, the effect of operating conditions on cleaning, proper operating conditions, Industry 5.0 and SDGs, limitations, and development opportunities, as described below.
4.1. Measurement and Computer Simulation
This section aims to link the fluid property measurement and computer simulation results to aid in the analysis and confirm the UCM’s suitability. Table 3 reports dynamic viscosity (μ), surface tension (γ), and density (ρ) described in Section 2.3 and Section 3.1 for conditions in Table 1. The measurements were repeated three times to find the average values and the standard deviations for reporting a significant number.

Table 3.
The measurement results of μ, γ, and ρ.
From Table 3, the μ and ρ decrease with increasing temperature, as expected. Significantly, solution U yields the highest μ of 1.52975 mPa·s at 30 °C and 0.65414 mPa·s at 60 °C, while solutions S, N, and W give similar values within 0.86574–0.90365 mPa·s at 30 °C and 0.51318–0.54945 mPa·s at 60 °C. Comparing the μ of 0.7972 mPa·s and the ρ of 995.6 kg/m3 reported in [27], and the γ of 0.0712 N/m reported in [28], water at 30 °C, the experimental errors are 8.60% for μ, 8.95% for ρ, and 1.52% for γ, confirming the measurements’ credibility, and the results reported in Table 3 are reasonably employed to help with analysis. Remarkably, the OCA 25 Optical Contact Angle could not be measured γ at 60 °C because it does not have a heater. However, according to the experiment [28], as the temperature increases, the surface tension decreases. The μ and ρ were assigned in the HRA and CFD simulations. The raw data of Table 3 are in the Supplementary Materials.
Figure 11 reveals the acoustic pressure determined by the HRA of (a) 30 °C and (b) 60 °C, on a vertical plane, centered at the UCM shown in a small picture on the bottom left, using water as a solution. Comparing Figure 9a and Figure 11, the acoustic pressure is distributed from the transducers to the solution, from the bottom up to above the UCM, as expected. The maximum acoustic pressure slightly decreased from 44.74 MPa at 30 °C to 44.66 MPa at 60 °C due to the decrease in μ and ρ reported in Table 3, aligned with the ultrasonic principle [4,6], as expected. Importantly, since the acoustic pressure can be distributed evenly throughout the UCM, the UCM is effectively usable in this research, and the center position is suitable for the ultrasonic cleaning test.
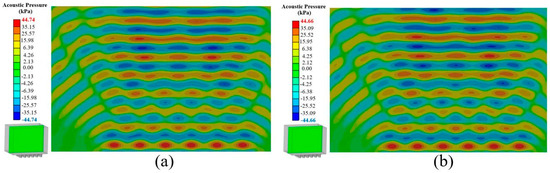
Figure 11.
The acoustic pressure determined by HRA at temperatures of (a) 30 °C and (b) 60 °C, using water as a solution.
Figure 12 reports the velocity and vector results of the solution flow rate of 5 L/min inside the UCM viewed from (a) the side and (b) the top. The black point is a mimic point representing the center position suitable for placing jewelry samples for cleaning. A small picture on the bottom left shows the view direction concerning the UCM. Sort by number, the solution released from the source flowed to numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9, sequentially. The greater the distance from the inlet, the lower the velocity, as expected. Notably, at number 7, the solution flowed to a jewelry sample as expected, with a velocity of about 0.01 m/s to aid ultrasonic cleaning in removing dirt, as mentioned in Figure 2. Moreover, for a higher flow rate of 5 L/min, both velocity and vector results showed a similar trend direction to that of 5 L/min but exhibited greater velocity.
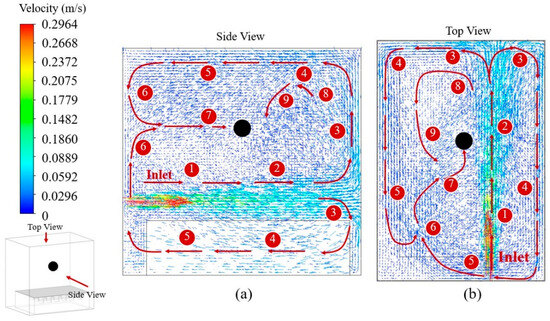
Figure 12.
