Electrical Vehicles: Current State of the Art, Future Challenges, and Perspectives
Abstract
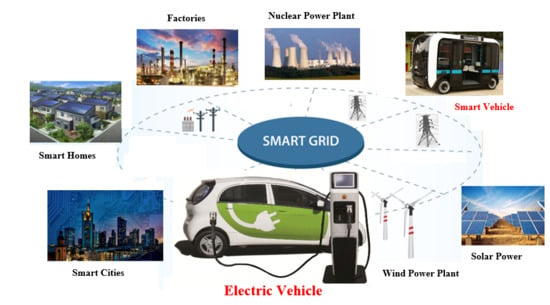
:1. Introduction
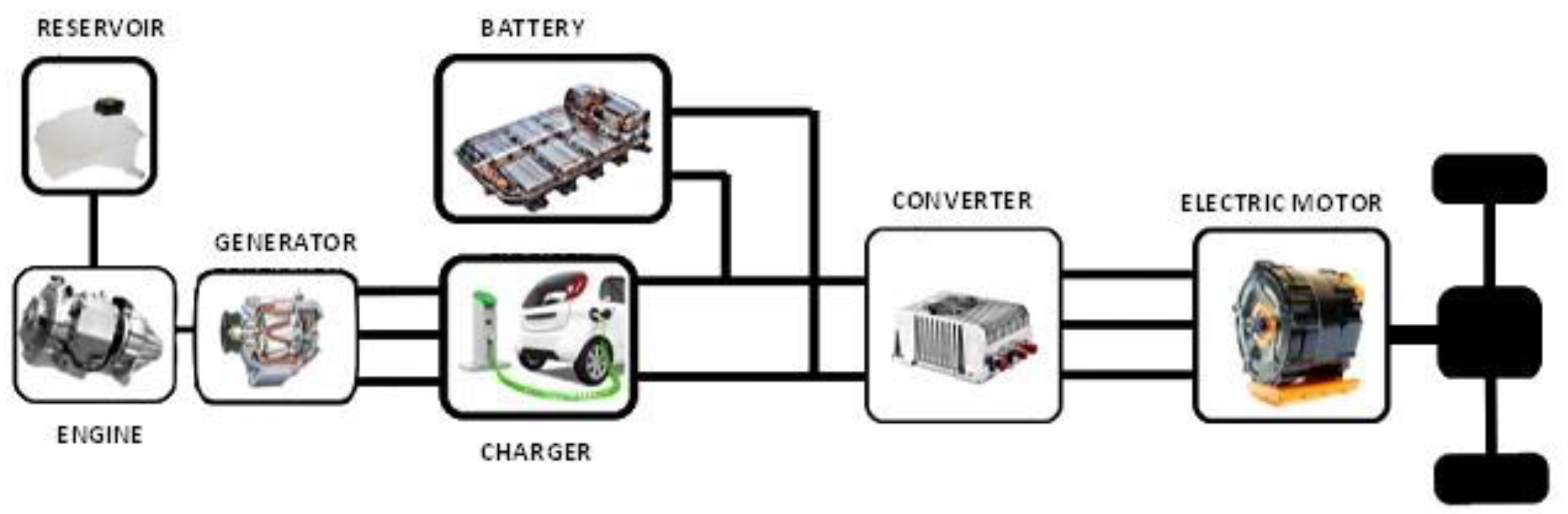
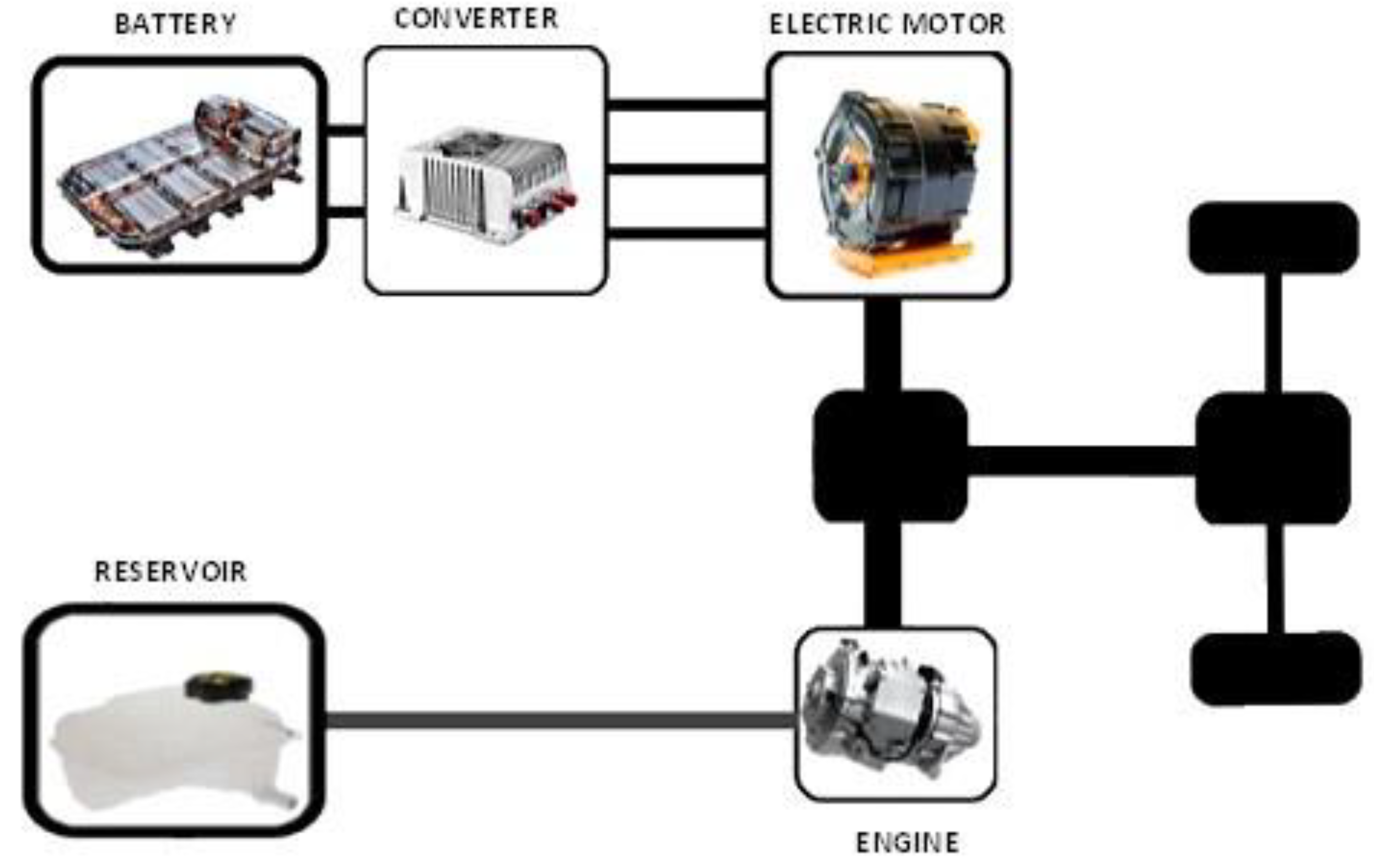
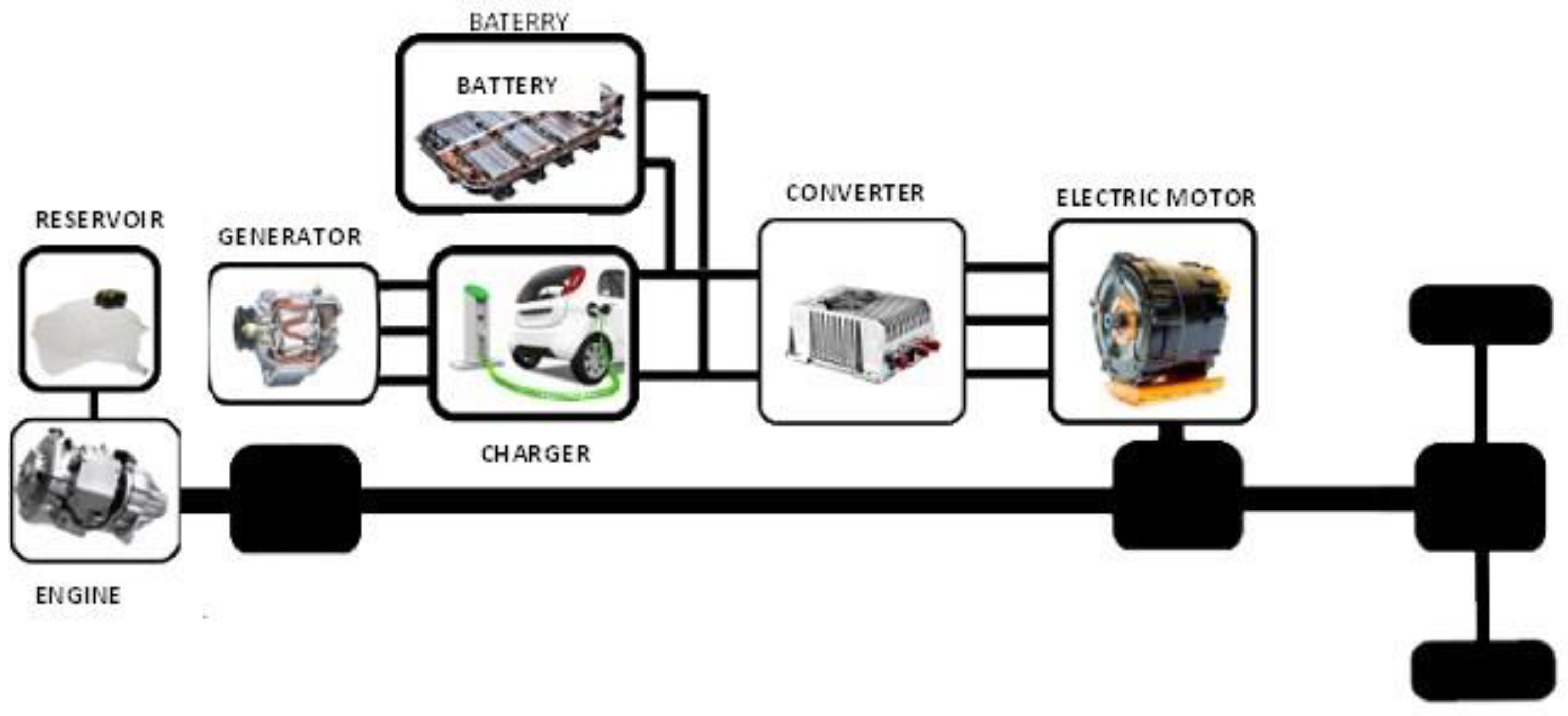
2. Hybrid Electric Vehicles
2.1. Micro Hybrid Stop-Start (μHV)
2.2. Mild Hybrid (MHV)
2.3. Full Hybrid (FHV)
2.3.1. Series Hybrid EVs (SHEV)
2.3.2. Parallel Hybrid EVs (PHEV)
2.3.3. Series-Parallel Hybrid EVs (SPHEV)
2.3.4. Fuel Cell Hybrid EVs (FCHEV)
2.3.5. Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV)
3. Charging Technology Analysis and Standards
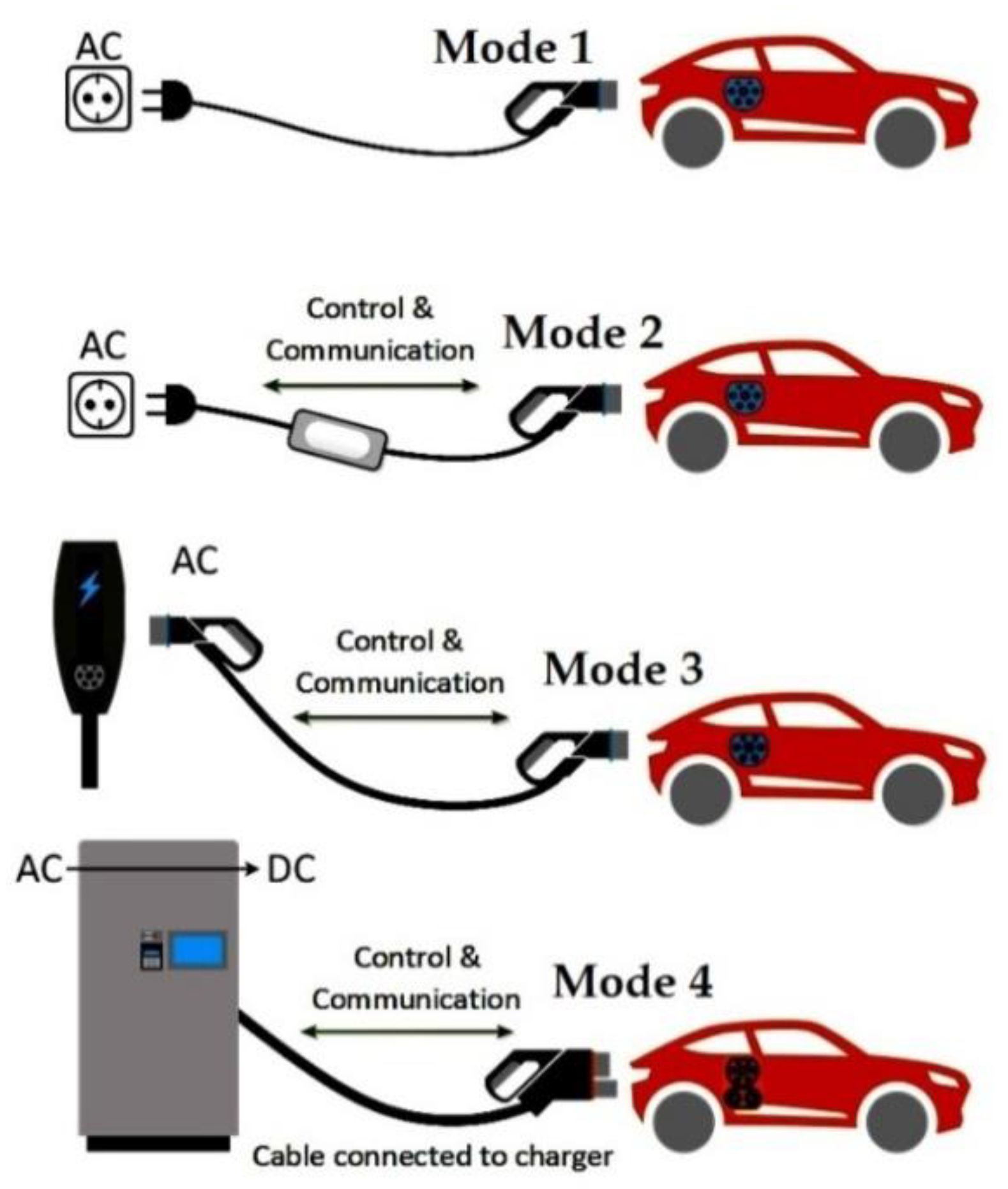
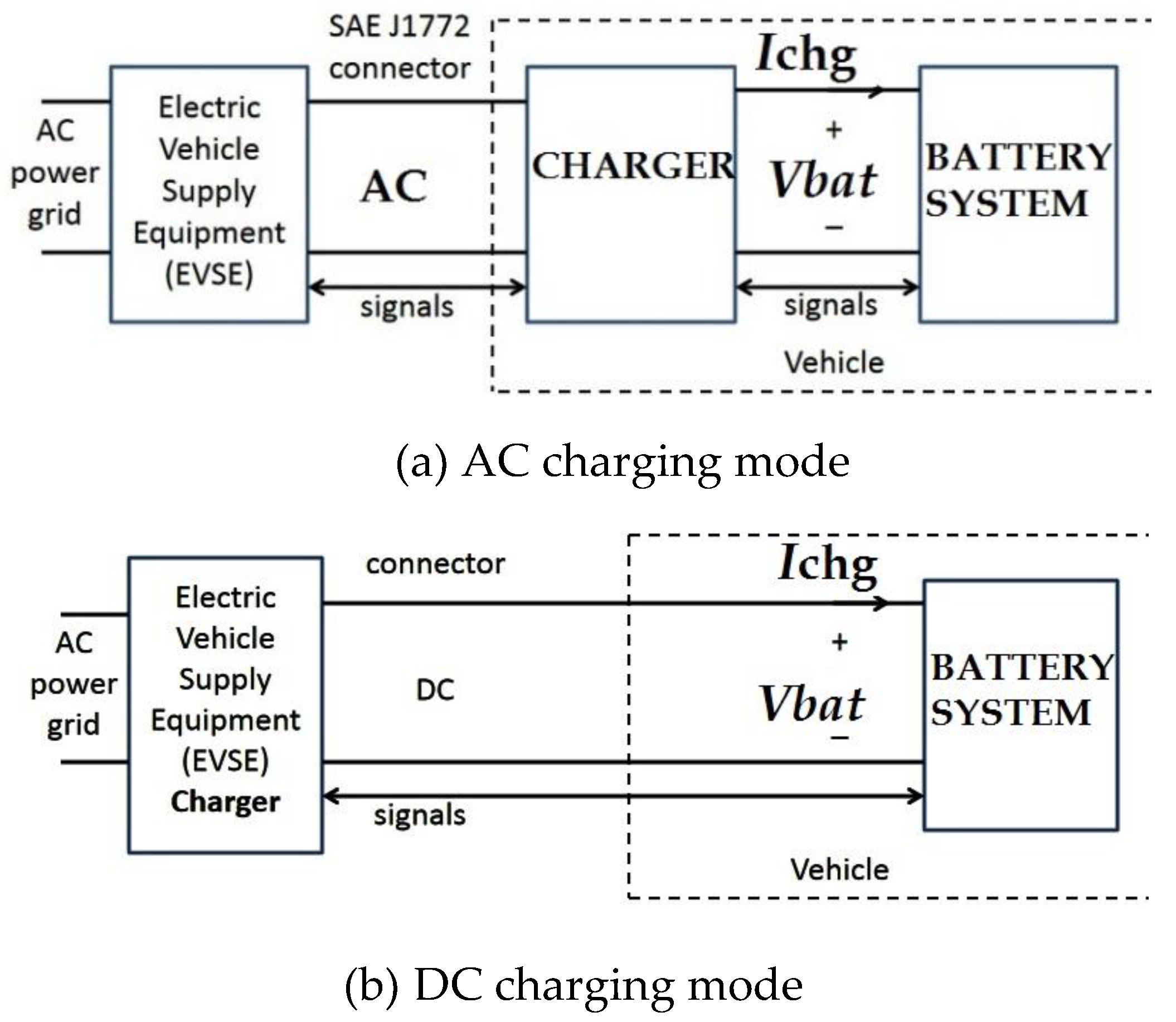
3.1. Charging Modes (IEC-61851-1)
3.1.1. AC Mode-1: Domestic Socket and Extension Cord
3.1.2. AC Mode-2: Slow Charge from a General Purpose Socket with an Electric Shock Protection Device (RCD) on the Cable
3.1.3. AC Mode-3: Semi-Fast Charging from a Special Socket
3.1.4. DC Mode 4: Fast Charging Using an External Charger in DC
3.2. Charging Levels
3.2.1. AC LEVEL-1
3.2.2. AC LEVEL-2
