Influence of Earthquake Rotational Components on the Seismic Safety of Steel Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
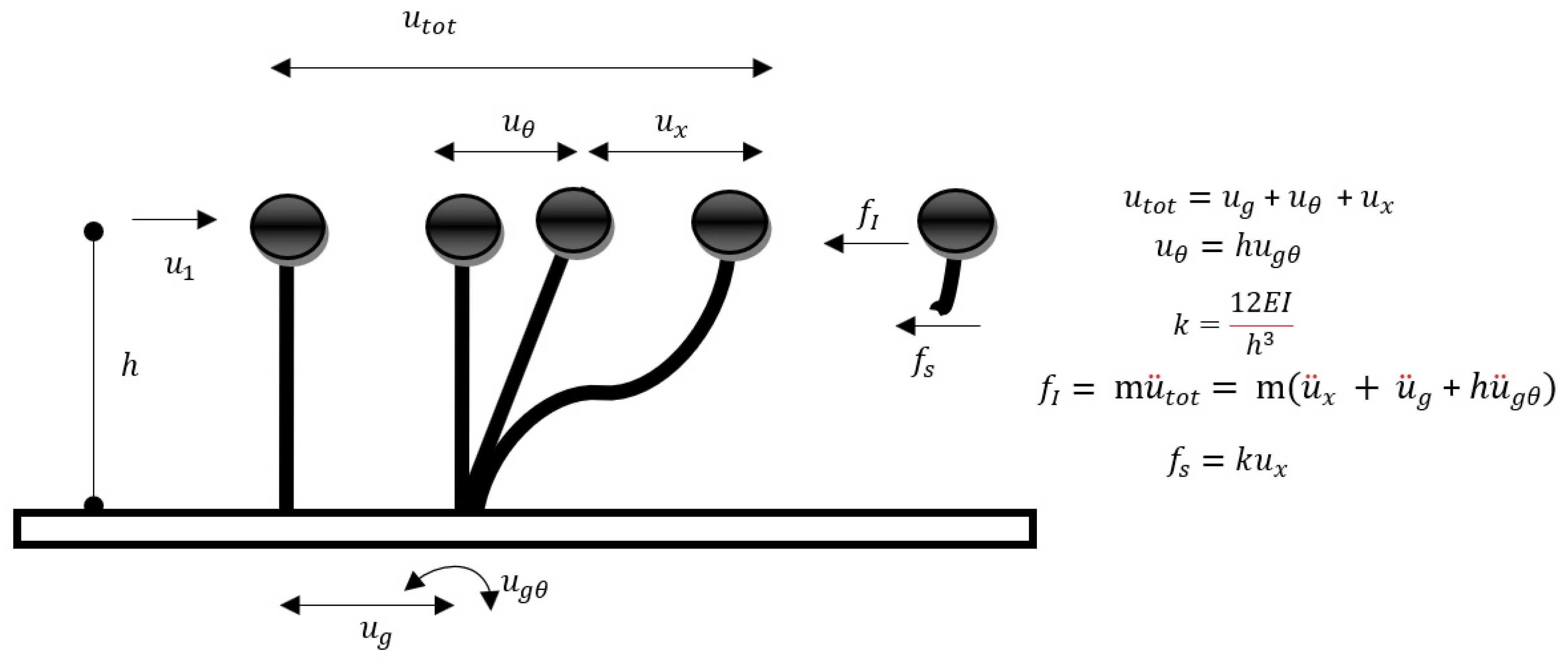
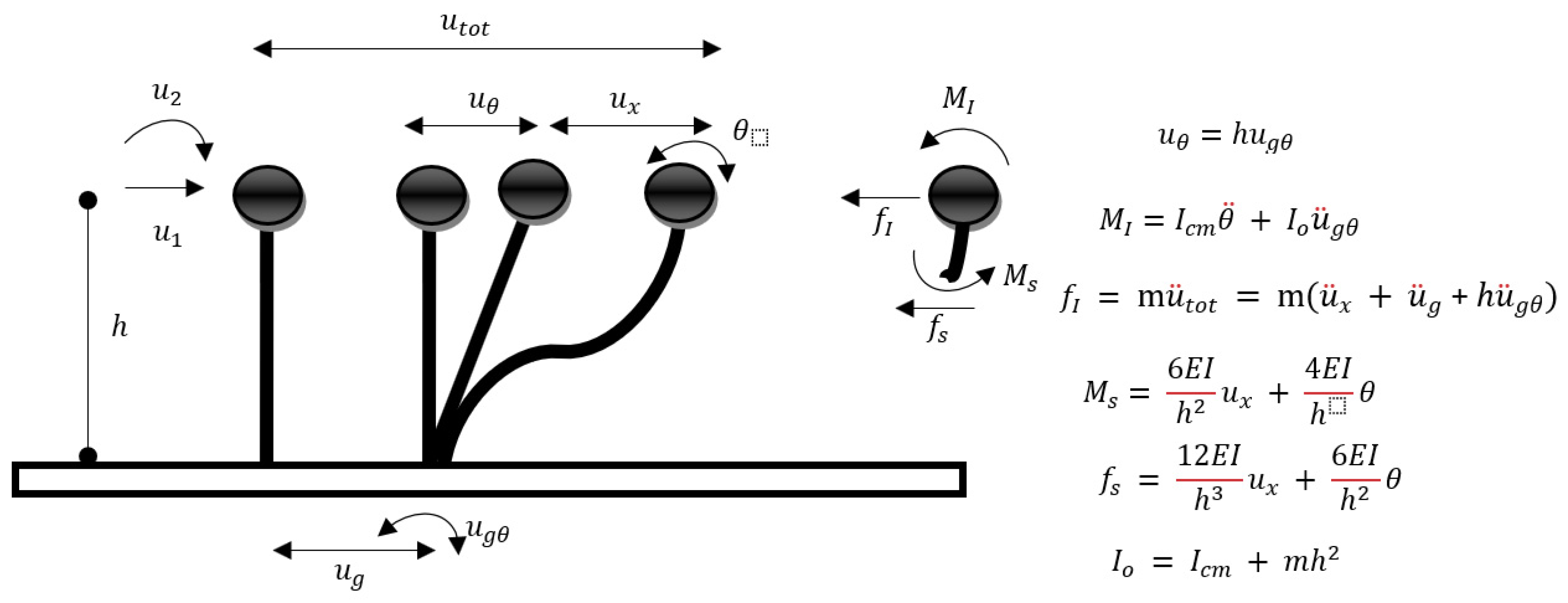
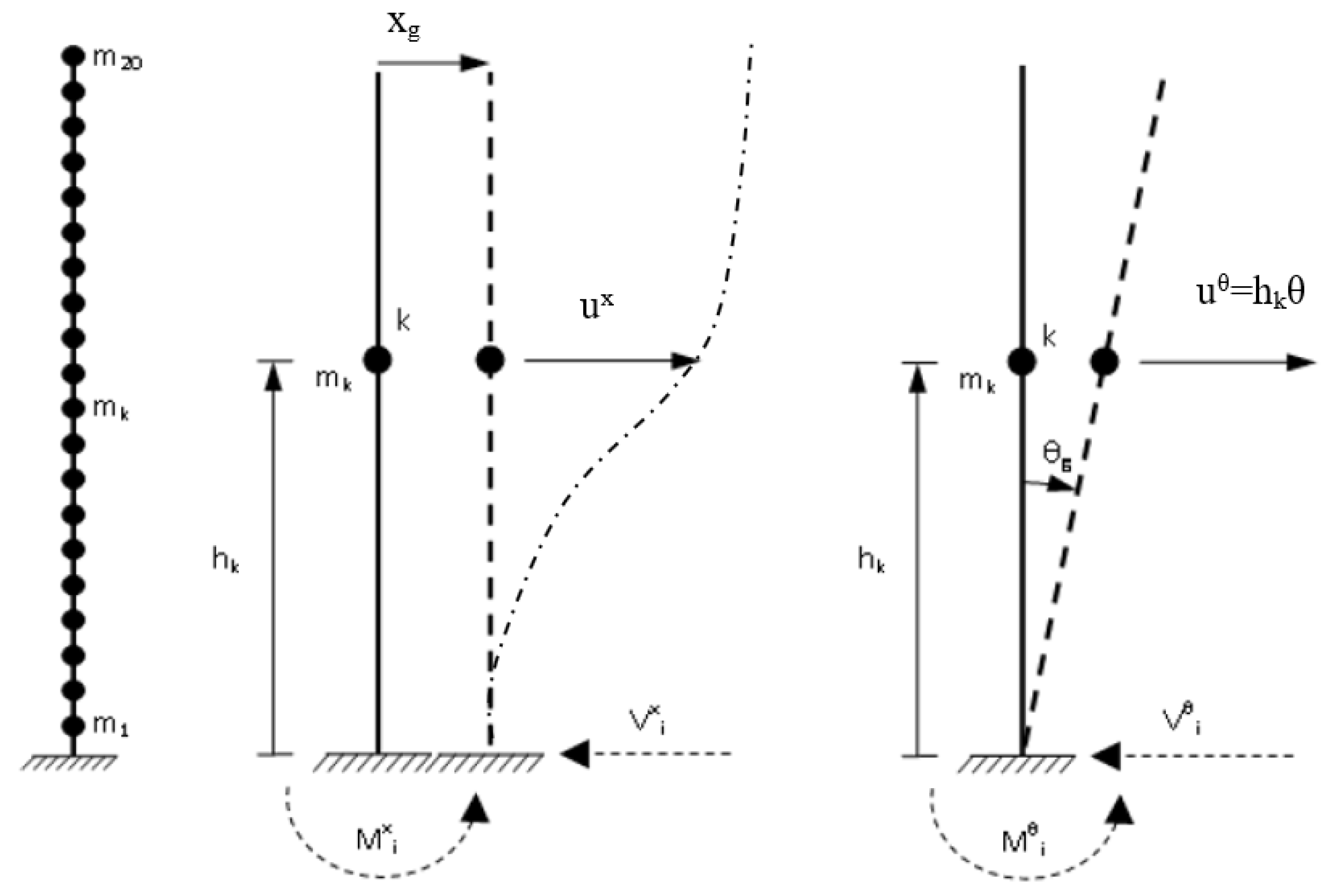
2. Theoretical Background
- {}:
- is the vector comprising the accelerations of the degrees of freedom of the structure relative to the base,
- {}:
- is the vector comprising the velocities of the degrees of freedom of the structure,
- {}:
- is the vector comprising the displacements of the degrees of freedom relative to the base,
- {m}:
- is the vector comprising the translational masses in the horizontal direction of the translational excitation. This vector coincides with the main diagonal of the mass matrix (M), if the vector {u} includes only the translational displacements in the horizontal direction of the excitation,
- g(t):
- is the translational ground acceleration,
- g(t):
- is the rotational acceleration at the base.
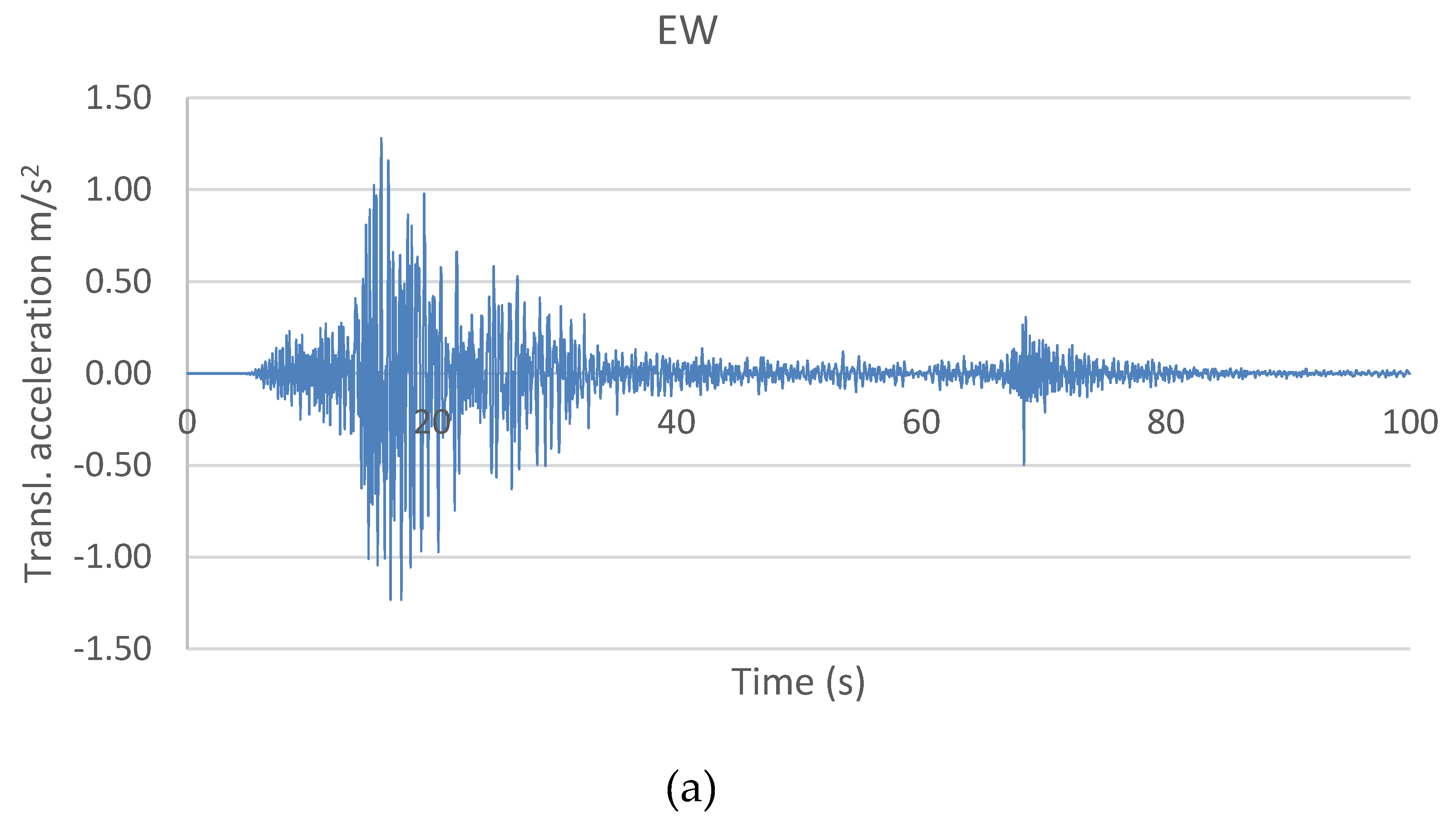
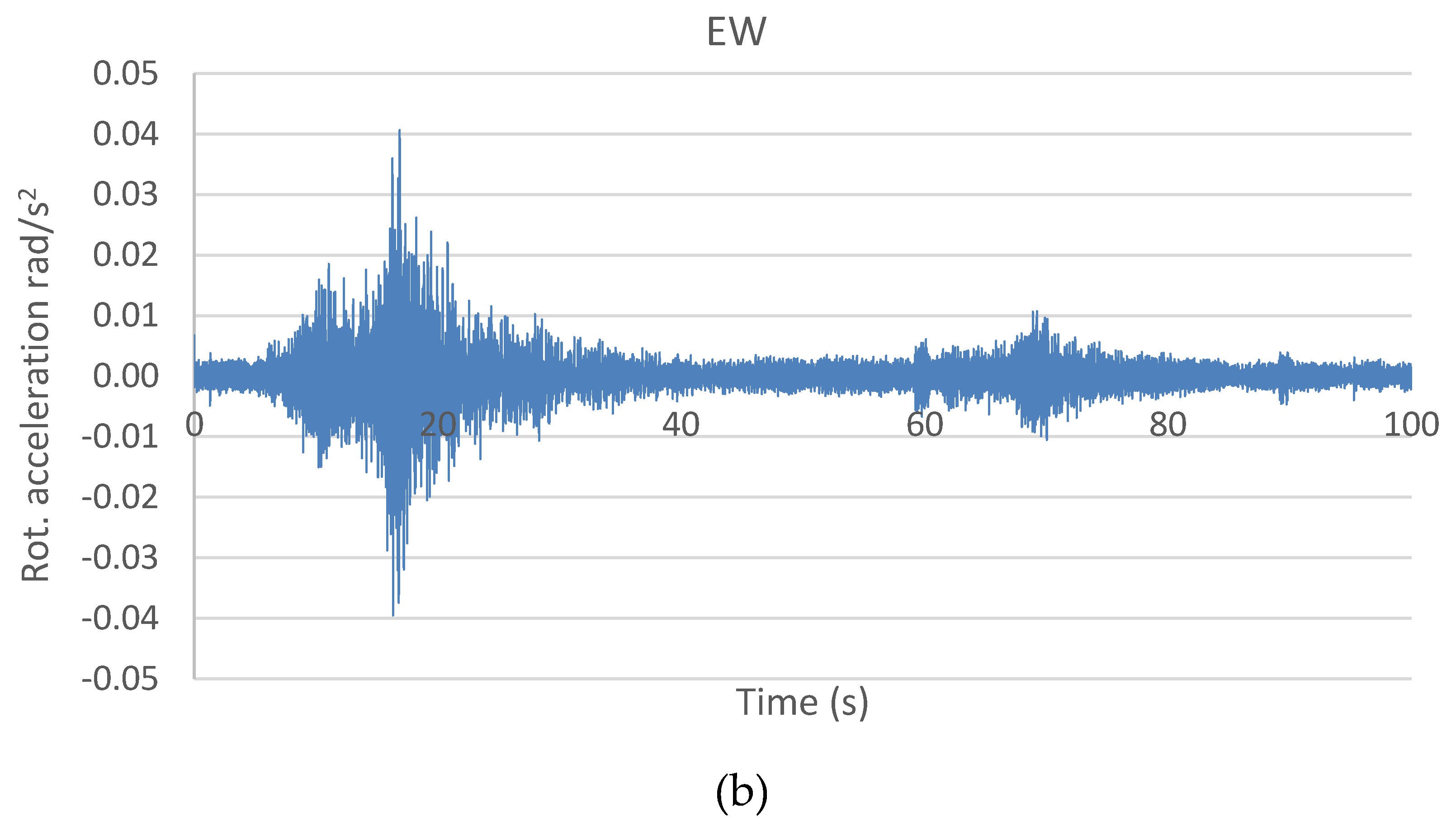
3. Case Studies, Numerical Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Droste, Z.; Teisseyre, R. Rotational and displacement components of ground motion as deduced from data of the azimuth system of seismographs. Publ. Inst. Geophys. Pol. Acad. Sci. 1976, 97, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Takeo, M. Rotational motions observed during an earthquake swarm in April 1998 off-shore Ito, Japan. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2009, 99, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igel, H.; Brokesova, J.; Evans, J.; Zembaty, Z. Advances in rotational seismology: Instrumentation, theory, observations, and engineering. J. Seismol. 2012, 16, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Huang, B.S.; Lee, W.H.K.; Lin, C.-J. Observing rotational and translational ground motions at the HGSD station in Taiwan from 2007 to 2008. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2009, 99, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassermann, J.; Lehndorfer, S.; Igel, H.; Schreiber, U. Performance test of a commercial rotational motions sensor. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2009, 99, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.W.; Trifunac, M.D. Rocking strong earthquake accelerations. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 1987, 6, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, A.; Boffi, G. On the rotational components of seismic motion. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1989, 18, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-N.; Sun, L.-Y.; Wang, S.-Y. Improved approach for obtaining rotational components of seismic motion. Nucl Eng. Des. 2004, 232, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Whittaker, A.S.; Constantinou, M.C. On estimating rotational components on ground motion using data recorded at a single station. J. Eng. Mech. ASCE 2012, 138, 1141–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, M. Inferred displacements, velocities and rotations of a long rigidy site during the 1979 Imperial Valley, California, earthquake. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1986, 14, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spudich, P.; Steck, L.K.; Hellweg, M.; Fletcher, J.B.; Baker, L. Transient stress at Parkfield, California, produced by the M 7.4 Landers earthquake of June 28, 1992: Observations from the UPSAR dense seismograph array. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spudich, P.; Fletcher, J.B. Observation and prediction of dynamic ground strains, tilts, and torsions caused by the Mw 6.0 2004 Parkfield, California, earthquake and aftershocks, derived from UPSAR array observations. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2008, 98, 1898–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Whittaker, A.S.; Constantinou, M.C. Extracting rotational components of using data recorded at multiple stations. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2013, 42, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Whittaker, A.S.; Constantinou, M.C. Characterizing rotational components of earthquake ground motion using a surface distribution method and response of sample structures. Eng. Struct. 