The velocity and vector of the solution flow inside the UCM viewed from (a) the side and (b) the top.
4.2. Effect of Operating Conditions on Cleaning
4.2.1. Ultrasonic Power Concentration Without Solution Flow
Figure 13 shows the ultrasonic power concentration (UPC) measured by the UPC3000 device at the UCM’s center position under various operating conditions, affected by detergents and temperatures without solution flow. For varying temperatures, the UPC decreased with increasing temperature, as expected, due to the receding of the μ and ρ, as reported in Table 3. Increasing the detergent concentrations in the solution raised the UPC, as expected, because increasing the detergent volume in the solution reduces the surface tension [4,6], resulting in easier generation of cavitation bubbles and higher cleaning efficiency. Using pure water without detergent resulted in the lowest UPC, while adding detergent to the solution increased the UPC because the γ reduced, as seen in Table 3, as expected. Solution U with 3% detergent produced the highest UPC of 19.5 W/L at 30 °C, and water without any detergent had the lowest UPC of 6 W/L at 30 °C. Comparing the UPCs for various detergent types, the U solution provided the highest UPC. At the same time, S and N solutions yielded insignificant differences in the UPC, which were lower than that of the U solution. In the ultrasonic principle [4,6], as viscosity increases, the UPC level decreases, since the μ of the U solution decreases. However, the μ of U solution is the highest, but provides a great UPC. A combined effect, as shown in Figure 3, might cause this; a chemical effect can be amplified by adding detergent, which then helps the ultrasonic effect to enhance the UPC level. Therefore, the U solution, which involves adding 3% detergent to the water, is effective and enhances ultrasonic cleaning.
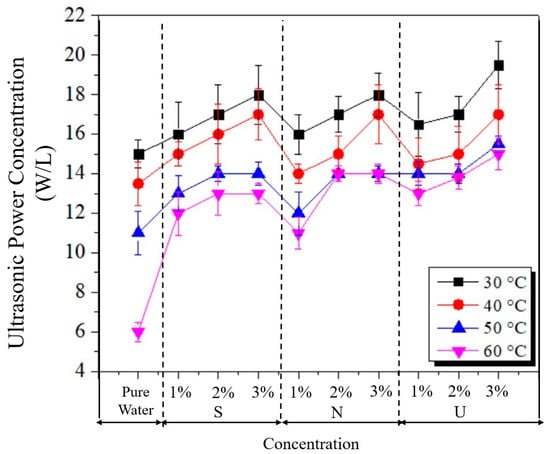
Figure 13.
Ultrasonic power concentration for various operating conditions without solution flow.
However, the detergent percentage was limited to 3%, since adding more than 3% detergent to the solution may cause toxicity. For example, the toxicity inhibits growth and may kill plants [29,30,31]. Accordingly, to lessen environmental impact, 3% detergent is an appropriate concentration, aligning with Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDGs:6): Clean water and sanitation [32]. Using less detergent reduces water pollution and promotes sustainable water management.
4.2.2. Ultrasonic Power Concentration with Solution Flow
Similarly, Figure 14 presents the UPC for various solution flow rates (Q), 0–25 L/min, in the UCM operated at (a) 30 °C, (b) 40 °C, (c) 50 °C, and (d) 60 °C—96 conditions in total. At a high Q, where Q is more than 5 L/min, the UPC decreases as Q increases. Therefore, a low Q is preferable to a high Q for the ultrasonic cleaning process. However, the highest UPC does not necessarily correspond to the highest cleaning efficiency. Consequently, the proper operating condition that provides the maximum cleaning efficiency needs to be investigated in the next section. The raw data of Figure 13 and Figure 14 are in the Supplementary Materials.
