Critical Factors Affecting Fire Safety in High-Rise Buildings in the Emirate of Sharjah, UAE
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Fire Factors Effecting Fire Management System in the Residential Buildings
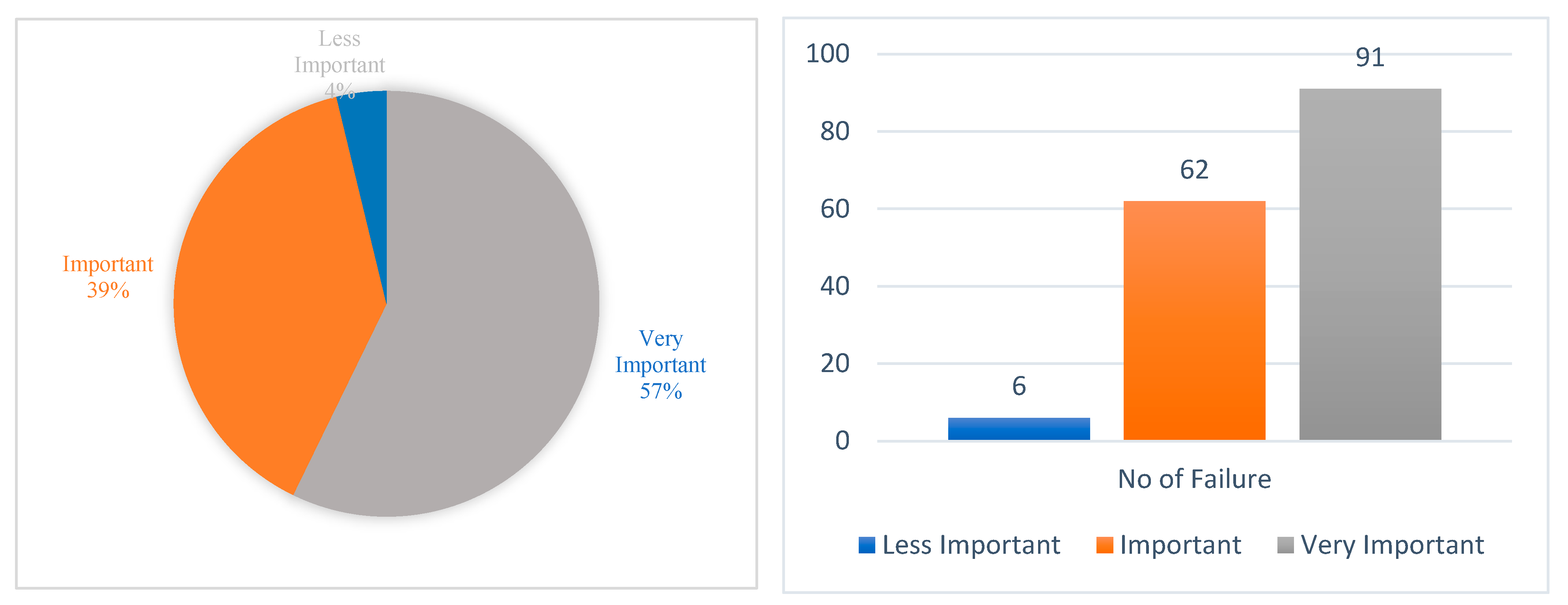
3.2. Failure Mode, Effect, and Criticality Analysis
3.3. Critical Success Factors Affecting the Fire Prevention Management Systems in the Emirate of Sharjah
4. Discussion
4.1. Fire Fighting Legislation
4.2. Compulsory Fire Legislation
4.3. Management of HRBs
4.4. Fire Research and Development
4.5. Accident Investigation
4.6. Contractor Attitude
4.7. Speed of Response and Rescue
4.8. Optimization of Fire Resources
4.9. Human Behavior
4.10. Fire Training
4.11. Knowledge of Fire Hazards
4.12. Culture of Society
4.13. Fire Fighting Technology
4.14. Absence or Poor Preventive Maintenance of Fire Fighting Systems
4.15. Fire Fighting Equipment
4.16. Residential Building Design
4.17. Flammable Materials
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.-Y.; Tao, G.; Zhang, L.-J. Fire Risk Assessment of High-rise Buildings Based on Gray-FAHP Mathematical Model. Procedia Eng. 2018, 211, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Z.; Liu, H.; Meng, N.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Kong, F. Mapping the knowledge domains of research on fire safety—An informetrics analysis. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 108, 103676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y. Big data in safety management: An overview. Saf. Sci. 2021, 143, 105414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, D. A POIs based method for determining spatial distribution of urban fire risk. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 154, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, L.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Yan, H. How fire safety management attended during the urbanization process in China? J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenehi, I.Y.; Mohamed, S.; Sarpin, N.; Masrom, M.A.N.; Zainal, R.; Azmi, M.A.M. The management of building fire safety towards the sustainability of Malaysian public universities. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 271, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodur, V.; Kumar, P.; Rafi, M.M. Fire hazard in buildings: Review, assessment and strategies for improving fire safety. PSU Res. Rev. 2019, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-H.; Wang, W.-C.; Wang, K.-C.; Shih, S.-Y. Applying building information modeling to support fire safety management. Autom. Constr. 2015, 59, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Turkan, Y. A BIM-based simulation framework for fire safety management and investigation of the critical factors affecting human evacuation performance. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 44, 101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haitao, C.; Leilei, L.; Jiuzi, Q. Accident Cause Analysis and Evacuation Countermeasures on the High-Rise Building Fires. Procedia Eng. 2012, 43, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimlyat, P.S.; Audu, A.U.; Ola-Adisa, E.O.; Gwatau, D. An evaluation of fire safety measures in high-rise buildings in Nigeria. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 35, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Y. A review on research of fire dynamics in high-rise buildings. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 2013, 3, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chow, W. Determination of Fire Load and Heat Release Rate for High-rise Residential Buildings. Procedia Eng. 2014, 84, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Q. Factor Analysis of High-Rise Building Fires Reasons and Fire Protection Measures. Procedia Eng. 2012, 45, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mauree, D.; Sun, Q.; Lin, H.; Scartezzini, J.; Wennersten, R. A review of approaches to low-carbon transition of high-rise residential buildings in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 131, 109990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, A. Thomas Bell-Wright International Consultants The Cladding Problem: Establishing and Assessing Safe Building Envelopes. Int. J. Conform. Assess. 2022, 1, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A. Climate change: The challenges for public health and environmental effects in UAE. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 193, 457–466. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ni, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Lu, K. A Comprehensive Investigation on the Fire Hazards and Environmental Risks in a Commercial Complex Based on Fault Tree Analysis and the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamee, M.; Meacham, B.; van Hees, P.; Bisby, L.; Chow, W.; Coppalle, A.; Dobashi, R.; Dlugogorski, B.; Fahy, R.; Fleischmann, C.; et al. IAFSS agenda 2030 for a fire safe world. Fire Saf. J. 2019, 110, 102889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-X.; Li, Q.; Jiang, L.