Microsecond Discharge Produced in Aqueous Solution for Pollutant Cr(VI) Reduction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
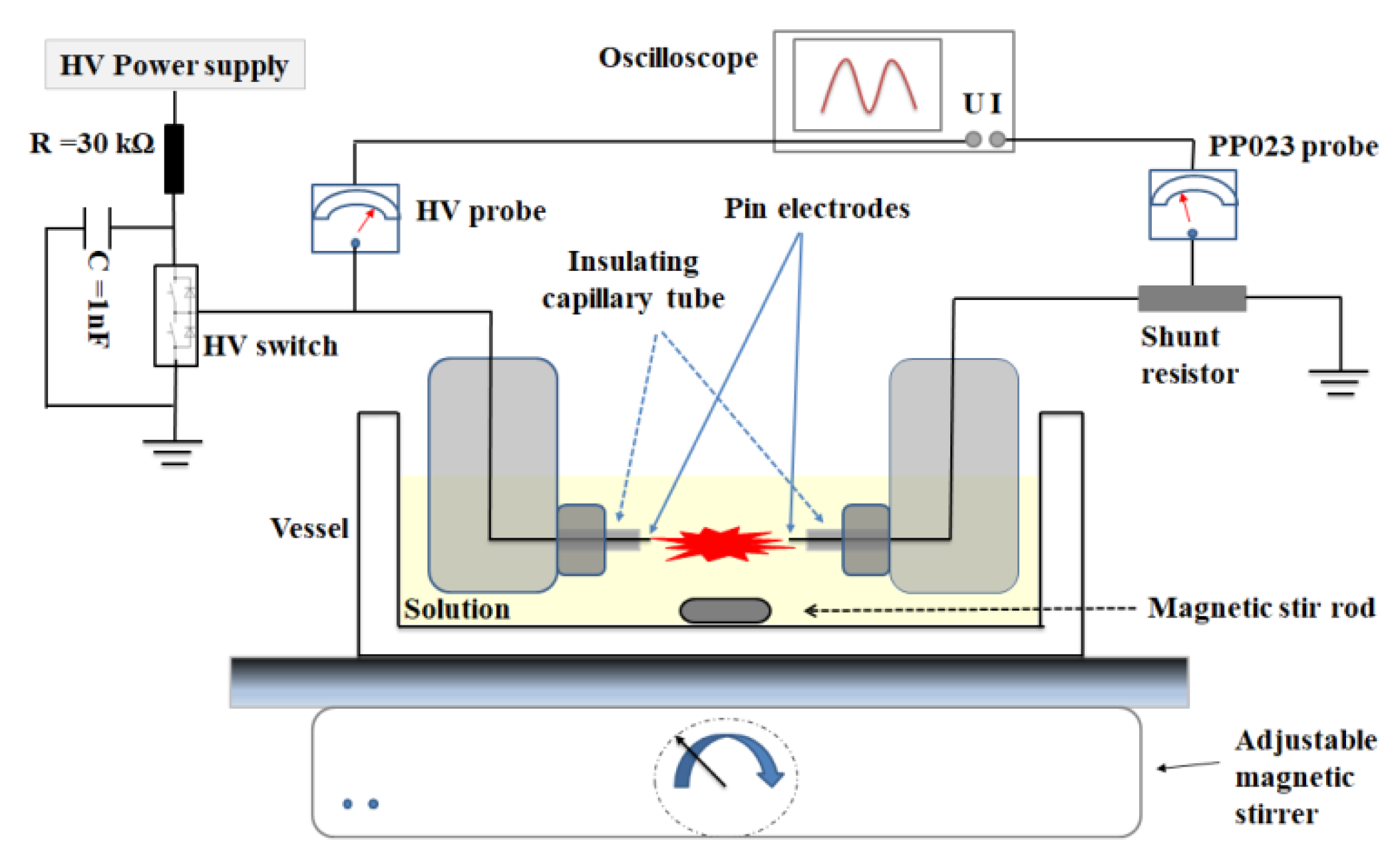
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
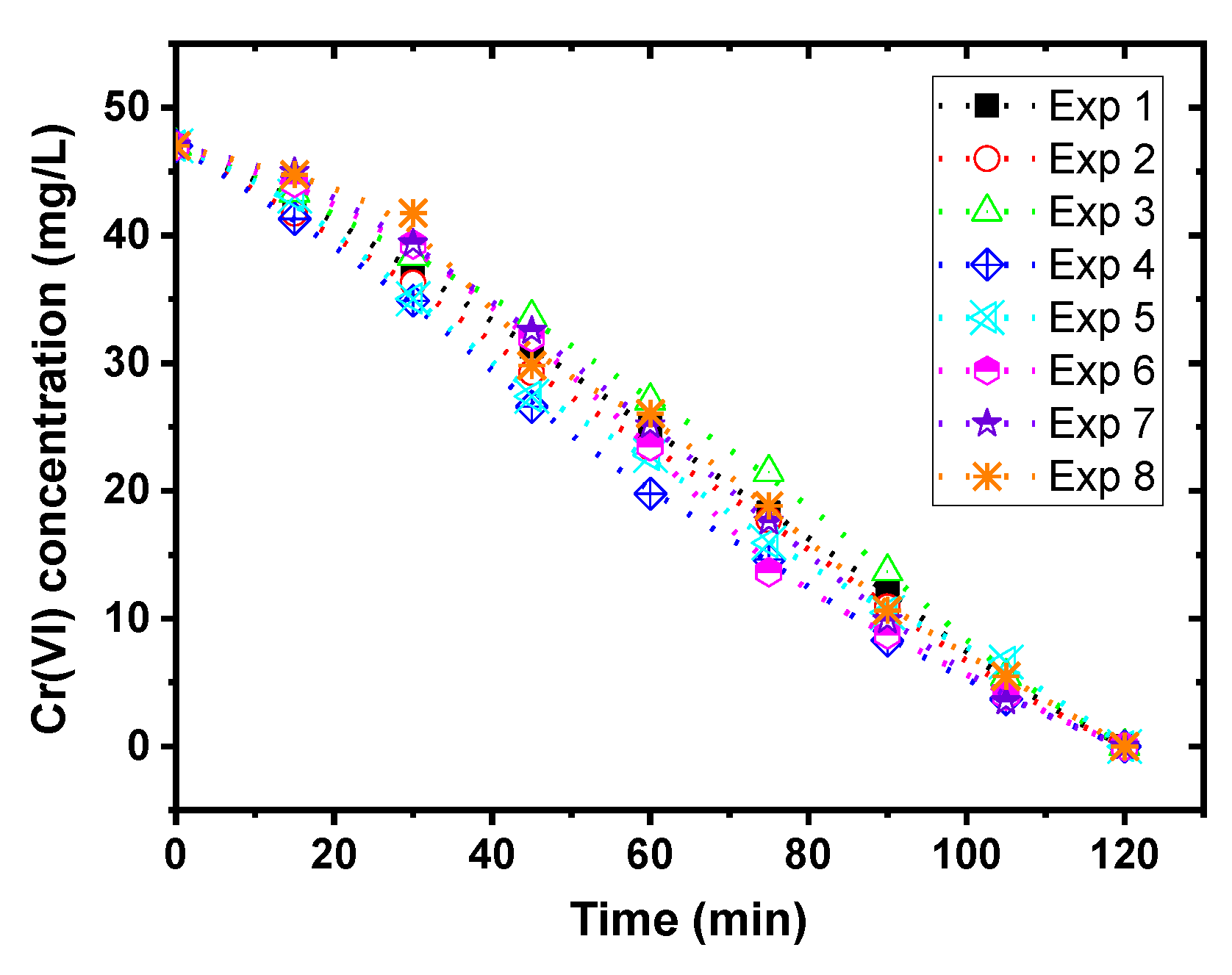
3.1. Achievement of Cr(VI) Reduction Process
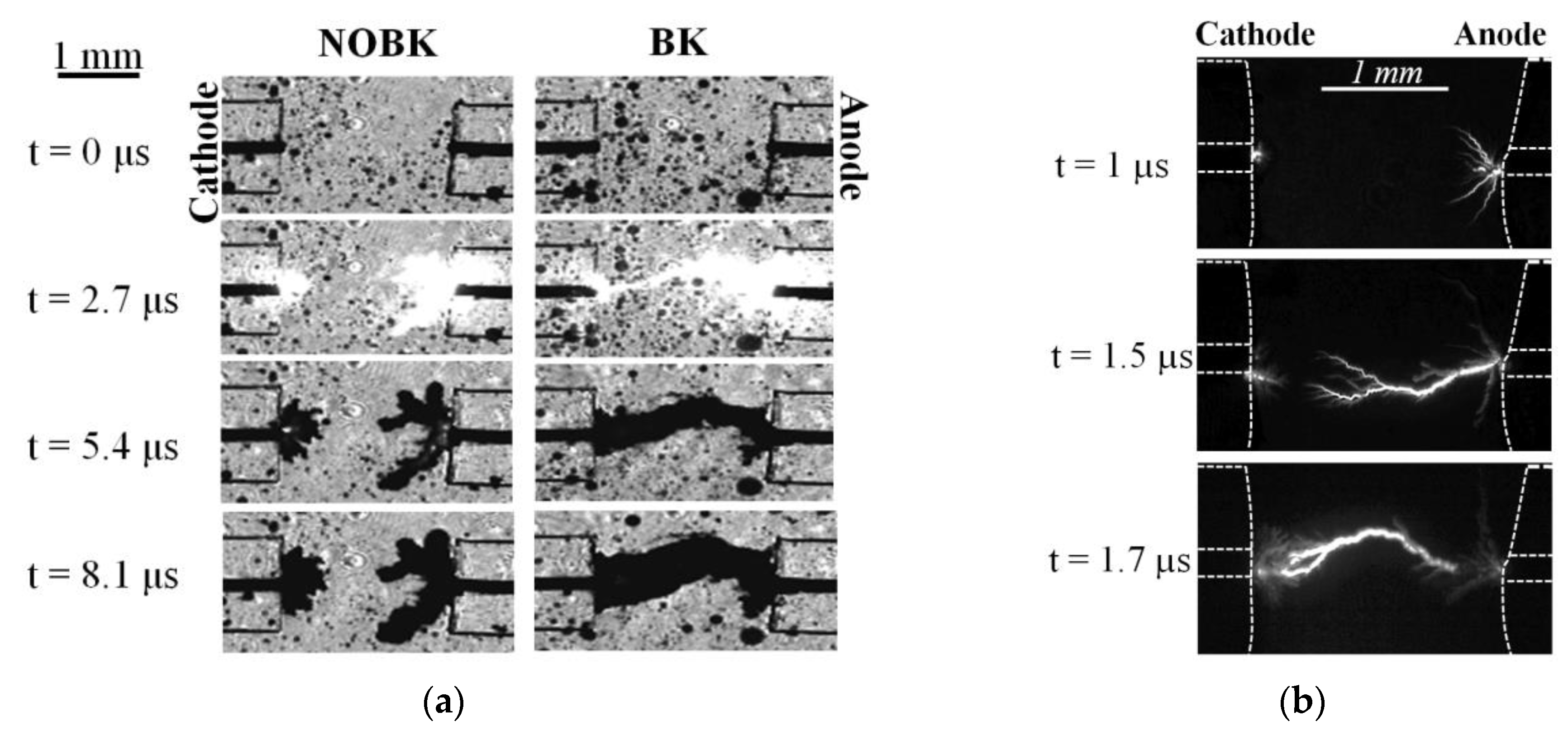
3.2. Discharge Characteristics Analysis
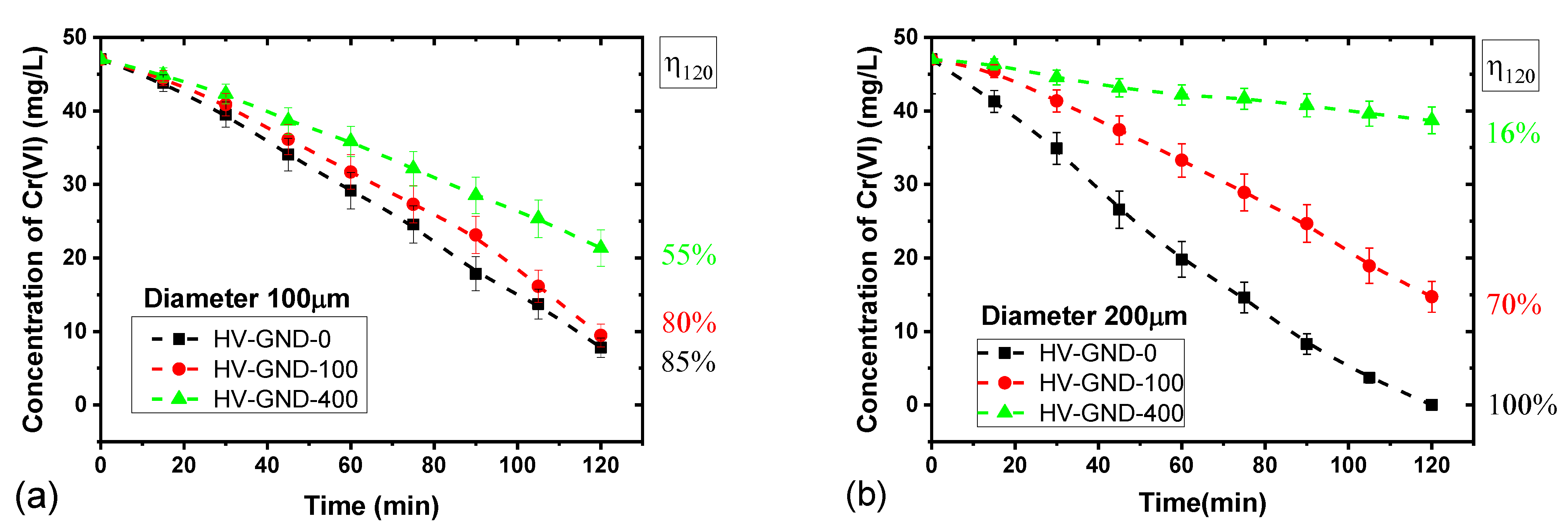
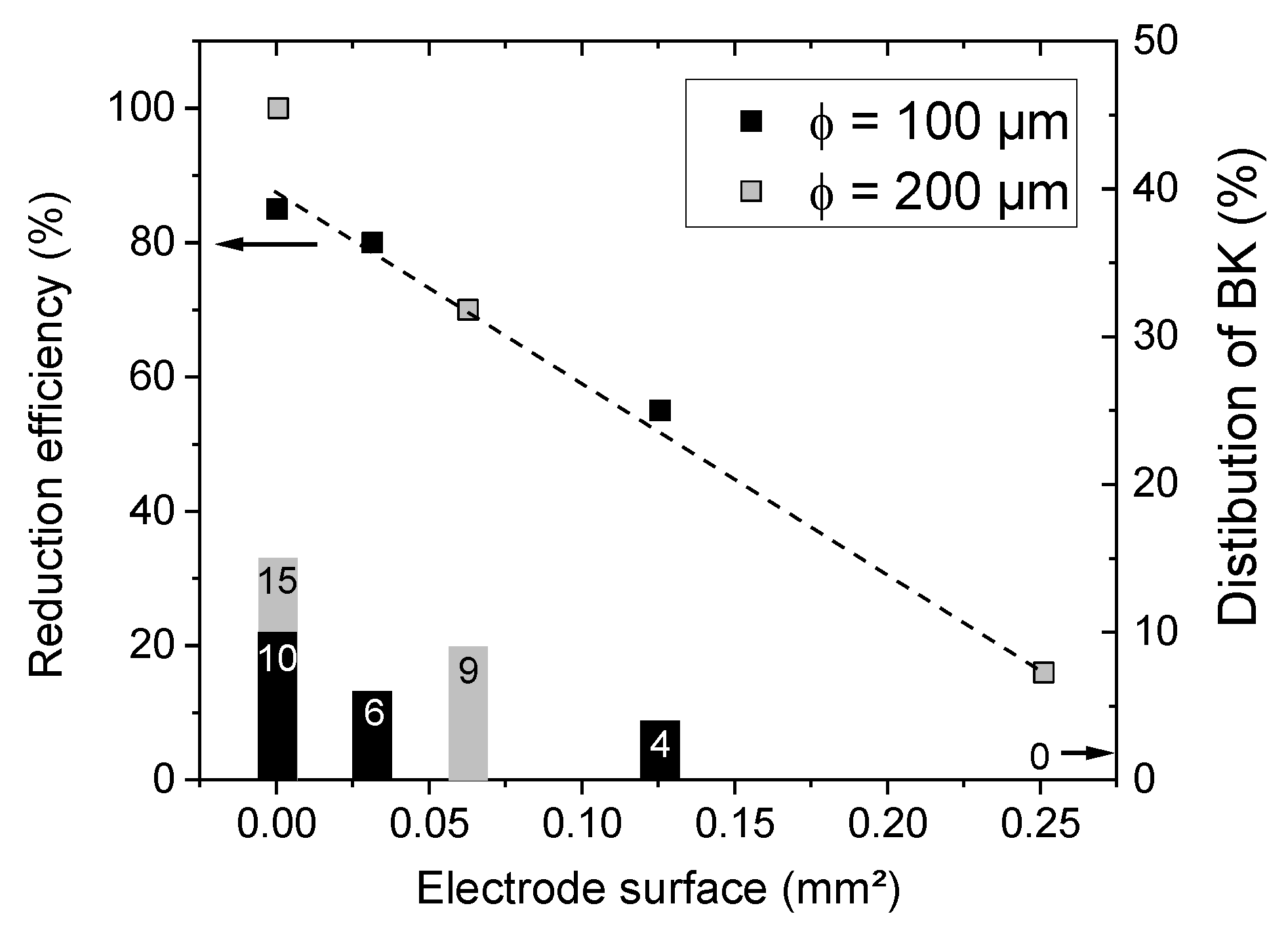
3.3. Influence of the Electrode Geometry
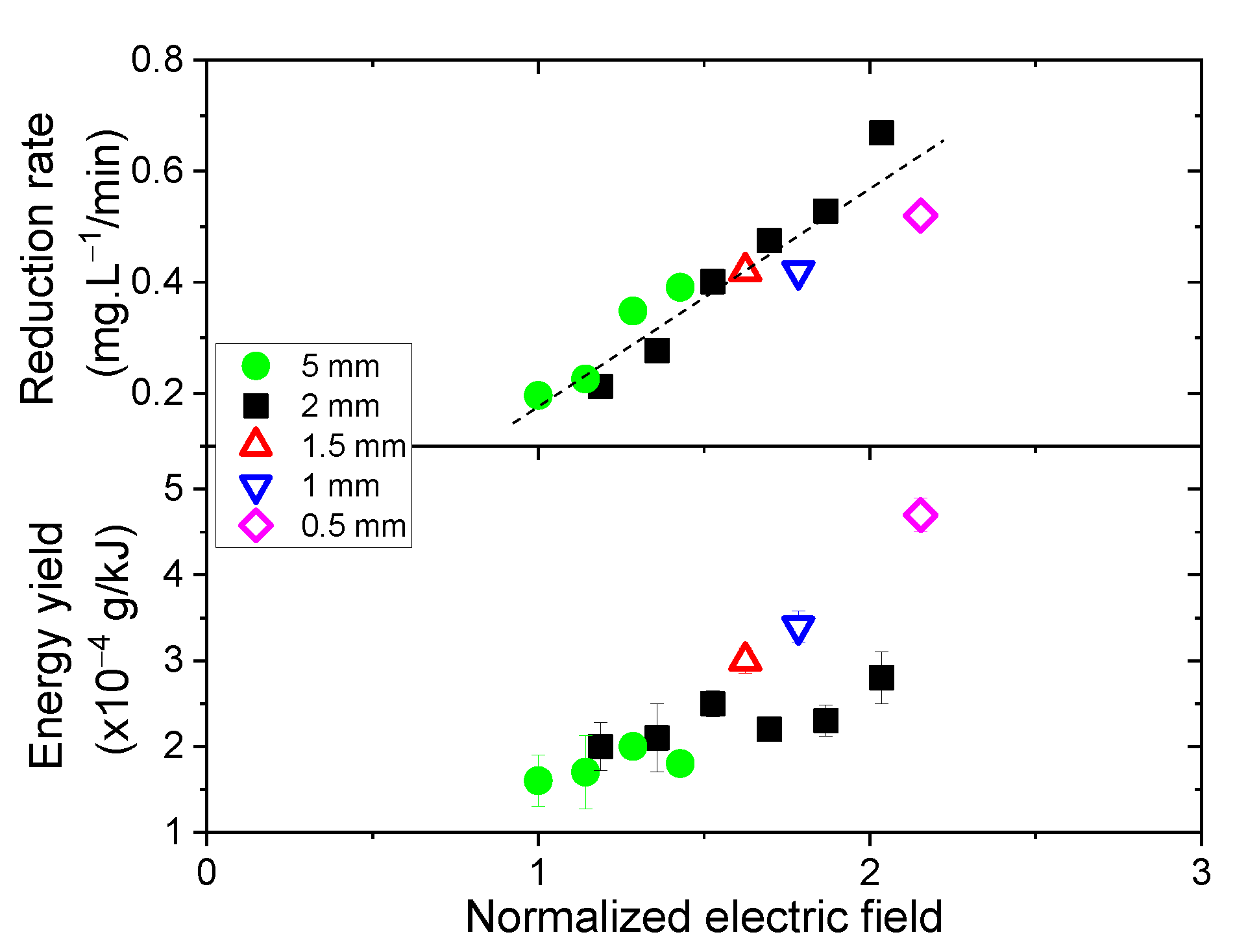
3.4. Influence of the Electric Field
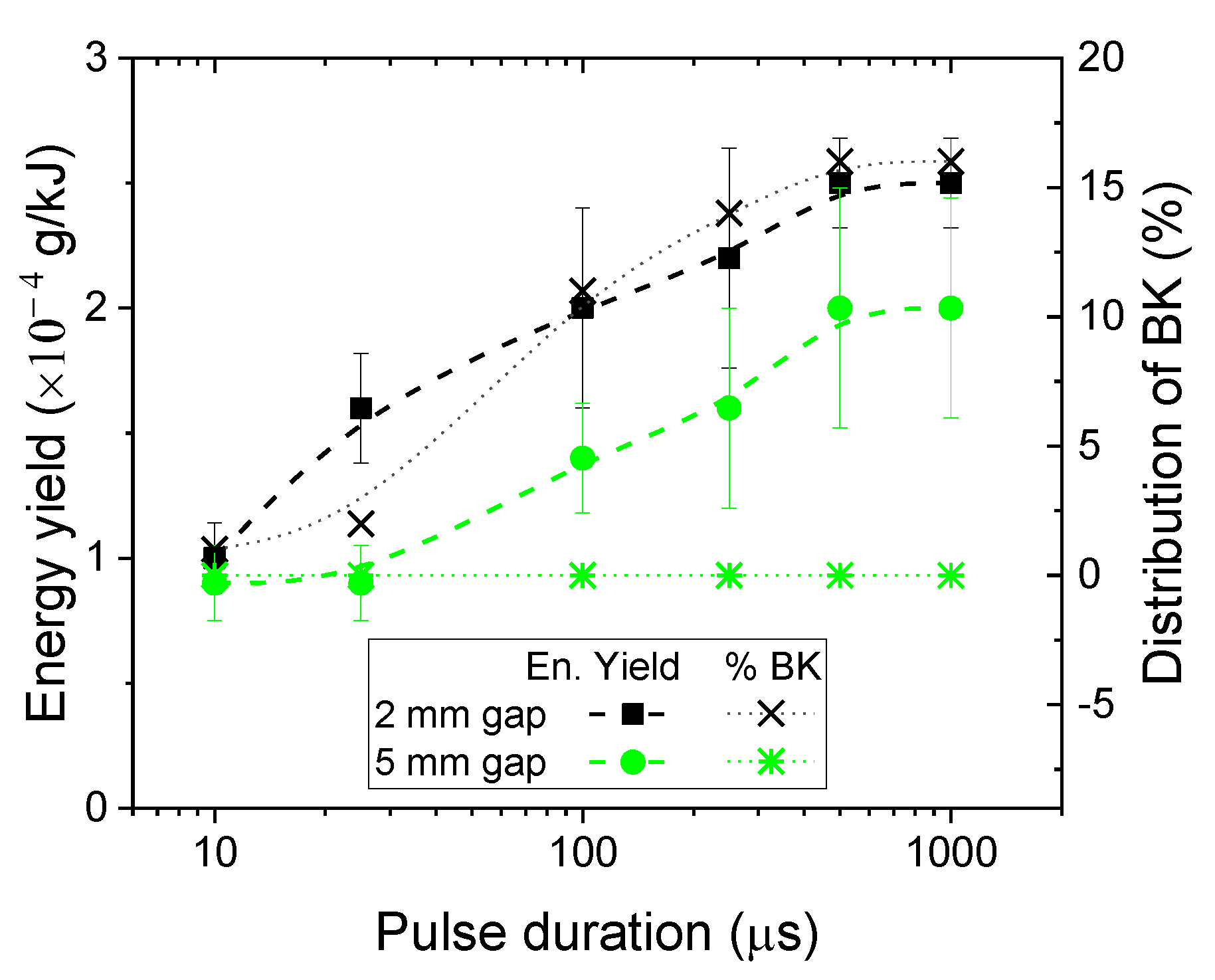
3.5. Influence of Pulse Duration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Figueroa, F.; Zamora-Ledezma, E.; Ni, M.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V.H. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Mahiya, S.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Contamination of Heavy Metals in Aquatic Media: Transport, Toxicity and Technologies for Remediation. Heavy Met. W. Presence Remov. Saf. 2015, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilbur, S.; Abadin, H.; Fay, M.; Yu, D.; Tencza, B.; Ingerman, L.; Klotzbach, J.; James, S. Toxicological Profile for Chromium; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi, S.; Serpone, N. In-liquid plasma: A novel tool in the fabrication of nanomaterials and in the treatment of wastewaters. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 47196–47218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.E. Plasma-based water purification: Challenges and prospects for the future. Phys. Plasma 2017, 24, 055501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Yan, J. Plasma Remediation Technology for Environmental Protection; Springer: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, R.P.; Thagard, S.M. Streamer-Like Electrical Discharges in Water: Part II. Environmental Applications. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2013, 33, 17–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, B.R.; Sato, M.; Sunka, P.; Hoffmann, M.R.; Chang, J.S. Electrohydraulic Discharge and Nonthermal Plasma for Water Treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 882–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Ghaffar, A.; Malik, S.A. Water purification by electrical discharges. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2001, 10, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiopoulou, E.; Gikas, P. Regulations for chromium emissions to the aquatic environment in Europe and elsewhere. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumolo, M.; Ancona, V.; Paola, D.D.; Losacco, D.; Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Chromium Pollution in European Water, Sources, Health Risk, and Remediation Strategies: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjasteh, A.; Dehghani, Z.; Lamichhane, P.; Kaushik, N.; Choi, E.H.; Kaushik, N.K. Recent Progress in Applications of Non-Thermal Plasma for Water Purification, Bio-Sterilization, and Decontamination. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatera, K.; Morimoto, Y.; Ueno, S.; Noguchi, S.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tanaka, F.; Suzuki, H.; Higashi, T. Cancer risks of hexavalent chromium in the respiratory tract. J. UOEH 2018, 40, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobkova, E.S.; Sungurova, A.V.; Rybkin, V.V. Reduction of chromium (VI) in aqueous solution by treatment with direct-current discharge at atmospheric-pressure in air. High Energy Chem. 2016, 50, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ponraj, S.B.; Dai, X.J. Reduction of aqueous chromium (VI) by plasma treatment of wastewater. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry (ISPC), Montréal, QU, Canada, 30 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Guo, J.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, J.; Wu, W.; Wu, M.; Xue, Q. A green approach towards simultaneous remediations of chromium (VI) and arsenic (III) in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z. Reduction and Removal of Aqueous Cr (VI) by Glow Discharge Plasma at the Gas-Solution Interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7841–7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, X. Plasma-Induced Reduction of Chromium (VI) in an Aqueous Solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8492–8497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Bush, R.T.; Sullivan, L.A.; Liu, J. Simultaneous Redox Conversion of Chromium (VI) and Arsenic (III) under Acidic Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6486–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Feng, J. Simultaneous removal of Cr (VI) and acid orange 7 from water solution by dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harianti, A.R.; Saksono, N. Application of plasma electrolysis method for simultaneous phenol and Cr (VI) wastewater deg-radation using Na2SO4 electrolyte. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1904, 020041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutov, D.A.; Sungurova, A.V.; Choukourov, A.; Rybkin, V.V. Kinetics and Mechanism of Cr (VI) Reduction in a Water Cathode Induced by Atmospheric Pressure DC Discharge in Air. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2016, 36, 1253–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamróz, P.; Gręda, K.; Pohl, P.; Żyrnicki, W. Atmospheric Pressure Glow Discharges Generated in Contact with Flowing Liquid Cathode: Production of Active Species and Application in Wastewater Purification Processes. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2014, 34, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.S.; Fagnon, N.; Vega, A.; Duten, X.; Forget, S.; Rond, C. Cr (VI) Reduction by Microsecond Pin-to-Pin Discharges Generated in an Aqueous Solution. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Hachair, A.; Hofmann, A. Hexavalent chromium quantification in solution: Comparing direct UV–visible spec-trometry with 1,5-diphenylcarbazide colorimetry. Compte Rendus Chimi. 2018, 21, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandana, L.; Lakshminarayana, B.; Subrahmanyam, C. Influence of hydrogen peroxide on the simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and methylene blue from aqueous medium under atmospheric pressure plasma jet. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2760–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rond, C.; Fagnon, N.; Vega, A.; Duten, X. Statistical analysis of a micro-pulsed electrical discharge in water. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 335204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rond, C.; Desse, J.M.; Fagnon, N.; Aubert, X.; Er, M.; Vega, A.; Duten, X. Time-resolved diagnostics of a pin-to-pin pulsed discharge in water: Pre-breakdown and breakdown analysis. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 335201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rond, C.; Desse, J.M.; Fagnon, N.; Aubert, X.; Vega, A.; Duten, X. Influence of applied voltage and electrical conductivity on underwater pin-to-pin pulsed discharge. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 025202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, B.; Fagnon, N.; Vega, A.; Duten, X.; Rond, C. Analysis of discharge regimes obtained by microsecond underwater electrical breakdown in regard to energy balance. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2021, 54, 365202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.S.; Rond, C.; Vega, A.; Duten, X.; Forget, S. Investigation of Hydrogen Peroxide Formation After Underwater Plasma Discharge. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2020, 40, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccato, P. Filamentary Plasma Discharge Inside Water: Initiation and Propagation of a Plasma in a Dense medium, PhD in Physique et Applications, Ecole Polytechnique. Ph.D. Thesis, LPP laboratory in Ecole Polytechnique Palaiseau, Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Georgescu, N. Gas Treatment with Repetitive Pulsed Corona Plasmas: Experiments with Various Geometries. IEEJ Trans. Fundam. Mater. 2004, 124, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Creijghton, Y.L.M. Pulsed Positive Corona Discharges: Fundamental Study and Application to Flue Gas Treatment. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Eindhoven, The Netherland, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Applied Voltage (kV) | 2 kV | 7 kV | 8 kV | 9 kV | 10 kV | 11 kV | 12 kV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduction rate (mg.L−1/min) | 0 | 0.21 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.67 |
| Number of BK/NOBK (%) | 0/100 | 1/99 | 12/88 | 15/85 | 24/76 | 25/75 | 55/45 |
| Average injected energy per pulse BK/NOBK (mJ) | -/3.4 | 28/36 | 36/47 | 42/54 | 51/73 | 59/83 | 66/95 |
| Energy yield (g/kJ) | 0 | 2.0 × 10−4 | 2.1 × 10−4 | 2.5 × 10−4 | 2.2 × 10−4 | 2.3 × 10−4 | 2.8 × 10−4 |
| Applied Voltage (kV) | 7 kV | 8 kV | 9 kV | 10 kV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduction rate (mg.L−1/min) | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.39 |
| Average energy per pulse (mJ) | 40 | 46 | 56 | 71 |
| Energy yield (g/kJ) | 1.6 × 10−4 | 1.7 × 10−4 | 2 × 10−4 | 1.8 × 10−4 |
| Method | Reduction Efficiency | Energy Yield (g/kJ) | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Above Liquid | DC pin-to-plate | 100% | 0.64 × 10−4 * | [18] |
| DC pin-to-plate | 100% | 1.4 × 10−4 * | [7] | |
| In Liquid | DC pin-to-plate | 96% | 6 × 10−5 * | [17] |
| DC pin-to-plate | 93% | 3.4 × 10−4 | [22] | |
| DC pin-to-plate | 97% | 4.9 × 10−4 * | [19] | |
| Pulse pin-to-pin | 100% | 4.7 × 10−4 | This work | |
| Applied Voltage (kV) | 8 kV | 9 kV | 10 kV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total injected Energy (kJ) | 16.7 | 18.8 | 21.3 |