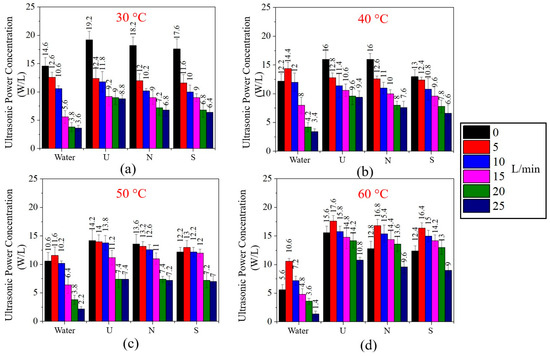
Figure 14.
The ultrasonic power concentration (UPC) for various solution flow rates, 0–25 L/min, in the UCM operated at (a) 30 °C, (b) 40 °C, (c) 50 °C, and (d) 60 °C.
4.3. The Proper Operating Condition
To determine the proper operating conditions, specific conditions were examined for their cleaning efficiency using the ultrasonic cleaning test mentioned in Section 3.2.3. Table 4 shows the operating conditions and the UPC transferred from Figure 14. The seven cases, designated as OP1–OP7, were selected because they resulted in a high UPC, ranking among the top two for each detergent type reported in Figure 14, using pure water at 30 °C as the base. Furthermore, regarding a production cost constraint, since pure water at 30 °C achieves a UPC of 14.6 W/L, if the result is below 14.6 W/L, the ultrasonic cleaning test is unnecessary because adding detergent increases production costs. Table 4 may have contributed to achieving high cleaning efficiency during testing with the jewelry samples.

Table 4.
Specific operating conditions for the ultrasonic cleaning test.
The ultrasonic cleaning test was conducted according to the diagram in Figure 7 under the operating conditions in Table 4. Each case used five jewelry samples in testing, resulting in a total of 35 samples. Then, SEM images and the weights of the pre-product (Wpr), polished product (Wpo), and clean product (Wcl) were recorded. After that, the cleaning efficiency (η) was calculated using Equation (5). Figure 15 reveals the η for cases in Table 4. Again, pure water without solution flow at 30 °C (OP1) yielded the η of 0.815%, the worst cleaning efficiency, although the water had the UPC of 14.6 W/L. This means that pure water, without detergent, at 30 °C, is insufficient for cleaning this type of jewelry; therefore, adding detergent (OP2–OP7) is better, as expected. Using only pure water is the least effective for cleaning, as it relies solely on ultrasonic effects without the support of chemical effects. When the ultrasonic cleaning test was operated at a temperature of 60 °C with a Q of 5 L/min, the η was within 53.609–93.890% (OP3, OP5, OP7), tremendously enhanced from operating at 30 °C without solution flow (OP2, OP4, OP6), which were within 6.667–22.088%. Regarding detergent types operated at 60 °C and a flow rate of 5 L/min, the U solution of 3% detergent achieved the highest η (93.890%). In contrast, the N and S solutions of 3% detergent produced moderate η (72.940%) and the lowest (53.609%), respectively. Therefore, OP3 is the proper operating condition for this type of jewelry, providing a cleaning efficiency of 93.890%. The OP3 has the highest η but has a moderate UPC of 17.6 W/L because of the combined effect explained as follows. According to Figure 2 and Figure 3, and Table 3, increasing the temperature reduces the μ, γ, and ρ of solution, resulting in the reduction of the ultrasonic effect, but the solution flow helps remove the outside dirt, U-type detergent boosts the chemical effect, and the dubbing that becomes soft and easily removed at high temperatures; thereby, increasing the combined effect and the cleaning efficiency. The raw data of Figure 15 are in the Supplementary Materials.
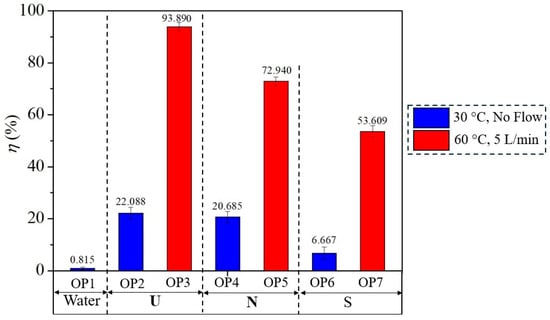
Figure 15.
