Evaluation of Shock Detection Algorithm for Road Vehicle Vibration Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. RVV Analysis Methods
2.1. Machine Learning Algorithms
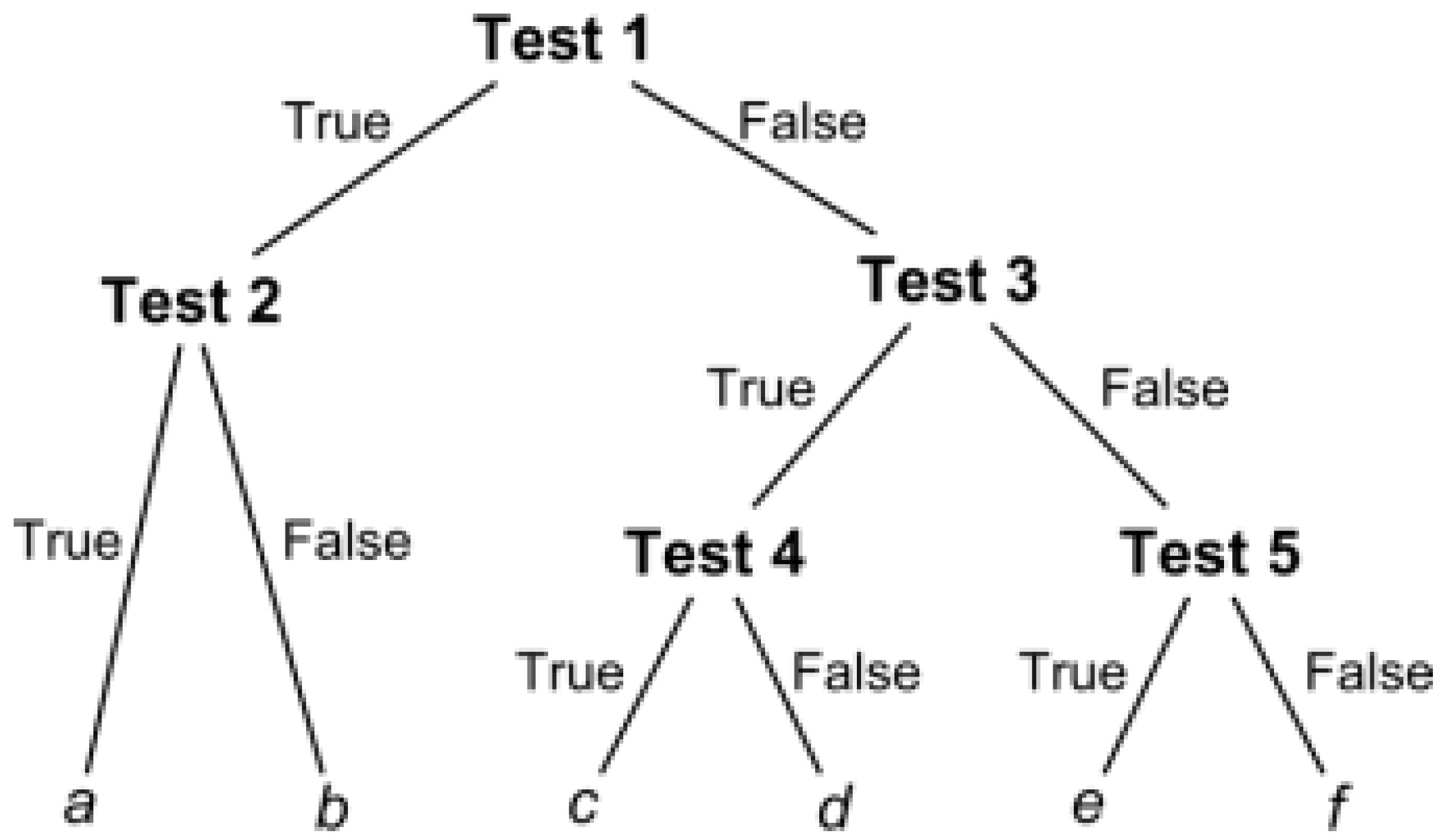
2.1.1. Decision Tree
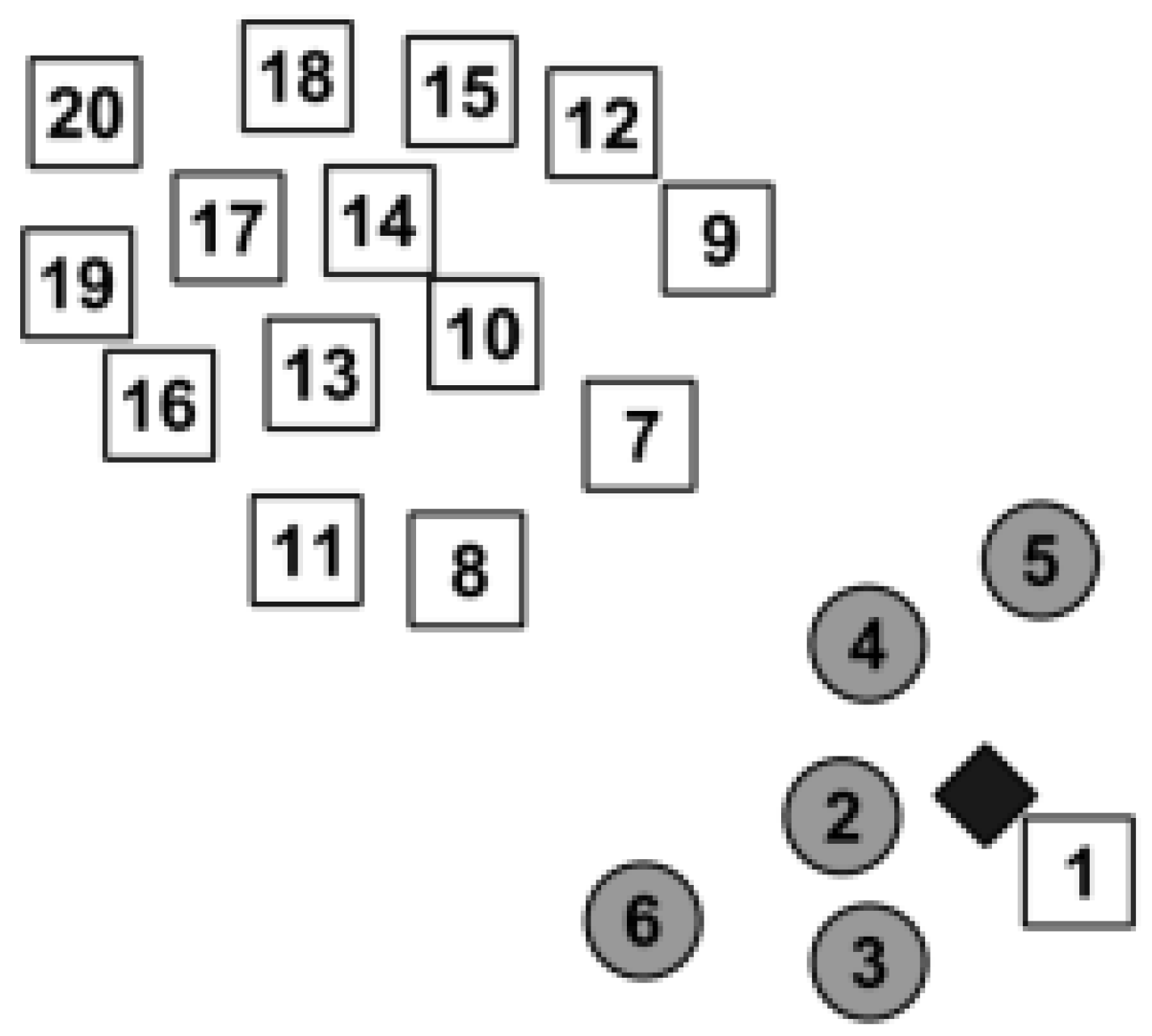
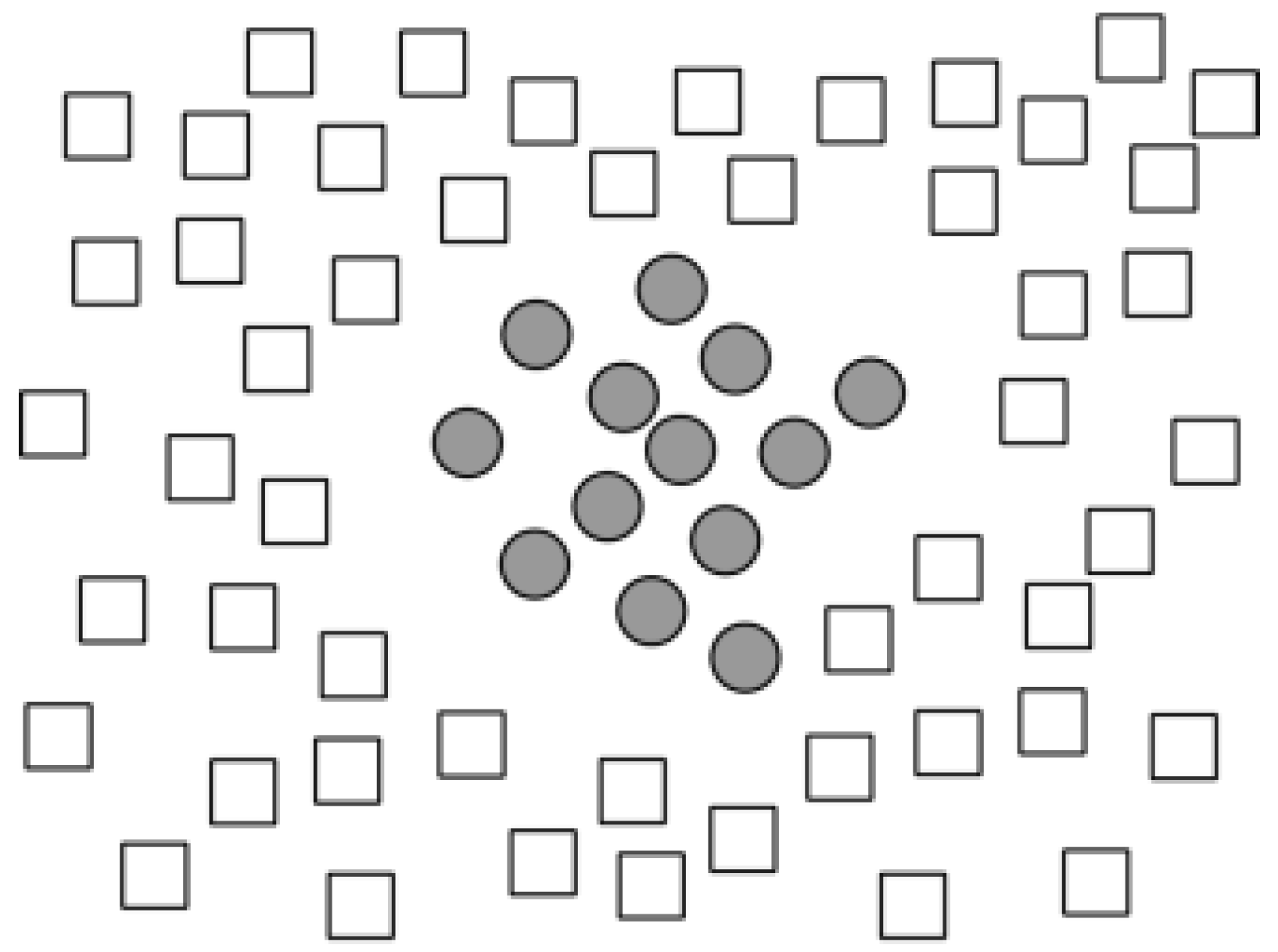