| Energy Yield (g/kJ) | 2.1 × 10−4 | 2.7 × 10−4 | 2.2 × 10−4 |
| Total Consumed Energy (kJ) | 125 | 146 | 150 |
| Global Energy Efficiency (g/kJ) | 2.7 × 10−5 | 3.2 × 10−5 | 3.1 × 10−5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, S.T.; Fagnon, N.; Vega, A.; Duten, X.; Forget, S.; Brugier, A.; Rabat, H.; Rond, C. Microsecond Discharge Produced in Aqueous Solution for Pollutant Cr(VI) Reduction. Plasma 2022, 5, 408-422. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5040030
Nguyen ST, Fagnon N, Vega A, Duten X, Forget S, Brugier A, Rabat H, Rond C. Microsecond Discharge Produced in Aqueous Solution for Pollutant Cr(VI) Reduction. Plasma. 2022; 5(4):408-422. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5040030
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Son Truong, Nicolas Fagnon, Arlette Vega, Xavier Duten, Sébastien Forget, Arnaud Brugier, Hervé Rabat, and Cathy Rond. 2022. "Microsecond Discharge Produced in Aqueous Solution for Pollutant Cr(VI) Reduction" Plasma 5, no. 4: 408-422. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5040030
APA StyleNguyen, S. T., Fagnon, N., Vega, A., Duten, X., Forget, S., Brugier, A., Rabat, H., & Rond, C. (2022). Microsecond Discharge Produced in Aqueous Solution for Pollutant Cr(VI) Reduction. Plasma, 5(4), 408-422. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma5040030






