Abstract
The sorptive reactivity of layered manganese (Mn) oxides is controlled by their layer and interlayer structure, which can be affected by processes such as metal coprecipitation. This study investigated the effects of Zn coprecipitation on the sorptive reactivity of δ-MnO2, a common layered Mn oxide mineral. Selected cation (i.e., Cd) and anion (i.e., phosphate and arsenate) species were used to probe the changes in δ-MnO2 sorptive reactivity. Cd uptake by δ-MnO2 was suppressed by Zn coprecipitation but total metal uptake (Cd and Zn) was enhanced, indicating more available vacancy sites (e.g., smaller particle size and higher vacancy site density) in Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2. Phosphate and arsenate sorption on δ-MnO2 was significantly enhanced by Zn-coprecipitation, and the enhancement was more effective compared to Zn sorption on pure δ-MnO2. X-ray diffraction and X-ray adsorption spectroscopy analysis did not detect the formation of surface precipitations and/or ternary complexes. The enhanced anion sorption on Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2 was likely due to the compensation of negative surface charge by sorbed Zn, as well as the structural modifications introduced by Zn coprecipitation. Results from this study can provide a better understanding on the interactions between metal-coprecipitated Mn oxides and other species in natural environments.
1. Introduction
Manganese oxides (MnOx), especially layered phyllomanganates, are important metal oxides in terrestrial and oceanic environments [,,]. Because of the high surface area, negative surface charge, vacancy sites, and high oxidative potential, phyllomanganates have a strong tendency to interact with and strongly influence the fate and transport of trace metals, such as Ni [,,,,], Co [,,,,,,], Pb [,,,,,], Cu [,,], Zn [,,,,,], and Cd [,]. Phyllomanganates can interact with metals in different ways (e.g., sorption, coprecipitation, incorporation), which in turn can affect the property and reactivity of the host mineral phases. During sorption onto δ-MnO2, metal cations can either directly incorporate into vacancy sites, or form surface sorption complexes above or below vacancies sites and/or at edge sites [,]. The ratio between incorporation and surface complexation (referred to as compatibility) is metal specific, and was suggested to be dependent on the differences in atomic size and charge between foreign metal cations and Mn(III, IV) [,], as well as the metal cation crystal field stability energy (CFSE) []. Sorption of metal cations on pre-formed MnOx (i.e., sorption) can replace interlayer Mn(II) and alkaline cations [,], and compensate for the negative surface charge, thus affecting the reactivity of MnOx towards other species [,,]. In comparison, the presence of metal cations during MnOx mineral formation (i.e., coprecipitation) can cause more significant changes in MnOx structure, such as layer stacking, average oxidation state [,,,], vacancy site density, and layer symmetry [], which also lead to modified mineral reactivity. For example, the presence of Ni, Co, Fe, and Cu during birnessite formation was found to significantly modify birnessite thermal stability, sorptive reactivity towards Pb, and oxidative reactivity towards As(III) [,,,].
The effects of metal coprecipitation on layered Mn oxides are also metal-specific. The compatibility of foreign metal ions in birnessite layers is Fe3+ < Ni2+ < Co3+ and the interruption of birnessite structures is in the reverse order Fe3+ > Ni2+ > Co3+ [,,]. Zn is an essential element and its biogeochemical cycles are affected by organic matters and Fe/Mn oxide minerals in soils and marine sediments [,,,,,,]. Zn shows the least compatibility with Mn oxides compared to other transition metals such as Ni or Co. As a result, upon sorption onto MnOx, Zn2+ never incorporates into vacancy sites, but always exists as sorbed species above/below vacancy sites [] and sometimes edge sites []. The local coordination environment of surface-sorbed Zn2+ is preferably tetrahedral (IVZn) at low Zn loadings and octahedral (VIZn) at high Zn loadings [,,], although it is also dependent on the crystallinity of the host MnOx phase []. A recent study by Grangeon et al. [] found that Zn2+ sorption on δ-MnO2 caused crystal dissolution, decrease of coherent scattering domain size, decrease of layer Mn(III) content, and increase of vacancy site density. Similar effects have not been observed for the sorption of other metal cations on MnOx. When Zn2+ was added during the formation of biogenic MnOx, it was found to interrupt the mineral layer stacking []. Our recent study showed that the presence of Zn2+ during abiotic δ-MnO2 formation has more significant impacts on δ-MnO2 structure compared to Zn sorption on pure δ-MnO2 []. These studies demonstrate the significant effects of Zn2+ treatment (either sorption or coprecipitation) on δ-MnO2 structure, which can potentially affect the sorptive reactivity of δ-MnO2. However, systematic investigations are still missing on the effects of Zn-coprecipitation on MnOx reactivities, such as those related to sorption or redox reactions.
This study systematically investigated the impact of Zn coprecipitation on the sorptive reactivity of δ-MnO2 toward both cations and anions. The Zn/Mn molar ratio used in this study was 0–0.2, which is within the range observed in the natural environment (0–0.005 in marine nodules and basin soils [,,], as high as 0.03 in coal mine drainage treatment system [] and 0.46 in contaminated sediments []). We used Cd2+ as a representative cation probe and phosphate and arsenate as representative anion probes to assess the change in δ-MnO2 sorptive reactivity. Cd is a toxic trace metal and its fate in the environment is strongly influenced by sorption onto metal oxyhydroxides, especially MnOx [,,]. Both phosphate and arsenate are important environmental anions, and their fate and transport are strongly influenced by interactions with geomedia [,,,,,,,]. Cd, phosphate, and arsenate sorption kinetics, isotherms, and pH edges on Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2 were compared with those on Zn-sorbed pure δ-MnO2 (hereafter referred to as Zn-sorbed δ-MnO2).
2. Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Pure and Zn-Coprecipitated δ-MnO2
All reagents used in this study were ACS (American Chemical Society) grade or higher. δ-MnO2 was synthesized [] in the presence of varied concentrations of Zn2+. A calculated amount of ZnSO4 was dissolved in 160 mL of 0.2964 mol L−1 MnSO4 solution to achieve the desired Zn/Mntotal ratio. This solution was pumped at a rate of 25 mL min−1 with a syringe pump into a beaker containing 160 mL of KMnO4 (5.0 g) and 180 mL of NaOH (3.5 g) under vigorous stirring. The molar ratio of Zn/Mntotal was 0, 0.01, 0.05, and 0.20. After overnight settlement, the solids were separated by vacuum filtration (0.22 µm), rinsed and dialyzed with deionized (DI) water, and freeze dried. Samples were labeled as pure, coppt0.01, coppt0.05, and coppt0.20 δ-MnO2 for the samples synthesized with initial Zn/Mn molar ratios of 0, 0.01, 0.05, and 0.20, respectively. A portion of the freezer-dried powders were digested using hydroxylamine hydrochloride and measured for elemental compositions (Zn, Mn) using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) (Agilent 7500a) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Initial Zn/Mntotal molar ratio in the synthesis suspension and final Zn/Mn molar ratio in the solid products.
2.2. Cation and Anion Sorption on Pure and Zn-Coprecipitated δ-MnO2
CdCl2, ZnSO4, Na2HPO4, and Na2HAsO4 were used to make 1 mol L−1 Cd2+, 1 mol L−1 Zn2+, 2.5 mmol L−1 phosphate, and 2.5 mmol L−1 arsenate stock solutions, respectively. A total of 10 mg pure or Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2 was suspended in 20 mL DI water and sonicated for 1 min to disperse the particles. For each sorption experiment, the calculated amount of stock solutions were added to achieve the desired sorbate concentration. The sorption isotherm and kinetic experiments were conducted at pH 6. The pH edge experiments were conducted at pH 4–8. The reaction vials were agitated end-to-end on an orbital shaker at 150 rpm. At certain time points, aliquots of the reaction suspension were taken and syringe filtered (0.22 µm). Phosphate [] and arsenate [] concentrations in the filtrates were measured using colorimetric methods on a UV-vis spectrometer (Cary 60, Agilent). Zn and Cd concentrations were determined using ICP-MS.
For Cd2+ sorption, the ionic strength was at 0.1 mol L−1 NaCl. Due to the relatively large pH fluctuation during sorption, 20 mmol L−1 MES (2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid) buffer was used to maintain the pH at 6. For phosphate and arsenate sorption, the ionic strength was at 10 mmol L−1 NaCl. No buffers were used as the pH fluctuation throughout experiments was relatively small. At 0, 3, 12, and 22 h, HCl and NaOH solutions were used to adjust the small pH changes.
To examine the possible surface precipitation or ternary complexation between anions and pre-loaded Zn, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray sorption spectroscopy (XAS) analysis were conducted on the reaction products (details in Supporting Information, SI, Text S1). Both Langmuir and Freundlich models were used to fit the isotherm data. For kinetic data, pseudo first order, pseudo second order, and particle diffusion models were used to fit the data.
For Cd2+ sorption on Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2, in order to investigate the overall metal cation uptake capacity, total metal uptake (both Cd2+ and Zn2+) was calculated using the following equation:
2.3. Cation and Anion Sorption on Zn-Sorbed δ-MnO2
Based on previous studies and our recent study [], when Zn is added during δ-MnO2 formation, it exists as surface sorbed species, but can introduce significant structural modification. In order to compare the effects of Zn-coprecipitation-induced structural modification on δ-MnO2 sorptive reactivity, we also conducted parallel experiments where pure δ-MnO2 with Zn sorption (i.e., Zn-sorbed δ-MnO2, with Zn concentrations comparable to the coprecipitation system) were used as the sorbent, with the subsequent addition of Cd2+, phosphate, and arsenate as sorbate.
Zn-sorbed δ-MnO2 samples were produced by reacting 0.5 g L−1 pure δ-MnO2 with varied concentrations of ZnSO4 (0.25–2 mmol L−1) at pH 6 and 0.1 mol L−1 NaCl background electrolyte. After shaking at 150 rpm for 24 h, the reaction reached steady state and the suspension was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm. The Zn concentration in the supernatant was measured by ICP-MS. Zn uptake was calculated by the difference of Zn concentration in the initial suspension and supernatant. After centrifugation, the remaining wet paste (Zn-sorbed δ-MnO2) was briefly rinsed with DI water, and resuspended in a small amount of DI water. Cd2+, phosphate, arsenate, and NaCl were added to the suspension following the procedures in Section 2.2 for sorption experiments. Sample labels are shown in Table 1.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cation Sorption on Pure and Zn Coprecipitated δ-MnO2
Cd sorption isotherms on Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2 are shown in Figure 1A. Increasing initial Cd concentration resulted in a gradual increase in Cd uptake. The Langmuir model was used to fit the data (Figure 1A, Table 2). The maximum Cd uptake (Cmax, mmol g−1) decreased slightly from 1.49 (pure δ-MnO2) to 1.38 (coppt0.05) and 1.20 (coppt0.20), indicating the competitive sorption between Cd and pre-loaded Zn. This decrease was not significant, considering that the fitting errors of Cmax were in the range of 0.03–0.07. In order to compare Zn-coprecipitated and Zn-sorbed δ-MnO2, sample sorb0.20 was also prepared by mixing 0.5 g L−1 pure δ-MnO2 and the calculated amount of ZnSO4 (Zn/Mn = 0.2). The Zn loading on sample sorb0.20 (Q = 0.99 mmol g−1) was much lower than the Zn coverage of the coppt0.20 sample (Q = 1.5 mmol g−1), although they had the same initial Zn/Mn concentration. A similar phenomenon was also observed for biogenic MnOx, i.e., Zn uptake by fungal MnOx was higher when Zn was present during MnOx formation, compared to Zn uptake by pre-formed pure MnOx []. With less surface-loaded Zn, Cd sorption on sample sorb0.20 was, however, more suppressed (1.1 mmol g−1) compared to sample coppt0.20 (1.2 mmol g−1). This was likely caused by the structural modifications of δ-MnO2 by Zn coprecipitation.
