Paget’s Disease of Bone and Normocalcemic Variant of Primary Hyperparathyroidism in an Osteoporotic Male: Exceptional Coexistence
Abstract
1. Introduction and Clinical Significance
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
3.1. Clinical Manifestations in Ailments of the Bone Metabolism
3.2. Bone Turnover Markers
3.3. Additional Pitfalls: Secondary Hyperparathyroidism in Paget’s Disease of Bone
3.4. Complications of Normocalcemic Primary Hyperparathyroidism
3.5. A Dual Perspective of the Case Management
3.6. Similar Cases in the Literature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, Y.J.; Sohn, Y.B.; Chung, Y.S. Updates on Paget’s Disease of Bone. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 37, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral Gudino, L. Paget’s disease of bone: 1877–2023. Etiology, and management of a disease on epidemiologic transition. Med. Clin. 2023, 161, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.J.; Pye, S.R.; Lunt, M.; Dixon, W.G.; Ashcroft, D.M.; O’Neill, T.W. Incidence of Paget’s disease of bone in the UK: Evidence of a continuing decline. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 5668–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husseini, J.S.; Oganesyan, R.; Staffa, S.J.; Huang, E.; Habibollahi, S.; Hemke, R.; Chang, C. Prevalence of Paget’s disease of bone: Review of consecutive abdominopelvic CT scans and literature. Acta Radiol. 2023, 64, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michou, L.; Gamache, P.; Guertin, J.R.; Tarride, J.E.; Brown, J.P.; Jean, S. Prevalence and incidence of Paget’s disease of bone: Temporal trend over 20 years in the province of Quebec, Canada. Bone 2023, 176, 116895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaganapalli, B.; Fallatah, I.; Alsubhi, F.; Shetty, P.J.; Awan, Z.; Elango, R.; Shaik, N.A. Paget’s disease: A review of the epidemiology, etiology, genetics, and treatment. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1131182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Wei, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Yue, H. Clinical Characteristics and Pathogenic Gene Identification in Chinese Patients with Paget’s Disease of Bone. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 850462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, S.J.; Wall, C. Paget’s disease of bone: A clinical update. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2021, 50, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuck, S.P.; Walker, J. Adult Paget’s disease of bone. Clin. Med. 2020, 20, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makaram, N.S.; Ralston, S.H. Genetic Determinants of Paget’s Disease of Bone. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2021, 19, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusano, N.E.; Cetani, F. Normocalcemic primary hyperparathyroidism. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 66, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilezikian, J.P.; Khan, A.A.; Silverberg, S.J.; Fuleihan, G.E.H.; Marcocci, C.; Minisola, S.; Perrier, N.; Sitges-Serra, A.; Thakker, R.V.; Guyatt, G.; et al. Evaluation and Management of Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Summary Statement and Guidelines from the Fifth International Workshop. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2022, 37, 2293–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sinha Gregory, N.; Andreopoulou, P.; Kashyap, S.; Cusano, N. Approach to the Patient: Normocalcemic Primary Hyperparathyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 110, e868–e877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosário, P.W.; Calsolari, M.R. Normocalcemic Primary Hyperparathyroidism in Adults Without a History of Nephrolithiasis or Fractures: A Prospective Study. Horm. Metab. Res. 2019, 51, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankova, I.; Lilova, L.; Petrova, D.; Dimitrova, I.; Stoynova, M.; Shinkov, A.; Kovatcheva, R. Biochemical characteristics and clinical manifestation of normocalcemic primary hyperparathyroidism. Endocrine 2024, 85, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Gillis, A.; Lindeman, B.; Chen, H.; Fazendin, J. Normocalcemic primary hyperparathyroidism: From pathophysiology to clinical management. Am. J. Surg. 2024, 235, 115812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilezikian, J.P. Primary Hyperparathyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3993–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inker, L.A.; Eneanya, N.D.; Coresh, J.; Tighiouart, H.; Wang, D.; Sang, Y.; Crews, D.C.; Doria, A.; Estrella, M.M.; Froissart, M.; et al. New Creatinine- and Cystatin C-Based Equations to Estimate GFR without Race. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberger Marques, J.V.; Moreira, C.A. Primary hyperparathyroidism. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 34, 101514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihashi, I.; Ishii, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Uchida, A.; Hara, H.; Tamaoka, A. Normocalcemic Primary Hyperparathyroidism Presenting with Muscle Weakness and Body Pain. Intern. Med. 2021, 60, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Hillenbrand, A.; Peth, S.; Hummel, R. Symptoms of Primary Hyperparathyroidism in Men and Women: The Same but Different? Visc. Med. 2020, 36, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillet, B.; Bertocchio, J.P.; Nominé-Criqui, C.; Kerlan, V. Chapter 2: Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Diagnosis. Ann. Endocrinol. 2025, 86, 101691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhroub, W.; Oweidat, M.; Alra’e, M.; Alayasa, R.Y. Atypically presented dysphagia in a patient with primary hyperparathyroidism that resolved after parathyroidectomy: A case report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2024, 124, 110480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsayen, F.Z.; Haddadi, Z.; Aggari, H.E.; Benramdane, H.; Aichouni, N.; Nasri, S.; Elharroudi, T.; Skiker, I.; Kamaoui, I. Dysphagia revealing a giant cystic parathyroid adenoma. Radiol. Case Rep. 2022, 17, 3556–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammit, M.; Siau, R.; Panarese, A. Importance of serum calcium in spontaneous neck haematoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e237267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikantha, L.; Amjad, E.H.; Beydoun, R. Sudden Odynophagia and Globus-A Unique Presentation of a Nonsecreting Parathyroid Adenoma: A Case Report and Literature Review. Case Rep. Otolaryngol. 2020, 2020, 6805805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.K. Advances in the diagnosis and the management of primary hyperparathyroidism. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2021, 12, 20406223211015965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendina, D.; De Filippo, G.; Merlotti, D.; Di Stefano, M.; Mingiano, C.; Giaquinto, A.; Evangelista, M.; Bo, M.; Arpino, S.; Faraonio, R.; et al. Increased Prevalence of Nephrolithiasis and Hyperoxaluria in Paget Disease of Bone. J. Clin. Endocrin. Metab. 2020, 105, dgaa576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schini, M.; Vilaca, T.; Gossiel, F.; Salam, S.; Eastell, R. Bone Turnover Markers: Basic Biology to Clinical Applications. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 417–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasikaran, S.D.; Miura, M.; Pikner, R.; Bhattoa, H.P.; Cavalier, E.; IOF-IFCC Joint Committee on Bone Metabolism (C-BM). Practical Considerations for the Clinical Application of Bone Turnover Markers in Osteoporosis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2023, 112, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, S.H.; Corral-Gudino, L.; Cooper, C.; Francis, R.M.; Fraser, W.D.; Gennari, L.; Guañabens, N.; Javaid, M.K.; Layfield, R.; O’Neill, T.W.