-R.; Zhou, Y.-H. Analysis of Chinese fire statistics during the period 1997–2017. Fire Saf. J. 2021, 125, 103400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, R.; Sridarran, P.; Abeynayake, M. Factors contributing to building fire incidents: A review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 10–12 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, J.F.; Chan, D.W. Developing a holistic fire risk assessment framework for building construction sites in Hong Kong. J. Construct. Res. 2020, 1, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautami, C.M.; Prajapati, M.; Khurana, R. Analysis of Factors Affecting Fire Safety Management of Residential Building: A Case Study. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2020, 7, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Reniers, G. Chemical industry in China: The current status, safety problems, and pathways for future sustainable development. Saf. Sci. 2020, 128, 104741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardjo, H.A.; Prihanton, M. The most critical issues and challenges of fire safety for building sustainability in Jakarta. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 29, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahed, T.A. Impact of Facility Management on Fire Safety Crisis in Bangladesh’s AEC Industry. Master’s Thesis, Metropolia University of Applied Science, Helsinki, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Akhimien, N.; Isiwele, A.J.; Adamolekun, M.O. Fire Safety in Buildings. J. Civil Environ. Eng. 2017, 4, 63–79. [Google Scholar]
- Dabous, S.A.; Ibrahim, F.; Feroz, S.; Alsyouf, I. Integration of failure mode, effects, and criticality analysis with multi-criteria decision-making in engineering applications: Part I–Manufacturing industry. Eng. Failure Ana. 2021, 122, 105264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, O.S.; Kumar, S. Analytic hierarchy process: An overview of applications. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 169, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, S.L.; De Man, A.F.; Simpson-Housley, P. Ego-Identity Achievement and Perception of Risk in Intimacy in Survivors of Stranger and Acquaintance Rape. Sex Roles 2002, 47, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, S.G.; Jeanneret, C.; Gales, J.; Antonellis, D.; Vaiciulyte, S. Human behaviour in informal settlement fires in Costa Rica. Saf. Sci. 2021, 142, 105384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzemer, L.W.; Ronchi, E.; Karsten, M.M.V.; Gwynne, S.; Frederiksen, J. A scoping review and bibliometric analysis of methods for fire evacuation training in buildings. Fire Saf. J. 2023, 136, 103742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, M.R. The Many Elements of Traditional Fire Knowledge: Synthesis, Classification, and Aids to Cross-cultural Problem Solving in Fire-dependent Systems Around the World. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhou, J.; Su, H.; Wu, Z. The design of experimental courses in safety culture. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, L. Linking maintenance strategies to performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2001, 70, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevega, T.; Jayasinghe, J.; Robert, D.; Bandara, C.; Kandare, E.; Setunge, S. Fire compliance of construction materials for building claddings: A critical review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 129582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | Factors | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building design | 5% |
| 2. | Fire regulations | 6% |
| 3. | Facilities management and policies | 5% |
| 4. | Rescue speed | 6% |
| 5. | Fire knowledge | 6% |
| 6. | Fire equipment | 6% |
| 7. | Human behavior | 5% |
| 8. | Firefighting maintenance | 5% |
| 9. | Fire culture of society | 5% |
| 10. | Fire training | 6% |
| 11. | Combustible materials | 6% |
| 12. | Fire enforcement regulations | 6% |
| 13. | Fire data analysis/availability | 4% |
| 14. | Accident investigation | 6% |
| 15. | Fire R&D | 4% |
| 16. | Fire technology | 5% |
| 17. | Public/contractor attitude | 5% |
| 18. | Staff assignment | 5% |
| 19. | Climate change | 4% |
| No. | Factors | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building design | 6% |
| 2. | Fire regulations | 7% |
| 3. | Facilities management and policies | 2% |
| 4. | Rescue speed | 7% |
| 5. | Fire knowledge | 9% |
| 6. | Fire equipment | 2% |
| 7. | Human behavior | 5% |
| 8. | Firefighting maintenance | 5% |
| 9. | Fire culture of society | 8% |
| 10. | Fire training | 5% |