2.1.2. k-Nearest Neighbors
2.1.3. Bagged Ensemble
2.1.4. Support Vector Machine
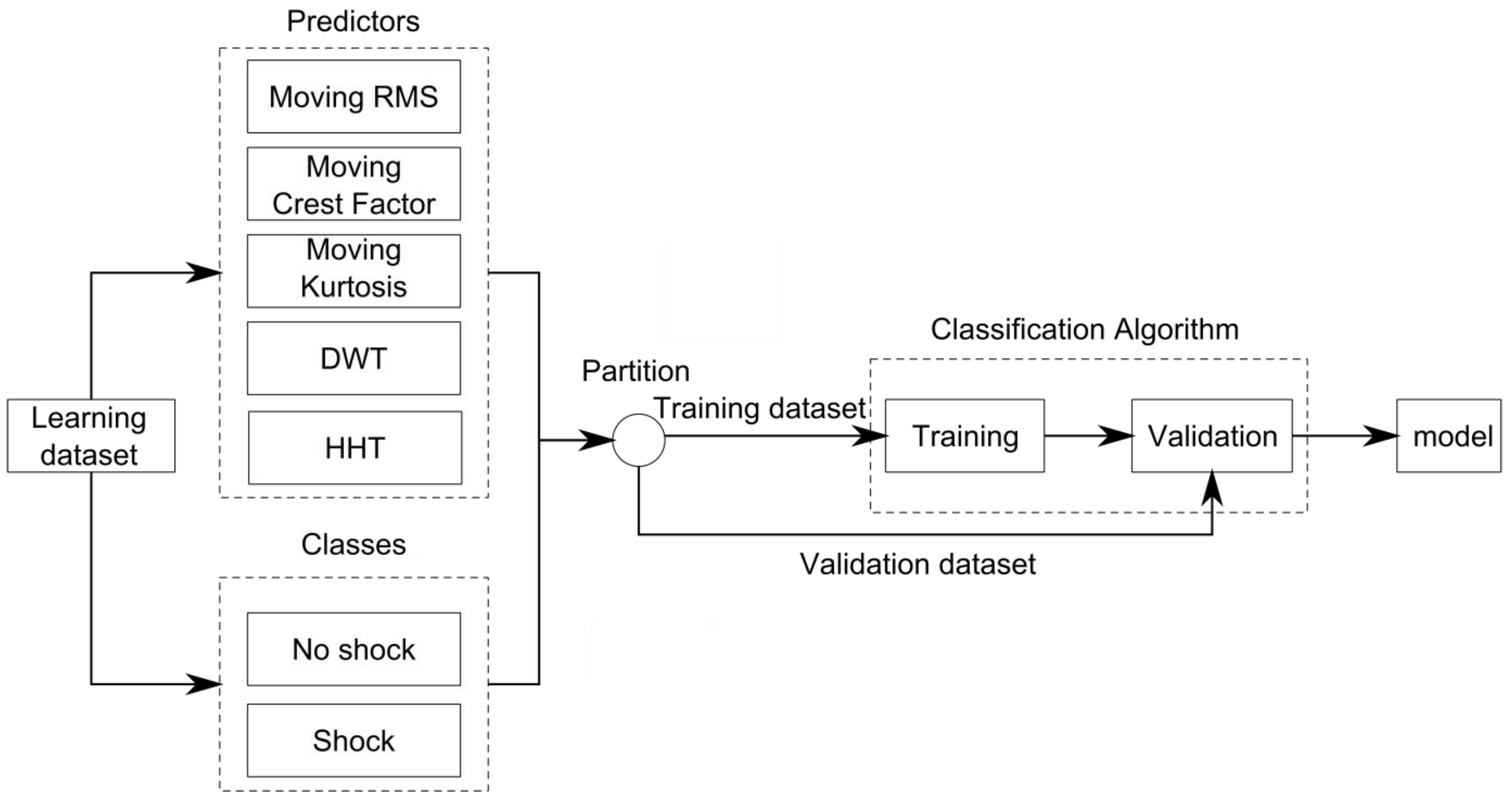
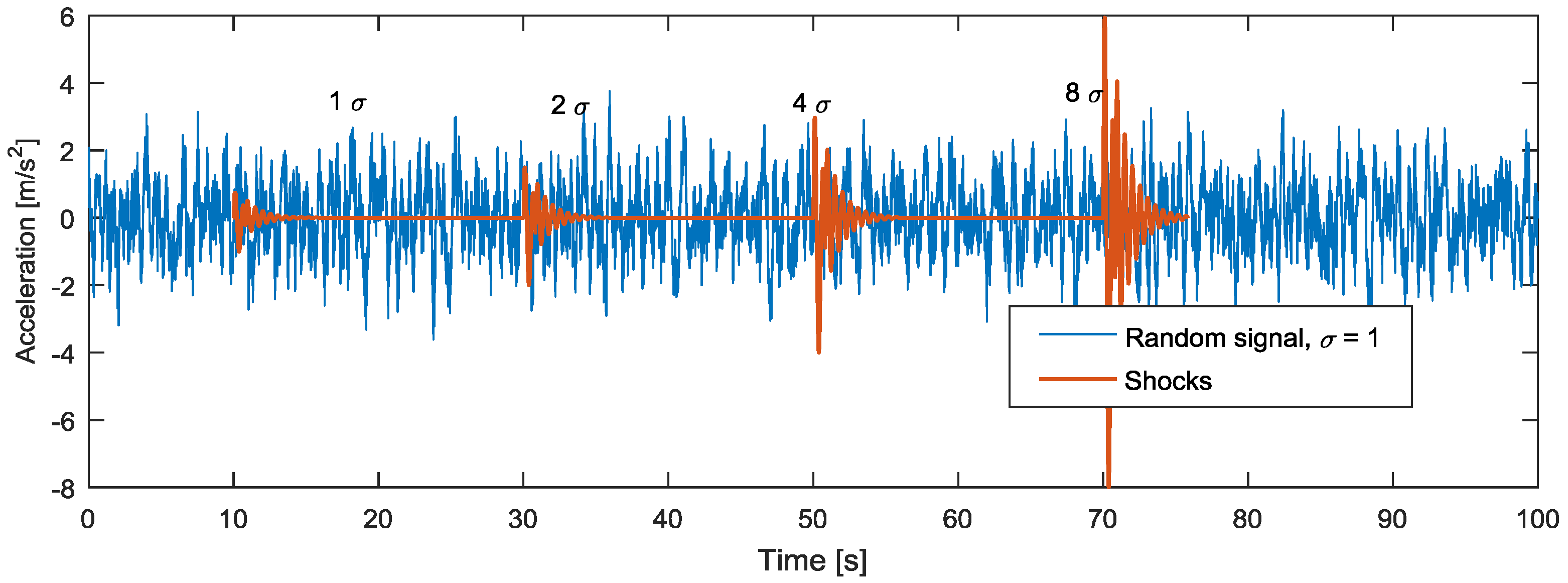
2.2. Synthetic RVV Signals
2.3. Predictors
2.3.1. Moving RMS
2.3.2. Moving Crest Factor
2.3.3. Moving Kurtosis
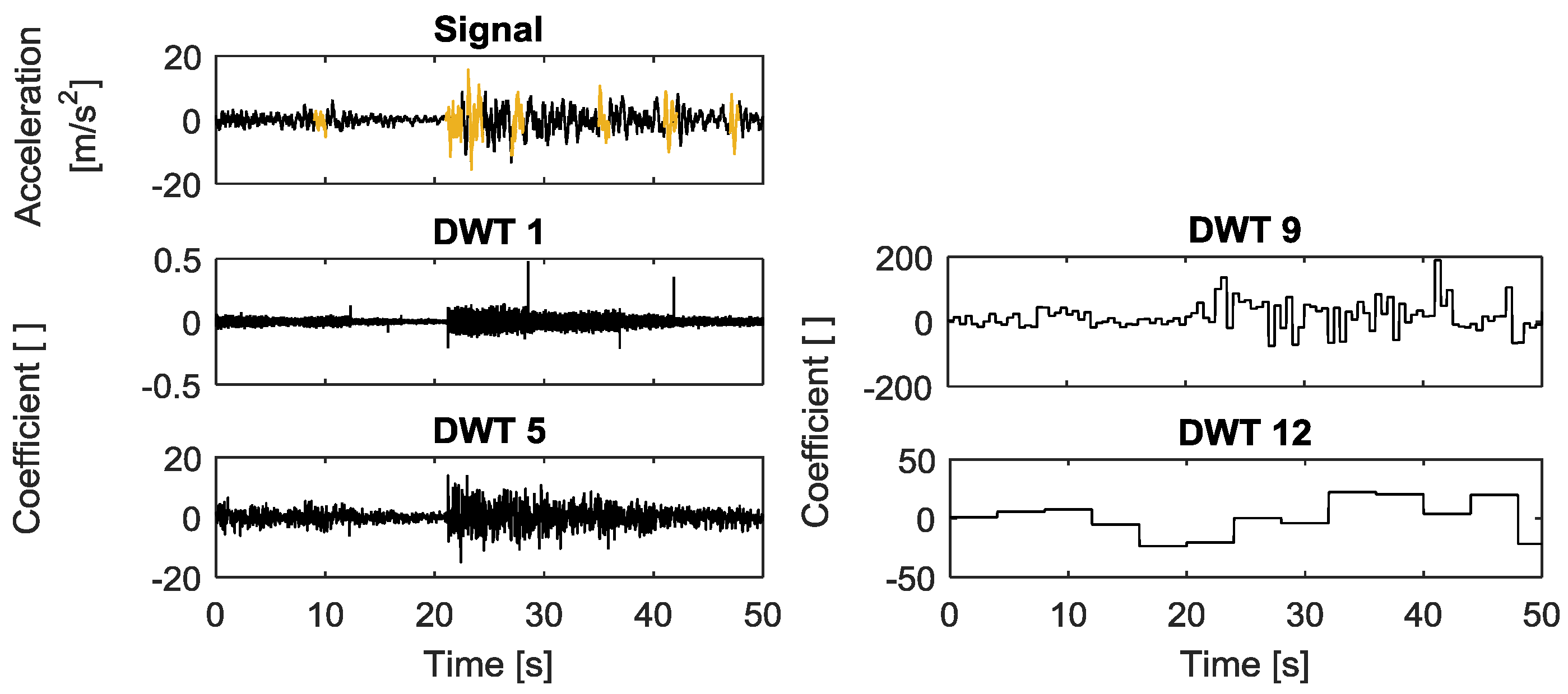
2.3.4. Discrete Wavelet Transform
