Soil Chemical Variation Along a Four-Decade Time Series of Reclaimed Water Amendments in Northern Idaho Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Sites
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analysis of Soil Chemical Properties
2.4. Soil Bulk Density and Nutrient Content
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
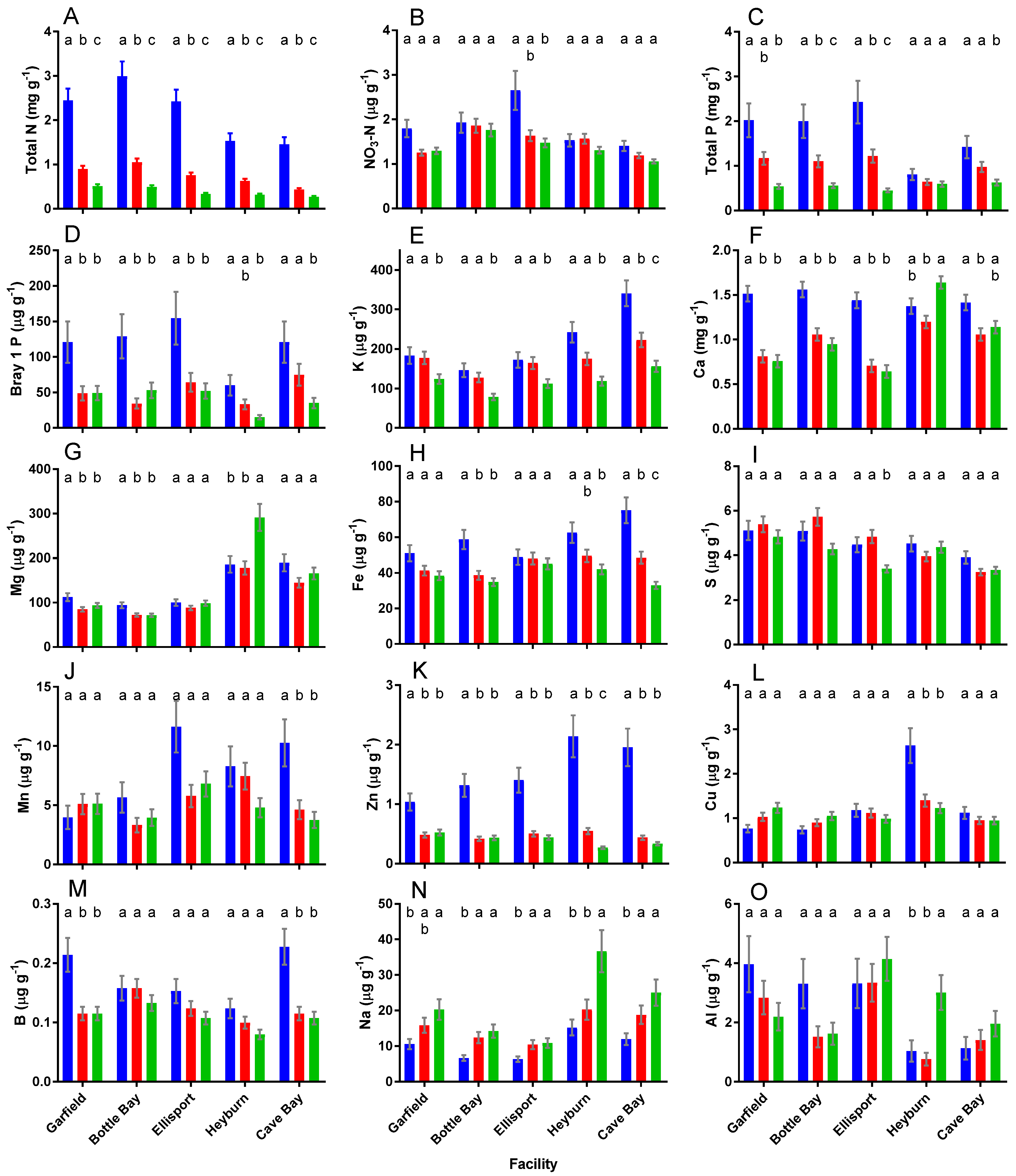
3.1. Response of Soil Chemical Variables to FWR Facility and Depth
3.2. Response of Soil Chemical Variables to Effluent Treatment
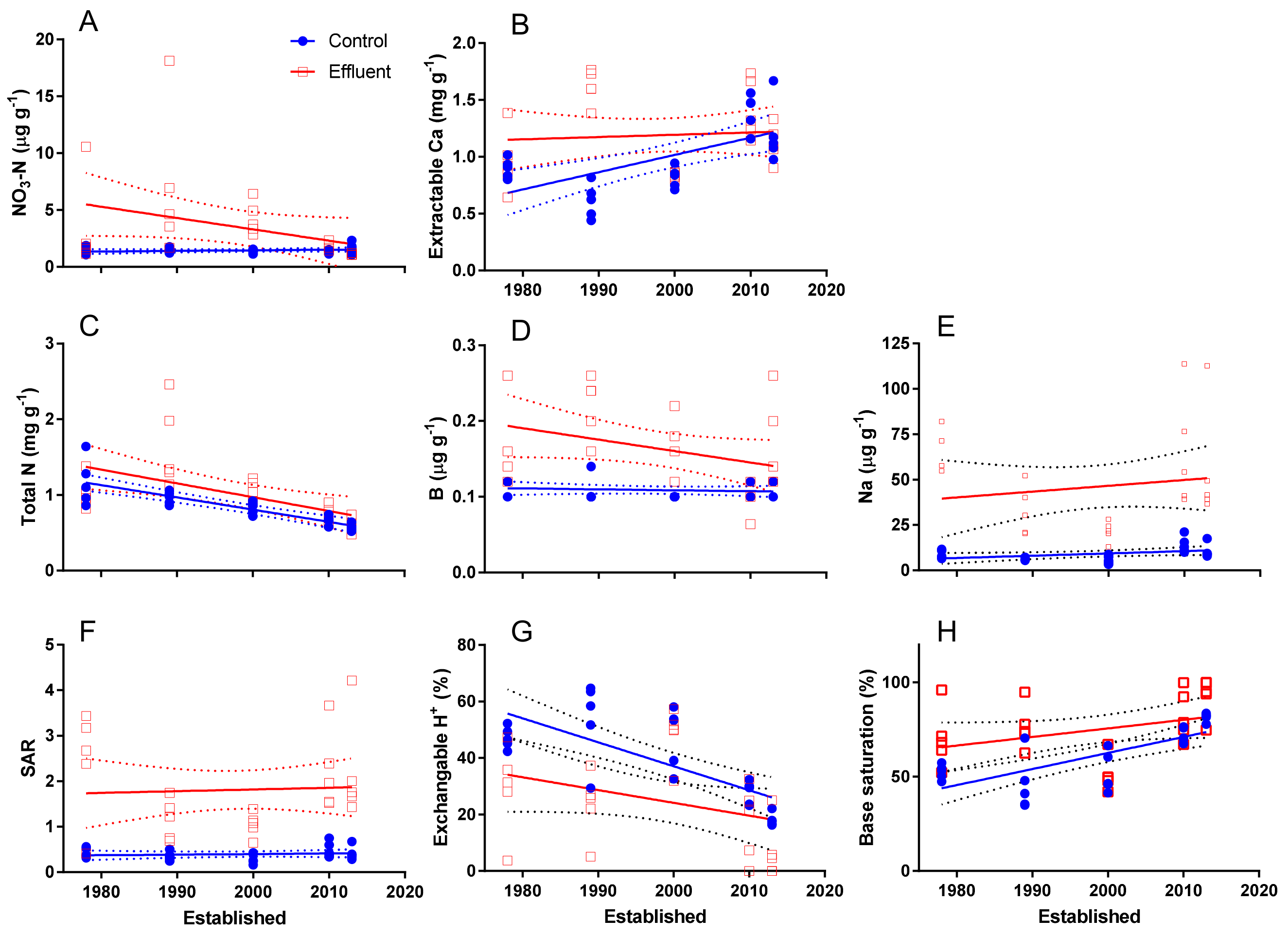
3.3. Time-Series Effect
3.4. Soil Nutrient Content
4. Discussion
4.1. Plant Nutrient Concentrations and Management
4.1.1. Nitrogen
4.1.2. Phosphorous
4.1.3. Other Nutrients and Exchange Capacity
4.2. Increased Salinity
4.3. Depth Response
4.4. Soil C/N Ratio
4.5. Soil Chemical Characteristics Along the Time Series
4.6. Applicable Regional Responses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shevah, Y. Water Resources, Water Scarcity Challenges, and Perspectives. ACS Symp. Ser. 2015, 1206, 10–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.S. Increasing agricultural water use efficiency to meet future food production. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 82, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fito, J.; Van Hulle, S.W.H. Wastewater reclamation and reuse potentials in agriculture: Towards environmental sustainability. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 2949–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lu, S.; Jiao, W.; Wang, M.; Chang, A.C. Reclaimed water: A safe irrigation water source? Environ. Dev. 2013, 8, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T. Irrigation with Treated Sewage Effluents. In Management of Water Use in Agriculture. Advanced Series in Agricultural Sciences; Tanji, K.K., Yaron, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1994; pp. 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Using Reclaimed Water for Agricultural and Landscape Irrigation in China: A Review. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 66, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radcliffe, J.C. Current status of recycled water for agricultural irrigation in Australia, potential opportunities and areas of emerging concern. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, E.; Schwarzbach, M.R.; Briggs, B.; Coats, E.R.; Coleman, M.D. Nutrient leaching potential along a time series of forest water reclamation facilities in northern Idaho. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesan, G.N.; Wang, H. Application of municipal and industrial residuals in New Zealand forests: An overview. Soil Res. 2003, 41, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, P.; Martins, C.; Couto, N.; Silva, J.; Mateus, E.P.; Ribeiro, A.B.; Pereira, C.S. Irrigation of soil with reclaimed wastewater acts as a buffer of microbial taxonomic and functional biodiversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarpour, M.; Mostafazadeh-Fard, B. The effects of treated wastewater on soil chemical properties using subsurface and surface irrigation methods. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 90, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leogrande, R.; Pedrero, F.; Nicolas, E.; Vitti, C.; Lacolla, G.; Stellacci, A.M. Reclaimed Water Use in Agriculture: Effects on Soil Chemical and Biological Properties in a Long-Term Irrigated Citrus Farm. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, S.; Liu, H.; Men, B.; Hao, Z.; Qian, P.; Yan, H.; Hao, Q.; Niu, Y.; et al. Impact of long-term reclaimed water irrigation on the distribution of potentially toxic elements in soil: An in-situ experiment study in the North China plain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonmez, S.; Buyuktas, D.; Okturen, F.; Citak, S. Assessment of different soil to water ratios (1:1, 1:2.5, 1:5) in soil salinity studies. Geoderma 2008, 144, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, M.B. Land Treatment of Waste Water; New Age International: New Delhi, India, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, H.T.L.; Hopmans, P.; Flinn, D.W.; Hillman, T.J. Nutrient accumulation in trees and soil following irrigation with municipal effluent in Australia. Environ. Pollut. 