| 11. | Combustible materials | 9% |
| 12. | Fire enforcement regulations | 9% |
| 13. | Accident investigation | 9% |
| 14. | Fire technology | 2% |
| 15. | Public/contractor attitude | 8% |
| 16. | Urbanization | 4% |
| 17. | Government structure | 3% |
| 18. | Urban planning | 1% |
| 19. | Resource allocation | 6% |
| Degree | Number | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| low | 1 | The defect is limited and cannot affect the effectiveness of the fire prevention management system |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| Medium | 4 | It can cause controllable failure |
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| High | 7 | It can weaken the fire protection system |
| 8 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 | ||
| Degree | Number | Occurrence |
| low | 1 | The defect applies to only a few parts of the system |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| Medium | 4 | The defect applies to 50% or more of the system components |
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| High | 7 | The defect applies to more than 75% of the components of the fire fighting system |
| 8 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 | ||
| Degree | Number | Detectability |
| High | 1 | There is a possibility of identifying the defect |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| Medium | 4 | There is a possibility of us not being able to identify the defect |
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| Low | 7 | There is a high probability of us not being able to identify the defect |
| 8 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 |
| Severity | Occurrence | Detection | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medium | Medium | Low | Very Important |
| Medium | Medium | Medium | Important |
| High | Medium | Low | Very Important |
| High | Medium | Medium | Important |
| High | High | Low | Very Important |
| High | High | Medium | Important |
| Factor: Fire Regulations | S | O | D | Risk | Fire Training | S | O | D | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| It does not include all types of residential buildings. | M | M | L | V.Imp | Workers not receiving fire fighting training. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Do not support continuous improvement in the fire prevention management system. | M | M | M | Important | Ineffective training. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Do not comply with the applicable procedures. | M | M | H | Not Imp | Training of employees is not mandatory. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Does not support research and development. | H | M | L | V.Imp | There are no mechanisms to achieve mandatory training | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| The investigation procedures in fire accidents are not required or specified. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Resetting the system and stopping the alarm by the building guard without verifying the fire. | H | H | M | Important |
| It did not specify the mechanisms and procedures for response and rescue. | H | M | L | V.Imp | Shutdown the system completely by disconnecting the electrical power source in the event of a frequent bell. | H | M | M | Important |
| It does not support optimum utilization of resources. | M | H | L | V.Imp | Fire pumps are in the off position. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| The requirements of the administrative structure did not specify the fire protection system at the level of the authority and stakeholders. | H | M | L | V.Imp | Fire pumps are isolated from power. | H | M | M | Important |
| It did not specify the procedures required to educate people about the fire. | H | L | L | Not Imp | Diesel pump without fuel. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Do not request reporting of near misses or fire incidents that did not require the intervention of firefighters. | H | H | L | V.Imp | The starting batteries in the diesel pump are disconnected or not working. | H | M | M | Important |
| There are no procedures in the legislation regulating the investigation of fire accidents. | H | H | L | V.Imp | The water tank is not full according to the design capacity of the fire extinguishing system. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Factor: fire enforcement regulations | S | O | D | Risk | Use the pump room as a material store room. | M | M | M | Important |
| The process of inspection of residential building is not carried out in a regular periodic manner. | H | M | L | V.Imp | Lack of knowledge of dealing with fire alarm panel and other extinguishing equipment. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Audit for licensed entities not carried out periodically. | H | M | L | V.Imp | The use of fire hoses to wash the corridors. | H | M | M | Important |