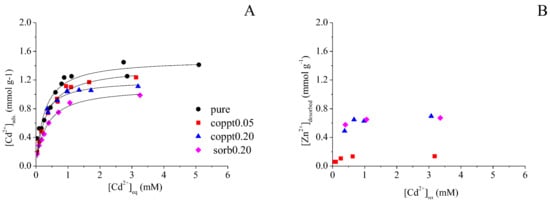
Figure 1.
(A) Cd2+ sorption isotherms on pure, Zn-coprecipitated (coppt0.05, coppt0.20) and Zn-sorbed (sorb0.20) δ-MnO2 samples. (B) Amount of Zn2+ release (desorption) during Cd2+ sorption. Solid lines are Langmuir model fitting results.

Table 2.
Langmuir model fitting results of Cd2+, phosphate, and arsenate sorption isotherms on pure, Zn-coprecipitated, and Zn-sorbed δ-MnO2.
Figure 1B shows the concentration of solution Zn during Cd sorption on samples coppt0.05, coppt0.20, and sorb0.20 δ-MnO2. With increasing initial Cd concentrations, more Zn was released into the solutions. However, the concentration of sorbed Cd was always higher than released Zn. This suggests that a fraction of Cd was sorbed via the exchange with Zn, and the rest of the Cd was sorbed on unoccupied surface sites. Because the surface sites of both coppt0.20 and sorb0.20 samples were already occupied by a large amount of Zn, they showed a similar amount of desorbed Zn (maximum ~0.70 mmol g−1), both higher than that of coppt0.05 (maximum ~0.17 mmol g−1). Total metal uptake (Equation (1)) was also calculated to compare the sorption capacity of different minerals (Figure 2). At low Cd concentrations, the total metal uptake increased with the increasing Cd concentration. The total metal uptake reached a plateau after ~1 mmol L−1 [Cd]eq (i.e., equilibrium Cd concentration in the reaction suspension), suggesting the saturation of available surface sites for cation sorption. Although Zn coprecipitation with δ-MnO2 decreased Cd sorption (due to the pre-occupation of surface sites by Zn), the overall metal uptake by coppt0.20 sample (~1.9 mmol g−1) was much higher than pure δ-MnO2 (~1.4 mmol g−1), suggesting significant structural modifications by Zn coprecipitation, e.g., increased availability of surface sites for cation sorption.
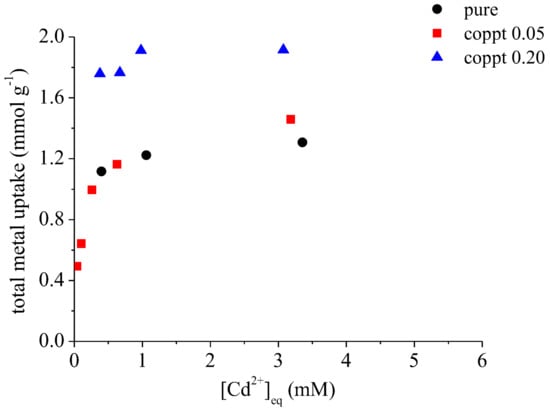
Figure 2.
Total metal uptake (calculated by Equation (1)) on pure and Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2 samples.
3.2. Anion Sorption on Pure and Zn Coprecipitated δ-MnO2
3.2.1. Phosphate and Arsenate Sorption on Pure δ-MnO2
The phosphate and arsenate sorption kinetics (both with 100 μmol L−1 initial concentration) are shown in Figure 3A,B. Both pseudo first and second order kinetic models were used to fit the kinetic data (Figure S4), and the first order model yielded a better fit (Table 2 and Table S2). Arsenate sorption had a faster sorption rate constant (k) and reached a higher uptake capacity at equilibrium. Phosphate pH edge experiments (Figure 4) showed a gradual increase in phosphate uptake by pure δ-MnO2 with decreasing pH, reaching a maximum at pH < 5, consistent with previous studies [,,].
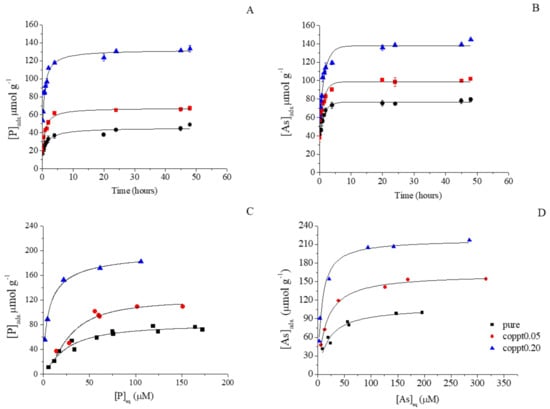
Figure 3.
(A) Phosphate and (B) arsenate sorption kinetics on pure, coppt0.05, and coppt0.20 δ-MnO2 samples. Solid lines are pseudo first order model fitting results. (C) Phosphate and (D) arsenate sorption isotherms on pure, coppt0.05, and coppt0.20 δ-MnO2 samples. Initial phosphate and arsenate concentrations are 100 μM. Solid lines show the Langmuir fitting results. Error bars represent results from duplicates.
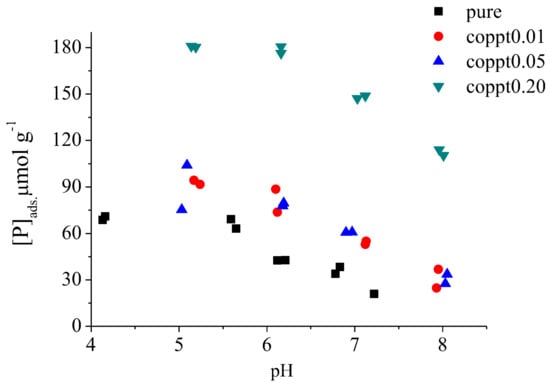
Figure 4.