1990, 63, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton-Brandao, D.; Scherrenberg, S.M.; van Lier, J.B. Reclamation of used urban waters for irrigation purposes—A review of treatment technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 122, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, R.D.; Wurzbacher, S.J.; Washko, S.E.; Wind, L.; Rice, A.M.; Coble, A.E.; Baldauf, N.; Johnson, B.; Wang, J.J.; Simpson, M. Long-term nitrogen addition decreases organic matter decomposition and increases forest soil carbon. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, S82–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedel, J.K.; Langer, T.; Siebe, C.; Stahr, K. Effects of long-term waste water irrigation on soil organic matter, soil microbial biomass and its activities in central Mexico. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 31, 414–421. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez–González, A.; Chapela–Lara, M.; Germán–Venegas, E.; Fuentes-García, R.; Río-Portilla, F.d.; Siebe, C. Changes in quality and quantity of soil organic matter stocks resulting from wastewater irrigation in formerly forested land. Geoderma 2017, 306, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusack, D.F.; Silver, W.L.; Torn, M.S.; Burton, S.D.; Firestone, M.K. Changes in microbial community characteristics and soil organic matter with nitrogen additions in two tropical forests. Ecology 2011, 92, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigoida, A.; Argyrokastritis, I. The effect of sub-irrigation with untreated and treated municipal wastewater on organic matter and nitrogen content in two different soils. Glob. NEST J. 2019, 1, 389–398. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Pei, L. Study on the effects of irrigation with reclaimed water on the content and distribution of heavy metals in soil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockway, D.G.; Urie, D.H.; Nguyen, P.V.; Hart, J.B. Wastewater and sludge nutrient utilization in forest ecosystems. In The Forest Alternative for Treatment and Utilization of Municipal and Industrial Wastes; Cole, D.W., Henry, C.L., Nutter, W.L., Eds.; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1986; pp. 221–245. [Google Scholar]
- NRC. Use of Reclaimed Water and Sludge in Food Crop Production; NRC: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1996; p. 178. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, M.D.; Shaw, T.M.; Kimsey, M.J.; Moore, J.A. Nutrition of Douglas-fir in the inland northwest. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, S11–S22. [Google Scholar]
- Parent, D.R.; Coleman, M.D. Grand fir nutrient management in the Inland Northwestern USA. Forests 2016, 7, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Andersen, M.N.; bin Qi, X.; Li, P.; yang Li, Z.; yang Fan, X.; Zhou, Y. Effects of reclaimed water irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on the chemical properties and microbial community of soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, G.; Messinger, J.; Greiner, M.; Husler, W.; Hertel, D.; Kirfel, K.; Kgel-Knabner, I.; Leuschner, C.; Rethemeyer, J.; Mueller, C.W. Soil organic carbon stocks in topsoil and subsoil controlled by parent material, carbon input in the rhizosphere, and microbial-derived compounds. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 122, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, G.M.; Weathers, K.C.; Arthur, M.A. Control of nitrogen loss from forested watersheds by soil carbon:Nitrogen ratio andtree species composition. Ecosystems 2002, 5, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aber, J.; Nadelhoffer, K.; Steudler, P.; Melillo, J. Nitrogen saturation in northern forest ecosystems-hypotheses and implications. BioScience 1989, 39, 378–386. [Google Scholar]