| The process of issuing certificates of compliance is not based on precise, specific, and strict criteria. | H | M | L | V.Imp | Fire Knowledge | S | O | D | Risk |
| The process of issuing certificates of completion is not based on precise, specific, and strict criteria. | H | M | L | V.Imp | Residents lack knowledge of fire hazards. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| Licensing processes for companies are not based on precise, specific, and strict criteria. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Residents lack knowledge of fire behavior and its causes. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| Failure to take the necessary measures against the procedures related to residential establishments that violate. | H | M | L | V.Imp | Residents lack knowledge of the procedures required in the event of a fire. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| Not to take punitive measures for licensed companies that violate legislation. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Residents lack knowledge of when to use fire equipment. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| Failure to check the qualification requirements of employees of licensed companies. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Fire Society culture | S | O | D | Risk |
| Lack of focus on obligating high-rise buildings. | H | M | L | V.Imp | The community’s religious culture of predestination does not support the possibility of avoiding fire accidents. | M | M | L | V.Imp |
| Facilities Management and policies | S | O | D | Risk | The culture of the community about the causes of fire varies among the residents of the same residential establishment. | M | M | L | V.Imp |
| Lack of safety management policies or procedures. | H | H | M | Important | The culture of the community does not support taking preventive measures against fire hazards. | M | M | L | V.Imp |
| No fire risk assessment is done. | H | H | L | V.Imp | The nature of the community in residential establishments Awareness of the consequences that can occur if a fire occurs in a residential building with large groups of residents. | M | M | M | Important |
| There is no record of fire hazards. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Negative culture about fires, which results from religious or ideological beliefs or racial behaviors. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| There is no internal inspection or audit. | H | H | M | Important | The culture of the population when hearing the sound of the fire alarm, as it is dealt with on the basis that it is a recurring technical failure, and the response is not performed. | H | H | M | Important |
| There is no emergency management plan for high-risk building. | H | H | M | Important | Fire Technology | S | O | D | Risk |
| There is no qualified employee who supervises the management of the fire system and risk management. | H | H | M | Important | It is not suitable for the nature of residential establishments in the Emirate of Sharjah. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| The absence of mandatory requirements for the sustain serviceability of fire protection systems in residential building. | M | M | M | Important | Inefficent. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| The owners of residential building consider that the resources provided for the management of the fire protection system are a waste of money and time. | H | M | M | Important | They are not certified based on reliable reliability procedures. | M | M | M | Important |
| Real estate companies that manage building do not put fire protection systems among their priorities. | H | H | M | Important | Not related to the latest technologies in the field of fire fighting. | M | M | M | Important |
| HVAC not included in the required preventive maintenance. | H | H | M | Important | Early detection of fires works poorly. | H | M | M | Important |
| Electrical connections are not included in the required preventive maintenance. | H | H | M | Important | The competent authority does not rely on early fire detection data. | H | H | M | Important |
| The elevator system is not connected to the alarm and fire fighting system. | M | M | M | Important | The early fire detection system is not approved by the Federal Fire Authority. | M | H | M | Important |
| Owners of residential building do not care about preventive maintenance. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Early detection of fires does not comply with the requirements and specifications of the Federal Authority. | H | M | M | Important |
| Real estate companies do not care about preventive maintenance. | H | M | M | Important | The technology used in fire detection is unsuitable and has frequent breakdowns. | H | M | M | Important |
