Abstract
Non-thermal dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma is an innovative and emerging field combining plasma physics, life science and clinical medicine for a wide-range of biological applications. Plasma techniques are applied in treating surfaces, materials or devices to realize specific qualities for subsequent special medical applications, plant seeds to improve the production and quality of crops, and living cells or tissues to realize therapeutic effects. Several studies that are summarized within this review show that non-thermal DBD plasma technique has potential biological applications in soybean sprout growth, chicken embryonic development and postnatal growth rate, and even male chicken reproductive capacity. The current developments in the non-thermal DBD plasma technique may be beneficial to improve plant and poultry productivity.
1. Introduction
Physical plasmas are excited ionized gases, which consist of charged particles, excited radicals, reactive atoms and molecules, emit electromagnetic radiation including infrared, visible and ultraviolet photons, and radiate transient electric fields [1]. The synergistic action with transient electric fields, charged species or ultraviolet photons may evoke unique feature for some of the plasma-based biomedical applications [2,3,4]. The type of energy input, input power, gas component, gas pressure, and radiation type of the electric field determine the exact composition and property of non-thermal plasmas [5]. In most cases, non-thermal plasmas for technical applications are generated by applying an electrical field to a neutral gas or gas mixture [6]. Recently, non-thermal plasmas are becoming of great interest for biological and biomedical applications because of the adjustable composition and temperature which allow the plasma to react with bio-objects safely.
A number of sources of non-thermal plasma (less than 40 °C) at atmospheric pressure are being optimized and stabilized to ensure their effective and safe biological applications. In recent years, mainly three basic types of non-thermal atmospheric plasma devices, including plasma jet, surface and volume dielectric barrier discharges (DBDs), have been partially applied in cells or tissues [7,8,9,10]. In a plasma jet, the electrode (pin, ring, or plate type) is located in a capillary or tube inside a pen-like device. The plasma is generated inside the device. The effluent is blown out along the gas flow through the tube and can directly contact the target. In a surface DBD, the plasma is generated around a circular or grid-like electrode which is isolated from a counter electrode. Both electrodes can serve as either high voltage or ground electrodes. In a volume DBD, the plasma is generated in the gap between an isolated high voltage electrode and target. These three types of non-thermal atmospheric plasma, which are generated inside small discharge gaps, consist of transient micro discharges or filaments with non-uniform and constricted property [10]. In recent years, non-thermal plasma-induced changes in the liquid environment of cells and reactive species generated in or transferred into liquid phases by plasma treatment are identified as the two main basic mechanisms of biological plasma action [10]. The detailed analysis of gas and liquid phase chemistries, the generation of energetic photons, and the parameters of the electric field are required for the mode of plasma action and the development of plasma sources for specific applications.
Although there are a great number of biomedical applications based on plasma-direct interaction with cells or tissues, the measurements of the electric field delivered in plasma jets or DBDs are limited. The axial electric field distribution in a helium plasma jet is inferred from the optical emission spectroscopic data and from the calibrated dielectric probe measurements [11], and the peak electric field amplitudes as high as 100 kV/cm suggest same order of magnitude as those measured for volume DBD in air [12]. The electric field value in surface DBD plasma as high as 700–1100 Td is calculated on the basis of experimental measurements of emission spectra of molecular nitrogen [13]. Therefore, the method of emission spectroscopy based on polarization-dependent Stark splitting and shifting of atomic lines is a powerful and practical tool to investigate the macroscopic field in the presence of a relatively strong electric discharge. For the measurement of low electric field strengths at atmospheric pressure, the method based on line intensity ratio is applied in cases where the Stark method cannot be used [14]. Robert et al. [15] performed the measurement and analysis of a transient electric field associated with helium and neon atmospheric pressure plasma propagation inside a long dielectric tube using a bi-component electro-optic probe (EOP) Kapteos probe and intensified charge-coupled device imaging. All these experimental measurements in the study of Robert et al. [15] are in excellent agreement with previous model calculations. His study shows that plasma jet propagation occurs in a region where longitudinal electric field exists ahead the ionization front position, which induces an increase of radial electric field component with a constant amplitude of several kV/cm [15]. In addition, Bourdon et al. [16] analyzed the detailed propagation mechanisms of plasma gun discharge with helium and nitrogen that the two- and three-body Penning reactions occurring in the plasma column behind the ionization front play a significant role on the discharge dynamics. A non-intrusive electro-optic probe set outside the tube is used to measure the magnitude of electric field, showing peak electric fields of the order of 45 kV/cm [16], which can be important for interactions of the plasma plume with surfaces in biomedical applications.
