A Comparison of Time-Frequency Methods for Real-Time Application to High-Rate Dynamic Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Time-Frequency Response Methods
2.1. Traditional TFR Methods
2.1.1. Short-Time Fourier Transform
2.1.2. Wavelet Transform
2.1.3. Wigner–Ville Distribution
2.2. Time-Frequency Reassignment
2.2.1. Synchrosqueezing Transform
2.2.2. Multi-Synchrosqueezing Transform
3. Methodology
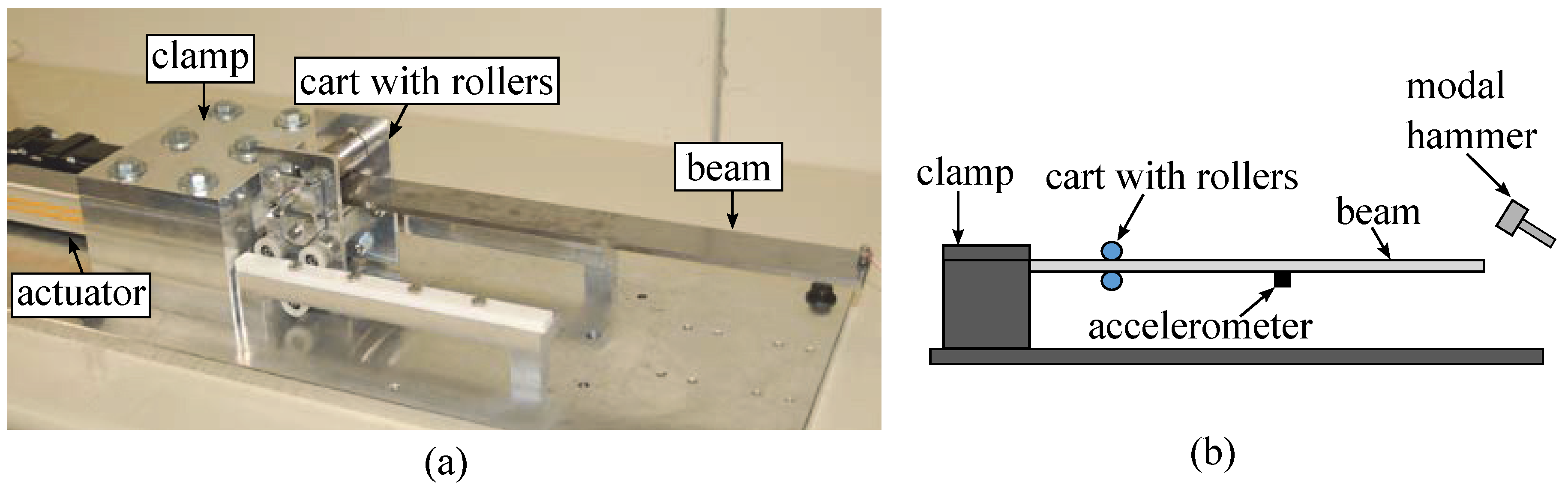
3.1. Experiment Setup
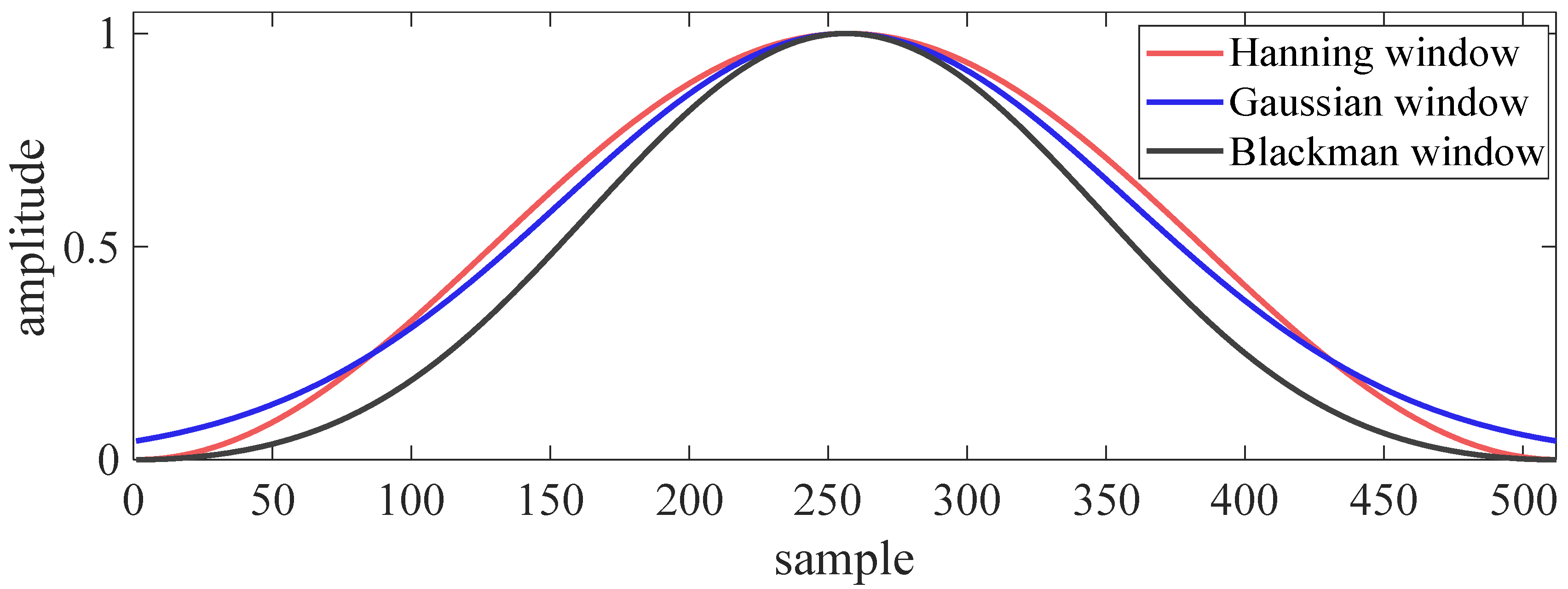