| Accident investigation | S | O | D | Risk | The technology used is not compared to other similar areas that apply good practices. | M | M | M | Important |
| Accidents are not investigated by the relevant fire authority. | H | H | L | V.Imp | The technology used has not been evaluated and tested. | H | M | M | Important |
| The investigation of fire accidents is carried out by the Public Prosecution Office for the purposes of providing evidence to the court, for the purpose of compensation procedures related to insurance, or for lawsuits only. The data of the investigation are confidential. | H | M | L | V.Imp | It does not support Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data, robotics, and the Internet of Things. | M | M | M | Important |
| There is no specialized department in the structure of the competent authority to investigate fire accidents. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Lack/improper Maintenance | S | O | D | Risk |
| There are no qualified personnel to investigate fire accidents at the competent authority. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Inefficiency of installation and maintenance contractors. | H | H | M | Important |
| Fire accident investigation data are not seen as important data that need to be obtained. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Lack of clarity about the mechanism for reporting alarm and fire fighting system malfunctions to the responsible installation and maintenance contractors. | H | H | M | Important |
| Some fire accidents are repeated periodically because fire accidents are not investigated. | H | H | L | V.Imp | The equipment used are of poor reliability. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| The root causes of fire accidents are unknown. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Lack of continuous supply of spare parts for devices and equipment. | H | M | M | Important |
| Fire accident data are confidential and may not be viewed or available for research and scientific studies. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Workers in fire fighting installation and maintenance contractors are not competent. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| There is not enough staff to carry out the investigation of fire accidents. | M | M | L | V.Imp | Contracts regulating the relationship between the management of the residential building and the maintenance companies of fire extinguishing systems have defects. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| The cause unknown in the fire accident investigations is acceptable to close the investigation. | H | M | L | V.Imp | Competent authority oversight is ineffective. | H | H | M | Important |
| The prevailing culture is that the task of the competent authority is to fight fires only. | M | M | L | V.Imp | Contractual procedures with residents restrict entry to residential apartments to remove faults. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Contractor Attitude | S | O | D | Risk | Manufacturing and design defects of the fire detection system. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Use the cheapest products to make the most profit. | H | M | M | Important | Absence of a maintenance record for the alarm and fire fighting system. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| The general view of fire requirements as a governmental requirement, rather than as a means to save lives. | H | M | M | Important | Preventive maintenance history labels for fire equipment can be tampered with. | H | M | M | Important |
| The lack of adequate control over the implementation of the requirements by the consulting firms. | H | H | M | Important | Fire equipment | S | O | D | Risk |
| Rescue speed | S | O | D | Risk | Fire extinguishing equipment is not in line with the development of fire hazards. | H | M | M | Important |
| The type of vehicles and equipment used by the competent authority. | H | M | H | Not Imp | Fire alarm systems in buildings use the Conventional type. | M | M | M | Important |
| Inadequate training of firefighters. | H | M | M | Important | Fire extinguishers rely on training residents to be able to use them. | H | H | M | Important |
| Traffic congestion to reach residential areas. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Not compatible with the technologies of the fourth industrial revolution | M | M | L | V.Imp |
| Geographical distribution of fire stations in the Emirate. | H | M | L | V.Imp | Building Design | S | O | D | Risk |