Phosphate sorption on pure, coppt0.05, and coppt0.20 δ-MnO2 samples as a function of pH. Initial phosphate concentration is 100 μM.
Both phosphate and arsenate sorption reactions were fast and completed within a few hours (Figure 3). Therefore, a 24-h reaction time was chosen for phosphate and arsenate isotherm experiments, and the results are shown in Figure 3C,D. Both Langmuir and Freundlich models were used to fit the data (Figure S3) and the Langmuir model showed a better fit (Table 3 and Table S1). The maximum sorption capacity for phosphate and arsenate were 81.33 and 109.45 μmol g−1, respectively. Both are a magnitude lower than those of cations, consistent with previous studies [,,,,]. The zero point charge (ZPC) of δ-MnO2 is around 2.8 [], resulting in a negatively-charged surface under a wide range of pH. At the studied pH range, phosphate exists mainly as H2PO4− and HPO42− (pKa = 7.21), while arsenate exists mainly as H2AsO4− and HAsO42− (pKa = 6.97) [,]. The electrostatic repulsion between oxyanions and the δ-MnO2 surface is the main cause for limited anion sorption. Manning et al. found that arsenate sorbed both on the edges and at the interlayer region of birnessite by forming bidentate binuclear corner-sharing complexes []. Several other studies proposed that arsenate only sorbs on edge sites, and attributed the relatively low arsenate sorption to the limited amount of reactive edge sites for arsenate bonding [,]. Triple layer modeling results showed that the sorption of phosphate is unlikely to be inner-sphere, but rather through the formation of out-sphere complexation with MnOx surface sites []. Wang et al. proposed that phosphate, silicate, and sulfate sorb on the edge sites of acid birnessite [], but direct experimental confirmation (e.g., spectroscopic analysis) are still needed to confirm the actual binding mechanism(s) of phosphate on MnOx [].

Table 3.
Pseudo first order model fitting results for phosphate and arsenate sorption kinetics on pure and Zn co-precipitated δ-MnO2.
3.2.2. Phosphate and Arsenate Sorption on Zn Coprecipitated δ-MnO2
With increasing Zn concentration for Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2, both phosphate and arsenate sorption were greatly enhanced (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Based on the Langmuir model fitting results of sorption isotherms, the phosphate sorption capacity increased from 81.3 (pure δ-MnO2) to 120.4 (coppt0.05) and 186.2 μmol g−1 (coppt0.20). The arsenate sorption capacity increased from 109.4 (pure δ-MnO2) to 162.2 (coppt0.05) and 218.0 μmol g−1 (coppt0.20). The slopes of the sorption isotherms also became steeper with higher Zn treatment, suggesting that Zn-coprecipitation enhanced the affinity of anion sorbates. Such increased affinity was also manifested in the larger K values from Langmuir model fitting (Table 2). Enhanced phosphate and arsenate uptake by Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2 was also observed for the kinetics and pH edge experiments. The sorption rate constants (k, Table 3) were higher for the coppt0.05 and coppt0.20 δ-MnO2 samples, compared to that of pure δ-MnO2. In Figure 4, the sorption edges of phosphate and arsenate shifted to higher pH values with increasing Zn content for Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2. Previous studies showed that the phosphate sorption edges of hydrous MnOx shifted to higher pH in Na+ and Ca2+ solutions or seawater, compared to that in water []. Co-existing metal cations [] can also exert similar effects on phosphate sorption. Therefore, metal cations on MnOx generally shift anion sorption edges to higher pH, regardless of cation species or whether the cation was added before or during anion sorption. This is possibly because cation sorption compensated for the negative surface charge of MnOx, thus increasing anion affinity for the surface, or the potential formation of ternary complex (es) and/or precipitate(s).
In order to compare the influences of Zn-coprecipitation with Zn-sorption, Zn-sorbed δ-MnO2 was prepared by mixing pure δ-MnO2 with 0.25, 0.75, 1, and 2 mmol L−1 Zn before anion sorption experiments. ICP-MS analysis of the supernatant suggested that 0.42, 0.99, 1.30, and 1.69 mmol g−1 Zn was sorbed on δ-MnO2, respectively (Table 1). δ-MnO2 with increasing Zn loading showed enhanced phosphate and arsenate sorption capacities (Figure 5). Comparatively, the sorption capacity of Zn-coprecipitated coppt0.20 sample (with 1.5 mmol g−1 Zn loading) for phosphate and arsenate was higher than that of all Zn-sorbed δ-MnO2 samples, even though the Zn loading on the sorb0.60 sample was higher than that of the coppt0.20 sample (Figure 5). This confirms the significant influences of structural modifications caused by Zn-coprecipitation with δ-MnO2.
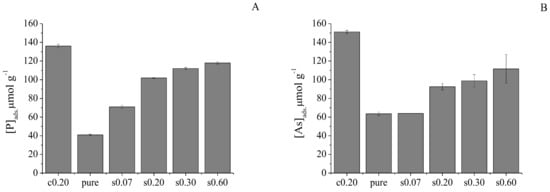
Figure 5.
Comparison of phosphate and arsenate sorption on Zn-sorbed and 0.2Zn co-precipitated δ-MnO2 (error bars represent results from duplicate experiments). “c” stands for “Zn-coprecipitation” samples and “s” for “Zn-sorption” samples. Initial phosphate and arsenate concentrations are 100 μM.