3.2.3. AC LEVEL-3: Semi-Fast Charging from a Special Socket
3.2.4. DC LEVELS Fast/Superfast Charging from an External Charger Providing DC Power
4. Wireless Charging Systems
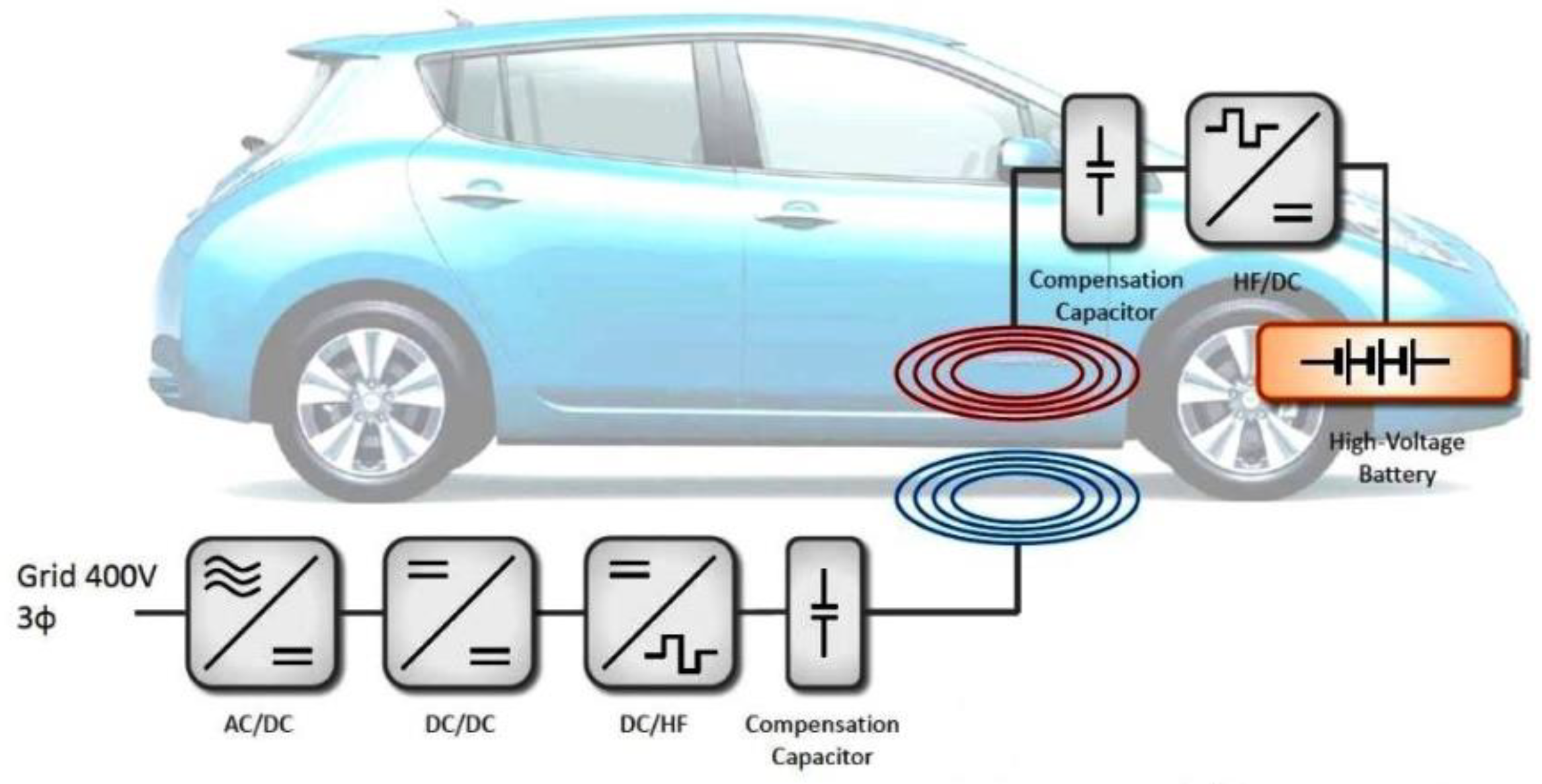
4.1. Static Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging System (S-WEVCS)
4.2. Dynamic Wireless Charging System for Electric Vehicles (D-WEVCS)
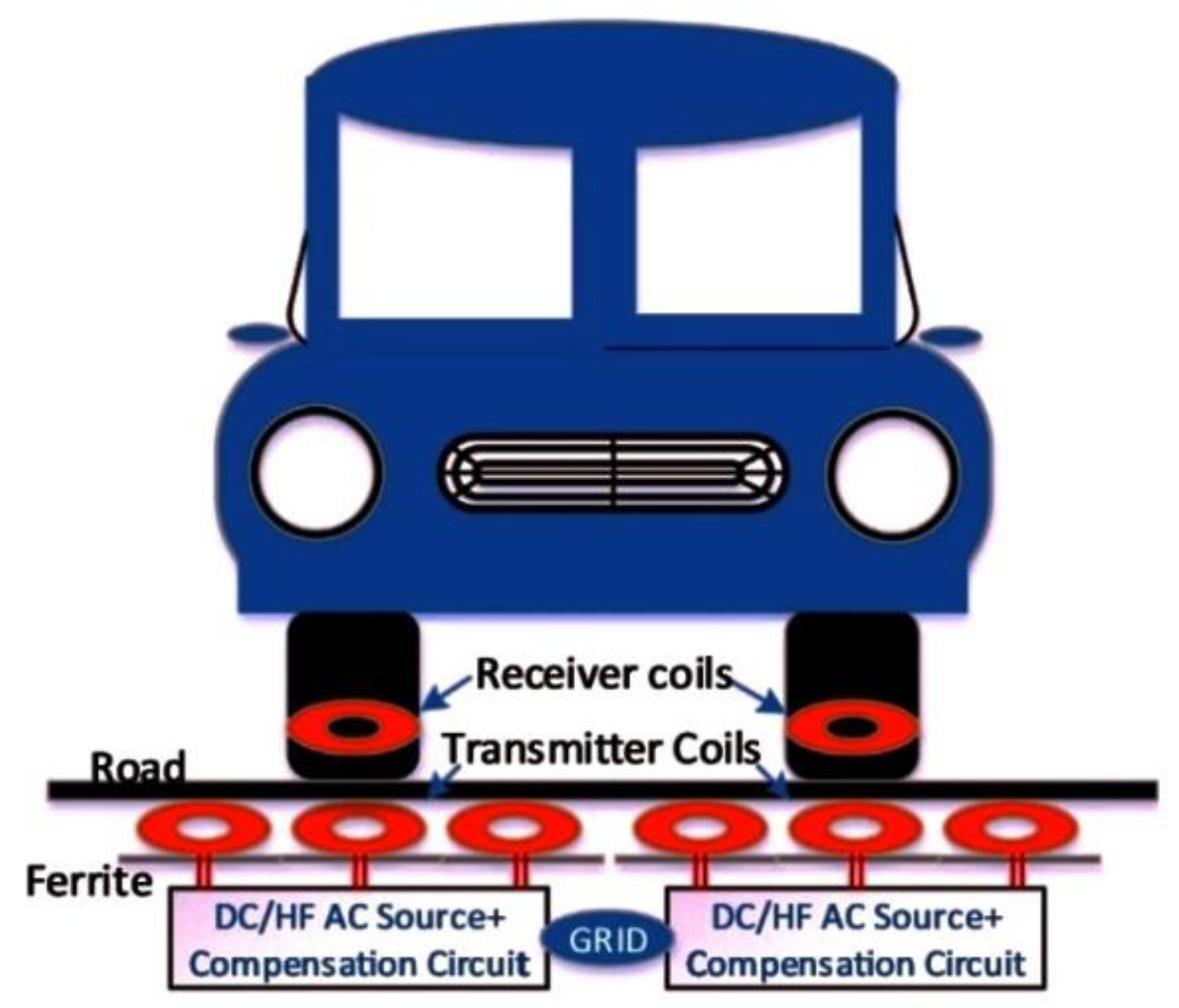
4.3. In-Wheel Wireless Charging Systems (IW-WCS)
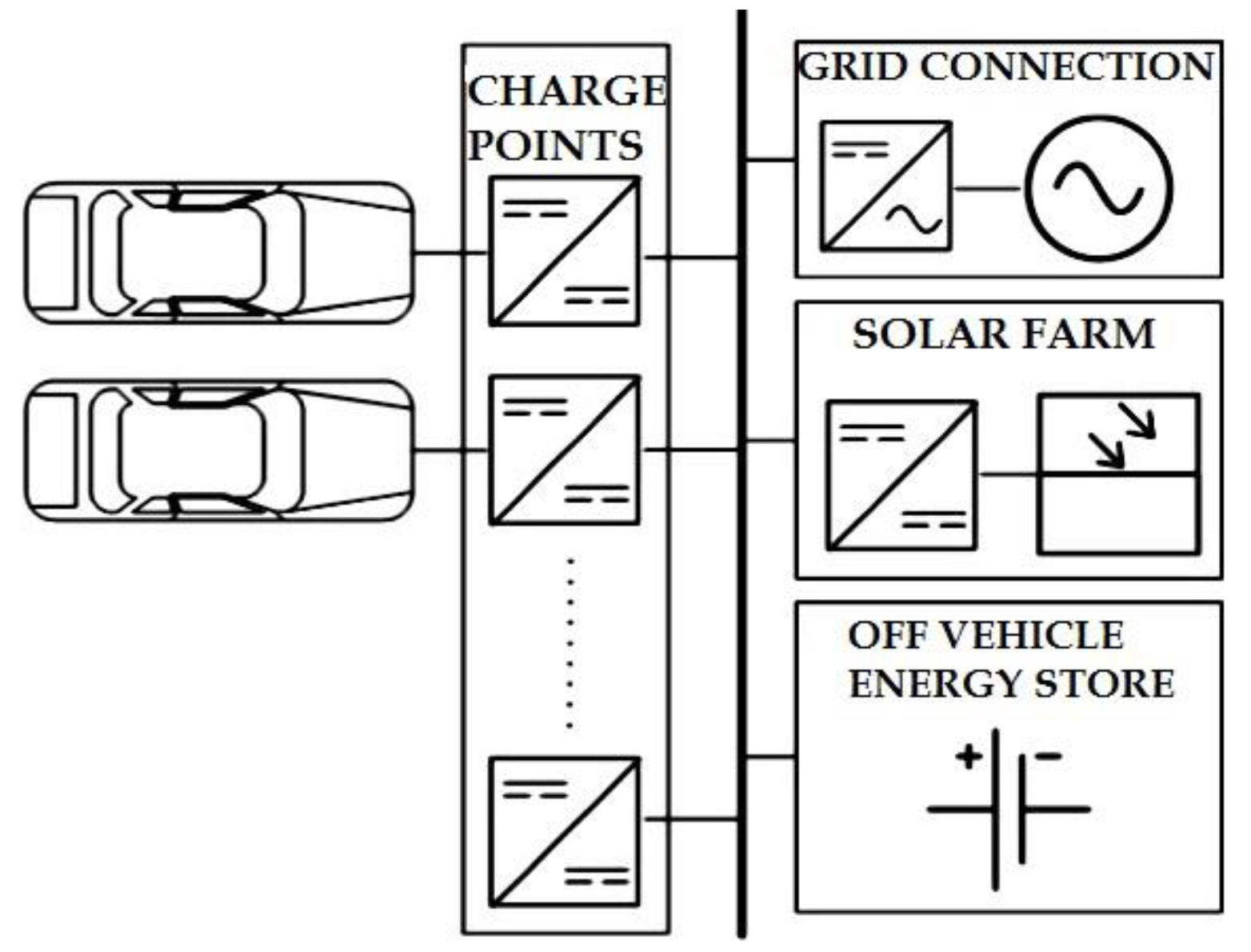
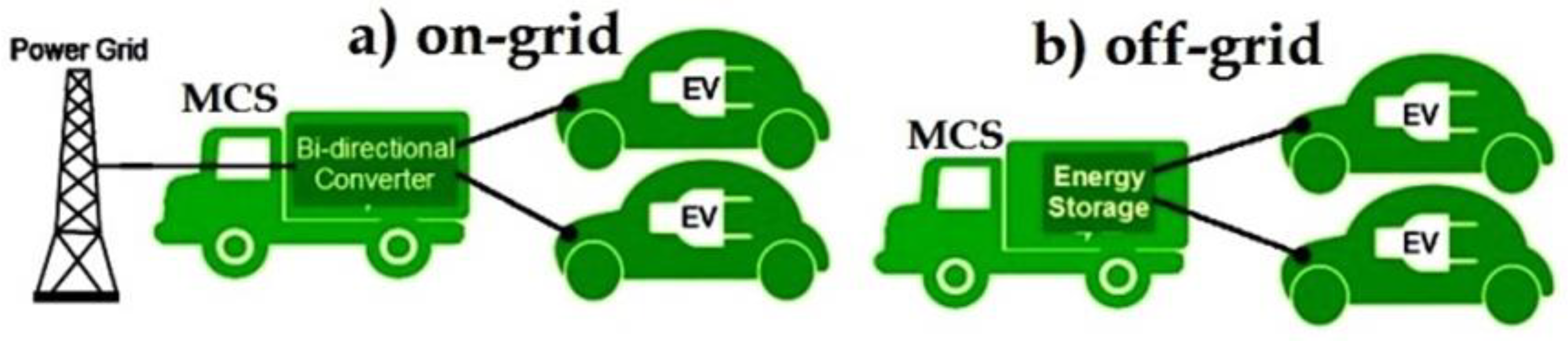
5. V2G Technology
6. Energy Management
6.1. Charging at Home
6.2. Charging at Work
6.3. Charging Fleet of Vehicles
6.4. Commercial Charge
6.5. Types of Charging Stations
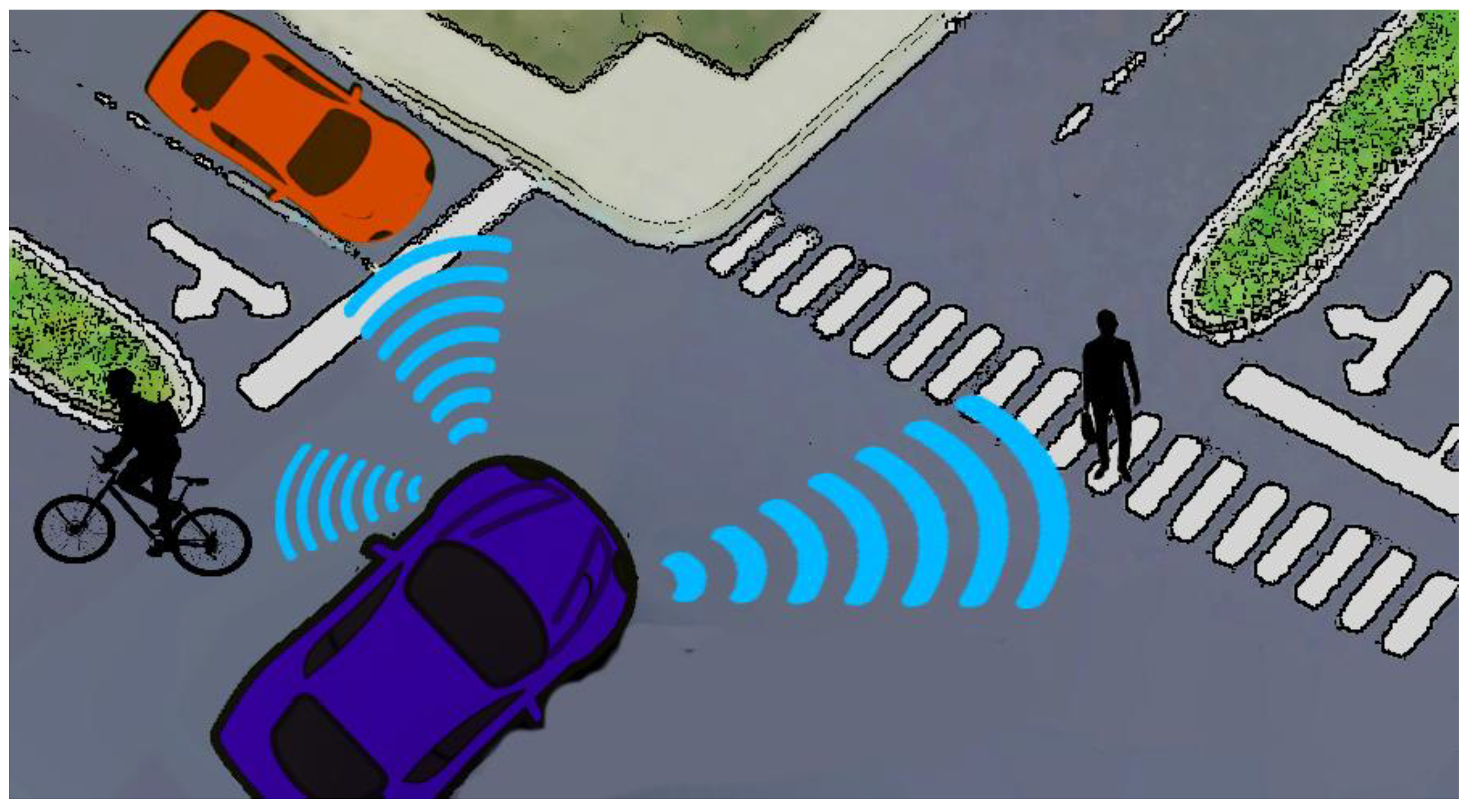
7. Autonomous Vehicles
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sthel, M.S.; Tostes, J.G.R.; Tavares, J.R. Current energy crisis and its economic and environmental consequences: Intense human cooperation. Nat. Sci. 2013, 5, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yong, J.Y.