Including Small Fires in Global Historical Burned Area Products: Promising Results from a Landsat-Based Product
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
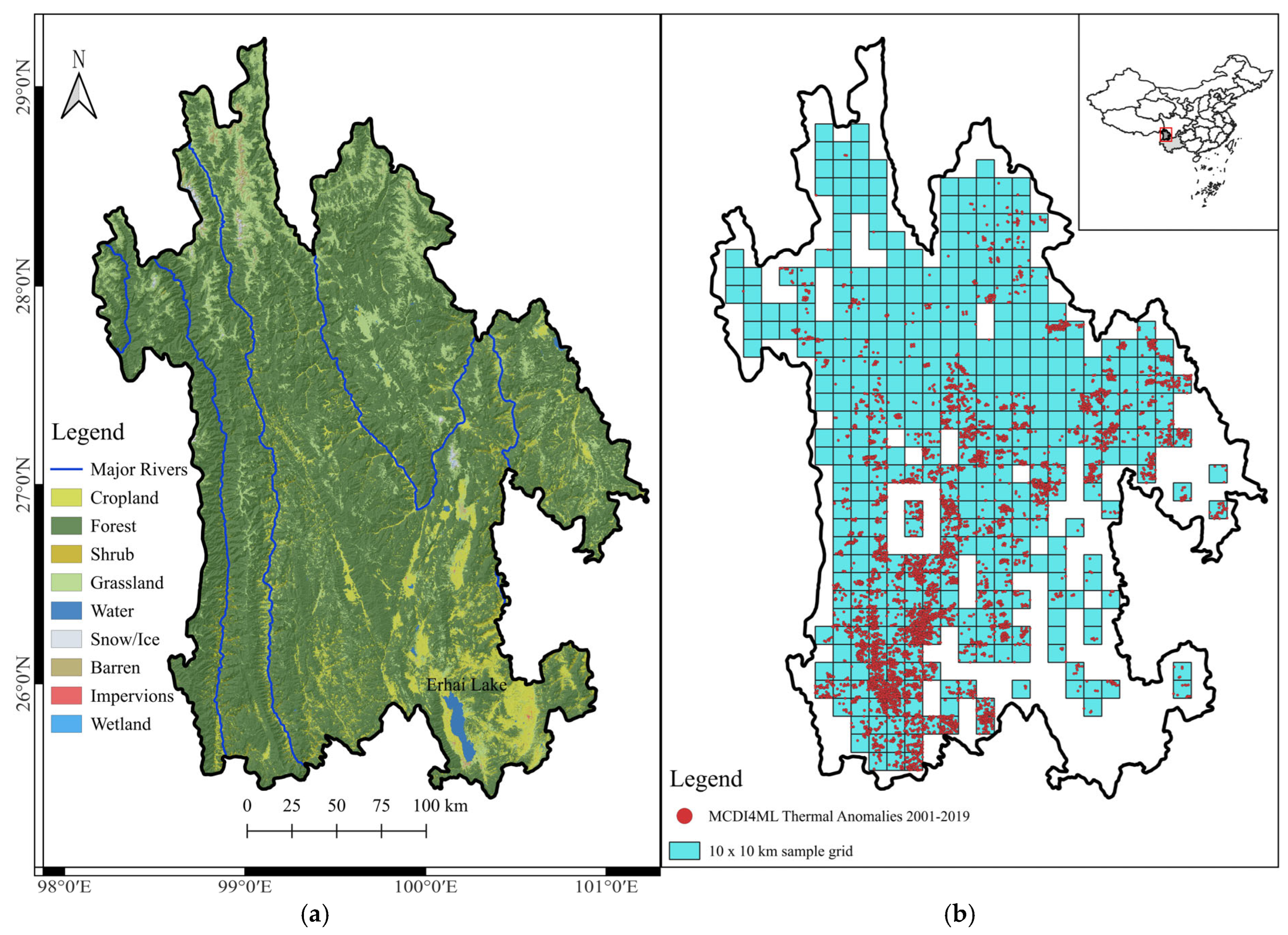
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Dataset Selection and Processing
2.3. Evaluation Method
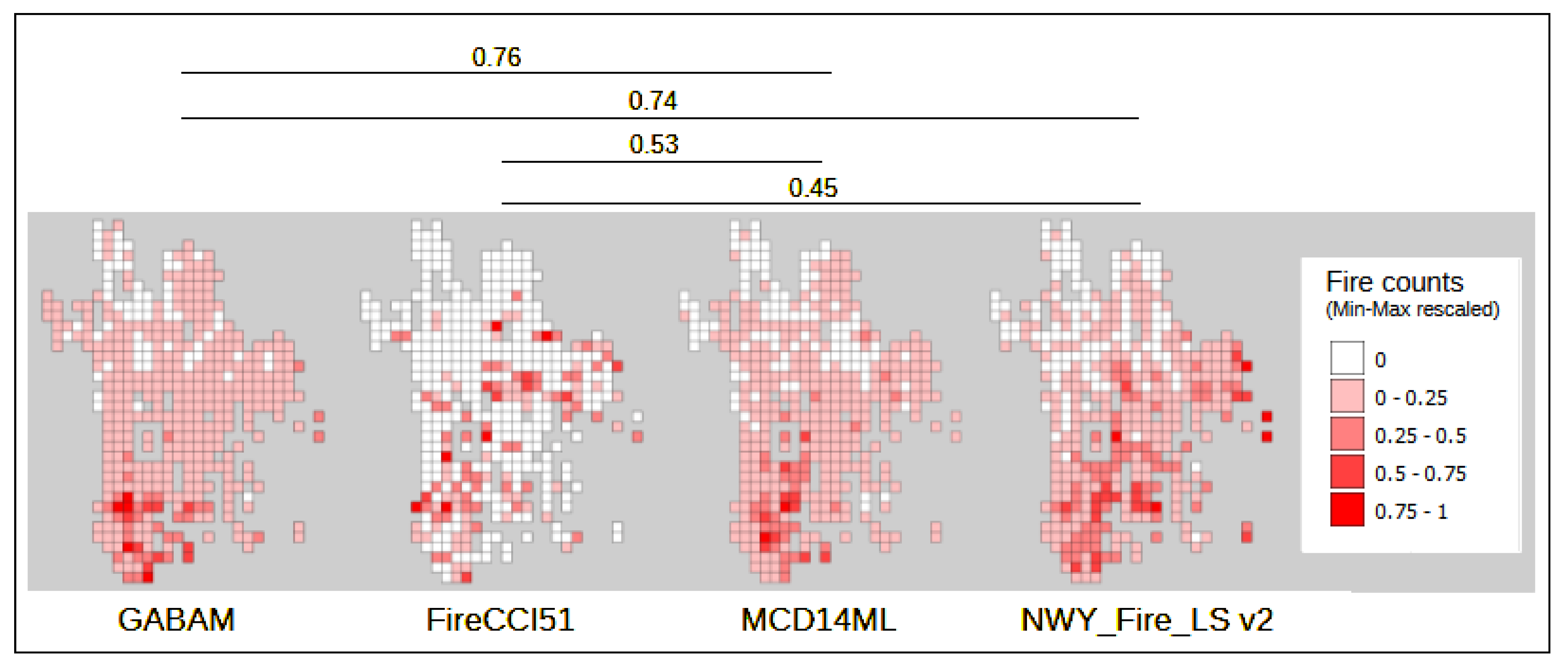
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Q.; Yu, L.; Du, Z.; Peng, D.; Hao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, P. An Overview of the Applications of Earth Observation Satellite Data: Impacts and Future Trends. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvieco, E.; Aguado, I.; Salas, J.; García, M.; Yebra, M.; Oliva, P. Satellite Remote Sensing Contributions to Wildland Fire Science and Management. Curr. For. Rep. 2020, 6, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinari, M.L.; Lizundia-Loiola, J.; Khairoun, A.; Roteta, E.; Storm, T.; Boettcher, M.; Danne, O.; Brockmann, C.; Chuvieco, E. Global and Continental Burned Area Detection from Remote Sensing: The FireCCI Products. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2023, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mouillot, F.; Schultz, M.G.; Yue, C.; Cadule, P.; Tansey, K.; Ciais, P.; Chuvieco, E. Ten Years of Global Burned Area Products from Spaceborne Remote Sensing-A Review: Analysis of User Needs and Recommendations for Future Developments. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvieco, E.; Mouillot, F.; van der Werf, G.R.; San Miguel, J.; Tanasse, M.; Koutsias, N.; García, M.; Yebra, M.; Padilla, M.; Gitas, I.; et al. Historical Background and Current Developments for Mapping Burned Area from Satellite Earth Observation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Velde, I.R.; van der Werf, G.R.; van Wees, D.; Schutgens, N.A.J.; Vernooij, R.; Houweling, S.; Tonucci, E.; Chuvieco, E.; Randerson, J.T.; Frey, M.M.; et al. Small Fires, Big Impact: Evaluating Fire Emission Estimates in Southern Africa Using New Satellite Imagery of Burned Area and Carbon Monoxide. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2023GL106122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wees, D.; van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Andela, N.; Chen, Y.; Morton, D.C. The Role of Fire in Global Forest Loss Dynamics. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 2377–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randerson, J.T.; Chen, Y.; Van der Werf, G.R.; Rogers, B.M.; Morton, D.C. Global Burned Area and Biomass Burning Emissions from Small Fires. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2012, 117, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramo, R.; Roteta, E.; Bistinas, I.; van Wees, D.; Bastarrika, A.; Chuvieco, E.; van der Werf, G.R. African Burned Area and Fire Carbon Emissions Are Strongly Impacted by Small Fires Undetected by Coarse Resolution Satellite Data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2011160118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Mickley, L.J.; Marlier, M.E.; DeFries, R.S.; Khan, M.F.; Latif, M.T.; Karambelas, A. Diagnosing Spatial Biases and Uncertainties in Global Fire Emissions Inventories: Indonesia as Regional Case Study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairoun, A.; Mouillot, F.; Chen, W.; Ciais, P.; Chuvieco, E. Coarse-Resolution Burned Area Datasets Severely Underestimate Fire-Related Forest Loss. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 170599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otón, G.; Lizundia-Loiola, J.; Pettinari, M.L.; Chuvieco, E. Development of a Consistent Global Long-Term Burned Area Product (1982–2018) Based on AVHRR-LTDR Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 103, 102473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizundia-Loiola, J.; Otón, G.; Ramo, R.; Chuvieco, E. A Spatio-Temporal Active-Fire Clustering Approach for Global Burned Area Mapping at 250 m from MODIS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.M.; Shimbo, J.Z.; Rosa, M.R.; Parente, L.L.; Alencar, A.; Rudorff, B.F.T.; Hasenack, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Ferreira, L.G.; Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; et