Our laboratory has already developed a non-thermal DBD plasma treatment system at an atmospheric pressure to generate electrically safe plasma [17,18,19,20,21,22]. In brief, the DBD plasma reactor consists of upper and lower disk-shaped electrodes with a diameter of 140 mm and a dielectric barrier with a thickness of 5 mm. The upper electrode has 19 needles with a thickness of 2 mm and a length of 5 mm. The plasma reactor is electrified by a high-voltage alternating current with an operating frequency of 60 Hz and pure argon flow rate of 1 l/min. A high voltage probe (1000×, P6015, Tektronix, Beaverton, OR, USA) and a current monitor (2100, Pearson current monitor, CA, USA) are used to measure the voltage and current. A digital oscilloscope (TBS1064, Tektronix) is used to record the electrical data. The discharge powers dissipated in the plasma reactor at different applied voltages are calculated using a voltage-charge Lissajous plot, and the charge is recorded by measuring the voltage across the 1.0 µF capacitor connected to the plasma reactor in series. An emission spectrometer (Maya 2000 Pro, Ocean Optics) is employed to obtain the emission spectrum for plasma discharge in argon. The detailed physical properties of non-thermal DBD plasma are shown in the study of Zhang et al. [20]. The detailed experimental procedures of the DBD plasma technique applied on soybean seeds [17], chicken embryos [18,19,20], chicken spermatozoa [21], and chicken Sertoli cells [22] have already been described in detail. DBD plasma technique without substantial gas heating has a variety of advantages in the promotion of plant growth [23], biomedical applications in the treatment of bacteria sterilization, wound-healing, blood coagulation, dental treatment, and cancer treatment, and enhancements in the cell transfection efficiency, cell proliferation and differentiation, and tissue regeneration [24]. Significant progress in the applications of the DBD plasma technique has promoted the development of a new research field termed plasma agriculture, which aims at improving the plant and animal productivity. This review summarizes the application of non-thermal DBD plasma technique on the growth regulation of soybean sprouts and the development of chickens.
2. Effect of Plasma on the Growth of Soybean Sprouts
Application of non-thermal plasma technology in the seed treatment is being a modern eco-agricultural high-tech technique which can stimulate seed germination and plant growth for promoting grain yields [23,25,26,27,28,29,30]. Recently, the hot spots in the research of plasma biological engineering are to cultivate plasma treating seeds by modifying the material surface and activating seeds to improve the quality and production of various crops [23,28,29,31,32]. The plasma treating seeds technology imitates the space ionosphere state to expose seed to gas ions, magnetic fields, rays, vacuum, etc., whose joint action activates the seed physiological activity and their potential anti-stress gene expression including drought, cold, and other stress resistance [23,26,31,33,34]. However, multi-generation experiments of plasma treating seeds suggest that long-term memory of plasma irradiation is engraved in seeds of the next generation with little gene mutation [35].
Atmospheric DBD plasma irradiation enhances the growth of radish sprouts [29], the seed germination rate and seedling growth of spinach by elevating gibberellin hormone and amylolytic enzyme-related gene expression [36], and the seed germination, growth parameters and yields of tomato because active particles and ultraviolet can penetrate into the capsule of seeds, resulting in the reduction of relative penetrability of cell velum and the improvement of root activities [37]. The appropriate non-thermal plasma exposure can increase seed germination, seedling growth, length of sprouts, activation of photosynthesis, and resistance to adversity, resulting in significant improvements in the quality and yield of crops [23,26,28,29,31,32,33]. However, different input power and duration of plasma exposure determine different influences on the plant growth properties. Low doses of plasma treatment significantly increase the seed germination, seedling growth, and the length and weight of sprouts, whereas high doses inhibit these growth parameters [23,38,39]. Therefore, the non-thermal plasma treatment condition for promoting plant growth should be optimized.
Soybean sprout is a common and basic culinary vegetable rich in nutrients and with simple culturing method in the Eastern Asian countries. The quality and yield of soybean sprouts are dependent on seed germination and vigour. The decrease of growth period and the increase of the quality and yield of soybean sprouts are crucial issues with considerable economic benefits for farmers. Ling et al. [28] found cold plasma treatments had stimulatory effects on soybean seed germination and seedling growth through improving seed’s water uptake and decreasing apparent contact angle. Our laboratory also has found that the seed germination and growth features of soybean sprouts were ameliorated by non-thermal DBD plasma exposure at an optimized condition. The result showed that exposure at 22.1 kV of plasma for 12 s exhibited the highest seed germination and production rates (significant increases of 0.15- and 0.67-fold, respectively, compared to the control) and the maximum growth of soybean sprouts (including the weight, stem and root lengths, with significant increases of 0.39-, 0.79-, and 0.88-fold, respectively, compared to the control) [17]. Figure 1a–c showed a representative 6-day-old soybean sprout appearance treated with different conditions of plasma. The statistically validity and significance between plasma-treated groups and control group were reported in detail in the study of Zhang et al. [17]. The sprout growth-promoting effect of plasma-treated soybean seeds was found to be mediated by increases in the soluble protein level which improves water retention capacity and imbibition [28,31], antioxidant enzyme activity which markedly improves active oxygen metabolism level for the acceleration of seed germination [40], gene expression of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which promotes the germination and growth of sprouts [40,41], target of rapamycin which increases root and shoot growth, cell size, and seed yield without visibly affecting plant morphology [42], and growth-regulating factor which plays important roles in regulating plant growth and development [43] in the stems and roots [17]. The technique of non-thermal DBD plasma-treated seeds adds an additional value and serves as an efficient approach to promote the growth of soybean sprouts. However, no genetic mutations in plasma-treated soybean seeds were claimed in this study, which need further investigations on mutagenicity and genotoxic effects on the next generation.
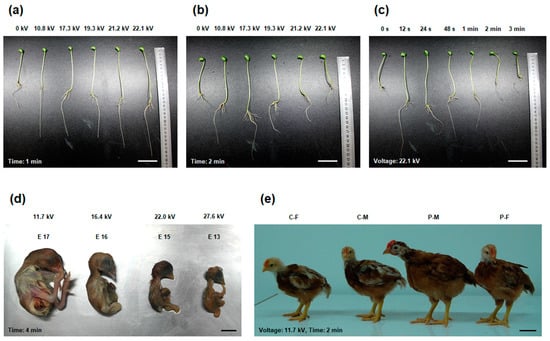
Figure 1.