| Distribution of firefighters to fire stations. | M | M | L | V.Imp | Failure to give sufficient priority to fire fighting at the design stage. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Incident-reporting mechanism. | H | M | L | V.Imp | Focusing on the areas of the apartments without taking into account the times and sufficient escape exits. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| Fire trucks are not given priority on the road. | H | L | L | Not Imp | Not allocating storage rooms in the apartments, forcing residents to use escape corridors as storages. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| Procedures followed during the accident. | H | M | L | V.Imp | Not focusing on the use of fire-insulating materials in the design stages of residential building. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| Resource allocation | S | O | D | Risk | Escape routes do not correspond to the population of the building. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Unequal distribution of workers in the centers of the competent fire authority. | M | M | L | V.Imp | The pumps of the fire fighting system do not correspond to the height of the residential building. | H | M | M | Important |
| There is no equality between workers in rescue centers and workers in preventive maintenance. | M | M | M | Important | Focus on reducing prices in order to reduce the safety of the population. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| The distribution of workers between fire fighting and fire prevention centers is not based on studies, research and scientific methodologies. | M | M | M | Important | Evacuation of residents from the upper floors of high-rise residential towers is not effective. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Lack of workers in the centers of the competent authority. | M | M | M | Important | Failure to take into account the design, evacuating the elderly and then other people. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| Economic measures at the level of the Government of Sharjah. | M | M | M | Important | Comparisons with successful and similar experiences in the field of designing residential building. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Establishing a competent local authority that affected the distribution of workers in fire fighting tasks. | M | L | M | Not Imp | Not including a control room specialized in monitoring alarm systems and surveillance cameras in residential building. | H | M | M | Important |
| Lack of information and comparisons about previous accidents | H | M | M | Important | Smoke detectors are not distributed over the entire area of the apartments. | H | M | M | Important |
| The prediction of accidents is inaccurate. | M | M | M | Important | Malfunctions in the sprinklers used in the fire extinguishing system. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Government structure | S | O | D | Risk | The gas sensor alarm is not connected to the fire alarm system. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| The structure of fire fighting at the level of the government of Sharjah, with overlapping roles, responsibilities, and authorities. | M | M | M | Important | Failure to link the status of the fire pumps to the main alarm panel. | H | H | M | Important |
| The structure of the Sharjah government does not support the flexibility of coordination between government agencies regarding the plan of fire fighting measures. | H | M | L | V.Imp | The absence of an alarm system or fire fighting in the old residential building. | H | M | M | Important |
| The position of the Sharjah Civil Defense Authority as a local authority and its compliance with federal and local requirements may hinder efficiency and impact. | M | M | M | Important | The absence of a pressure test mechanism in the fire fighting system in the entire residential building. | H | M | M | Important |
| Fire fighting training which is supervised by another body in the government structure. | M | H | M | Important | Combustible materials | S | O | D | Risk |
| The early warning system, which is not directly supervised by the Sharjah Civil Defense. | H | H | L | V.Imp | The use of flammable materials in the exterior cladding of residential building. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| The management of the early warning system by a semi-governmental company, which hinders its accountability. | H | H | L | V.Imp | The use of combustible materials in different areas of residential building when carrying out construction. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| Absence of a national strategy to combat fire in the Emirate of Sharjah. | H | M | M | Important | The use of flammable materials by residents of residential building. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| Urban planning | S | O | D | Risk | Flammable materials are not precisely defined and precautions are not taken to reduce their risks. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Overcrowded residential areas do not allow fire fighting vehicles to reach the accident at the required speed. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Urbanization | S | O | D | Risk |