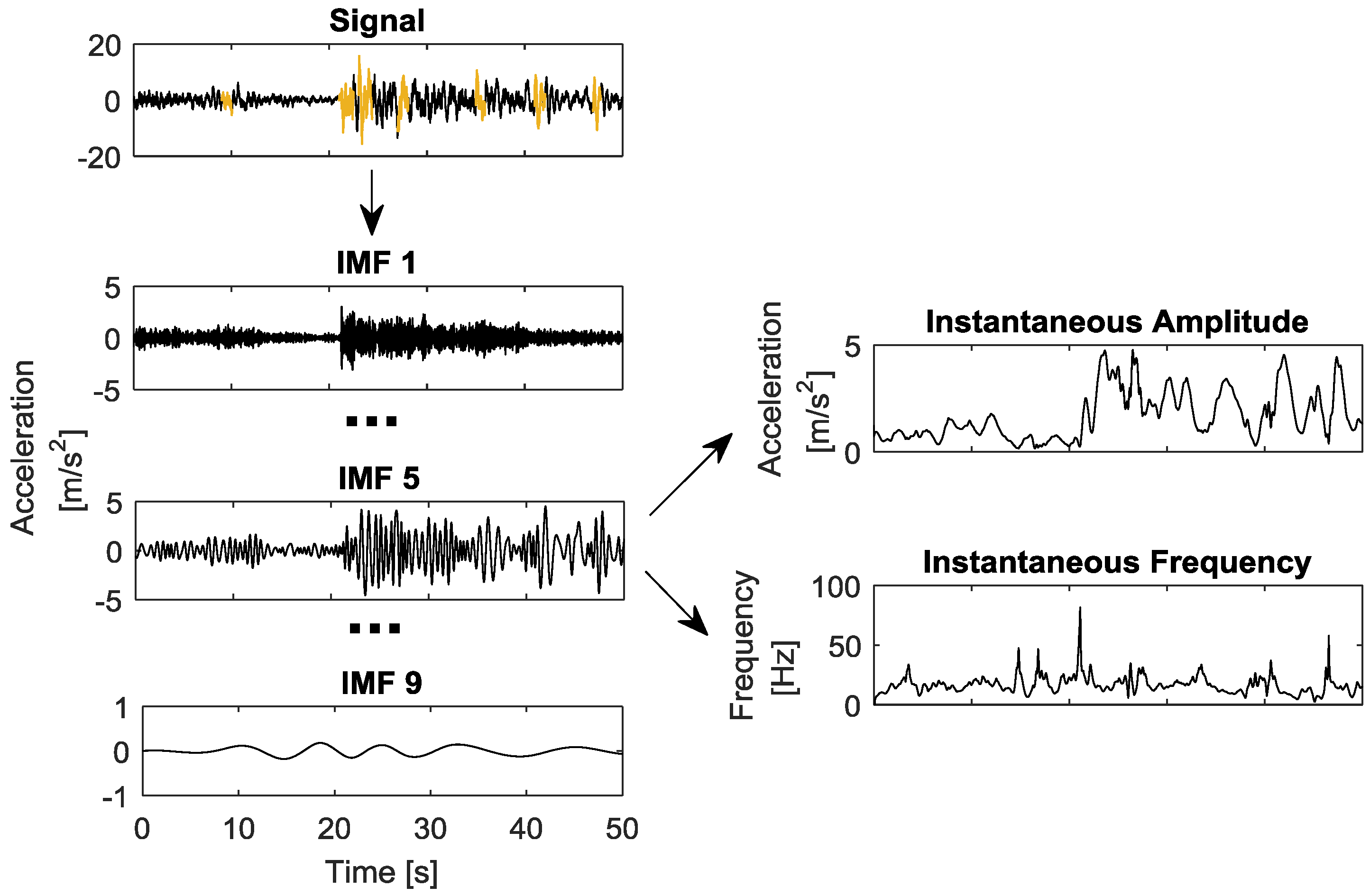
2.3.5. Hilbert-Huang Transform Predictors
- In the whole dataset, the number of extrema and number of zero-crossings must either be equal to each other, or differ by one at most;
- At any point, the mean value of the envelopes defined by the local maxima and local minima is zero.