Effects of non-thermal dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma treatment on soybean sprout growth and chicken development. (a) Representative 6-day-old soybean sprout appearance treated with plasma at different voltages for 1 min. Scale bar: 5.0 cm. (b) Representative 6-day-old soybean sprout appearance treated with plasma at different voltages for 2 min. Scale bar: 5.0 cm. (c) Representative 6-day-old soybean sprout appearance treated with plasma at 22.1 kV for different durations. Scale bar: 5.0 cm. Twenty soybean seeds in each group were treated, and each experiment was performed three times. The statistical validity was shown in the study of Zhang et al. [17]. (d) Representative chicken embryos from stage HH 20 were treated with plasma at different voltages for 4 min. Scale bar: 1.0 cm. The death day was estimated according to the Hamburger-Hamilton stages. E represents the embryonic day. Eight fertilized eggs in each group were treated, and this experiment was performed three times. The statistical validity was shown in the study of Zhang et al. [18]. (e) Representative growth status of female and male chickens on day 30 after plasma treatment on fertilized eggs at a voltage of 11.7 kV for 2 min. Scale bar: 5.0 cm. C-F represents female chicken in the control group; C-M represents male chicken in the control group; P-M represents male chicken in the plasma treatment group. P-F represents female chicken in the plasma treatment group. Twenty plasma-treated females and 20 plasma-treated males in each group were analyzed, and this experiment was performed three times. The statistical validity was shown in the study of Zhang et al. [19].
3. Plasma Application in Chicken Growth
After the observation of plasma positive effects on soybean sprout growth, the influence of non-thermal DBD plasma on the development of animals’ embryo, postnatal growth, and even the reproductive capacity was investigated. Chicken has unique embryonic development characteristics due to the oviparity; this allows the easy treatment of chicken embryos without influences from the matrix and external environment. Different development stages of chicken embryos exhibit a different resistibility to some adverse external factors [44]. Exposing the chicken embryos at Hamburger-Hamilton (HH) stage 20, when they have established major and identifiable organs to sustain life after hatching, to non-thermal DBD plasma at a voltage range of 11.7–27.6 kV for 4 min resulted in embryonic death in a dose-dependent manner; on average, they died at stages embryonic day 17 (E17), E16, E15, and E13, respectively, compared to the control (no plasma treatment; 0 kV) [18]. Figure 1d showed a representative chicken embryo appearance treated with different voltages of plasma, indicating that exposure to plasma at higher voltages for 4 min increased the rate of embryo death. However, plasma exposure at a lower voltage and shorter duration improved the embryonic development [18]. In vitro experiments reveals that low-dose plasma treatment increases the proliferation of cells [45,46] and the growth of limbs [47], whereas a high dose shows anti-proliferative effects [48,49]. Furthermore, longer durations of plasma exposure decreases cell viability and proliferation [50], induces cell toxicity [46], and increases cell apoptosis [51]. These findings indicated that 4 min of plasma treatment at a voltage range of 11.7–27.6 kV would be lethal to the chicken embryonic development. Therefore, the intensity and exposure time of non-thermal plasma should be sufficiently appropriate for potential growth-promoting effects in chickens when this plasma technique is employed on the fertilized eggs.
The physical properties of non-thermal DBD plasma developed in our laboratory showed that plasma discharge inevitably did not occur uniformly at all positions because of the oval shape of eggs and current pulses were generated randomly rather than periodically because of the non-uniform plasma discharge [20]. Plasma discharge characteristics depend on the applied voltage, electrode geometry, dielectric type, dielectric thickness, and discharge gap. Furthermore, our non-thermal DBD plasma system showed that the current was basically sinewave, but there were many current pulses superimposed on the sinewave. The current waveform which looked like sinewave was the displacement current with no active role in the plasma discharge. Only the current pulses superimposed over the sinewave represented a conduction current which was associated with the discharge filaments [20]. In addition, the emission spectrum of argon plasma showed there were several strong or weak ultraviolet A and B wavelengths, and the optical emission spectrum was found with a range of 200–650 nm. Plasma-emitted ultraviolet photons at various wavelengths transmission across the egg was limited due to the presence of an egg shell. Although argon plasma also emits various visible photons in the range of 700~850 nm due to Ar (I) [52], it is believed that visible photons of larger wavelengths having low energies cannot affect the inside of eggs. Therefore, it is reasonable to exclude the effect of ultraviolet/visible light emission on the chicken embryos.
Numerous small and spherical pores in the palisades region of eggshell permit the diffusion of metabolic gases [53] and potential diffusion of active charged and neutral particles in plasma, which notably produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) when they react on the surface of cells or tissues [54,55,56]. Although it is unclear how the ROS are delivered into the real biological targets and the exact interaction with various components of a tissue when considering the lifetime, diffusion rate, and major physical barriers to traverse [24], the diffusion and delivery of plasma-generated ROS or stimulation of intracellular ROS generating mechanisms as a result of non-thermal DBD plasma treatment [57,58] has been suggested to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation [46,59] in low-doses and cell death [57,60,61] in high-doses. Non-thermal DBD plasma-generated appropriate extracellular ROS increases skeletal cell differentiation and limb development of mice through the activation and amplification of intracellular ROS-sensitive signaling pathways [47]. However, excessive accumulation of intracellular ROS induces cell apoptosis [22,60,62]. In addition, inappropriate non-thermal DBD plasma treatment generated excessive ROS, elevated mRNA expression of NOX4 which catalyzes the reduction of molecular oxygen to generate ROS [63,64,65], and decreased NRF2 level which directly affects ROS level by regulating the antioxidant defense system [66,67,68] in the skeletal muscle of dead embryos [18]. Therefore, inappropriate plasma-induced chicken embryonic death is resulted from the excessive accumulation of intracellular ROS and the disruption of antioxidant signaling pathways.