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.G.; Tan, K.M.; Mithulananthan, N. A review on the state-of-the-art technologies of electric vehicle, its impacts and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 49, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Ouyang, M. Review of electric vehicle technologies progress and development prospect in China. World Electr. Veh. J. 2013, 6, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Un-Noor, F.; Padmanaban, S.; Mihet-Popa, L.; Mollah, M.N.; Hossain, E. A Comprehensive study of key electric vehicle (EV) components, technologies, challenges, impacts, and future direction of development. Energies 2017, 10, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, J.A.; Soares, F.; Almeida, P. Integration of Electric Vehicles in the Electric Power System. Proc. IEEE 2011, 99, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteiro, V.; Afonso, J.A.; Ferreira, J.C.; Afonso, J.L. Vehicle electrification: New challenges and opportunities for smart grids. Energies 2018, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chau, K.T.; Jiang, C.; Han, W.; Lee, C.H.T. State-of-the-art electromagnetics research in electric and hybrid vehicles. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2017, 159, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, K.V.; Bansal, H.O.; Singh, D. A comprehensive review on hybrid electric vehicles: Architectures and components. J. Mod. Transp. 2019, 27, 77–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mwasilu, F.; Justo, J.J.; Kim, E.-K.; Do, T.K.; Jung, J.-W. Electric vehicles and smart grid interaction: A review on vehicle to grid and renewable energy sources integration. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, K.; Dubarry, M.; Glick, M.B. The viability of vehicle-to-grid operations from a battery technology and policy perspective. Energy Policy 2018, 113, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.D.; Zhang, M.K. Using vehicle-to-grid technology for frequency regulation and peak-load reduction. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 3972–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, H.; Cruden, A. Modular strategy for aggregator control and data exchange in large