The Impact of Tetraethyl Pyrophosphate (TEPP) Pesticide on the Development and Behavior of Danio rerio: Evaluating the Potential of Cork Granules as a Natural Adsorbent for TEPP Removal from Aqueous Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Solutions
2.2. Reconstituted Water Solution
2.3. Zebrafish Collection and Maintenance
2.4. Preparation of the Cork Granules
2.5. Adsorption Experiments
2.6. Experimental Design
2.7. Fish Embryo Toxicity (FET) Assays
2.8. Biometric Parameters Analyses
2.9. Light–Dark Preference Assay
2.10. Swimming Resistance Test
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cork Granules and TEPP Adsorption
3.2. Toxicity of TEPP and Cork + TEPP on the Viability of Embryos
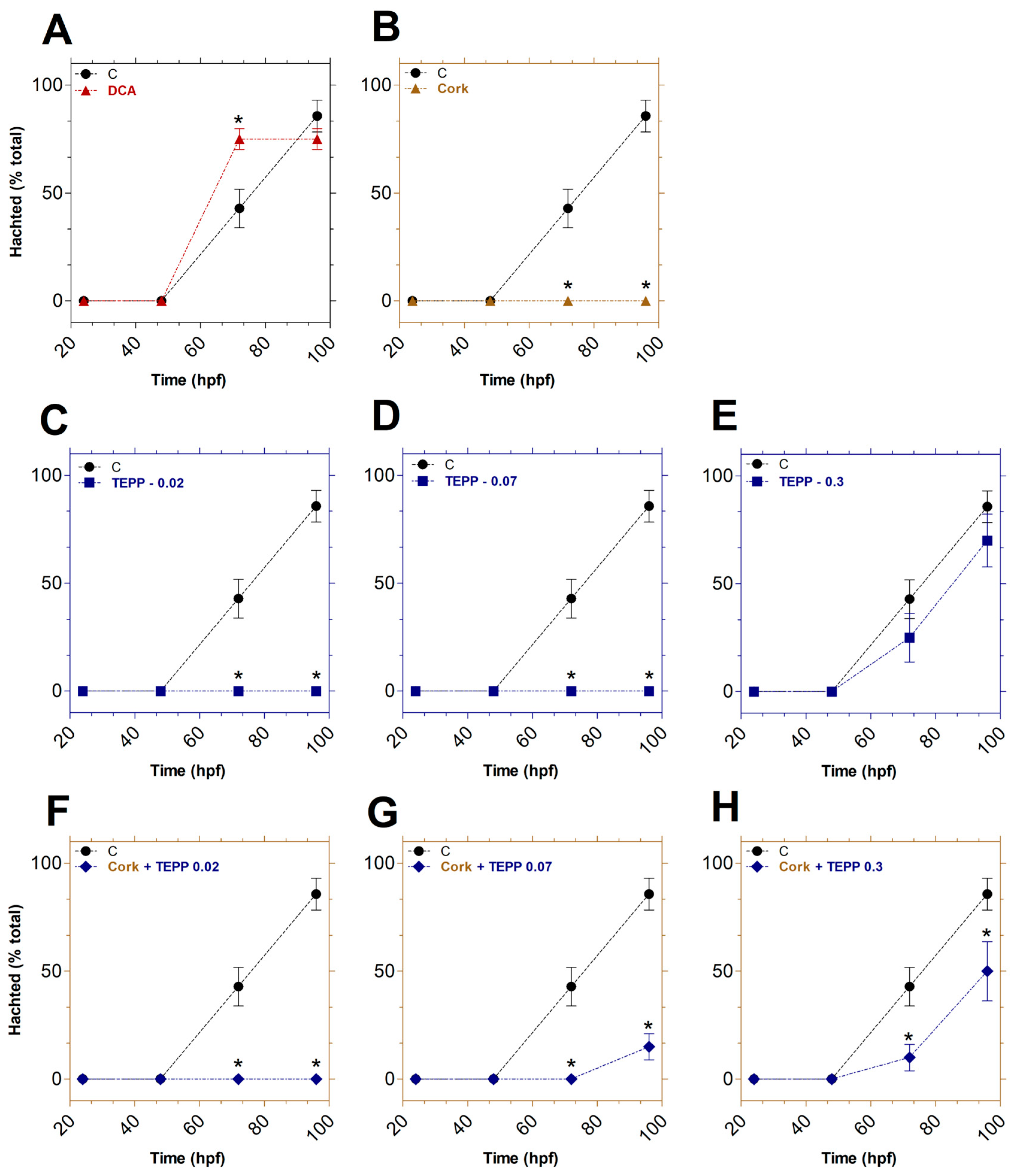
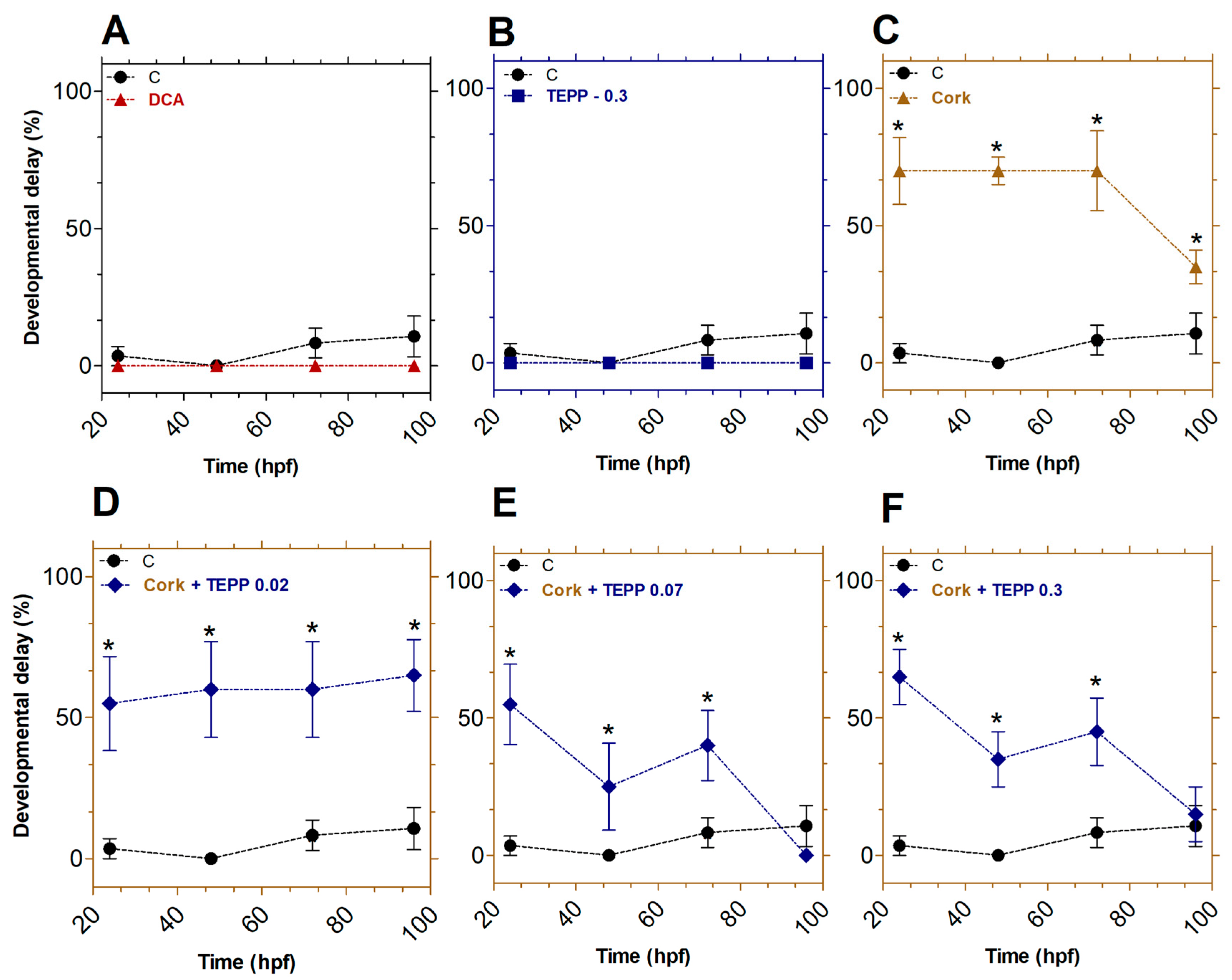
3.3. Effects of TEPP and Cork + TEPP on the Developmental Abnormalities
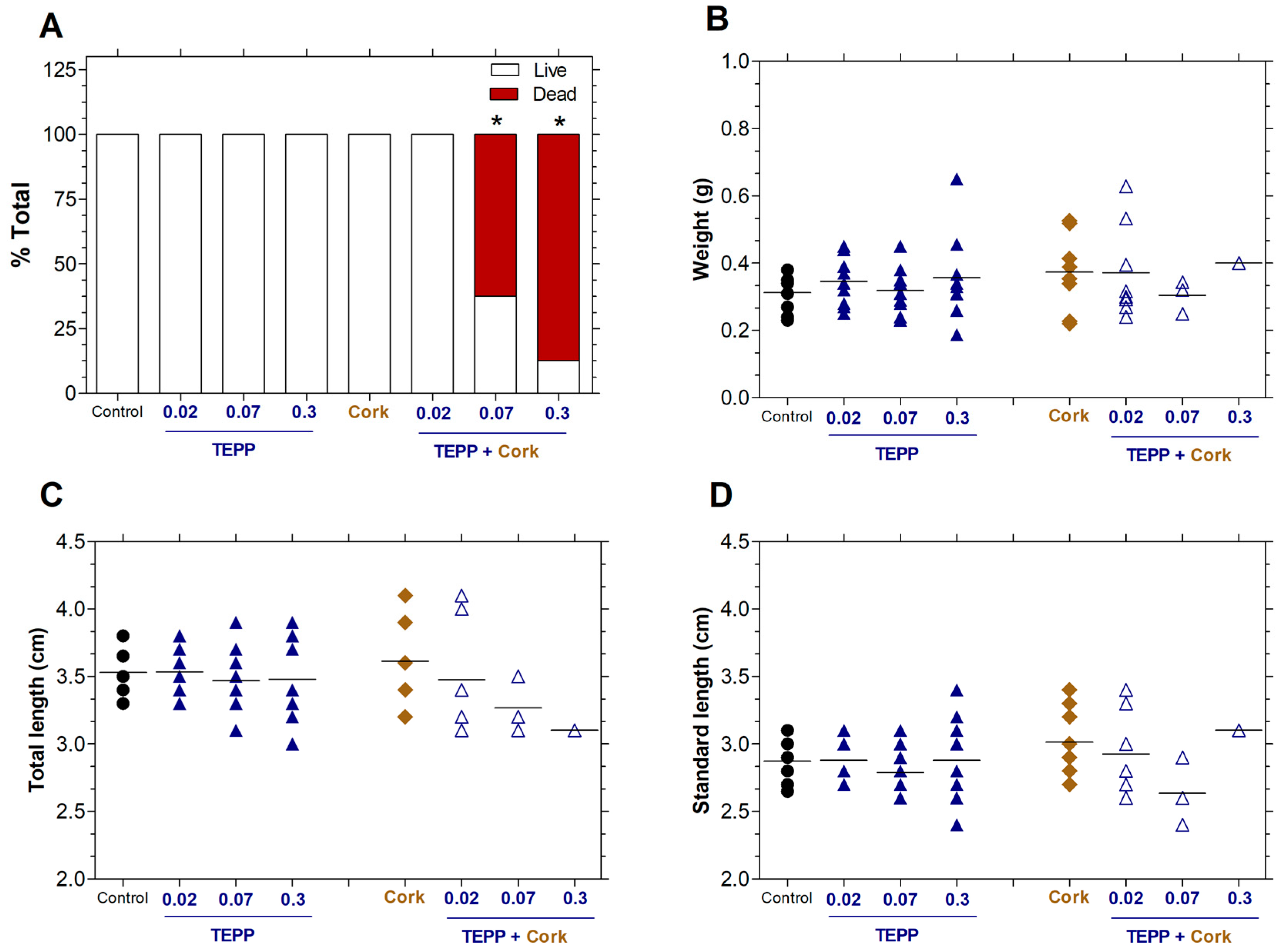
3.4. Toxicity of TEPP and Cork + TEPP on the Viability of Zebrafish Juveniles
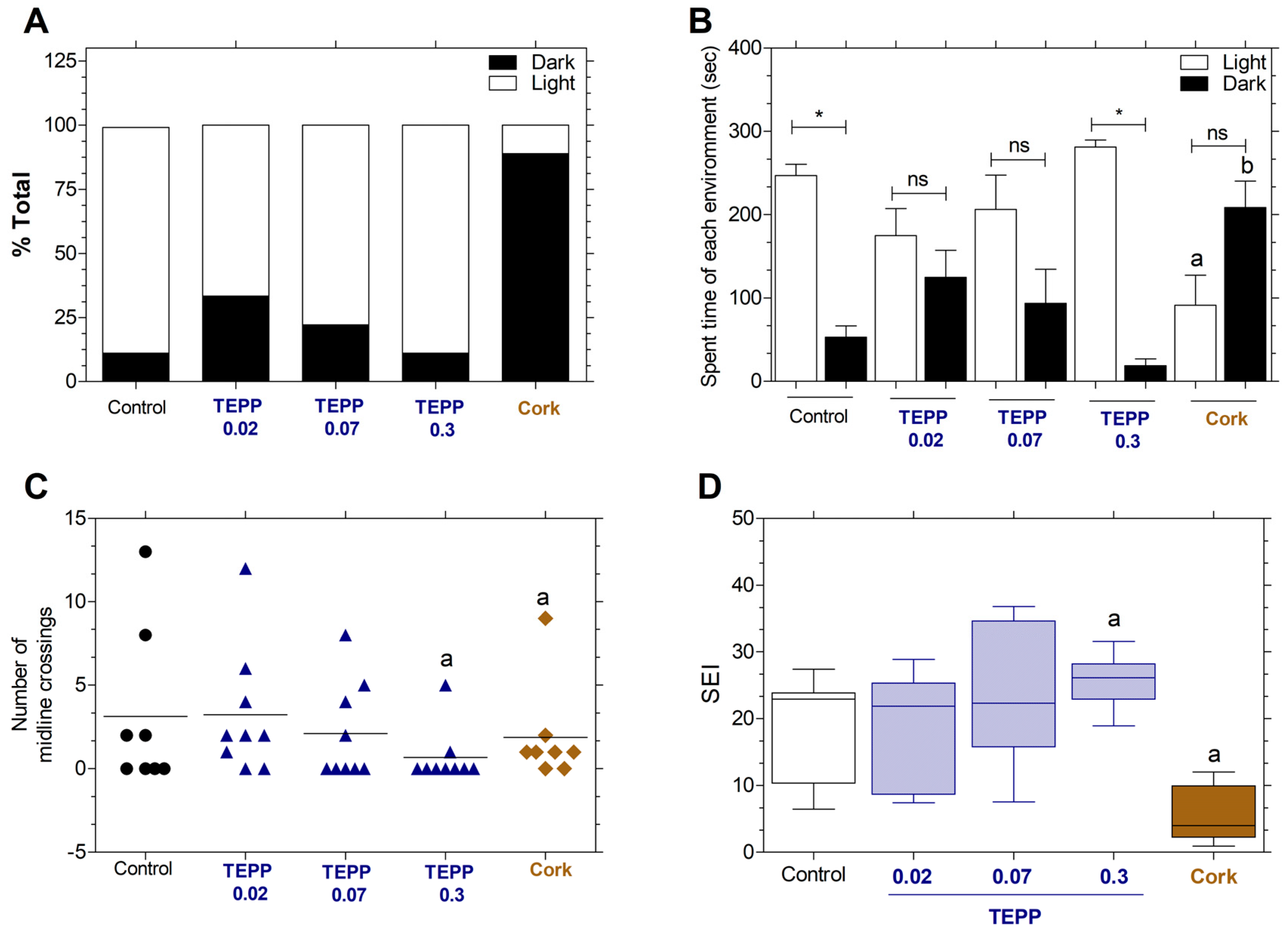
3.5. Effects of TEPP and Cork on Behavior Fish (Light–Dark Environment Preference)
3.6. Effects of TEPP and Cork on Behavior Fish (Swimming Endurance Test)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| ACh | Acetylcholine |
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| DCA | 3,4-Dichloroaniline |
| FET | Fish Embryo Toxicity |
| hpf | Hours Post-Fertilization |
| IC50 | Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| OPs | Organophosphates |
| PC12 | Pheochromocytoma cell line (rat adrenal medulla-derived cells) |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| SEI | Swimming Endurance Index |
| TEPP | Tetraethyl Pyrophosphate |
| ZET | Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity |
References