2015, 99, 685–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falamarz-Sheikhabadi, M.R.; Zerva, A.; Ghafory-Ashtiany, M. Revised Seismic Intensity Parameters for Middle-Field Horizontal and Rocking Strong Ground Motions. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falamarz-Sheikhabadi, M.R. Simplified relations for the application of rotational components to seismic design codes. Eng. Struct. 2014, 59, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbaa, S.; Hollender, F.; Perron, V.; Imtiaz, A.; Bard, P.; Mariscal, A.; Cochard, A.; Dujardin, A. Analysis of rotation sensor data from the SINAPS@ Kefalonia (Greece) post-seismic experiment—Link to surface geology and wavefield characteristics. Earth Planets Space 2017, 69, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perron, V.; Hollender, F.; Mariscal, A.; Theodoulidis, N.; Andreou, C.; Bard, P.; Cornou, C.; Cottereau, R.; Cushing, E.M.; Frau, A.; et al. Accelerometer, Velocimeter Dense-Array, and Rotation Sensor Datasets from the Sinaps@ Postseismic Survey (Cephalonia 2014–2015 Aftershock Sequence). Seismol. Res. Lett. 2018, 89, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1998-6. Eurocode 8: Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance—Part 6: Towers, Masts and Chimneys; Brussels, Belgium. 