al. Reconstructing Three Decades of Land Use and Land Cover Changes in Brazilian Biomes with Landsat Archive and Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawbaker, T.J.; Vanderhoof, M.K.; Schmidt, G.L.; Beal, Y.J.; Picotte, J.J.; Takacs, J.D.; Falgout, J.T.; Dwyer, J.L. The Landsat Burned Area Algorithm and Products for the Conterminous United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 244, 111801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidenshink, J.; Schwind, B.; Brewer, K.; Zhu, Z.; Quayle, B.; Howard, S. A Project for Monitoring Trends in Burn Severity. Fire Ecol. Spec. Issue 2007, 3, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Zhang, Z.; He, G.; Jiao, W.; Tang, C. 30 m Resolution Global Annual Burned Area Mapping Based on Landsat Images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbyla, D.L.; Kasischke, E.S.; Hoy, E.E. Seasonal and Topographic Effects on Estimating Fire Severity from Landsat TM/ETM+ Data. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2008, 17, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornacca, D.; Ren, G.; Xiao, W. Small Fires, Frequent Clouds, Rugged Terrain and No Training Data: A Methodology to Reconstruct Fire History in Complex Landscapes. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2020, 30, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humber, M.L.; Boschetti, L.; Giglio, L.; Justice, C.O. Spatial and Temporal Intercomparison of Four Global Burned Area Products. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 460–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, L.; Roy, D.P.; Justice, C.O.; Humber, M.L. MODIS-Landsat Fusion for Large Area 30m Burned Area Mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 161, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, C.H.; Benson, N.C. Landscape Assessment: Ground Measure of Severity, the Composite Burn Index; and Remote Sensing of Severity, the Normalized Burn Ratio; USDA Forest Service General Technical Report: Ogden, UT, USA, 2006.