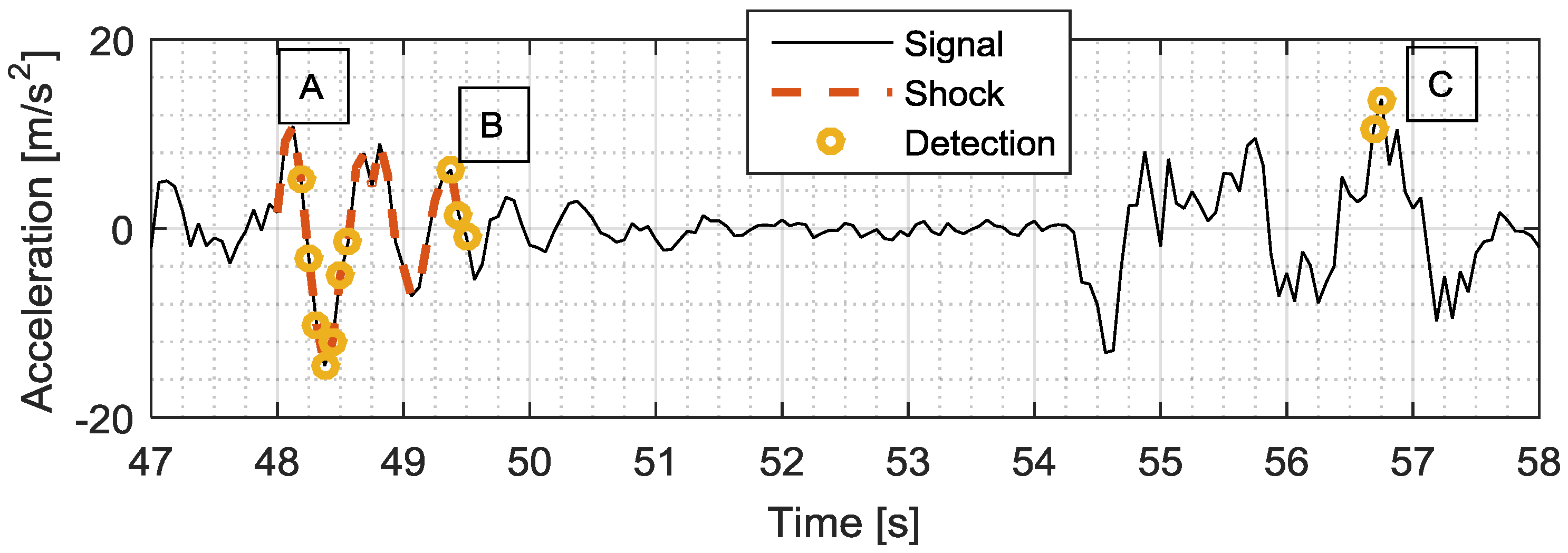
2.3.6. Detection Enhancement Algorithm
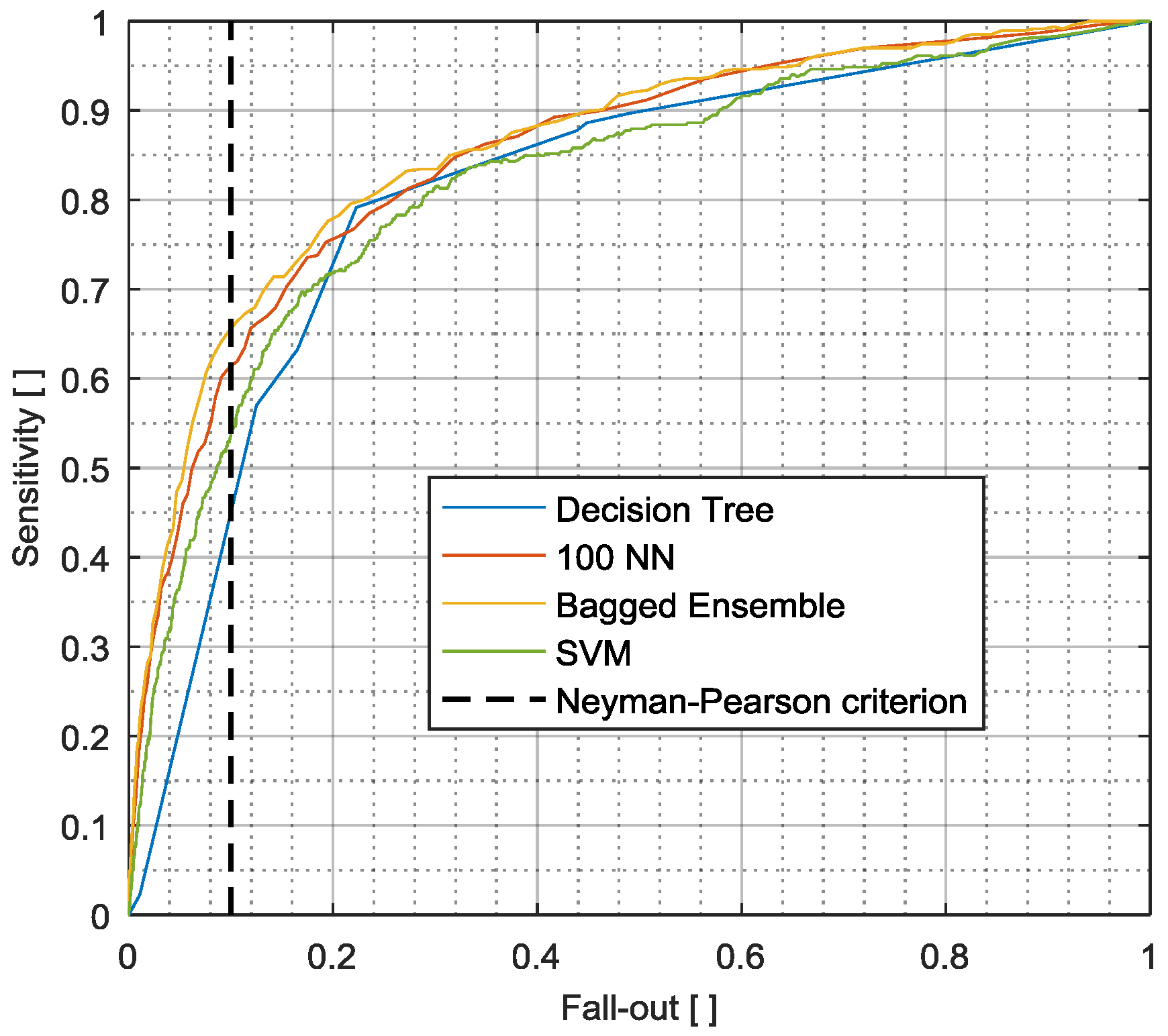
3. Classifier Evaluation
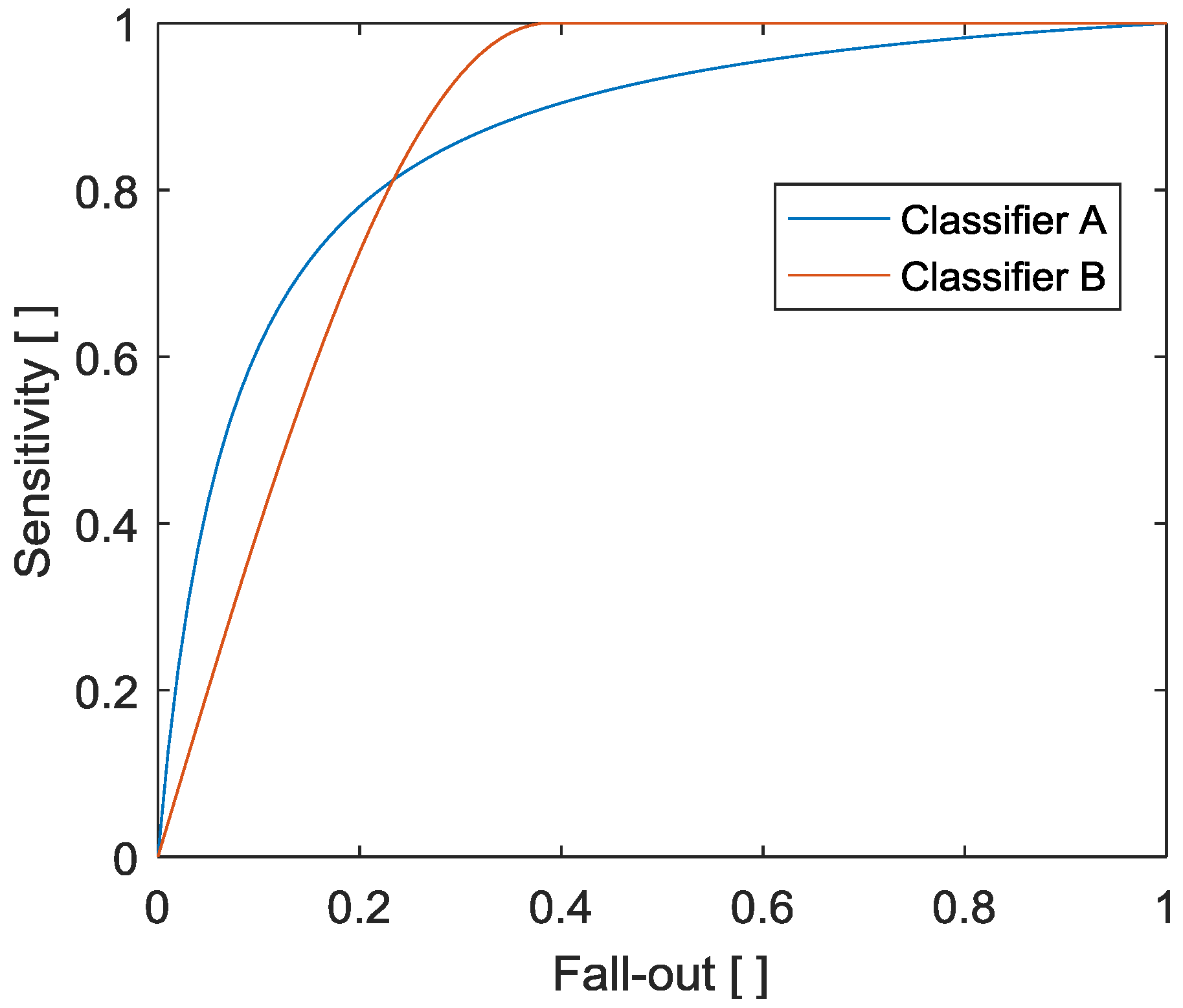
3.1. Classical Detection Assessment
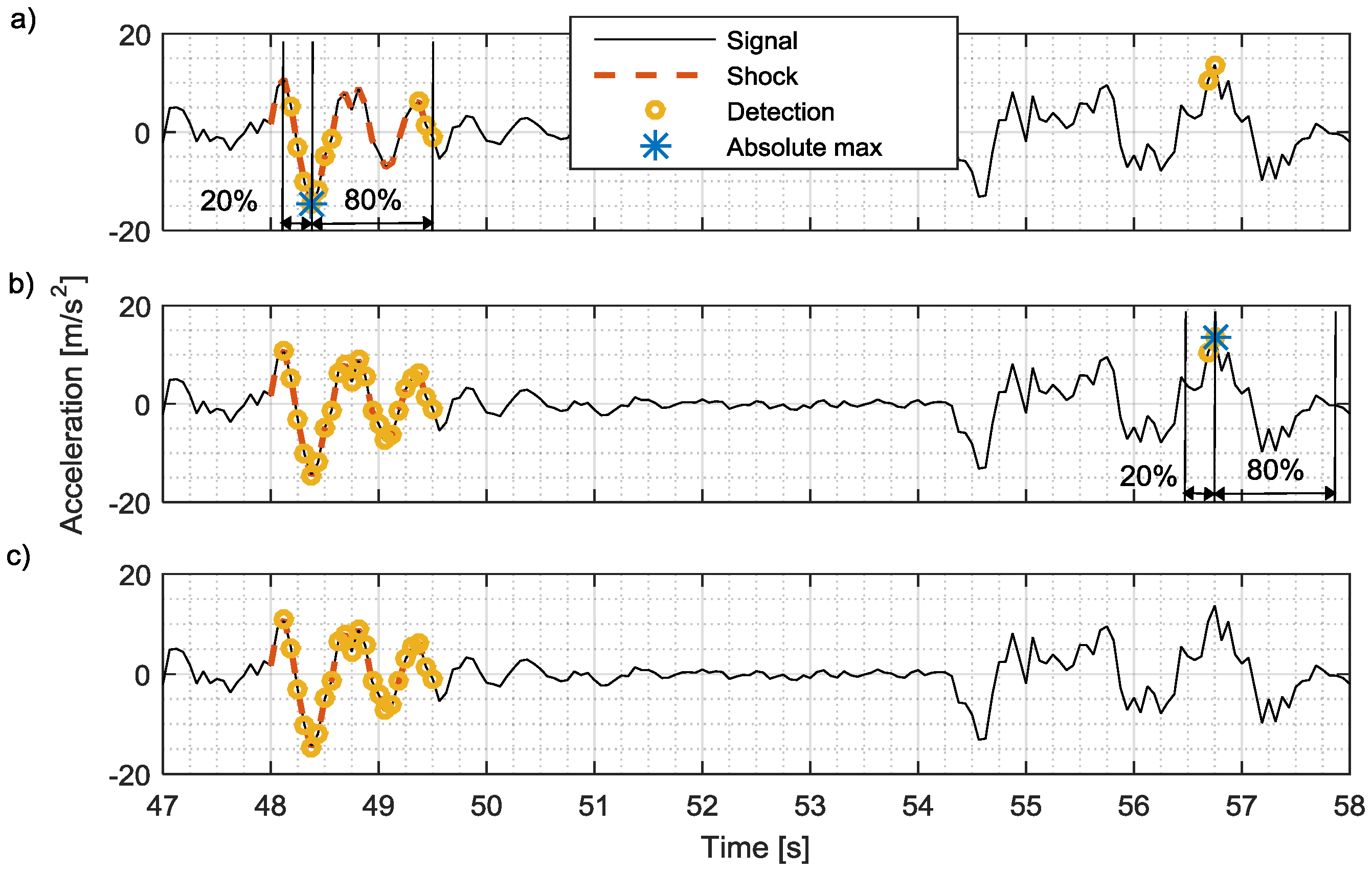
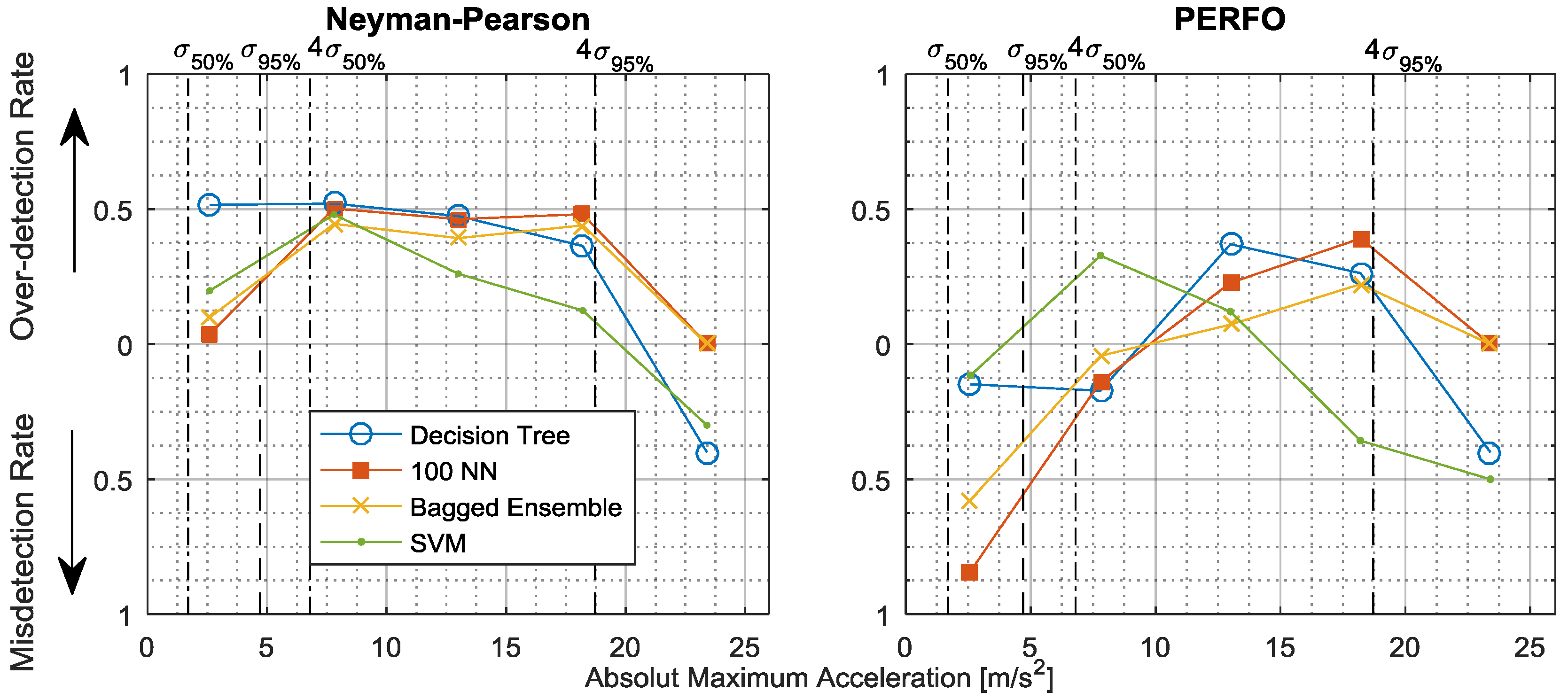
3.1.1. Optimal Operation Point