3.3. Effect of Zn Coprecipitation on the Sorptive Reactivity of δ-MnO2
3.3.1. Mechanisms for Cation Sorption on Zn-Coprecipitated δ-MnO2
Previous studies have shown that sorbed Cd2+ on MnOx existed as triple corner-sharing surface complexes below and/or above vacancy sites without incorporation into MnOx layers [,,]. Zn coprecipitation with δ-MnO2 can affect Cd uptake by modifying surface charges, particle size, and vacancy site density. In previous studies, the effects of metal coprecipitation with birnessite on mineral sorptive reactivity are metal-specific, possibly depending on the ratio of metal incorporation/(surface complexion + incorporation), with Co 90–100%, Ni 10–45%, Cu 0–20%, and Zn 0% [,,]. Co coprecipitation with MnOx was shown to enhance Pb2+ sorption on birnessite [] and cryptomelane [], and the authors proposed that Co substitution of Mn(IV) led to a more negatively-charged surface and more sorption sites (hydroxyl groups in CoOOH). Compared to Co, Ni coprecipitation with acid birnessite led to less Mn(IV) substitution (10–45% of Ni) vs. surface-sorbed species []. Surface-complexed Ni occupied surface vacancy sites and decreased the sorption capacity towards Zn2+ and Pb2+ []. Similar to the effects of coprecipitation, pre-sorbed metal cations can decrease MnOx sorption capacity toward Pb2+ [,], Cu2+, Zn2+, and Cd2+ []. Zn was not observed to substitute or incorporate (0% of Zn) in δ-MnO2 or phyllomanganate layers, due to the large atomic difference between Zn and Mn(III, IV) and crystal field stabilization energy [,]. Therefore, Zn-coprecipitation could block surface vacancy sites, preventing further cation (e.g., Cd) sorption. Zn also compensated δ-MnO2 negative surface charges (Figure S1 and Text S2), which also reduces the affinity between the cations (e.g., Cd) and the δ-MnO2 surface.
This study shows that Zn coprecipitated δ-MnO2 possesses a larger sorptive capacity towards Cd than Zn-sorbed δ-MnO2 at similar or even higher Zn loadings, suggesting that Zn coprecipitation not only blocked surface vacancy sites, but also affected the structural properties of δ-MnO2. Grangeon et al. found that Zn sorption can expel Mn(III) within δ-MnO2 layers [], leading to more vacancy sites and potentially increased sorption capacity towards metal cations []. Our recent study found that Zn coprecipitation had significant effects on δ-MnO2 structure, causing a significantly reduced layer size and layer stacking and less Mn(III) occupation on vacancy sites []. These structural modifications might account for the higher total metal uptake by Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2 than pure δ-MnO2. Yu et al. [] also found more Zn uptake during biogenic MnOx formation compared to Zn sorption on pre-formed biogenic MnOx. It is likely that Zn inhibited the growth of fungal MnOx and resulted in lower crystallinity MnOx with a higher metal uptake capacity.
3.3.2. Solid Phase Analysis for Anion Sorption on Zn-Coprecipitated δ-MnO2
XRD and As K-edge extended X-ray absorption fine edge structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy were conducted to characterize the solid products from sorption experiments, in order to explore the possible mechanisms underlying the effects of Zn-coprecipitation on sorptive reactivity. Pure δ-MnO2 were mixed with 2 mmol L−1 Zn2+ (higher than coppt0.20 Zn loading) and 200 μmol L−1 phosphate (highest phosphate concentration used in this study), and no bulk precipitation was identified by XRD (Figure S6). The rising peak at 1.6–1.9 Å in the XRD spectra can be attributed to trace metal occupation on the vacancy sites [].
Figure 6 shows the As EXAFS data of 100 μmol L−1 arsenate sorption on 0.5 g L−1 pure and coppt0.20 δ-MnO2. No significant differences were observed for the spectra of the two samples. Fourier transformed (FT) spectra showed the two major peaks corresponding to As-O and As-Mn shells. Shell-by-shell fitting (Table S3) revealed ~4 oxygen atoms at ~1.69 Å, consistent with the tetrahedral coordination of arsenate [,]. The second shell fitting indicated an As-Mn distance of 3.17–3.18 Å, suggesting the formation of bidentate binuclear complex of As on δ-MnO2 surfaces, consistent with the previously reported 3.17–3.22 Å range [,]. No additional pathways (e.g., As-Zn) were detected, suggesting no significant amount of ternary surface complex(es) and/or precipitation during arsenate sorption on Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2. Previous EXAFS studies also did not find ternary complex formation among arsenate, MnOx, and sorbed Zn/Pb [], or precipitation of Mn2+ and arsenate produced during arsenite oxidation by MnOx [].
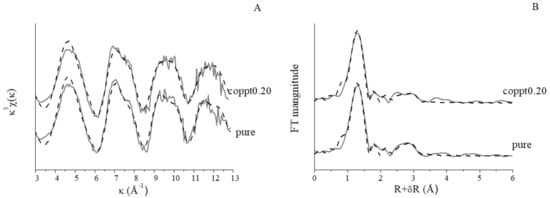
Figure 6.
k3-weighted As extended X-ray absorption fined structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy (A) and Fourier transformed spectra (not corrected for phase shift) (B) of arsenate sorption on pure and coppt0.20 δ-MnO2 samples. Raw and fitted data are in solid and dotted lines, respectively.
3.3.3. Mechanisms for Anion Sorption on Zn-Coprecipitated δ-MnO2
Metal cations can influence phosphate and arsenate sorption in several ways. First, pre-existing cations on the δ-MnO2 surface might compete with anions for sorption sites. Yao et al. proposed that Ca2+ and Mg2+ can suppress phosphate sorption on hydrous MnOx by occupying surface sites and forming phosphate complexes in the solution []. Power et al. found that sorbed Zn2+ slowed down arsenite oxidation by blocking δ-MnO2 surface sites for arsenite complexation and electron transfer []. To verify the presence of competitive sorption, we monitored the release of metals (Zn and total Mn) from the coppt0.20 sample equilibrated with 10 mmol L−1 NaCl solution with or without 100 μmol L−1 phosphate (Figure S7). Mn was not detected in the solution. Desorbed Zn was ~9 μmol L−1 when 0.2coppt birnessite was equilibrated with 100 μmol L−1 phosphate and ~8 μmol L−1 without P after 24 h (Figure S7). Phosphate did not induce substantial Zn desorption, suggesting little competition between Zn and phosphate, likely due to the different sorption sites that they prefer. Zn sorbs mostly at interlayer vacancy sites [,], while anions such as phosphate, silicate, and sulfate are generally considered to complex at edge sites of birnessite layers [].