- Boschetti, L.; Roy, D.P.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Humber, M.L. Collection 6 MODIS Burned Area Product User’s Guide-Version 1.0. In User Guide; NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2016; Version 1; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Chuvieco, E. Validation of the 2008 MODIS-MCD45 Global Burned Area Product Using Stratified Random Sampling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 144, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, M.; Olofsson, P.; Stehman, S.V.; Tansey, K.; Chuvieco, E. Stratification and Sample Allocation for Reference Burned Area Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 203, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.V.; Loboda, T.V.; Giglio, L.; McCarty, G.W. A MODIS-Based Burned Area Assessment for Russian Croplands: Mapping Requirements and Challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 506–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasko, K.; Vadrevu, K.P.; Tran, V.T.; Ellicott, E.; Nguyen, T.T.N.; Bui, H.Q.; Justice, C. Satellites May Underestimate Rice Residue and Associated Burning Emissions in Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 085006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Marlier, M.E.; Karambelas, A.; Jain, M.; Singh, S.; Singh, M.K.; Gautam, R.; Defries, R.S. Missing Emissions from Post-Monsoon Agricultural Fires in Northwestern India: Regional Limitations of Modis Burned Area and Active Fire Products. Environ. Res. Commun. 2019, 1, 059501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Shevade, V.; Baer, A.E.; Loboda, T.V. Missing Burns in the High Northern Latitudes: The Case for Regionally Focused Burned Area Products. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Kobayashi, H.; Kan, Y.; Saito, M. Size-Dependent Validation of MODIS MCD64A1 Burned Area over Six Vegetation Types in Boreal Eurasia: Large Underestimation in Croplands. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Xia, X.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, S. Validating MCD64A1 and FireCCI51 Burned Area Mapping in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2285345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornacca, D.; Ren, G.; Xiao, W. Performance of Three MODIS Fire Products (MCD45A1, MCD64A1, MCD14ML), and ESA Fire_CCI in a Mountainous Area of Northwest Yunnan, China, Characterized by Frequent Small Fires. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franquesa, M.; Vanderhoof, M.K.; Stavrakoudis, D.G.; Gitas, I.Z.; Roteta, E.; Padilla, M.; Chuvieco, E. Development of a Standard Database of Reference Sites for Validating Global Burned Area Products. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3229–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.M.; Dinerstein, E.; Wikramanayake, E.D.; Burgess, N.D.; Powell, G.V.N.; Underwood, E.C.; D’Amico, J.A.; Itoua, I.; Strand, H.E.; Morrison, J.C.; et al. Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World: A New Map of Life on Earth. Bioscience 2001, 51, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.; Buytaert, W.; Peaver, L.; Wheater, H. Evaluation of Precipitation Products over Complex Mountainous Terrain: A Water Resources Perspective. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, D.J.; Walsh, S.J. Remote Sensing of Mountain Environments. Geogr. Compass 2009, 3, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Q. The Subtropical Vegetation of Southwestern China: Plant Distribution, Diversity and Ecology. In Plant and Vegetation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 11, ISBN 978-94-017-9740-5. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.Q.; Ohsawa, M. Ecology of Subtropical Evergreen Broad-Leaved Forests of Yunnan, Southwestern China as Compared to Those of Southwestern Japan. J. Plant Res. 2009, 122, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Long, T.; He, G.; Wei, M.; Tang, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; She, W.; Zhang, X. Study on Global Burned Forest Areas Based on Landsat Data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2020, 86, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pausas, J.G.; Su, W.; Luo, C.; Shen, Z. A Shrubby Resprouting Pine with Serotinous Cones Endemic to Southwest China. Ecology 2021, 102, e03282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Luo, X.; Liang, P.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Sun, H.; Pan, K.