- Magill, A.H.; Aber, J.D.; Currie, W.S.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Martin, M.E.; McDowell, W.H.; Melillo, J.M.; Steudler, P. Ecosystem response to 15 years of chronic nitrogen additions at the Harvard Forest LTER, Massachusetts, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 196, 7–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, B.; Wilson, E.J.; Emmett, B.A. Evaluating critical loads of nutrient nitrogen and acidity for terrestrial systems using ecosystem-scale experiments (NITREX). For. Ecol. Manag. 1998, 101, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Duan, L.; Du, E.; de Vries, W. Chapter 14—Indicators and thresholds for nitrogen saturation in forest ecosystems. In Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition to Global Forests; Du, E., de Vries, W., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 249–261. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, J. Critical Loads for Sulphur and Nitrogen. In Proceedings of the Air Pollution and Ecosystems; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbach, M.; Brooks, E.S.; Heinse, R.; Joshi, E.; Coleman, M.D. Estimating Drainage from Forest Water Reclamation Facilities Based on Drain Gauge Measurements. Hydrology 2024, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, E.; Coleman, M.D. Tree Growth and Vegetation Diversity in Northern Idaho Forest Water Reclamation Facilities. Forests 2023, 14, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, P.A.; Wilson, M.A.; Burt, R.; Lammers, D.; Thorson, T.D.; McGrath, C.L.; Peterson, N. Andic Soils of the Inland Pacific Northwest, USA: Properties and Ecological Significance. Soil Sci. 2005, 170, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Survey Staff. Official Soil Series Descriptions. Available online: https://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov/app/ (accessed on 8 February 2025).
- Pickett, S.T.A. Space-for-time substitution as an alternative to long-term studies. In Long-Term Studies in Ecology; Likens, G.E., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 110–135. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J. Lab Procedures and Methods. Available online: https://uwlab.soils.wisc.edu/about-us/lab-procedures-and-methods/ (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Miller, R.O.; Kissel, D.E. Comparison of Soil pH Methods on Soils of North America. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eik, K.; Hanway, J.J. Simultaneous extraction of P and K from IOWA soils with bray 1 solution containing NH4Cl. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1986, 17, 1203–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuman, L.M. Comparison of exchangeable Al, extractable Al, and Al in soil fractions. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1990, 70, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, F.T. Boron. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 9, pp. 431–447. [Google Scholar]
- Schollenberger, C.J.; Simon, R.H. Determination of exchange capacity and exchangeable bases in soil—Ammonium acetate method. Soil Sci. 1945, 59, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Bhumbla, D.K.; Keefer, R.F. Recommended soil sulfate-S tests. Recommended soil testing procedures for the northeastern United States. Northeast Reg. Bull. 1995, 493, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, W.L.; Norvell, W. Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1978, 42, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, M.E.; Miller, W.P. Cation exchange capacity and exchange coefficients. In Methods of soil analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 5, pp. 1201–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, D.S.; Ketterings, Q. Recommended methods for determining soil cation exchange capacity. Publication No. 493. In Recommended Soil Testing Procedures for the Northeastern United States, 3rd ed.; University of Delaware: Newark, DE, USA, 2011; pp. 