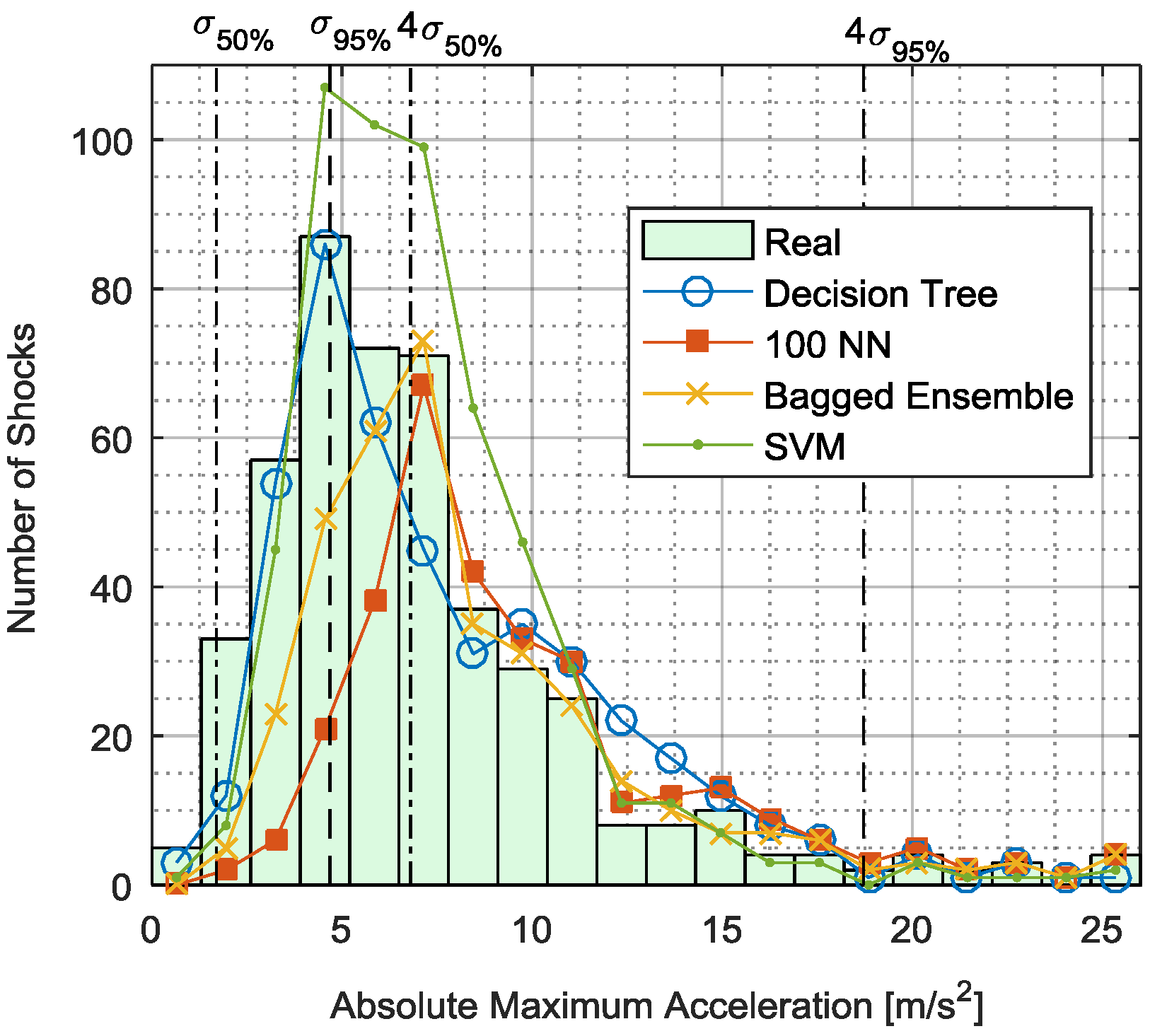
3.1.2. Neyman-Pearson Maximum Amplitude Distribution
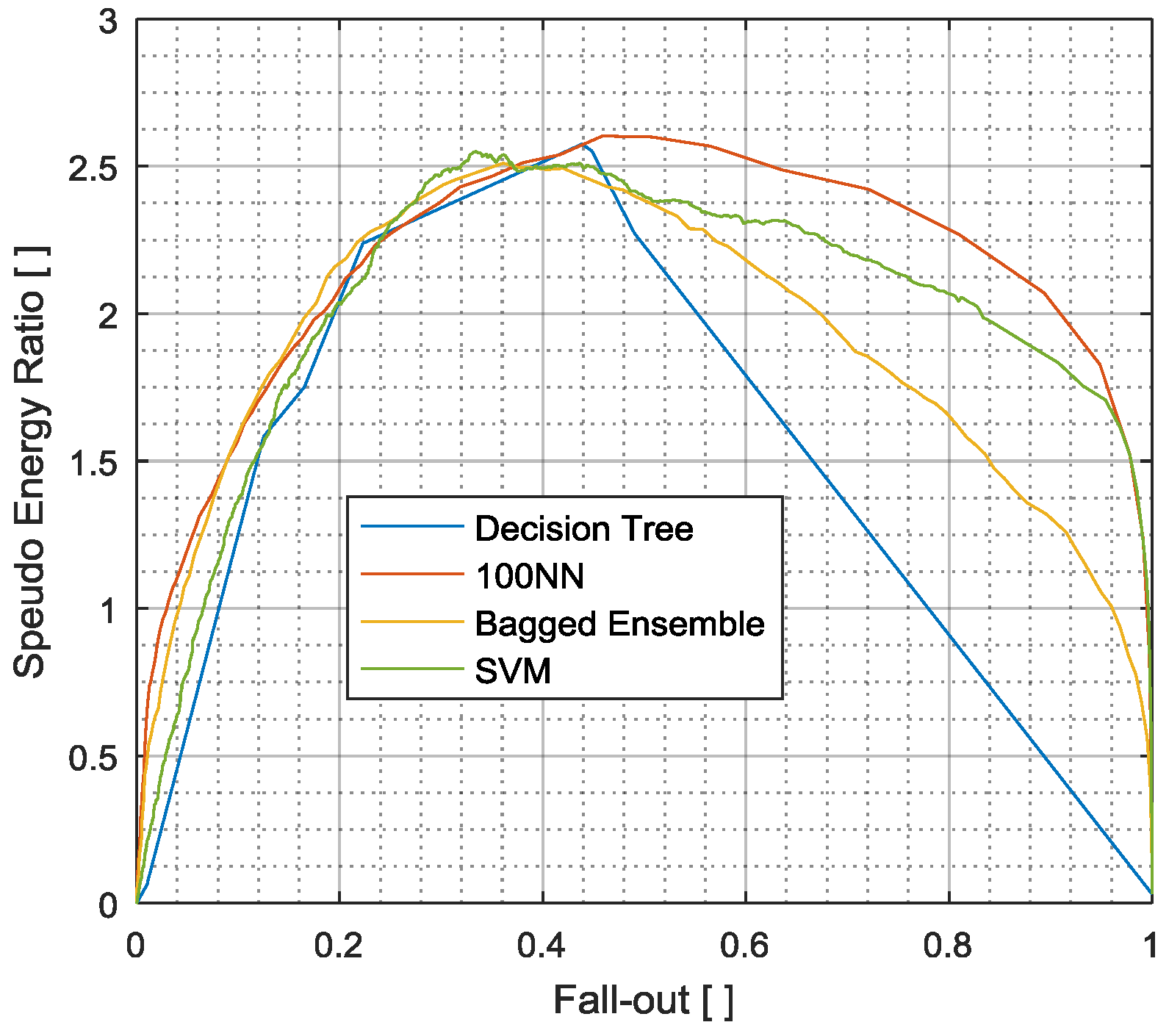
3.2. Pseudo-Energy Ratio/Fall-Out (PERFO) Curve
PERFO Maximum Amplitude Distribution
3.3. Comparison of Evaluation Measurands
4. Summary of Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ASTM International. Test Method for Random Vibration Testing of Shipping Containers; ASTM-D4728; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Defense Test Method Standard. Environmental Test Methods and Engineering Guides; MIL-STD-810F; Department of Defense Test Method Standard: Columbus, OH, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- BSI. Packaging. Complete, Filled Transport Packages and Unit Loads. Vertical Random Vibration Test; ISO-13355; BSI: London, UK, 2002; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- ISTA. Test Series. Available online: https://www.ista.org/pages/procedures/ista-procedures.php (accessed on 5 October 2016).