| Planning parking lots around residential building hinders the work of emergency and fire fighting teams. | H | H | L | V.Imp | Residents from outside the country are not prepared to deal with the dangers of fire in residential building. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| Concentration of high-rise buildings in specific areas. | H | H | M | Important | Immigrants from non-urban areas are causing fires because they are not aware of its dangers. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| The closeness of the towers to each other, which threatens the possibility of the transmission of fire from one tower to another. | H | H | M | Important | Lack of knowledge of the correct procedures for dealing at the time of fire for the expatriate population from non-urban areas. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| The narrow distance between residential buildings and the main road, which increases the risks to the residents in the event of evacuation and hinders emergency operations. | H | H | M | Important | Failure to conduct studies of fire risks resulting from the residence of expatriates from non-urban areas in high-rise buildings. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| The lack of planning for fire stations among the public building in the city. | H | M | M | Important | Not specifying the maximum height in residential areas. | H | M | M | Important |
| Narrow roads, which impede the arrival of ambulances and fire fighting on time. | H | M | M | Important | Accommodation of state and non-urban migrant workers in multi-floored housing building. | H | M | L | V.Imp |
| Human behavior | S | O | D | Risk | |||||
| Some religious beliefs. | H | L | L | Not Imp | |||||
| Smoking addiction. | H | M | M | Important | |||||
| Improper use of electrical appliances and equipment. | H | M | L | V.Imp | |||||
| Cooking and grilling. | H | M | L | V.Imp | |||||
| Deliberately closing smoke detectors | H | M | M | Important | |||||
| Handling of cooking gas. | H | M | L | V.Imp | |||||
| Dealing with HVAC equipment. | H | M | M | Important | |||||
| Children’s behavior | M | M | L | V.Imp | |||||
| The use of incense. | H | H | L | V.Imp |
| No. | Factors | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building design | 7% |
| 2. | Fire regulations | 8% |
| 3. | Rescue speed | 8% |
| 4. | Fire knowledge | 11% |
| 5. | Human behavior | 6% |
| 6. | Firefighting maintenance | 6% |
| 7. | Fire culture of society | 9% |
| 8. | Fire training | 6% |
| 9. | Combustible materials | 11% |
| 10. | Fire enforcement regulations | 11% |
| 11. | Accident investigation | 11% |
| 12. | Urbanization | 9% |
| Factors | Weight | Sub-Factor | Sub-weight | Total Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building design | 0.069 | Building in design phase | 0.209 | 0.014 |
| Building in construction phase | 0.248 | 0.017 | ||
| Building in use phase | 0.226 | 0.016 | ||
| Building in change phase | 0.184 | 0.013 | ||
| Building in demolition phase | 0.134 | 0.009 | ||
| Fire regulations | 0.077 | Legislation breakdown | 0.193 | 0.015 |
| Fire regulations scope | 0.268 | 0.021 | ||
| Fire regulations efficiency | 0.539 | 0.042 | ||
| Rescue speed | 0.079 | Compliance to the fire regulations | 0.316 | 0.025 |
| Distance from the fire station | 0.208 | 0.016 | ||
| Building height | 0.214 | 0.017 | ||
| Knowledge, ability, training, and experience | 0.262 | 0.021 | ||
| Fire knowledge | 0.106 | Beliefs related to fire knowledge | 0.362 | 0.038 |
| Practices related to fire knowledge | 0.411 | 0.043 | ||
| Philosophies related to fire knowledge | 0.228 | 0.024 | ||
| Human behavior | 0.059 | Human behavior: proactive | 0.572 | 0.034 |
| Human behavior: reactive | 0.257 | 0.015 | ||
| Human behavior: neutral | 0.171 | 0.010 | ||
| Firefighting maintenance | 0.058 | Firefighting maintenance: training | 0.106 | 0.006 |
| Firefighting maintenance: resources | 0.138 | 0.008 | ||
| Firefighting maintenance: integration | 0.135 | 0.008 | ||
| Firefighting system: reactive maintenance | 0.174 | 0.010 | ||
| Firefighting system: proactive maintenance | 0.257 | 0.015 | ||
| Firefighting system: predictive maintenance | 0.190 | 0.011 | ||
| Fire culture of society | 0.088 | Values related to fire culture | 0.200 | 0.017 |
| Conditions related to fire culture | 0.179 | 0.016 | ||
| Procedures related to fire culture | 0.282 | 0.025 | ||
| Behaviors related to fire culture | 0.339 | 0.030 | ||
| Fire training | 0.060 | Fire training: theory | 0.188 | 0.011 |
| Fire training: practical | 0.459 | 0.028 | ||
| Fire training: methodology | 0.353 | 0.021 | ||
| Combustible materials | 0.106 | The building is fully covered with cladding | 0.457 | 0.048 |
| The building is partial covered with cladding | 0.293 | 0.031 | ||