The cleaning efficiency (η) of the ultrasonic cleaning test.
To confirm the η, Figure 16 and Figure 17 show sample results of the SEM images and the weights from the ultrasonic cleaning test of OP1 and OP3, respectively: (a) pre-product, (b) polished product, and (c) clean product. As expected, in (a), the jewelry sample was tidy since it was just released from the drying process mentioned in Figure 1. When it was polished, the dubbing adhered to its surface, increasing its weight as shown in (b). After ultrasonic cleaning, the dubbing was not wholly removed. Some pieces of dubbing still remain on the sample’s surface, as seen in (c). These SEM images confirmed the η as reported in Figure 15, that ultrasonic cleaning can dislodge the dubbing, resulting in a cleaner sample, and emphasized that cleaning efficiency depends on operating conditions. However, the employed operating conditions, OP1–OP7, were unable to eradicate the dubbing. Notably, OP3 is the proper operating condition, achieving a 93.890% cleaning efficiency, which resulted in Figure 17c being cleaner than Figure 16c, similar to Figure 17a, as expected. It is necessary to find the optimum operating conditions for the η of 100%, which may be for further research. The detergent usage guide provided by the vendor recommends using no more than 3% for optimal cleaning efficiency; however, excessive use can be wasteful and harmful to the environment. This research found that OP3 had a 93.890% cleaning efficiency, which benefits the jewelry manufacturer.
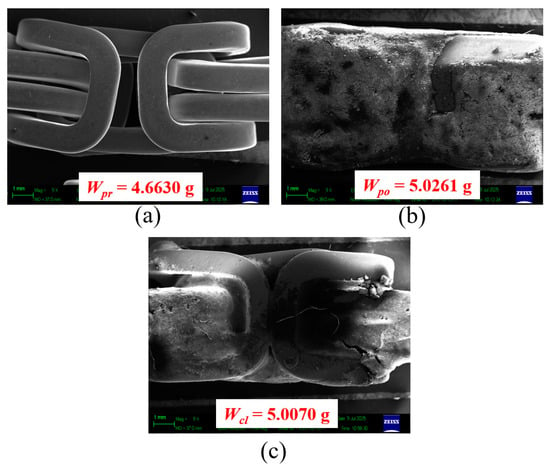
Figure 16.
SEM images and the weights of the samples from the ultrasonic cleaning test of OP1: (a) pre-product, (b) polished product, and (c) clean product.
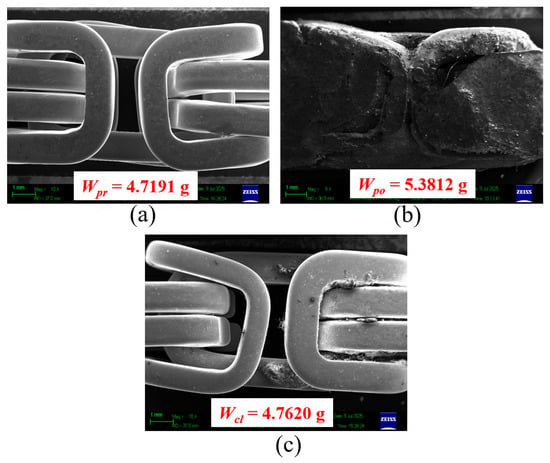
Figure 17.
SEM images and the weights of the samples from the ultrasonic cleaning test of OP3: (a) pre-product, (b) polished product, and (c) clean product.
4.4. Industry 5.0, SDGs, Limitations, and Development Opportunities
Industry 5.0 [33] emphasizes human-centricity, sustainability, and resilience, supporting ultrasonic cleaning technology in jewelry manufacturing. This technology reduces water, chemical, and energy use, and cleaning time while enhancing worker safety. When integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), it enables real-time monitoring to improve production accuracy and minimize waste, aligning with personalized production. Ultrasonic cleaning thus boosts efficiency, quality, and eco-friendliness, creating safer, sustainable, and human-centered jewelry manufacturing in Industry 5.0.