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Paget’s Disease of Bone in Adults: A Clinical Guideline. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019, 34, 579–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillett, M.J.; Vasikaran, S.D.; Inderjeeth, C.A. The Role of PINP in Diagnosis and Management of Metabolic Bone Disease. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2021, 42, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nofal, A.A.; Altayar, O.; BenKhadra, K.; Qasim Agha, O.Q.; Asi, N.; Nabhan, M.; Prokop, L.J.; Tebben, P.; Murad, M.H. Bone turnover markers in Paget’s disease of the bone: A Systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2015, 26, 1875–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc, P. Biochemical bone turnover markers in hormonal disorders in adults: A narrative review. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 43, 1409–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ramírez, J.; Gómez-Valdazo, A.; Luengo, P.; Porrero, B.; Osorio, I.; Rivas, S. Comparative prospective study on the presentation of normocalcemic primary hyperparathyroidism. Is it more aggressive than the hypercalcemic form? Am. J. Surg. 2020, 219, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendina, D.; Falchetti, A.; Diacinti, D.; Bertoldo, F.; Merlotti, D.; Giannini, S.; Cianferotti, L.; Girasole, G.; Di Monaco, M.; Gonnelli, S.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of Paget’s disease of bone: Position paper from the Italian Society of Osteoporosis, Mineral Metabolism and Skeletal Diseases (SIOMMMS). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2024, 47, 1335–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panuccio, V.A.; Tripepi, R. Paget’s Disease and Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Is Healing Possible? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, M.L.; Falchetti, A. What is the relationship between Paget’s disease of bone and hyperparathyroidism? J. Bone Miner. Res. 2006, 21 (Suppl. S2), P69–P74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendina, D.; De Filippo, G.; Merlotti, D.; Di Stefano, M.; Succoio, M.; Muggianu, S.M.; Bianciardi, S.; D’Elia, L.; Coppo, E.; Faraonio, R.; et al. Vitamin D Status in Paget Disease of Bone and Efficacy-Safety Profile of Cholecalciferol Treatment in Pagetic Patients with Hypovitaminosis, D. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2019, 105, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.C.; Cusano, N.E.; Bilezikian, J.P. Primary hyperparathyroidism. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 38, 101247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandra, S.; Wang, R.; Akhund, R.; Allahwasaya, A.; Lindeman, B.; Fazendin, J.; Gillis, A.; Chen, H. Patients with normocalcemic versus hypercalcemic hyperparathyroidism: What’s really the difference? Am. J. Surg. 2025, 244, 116272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, G.; Espiard, S.; Buffet, C.; Ben Hamou, A.; Henry, H.; Paladino, N.C.; Sebag, F.; Goichot, B. Chapter 11: Treatment modalities. Ann. Endocrinol. 2025, 86, 101700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, S.; Mosbah, H.; Donatini, G.; Brunaud, L.; Chabre, O.; Vezzosi, D. Chapter 9: Indications for the treatment of primary hyperparathyroidism. Ann. Endocrinol. 2025, 86, 101698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, C.E.; Stanciu-Găvan, C.; Vasilescu, F.; Dumitru, A.V.; Ciuche, A. Attitude of the surgical approach in hyperparathyroidism: A retrospective study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha-Bezerra, P.; Vieira, R.; Amaral, F.; Cartaxo, H.; Lima, T.; Montarroyos, U.; Bandeira, F. Better performance of four-dimension computed tomography as a localization procedure in normocalcemic primary hyperparathyroidism. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 62, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nistor, C.E.; Bugala, N.M.; Daguci, C.; Daguci, L.; Diaconu, O.A.; Rica, A.M. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 syndrome and osteoporosis. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2023, 35 (Suppl. S1), S387. [Google Scholar]
- Bandeira, L.; Silva, B.C.; Bilezikian, J.P. Male osteoporosis. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 66, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuggle, N.R.; Beaudart, C.; Bruyère, O.; Abrahamsen, B.; Al-Daghri, N.; Burlet, N.; Chandran, M.; Rosa, M.M.; Cortet, B.; Demonceau, C.; et al. Evidence-Based Guideline for the management of osteoporosis in men. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2024, 20, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinonapoli, G.; Ruggiero, C.; Meccariello, L.; Bisaccia, M.; Ceccarini, P.; Caraffa, A. Osteoporosis in Men: A Review of an Underestimated Bone Condition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Makras, P.; Tournis, S.; Anastasilakis, A.D. Off-label uses of denosumab in metabolic bone diseases. Bone 2019, 129, 