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.-H.; Zhang, X.-S.; Vogt, R.D.; Xiao, J.-S.; Zhao, D.-W.; Xiang, R.-J.; Luo, J.-H. Evaluating controlling factors to Al i/(Ca+ Mg) molar ratio in acidic soil water, Southern and Southwestern China: Multivariate approach. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 129, 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- USSL. Determination of the properties of saline and alkali soils. In Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; Volume Agriculture Handbook No. 60; USDA ARS: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; pp. 7–33. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, V.D. Soil phosphorus saturation ratio for risk assessment in land use systems. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoumans, O.F. Determination of the degree of phosphate saturation in noncalcareous soils. In Methods of Phosphorus Analysis for Soils, Sediments, Residuals, and Waters, 2nd ed.; Kovar, J., Pierzynski, G., Eds.; Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin; Southern Extension and Research Activity (SERA); North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2009; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Andraski, B.J. Balloon and core sampling for determining bulk density of alluvial desert soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Meiwes, K.J.; Khanna, P.K.; Ulrich, B. Parameters for describing soil acidification and their relevance to the stability of forest ecosystems. For. Ecol. Manag. 1986, 15, 161–179. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, G.R. Particle density. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 504–505. [Google Scholar]
- Littell, R.C.; Milliken, G.A.; Stroup, W.W.; Wolfinger, R.D. SAS for Mixed Models, 2nd ed.; SAS Institute, Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2006; p. 633. [Google Scholar]
- Eveborn, D.; Kong, D.G.; Gustafsson, J.P. Wastewater treatment by soil infiltration: Long-term phosphorus removal. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2012, 140, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanakakis, V.A.; Paranychianakis, N.V.; Londra, P.A.; Angelakis, A.N. Effluent application to the land: Changes in soil properties and treatment potential. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalacin, D.; Bienes, R.; Sastre-Merln, A.; Martnez-Prez, S.; Garca-Daz, A. Influence of reclaimed water irrigation in soil physical properties of urban parks: A case study in Madrid (Spain). Catena 2019, 180, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Shahrivar, A.A.; Hagare, D.; Maheshwari, B. Impact of Recycled Water Irrigation on Soil Salinity and Its Remediation. Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Coleman, M.a. Soil Soluble Nitrogen Availability across an Elevation Gradient in a Cold-Temperate Forest Ecosystem. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, S217–S224. [Google Scholar]
- Högberg, P.; Lucas, R.W.; Högberg, M.N.; Skyllberg, U.; Egnell, G.; Larson, J.; Binkley, D. What happens to trees and soils during five decades of experimental nitrogen loading? For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 553, 121644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polglase, P.J.; Tompkins, D.; Stewart, L.G.; Falkiner, R.A. Mineralization and leaching of nitrogen in an effluent-irrigated pine plantation. J. Environ. Qual. 1995, 24, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, E.; de Vries, W. (Eds.) Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition to Global Forests; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 169–182. [Google Scholar]
