A Scientometric Research on Applications and Advances of Fire Safety Evacuation in Buildings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Scientometric Analysis
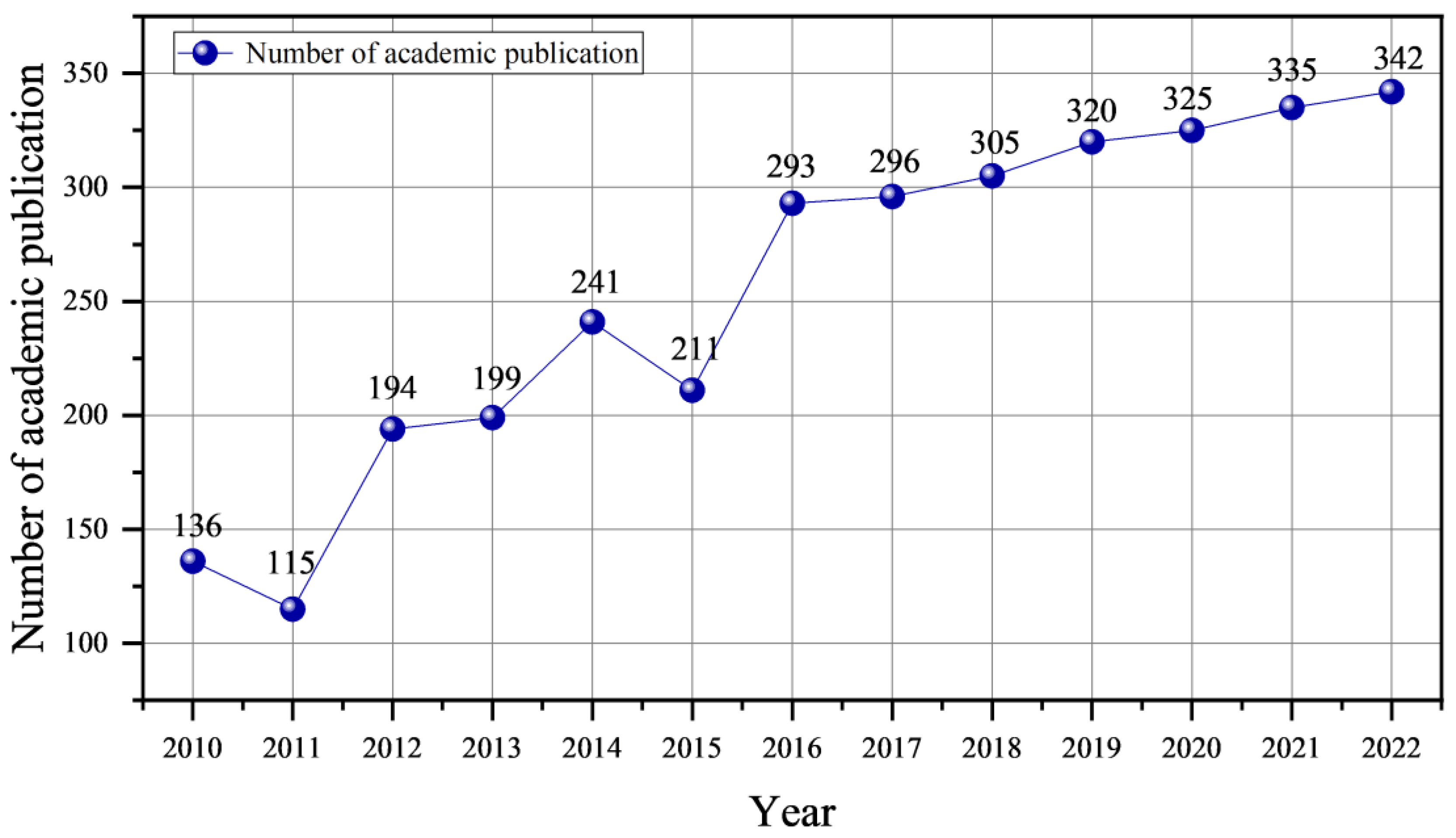
3.1. Year and Quantitative Analysis of Academic Publications
3.2. Leading Journals and Conference Proceedings
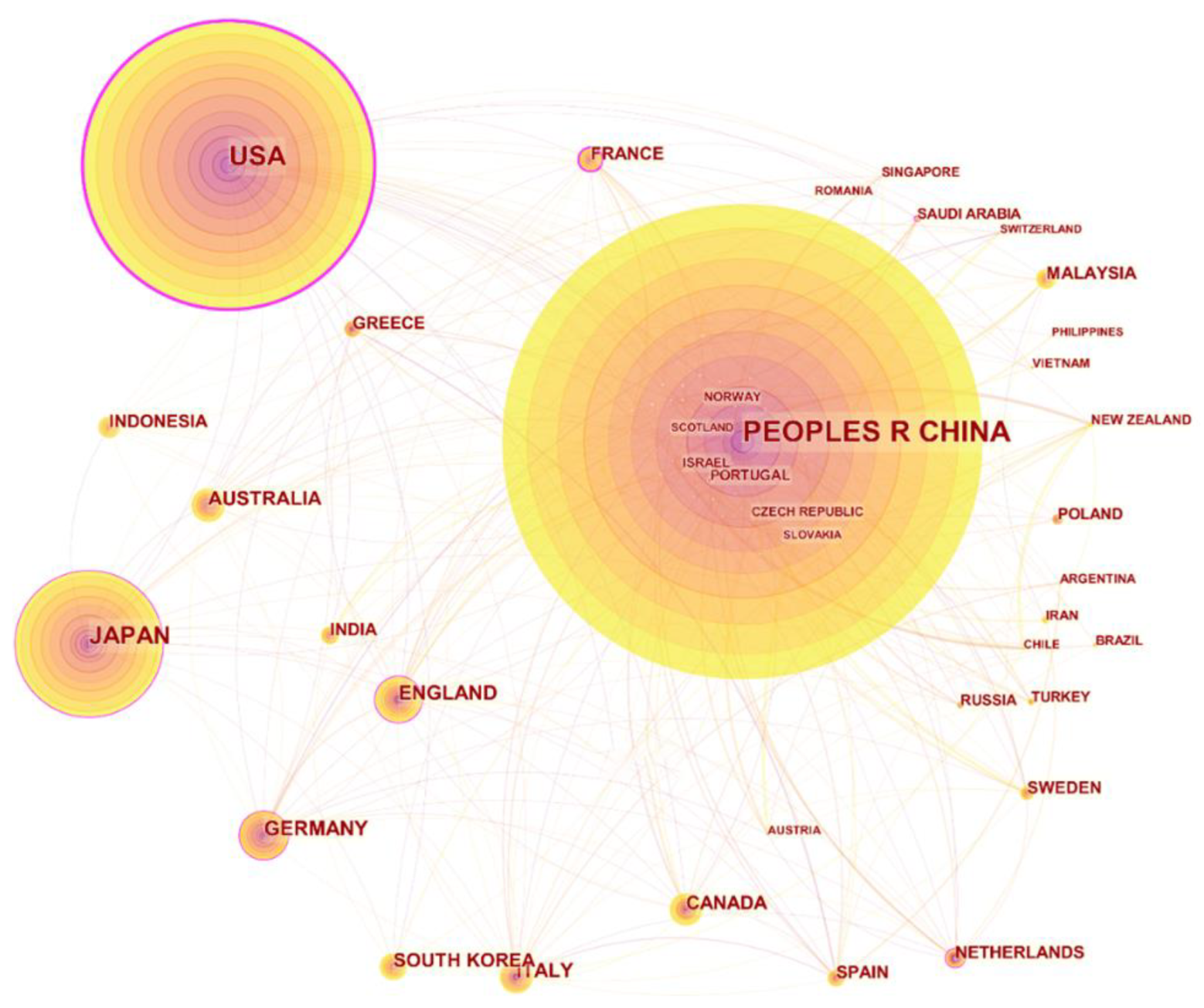
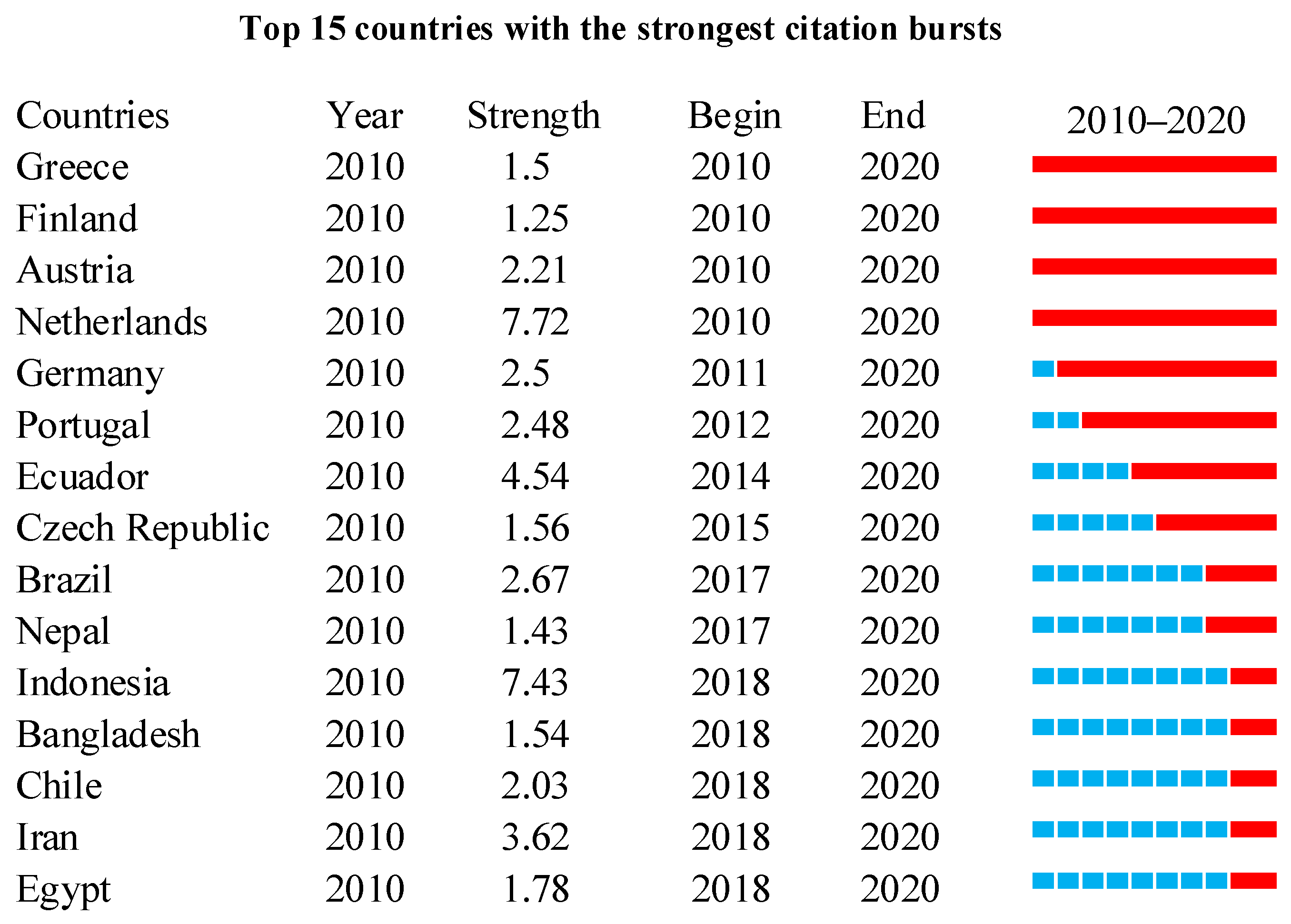
3.3. Network of Countries
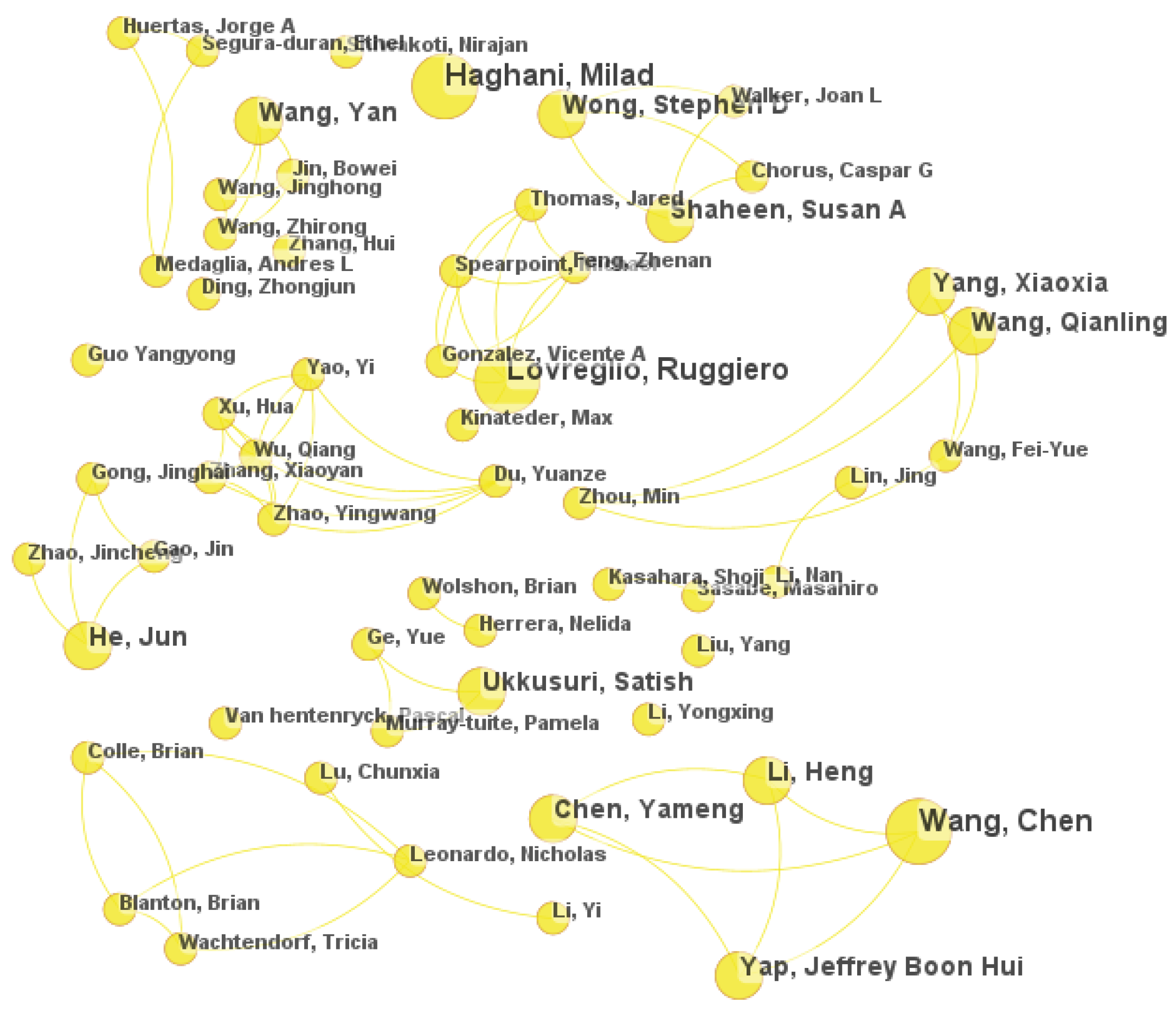
3.4. Network of Authorships
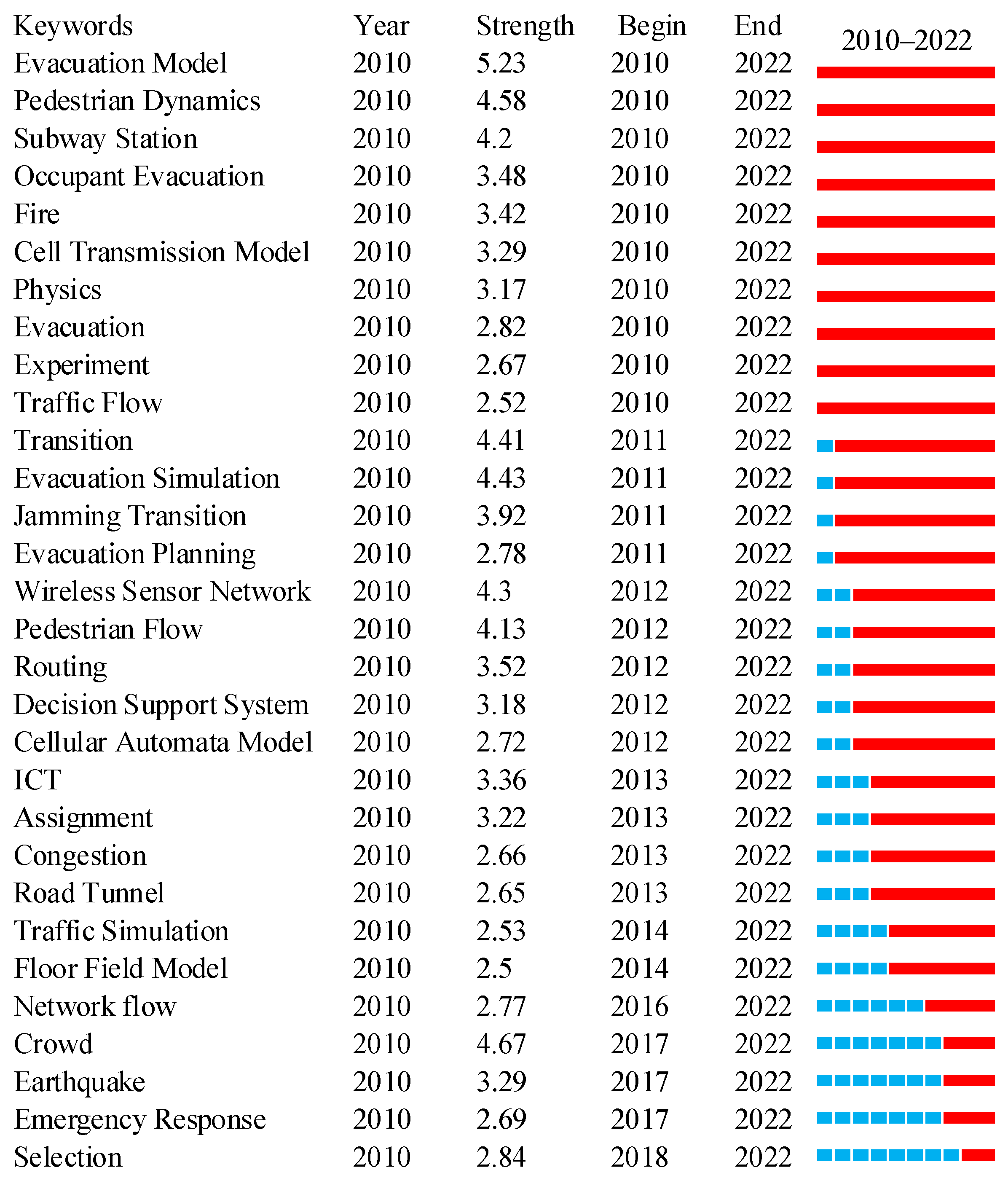
3.5. Keywords Analysis
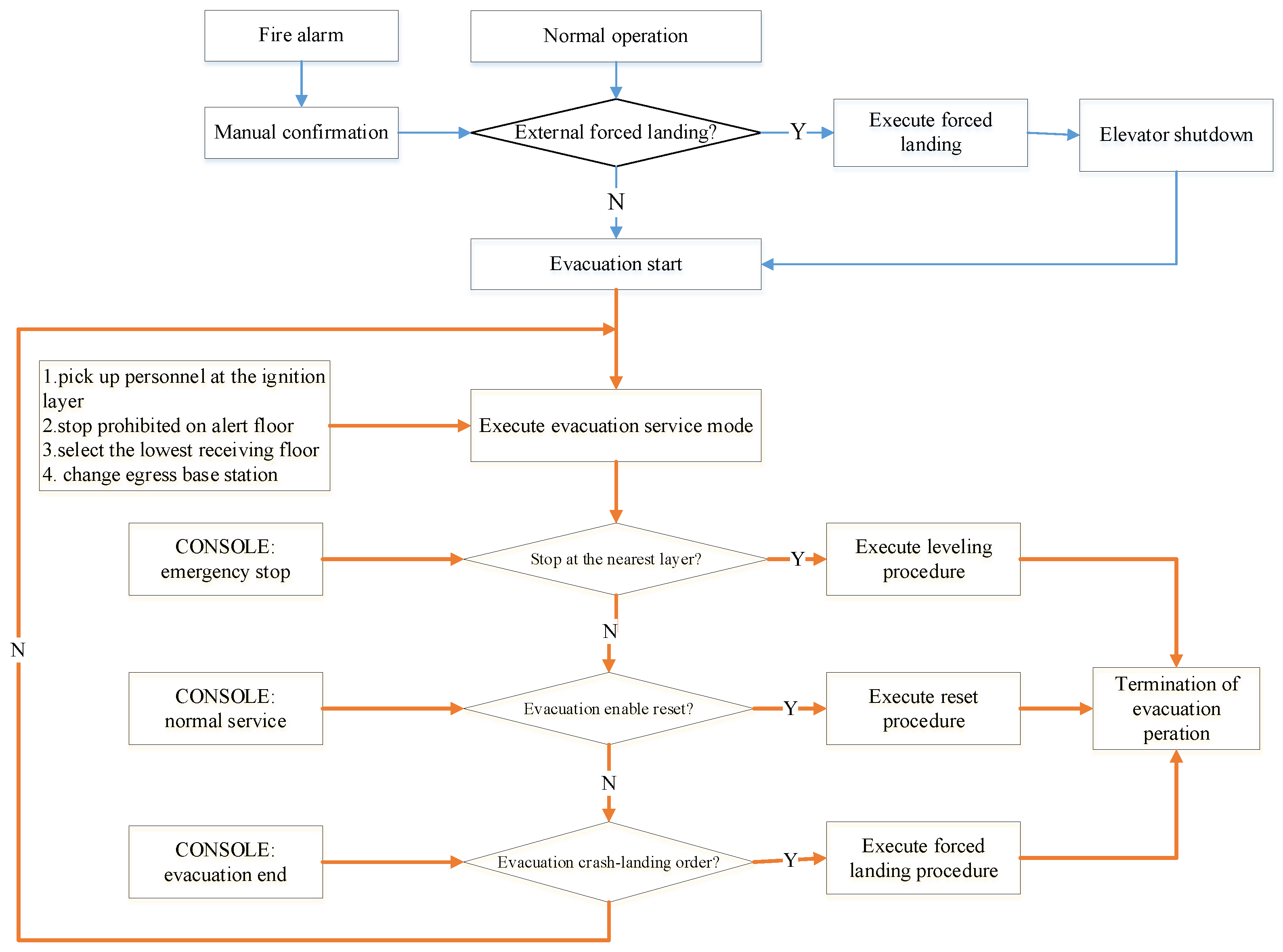
4. Research Approaches of Fire Safety Evacuation
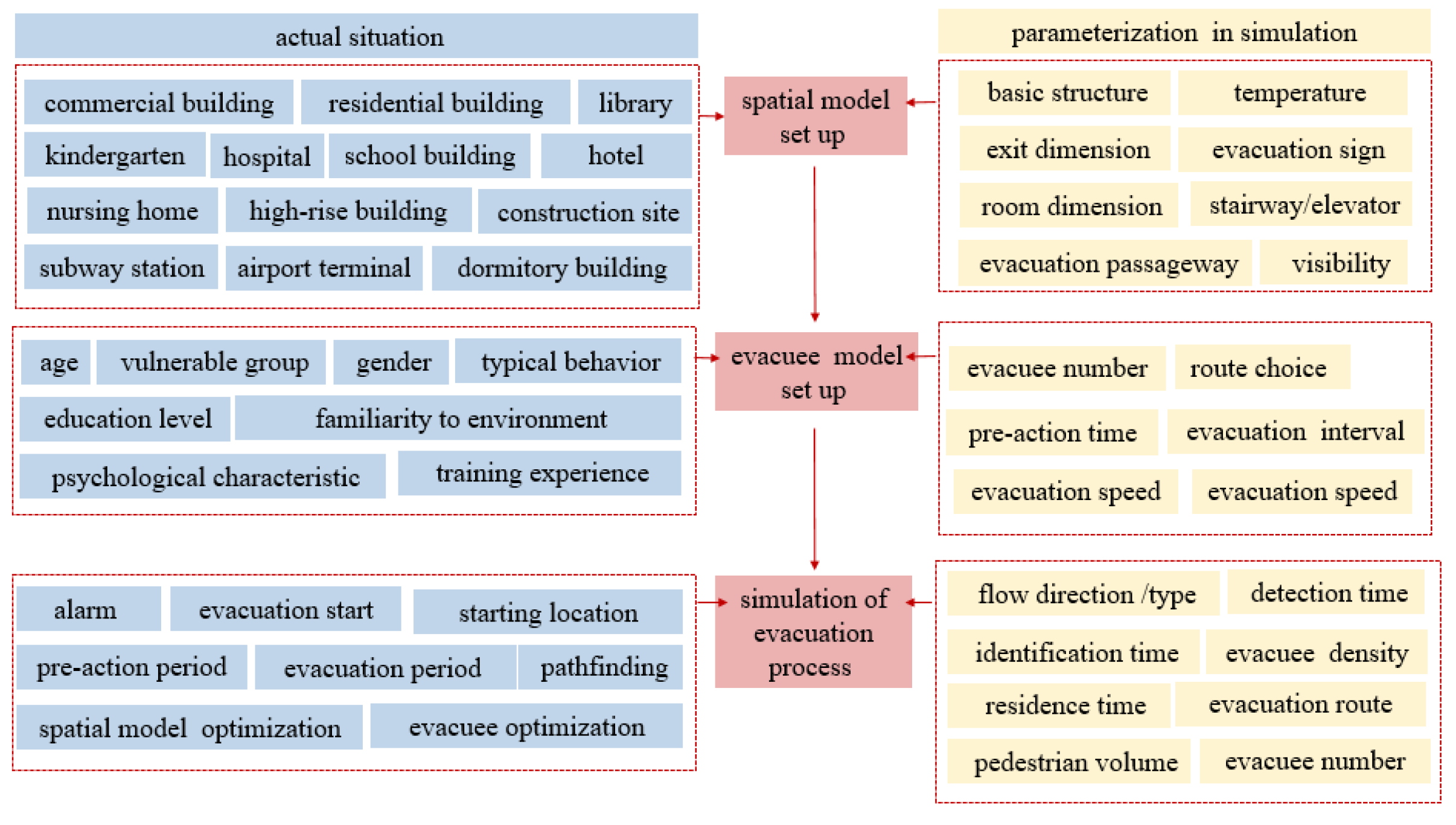
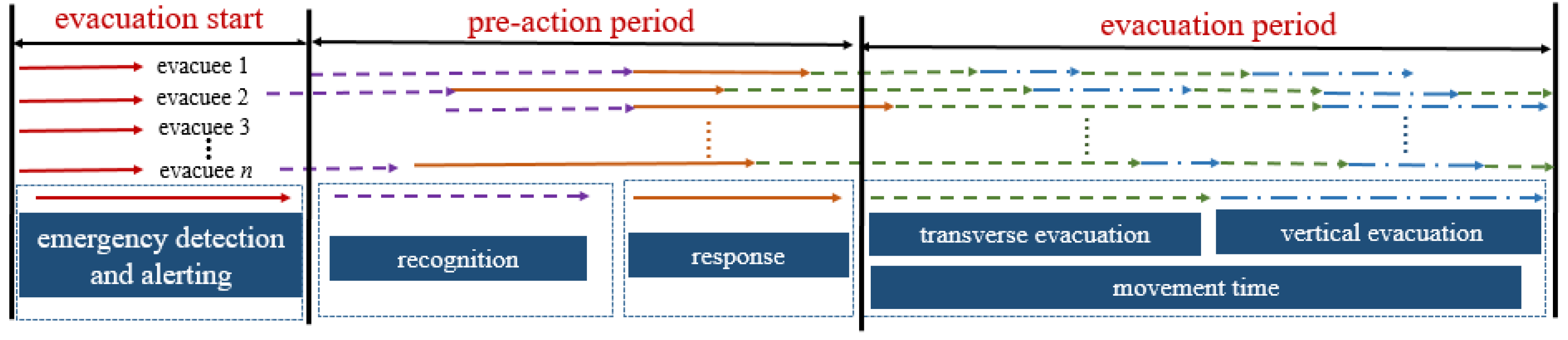
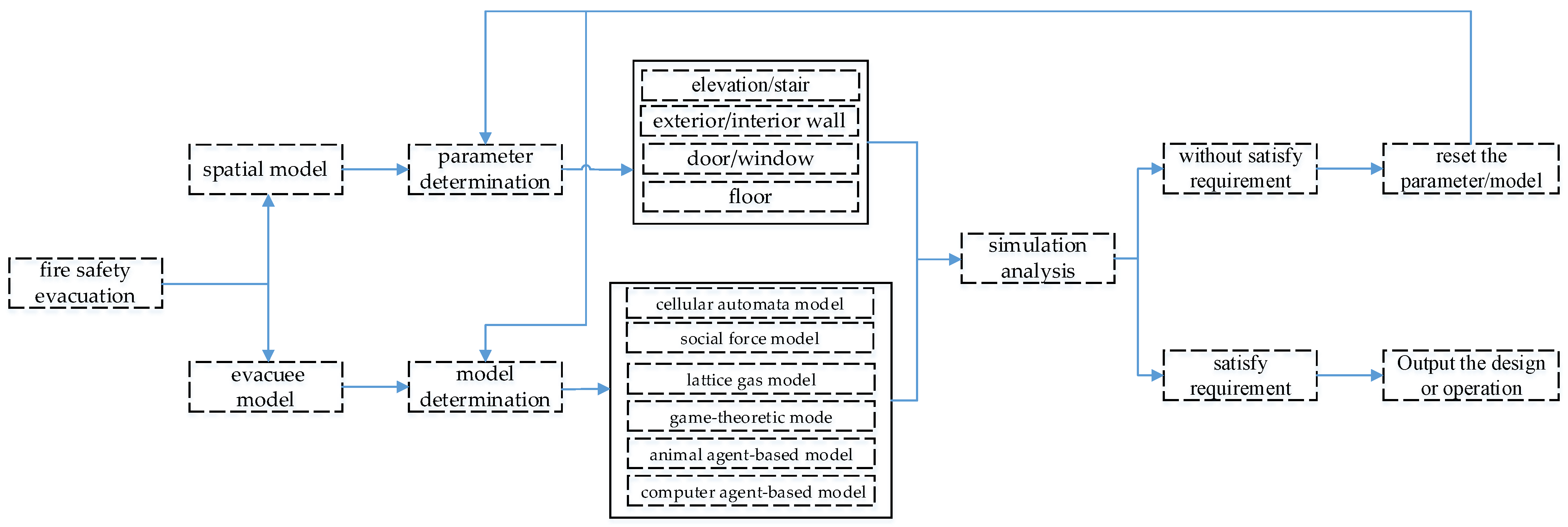
4.1. Evacuation Models
4.2. Experiment Methods
5. Research Contents of Fire Safety Evacuation
5.1. Research Objects
5.2. Evacuation Environments
5.3. Disaster Classification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, R.R.; Garfin, D.R.; Silver, R.C. Evacuation from natural disasters: A systematic review of the literature. Risk Anal. 2017, 37, 812–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobes, M.; Helsloot, I.; de Vries, B.; Post, J.G. Building safety and human behaviour in fire: A literature review. Fire Saf. J. 2010, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, O.F.; Galea, E.R.; Hulse, L.M. A review of the literature on human behaviour in dwelling fires. Saf. Sci. 2018, 109, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinateder, M.T.; Kuligowski, E.D.; Reneke, P.A.; Peacock, R.D. Risk perception in fire evacuation behavior revisited: Definitions, related concepts, and empirical evidence. Fire Sci. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Chen, T.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, Y. State-of-the-art high-rise building emergency evacuation behavior. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2021, 561, 125168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauberman, G. Scoping review of fire safety behaviors among high-rise occupants: Implications for public health nursing. Public Health Nurs. 2020, 37, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, G.; D’Orazio, M.; Quagliarini, E. Towards a “behavioural design” approach for seismic risk reduction strategies of buildings and their environment. Saf. Sci. 2016, 86, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, A.; Javadi, S.; Moghanmi, R.M. Emergency management systems after disastrous earthquakes using optimization methods: A comprehensive review. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2020, 149, 102885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kako, M.; Steenkamp, M.; Ryan, B.; Arbon, P.; Takada, Y. Best practice for evacuation centres accommodating vulnerable populations: A literature review. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 46, 101497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, S.; Pennock, M.J. Social media applications and emergency management: A literature review and research agenda. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2018, 28, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, H.; Kuligowski, E.D.; Gwynne, S.M.V.; Butler, K.M. Human response to emergency communication: A review of guidance on alerts and warning messages for emergencies in buildings. Fire Technol. 2017, 53, 1641–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Lin, J.; Becerik-Gerber, B.; Li, N. Human-building-emergency interactions and their impact on emergency response performance: A review of the state of the art. Saf. Sci. 2020, 127, 104691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Dong, H.; Ioannou, P.A.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.-Y. Guided crowd evacuation: Approaches and challenges. J. Autom. Sin. 2019, 6, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Dou, Z.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Mebarki, A. A review of cellular automata models for crowd evacuation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 526, 120752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, F.; Khorasani-Zavareh, D.; Kavousi, A.; Mohammadi, R. A system approach on safe emergency evacuation in subways: A systematic literature review. Arch. Trauma Res. 2019, 8, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, N.; Simpson, J.N. Pediatric disaster preparedness: Identifying challenges and opportunities for emergency department planning. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2019, 31, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhu, R.; Li, N.; Becerik-Gerber, B. How occupants respond to building emergencies: A systematic review of behavioral characteristics and behavioral theories. Saf. Sci. 2020, 122, 104540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulou, C.; Konstantinidou, M.; Kepaptsoglou, K.; Stathopoulos, A. Its technologies for decision making during evacuation operations: A review. J. Transp. Eng. Part A-Syst. 2020, 146, 04020010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.; Al-Hussein, M.; Ahmad, R. A scientometric analysis and critical review of computer vision applications for construction. Autom. Constr. 2019, 107, 102947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Goerlandt, F.; Reniers, G. An overview of scientometric mapping for the safety science community: Methods, tools, and framework. Saf. Sci. 2021, 134, 105093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelam, S.; Sood, S.K. A scientometric review of global research on smart disaster management. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2021, 68, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, L.D. The scientometric analysis of the research on microalgae-based wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 25339–25348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghimien, E.I.; Aghimien, L.M.; Petinrin, O.O.; Aghimien, D.O. High-performance computing for computational modelling in built environment-related studies- a scientometric review. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 2020, 19, 1138–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, K.; Lai, X.; Antwi-Afari, M. A scientometric review of system dynamics applications in construction management research. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Vu, H.L.; Huang, H.L. Fifty years of accident analysis& prevention: A bibliometric and scientometric overview. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 144, 105568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.Y.; Zou, Y.; Gidado, K.; Ashton, P.; Painting, N. Scientometric analysis of bim based research in construction engineering and management. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2018, 26, 1750–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.B. A scientometric review of global bim research: Analysis and visualization. Autom. Constr. 2017, 80, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, P.; Chen, J. Optimal emergency evacuation route planning model based on fire prediction data. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renne, J.; Wolshon, B.; Murray-Tuite, P.; Pande, A. Emergence of resilience as a framework for state departments of transportation (dots) in the United States. Transp. Res. Part D 2019, 82, 102178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spartalis, E.; Georgoudas, I.G.; Sirakoulis, G.C. Ca crowd modeling for a retirement house evacuation with guidance. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2014, 8751, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giitsidis, T.; Dourvas, N.I.; Sirakoulis, G.C. Parallel implementation of aircraft disembarking and emergency evacuation based on cellular automata. Int. J. High Perform. Comput. Appl. 2015, 18, 1094342015584533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, P.V.R.; Ranauro, D.O.; Mol, A.C.D.A.; Jatoba, A.; de Siqueira, A.P.L. Using Serious Game in Public Schools for Training Fire Evacuation Procedures. Int. J. Serious Games 2022, 9, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wąs, J. Egress Modeling through Cellular Automata Based Multi-Agent Systems. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2012, 7270, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.C.; Hijazi, I.; Mebarki, A.; Meouche, R.E.; Abune’Meh, M. Indoor guided evacuation: Tin for graph generation and crowd evacuation. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 7, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, J.; Yi, W.; Zheng, X. Modeling crowd evacuation via behavioral heterogeneity-based social force model. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 15476–15486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.X.; Pan, S.L.; Chen, Q. Simulation of pedestrian evacuation in stampedes based on a cellular automaton model. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2020, 104, 102147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, N.A.; Majid, M.A.; Adam, K.; Allegra, M. Social force as a microscopic simulation model for pedestrian behavior in crowd evacuation. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2018, 24, 7611–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.X.; Ni, Z.R. Improved social force model based on navigation points for crowd emergent evacuation. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 16, 1309–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Zhao, L.; Chen, M.; Luo, R. Fuzzy social force model for pedestrian evacuation under view-limited condition. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 2879802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makmul, J. A social force model for pedestrians’ movements affected by smoke spreading. Model. Simul. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8819076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolivand, H.; Rahim, M.S.; Sunar, M.S.; Fata, A.Z.A.; Wren, C. An integration of enhanced social force and crowd control models for high-density crowd simulation. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 33, 6095–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Fan, W.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J. Simulating crowd evacuation in a social force model with iterative extended state observer. J. Adv. Transp. 2020, 2020, 4604187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.Y.; Cui, H.J.; Zhu, M.Q. Improved social force model for rescue action during evacuation. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 34, 2050273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, W.; Tu, Y.; Hua, X. Modelling unidirectional crowd motion in a corridor with statistical characteristics of pedestrian movements. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 7483210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.Z.; Dong, L.Y. A floor field real-coded lattice gas model for crowd evacuation. Europhys. Lett. 2017, 119, 10003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Yang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Shi, Q. Modeling pedestrian flow on multi-storey stairs considering turning behavior. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2017, 28, 1750034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, B. Evacuation of pedestrians with two motion modes for panic system. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.Y.; Huang, H.J.; Zhang, Y.M. An extended mobile lattice gas model allowing pedestrian step size variable. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2015, 424, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzat, S.; Kuperman, M.N. Game theory in models of pedestrian room evacuation. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 032806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, V.; Lee, C.E.; Lees, M.H.; Cheong, S.A.; Sloot, P. Quantitative comparison between crowd models for evacuation planning and evaluation. Eur. Phys. J. B 2014, 87, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, J.; You, S.; Wei, J. Modeling of pedestrian evacuation under fire emergency based on an extended heterogeneous lattice gas model. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2013, 392, 1994–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigos, A.; Mohlin, E.; Ronchi, E. The cry wolf effect in evacuation: A game-theoretic approach. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 526, 120890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.M.; Venkat, V.I.; De Wilde, P. The impact of potential crowd behaviours on emergency evacuation: An evolutionary game-theoretic approach. J. Artif. Soc. Soc. Simul. 2019, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnwald, A.; Wollherr, D. Human-like motion planning based on game theoretic decision making. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2019, 11, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morten, G.; Granmo, O.-C.; Radianti, J. Escape planning in realistic fire scenarios with Ant Colony Optimisation. Appl. Intell. 2015, 42, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, B.; Lu, D.; Zhang, G. A path planning approach for crowd evacuation in buildings based on improved artificial bee colony algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 68, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.J.; Lu, D.J.; Liu, H. Strategies to utilize the positive emotional contagion optimally in crowd evacuation. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 11, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.L.; Zhang, T.; Xiao, Y.J. Application research of ant colony cellular optimization algorithm in population evacuation path planning. Acta Phys. Sin. 2020, 69, 080504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyomubyeyi, O.; Pilesjö, P.; Mansourian, A. Evacuation planning optimization based on a multi-objective artificial bee colony algorithm. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Y.; Pota, H.R.; Shen, W. Evacuation path optimization based on quantum ant colony algorithm. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2016, 30, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcael, E.; Gonzalez, V.; Orozco, F.; Vargas, S.; Pantoja, A.; Moscoso, P. Ant colony optimization model for tsunamis evacuation routes. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2014, 29, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, N.; Selamat, H.; Ismail, F.S.; Lutfy, O.F.; Haniff, M.F.; Nordin, I.N.A.M. Optimized exit door locations for a safer emergency evacuation using crowd evacuation model and artificial bee colony optimization. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2019, 131, 109505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Kang, J.; Cao, W. Analysis of flood evacuation process in vulnerable community with mutual aid mechanism: An agent-based simulation framework. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, T. Agent-based simulation of fire emergency evacuation with fire and human interaction model (Retraction of vol 49, pg1130, 2011). Saf. Sci. 2012, 50, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, E.; Menassa, C.C. Agent-based modeling of occupants and their impact on energy use in commercial buildings. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2012, 26, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heliövaara, S.; Korhonen, T.; Hostikka, S.; Ehtamo, H. Counterflow model for agent based simulation of crowd dynamics. Build. Environ. 2012, 48, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, G.; D’Orazio, M.; Quagliarini, E.; Spalazzi, L. An agent-based model for earthquake pedestrians’ evacuation simulation in urban scenarios. Transp. Res. Procedia 2014, 2, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimellaro, G.P.; Ozzello, F.; Vallero, A.; Mahin, S.; Shao, B. Simulating earthquake evacuation using human behavior models. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 46, 985–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mostafizi, A.; Cramer, L.A.; Cox, D.; Park, H. An agent-based model of a multimodal near-field tsunami evacuation: Decision-making and life safety. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2016, 64, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafizi, A.; Wang, H.; Cox, D.; Dong, S. An agent-based vertical evacuation model for a near-field tsunami: Choice behavior, logical shelter locations, and life safety. Int. J. Disaster Risk 2019, 34, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, J.; Kim, N.; Wysk, R.A.; Rothrock, L.; Son, Y.-J.; Oh, Y.-G.; Lee, S. Agent-based simulation of affordance-based human behaviors in emergency evacuation. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2013, 32, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasereka, S.; Kasoro, N.; Kyamakya, K.; Goufo, E.-F.D.; Chokki, A.P.; Yengo, M.V. Agent-based modelling and simulation for evacuation of people from a building in case of fire. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 130, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Yu, Y. Calculation of mixed evacuation of stair and elevator using evacnet4. Procedia Eng. 2013, 62, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemelyanenko, S.; Ivanusa, A.; Yakovchuk, R.; Kuzyk, A. Fire risks of public buildings. Ser. Geol. Technol. Sci. 2020, 6, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Wu, X.; Guo, X. Study on intelligent algorithm of guide partition for emergency evacuation of a subway station. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 14, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.H.; Shao, P.C.; Kuo, F.M. Stampede events and strategies for crowd management. J. Disaster Res. 2019, 14, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alginahi, Y.M.; Mudassar, M.; Kabir, M.N.; Tayan, O. Analyzing the crowd evacuation pattern of a large densely populated building. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 3289–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.S.; Lu, W. Research on kindergarten children evacuation: Analysis of characteristics of the movement behaviours on stairway. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 50, 101718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Turkan, Y. A bim-based simulation framework for fire safety management and investigation of the critical factors affecting human evacuation performance. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 44, 101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Du, M.H.; Tang, Y.F.; Zhang, Q. An analysis on the fire model and the safety evacuation based on bim. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1065–1069, 2386–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.S.; Liu, C.C.; Wu, I. A bim-based visualization and warning system for fire rescue. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 37, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, X.; Zeng, X.; Guan, H. Post-earthquake fire simulation considering overall seismic damage of sprinkler systems based on bim and femap-58. Autom. Constr. 2018, 90, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Zhang, B.-Y.; Shao, C.-F.; Xing, Y. Exit selection strategy in pedestrian evacuation simulation with multi-exits. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23, 050512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimakis, N.; Filippoupolitis, A.; Gelenbe, E. Distributed building evacuation simulator for smart emergency management. Comput. J. 2010, 53, 1384–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; Daour, I.A. Planning labor evacuation for construction sites using bim and agent-based simulation. Saf. Sci. 2018, 109, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehbe, R.; Shahrour, I. A bim-based smart system for fire evacuation. Future Internet 2021, 13, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Sawaguchi, Y.; Nishiki, S. Simulation of tunnel fire for evacuation safety assessment. Safety 2018, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Pang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y. Three-dimensional indoor fire evacuation routing. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Ou, Z.; Zhang, G.; Deng, Y.; Tian, M. BIM and computer vision-based framework for fire emergency evacuation considering local safety performance. Sensors 2021, 21, 3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Niu, M.; Wan, F. Study on Fire Smoke Distribution and Safety Evacuation of Subway Station Based on BIM. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.N.I.; Peng, Y.; Yiran, C.; Shouse, R.C. Disaster resilience through big data: Way to environmental sustainability. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 51, 101769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañas, E.L.; Plá, J.; Herrero, G.M.; Gervás, P. Augmented reality and indoors Wi-Fi positioning for conducting fire evacuation drills using mobile phones. In Proceedings of the 4th Symposium of Ubiquitous Computing and Ambient Intelligence UCAmI, Toledo, Spain, 1 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Zhang, H.; Dong, W. A review of emerging trends in global PPP research: Analysis and visualization. Scientometrics 2016, 107, 1111–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2009, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, V.; Venkatesan, S.P.; Goh, M. Decision-making models for supply chain risk mitigation: A review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 113, 646–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, V.; Jan, N.; Waltman, L. CitNetExplorer: A new software tool for analyzing and visualizing citation networks. J. Informetr. 2014, 8, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiftsis, A.; Georgoudas, I.G.; Sirakoulis, G.C. Real data evaluation of a crowd supervising system for stadium evacuation and its hardware implementation. IEEE Syst. J. 2016, 10, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, G.; Lovreglio, R.; Quagliarini, E. Proposing behavior-oriented strategies for earthquake emergency evacuation:a behavioral data analysis from New Zealand, Italy and Japan. Saf. Sci. 2019, 116, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambie, E.S.; Wilson, T.M.; Brogt, E.; Johnston, D.M.; Ardagh, M.; Deely, J.; Jensen, S.; Feldmann-Jensen, S. Closed circuit television(cctv) earthquake behaviour coding methodology: Analysis of christchurch public hospital video data from the 22 february christchurch earthquake event. Nat. Hazards 2017, 86, 1175–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Shiwakoti, N.; Yang, M. Video-based analysis of school students’ emergency evacuation behavior in earthquakes. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2016, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambie, E.; Wilson, T.M.; Johnston, D.M.; Jensen, S.; Brogt, E.; Doyle, E.E.H.; Lindell, M.K.; Helton, W.S. Human behaviour during and immediately following earthquake shaking: Developing a methodological approach for analysing video footage. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 249–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovreglio, R.; Gonzalez, V.; Feng, Z.; Amor, R.; Spearpoint, M.; Thomas, J.; Trotter, M.; Sacks, R. Prototyping virtual reality serious games for building earthquake preparedness: The auckland city hospital case study. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 38, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, P.; Valeria, C.; Luca, P. Emotional and behavioural reactions to tremors of the umbria-marche earthquake. Disasters 2012, 36, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, K.; Chang, J.; Beatson, A.; Morahan, C. Public perceptions of building seismic safety following the canterbury earthquakes:a qualitative analysis using twitter and focus groups. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2015, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, R.; Wang, Q. An experimental study of visibility effect on evacuation speed on stairs. Fire Saf. J. 2018, 96, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, F.; Song, W.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Liew, K. Investigation of human behavior in emergent evacuation from an underground retail store. Procedia Eng. 2014, 71, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobes, M.; Helsloot, I.; de Vries, B.; Post, J. Exit choice, (pre-) movement time and (pre-) evacuation behavior in hotel fire evacuation—Behavioural analysis and validation of the use of serious gaming in experimental research. Procedia Eng. 2010, 3, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulos, A.; Tocornal, F.; de la Llera, J.C.; Mitrani-Reiser, J. Validation of an agent-based building evacuation model with a school drill. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 97, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.-M.; Song, W.-G.; Li, Z.-J.; Tian, W.; Lv, W.; Ma, J.; Xiao, X. Experimental study on evacuation process in a stairwell of a high-rise building. Build. Environ. 2012, 47, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Qiu, H.; Lin, P.; Lo, S.M.; Lo, J.T.Y. Towards a smart elevator-aided fire evacuation scheme in high-rise apartment buildings for elderly. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 90690–90705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.J.; Lo, S.M.; Ma, J.; Liu, S.B.; Liao, G.X. A study on people’s attitude to the use of elevators for fire escape. Fire Technol. 2014, 50, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Song, W.; Tian, W.; Lo, S.M.; Liao, G. Experimental study on an ultra high-rise building evacuation in china. Saf. Sci. 2012, 50, 1665–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Klingsch, W.; Schadschneider, A.; Seyfried, A. Experimental study of pedestrian flow through a T-junction. Traffic Granul. Flow 2013, 11, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Klingsch, W.; Schadschneider, A.; Seyfried, A. Ordering in bidirectional pedestrian flows and its influence on the fundamental diagram. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2012, 02, P02002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Seyfried, A. Comparison of intersecting pedestrian flows based on experiments. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 405, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltes, M.; Zhang, J.; Tordeux, A.; Schadschneider, A.; Seyfried, A. Empirical results of pedestrian and evacuation dynamics. In Encyclopedia of Complexity and Systems Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, D.; Jones, C.; Trugman, A.T.; Varga, K.; Plantinga, A.J.; Carvalho, L.M.V.; Thompson, C.; Gellman, J.; Daum, K. Simulating potential impacts of fuel treatments on fire behavior and evacuation time of the 2018 Camp Fire in northern California. Fire 2022, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauslar, N.J.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Marsh, P.T. The 2017 North Bay and Southern California fires: A case study. Fire 2018, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, R.D.; Hoskins, B.L.; Kuligowski, E.D. Overall and local movement speeds during fire drill evacuations in buildings up to 31 stories. In Pedestrian and Evacuation Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, G.; Yamori, K.; Miyashita, T.; Urra, L.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. Combination of school evacuation drill with tsunami inundation simulation: Consensus-making between disaster experts and citizens on an evacuation strategy. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 51, 101803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, G.N.; Lennon, P.F.; O’Raw, J. Toward fire safe schools: Analysis of modelling speed and specific flow of children during evacuation drills. Fire Technol. 2020, 56, 605–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Song, Z.; Gao, J. Evacuation performance of participants in an offshore platform under smoke situations. Ocean Eng. 2020, 216, 107739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.M.; Jiang, L.X.; Li, X.L.; Qi, W.; Chen, L.Z. Experimental study on the movement characteristics of 5–6 years old chinese children when egressing from a pre-school building. Saf. Sci. 2019, 113, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, T.; Yamori, K. Consideration of evacuation drills utilizing the capabilities of people with special needs. J. Disaster Res. 2020, 15, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahouti, A.; Lovreglio, R.; Gwynne, S.; Jackson, P.; Datoussaïd, S.; Hunt, A. Human behaviour during a healthcare facility evacuation drills: Investigation of pre-evacuation and travel phases. Saf. Sci. 2020, 129, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaime, S. Factors motivating mexico city residents to earthquake mass evacuation drills. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 49, 101661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, J.; Mitsuhara, H.; Shishibori, M. Game-based evacuation drill using augmented reality and head-mounted display. Emerald Insight 2016, 13, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobes, M.; Helsloot, I.; de Vries, B.; Post, J.G.; Oberijé, N.; Groenewegen, K. Way finding during fire evacuation; an analysis of unannounced fire drills in a hotel at night. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolghasemzadeh, P. A comprehensive method for environmentally sensitive and behavioral microscopic egress analysis in case of fire in buildings. Saf. Sci. 2013, 59, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Yap, J.B.H.; Li, H.; Zhang, S. Emergency evacuation simulation at starting connection of cross-sea bridge: Case study on haicang avenue subway station in xiamen rail transit Line. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 29, 101163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinateder, M.; Ronchi, E.; Nilsson, D.; Kobes, M.; Mülberger, A. Virtual Reality for Fire Evacuation Research. In Proceedings of the 2014 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems, Warsaw, Poland, 7–10 September 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Luh, P.B.; Marsh, K.L.; Gifford, T.; Tucker, A. Guidance optimization of building evacuation considering psychological features in route choice. In Proceedings of the 11th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Shenyang, China, 29 June–4 July 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 2669–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, K.L.; Wilkie, C.T.; Luh, P.B.; Zhang, Z.; Gifford, T.; Olderman, N. Crowd guidance in building emergencies: Using virtual reality experiments to confirm macroscopic mathematical modeling of psychological variables. In Pedestrian and Evacuation Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchi, E.; Nilsson, D.; Kojić, S.; Eriksson, J.; Lovreglio, R.; Modig, H.; Walter, A.L. Virtual reality experiment on flashing lights at emergency exit portals for road tunnel evacuation. Fire Technol. 2016, 52, 623–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, N.; Cao, L.J. Emotional response- based approach for assessing the sense of presence of subjects in virtual building evacuation studies. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2017, 31, 04017028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrée, K.; Nilsson, D.; Eriksson, J. Evacuation experiments in a virtual reality high-rise building: Exit choice and waiting time for evacuation elevators. Fire Mater. 2016, 40, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhim, E.M.; Cherkaoui, A. Simulating pre-evacuation behavior in a virtual fire environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2018 9th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies, Bengaluru, India, 10–12 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.J.; Lin, J.; Li, N. A virtual reality based udy of indoor fire evacuation after active or passive spatial exploration. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 90, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Wang, C.B.; He, G.Q. A vr-based, hybrid modeling approach to fire evacuation simulation. ASSOC Comput. Mach. 2018, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.-Q.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Z.-Q.; Pan, Z.-G. Efficient scene playback and evacuation decision in the configurable 3d virtual emergency scenes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Virtual Reality and Visualization, Hangzhou, China, 24–26 September 2016; pp. 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinateder, M.; Wirth, T.D.; Warren, W.H. Crowd dynamics in virtual reality. In Crowd Dynamics, Volume I Modeling and Simulation in Science, Engineering and Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, D.; Boeira, C.; Rockenbach, G.; Maurer, G.; Antonitsch, A.; Musse, S.R. Simulating virtual humans crowds in facilities. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th Brazilian Symposium on Computer Games and Digital Entertainment (SBGames), Foz do Iguacu, Brazil, 29 October–1 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 343–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, D.-W.; Liu, Z.-G.; Lou, Y.-R. The Development and Evaluation of Virtual Reality Platform for Emergency Evacuation in Coal Mines; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlberger, A.; Kinateder, M.; Brütting, J.; Eder, S.; Müller, M.; Gromer, D.; Pauli, P. Influence of information and instructions on human behavior in tunnel accidents: A virtual reality study. J. Virtual Real. Broadcast. 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Zhang, J.; Xia, L.; Song, W.; Bode, N.W. Comparing the route-choice behavior of pedestrians around obstacles in a virtual experiment and a field study. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2019, 107, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, K.; Mitsuhara, H.; Shishibori, M. Evacuation instruction training system using augmented reality and a smartphone-based head mounted display. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Disaster Management, Vienna, Austria, 13–15 December 2016; pp. 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhara, H.; Iguchi, K.; Kawai, J. Using digital game, augmented reality, and head mounted displays for immediate-action commander training. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2017, 12, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Han, R. Rescueme: An indoor mobile augmented-reality evacuation system by personalized pedometry. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Asia-Pacific Services Computing Conference, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 12–15 December 2011; pp. 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lochhead, I.; Hedley, N. Mixed reality emergency management: Bringing virtual evacuation simulations into real-world built environments. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2018, 12, 190–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, S.; La Mendola, S.; Wahlqvist, J.; Rios, O.; Nilsson, D.; Ronchi, E. Virtual reality evacuation experiments on way-finding systems for the future circular collider. Fire Technol. 2019, 55, 2319–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Lo, S.M.; Sun, J.H.; Wang, Q.-S.; Mu, H.-L. Qualitative simulation of the panic spread in large scale evacuation. Simulation 2012, 88, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghani, M.; Sarvi, M. Stated and revealed exit choices of pedestrian crowd evacuees. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2017, 95, 238–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmanová, H.; Kuklík, L.; Pešková, V.; Bukáček, M.; Hrabák, P.; Vašata, D. Evacuation trials from a double-deck electric train unit: Experimental data and sensitivity analysis. Saf. Sci. 2022, 146, 105523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.L.; Parigi, P.; Law, K.H.; Latombe, J.-C. Simulating individual, group, and crowd behaviors in building egress. Simulation 2015, 91, 825–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodur, V.K.R.; Venkatachari, S.; Naser, M.Z. Egress parameters influencing emergency evacuation in high-rise buildings. Fire Technol. 2019, 56, 2035–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdi, H.A.; Al-Megren, S.; Althunyan, R.; Almulifi, A. Effect of exit placement on evacuation plans. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 269, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguslawski, P.; Mahdjoubi, L.; Zverovich, V.; Fadli, F. A dynamic approach for evacuees distribution and optimal routing in hazardous environments. Autom. Constr. 2018, 94, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, N.; Kakosimos, K.E.; Adia, N.; Véchot, L. Concept and demonstration of a fully coupled and dynamic exposure-response methodology for crowd evacuation numerical modelling in airborne-toxic environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, G.; Quagliarini, E.; D’Orazio, M. Towards creating a combined database for earthquake pedestrians’ evacuation models. Saf. Sci. 2016, 82, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-H.; Yan, W.-Y.; Zhi, Y.-R.; Jiang, J.-C. Investigation of the panic psychology and behaviors of evacuation crowds in subway emergencies. Procedia Eng. 2016, 135, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.H.; Chen, X.H.; Jian, N.J. Impact analysis of human factors on pedestrian traffic characteristics. Fire Saf. J. 2012, 52, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Zhao, Y.C.; Kim, N.H.; Ahn, Y.H. Home modifications for older people with cognitive impairments: Mediation analysis of caregivers’ information needs and perceptions of fall risks. Int. J. Older People Nurs. 2019, 14, e12240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Yu, P.; Gong, J.; Shen, S.; Huang, L.; Liang, J. Modelling simulation and analysis of the evacuation process on stairs in a multi-floor classroom building of a primary school. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2017, 469, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Song, W.; Yuen, K.K.R. A comparative study on the bottleneck flow between preschool children and adults under different movement motivations. Saf. Sci. 2020, 121, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.J.; Wu, H.Y.; Chou, C.C. Evacuation simulation in a cultural asset fire: Impact of fire emergency evacuation facilities for people with disabilities on evacuation time. Fire 2022, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Lee, S.; Hwang, S.; Park, M.; Lee, H.-S. Comparison of emergency response abilities and evacuation performance involving vulnerable occupants in building fire situations. Sustainability 2019, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; You, L.; Chen, P. Experiment and simulation of the bidirectional pedestrian flow model with overtaking and herding behavior. Int. J. Mordern Phys. C 2015, 26, 1550131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.S.; Yang, Z.F.; Rong, J.; Liu, X. Study on the weaving behavior of high density bidirectional pedestrian flow. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 765659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, G.; Santarelli, S.; Quagliarini, E.; D’Orazio, M. Dynamic guidance tool for a safer earthquake pedestrian evacuation in urban systems. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 65, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.M.; Lv, W.; Jiang, L.-X.; Xu, Q.-F.; Song, W.-G. Observation, simulation and optimization of the movement of passengers with baggage in railway station. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2015, 26, 1550124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Song, Y. Fire evacuation in metro stations: Modeling research on the effects of two key parameters. Sustainability 2020, 12, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirik, E.; Bogdanov, A.; Sushkova, O.; Gravit, M.; Shabunina, D.; Rozov, A.; Vitova, T.; Lazarev, Y. Fire Safety in Museums: Simulation of Fire Scenarios for Development of Control Evacuation Schemes from the Winter Palace of the Hermitage. Buildings 2022, 12, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravit, M.; Kirik, E.; Savchenko, E.; Vitova, T.; Shabunina, D. Simulation of evacuation from stadiums and entertainment arenas of different epochs on the example of the Roman Colosseum and the Gazprom Arena. Fire 2022, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdi, H.; Alzuhair, A.; Alotaibi, D.; Alsweed, H.; Almoqayyad, N.; Albaqami, R.; Althnian, A.; Alnabhan, N.; Al Islam, A.B.M.A. Crowd evacuation in Hajj stoning area: Planning through modeling and simulation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.Y.; Ho, W.M. A modified entropy-based dynamic gravity model for the evacuation trip distribution problem during typhoons. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2016, 39, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durage, S.W.; Kattan, L.; Wirasinghe, S.C.; Ruwanpura, J.Y. Evacuation behaviour of households and drivers during a tornado. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 1495–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, B.; Qiu, S.; Li, Z.; Qiu, X. Agent-based modeling of emergency evacuation in a railway station square under sarin terrorist attack. Int. J. Model. Simul. Sci. Comput. 2017, 8, 1750022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.-W.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chuang, Y.-J.; Hsiao, G.L.-K. Using smartphones for indoor fire evacuation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, P.; De Iuliis, M.; Marasco, S.; Domaneschi, M.; Cimellaro, G.P.; Villa, V. Fire emergency evacuation from a school building using an evolutionary virtual reality platform. Buildings 2022, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| (a) Journals Publications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Journal Title | Number of Articles | % Total Publications |
| Safety Science | 131 | 3.95% |
| Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications | 114 | 3.42% |
| Transportation Research Record | 92 | 2.77% |
| Procedia Engineering | 77 | 2.31% |
| Fire | 70 | 2.13% |
| Transportation Research Procedia | 42 | 1.29% |
| Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory | 40 | 1.18% |
| Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies | 39 | 1.10% |
| Journal of Disaster Research | 36 | 1.06% |
| PLOS ONE | 35 | 1.02% |
| Applied Mechanics and Materials | 33 | 0.95% |
| IEEE Access | 31 | 0.83% |
| Mathematical Problems in Engineering | 27 | 0.83% |
| Advances in Intelligent Systems Research | 27 | 0.80% |
| Journal of Advanced Transportation | 24 | 0.72% |
| Sustainability | 24 | 0.72% |
| Chinese Physics B | 21 | 0.65% |
| Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness | 21 | 0.65% |
| International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 21 | 0.65% |
| International Journal of Modern Physics C | 21 | 0.65% |
| Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence | 21 | 0.65% |
| (b) Conference Proceedings Publications | ||
| Conference Title | Number of Articles | % Total Publications |
| Conference on Pedestrian and Evacuation Dynamics (PED) | 123 | 3.73% |
| International Conference on Performance Based Fire and Fire Protection Engineering (ICPBFFPE) | 52 | 1.56% |
| IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science | 31 | 0.95% |
| International Conference on Evacuation Modeling and Management | 17 | 0.53% |
| International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC) | 16 | 0.49% |
| Winter Simulation Conference (WSC) | 15 | 0.46% |
| International Symposium on Safety Science and Technology (ISSST) | 12 | 0.38% |
| Traffic and Granular Flow | 8 | 0.27% |
| IEEE International Conference on Systems Man and Cybernetics (SMC) | 7 | 0.23% |
| International Conference on Cellular Automata for Research and Industry (CACRI) | 6 | 0.19% |
| International Conference on Urban Transport and the Environment (ICUTE) | 6 | 0.19% |
| International Conference on Civil Engineering and Transportation (ICCET) | 6 | 0.19% |
| IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM) | 6 | 0.19% |
| World Conference of Associated Research Centers for the Urban Underground Space (ACUUS) | 4 | 0.15% |
| International Symposium on Transportation and Traffic Theory (ISTTT) | 4 | 0.15% |
| International Conference on Computer Simulation in Risk Analysis and Hazard Mitigation | 4 | 0.15% |
| Construction Research Congress | 4 | 0.15% |
| ASIA Conference on Information Systems for Crisis Response and Management (ISCRAM) | 4 | 0.15% |
| Model Type | Evacuee Characteristic | Evacuation Behavior | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motion | Variable | Type | Avoidance | Reentry | Following | Nearby | Guideline | |
| Cellular automata | UD (direction) | US (0/1) | SD | UI | UI | UI | UD | UD |
| Social force | UD (speed) | UD | UD | UI | UI | UD | UD | UD |
| Lattice gas | UD (direction) | US (0/1) | SD | UI | UI | UD | UD | UD |
| Game-theoretic | UD | SD | UD | UD | UD | UD | UD | UD |
| Animal agent-based | UD | SD | US | SD | SD | SD | SD | SD |
| Computer agent-based | UD | UD | UD | SD | SD | SD | SD | SD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Du, H.; Yao, G. A Scientometric Research on Applications and Advances of Fire Safety Evacuation in Buildings. Fire 2023, 6, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6030083
Yang Y, Du H, Yao G. A Scientometric Research on Applications and Advances of Fire Safety Evacuation in Buildings. Fire. 2023; 6(3):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6030083
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yang, Hongbo Du, and Gang Yao. 2023. "A Scientometric Research on Applications and Advances of Fire Safety Evacuation in Buildings" Fire 6, no. 3: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6030083
APA StyleYang, Y., Du, H., & Yao, G. (2023). A Scientometric Research on Applications and Advances of Fire Safety Evacuation in Buildings. Fire, 6(3), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6030083