115048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, P.; Rasmussen, A.Q.; Kvist, T.M.; Andersen, U.B.; Jørgensen, N.R. Paget’s disease of the bone after treatment with Denosumab: A case report. Bone 2012, 50, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostine, M.; Mehsen-Cetre, N.; Bannwarth, B. Denosumab-induced severe hypocalcemia in a patient with Paget’s disease of bone and impaired renal function. Therapie 2017, 72, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuthiah, N.; Er, C. Effective Treatment of Paget’s Disease of the Bone in a Chinese Woman. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2018, 47, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, I.R.; Sharma, S.; Kalluru, R.; Eagleton, C. Treatment of Paget’s Disease of Bone with Denosumab: Case Report and Literature Review. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2016, 99, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Puri, A.; Shah, S.; Rekhi, B.; Gulia, A. Giant Cell Tumor Developing in Paget’s Disease of Bone: A Case Report with Review of Literature. J. Orthop. Case Rep. 2016, 6, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Slavin, J.; McLachlan, S.A.; Choong, P. Anti-osteoclastic agent, denosumab, for a giant cell tumor of the bone with concurrent Paget’s disease: A case report. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2105–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magvanjav, O.; Bergwitz, C. Treatment of Extraosseous Giant Cell Tumor of Bone and Calcitriol-Mediated Hypercalcemia With Denosumab in Paget Disease. JCEM Case Rep. 2025, 3, luaf031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamalumpundi, V.; Shams, E.; Torfah, M.; Correia, M.L. Amelioration of Paget Disease of Bone After Denosumab for Osteopenia. AACE Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 9, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutteridge, D.H.; Gruber, H.E.; Kermode, D.G.; Worth, G.K. Thirty cases of concurrent Paget’s disease and primary hyperparathyroidism: Sex distribution, histomorphometry, and prediction of the skeletal response to parathyroidectomy. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1999, 65, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, M.; Arroyo, M.; Collado, A.S.; Gallardo, E.C.; Montes, S.; Olmos, J.M. Primary Lymphoma Arising in Paget’s Disease in A Patient with Primary Hyperparathyroidism. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2025, 12, 004778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, W.W.; Bridger, G.P.; Baldwin, M.; Donellan, M. Recurrent giant cell tumour of the maxilla associated with both Paget’s disease and primary hyperparathyroidism. ANZ J. Surg. 2003, 73, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, T.C.; Evans, M.C.; Spiro, T.P.; Ibbertson, H.K. Coexisting Paget’s disease of bone and hyperparathyroidism. N. Z. Med. J. 1980, 91, 134–136. [Google Scholar]