Ultrasonic cleaning under proper conditions, based on this research, is an approach that promotes environmental sustainability, health, and resource efficiency, aligning with several SDGs [32]. The direct benefits of this research pave the way for SDG 9: industry innovation and infrastructure. Table 5 reports the UCM energy consumption under specific operating conditions outlined in Table 4. The UCM energy consumption includes the energy used in the generator, heater, and water pump. From this table, although cases: OP1, OP2, OP4, and OP6, consumed the least energy (0.075 kWh), the η are 0.815%, 22.088%, 20.685%, and 6.667%, which indicate low cleaning efficiency, making them unsuitable and not worthwhile for industrial scale. Although cases OP3, OP5, and OP7 have the same energy consumption (1.550 kWh), OP3 is superior to 72.940% (OP5) and 53.609% (OP7), as it yielded 93.890%, achieving a high cleaning efficiency. Therefore, this research helps to make energy consumption more efficient, thereby improving the jewelry cleaning process and aligning with SDG 9.

Table 5.
The UCM energy consumption and the cleaning efficiency (η).
The add-on benefits of this research are devoted to SDGs: 3, 6, 12, and 13. Reducing detergent levels and water volume to appropriate levels and decreasing chemical discharges into natural water bodies help to preserve water quality and minimize impacts on aquatic life, aligning with SDG 6: Clean water and sanitation. They also advance SDG 12: Sustainable consumption and production, through waste reduction and resource efficiency. Additionally, ultrasonic cleaning reduces chemical and water usage, enhances cleaning effectiveness, and can be integrated with intelligent systems to decrease energy and carbon footprints, aligning with SDG 13: Climate Action, and contributing to safer working environments, supporting SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being.
This study was conducted under controlled conditions that may not fully reflect all jewelry cleaning situations. Only one jewelry type—a silver bracelet without gemstones—was tested, limiting the generalizability of the results to items with different materials, shapes, or delicate stones. Detergent concentration was limited to 3% to prevent environmental toxicity, and temperature was restricted to 60 °C, the UCM’s safe operating limit; therefore, effects beyond these ranges remain unknown. However, limiting the detergent volume to 3% is a preliminary suggestion, as noted in [29,30,31]. Additional experiments are necessary to determine the actual toxicity of the remaining solution after ultrasonic cleaning, and the proper percentage of detergent volume may need to be adjusted to an accurate percentage. Moreover, the experiments used a single ultrasonic frequency (40 kHz) and a single UCM design, so the results might differ with other machines or frequencies. Flow rates were limited to the equipment’s range (0–25 L/min), excluding more extreme conditions. In simulations, the UCM geometry was simplified and the SST k-ε, which could affect flow and acoustic predictions. The Reynolds Stress Model and the mixture model may be suitable for the solution flow in the UCM, thereby improving CFD accuracy [34]. According to the literature review, there is currently no CFD software that can accurately predict both the solution flow field and acoustic pressure field simultaneously. The research that studies the solution flow and factors affecting the cleaning efficiency, for example, in [15], investigates the flow and acoustic pressure separately. If a computer simulation is available that can study both fields simultaneously, it would be appropriate to use it to re-examine this problem and confirm its validity. However, computer simulation is a tool to help with analysis. The CFD and HRA results presented in this research are sufficient to support the conclusion. Cleaning performance was primarily assessed based on dubbing removal, rather than other contaminants, and the long-term effects on jewelry integrity or the environmental impact of detergent-laden wastewater were not fully examined.