Secondly, the presence of metal cations may compensate the negative surface charge of δ-MnO2, thus reducing the electrostatic repulsion between δ-MnO2 surface and anions and enhancing anion sorption. In general, anion uptake by negatively-charged Mn oxides is limited, and anions are more likely to be associated with more positively charged Fe and Al (oxhydr)oxides [,,]. However, charge compensation through cation sorption/coprecipitation can significantly enhance anion sorption on MnOx. Vilallobos et al. found that Zn2+ and Pb2+ sorption on δ-MnO2 and birnessite enhanced the sorption of arsenate []. Kawashima et al. [] found that co-existing Ca2+, Mg2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, Mn2+, Co2+, and Ni2+ greatly enhanced phosphate sorption on hydrous MnOx over a wide range of pH. The order of enhancement by alkaline earth elements is Ba2+ > Sr2+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+, suggesting that cations with smaller hydrated radii (i.e., higher charge density) are more likely to promote anion sorption. A previous study showed that in seawater (containing concentrated Ca2+, Na+, K+, Mg2+, and other metal cations), phosphate uptake by hydrous Mn oxides was comparable to that by goethite, and even higher than goethite at pH < 4 []. Mn2+-rich hydrous Mn oxides were also shown to play important roles in As accumulation in Biwa lake sediments in Japan []. The study suggested that, since Mn oxides are important oxidants for arsenite, the resulting arsenate can accumulate on MnOx surfaces that are charge compensated by cations (Mn, Ni, and earth alkaline cations).
Thirdly, the common presence of metals during MnOx formation in the natural environment is likely to modify the MnOx structure and enhance the anion uptake capacity, especially metals with limited incorporation into MnOx vacancy sites such as Zn and Ni []. As discussed above, Zn-sorption was not as effective as Zn-coprecipitation for the enhancement of phosphate and arsenate sorption on δ-MnO2, due to the structural modifications by Zn-coprecipitation. Zn sorption was shown to cause δ-MnO2 dissolution and caused 15–20% reduction in the lateral coherent domain size after ~12 h at pH 5–7 []. Zn coprecipitation caused even greater effects on the δ-MnO2 layer structure []. Reduced layer size can expose more available edges for anions, which mostly sorb onto edge sites [].
4. Conclusions
In this study, Cd was chosen as a cation probe while phosphate and arsenate were chosen as anion probes to investigate the effects of Zn-coprecipitation on the sorptive reactivity of δ-MnO2. Compared to pure δ-MnO2, Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2 phases are less negatively charged, and have a smaller layer size and less layer Mn(III) occupation on vacancy sites. Pre-loaded Zn, either coprecipitated or sorbed, inhibited Cd sorption on δ-MnO2, due to the competition between Zn and Cd. Total metal uptake (Zn + Cd) was enhanced as a result of the above-mentioned structural changes. Zn-sorbed δ-MnO2 has a smaller Cd sorption capacity than Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2, even if the latter has less pre-loaded Zn. The charge-compensated Zn-δ-MnO2 surface showed significantly enhanced sorptive capacity toward the anions phosphate and arsenate. Higher sorption capacity, higher affinity, faster kinetics, and a right-shifted sorption edge were observed for phosphate and arsenate sorption on Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2, compared to pure δ-MnO2. Compared to Zn-sorbed δ-MnO2 samples, Zn-coprecipitation was more effective in enhancing anion sorption. No significant amount of ternary surface complex and/or precipitates were detected for phosphate and arsenate sorption on Zn treated δ-MnO2. This study quantified the sorptive reactivities of MnOx under complex conditions close to realistic environments and revealed the underlying mechanisms. Our study suggests that the roles of MnOx in regulating anion fate and transport should be re-visited by considering the impacts (e.g., structural modification, surface charge compensation) of metal presence during (i.e., coprecipitation) and after MnOx formation (i.e., sorption). As metal coprecipitation with MnOx minerals can be a common environmental process, our findings can help better understand the roles of MnOx in the biogeochemical cycles of nutrients, metals and organic contaminants.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2571-8789/2/2/19/s1. XRD and XAS experiment details; summary of δ-MnO2 structure modifications by Zn coprecipitation (e.g., surface charge measurements); Zn and Cd sorption on pure δ-MnO2; Sorption isotherm normalized by BET surface area instead of by mass; fitting results of cation and anion sorption isotherms and kinetics using different sorption models; shell-by-shell fitting results of As EXAFS spectra; Zn release from Zn-coprecipitated δ-MnO2 with and without the presence of phosphate.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge funding support from NASA grant #NNA15BB03A and NSF grant #1710285. We appreciate the support from beamline scientist Qing Ma at APS Beamline 5-BM-D. Portions of this research were conducted at the Advanced Photon Source (APS). Use of the Advanced Photon Source was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science and Office of Basic Energy Sciences.