| The building is without cladding | 0.250 | 0.026 | ||
| Fire enforcement regulations | 0.106 | Fire enforcement regulations depend on fines for non-compliant facilities | 0.270 | 0.029 |
| Non-compliant facilities may be prohibited by fire enforcement regulations | 0.412 | 0.043 | ||
| Building owners who violate fire regulations are brought to trial | 0.318 | 0.034 | ||
| Accident investigation | 0.106 | Report major/minor/near-miss fire accident | 0.188 | 0.020 |
| Investigation major/minor/near-miss fire accident | 0.231 | 0.024 | ||
| Analysis major/minor/near-miss fire accident | 0.189 | 0.020 | ||
| Corrective actions to the cause of fire accident | 0.218 | 0.023 | ||
| Preventative actions to the cause of fire accident | 0.175 | 0.018 | ||
| Urbanization | 0.088 | Awareness of newcomer by the real estate companies | 0.329 | 0.029 |
| Training of new employees by their employers | 0.460 | 0.040 | ||
| Awareness of newcomer with visa procedures | 0.210 | 0.018 |
| No. | Sub-Factors | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | The building is fully covered with cladding | 5% |
| 2. | The effect of stopping activities in the HRBs that are non-compliant with fire regulations | 4% |
| 3. | Residents practices related to fire knowledge | 4% |
| 4. | Fire regulations efficiency | 4% |
| 5. | Training of new employees by their employers | 4% |
| 6. | Residents believes related to fire knowledge | 4% |
| 7. | The effect of proactive resident behavior during the fire accident | 3% |
| 8. | The effect of brought to trial HRBs owners violate fire regulations | 3% |
| 9. | The building is partially covered with cladding | 3% |
| 10. | Resident behaviors related to fire culture | 3% |
| 11. | Fire awareness of newcomer by the real estate companies | 3% |
| 12. | The effect of fines for non-compliant HRBs | 3% |
| 13. | Practical fire training | 3% |
| 14. | The effect of the building being without cladding | 3% |
| 15. | HRBs in full compliance with the fire regulations | 3% |
| 16. | Procedures implemented in the HRB by the residents related to fire culture | 2% |
| 17. | Investigation major/minor/near-miss fire accident | 2% |
| 18. | Philosophies of residents related to fire knowledge | 2% |
| 19. | Corrective actions to the cause of fire accident | 2% |
| 20. | Fire training: methodology | 2% |
| 21. | Firefighters’ knowledge, ability, training and experience | 2% |
| 22. | Scope of fire regulations | 2% |
| 23. | Analysis of major/minor/near-miss fire accident | 2% |
| 24. | Report major/minor/near-miss fire accident | 2% |
| 25. | Preventative actions to the cause of fire accident | 2% |
| 26. | Awareness of newcomer with visa procedures | 2% |
| 27. | Values related to fire culture | 2% |
| 28. | Fire arrangements for the building during construction phase | 2% |
| 29. | High-rise building height | 2% |
| 30. | Building distance from the fire station | 2% |
| 31. | Conditions of the HRB effected the fire culture | 2% |
| 32. | The fire arranegements for building in use phase | 2% |
| 33. | The effect of reactive residents behavior during fire accident | 2% |
| 34. | Firefightin system proactive maintenance | 1% |
| 35. | Legislation to be breakdown (laws, regulations, standards, and guidelines) | 1% |
| 36. | Fire to be considered from building design phase | 1% |
| 37. | Fire arranegements for the building in case of change of purpose | 1% |
| 38. | Fire training: theory | 1% |
| 39. | Firefighting system predictive maintenance | 1% |
| 40. | Firefighting system reactive maintenance | 1% |
| 41. | Residents behavior to be nutral during fire accident | 1% |
| 42. | Fire arrangements for the building in demolition phase | 1% |
| 43. | Firefighting maintenance: resources | 1% |
| 44. | Firefighting maintenance: integration | 1% |
| 45. | Firefighting maintenance: training | 1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omar, M.; Mahmoud, A.; Abdul Aziz, S.B. Critical Factors Affecting Fire Safety in High-Rise Buildings in the Emirate of Sharjah, UAE. Fire 2023, 6, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6020068
Omar M, Mahmoud A, Abdul Aziz SB. Critical Factors Affecting Fire Safety in High-Rise Buildings in the Emirate of Sharjah, UAE. Fire. 2023; 6(2):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6020068
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmar, Musab, Abdelgadir Mahmoud, and Sa’ardin Bin Abdul Aziz. 2023. "Critical Factors Affecting Fire Safety in High-Rise Buildings in the Emirate of Sharjah, UAE" Fire 6, no. 2: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6020068
APA StyleOmar, M., Mahmoud, A., & Abdul Aziz, S. B. (2023). Critical Factors Affecting Fire Safety in High-Rise Buildings in the Emirate of Sharjah, UAE. Fire, 6(2), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6020068