- Charles, D. Derivation of Environment Descriptions and Test Severities from Measured Road Transportation Data. J. IES 1993, 36, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Rouillard, V. On the Synthesis of Non-Gaussian Road Vehicle Vibrations. Ph.D. Thesis, Monash University, Melbourn, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kipp, W.I. Random Vibration Testing of Packaged-Products: Considerations for Methodology Improvement. In Proceedings of the 16th IAPRI World Conference on Packaging, Bangkok, Thailand, 8–12 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rouillard, V.; Sek, M. Creating Transport Vibration Simulation Profiles from Vehicle and Road Characteristics. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2013, 26, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouillard, V. Generating Road Vibration Test Schedules from Pavement Profiles for Packaging Optimization. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2008, 21, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouillard, V.; Bruscella, B.; Sek, M. Classification of road surface profiles. J. Transp. Eng. 2000, 126, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruscella, B.; Rouillard, V.; Sek, M. Analysis of road surface profiles. J. Transp. Eng. 1999, 125, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruscella, B. The Analysis and Simulation of the Spectral and Statistical Properties of Road Roughness for Package Performance Testing; Department of Mechanical Engineering, Victoria University of Technology: Melbourne, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Romeu-Martinez, M.-A.; Rouillard, V.; Cloquell-Ballester, V.-A. A Model for the Statistical Distribution of Road Vehicle Vibrations. In World Congress on Engineering 2007: WCE 2007; Imperial College London: London, UK, 2007; pp. 1225–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Romeu-Martinez, M.-A.; Singh, S.P.; Cloquell-Ballester, V.-A. Measurement and analysis of vibration levels for truck transport in Spain as a function of payload, suspension and speed. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2008, 21, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouillard, V.; Sek, M.A. A statistical model for longitudinal road topography. Road Transp. Res. 2002, 11, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rouillard, V. Quantifying the Non-stationarity of Vehicle Vibrations with the Run Test. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2014, 27, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouillard, V.; Sek, M.A. Monitoring and simulating non-stationary vibrations for package optimization. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2000, 13, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouillard, V.; Sek, M.A. Synthesizing Nonstationary, Non-Gaussian Random Vibrations. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2010, 23, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinwolf, A.; Connon, W.H., III. Limitations of the Fourier transform for describing test course profiles. Sound Vib. 2005, 39, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Fwa, T.; Zhe, Z. Wavelet analysis and interpretation of road roughness. J. Transp. Eng. Asce 2005, 131, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, D.; Nakamura, N.; Roy, P.; Orikasa, T.; Ishikawa, Y.; Kitazawa, H.; Shiina, T. Wavelet analysis of shock and vibration on the truck bed. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2008, 21, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepine, J.; Rouillard, V.; Sek, M. Wavelet Transform to Index Road Vehicle Vibration Mixed Mode Signals. In Proceedings of the ASME 2015 Noise Control and Acoustics Division Conference at InterNoise 2015, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–12 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ayenu-Prah, A.; Attoh-Okine, N. Comparative study of Hilbert–Huang transform, Fourier transform and wavelet transform in pavement profile analysis. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2009, 47, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, K.R. An Improved Method for Simulation of Vehicle Vibration Using a Journey Database and Wavelet Analysis for the Pre-Distribution Testing of Packaging. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bath, Bath, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lepine, J.; Rouillard, V.; Sek, M. Using the Hilbert-Huang transform to identify harmonics and transients within random signals. In Proceedings of the 8th Australasian Congress on Applied Mechanics: ACAM 8, Melbourne, Australia, 25–26 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Tao, J. Modeling and simulation of non-stationary vehicle vibration signals based on Hilbert spectrum. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 50, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepine, J.; Sek, M.; Rouillard, V. Mixed-Mode Signal Detection of Road Vehicle Vibration Using Hilbert-Huang Transform. In Proceedings of the ASME 2015 Noise Control and Acoustics Division Conference at InterNoise 2015, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–12 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lepine, J.; Rouillard, V.; Sek, M. Evaluation of machine learning algorithms for detection of road induced shocks buried in vehicle vibration signals. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouillard, V.; Lamb, M. On the Effects of Sampling Parameters When Surveying Distribution Vibrations. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2008, 21, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepine, J.; Rouillard, V.; Sek, M. On the Use of Machine Learning to Detect Shocks in Road Vehicle Vibration Signals. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2016, 30, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonhenchob, V.; Singh, S.P.; Singh, J.J.; Stallings, J.; Grewal, G. Measurement and Analysis of Vehicle Vibration for Delivering Packages in Small-Sized and Medium-Sized Trucks and Automobiles. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2012, 25, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, B. Developing a Random Vibration Profile Standard; International Safe Transit Association: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rouillard, V.; Richmond, R. A novel approach to analysing and simulating railcar shock and vibrations. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2007, 20, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepine, J. An Optimised Machine Learning Algorithm for Detecting Shocks in Road Vehicle Vibration. Ph.D. Thesis, College of Engineering and Science, Victoria University, Melbourne, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J.; Franklin, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference and Prediction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, S.; Girolami, M. A First Course in Machine Learning; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cherkassky, V.; Mulier, F.M. Learning from Data: Concepts, Theory, and Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shalev-Shwartz, S.; Ben-David, S. Understanding Machine Learning: From Theory to Algorithms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cebon, D. Handbook of Vehicle-Road Interaction/David Cebon: Lisse; Swets & Zeitlinger: Abingdon, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E.; Wu, M.-L.C.; Long, S.R.; Shen, S.S.; Qu, W.; Gloersen, P.; Fan, K.L. A confidence limit for the empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectral analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2003, 459, 2317–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, A.P. The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recogn. 1997, 30, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H. AUC: A better measure than accuracy in comparing learning algorithms. In Advances in Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 329–341. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, D.M.W. The problem of Area Under the Curve. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Information Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 23–25 March 2012; pp. 567–573. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, E. Introduction to Neyman and Pearson (1933) on the problem of the most efficient tests of statistical hypotheses. In Breakthroughs in Statistics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1992; pp. 67–72. [Google Scholar]


| Classifier | AUC | Neyman-Pearson | PERFO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decision Tree | 0.81 | 0.45 | 0.08 |
| 100NN | 0.85 | 0.61 | 0.03 |
| Bagged Ensemble | 0.86 | 0.65 | 0.04 |
| SVM | 0.82 | 0.54 | 0.07 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lepine, J.; Rouillard, V. Evaluation of Shock Detection Algorithm for Road Vehicle Vibration Analysis. Vibration 2018, 1, 220-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration1020016
Lepine J, Rouillard V. Evaluation of Shock Detection Algorithm for Road Vehicle Vibration Analysis. Vibration. 2018; 1(2):220-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration1020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleLepine, Julien, and Vincent Rouillard. 2018. "Evaluation of Shock Detection Algorithm for Road Vehicle Vibration Analysis" Vibration 1, no. 2: 220-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration1020016
APA StyleLepine, J., & Rouillard, V. (2018). Evaluation of Shock Detection Algorithm for Road Vehicle Vibration Analysis. Vibration, 1(2), 220-238. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration1020016