Author Contributions
Yuanzhi Tang and Shiliang Zhao conceived and designed the experiments; Shiliang Zhao and Chenning Li performed the experiments and analyzed the data; Pan Liu, Rixiang Huang, and Emily Saad contributed to sample analysis; Shiliang Zhao wrote the paper; Yuanzhi Tang and Rixiang Huang edited the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Taylor, R.; McKenzie, R.; Norrish, K. The mineralogy and chemistry of manganese in some Australian soils. Soil Res. 1964, 2, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manceau, A.; Lanson, B.; Drits, V.A. Structure of heavy metal sorbed birnessite. Part III: Results from powder and polarized extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 2639–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P. Kinetics of redox reactions on manganese oxides and its impact on environmental quality. In Rates of Soil Chemical Processes; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1991; pp. 191–230. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, P.; Axe, L.; Tyson, T.A. XAS Studies of Ni and Zn Sorbed to Hydrous Manganese Oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4515–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, C.L.; Sherman, D.M. Sorption of Ni by birnessite: Equilibrium controls on Ni in seawater. Chem. Geol. 2007, 238, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenne, E.A. Controls on Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn concentrations in soils and water: The significant role of hydrous Mn and Fe oxides. Adv. Chem. 1968, 73, 337–387. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Tan, W.; Zheng, L.; Cui, H.; Qiu, G.; Liu, F.; Feng, X. Characterization of Ni-rich hexagonal birnessite and its geochemical effects on aqueous Pb2+/Zn2+ and As (III). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 93, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decrée, S.; Pourret, O.; Baele, J.-M. Rare earth element fractionation in heterogenite (CoOOH): Implication for cobalt oxidized ore in the Katanga Copperbelt (Democratic Republic of Congo). J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 159, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manceau, A.; Silvester, E.; Bartoli, C.; Lanson, B.; Drits, V.A. Structural mechanism of Co2+ oxidation by the phyllomanganate buserite. Am. Mineral. 1997, 82, 1150–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Liu, Y.; Koopal, L.K.; Feng, X.; Chu, S.; Zhu, M.; Liu, F. High Co-doping promotes the transition of birnessite layer symmetry from orthogonal to hexagonal. Chem. Geol. 2015, 410, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Liu, F.; Feng, X.; Hu, T.; Zheng, L.; Qiu, G.; Koopal, L.K.; Tan, W. Effects of Fe doping on the structures and properties of hexagonal birnessites–Comparison with Co and Ni doping. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 117, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manceau, A.; Llorca, S.; Calas, G. Crystal chemistry of cobalt and nickel in lithiophorite and asbolane from New Caledonia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Feng, X.; Qiu, G.; Tan, W.; Liu, F. Characterization of Co-doped birnessites and application for removal of lead and arsenite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, K.D.; Refson, K.; Sposito, G. Surface complexation of Pb (II) by hexagonal birnessite nanoparticles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 6731–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Feng, X.; Tan, W.; Koopal, L.K.; Hu, T.; Zhu, M.; Liu, F. Structure and properties of vanadium (V)-doped hexagonal turbostratic birnessite and its enhanced scavenging of Pb2+ from solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 288, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, Y.M.; Lion, L.W.; Ghiorse, W.C.; Shuler, M.L. Production of biogenic Mn oxides by Leptothrix discophora SS-1 in a chemically defined growth medium and evaluation of their Pb adsorption characteristics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, Q.Q.; Liu, F.; Qiu, G.H.; Tan, W.F.; Feng, X.H. Pb2+ adsorption on birnessite affected by Zn2+ and Mn2+ pretreatments. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, M.; Bargar, J.; Sposito, G. Mechanisms of Pb (II) sorption on a biogenic manganese oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, J.; Bargar, J.R.; Sposito, G. Copper sorption by the edge surfaces of synthetic birnessite nanoparticles. Chem. Geol. 2015, 396, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, D.M.; Peacock, C.L. Surface complexation of Cu on birnessite (δ-MnO2): Controls on Cu in the deep ocean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 6721–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangeon, S.; Manceau, A.; Guilhermet, J.; Gaillot, A.-C.; Lanson, M.; Lanson, B. Zn sorption modifies dynamically the layer and interlayer structure of vernadite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 85, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonfueng, T.; Axe, L.; Yee, N.; Hahn, D.; Ndiba, P.K. Zn sorption mechanisms onto sheathed Leptothrix discophora and the impact of the nanoparticulate biogenic Mn oxide coating. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 333, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Tani, Y.; Naitou, H.; Miyata, N.; Tojo, F.; Seyama, H. Zn (II) sequestration by fungal biogenic manganese oxide through enzymatic and abiotic processes. Chem. Geol. 2014, 383, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Axe, L. Modeling Cd and Zn sorption to hydrous metal oxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.S.; Bersillon, J.-L.; Gopal, K. Adsorption of Cd2+ on hydrous manganese dioxide from aqueous solutions. Desalination 2006, 194, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, X.; Villalobos, M.; Tan, W.; Liu, F. Sorption behavior of heavy metals on birnessite: Relationship with its Mn average oxidation state and implications for types of sorption sites. Chem. Geol. 2012, 292–293, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.D.; Refson, K.; Sposito, G. Understanding the trends in transition metal sorption by vacancy sites in birnessite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 101, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, M.; Tainaka, Y.; Hori, T.; Koyama, M.; Takamatsu, T. Phosphate adsorption onto hydrous manganese(IV) oxide in the presence of divalent cations. Water Res. 1986, 20, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangeon, S.; Lanson, B.; Lanson, M.; Manceau, A. Crystal structure of Ni-sorbed synthetic vernadite: A powder X-ray diffraction study. Mineral. Mag. 2008, 72, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, L.E.; Arai, Y.; Sparks, D.L. Zinc adsorption effects on arsenite oxidation kinetics at the birnessite-water interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalobos, M.; Escobar-Quiroz, I.N.; Salazar-Camacho, C. The influence of particle size and structure on the sorption and oxidation behavior of birnessite: I. Adsorption of As (V) and oxidation of As (III). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 125, 564–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Xiang, Q.; Liu, F.; Xiong, J.; Koopal, L.K.; Zheng, L.; Ginder-Vogel, M.; Wang, M.; Feng, X.; Tan, W. Local structure of Cu2+ in Cu-doped hexagonal turbostratic birnessite and Cu2+ stability under acid treatment. Chem. Geol. 2017, 4666, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opfergelt, S.; Cornélis, J.-T.; Houben, D.; Givron, C.; Burton, K.; Mattielli, N. The influence of weathering and soil organic matter on Zn isotopes in soils. Chem. Geol. 2017, 466, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkle, M.A.; Dye, K.G.; Catalano, J.G. Impact of Mn (II)-Manganese Oxide Reactions on Ni and Zn Speciation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drits, V.A.; Lanson, B.; Bougerol-Chaillout, C.; Gorshkov, A.I.; Manceau, A. Structure of heavy-metal sorbed birnessite: Part 2. Results from electron diffraction. Am. Mineral. 2002, 87, 1646–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Sasaki, K.; Tanaka, K.; Ohnuki, T.; Hirajima, T. Zinc sorption during bio-oxidation and precipitation of manganese modifies the layer stacking of biogenic birnessite. Geomicrobiol. J. 2013, 30, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Q.; Sun, J.; Borkiewicz, O.; Huang, R.; Saad, E.; Fields, B.; Chen, S.; Zhu, M.; Tang, Y. Effect of Zn2+ presence during mineral formation on the structure of layered Mn oxides. Chem. Geol. Submitted in 2017.