- Stanton, B.; Gantz, C.; Coleman, M.D.; Comnick, J.; Cooke, A.; Rogers, L.; Espinoza, J.; Heppenstall, M.; Shuren, R.; Kallestad, J.C.; et al. Growing Hybrid Poplar for Bioenergy in the PNW, EM123; Agriculture and Natural Resources Extension, Washington State University: Pullman, WA, USA, 2023; p. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Wuenscher, R.; Unterfrauner, H.; Peticzka, R.; Zehetner, F. A comparison of 14 soil phosphorus extraction methods applied to 50 agricultural soils from Central Europe. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruba, P.; Mulder, J. Tree species affect cation exchange capacity (CEC) and cation binding properties of organic matter in acid forest soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedbabis, S.; Rouina, B.B.; Boukhris, M.; Ferrara, G. Effect of irrigation with treated wastewater on soil chemical properties and infiltration rate. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Abegunrin, T.P.; Awe, G.O.; Idowu, D.O.; Adejumobi, M.A. Impact of wastewater irrigation on soil physico-chemical properties, growth and water use pattern of two indigenous vegetables in southwest Nigeria. Catena 2016, 139, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarchouna, L.G.; Merdy, P.; Raynaud, M.; Pfeifer, H.-R.; Lucas, Y. Effects of long-term irrigation with treated wastewater. Part I: Evolution of soil physico-chemical properties. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Lin, Y. Comparison of soil chemical properties prior to and five to eleven years after recycled water irrigation. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D.M.; Robb, T.; Elliott, H.; Watson, J.E. Impact of long-term wastewater irrigation on the physicochemical properties of humid region soils:“The Living Filter” site case study. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 178, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, S.M.B.; Dohrmann, A.B.; Gillor, O.; Christensen, B.T.; Merbach, I.; Tebbe, C.C. Soil properties and habitats determine the response of bacterial communities to agricultural wastewater irrigation. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 146–158. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Schmidhalter, U. Drought and salinity: A comparison of their effects on mineral nutrition of plants. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 541–549. [Google Scholar]
- Ahrends, B.; Fortmann, H.; Meesenburg, H. The Influence of Tree Species on the Recovery of Forest Soils from Acidification in Lower Saxony, Germany. Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.M.; Perdrial, N.; Treto, V.; D’Amato, A.W.; Smith, G.A.; Richardson, J.B. Influence of parent material mineralogy on forest soil nutrient release rates across a nutrient richness gradient. Geoderma 2024, 451, 117081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, M.T.; Moore, J.A.; Shaw, T.M.; Mika, P.G. Foliar nutrient and tree growth response of mixed-conifer stands to three fertilization treatments in northeast Oregon and north central Washington. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 132, 183–198. [Google Scholar]
- Brockley, R.P. Effects of 12 years of repeated fertilization on the foliar nutrition and growth of young lodgepole pine in the central interior of British Columbia. Can. J. For. Res. 2007, 37, 2115–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.A.; Kimsey, M.J.; Garrison-Johnston, M.; Shaw, T.M.; Mika, P.; Poolakkal, J. Geologic soil parent material influence on Forest surface soil chemical characteristics in the inland northwest, USA. Forests 2022, 13, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, T.; Ruuhola, T.; Dell, B. Boron in forest trees and forest ecosystems. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 260, 2053–2069. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Guidelines for Water Reuse; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 643. [Google Scholar]
- Homann, P.S.; Van Miegroet, H.; Cole, D.W.; Gordon, V.W. Cation Distribution, Cycling, and Removal from Mineral Soil in Douglas-Fir and Red Alder Forests. Biogeochemistry 1992, 16, 121–150. [Google Scholar]