Furthermore, Zhang et al. [18] found that inappropriate plasma exposure reduced ATP production and growth factor level by regulating their gene expression in the skeletal muscle tissue of the dead chicken embryos. Several studies have attempted to characterize DNA damage and the associated cellular responses induced by atmospheric pressure plasma in a dose-dependent manner, indicating a critical role of reactive species in plasma-induced damage to DNA [45,61,69,70,71,72,73,74,75]. Work by The Leibniz Institute for Plasma Science and Technology (INP Greifswald), investigated atmospheric pressure plasma which was generated with different feed gas conditions corresponding to distinct reactive species patterns for their genotoxic potential, showing that no increase of micronuclei formation was found in plasma-treated cells by a high-throughput micronucleus assay indicative for mutagenicity [76]. Detailed investigations using well-established experimental procedures demonstrate that detrimental plasma effects on DNA result in cellular repair processes and induction of cell apoptosis [77,78], but no increased risk for genotoxic effect and no mutagenic potential are induced by the non-thermal atmospheric plasma to ensure safe biomedical applications [78,79]. However, no genetic mutations in plasma-treated chicken embryos were revealed in the study of Zhang et al. [18]. Therefore, further detections of mutagenic effect and potential genotoxicity on chicken embryonic development are necessary to evaluate the safe application of non-thermal DBD plasma in poultry.
The appropriate application of non-thermal DBD plasma technique on fertilized eggs before hatching was found to improve the postnatal growth rate in chickens [19,20]. Plasma-treated chicken embryos from stage HH 20 (at a voltage of 11.7 kV for 2 min) exhibited the maximum growth rate (including the average daily gain and tibia length, with significant increases of 0.10- and 0.14-fold in females, 0.34- and 0.16-fold in males, respectively, compared to females and males in the control group) on day 30, and particularly a significant improvement was observed in the growth of male chickens [19]. Figure 1e showed a representative 30-day-old chicken appearance after the optimal condition of non-thermal DBD plasma treatment. Serum growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 which contribute to improve the energy metabolism and protein synthesis for muscle and bone growth in poultry [80,81], thyroid hormones which play an important role skeletal muscle differentiation and growth [82], testosterone which increases the synthesis of myofibril and sarcoplasmic proteins and stimulates skeletal muscle ATP concentration and energy metabolism [83], and ATP levels were significantly increased in plasma-treated chickens; these metabolic improvements were found to be mediated by the regulation of demethylation levels in the skeletal muscle and thyroid gland [19]. However, next-generation chickens which were obtained from plasma direct-treated parents had no significant differences in the hatching rate, average daily gain, length of tibia, and concentrations of serum hormones (including growth hormone, thyroid hormones, insulin-like growth factor 1, and testosterone) and ATP, because their mothers had no significant changes in the female reproductive capacity (including the serum estradiol and progesterone levels which regulate egg production and quality [84,85,86], egg-laying rate, and egg weight) following the plasma treatment [20]. Hens primarily determine the development of offspring embryos and the postnatal growth [87]. At the same time, the weight of a fertilized chicken egg affects the hatch and growth of their offspring, and this maternal environment can influence the growth characteristics of their progeny lastingly [88]. Although offspring of plasma-treated parents fail to inherit excellent growth properties, non-thermal DBD plasma direct-treated generation suggests a potentially viable and valuable strategy to improve the chicken growth rate in the poultry industry.
4. Plasma Improves Male Chicken Fertility
Fertility is a trait of major interest in the poultry industry because it determines the profitability of production. Chicken sperm quality influences the male fertility and the hatchability of fertilized eggs [89], which are the ultimate objective of poultry breeder management. Spermatozoa are highly specialized cells which require high ATP level for providing the energy to ensure motility and fertilization potential [90]. The numerous mitochondria in the intermediate piece of chicken sperm provide the energy for flagellum movement to reach the fertilization site in the infundibulum [91]. Sperm quality and fertility also require ROS homeostasis between generation and scavenging activity [92]. Low and physiological concentrations of ROS stimulate sperm capacitation and acrosome reaction to ensure fertilization [89,93], but high concentrations of ROS lead to sperm DNA damage, impaired acrosome integrity, and decreased motility, viability, and fertilization capacity [92,94,95]. Zhang et al. [21] reported that the appropriate treatment condition of non-thermal DBD plasma increased the chicken sperm motility in vitro by controlling the ROS balance and increasing the ATP level and respiratory enzyme activity in the mitochondria; this resulted from the regulation of the demethylation levels of genes involved in antioxidant defense and energetic metabolism [21]. Sperm DNA methylation levels are associated with sperm motility, but not with sperm viability or morphology [96]. However, hypermethylation results in impaired sperm morphology [97], low sperm motility [98,99], infertility [100], and even sperm apoptosis [101]. In addition, the reproductive performance in 40-week-old male chickens which were hatched from non-thermal DBD plasma-treated fertilized eggs was investigated and the results showed that plasma treatment significantly increased serum testosterone level, sperm count, motility, and total fertility in male chickens [20]. Therefore, the plasma technique might be applied to elevate male fertility in poultry breeding.