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, J.P.; Obernhueber, P.; Weber, B. Response of a nuclear plant on aseismic bearings to horizontally propagating waves. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1983, 11, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politopoulos, I. Response of seismically isolated structures to rocking-type actions. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2010, 39, 325–342. [Google Scholar]
- Bonev, Z.; Blagov, D.; Vaseva, E.; Mladenov, K. Accounting the rotational component of Seismic action on towers, masts and chimneys according to BDS EN 1998-6. International conference UACG-2009: Science and Practice. Fascicule VIII 2009, XLIV, 185–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zembaty, Z. Rotational seismic code definition in Eurocode 8, Part 6, for slender tower-shaped structures. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2009, 99, 1483–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zembatyy, Z.; Boffi, G. Effect of rotational seismic ground motion on dynamic response of slender towers. Eur. Earthq. Eng. 1994, 8, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zembaty, Z.; Mutke, G.; Nawrocki, D.; Bobra, P. Rotational ground-motion records from induced seismic events. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2017, 88, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falamarz-Sheikhabadi, M.R.; Ghafory-Ashtiany, M. Rotational components in structural loading. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2015, 75, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falamarz-Sheikhabadi, M.R.; Zerva, A.; Ghafory-Ashtiany, M. Mean absolute input energy for in-plane vibrations of multiple-support structures subjected to horizontal and rocking components. J. Probab. Eng. Mech. 2016, 45, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Constantinou, M.C.; Whittaker, A.S. An equivalent accidental eccentricity to account for the effects of torsional ground motion on structures. Eng. Struct. 2014, 69, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-La-Llera, J.C.; Chopra, A.K. Accidental torsion in buildings due to base rotational excitation. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1994, 23, 1003–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Nigbor, R.L.; Chen, Q.; Steidl, J. Engineering analysis of measured rotational ground motions at GVDA. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2016, 87, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pnevmatikos, N.G.; Papavasileiou, G.S.; Konstandakopoulou, F.D.; Papagiannopoulos, G.A. Influence of Rotational Component of Earthquake Excitation to the Response of Steel Slender Frame. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Freienbach, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 968, pp. 294–300. [Google Scholar]