- Hüttl, R.F.; Wisniewski, J. Fertilization as a tool to mitigate forest decline associated with nutrient deficiencies. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1987, 33, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo, A.; Snchez, M.J.; Betancourt, L.S.; Ramos, O.; Vicens, I. A Stoichiometric Comparison of Primary and Secondary Forest Stands on Acid Soils. Caribb. Nat. 2023, 89, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ågren, G.I.; Wetterstedt, J.Å.M.; Billberger, M.F.K. Nutrient limitation on terrestrial plant growth–modeling the interaction between nitrogen and phosphorus. New Phytol. 2012, 194, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawn, D.; Bohn, H.L.; O’Connor, G.A. Soil Chemistry, 5th ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Lu, S.; Pan, N.; Jiao, W. Impacts of long-term reclaimed water irrigation on soil salinity accumulation in urban green land in Beijing. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 7401–7410. [Google Scholar]
- Adrover, M.; Farrús, E.; Moyà, G.; Vadell, J. Chemical properties and biological activity in soils of Mallorca following twenty years of treated wastewater irrigation. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, S188–S192. [Google Scholar]
- Klay, S.; Charef, A.; Ayed, L.; Houman, B.; Rezgui, F. Effect of irrigation with treated wastewater on geochemical properties (saltiness, C, N and heavy metals) of isohumic soils (Zaouit Sousse perimeter, Oriental Tunisia). Desalination 2010, 253, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Luo, J.; Park, E.; Barcaccia, G.; Masin, R. Soil salinization in agriculture: Mitigation and adaptation strategies combining nature-based solutions and bioengineering. iScience 2024, 27, 108830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, G.J. Sodicity. In: Handbook of Soil Sciences. In Resource Management and Environmental Impacts, 2nd ed.; Huang, P., Li, Y., Sumner, M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jobbagy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. The distribution of soil nutrients with depth: Global patterns and the imprint of plants. Biogeochemistry 2001, 53, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynicka, J.D.; Pett-Ridge, J.C.; Perakis, S.S. Nitrogen enrichment regulates calcium sources in forests. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 4067–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, J.I. Soil Nitrifiers and Nitrification. In Nitrification; Ward, B.B., Arp, D.J., Klotz, M.G., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 347–383. [Google Scholar]
- de Francisco, M.; Romeiro, A.; Dures, L.; lvarez-Torrellas, S.; Ibaez, M.A.; Almendros, P. Environmental Behaviour of Synthesized and Commercial Agricultural Zinc Products: Leaching, Migration, and Availability in Soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 5293–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.L.; Watson-Stegner, D. Evolution model of pedogenesis. Soil Sci. 1987, 143, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, C.; Houle, D.; Gagnon, C.; Courchesne, F. The relationships of soil total nitrogen concentrations, pools and C:N ratios with climate, vegetation types and nitrate deposition in temperate and boreal forests of eastern Canada. Catena 2017, 152, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, F.S.; Matson, P.A.; Vitousek, P.M. Principles of terrestrial ecosystem ecology, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. xv. 529p. [Google Scholar]
- Hadas, A.; Rawitz, E.; Etkin, H.; Margolin, M. Short-term variations of soil physical properties as a function of the amount and C/N ratio of decomposing cotton residues. I. Soil Aggreg. Aggreg. Tensile Strength. Soil Tillage Res. 1994, 32, 183–198. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, A.M.; Jat, H.S.; Choudhary, M.; Abdelaty, E.F.; Sharma, P.C.; Jat, M.L. Conservation agriculture effects on soil water holding capacity and water-saving varied with management practices and agroecological conditions: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, S.F.; Lal, R. Nitrogen management affects carbon sequestration in North American cropland soils. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2007, 26, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richenderfer, J.L.; Sopper, W.E. Effect of spray irrigation of treated municipal sewage effluent on the accumulation and decomposition of the forest floor. In Utilization of Municipal Sewage Effluent and Sludge on Forest and Disturbed Land; Sopper, W.E., Kerr, S.N., Eds.; Pennsylvania State University Press: University Park, PA, USA, 1979; pp. 163–177. [Google Scholar]