- Georg, P. History of Organophosphorus Cholinesterase Inhibitors & Reactivators. Mil. Med. Sci. Lett. 2015, 84, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu-Villaça, Y.; Levin, E.D. Developmental Neurotoxicity of Succeeding Generations of Insecticides. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.R.; Lima, J.M.F.A.; Echeverry, M.B.; Alberto-Silva, C. Haloperidol-Induced Catalepsy and Its Correlations with Acetylcholinesterase Activity in Different Brain Structures of Mice. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, D.M.; Brecht, K.M.; Koplovitz, I.; Sweeney, R.E. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition: Does It Explain the Toxicity of Organophosphorus Compounds? Arch. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddleston, M.; Buckley, N.A.; Eyer, P.; Dawson, A.H. Management of Acute Organophosphorus Pesticide Poisoning. Lancet 2008, 371, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, J. Poisoning Due to Tetraethylpyrophosphate. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1949, 141, 192–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Àngels Olivella, M.; Caixach, J.; Planas, C.; Oliveras, A.; Jové, P. Concentrations of Organochlorine Pesticides and 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole in Cork Bark. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Kazeroon, R.A.; Gholami, A. Cross-Linked Magnetic Chitosan/Activated Biochar for Removal of Emerging Micropollutants from Water: Optimization by the Artificial Neural Network. Water 2019, 11, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Zhou, J.L.; Robinson, B.; Ohashi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Kindaichi, T.; Farraji, H.; Vakili, M. Pesticides in Aquatic Environments and Their Removal by Adsorption Methods. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintor, A.M.A.; Ferreira, C.I.A.; Pereira, J.C.; Correia, P.; Silva, S.P.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Botelho, C.M.S.; Boaventura, R.A.R. Use of Cork Powder and Granules for the Adsorption of Pollutants: A Review. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3152–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aguiar, T.R.; Guimarães Neto, J.O.A.; Şen, U.; Pereira, H. Study of Two Cork Species as Natural Biosorbents for Five Selected Pesticides in Water. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, J.S.; Morés, L.; Carasek, E. Exploring the Use of Cork Pellets in Bar Adsorptive Microextraction for the Determination of Organochloride Pesticides in Water Samples with Gas Chromatography/Electron Capture Detection Quantification. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1645, 462099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carriço, C.M.; Tiritan, M.E.; Cidade, H.; Afonso, C.; Silva, J.R.E.; Almeida, I.F. Added-Value Compounds in Cork By-Products: Methods for Extraction, Identification, and Quantification of Compounds with Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Interest. Molecules 2023, 28, 3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafra, G.; Spudeit, D.; Brognoli, R.; Merib, J.; Carasek, E. Expanding the Applicability of Cork as Extraction Phase for Disposable Pipette Extraction in Multiresidue Analysis of Pharmaceuticals in Urine Samples. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1102–1103, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, H. Cork: Biology, Production and Uses; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; p. 336. [Google Scholar]
- Marzi Khosrowshahi, E.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Tuzen, M.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R.; Nemati, M. Application of Magnetic Carbon Nano-Onions in Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction Combined with DLLME for Extraction of Pesticide Residues from Water and Vegetable Samples. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 3592–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Huang, Z.; Shang, C.; Wang, L.; Qiu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, D. Design and Synthesis of Amphiphilic Carboxyl-Functionalized Magnetic Polymer Microspheres for Fast Determination of Paraquat and Its Four Metabolites in Human Urine Samples Prior to Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1670, 462998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blini Marengo Malheiros, F.; Vicente, E.F.; Gois Morales, A.; Alberto-Silva, C. Efficiency of the Removal of Tetraethyl Pyrophosphate (TEPP) Pesticide in Water: Use of Cork Granules as a Natural Adsorbent on Acetylcholinesterase Activity in Neuronal PC12 Cell. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2022, 57, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikari, A. Caging Techniques for Field Exposures of Fish to Chemical Contaminants. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, C. The Husbandry of Zebrafish (Danio rerio): A Review. Aquaculture 2007, 269, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test. OECD Guidel. Test. Chem. 2013, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.N.; Simão, V.; Merib, J.; Carasek, E. Use of Green Coating (Cork) in Solid-Phase Microextraction for the Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides in Water by Gas Chromatography-Electron Capture Detection. Talanta 2015, 134, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 15088:2007—Water Quality—Determination of the Acute Toxicity of Waste Water to Zebrafish Eggs (Danio rerio). Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/37368.html (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Pinho, B.R.; Santos, M.M.; Fonseca-Silva, A.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Oliveira, J.M.A. How Mitochondrial Dysfunction Affects Zebrafish Development and Cardiovascular Function: An in Vivo Model for Testing Mitochondria-Targeted Drugs. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1072–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenca, A.L.R.; Simonato, J.D.; Meletti, P.C. Acute Exposure of Embryo, Larvae and Adults of Danio Rerio to Fipronil Commercial Formulation Reveals Effects on Development and Motor Control. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, E.L.; Medalha, C.C.; Mattioli, R. Natural Preference of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) for a Dark Environment. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1999, 32, 1551–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; de Brito, T.M.; da Silva Batista, A.W.; Herculano, A.M.; Morato, S.; Gouveia, A. Measuring Anxiety in Zebrafish: A Critical Review. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 214, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, L.R.; Gravato, C.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Morgado, F.; Guilhermino, L. Acute Effects of Copper and Mercury on the Estuarine Fish Pomatoschistus Microps: Linking Biomarkers to Behaviour. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 1416–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, F.R.; Accoroni, K.A.G.; Gravato, C.; de Oliveira, D.P. Early Life Stage Assays in Zebrafish. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2240, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivantsova, E.; Konig, I.; Souders, C.L.; McNabney, D.; Simmons, D.D.B.; Martyniuk, C.J. Lipidomic, Metabolomic, and Behavior Responses of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Exposed to Environmental Levels of the Beta Blocker Atenolol. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toni, M.; Arena, C.; Cioni, C.; Tedeschi, G. Temperature- and Chemical-Induced Neurotoxicity in Zebrafish. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1276941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, Í.F.S.; Souza, T.M.; Vieira, L.R.; Marchi, F.C.; Nascimento, A.P.; Farias, D.F. Toxicity Testing of Pesticides in Zebrafish-a Systematic Review on Chemicals and Associated Toxicological Endpoints. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 10185–10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassereau, J.; Ferré, M.; Chevrollier, A.; Codron, P.; Verny, C.; Homedan, C.; Lenaers, G.; Procaccio, V.; May-Panloup, P.; Reynier, P. Neurotoxicity of Insecticides. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 2988–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanibuchi, F.; Nishida, T.; Yamashita, H.; Hidaka, K.; Koshiya, K.; Tsukamoto, S.; Usuda, S. Characterization of a Novel Muscarinic Receptor Agonist, YM796: Comparison with Cholinesterase Inhibitors in in Vivo Pharmacological Studies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 265, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braida, D.; Paladini, E.; Griffini, P.; Lamperti, M.; Maggi, A.; Sala, M. An Inverted U-Shaped Curve for Heptylphysostigmine on Radial Maze Performance in Rats: Comparison with Other Cholinesterase Inhibitors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 302, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braida, D.; Paladini, E.; Griffini, P.; Lamperti, M.; Colibretti, L.; Sala, M. Long-Lasting Antiamnesic Effect of a Novel Anticholinesterase Inhibitor (MF268). Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1998, 59, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, E.; Bucherelli, C. The Inverted “u-Shaped” Dose-Effect Relationships in Learning and Memory: Modulation of Arousal and Consolidation. Nonlinearity Biol. Toxicol. Med. 2005, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasing, K. A Threshold Model for Opposing Actions of Acetylcholine on Reward Behavior: Molecular Mechanisms and Implications for Treatment of Substance Abuse Disorders. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 312, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzenchi Proca, T.M.; Solcan, C.; Solcan, G. Neurotoxicity of Some Environmental Pollutants to Zebrafish. Life 2024, 14, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, C.R.D.; Linhares, A.G.; Oliveira, V.M.; França, R.C.P.; Carvalho, E.V.M.M.; Bezerra, R.S.; de Carvalho, L.B. Comparative Effect of Pesticides on Brain Acetylcholinesterase in Tropical Fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 441, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequin, S.; Chassagne, D.; Karbowiak, T.; Gougeon, R.; Brachais, L.; Bellat, J.P. Adsorption Equilibria of Water Vapor on Cork. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3438–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, V.F.; Priolo, G.; Alves, A.C.; Cabral, M.F.; Delerue-Matos, C. Adsorption Behavior of Alpha -Cypermethrin on Cork and Activated Carbon. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2007, 42, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, J.; Lopes, P.; Mateus, N.; de Freitas, V. Cork, a Natural Choice to Wine? Foods 2022, 11, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malheiros, F.B.M.; Souza, L.V.R.d.; Morales, A.G.; Vicente, E.F.; Meletti, P.C.; Alberto-Silva, C. The Impact of Tetraethyl Pyrophosphate (TEPP) Pesticide on the Development and Behavior of Danio rerio: Evaluating the Potential of Cork Granules as a Natural Adsorbent for TEPP Removal from Aqueous Environments. Clean Technol. 2025, 7, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol7030054
Malheiros FBM, Souza LVRd, Morales AG, Vicente EF, Meletti PC, Alberto-Silva C. The Impact of Tetraethyl Pyrophosphate (TEPP) Pesticide on the Development and Behavior of Danio rerio: Evaluating the Potential of Cork Granules as a Natural Adsorbent for TEPP Removal from Aqueous Environments. Clean Technologies. 2025; 7(3):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol7030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalheiros, Fernanda Blini Marengo, Lorrainy Victoria Rodrigues de Souza, Angélica Gois Morales, Eduardo Festozo Vicente, Paulo C. Meletti, and Carlos Alberto-Silva. 2025. "The Impact of Tetraethyl Pyrophosphate (TEPP) Pesticide on the Development and Behavior of Danio rerio: Evaluating the Potential of Cork Granules as a Natural Adsorbent for TEPP Removal from Aqueous Environments" Clean Technologies 7, no. 3: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol7030054
APA StyleMalheiros, F. B. M., Souza, L. V. R. d., Morales, A. G., Vicente, E. F., Meletti, P. C., & Alberto-Silva, C. (2025). The Impact of Tetraethyl Pyrophosphate (TEPP) Pesticide on the Development and Behavior of Danio rerio: Evaluating the Potential of Cork Granules as a Natural Adsorbent for TEPP Removal from Aqueous Environments. Clean Technologies, 7(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol7030054