scale Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) applications. Energy Procedia 2018, 151, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimin Zhou, Y.; Li, X. Vehicle to Grid Technology: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2015 34th Chinese Control Conference, Hangzhou, China, 28–30 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Daim, T.U.; Wang, X.; Cowan, K.; Shott, T. Technology roadmap for smart electric vehicle-to-grid (V2G) of residential chargers. J. Innov. Entrep. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krainyukov, A.; Krivchenkov, A.; Saltanovs, R. Performance analysis of wireless communications for V2G applications using WPT technology in energy transfer. Procedia Eng. 2017, 178, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabio Arena, F.; Pau, G. An overview of vehicular communications. Future Internet 2019, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, M.; Ota, K.; Dong, M. Foud: Integrating fog and cloud for 5G-enabled V2G networks. IEEE Netw. 2017, 31, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Yu, G.; Liu, J.; Deng, F. Design of V2G auxiliary service system based on 5G technology. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Beijing, China, 26–28 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Q. Architecture design and implementation of an autonomous vehicle. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 21956–21970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.C.; Bouscayrol, A.; Chen, K. Electric, Hybrid, and Fuel-Cell Vehicles: Architectures and Modeling. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2010, 59, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donateo, T. Hybrid Electrical Vehicles; InTech Publications: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vidyanandan, K.V. Overview of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles. Energy Scan 2018, 3, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Propfe, B.; Redelbach, M.; Santini, D.J.; Friedrich, H. Cost analysis of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles including maintenance & repair costs and resale values. In Proceedings of the EVS26 International Battery, Hybrid and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Symposium, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 6–9 May 2012; pp. 886–895. [Google Scholar]
- Falvo, Μ.C.; Sbordone, D.; Bayram, I.S.; Devetsikiotis, M. EV Charging stations and modes: International standards. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion, Ischia, Italy, 18–20 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Botsford, C.; Szczepanek, A. Fast charging vs. slow charging: Pros and cons for the new age of electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the International Battery, Hybrid and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Symposium, Stavanger, Norway, 13–16 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, P.-Y.; Karagiannidis, G. Charging schemes for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles in smart grid: A survey. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 6846–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAE International. Available online: https://www.sae.org/ (accessed on 22 December 2019).