Future work could expand testing to different types of jewelry, including gemstone-set and intricate designs, to confirm performance across a wider range of applications. Studying the chemical contaminants that might remain in jewelry after cleaning is also interesting. Exploring higher detergent concentrations, alternative eco-friendly agents, and broader temperature ranges may improve efficiency and sustainability. Trials with various ultrasonic frequencies, multiple UCM designs, and optimized flow patterns could enhance cleaning results. Integrating IoT and AI could allow real-time monitoring, adaptive control, and predictive maintenance. Conducting comprehensive environmental assessments, such as wastewater treatment and life-cycle analysis, would reinforce sustainability claims. Additionally, developing methods to achieve complete (100%) cleaning efficiency while maintaining jewelry integrity remains a key goal.
5. Conclusions
This research examined how detergent type and concentration, solution temperature, and flow rate affect ultrasonic cleaning efficiency in jewelry manufacturing, combining experimental trials with computer simulations. Harmonic response analysis was used to study acoustic pressure distribution, while computational fluid dynamics revealed solution flow behavior inside the ultrasonic cleaning machine. These analyses were validated through actual cleaning tests on silver bracelet samples under real factory conditions.
The findings showed that cleaning efficiency depends on the interplay between ultrasonic and chemical effects. Adding detergent lowered the surface tension, promoting cavitation bubble formation, while higher temperatures (up to 60 °C) softened dirt and improved the cleaning action. Moderate solution flow enhanced dirt removal through the combined effect of ultrasonic and chemical effects, whereas excessive flow reduced cavitation intensity. Among all tested conditions, the highest cleaning efficiency (93.890%) was achieved using 3% U-type detergent at 60 °C with a flow rate of 5 L/min (OP3). In contrast, pure water at room temperature without flow produced the lowest efficiency (0.815%). While ultrasonic power concentration (UPC) influenced the results, the highest UPC did not always correspond to the highest cleaning efficiency, indicating that optimal results require balanced parameters.
The study also aligns with sustainability goals, as limiting detergent concentration to 3% reduces environmental impact in accordance with SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation). The methodology demonstrates that integrating simulations with experiments can effectively optimize ultrasonic cleaning processes for industrial applications.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cleantechnol7040083/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.J. and J.T.; methodology, N.J.; software, C.C.; validation, N.J., C.C. and J.T.; formal analysis, J.T.; investigation, J.T.; resources, N.J.; data curation, N.J.; writing—original draft preparation, J.T.; writing—review and editing, J.T.; visualization, C.C.; supervision, J.T.; project administration, J.T.; funding acquisition, J.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the School of Integrated Innovative Technology, King Mongkut’s Institute of Technology, Ladkrabang, grant number 2567-02-10-003.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Measurement instruments were kindly provided by Boonchooy Soontornworajit, Yuttanant Boonyongmaneerat, and Pasuda Supplies and Services Co., Ltd. The authors would like to thank everyone involved.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- GIT Information Center, Thailand Gem and Jewelry Import-Export Performance January-December 2024. Available online: https://infocenter.git.or.th/en/article/article-20250207 (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Atsawawongwiwat, P.; Sanohkham, B.; Kobjaiklang, C. Casual factors influencing the success of the genuine jewelry retail industry in Thailand. Thai Interdiscip. Sustain. Rev. 2024, 13, 313–328. (In Thai) [Google Scholar]
- Busnaina, A.; Kashkoush, I. The effect of time, temperature, and particle size on submicron particle removal using ultrasonic cleaning. Chem. Eng. Comm. 1993, 125, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, F.J. Ultrasonic cleaning and washing of surfaces. Power Ultrason. 2015, 577–609. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9781782420286000193?via%3Dihub (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Verhaagen, B.; Rivas, D.F. Measuring cavitation and its cleaning effect. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 29, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, F.J. Ultrasonics-Number and Size of Cavitation Bubbles. Available online: https://www.blackstone-ney.com/blog/ultrsonics-number-and-size-of-cavitation-bubbles/ (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Kanegsberg, B.; Kanegberg, E. Handbook for Critical Cleaning: Applications, Processes, and Controls, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Srathonghuam, K.; Wonganu, B.; Busayaporn, W.; Thongsri, J. Vibration analysis and development of a submersible ultrasonic transducer for an application in the inhibitory activity of pathogenic bacteria. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 142362–142373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goris, Q.; Adams, M.; Stefanidis, G.D.; Gerven, T.V. An in-depth comparison of the ultrasonic horn and plate transducers: Building from fundamentals to application. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2025, 215, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phophayu, S.; Thongsri, J. Vibration analysis of 28 kHz transducer for ultrasonic cleaning based on harmonic response analysis. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2312, 012072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangsopa, W.; Thongsri, J. Development of an industrial ultrasonic cleaning tank based on harmonic response analysis. Ultrasonics 2019, 91, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phopayu, S.; Kliangklom, K.; Thongsri, J. Harmonic response analysis of tank design effect on ultrasonic cleaning process. Fluids 2022, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.J.; Vévert, C.; Lee, J.; Bussemaker, M.J. Combined effects of flow, surface stabilization and salt concentration in aqueous solution to control and enhance sonoluminescence. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, R.J.; Vévert, C.; Lee, J.; Bussemaker, M.J. Flow effect on phenol degradation and sonoluminescence at different ultrasonic frequencies. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 63, 104892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangsopa, W.; Thongsri, J. A novel ultrasonic cleaning tank developed by harmonic response analysis and computational fluid dynamics. Metals 2020, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, S.B.; Nagarajan, R. Chapter 6-Ultrasonic Cleaning. In Developments in Surface Contamination and Cleaning; Kohli, R., Mittal, K.L., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 225–280. [Google Scholar]
- Phanomwan na Ayudhya, P.; Tangjitsitcharoen, S. Reduction of defects in jewelry manufacturing. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 215, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Feng, H.; Pearlstein, A.J. Continuous-flow ultrasonic washing system for fresh produce surface decontamination. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 16, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys, Inc. Harmonic Analysis; ANSYS Inc.: Southpointe, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y. A novel technique to predict harmonic response of particle-damping structure based on ANSYS® secondary development technology. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 144, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS, Inc. Chapter 1 Basic Fluid Flow. In Fluent Theory Guide; ANSYS Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- ANSYS, Inc. Chapter 4 Turbulence. In Fluent Theory Guide; ANSYS Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- ThermoFisher Scientific, HAAKETM MARSTM Rheometer. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/379-0600?SID=srch-srp-379-0600 (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Dataphysics Understanding Interfaces, Optical Contact Angle Measuring and Contour Analysis System of the OCA Series. Available online: https://www.dataphysics-instruments.com/products/oca/ (accessed on 29 July 2025).
- NGL Cleaning Technology, UPC 3000 Ultrasonic Process Controller. Available online: https://www.ngl-group.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/upc-3000-en-pdf.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- A&D Company, Ltd., GR Series Analytical Balances: Instruction Manual GR-200. Available online: https://www.aandd.jp/products/manual/balances/gr.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Anton Paar GmbH, Viscosity Table-Measurement Data. Available online: https://wiki.anton-paar.com/th-th/water/ (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- The Engineering ToolBox, Surface Tension of Water. Available online: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/surface-tension-d_962.html (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Issayeva, A.U.; Syrlybayeva, E.Z.; Zhymadullayeva, A.I.; Balgabekova, A. The effect of detergents on the anatomical changes in the roots of beans. J. Educ. Policy Entrep. Res. 2015, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.A.; Khodadoos, F. Effects of detergents on natural ecosystems and wastewater treatment process: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollu. Res. 2019, 26, 26439–26448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, H.; Karimi, S. Effect of contaminated water (handwashing detergent) on seed germination traits in wheat, mung bean, and chickpea. Tenside Surf. Deterg. 2024, 61, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Development Programme. What Are the Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.undp.org/sustainable-development-goals (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Xu, X.; Lu, Y.; Vogel-Heuser, B.; Wang, L. Industry 4.0 and industry 5.0-inception, conception and perception. J. Manu. Sys. 2021, 61, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Mikielewicz, J.; Ziółkowski, P.; Mikielewicz, D. Optimizing CO2 purification in a negative CO2 emission power plant. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2024, 47, e202300568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).