- Page-Dumroese, D.S.; Jurgensen, M.F. Soil carbon and nitrogen pools in mid- to late-successional forest stands of the northwestern United States: Potential impact of fire. Can. J. For. Res. 2006, 36, 2270–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Jiang, J.; Liu, F.; Chang, Z.; Yu, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.-P.; Yan, J. Phosphorus addition promotes plant nitrogen uptake mainly via enhancing microbial activities: A global meta-analysis. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 188, 104927. [Google Scholar]
- DeForest, J.L.; Otuya, R.K. Soil nitrification increases with elevated phosphorus or soil pH in an acidic mixed mesophytic deciduous forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 142, 107716. [Google Scholar]
- Phogat, V.K.; Tomar, V.S.; Dahiya, R. Soil physical properties. In Soil Science: An Introduction; Indian Society of Soil Science: New Delhi, Indian, 2015; pp. 135–171. [Google Scholar]
- Panhwar, Q.A.; Ali, A.; Naher, U.A.; Memon, M.Y. Fertilizer management strategies for enhancing nutrient use efficiency and sustainable wheat production. In Organic Farming; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 17–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bauder, J.W.; Brock, T.A. Irrigation water quality, soil amendment, and crop effects on sodium leaching. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2001, 15, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, J.N. Investigation on using magnetic water technology for leaching high saline-sodic soils. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 519. [Google Scholar]
- Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C. Nitrate leaching in temperate agroecosystems: Sources, factors and mitigating strategies. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2002, 64, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergh, J.; Linder, S.; Lundmark, T.; Elfving, B. The effect of water and nutrient availability on the productivity of Norway spruce in northern and southern Sweden. For. Ecol. Manag. 1999, 119, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Miegroet, H.; Norby, R.J.; Tschaplinski, T.J. Nitrogen fertilization strategies in short-rotation sycamore. For. Ecol. Manag. 1994, 64, 13–24. [Google Scholar]


| Reclamation Facility | Latitude | Longitude | Year Established | MAP (mm) | MAT (°C) | Precipitation Nov–Mar (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cave Bay | 47.4703° N | 116.8803° W | 2010 | 534 | 8.4 | 57 |
| Heyburn | 47.3462° N | 116.7821° W | 2013 | 663 | 8.2 | 60 |
| Ellisport Bay | 48.2159° N | 116.2696° W | 2000 | 633 | 7.7 | 55 |
| Bottle Bay | 48.2018° N | 116.4207° W | 1989 | 752 | 7.4 | 57 |
| Garfield Bay | 48.2287° N | 116.4384° N | 1978 | 709 | 7.4 | 57 |
| Reclamation Facility | Texture | Parent Material | Surficial Deposits | Ecological Site Class | Soil Series |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cave Bay | Gravelly loam | Basalt | Loess (thin) | Warm-mesic, xeric | Lacy |
| Heyburn | Silt loam | Loess | Volcanic ash | Warm-frigid, xeric | Carlinton |
| Ellisport Bay | Silt loam | Glacial till | Volcanic ash | Frigid, udic | Pend Oreille |
| Bottle Bay | Silt loam | Glacial till | Volcanic ash | Frigid, udic | Pend Oreille |
| Garfield Bay | Silt loam | Glacial till | Volcanic ash | Frigid, udic | Pend Oreille |
| Effect | Levels | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 2 | Control, Effluent |
| Depth | 3 | 0–15, 15–45, 45–75 cm |
| Facilities | 5 | See Table 1 and Table 2 |
| Replicate plots | 5 | |
| Total sample plots | 150 | |
| Subsamples per plot | 3 | Soil chemical analyses |
| 2 | Bulk density |