- Carsote, M.; Valea, A.; Dumitru, N.; Terzea, D.; Petrova, E.; Albu, S.; Buruiana, A.; Ghemigian, A. Metastases in daily endocrine practice. Arch. Balk. Med. Union 2016, 51, 476–480. [Google Scholar]
- Nica, S.; Sionel, R.; Maciuca, R.; Csutak, O.; Ciobica, M.L.; Nica, M.I.; Chelu, I.; Radu, I.; Toma, M. Gender-Dependent Associations Between Digit Ratio and Genetic Polymorphisms, BMI, and Reproductive Factors. Rom. J. Mil. Med. 2025, 128, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.K.; Rivera-Ramirez, L.E.; Errington, L.W.; Scheper, M.A. Synchronous Paget disease of bone and hyperparathyroidism: Report of a case with extensive craniofacial involvement. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2011, 111, e19–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber-Schoenauer, U.; Cadamuro, J.; Kipman, U.; Stoellinger, E.; Lichtenauer, M.; Paar, V.; Kedenko, L.; Guggenbichler, K.; Paulweber, B.; Pirich, C.; et al. Non-Oxidised Parathyroid Hormone and a Panel of Markers of Calcium-Phosphate Metabolism for Analysis of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism in Selected Patient Groups-A Quality Assurance Project. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilczek, H.; Kanka, J. Coincidence of Paget disease of bone and primary hyperparathyroidism. Sb. Lek. 1993, 94, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Stathopoulos, I.P.; Trovas, G.; Lampropoulou-Adamidou, K.; Benetos, I.S.; Vamvakidis, K.; Vlachodimitropoulos, D.; Chronopoulos, E.; Papaioannou, N.A. Coexistence of paget disease of bone and primary hyperparathyroidism; a diagnostic challenge. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2013, 13, 255–258, quiz 257–258. [Google Scholar]
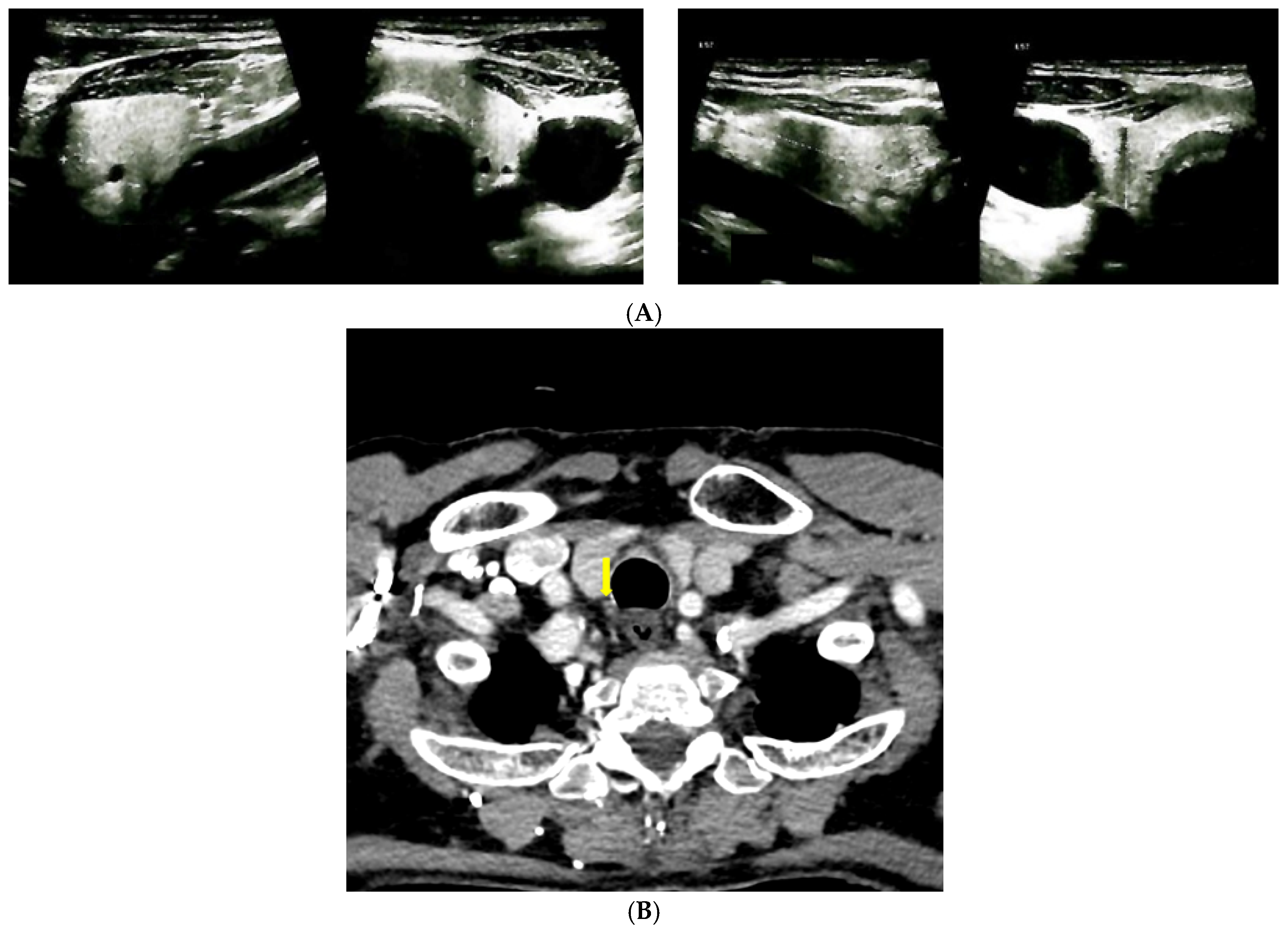
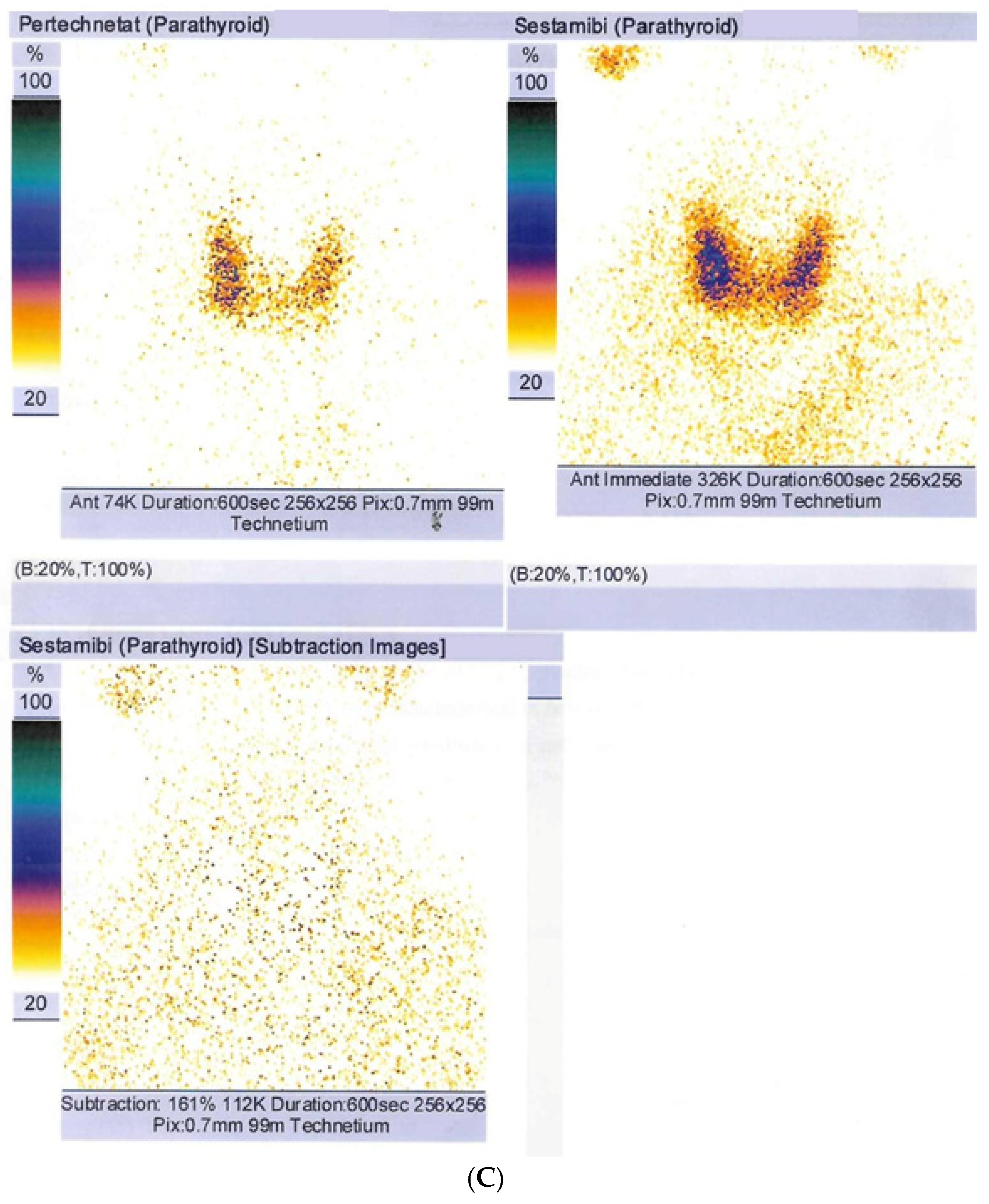
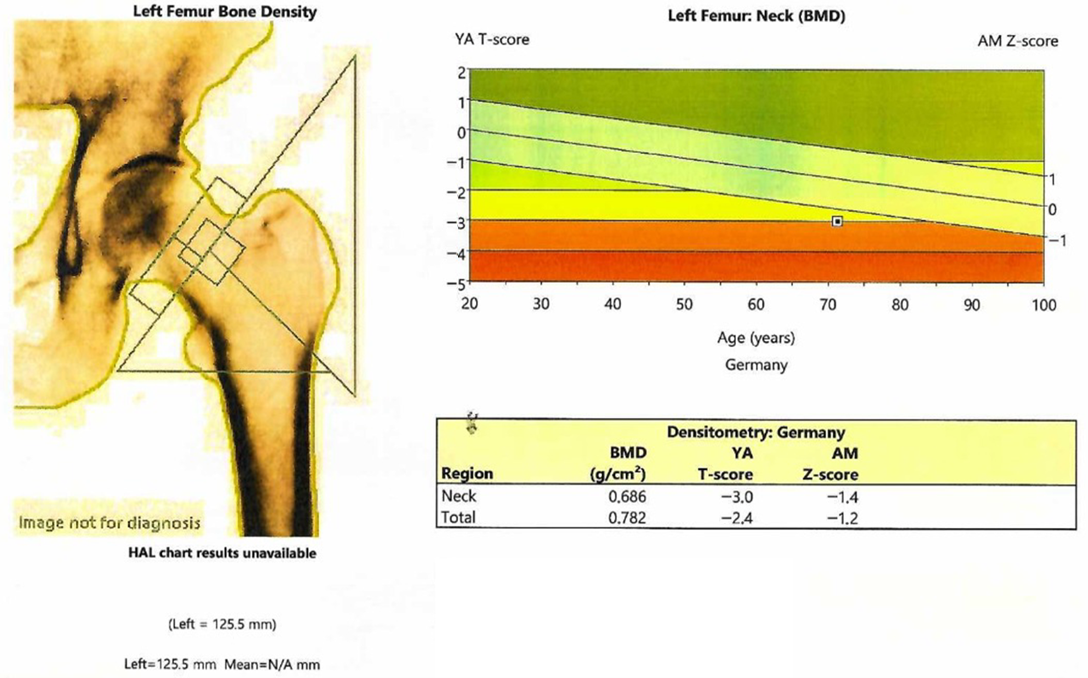
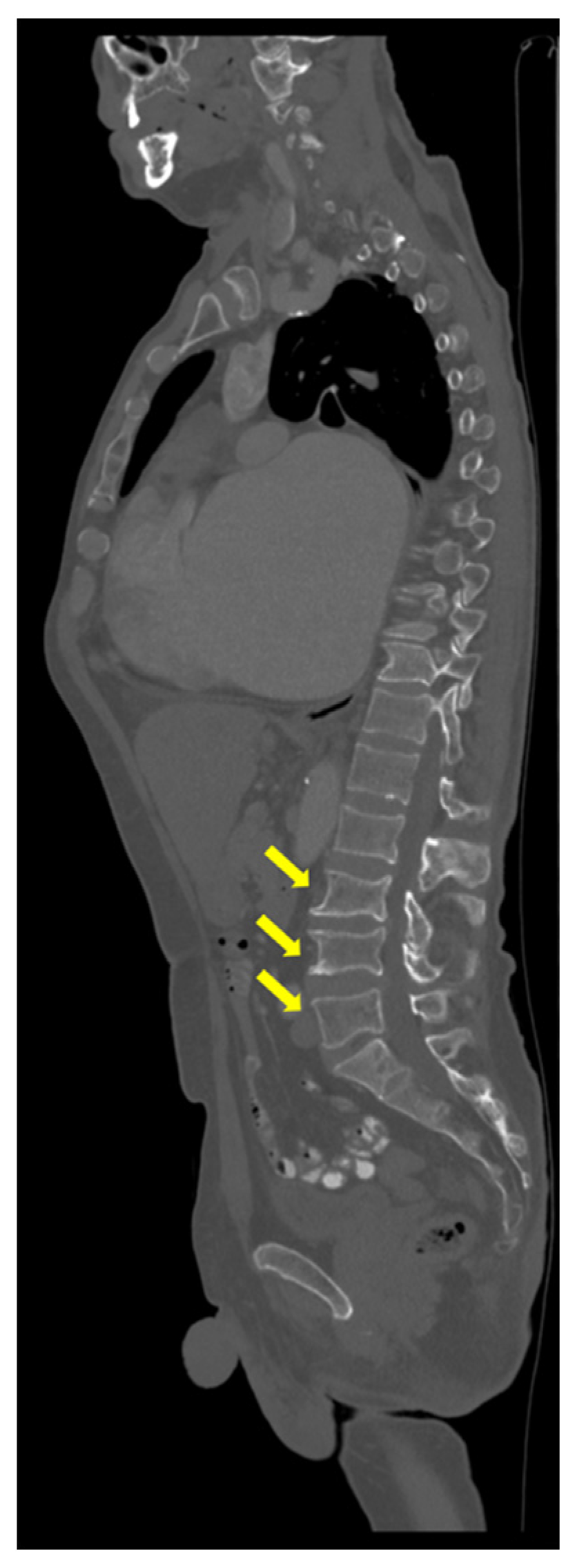
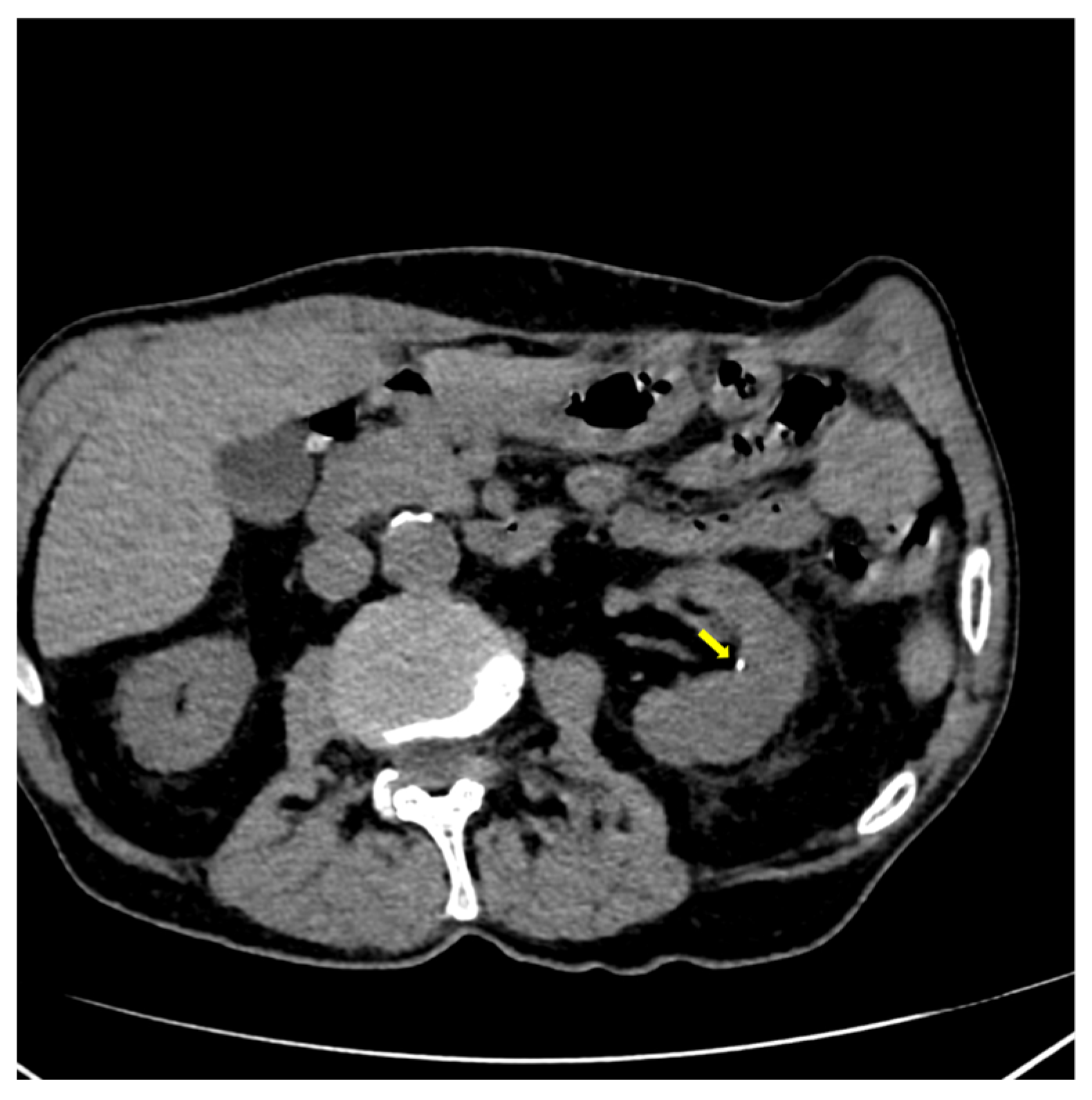

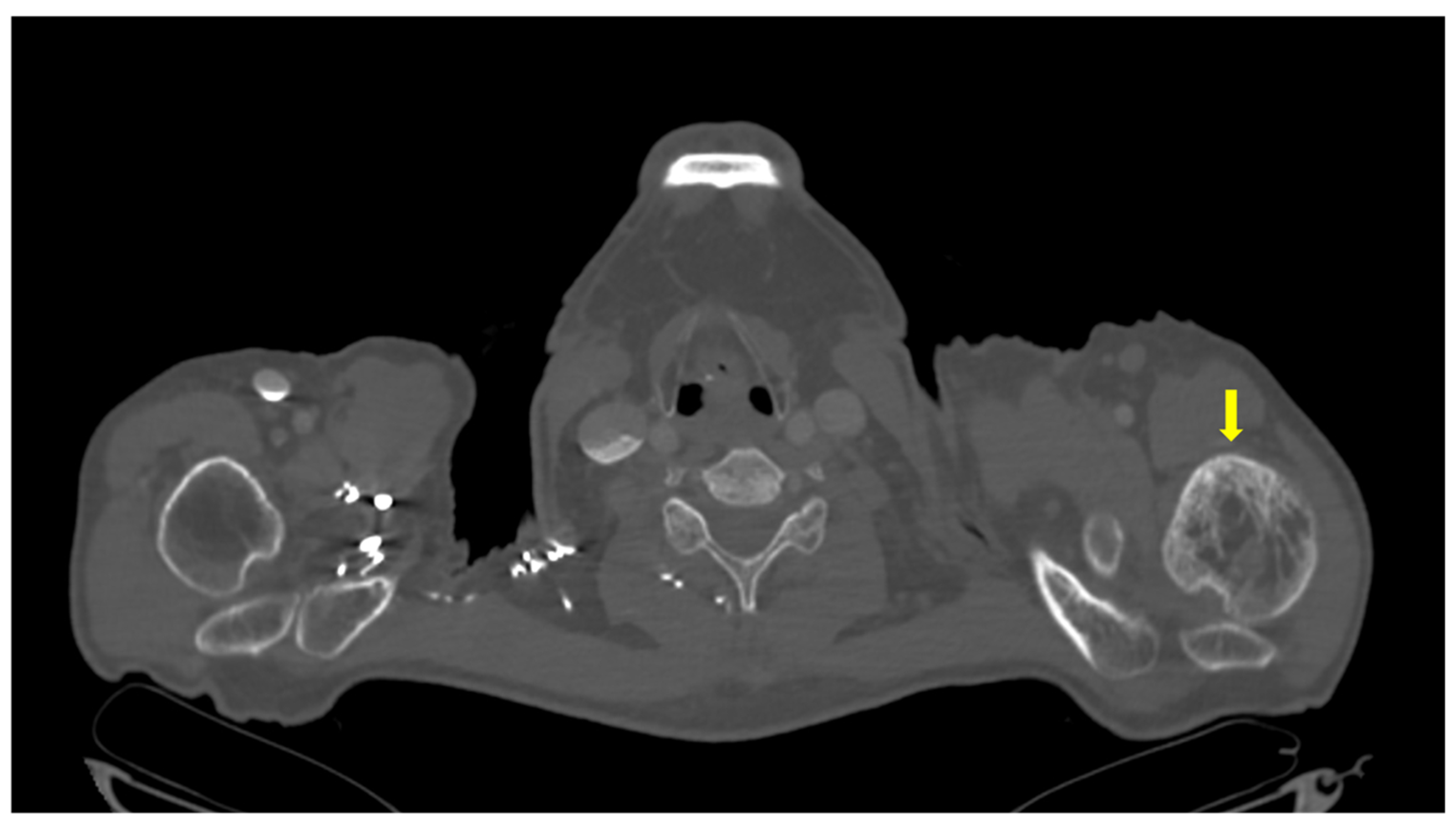
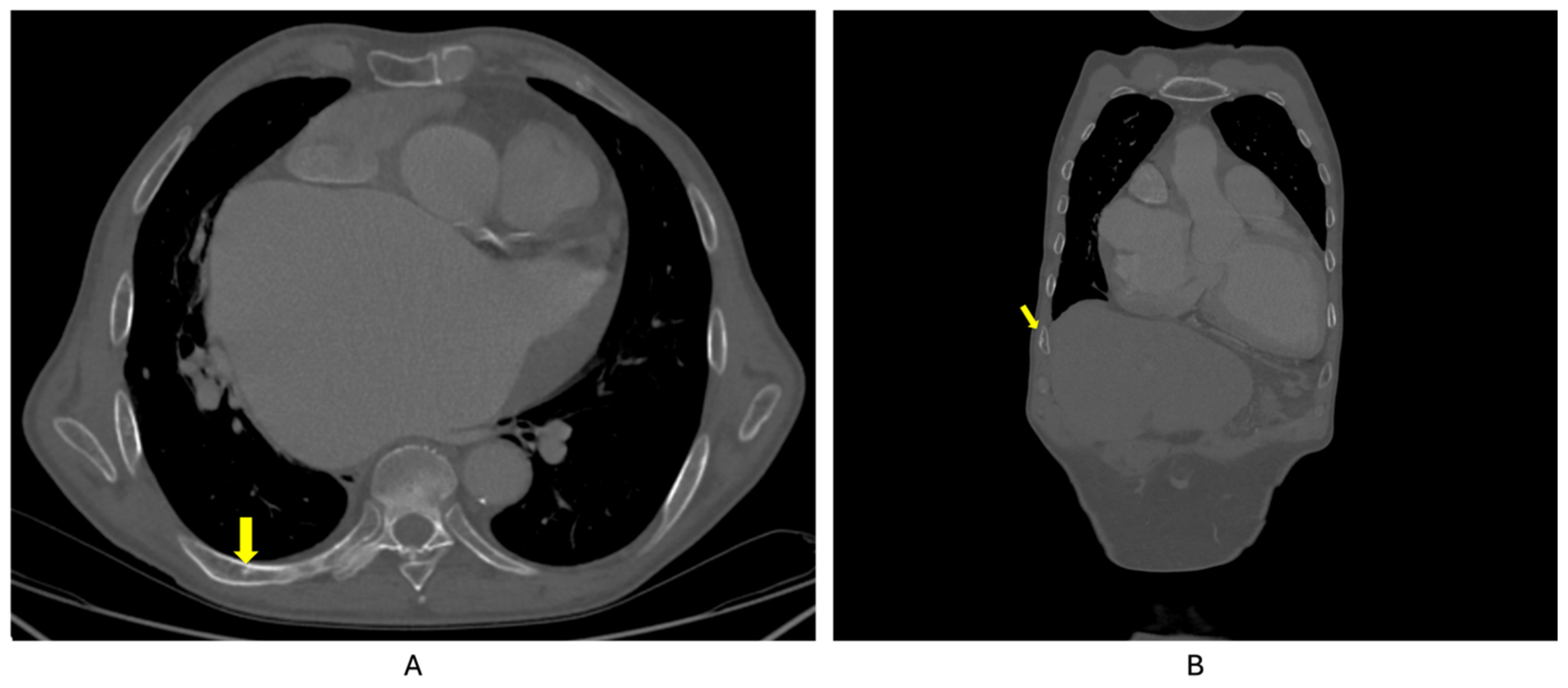
| Parameter (Unit) | Pre-Admission (Within 12 Months) | On Current Admission | Normal Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral Metabolism | |||
| Serum total calcium (mg/dL) | 9.36, repeated 9.79 | 9.3, repeated 8.9 | 8.4–10.2 |