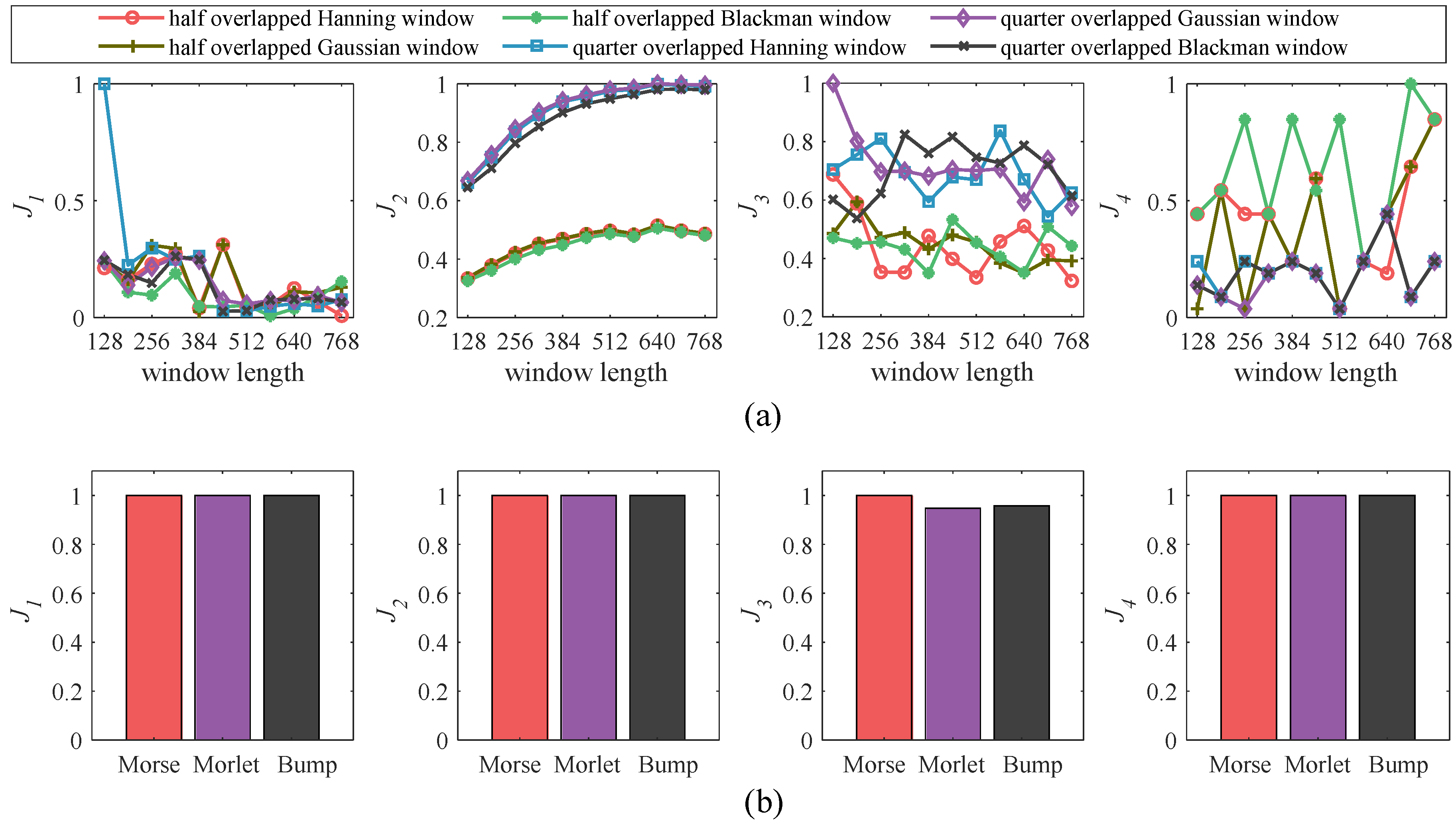
3.2. Performance Analysis
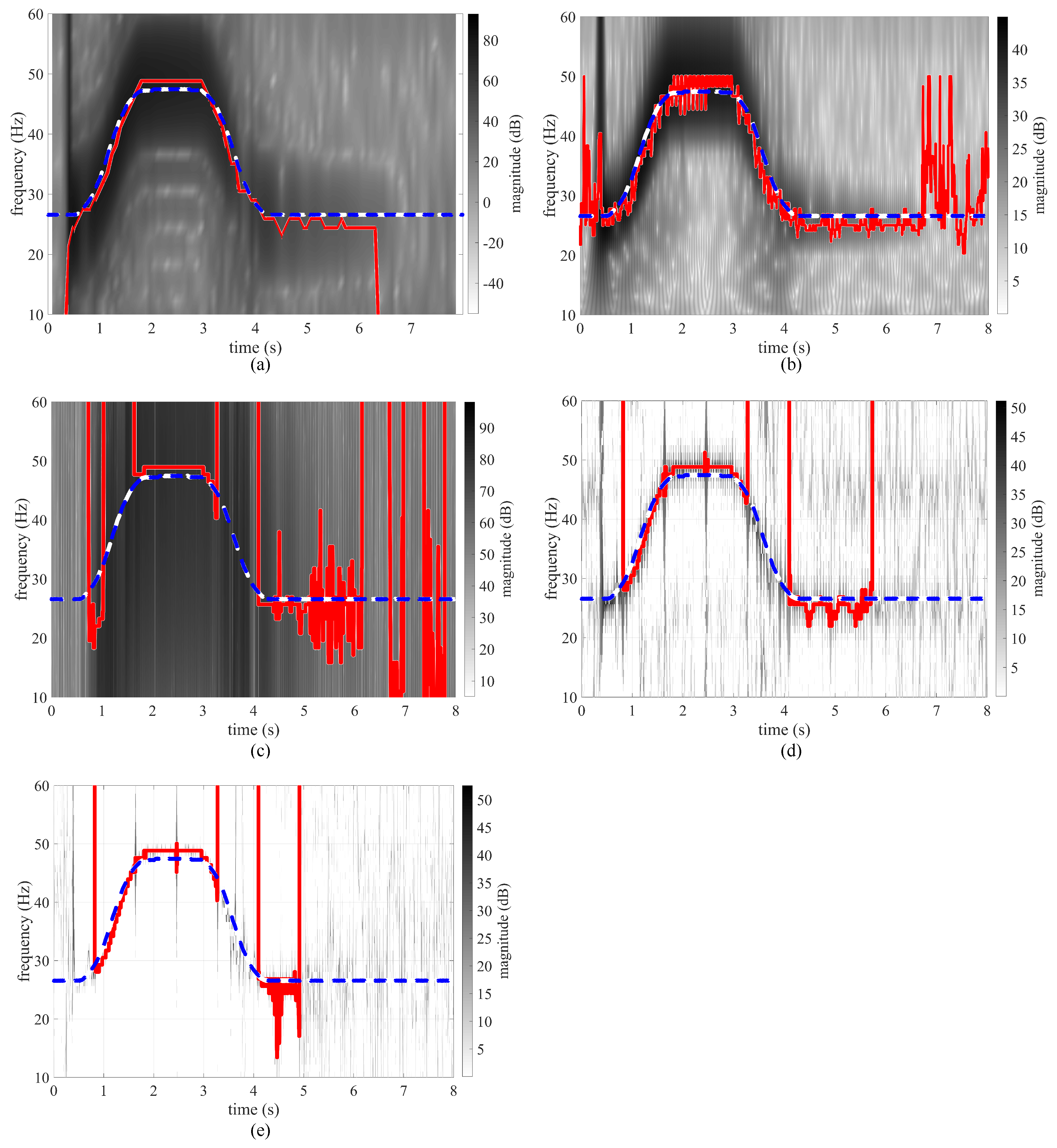
4. Results and Discussion
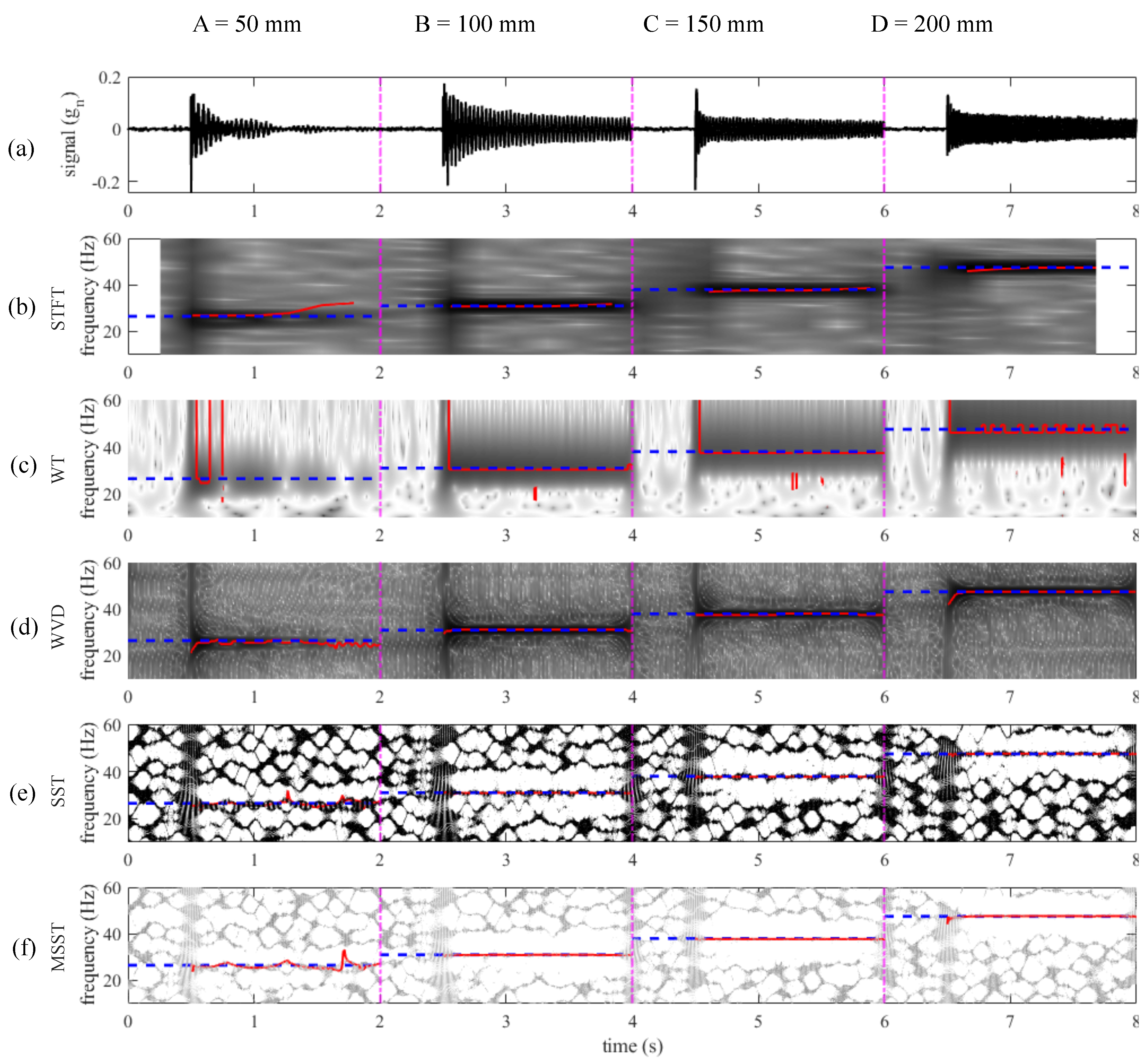
4.1. Fixed Cart Configuration
4.2. Moving Cart Configuration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TFR | Time-frequency representation |
| STFT | Short-time Fourier Transform |
| WT | Wavelet transform |
| WVD | Wigner–Ville distribution |
| SST | Synchrosqueezed transform |
| MSST | Multi-synchrosqueezed transform |
References
- Hong, J.; Laflamme, S.; Dodson, J.; Joyce, B. Introduction to State Estimation of High-Rate System Dynamics. Sensors 2018, 18, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, J.; Joyce, B.; Hong, J.; Laflamme, S.; Wolfson, J. Microsecond State Monitoring of Nonlinear Time-Varying Dynamic Systems. Volume 2: Modeling, Simulation and Control of Adaptive Systems Integrated System Design and Implementation Structural Health Monitoring. Proceedings of the ASME 2017 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, Snowbird, UT, USA, 18–20 September 2017, American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Laflamme, S.; Cao, L.; Dodson, J.; Joyce, B. Variable input observer for nonstationary high-rate dynamic systems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 32, 5015–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Syam, P.; Das, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.K. Review on model reference adaptive system for sensorless vector control of induction motor drives. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2015, 9, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Laflamme, S.; Leifsson, L. Computational Framework for Dense Sensor Network Evaluation Based on Model-Assisted Probability of Detection. Mater. Eval. 2020, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Laflamme, S.; Hong, J.; Dodson, J. Online Parameter Estimation under Non-Persistent Excitations for High-Rate Dynamic Systems. In Review.