- Pnevmatikos, N.G.; Papavasileiou, G.S.; Konstandakopoulou, F.D.; Papagiannopoulos, G.A. Analysis of a steel structure considering the rotational and translational components of the earthquake excitation. In Proceedings of the 4th Hellenic National Conference on Earthquake Engineering and Technical Seismology, Athens, Greece, 5–7 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, A. Dynamics of structures. In Theory and Application to Earthquake Engineering, 3rd ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Bergen, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- SAP2000, Computers and Structures, Inc. Linear and Nonlinear, Static and Dynamic Analysis and Design of Three-Dimensional Structures; Computers and Structures, Inc.: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
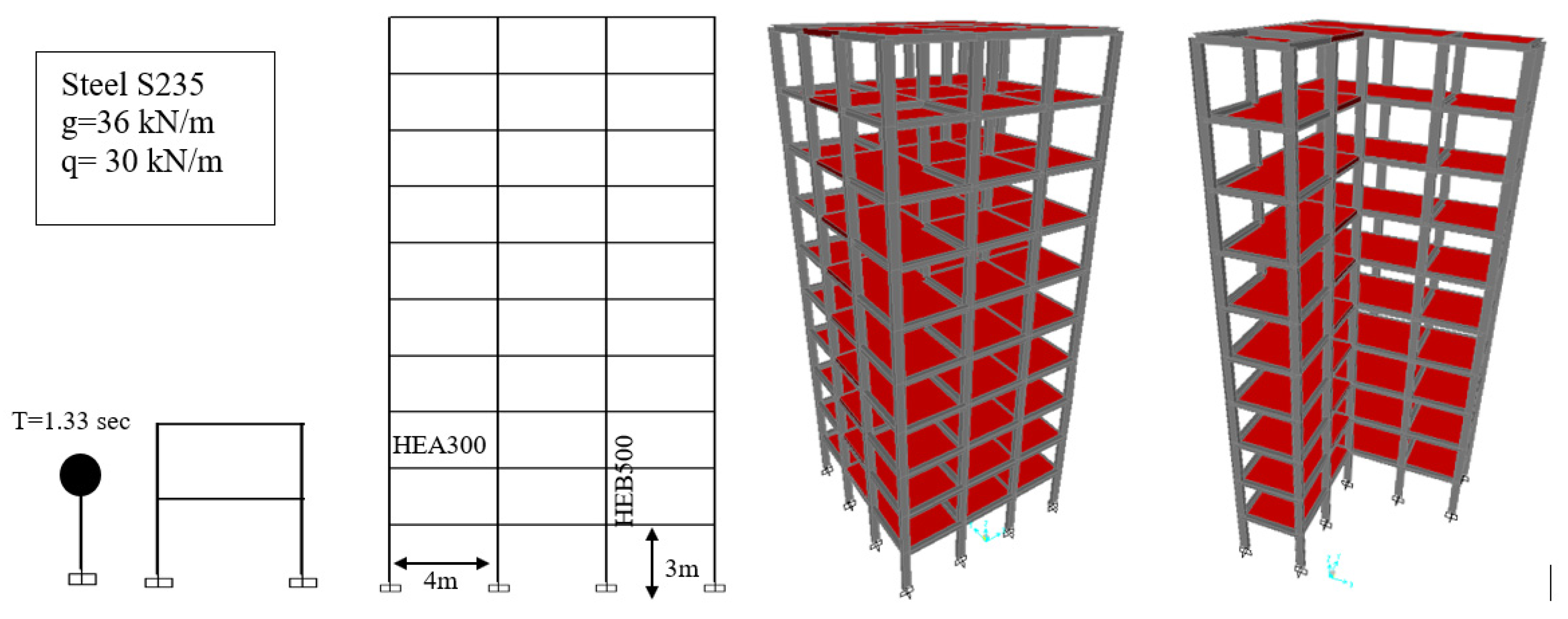
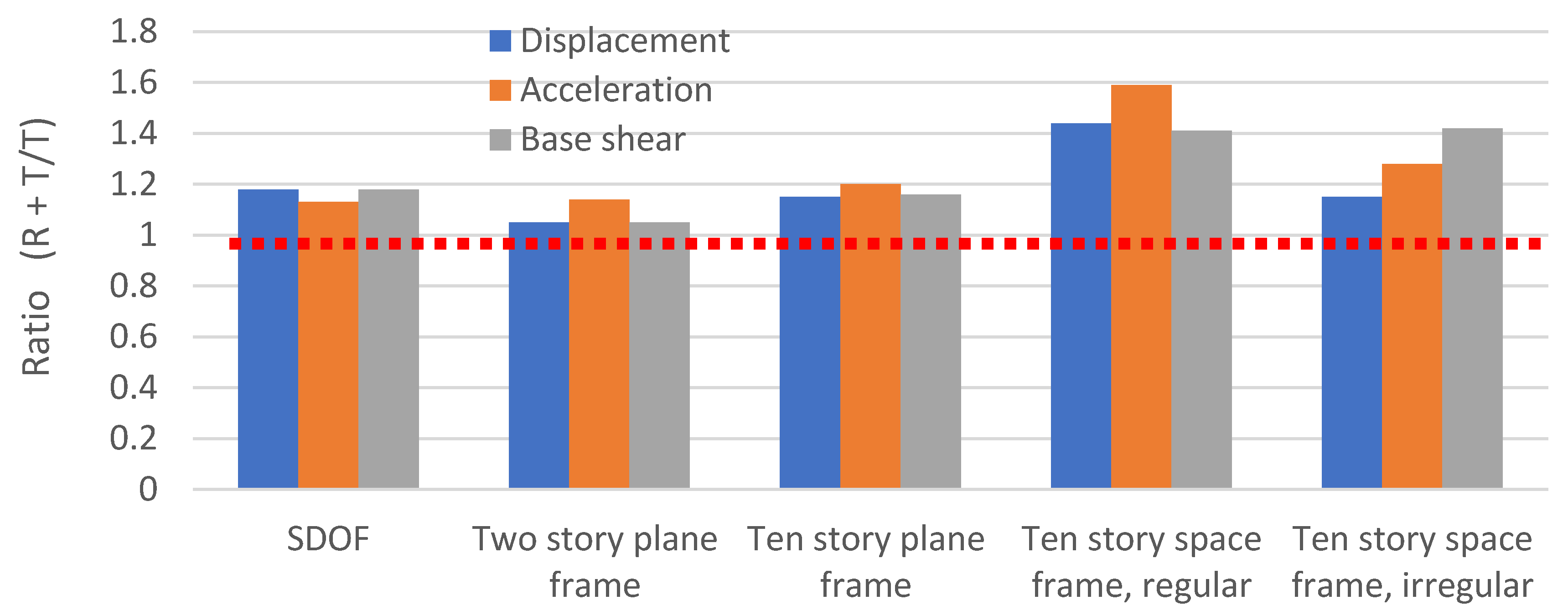
| Structural Model | Response | Top Displacement (cm) | Top Acceleration (m/sec2) | Base Shear (kN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDOF (T = 1.5 sec) | 1.18 | 1.13 | 1.18 | |
| Two-storey plane frame | 1.05 | 1.14 | 1.05 | |
| Ten-storey plane frame (T1 = 1.5 sec) | 1.15 | 1.20 | 1.16 | |
| Ten-storey space frame, regular | EW | 1.45 | 1.58 | 1.42 |
| NS | 1.30 | 1.40 | 1.45 | |