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Pang, X. Fire from Policy, Human Interventions, or Biophysical Factors? Temporal–Spatial Patterns of Forest Fire in Southwestern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 474, 118381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Global Land Cover Mapping at 30 m Resolution: A POK-Based Operational Approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA. Land Cover CCI Product User Guide, Version 2; UCLouvain: Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Giglio, L.; Schroeder, W.; Justice, C.O. The Collection 6 MODIS Active Fire Detection Algorithm and Fire Products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Masek, J.G.; Wolfe, R.; Gao, F.; Huang, C.; Vermote, E.F.; Sexton, J.O.; Ederer, G. Improved Forest Change Detection with Terrain Illumination Corrected Landsat Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhao, F.; Shu, L.; Wang, M. Distribution Characteristics and the Influence Factors of Forest Fires in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 310, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhoof, M.K.; Brunner, N.; Beal, Y.J.G.; Hawbaker, T.J. Evaluation of the U.S. Geological Survey Landsat Burned Area Essential Climate Variable across the Conterminous U.S. Using Commercial High-Resolution Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.; de Beurs, K.M.; Neeson, T.M. Evaluation of Low-Resolution Remotely Sensed Datasets for Burned Area Assessment within the Wildland-Urban Interface. Remote Sens. Appl. 2022, 26, 100752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Boschetti, L.; Roy, D.P.; Humber, M.L.; Justice, C.O. The Collection 6 MODIS Burned Area Mapping Algorithm and Product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ibarzabal, J.; Franquesa, M.; Rodriguez-Montellano, A.; Bastarrika, A. Sentinel-2 Reference Fire Perimeters for the Assessment of Burned Area Products over Latin America and the Caribbean for the Year 2019. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagis, T.; Gitas, I.Z. Assessing the Accuracy of MODIS MCD64A1 C6 and FireCCI51 Burned Area Products in Mediterranean Ecosystems. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessôa, A.C.M.; Anderson, L.O.; Carvalho, N.S.; Campanharo, W.A.; Silva Junior, C.H.L.; Rosan, T.M.; Reis, J.B.C.; Pereira, F.R.S.; Assis, M.; Jacon, A.D.; et al. Intercomparison of Burned Area Products and Its Implication for Carbon Emission Stimations in the Amazon. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.V.; Argueta, F.; Giglio, L. Validation of MCD64A1 and FireCCI51 Cropland Burned Area Mapping in Ukraine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrita, Y.; Cochrane, M.A.; Suwarsono; Priyatna, M.; Sukowati, K.A.D.; Khomarudin, M.R. Evaluating Accuracy of Four MODIS-Derived Burned Area Products for Tropical Peatland and Non-Peatland Fires. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 035015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franquesa, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Chuvieco, E. Assessment and Characterization of Sources of Error Impacting the Accuracy of Global Burned Area Products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornacca, D.; Ren, G.; Xiao, W. Evaluating the Best Spectral Indices for the Detection of Burn Scars at Several Post-Fire Dates in a Mountainous Region of Northwest Yunnan, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; He, Y.; Tong, A. Evaluation of Spectral Indices for Estimating Burn Severity in Semiarid Grasslands. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2016, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Zhang, Z.; Long, T.; He, G.; Wang, G.; Peng, Y.; Xu, Z. High Resolution (30 m) Burned Area Product Improves the Ability for Carbon Emission Estimation in Africa. Earths Future 2024, 12, e2024EF005051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubkova, M.; Lötter, M.; Bronkhorst, F.; Giglio, L. Assessment of the Effectiveness of Coarse Resolution Fire Products in Monitoring Long-Term Changes in Fire Regime within Protected Areas in South Africa. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 104064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clelland, A.A.; Marshall, G.J.; Baxter, R.; Potter, S.; Talucci, A.C.; Rady, J.M.; Genet, H.; Rogers, B.M.; Natali, S.M. Annual and Seasonal Patterns of Burned Area Products in Arctic-Boreal North America and Russia for 2001–2020. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Aljaddani, A.H.; Cohen, W.B.; Qiu, S.; Zhou, C. Continuous Monitoring of Land Disturbance Based on Landsat Time Series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238, 111116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.B. Detecting Trends in Forest Disturbance and Recovery Using Yearly Landsat Time Series: 1. LandTrendr-Temporal Segmentation Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Goward, S.N.; Masek, J.G.; Thomas, N.; Zhu, Z.; Vogelmann, J.E. An Automated Approach for Reconstructing Recent Forest Disturbance History Using Dense Landsat Time Series Stacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, P.; Bullock, E.L.; Woodcock, C.E.; Olofsson, P. A Suite of Tools for Continuous Land Change Monitoring in Google Earth Engine. Front. Clim. 2020, 2, 576740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbesselt, J.; Hyndman, R.; Newnham, G.; Culvenor, D. Detecting Trend and Seasonal Changes in Satellite Image Time Series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.F.; Tollerud, H.J.; Barber, C.P.; Zhou, Q.; Dwyer, J.L.; Vogelmann, J.E.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Stehman, S.V.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Lessons Learned Implementing an Operational Continuous United States National Land Change Monitoring Capability: The Land Change Monitoring, Assessment, and Projection (LCMAP) Approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238, 111356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, T.