| Effect | C | N | NO3 | P | PO4 | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | S | Mn | Zn | Cu | B | Na |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||||
| F | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||
| D | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| T × F | *** | *** | *** | *** | |||||||||||
| T × D | * | * | * | *** | * | ** | *** | *** | *** | ||||||
| F × D | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | ||||
| T × F × D | *** | ** | * | ** | *** | *** | |||||||||
| Effect | Al | pH | BpH | C:N | Salt | SAR | PSR | CEC | exCa | exMg | exK | exNa | exH | exAl | BS |
| T | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | ** | * | *** | *** | *** | ||||
| F | *** | *** | *** | *** | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| D | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| T × F | *** | *** | *** | * | *** | * | ** | ||||||||
| T × D | ** | *** | *** | ** | * | *** | * | ||||||||
| F × D | *** | *** | *** | *** | * | *** | *** | ** | ** | *** | ** | * | ** | ** | |
| T × F × D | ** | * | * | * | ** | * |
| Effect | C | N | NO3 | P | PO4 | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | S | Mn | Zn | Cu | B | Na |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | *** | ** | ** | *** | *** | ||||||||||
| E | *** | *** | * | ** | *** | * | *** | ** | *** | ** | *** | ** | * | ||
| D | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | * | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| T × E | - | - | ** | ** | - | - | |||||||||
| T × D | - | - | * | ** | ** | *** | - | - | |||||||
| E × D | - | - | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | * | ** | *** | *** | *** | - | - | |
| T × E × D | - | - | * | ** | ** | *** | - | - | |||||||
| Effect | Al | pH | BpH | C:N | Salt | SAR | PSR | CEC | exCa | exMg | exK | exNa | exH | exAl | BS |
| T | *** | *** | *** | *** | |||||||||||
| E | *** | *** | ** | * | *** | *** | ** | * | *** | ** | *** | ||||
| D | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | ** | *** | |
| T × E | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| T × D | ** | - | - | - | - | * | - | - | |||||||
| E × D | *** | ** | - | *** | - | *** | *** | - | - | *** | * | - | ** | - | |
| T × E × D | ** | - | - | - | - | * | - | - |
| Effect | C | N | NO3 | P | PO4 | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | S | Mn | Zn | Cu | B | Na | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | * | *** | *** | *** | |||||||
| F | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| T × F | ** | *** | * | *** | * | ** |
| Effect | C | N | NO3 | P | PO4 | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | S | Mn | Zn | Cu | B | Na | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | *** | *** | * | ** | *** | *** | ||||||||||
| E | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |||||
| T × E | - | - | *** | - | - | - | * | - | *** | ** | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wedajo, T.G.; Joshi, E.; Hu, R.; Strawn, D.G.; Coleman, M.D. Soil Chemical Variation Along a Four-Decade Time Series of Reclaimed Water Amendments in Northern Idaho Forests. Soil Syst. 2025, 9, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020032
Wedajo TG, Joshi E, Hu R, Strawn DG, Coleman MD. Soil Chemical Variation Along a Four-Decade Time Series of Reclaimed Water Amendments in Northern Idaho Forests. Soil Systems. 2025; 9(2):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020032
Chicago/Turabian StyleWedajo, Temesgen G., Eureka Joshi, Ruifang Hu, Daniel G. Strawn, and Mark D. Coleman. 2025. "Soil Chemical Variation Along a Four-Decade Time Series of Reclaimed Water Amendments in Northern Idaho Forests" Soil Systems 9, no. 2: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020032
APA StyleWedajo, T. G., Joshi, E., Hu, R., Strawn, D. G., & Coleman, M. D. (2025). Soil Chemical Variation Along a Four-Decade Time Series of Reclaimed Water Amendments in Northern Idaho Forests. Soil Systems, 9(2), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems9020032