- Downey, A.; Hong, J.; Dodson, J.; Carroll, M.; Scheppegrell, J. Millisecond model updating for structures experiencing unmodeled high-rate dynamic events. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 138, 106551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boashash, B. Chapter 15—Time-Frequency Diagnosis, Condition Monitoring, and Fault Detection. In Time-Frequency Signal Analysis and Processing, 2nd ed.; Boashash, B., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 857–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, D.; Pabla, B.S. The Vibration Monitoring Methods and Signal Processing Techniques for Structural Health Monitoring: A Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2015, 23, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörfler, M.; Matusiak, E. Nonstationary Gabor frames-approximately dual frames and reconstruction errors. Adv. Comput. Math. 2015, 41, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul Busch, T.H.; Lahti, P. Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. Phys. Rep. 2007, 452, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Wang, E. Time-frequency analysis of seismic data using synchrosqueezing wavelet transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 2042–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Sadhu, A.; Liu, K. Condition assessment of structure with tuned mass damper using empirical wavelet transform. J. Vib. Control 2017, 24, 4850–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhu, A.; Sony, S.; Friesen, P. Evaluation of progressive damage in structures using tensor decomposition-based wavelet analysis. J. Vib. Control 2019, 25, 2595–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, S.; Chakraborty, A. Sequential clustering of synchrosqueezed wavelet transform coefficients for efficient modal identification. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 9, 271–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, P. Multisynchrosqueezing Transform. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 5441–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudan, M.; Vogel, C. Correction Structures for Linear Weakly Time-Varying Systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2012, 59, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.H.; Meignen, S. High-Order Synchrosqueezing Transform for Multicomponent Signals Analysis—With an Application to Gravitational-Wave Signal. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 3168–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, B.; Dodson, J.; Laflamme, S.; Hong, J. An Experimental Test Bed for Developing High-Rate Structural Health Monitoring Methods. Shock Vib. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabor, D. Theory of communication. Part 1: The analysis of information. J. Inst. Electr.-Eng.-Part III Radio Commun. Eng. 1946, 93, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Liang, M.; Chu, F. Recent advances in time–frequency analysis methods for machinery fault diagnosis: A review with application examples. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 38, 165–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S. A wavelet tour of signal processing. In The Sparse Way; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Flandrin, P. Time-Frequency/Time-Scale Analysis; Academic press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Boashash, B.; Black, P. An efficient real-time implementation of the Wigner–Ville distribution. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1987, 35, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, S.C. Time-Frequency Analysis of Systems with Changing Dynamic Properties; Earthquake Engineering Research Laboratory: Reno, NV, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, G. The Synchrosqueezing transform for instantaneous spectral analysis. In Excursions in Harmonic Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 4, pp. 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewins, D.J. Modal Testing: Theory, Practice, and Application; Research Studies Press: Letchworth, UK; Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Chen, J.; Dong, G. Chirplet Wigner–Ville distribution for time–frequency representation and its application. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 41, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olhede, S.; Walden, A. Generalized Morse wavelets. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 2661–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cai, H.; Jiang, Q. Adaptive synchrosqueezing transform with a time-varying parameter for non-stationary signal separation. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2020, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatsenko, D.; McClintock, P.; Stefanovska, A. Extraction of instantaneous frequencies from ridges in time–frequency representations of signals. Signal Process. 2016, 125, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| TFR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | (Hz) | () | (ms) | (ms) |
| STFT | 0.384 | 0.012 | 6.9 | 286 |
| WT | 0.729 | 0.0220 | 242 | 44 |
| WVD | 0.316 | 0.0573 | 1093 | 51 |
| SST | 0.095 | 1 | 10,505 | 1 |
| MSST | 0.155 | 0.6667 | 12,236 | 1 |
| TFR | Window | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | (Hz) | (ms) | (ms) |
| STFT | 0.54 | 3.8 | 82 |
| WT | 0.56 | 9.3 | 82 |
| WVD | 1.88 | 262 | 819 |
| SST | 0.91 | 288 | 819 |
| MSST | 0.66 | 543 | 819 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, J.; Laflamme, S.; Singh, P.; Sadhu, A.; Dodson, J. A Comparison of Time-Frequency Methods for Real-Time Application to High-Rate Dynamic Systems. Vibration 2020, 3, 204-216. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration3030016
Yan J, Laflamme S, Singh P, Sadhu A, Dodson J. A Comparison of Time-Frequency Methods for Real-Time Application to High-Rate Dynamic Systems. Vibration. 2020; 3(3):204-216. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration3030016
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Jin, Simon Laflamme, Premjeet Singh, Ayan Sadhu, and Jacob Dodson. 2020. "A Comparison of Time-Frequency Methods for Real-Time Application to High-Rate Dynamic Systems" Vibration 3, no. 3: 204-216. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration3030016
APA StyleYan, J., Laflamme, S., Singh, P., Sadhu, A., & Dodson, J. (2020). A Comparison of Time-Frequency Methods for Real-Time Application to High-Rate Dynamic Systems. Vibration, 3(3), 204-216. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration3030016