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Coops, N.C.; Hobart, G.W. An Integrated Landsat Time Series Protocol for Change Detection and Generation of Annual Gap-Free Surface Reflectance Composites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, L.; Sloat, L.; Mesquita, V.; Consoli, D.; Stanimirova, R.; Hengl, T.; Bonannella, C.; Teles, N.; Wheeler, I.; Hunter, M.; et al. Annual 30-m Maps of Global Grassland Class and Extent (2000–2022) Based on Spatiotemporal Machine Learning. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, X. Global Annual Wetland Dataset at 30 m with a Fine Classification System from 2000 to 2022. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Hall, J.; Van Wees, D.; Andela, N.; Hantson, S.; Giglio, L.; Van Der Werf, G.R.; Morton, D.C.; Randerson, J.T. Multi-Decadal Trends and Variability in Burned Area from the Fifth Version of the Global Fire Emissions Database (GFED5). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 5227–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, A.; Jin, H.; Bian, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, G.; Qin, Z.; Huang, C. An Enhanced Spatial and Temporal Data Fusion Model for Fusing Landsat and Modis Surface Reflectance to Generate High Temporal Landsat-like Data. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5346–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscalleda-Alvarez, J.; Moro, D.; Van Dongen, R. A Multi-Scale Assessment of Fire Scar Mapping in the Great Victoria Desert of Western Australia. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2021, 30, 886–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FireCCI51 | GABAM | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Low–High Threshold | High Frequency Sample Squares | Reference Fires | TP | FN | FP | PA | UA | TP | FN | FP | PA | UA |
| 2001 | 2 | 23 | 8 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | NaN | 6 | 2 | 5 | 0.75 | 0.55 |
| 2002 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | NaN | 6 | 1 | 1 | 0.86 | 0.86 |
| 2003 | 3 | 20 | 13 | 1 | 12 | 0 | 0.08 | 1 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 0.54 | 0.64 |
| 2004 | 4 | 26 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | NaN | 8 | 2 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.73 |
| 2005 | 4 | 17 | 18 | 0 | 18 | 0 | 0 | NaN | 2 | 16 | 0 | 0.11 | 1 |
| 2006 | 7 | 39 | 18 | 3 | 15 | 1 | 0.17 | 0.75 | 14 | 4 | 1 | 0.78 | 0.93 |
| 2007 | 6 | 34 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 | NaN | 14 | 1 | 1 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| 2008 | 3 | 16 | 11 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 | NaN | 9 | 2 | 4 | 0.82 | 0.69 |
| 2009 | 6 | 41 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 0.25 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0.88 | 1 |
| 2010 | 10 | 43 | 18 | 1 | 17 | 0 | 0.06 | 1 | 14 | 4 | 0 | 0.78 | 1 |
| 2011 | 4 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | NaN | 9 | 1 | 0 | 0.9 | 1 |
| 2014 | 30 | 86 | 14 | 6 | 8 | 1 | 0.43 | 0.86 | 11 | 3 | 1 | 0.79 | 0.92 |
| 2015 | 4 | 24 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.67 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| 2016 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | NaN | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0.71 | 1 |
| 2017 | 5 | 12 | 12 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | NaN | 6 | 6 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.75 |
| 2018 | 2 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | NaN | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0.22 | 1 |
| 2019 | 3 | 14 | 12 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | NaN | 8 | 4 | 0 | 0.67 | 1 |
| Overall study period | 198 | 15 | 183 | 3 | 0.08 | 0.83 | 135 | 63 | 23 | 0.68 | 0.85 | ||
| BA < 25 ha (n = 41) | BA 25–100 ha (n = 71) | BA > 100 ha (n = 86) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | PA | TP | PA | TP | PA | |
| GABAM | 26 | 0.63 | 42 | 0.59 | 67 | 0.78 |
| FireCCI51 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0.06 | 11 | 0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fornacca, D.; Ye, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, W. Including Small Fires in Global Historical Burned Area Products: Promising Results from a Landsat-Based Product. Fire 2025, 8, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8110422
Fornacca D, Ye Y, Li X, Xiao W. Including Small Fires in Global Historical Burned Area Products: Promising Results from a Landsat-Based Product. Fire. 2025; 8(11):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8110422
Chicago/Turabian StyleFornacca, Davide, Yuhan Ye, Xiaokang Li, and Wen Xiao. 2025. "Including Small Fires in Global Historical Burned Area Products: Promising Results from a Landsat-Based Product" Fire 8, no. 11: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8110422
APA StyleFornacca, D., Ye, Y., Li, X., & Xiao, W. (2025). Including Small Fires in Global Historical Burned Area Products: Promising Results from a Landsat-Based Product. Fire, 8(11), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8110422