| ALL (6 DOF) | 1.44 | 1.59 | 1.41 | |
| Ten-storey space frame, irregular | EW | 1.24 | 1.39 | 1.36 |
| NS | 1.39 | 1.56 | 1.48 | |
| ALL (6 DOF) | 1.15 | 1.28 | 1.42 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pnevmatikos, N.; Konstandakopoulou, F.; Papagiannopoulos, G.; Hatzigeorgiou, G.; Papavasileiou, G. Influence of Earthquake Rotational Components on the Seismic Safety of Steel Structures. Vibration 2020, 3, 42-50. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration3010005
Pnevmatikos N, Konstandakopoulou F, Papagiannopoulos G, Hatzigeorgiou G, Papavasileiou G. Influence of Earthquake Rotational Components on the Seismic Safety of Steel Structures. Vibration. 2020; 3(1):42-50. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration3010005
Chicago/Turabian StylePnevmatikos, Nikos, Foteini Konstandakopoulou, George Papagiannopoulos, George Hatzigeorgiou, and Georgios Papavasileiou. 2020. "Influence of Earthquake Rotational Components on the Seismic Safety of Steel Structures" Vibration 3, no. 1: 42-50. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration3010005
APA StylePnevmatikos, N., Konstandakopoulou, F., Papagiannopoulos, G., Hatzigeorgiou, G., & Papavasileiou, G. (2020). Influence of Earthquake Rotational Components on the Seismic Safety of Steel Structures. Vibration, 3(1), 42-50. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration3010005