- Jenkyns, H.C. Fossil manganese nodules from the west Sicilian Jurassic. Eclogae Geol. Helv. 1970, 63, 741–774. [Google Scholar]
- Childs, C.W. Composition of iron-manganese concretions from some New Zealand soils. Geoderma 1975, 13, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manceau, A.; Tamura, N.; Celestre, R.S.; MacDowell, A.A.; Geoffroy, N.; Sposito, G.; Padmore, H.A. Molecular-scale speciation of Zn and Ni in soil ferromanganese nodules from loess soils of the Mississippi Basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Zhang, G.; Heaney, P.J.; Webb, S.M.; Burgos, W.D. Characterization of manganese oxide precipitates from Appalachian coal mine drainage treatment systems. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanson, B.; Marcus, M.A.; Fakra, S.; Panfili, F.; Geoffroy, N.; Manceau, A. Formation of Zn–Ca phyllomanganate nanoparticles in grass roots. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meng, Y.-T.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Zhang, L.-M.; He, J.-Z. Biogenic Mn oxides for effective adsorption of Cd from aquatic environment. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2577–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.; Li, Y.; Hua, X. Investigation of Fe, Mn oxides and organic material in surface coatings and Pb, Cd adsorption to surface coatings developed in different natural waters. Microchem. J. 2001, 70, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Millero, F.J. Adsorption of Phosphate on Manganese Dioxide in Seawater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violante, A.; Pigna, M. Competitive sorption of arsenate and phosphate on different clay minerals and soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; De Cristofaro, A.; Violante, A. Effect of pH, phosphate and oxalate on the adsorption/desorption of arsenate on/from goethite. Soil Sci. 2001, 166, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.S.; Beattie, J.K.; Coleman, L.M.; Jones, D.R. Hydrolysis of an organophosphate ester by manganese dioxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, K.M.; Hanh, H.T.; Kim, K.W. Arsenic geochemistry and human health in South East Asia. Rev. Environ. Health 2011, 26, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, J.I.; Tani, Y.; Miyata, N.; Seyama, H.; Mitsunobu, S.; Naitou, H. Concurrent sorption of As (V) and Mn (II) during biogenic manganese oxide formation. Chem. Geol. 2012, 306, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, M.A.; Manceau, A.; Kersten, M. Mn, Fe, Zn and As speciation in a fast-growing ferromanganese marine nodule. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 3125–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Farrow, C.L.; Post, J.E.; Livi, K.J.T.; Billinge, S.J.L.; Ginder-Vogel, M.; Sparks, D.L. Structural study of biotic and abiotic poorly-crystalline manganese oxides using atomic pair distribution function analysis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 81, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J. A modified single solution method for determination of phosphate uptake by rye. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1952, 48, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lenoble, V.; Deluchat, V.; Serpaud, B.; Bollinger, J.-C. Arsenite oxidation and arsenate determination by the molybdene blue method. Talanta 2003, 61, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balistrieri, L.S.; Chao, T. Adsorption of selenium by amorphous iron oxyhydroxide and manganese dioxide. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.; Zaman, M.I.; Khan, S. pH effect on phosphate sorption by crystalline MnO2. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 301, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, S.; Zaman, M.I.; Khan, S. Temperature effect on the mechanism of phosphate anions sorption by β-MnO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 141, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouvrard, S.; Simonnot, M.-O.; Sardin, M. Reactive behavior of natural manganese oxides toward the adsorption of phosphate and arsenate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L. Evrionmental Soil Chemistru; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, B.A.; Fendorf, S.E.; Bostick, B.; Suarez, D.L. Arsenic (III) oxidation and arsenic (V) adsorption reactions on synthetic birnessite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschamps, E.; Ciminelli, V.S.; Weidler, P.G.; Ramos, A.Y. Arsenic sorption onto soils enriched in Mn and Fe minerals. Clays Clay Miner. 2003, 51, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liao, X.; Xu, W.; Ren, Y.; Livi, K.J.; Zhu, M. Synthesis of Birnessite in the Presence of Phosphate, Silicate, or Sulfate. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 10248–10258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanson, B.; Drits, V.A.; Gaillot, A.-C.; Silvester, E.; Plançon, A.; Manceau, A. Structure of heavy-metal sorbed birnessite: Part 1. Results from X-ray diffraction. Am. Mineral. 2002, 87, 1631–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, F.; Zhu, M.; Feng, X.; Zhang, J.; Yin, H. Structure and properties of Co-doped cryptomelane and its enhanced removal of Pb2+ and Cr3+ from wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Liu, F.; Feng, X.; Liu, M.; Tan, W.; Qiu, G. Co2+-exchange mechanism of birnessite and its application for the removal of Pb2+ and As (III). J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 196, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafferty, B.J.; Ginder-Vogel, M.; Zhu, M.; Livi, K.J.; Sparks, D.L. Arsenite oxidation by a poorly crystalline manganese-oxide. 2. Results from X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8467–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, K.D.; Refson, K.; Sposito, G. Zinc surface complexes on birnessite: A density functional theory study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Adsorptive removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions using iron oxide tailings. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanada, S.; Kabayama, M.; Kawasaki, N.; Sakiyama, T.; Nakamura, T.; Araki, M.; Tamura, T. Removal of phosphate by aluminum oxide hydroxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 257, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S.; Hering, J.G. Comparison of arsenic (V) and arsenic (III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: Implications for arsenic mobility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamatsu, T.; Kawashima, M.; Koyama, M. The role of Mn2+-rich hydrous manganese oxide in the accumulation of arsenic in lake sediments. Water Res. 1985, 19, 1029–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).