- Panchal, C.; Stegen, S.; Lu, J. Review of static and dynamic wireless electric vehicle charging system. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2018, 21, 922–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Chau, K.T.; Liu, C.; Chan, C.C. Overview of wireless power transfer for electric vehicle charging. In Proceedings of the World Electric Vehicle Symposium and Exhibition (EVS27), Barcelona, Spain, 17–20 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Magudeswaran, P.; Pradheeba, G.; Priyadharshini, S.; Flora, M.S. Dynamic wireless electric vehicle chargins system. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 6, 6609–6615. [Google Scholar]
- Mazharov, N.D.; Hristov, S.M.; Dichev, D.A.; Zhelezarov, I.S. Some problems of dynamic contactless charging of electric vehicles. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2017, 14, 7–26. [Google Scholar]
- Panchal, C.; Lu, J.; Stegen, S. Static in-wheel wireless charging systems for electric vehicles. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2017, 6, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Kruegera, H.; Crudena, A. Modular strategy for aggregator control and data exchange in large scale Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) applications. In Proceedings of the 3rd Annual Conference in Energy Storage and Its Applications, 3rd CDT-ESA-AC, Sheffield, UK, 11–12 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Galiveeti, H.R.; Goswami, A.K.; Choudhury, N.B.D. Impact of plug-in electric vehicles and distributed generation on reliability of distribution systems. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaja, T.W.; Susanti, V.; Mirdanies, M.; Muharam, A. V2G development on public vertical parking lot to support community energy management system. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dongqi Liu, D.; Zhong, Q.-C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G. Modeling and control of a V2G charging station based on the synchronverter technology. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan Collin, R.; Miao, Y.; Yokochi, A.; Enjeti, P.; Jouanne, A. Advanced electric vehicle fast-charging technologies. Energies 2019, 12, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, Τ.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, B. Modeling and solving method for supporting ‘Vehicle-to-Anything’ EV charging mode. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atmajaa, T.D.; Mirdanies, M. Electric vehicle mobile charging station dispatch algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Energy Engineering and Application, ICSEEA 2014, Bandung, Indonesia, 14–16 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, C.-Y.; Chynoweth, J.; Qiu, C.; Chu, C.-C.; Gadh, R. Design of fast response smart electric vehicle charging infrastructure. In Proceedings of the Green Energy and Systems Conference, Long Beach, CA, USA, 25 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Balasubramani, A.; Ye, Z. Optimal planning of renewable generations for electric vehicle charging station. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC) 2018, Maui, HI, USA, 5–8 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.-T. System planning of grid-connected electric vehicle charging stations and key technologies: A review. Energies 2019, 12, 4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saldaña, G.; Martin, J.I.C.; Zamora, I.; Asensio, F.J.; Oñederra, O. Electric vehicle into the grid: Charging methodologies aimed at providing ancillary services considering battery degradation. Energies 2019, 12, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hove, A.; Sandalow, D. Electric Vehicle Charging in China and the United States. Columbia, School of International and Public Affairs, Center on Global Energy Policy. Available online: https://energypolicy.columbia.edu/sites/default/files/file-uploads/EV_ChargingChina-CGEP_Report_Final.pdf) (accessed on 22 December 2019).
- Yang, S.-N.; Wang, H.W.; Gan, C.H.; Lin, Y.B. Mobile charging station service in smart grid networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Smart Grid Communications 2012 Symposium-Smart Grid Services and Management Models, Tainan City, Taiwan, 5–8 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Sahinoglu, Z.; Tao, Z.; Teo, K.H. Electric vehicles network with nomadic portable charging stations. In Proceedings of the IEEE 72nd Vehicular Technology Conference Fall (VTC 2010-Fall), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 6–9 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Ma, J.; Shen, X. Compensation of charging station overload via on-road mobile energy storage scheduling. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (Globecom), Waikola, HI, USA, 9–13 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Krasniqi, X.; Hajrizi, E. Use of IoT technology to drive the automotive industry from connected to full autonomous vehicles. IFAC Pap. Online 2016, 49, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian Paden, B.; ˇCáp, M.; Yong, S.Z.; Yershov, D.; Frazzoli, E. A survey of motion planning and control techniques for self-driving urban vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2016, 1, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González, D.; Pérez, J.; Milanés, V.; Nashashibi, F. A review of motion planning techniques for automated vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lema, M.A.; Laya, A.; Mahmoodi, T.; Cuevas, M.; Sachs, J.; Markendahl, J.; Dohler, M. Business case and technology analysis for 5G low latency applications. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 5917–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alberio, M.; Parladori, G. Innovation in automotive: A challenge for 5G and beyond network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference of Electrical and Electronic Technologies for Automotive, Torino, Italy, 15–16 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Heiko, G.S.; Xiaolong, H. Autonomous Driving in the iCity-HD Maps as a Key Challenge of the Automotive Industry. Engineering 2016, 2, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Simsek, M.; Aijaz, A.; Dohler, M.; Sachs, J.; Fettweis, G. 5G-Enabled Tactile Internet. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2016, 34, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campolo, C.; Molinaro, A.; Iera, A.; Menichella, F. 5G Network Slicing for Vehicle-to-Everything Services. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skouras, T.A.; Gkonis, P.K.; Ilias, C.N.; Trakadas, P.T.; Tsampasis, E.G.; Zahariadis, T.V. Electrical Vehicles: Current State of the Art, Future Challenges, and Perspectives. Clean Technol. 2020, 2, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol2010001
Skouras TA, Gkonis PK, Ilias CN, Trakadas PT, Tsampasis EG, Zahariadis TV. Electrical Vehicles: Current State of the Art, Future Challenges, and Perspectives. Clean Technologies. 2020; 2(1):1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol2010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkouras, Theodoros A., Panagiotis K. Gkonis, Charalampos N. Ilias, Panagiotis T. Trakadas, Eleftherios G. Tsampasis, and Theodore V. Zahariadis. 2020. "Electrical Vehicles: Current State of the Art, Future Challenges, and Perspectives" Clean Technologies 2, no. 1: 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol2010001
APA StyleSkouras, T. A., Gkonis, P. K., Ilias, C. N., Trakadas, P. T., Tsampasis, E. G., & Zahariadis, T. V. (2020). Electrical Vehicles: Current State of the Art, Future Challenges, and Perspectives. Clean Technologies, 2(1), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol2010001