| Serum ionized calcium (mg/dL) *** | 4.11, repeated 3.98 | 3.9–4.9 | |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 3.2, repeated 3.69 | 2.3–4.7 | |
| Total proteins (g/dL) *** | 7, repeated 6.4 | 6.4–8.6 | |
| PTH (pg/mL) | 135.8, repeated 256.6 * | 163.7, repeated 109.4 | 17.3–74.1 |
| 25-hydroxyvitamin D (ng/mL) | 36.61, repeated 48 ** | 36.6 ** | 20–100 |
| 24 h urinary calcium (g/24 h) | 0.07 | 0.07–0.3 | |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 84 | 40–150 | |
| Osteocalcin (ng/mL) | 66.93 | 14–46 | |
| CrossLaps (ng/mL) | 1.72 | 0.118–0.776 | |
| P1NP (ng/mL) | 132.5 | 20.25–76.31 | |
| Non-Mineral Metabolism | |||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.03 | 0.5–1.2 | |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 61 | 18–55 | |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 78 | Normal (Stage 1): >90 | |
| Stage 2: 60–89 | |||
| Stage 3a: 45–59 | |||
| Stage 3b: 30–44 | |||
| Stage 4: 15–29 | |||
| Stage 5: <15 | |||
| Fasting glycaemia (mg/dL) | 99.8 | 74–106 | |
| ALT (U/L) | 23 | 0–55 | |
| AST (U/L) | 23 | 5–34 | |
| TSH (µIU/mL) | 4.09 | 0.35–4.94 | |
| Free T4 (pmol/L) | 14.89 | 9–19 | |
| BMD (g/cm2) | T-Score | Z-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1-L4 Lumbar | 0.882 | −2.9 | −1.8 |
| Femoral neck | 0.686 | −3.0 | −1.4 |
| Total hip | 0.782 | −2.4 | −1.2 |
| Third distal radius | 0.811 | −1.8 | −1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gheorghe, A.-M.; Ionescu, O.P.; Costachescu, M.; Sima, O.-C.; Carsote, M. Paget’s Disease of Bone and Normocalcemic Variant of Primary Hyperparathyroidism in an Osteoporotic Male: Exceptional Coexistence. Reports 2025, 8, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8030180
Gheorghe A-M, Ionescu OP, Costachescu M, Sima O-C, Carsote M. Paget’s Disease of Bone and Normocalcemic Variant of Primary Hyperparathyroidism in an Osteoporotic Male: Exceptional Coexistence. Reports. 2025; 8(3):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8030180
Chicago/Turabian StyleGheorghe, Ana-Maria, Oana Petronela Ionescu, Mihai Costachescu, Oana-Claudia Sima, and Mara Carsote. 2025. "Paget’s Disease of Bone and Normocalcemic Variant of Primary Hyperparathyroidism in an Osteoporotic Male: Exceptional Coexistence" Reports 8, no. 3: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8030180
APA StyleGheorghe, A.-M., Ionescu, O. P., Costachescu, M., Sima, O.-C., & Carsote, M. (2025). Paget’s Disease of Bone and Normocalcemic Variant of Primary Hyperparathyroidism in an Osteoporotic Male: Exceptional Coexistence. Reports, 8(3), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8030180