5. Conclusions
Taken together, this review suggests an applicative technique that an optimal non-thermal DBD plasma technique could be applied on soybean seeds and chicken embryos as a safe and valuable approach for promoting soybean sprout growth, chicken embryonic development and postnatal growth, and even male chicken fertility, which are beneficial to improving plant and poultry productivity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.J.Z., T.K. and D.K.J.; methodology, J.J.Z.; software, J.J.Z.; validation, T.K., S.B.K. and D.K.J.; formal analysis, J.J.Z.; investigation, J.J.Z.; resources, T.K., S.B.K. and D.K.J.; data curation, J.J.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.J.Z.; writing—review and editing, T.K., S.B.K. and D.K.J.; visualization, T.K. and D.K.J.; supervision, D.K.J.; project administration, T.K. and D.K.J.; funding acquisition, D.K.J.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (MOTIE), Korea, under the “Regional Specialized Industry Development Program (R&D, P0002062)” supervised by the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the R&D Program of “Plasma Advanced Technology for Agriculture and Food (Plasma Farming)” through the National Fusion Research Institute of Korea (NFRI). The authors would like to thank the China Scholarship Council for providing Jiao Jiao Zhang with a scholarship.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- von Woedtke, T.; Reuter, S.; Masur, K.; Weltmann, K.D. Plasmas for medicine. Phys. Rep. 2013, 530, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalia Yu, B.; Mark, J.K. Intracellular electric fields produced by dielectric barrier discharge treatment of skin. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 185206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.X.; Yang, A.J.; Wang, X.H.; Rong, M.Z.; Iza, F.; Kong, M.G. Wall fluxes of reactive oxygen species of an rf atmospheric-pressure plasma and their dependence on sheath dynamics. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 305205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, B.G. The emerging role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in redox biology and some implications for plasma applications to medicine and biology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 263001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beate, H.; Thomas von, W.; Klaus-Dieter, W.; Ulrike, L. Non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma possible application in wound healing. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrads, H.; Schmidt, M. Plasma generation and plasma sources. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2000, 9, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbary, G.; Shimizu, T.; Li, Y.F.; Stolz, W.; Thomas, H.M.; Morfill, G.E.; Zimmermann, J.L. Cold atmospheric plasma devices for medical issues. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2013, 10, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousfi, M.; Merbahi, N.; Pathak, A.; Eichwald, O. Low-temperature plasmas at atmospheric pressure: Toward new pharmaceutical treatments in medicine. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 28, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setsuhara, Y. Low-temperature atmospheric-pressure plasma sources for plasma medicine. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 605, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltmann, K.D.; Metelmann, H.R.; von Woedtke, T. Low temperature plasma applications in medicine. Eur. News 2016, 47, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, A.; Laroussi, M.; Pervez, M.R. Atmospheric pressure He-air plasma jet: Breakdown process and propagation phenomenon. AIP Adv. 2013, 3, 062117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, L.; Danil, D.; Alexander, F. Uniform and non-uniform modes of nanosecond-pulsed dielectric barrier discharge in atmospheric air: Fast imaging and spectroscopic measurements of electric fields. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 252003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starikovskaia, S.M.; Allegraud, K.; Guaitella, O.; Rousseau, A. On electric field measurements in surface dielectric barrier discharge. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 124007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradović, B.M.; Cvetanović, N.; Ivković, S.S.; Sretenović, G.B.; Kovačević, V.V.; Krstić, I.B.; Kuraica, M.M. Methods for spectroscopic measurement of electric field in atmospheric pressure helium discharges. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 77, 30802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, E.; Darny, T.; Dozias, S.; Iseni, S.; Pouvesle, J.M. New insights on the propagation of pulsed atmospheric plasma streams: From single jet to multi jet arrays. Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 122007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, A.; Darny, T.; Pechereau, F.; Pouvesle, J.-M.; Viegas, P.; Iséni, S.; Robert, E. Numerical and experimental study of the dynamics of a μs helium plasma gun discharge with various amounts of N2 admixture. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2016, 25, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Jo, J.O.; Huynh, D.L.; Mongre, R.K.; Ghosh, M.; Singh, A.K.; Lee, S.B.; Mok, Y.S.; Hyuk, P.; Jeong, D.K. Growth-inducing effects of argon plasma on soybean sprouts via the regulation of demethylation levels of energy metabolism-related genes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Jo, J.O.; Huynh, D.L.; Ghosh, M.; Kim, N.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, H.K.; Mok, Y.S.; Kwon, T.; Jeong, D.K. Lethality of inappropriate plasma exposure on chicken embryonic development. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 85642–85654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Wang, X.Z.; Kwon, T.; Huynh, D.L.; Chandimali, N.; Kim, N.; Kang, T.Y.; Ghosh, M.; Gera, M.; Lee, S.B.; et al. Innovative approach of non-thermal plasma application for improving the growth rate in chickens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Huynh, D.L.; Chandimali, N.; Kang, T.Y.; Kim, N.; Mok, Y.S.; Kwon, T.; Jeong, D.K. Growth and male reproduction improvement of non-thermal dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment on chickens. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 205201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Do, H.L.; Chandimali, N.; Lee, S.B.; Mok, Y.S.; Kim, N.; Kim, S.B.; Kwon, T.; Jeong, D.K. Non-thermal plasma treatment improves chicken sperm motility via the regulation of demethylation levels. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Wang, X.Z.; Luong Do, H.; Chandimali, N.; Kang, T.Y.; Kim, N.; Ghosh, M.; Lee, S.B.; Mok, Y.S.; Kim, S.B.; et al. MicroRNA-7450 regulates non-thermal plasma-induced chicken Sertoli cell apoptosis via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.F.; He, X.; Li, L.; Li, J.G.; Shao, H.L.; Xu, Q.L.; Ye, R.H.; Dong, Y.H. Effect of cold plasma treatment on seed germination and growth of wheat. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2014, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szili, E.J.; Hong, S.-H.; Oh, J.-S.; Gaur, N.; Short, R.D. Tracking the penetration of plasma reactive species in tissue models. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mraz, I.; Beran, P.; Sera, B.; Gavril, B.; Eugen, H. Effect of low-temperature plasma treatment on the growth and reproduction rate of some plant pathogenic bacteria. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 96, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.F.; Lu, Y.F.; Li, J.G.; Li, L.; He, X.; Shao, H.L.; Dong, Y.H. Effect of seed treatment by cold plasma on the resistance of tomato to Ralstonia solanacearum (Bacterial Wilt). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; He, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, R.; Chen, W.; Yang, S. Effects of atmospheric pressure air plasma pretreatment on the seed germination and early growth of andrographis paniculata. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2014, 16, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Jiafeng, J.; Jiangang, L.; Minchong, S.; Xin, H.; Hanliang, S.; Yuanhua, D. Effects of cold plasma treatment on seed germination and seedling growth of soybean. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarinont, T.; Amano, T.; Kitazaki, S.; Koga, K.; Uchida, G.; Shiratani, M.; Hayashi, N. Growth enhancement effects of radish sprouts: Atmospheric pressure plasma irradition vs. heat shock. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 518, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoshi, K.; Kazunori, K.; Masaharu, S.; Nobuya, H. Growth enhancement of radish sprouts induced by low pressure O2 radio frequency discharge plasma irradiation. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 51, 01AE01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.; Shapira, Y.; Grynyov, R.; Whyman, G.; Bormashenko, Y.; Drori, E. Interaction of cold radiofrequency plasma with seeds of beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 4013–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sera, B.; Sery, M.; Stranak, V.; Spatenka, P.; Tichy, M. Does cold plasma affect breaking dormancy and seed germination? A study on seeds of lamb’s quarters (Chenopodium album agg.). Plasma Sci. Technol. 2009, 11, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volin, J.C.; Denes, F.S.; Young, R.A.; Park, S.M.T. Modification of seed germination performance through cold plasma chemistry technology. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 1706–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, R.; Yan, J. Study on activation and improvement of crop seeds by the application of plasma treating seeds equipment. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 655, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarinont, T.; Amano, T.; Koga, K.; Shiratani, M.; Hayashi, N. Multigeneration effects of plasma irradiation to seeds of Arabidopsis Thaliana and Zinnia on their growth. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2015, 1723, mrsf14-1723-g03-04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.-H.; Choi, K.-H.; Pengkit, A.; Im, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, Y.; Hong, E.J.; Jung, S.K.; Choi, E.-H.; et al. Effects of high voltage nanosecond pulsed plasma and micro DBD plasma on seed germination, growth development and physiological activities in spinach. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 605, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, W. Introduction of a new atmospheric pressure plasma device and application on tomato seeds. Agric. Sci. 2011, 2, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henselova, M.; Slovakova, L.; Martinka, M.; Zahoranova, A. Growth, anatomy and enzyme activity changes in maize roots induced by treatment of seeds with low-temperature plasma. Biologia 2012, 67, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhayal, M.; Lee, S.-Y.; Park, S.-U. Using low-pressure plasma for Carthamus tinctorium L. seed surface modification. Vacuum 2006, 80, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.Q.; Huang, M.J.; Ma, B.Z.; Ma, T.C. Stimulating effects of seed treatment by magnetized plasma on tomato growth and yield. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2005, 7, 3143–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perl, M. ATP synthesis and utilization in the early stage of seed germination in relation to seed dormancy and quality. Physiol. Plant. 1986, 66, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprost, D.; Yao, L.; Sormani, R.; Moreau, M.; Leterreux, G.; Nicolai, M.; Bedu, M.; Robaglia, C.; Meyer, C. The Arabidopsis TOR kinase links plant growth, yield, stress resistance and mRNA translation. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omidbakhshfard, M.A.; Proost, S.; Fujikura, U.; Mueller-Roeber, B. Growth-regulating factors (GRFs): A small transcription factor family with important functions in plant biology. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavlock, R.J.; Daston, G.P. Drug Toxicity in Embryonic Development I: Advances in Understanding Mechanisms of Birth Defects: Morphogenesis and Processes at Risk, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 519–548. ISBN 978-3-642-60445-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kalghatgi, S.; Kelly, C.M.; Cerchar, E.; Torabi, B.; Alekseev, O.; Fridman, A.; Friedman, G.; Azizkhan-Clifford, J. Effects of non-thermal plasma on mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalghatgi, S.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, A.; Clyne, A.M. Endothelial cell proliferation is enhanced by low dose non-thermal plasma through fibroblast growth factor-2 release. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernets, N.; Zhang, J.; Steinbeck, M.J.; Kurpad, D.S.; Koyama, E.; Friedman, G.; Freeman, T.A. Nonthermal atmospheric pressure plasma enhances mouse limb bud survival, growth, and elongation. Tissue Eng. Part A 2015, 21, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieft, I.E.; Kurdi, M.; Stoffels, E. Reattachment and apoptosis after plasma-needle treatment of cultured cells. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2006, 34, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, N.; Fujita, R.; Kawano, F.; Takahashi, K.; Ohira, T.; Shibaguchi, T.; Nakata, K.; Ohira, Y. Retardation of C2C12 myoblast cell proliferation by exposure to low-temperature atmospheric plasma. J. Physiol. Sci. 2014, 64, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzer, J.; Heuer, K.; Demir, E.; Hoffmanns, M.A.; Baldus, S.; Fuchs, P.C.; Awakowicz, P.; Suschek, C.V.; Opländer, C. Non-thermal dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) effects on proliferation and differentiation of human fibroblasts are primary mediated by hydrogen peroxide. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haertel, B.; Volkmann, F.; von Woedtke, T.; Lindequist, U. Differential sensitivity of lymphocyte subpopulations to non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Fujiwara, H.; Kondo, M.; Kuraseko, H. Optical emission spectroscopy of atmospheric pressure microwave plasmas. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 054908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hincke, M.T.; Nys, Y.; Gautron, J.; Mann, K.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A.B.; McKee, M.D. The eggshell: Structure, composition and mineralization. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 1266–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchenbecker, M.; Bibinov, N.; Kaemlimg, A.; Wandke, D.; Awakowicz, P.; Viol, W. Characterization of DBD plasma source for biomedical applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 045212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, A.; Chirokov, A.; Gutsol, A. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure discharges. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, R1–R24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, G.; Friedman, G.; Gutsol, A.; Shekhter, A.B.; Vasilets, V.N.; Fridman, A. Applied plasma medicine. Plasma Process. Polym. 2008, 5, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Truong, B.; Patel, S.; Kaushik, N.; Choi, E.H.; Fridman, G.; Fridman, A.; Miller, V. Nanosecond-pulsed DBD plasma-generated reactive oxygen species trigger immunogenic cell death in A549 lung carcinoma cells through intracellular oxidative stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zou, F.; Zhao, S.; Lu, X.; Yang, G.; He, G.; Ostrikov, K. Plasma-induced death of HepG2 cancer cells: Intracellular effects of reactive species. Plasma Process. Polym. 2011, 9, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbeck, M.J.; Chernets, N.; Zhang, J.; Kurpad, D.S.; Fridman, G.; Fridman, A.; Freeman, T.A. Skeletal cell differentiation is enhanced by atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackert, S.; Haertel, B.; Wende, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Lindequist, U. Influence of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma on cellular structures and processes in human keratinocytes (HaCaT). J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 70, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ha, C.S.; Hwang, S.W.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, G.C.; Lee, K.W.; Song, K. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma preferentially induces apoptosis in p53-mutated cancer cells by activating ROS stress-response pathways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.C.; Piao, M.J.; Hewage, S.R.K.M.; Han, X.I.A.; Kang, K.A.; Jo, J.O.; Mok, Y.S.; Shin, J.H.; Park, Y.; Yoo, S.J.; et al. Non-thermal dielectric-barrier discharge plasma damages human keratinocytes by inducing oxidative stress. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, K.; Zhang, M.; Benkhoff, S.; Mieth, A.; Pliquett, R.; Kosowski, J.; Kruse, C.; Luedike, P.; Michaelis, U.R.; Weissmann, N.; et al. Nox4 is a protective reactive oxygen species generating vascular NADPH oxidase. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, J.; Ago, T.; Matsushima, S.; Zhai, P.; Schneider, M.D.; Sadoshima, J. NADPH oxidase 4 (Nox4) is a major source of oxidative stress in the failing heart. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15565–15570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ershova, E.S.; Sergeeva, V.A.; Chausheva, A.I.; Zheglo, D.G.; Nikitina, V.A.; Smirnova, T.D.; Kameneva, L.V.; Porokhovnik, L.N.; Kutsev, S.I.; Troshin, P.A.; et al. Toxic and DNA damaging effects of a functionalized fullerene in human embryonic lung fibroblasts. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2016, 805, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinan, S.B.; Zhang, D.; Hannink, M.; Arvisais, E.; Kaufman, R.J.; Diehl, J.A. Nrf2 is a direct PERK substrate and effector of PERK-dependent cell survival. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2003, 23, 7198–7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q. Role of Nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Nioi, P.; Pickett, C.B. The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J. Boil. Chem. 2009, 284, 13291–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalghatgi, S.; Fridman, A.; Azizkhan-Clifford, J.; Friedman, G. DNA damage in mammalian cells by non-thermal atmospheric pressure microsecond pulsed dielectric barrier discharge plasma is not mediated by ozone. Plasma Process. Polym. 2012, 9, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, M.; Guay, D.; Coulombe, S.; Leask, R.L. Effects of non-thermal plasmas on DNA and mammalian cells. Plasma Process. Polym. 2010, 7, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, H.; Miura, T.; Kurita, H.; Takashima, K.; Mizuno, A. Biological evaluation of DNA damage in bacteriophages inactivated by atmospheric pressure cold plasma. Plasma Process. Polym. 2010, 7, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, D.; Cox, L.J.; Hyland, W.B.; McMahon, S.J.; Reuter, S.; Graham, W.G.; Gans, T.; Currell, F.J. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma jet interactions with plasmid DNA. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 043701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.J.; Kim, W.; Kim, K.T.; Lee, J.K. DNA damage and mitochondria dysfunction in cell apoptosis induced by nonthermal air plasma. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 021502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahnev, B.; Bowden, M.D.; Stypczyńska, A.; Ptasińska, S.; Mason, N.J.; Braithwaite, N.S.J. A novel method for the detection of plasma jet boundaries by exploring DNA damage. Eur. Phys. J. D 2014, 68, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalghatgi, S.; Azizkhan-Clifford, J. DNA damage in mammalian cells by non-thermal atmospheric pressure microsecond pulsed dielectric barrier discharge plasma is not mediated via lipid peroxidation. Plasma Med. 2011, 1, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Schmidt, A.; Kramer, A.; Metelmann, H.-R.; Adler, F.; von Woedtke, T.; Niessner, F.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Wende, K. High throughput image cytometry micronucleus assay to investigate the presence or absence of mutagenic effects of cold physical plasma. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2018, 59, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strassenburg, S.; Greim, U.; Bussiahn, R.; Haertel, B.; Wende, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Lindequist, U. Comparison of biological effects on human keratinocytes using different plasma treatment regimes. Plasma Med. 2013, 3, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wende, K.; Straßenburg, S.; Haertel, B.; Harms, M.; Holtz, S.; Barton, A.; Masur, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Lindequist, U. Atmospheric pressure plasma jet treatment evokes transient oxidative stress in HaCaT keratinocytes and influences cell physiology. Cell Boil. Int. 2013, 38, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wende, K.; Bekeschus, S.; Schmidt, A.; Jatsch, L.; Hasse, S.; Weltmann, K.D.; Masur, K.; von Woedtke, T. Risk assessment of a cold argon plasma jet in respect to its mutagenicity. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2016, 798–799, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhuis, J.D.; Roemmich, J.N.; Richmond, E.J.; Rogol, A.D.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Mauras, N.; Bowers, C.Y. Endocrine control of body composition in infancy, childhood, and puberty. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 114–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, K.; Nagao, K.; Okumura, J. Nutritional and tissue specificity of IGF-I and IGFBP-2 gene expression in growing chickens. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 18, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, J.H.D.; Williams, G.R. Role of thyroid hormones in skeletal development and bone maintenance. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 135–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadi, F. Cellular and molecular mechanisms responsible for the action of testosterone on human skeletal muscle. A basis for illegal performance enhancement. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebedeva, I.Y.; Lebedev, V.A.; Grossmann, R.; Parvizi, N. Age-dependent role of steroids in the regulation of growth of the hen follicular wall. Reprod. Boil. Endocrinol. 2010, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wistedt, A.; Ridderstrale, Y.; Wall, H.; Holm, L. Exogenous estradiol improves shell strength in laying hens at the end of the laying period. Acta Vet. Scand. 2014, 56, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, W.L.; Liu, H.-K. Progesterone injection and egg production in Turkey Hens. Boil. Reprod. 2004, 71, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janczak, A.M.; Torjesen, P.; Palme, R.; Bakken, M. Effects of stress in hens on the behaviour of their offspring. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 107, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, L.M.; Sparks, N.H.C.; Rutherford, K.M.D. Early experiences matter: A review of the effects of prenatal environment on offspring characteristics in poultry. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.U. Antioxidants and poultry semen quality. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2011, 67, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misro, M.M.; Ramya, T. Fuel/Energy Sources of Spermatozoa. In Male Infertility: Contemporary Clinical Approaches, Andrology, ART & Antioxidants, 1st ed.; Parekattil, S.J., Agarwal, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 209–223. ISBN 978-1-4614-3335-4. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Alves, S.; Grasseau, I.; Metayer-Coustard, S.; Praud, C.; Froment, P.; Blesbois, E. Central role of 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase in chicken sperm functions. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 91, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.K.; Bilaspuri, G.S. Impacts of oxidative stress and antioxidants on semen functions. Vet. Med. Int. 2011, 2011, 686137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, P.B.; Bucak, M.N.; Sarıözkan, S.; Sakin, F.; Yeni, D.; Çiğerci, İ.H.; Ateşşahin, A.; Avdatek, F.; Gündoğan, M.; Büyükleblebici, O. The effect of raffinose and methionine on frozen/thawed Angora buck (Capra hircus ancryrensis) semen quality, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities. Cryobiology 2010, 61, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, H.D.; Welch, G.R. Effects of reactive oxygen species on sperm function. Theriogenology 2012, 78, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, B.R.; Shibuya, F.Y.; Kawaoku, A.J.T.; Losano, J.D.A.; Angrimani, D.S.R.; Dalmazzo, A.; Nichi, M.; Pereira, R.J.G. Impact of induced levels of specific free radicals and malondialdehyde on chicken semen quality and fertility. Theriogenology 2017, 90, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montjean, D.; Zini, A.; Ravel, C.; Belloc, S.; Dalleac, A.; Copin, H.; Boyer, P.; McElreavey, K.; Benkhalifa, M. Sperm global DNA methylation level: Association with semen parameters and genome integrity. Andrology 2015, 3, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassuto, N.G.; Montjean, D.; Siffroi, J.P.; Bouret, D.; Marzouk, F.; Copin, H.; Benkhalifa, M. Different levels of DNA methylation detected in human sperms after morphological selection using high magnification microscopy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6372171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houshdaran, S.; Cortessis, V.K.; Siegmund, K.; Yang, A.; Laird, P.W.; Sokol, R.Z. Widespread epigenetic abnormalities suggest a broad DNA methylation erasure defect in abnormal human sperm. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montjean, D.; De La Grange, P.; Gentien, D.; Rapinat, A.; Belloc, S.; Cohen-Bacrie, P.; Menezo, Y.; Benkhalifa, M. Sperm transcriptome profiling in oligozoospermia. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2012, 29, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aston, K.I.; Uren, P.J.; Jenkins, T.G.; Horsager, A.; Cairns, B.R.; Smith, A.D.; Carrell, D.T. Aberrant sperm DNA methylation predicts male fertility status and embryo quality. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 104, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzideh, J.; Scott, R.J.; Aitken, R.J. Analysis of the global methylation status of human spermatozoa and its association with the tendency of these cells to enter apoptosis. Andrologia 2013, 45, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).