Abstract
This study aimed to assess the biomechanical behavior of endocrown-restored mandibular molars according to “margin design” and “coverage extent” using finite element analysis (FEA). Six 3D solid models were fabricated, namely, those with complete occlusal coverage: A (butt joint), B (anatomic margin); partial coverage (two mesial cusps): C (butt joint), D (anatomic margin); and partial coverage with mesial class II cavity: E (butt joint), F (anatomic margin). All models received lithium disilicate endocrowns (2.0 mm thickness and 4.0 mm central retainer cavity depth). A 300 N vertical load was applied to the occlusal surface, while a 250 N oblique load was applied at 45° to the lingual inclined planes of the buccal cusps. The maximum von Mises stress (VMS) distribution patterns were calculated for the endocrown, tooth structure, and cement layer. The VMS on the prepared teeth and cement layer showed subtle differences between the tested models under vertical loads. The anatomic margin (partial and complete coverage) exhibited a more homogeneous stress distribution and offered a more adhesive area of the tooth structure. Under oblique loading, the anatomic margin (complete and partial), except Model D, exhibited the lowest VMS in the cement layer. An anatomically based endocrown could be a promising alternative to the butt joint design, providing better-devised endocrown restorations, which could potentially yield a more benign stress dissipation.
1. Introduction
Restoring endodontically treated teeth (ETT) remains a clinical challenge in dentistry [1,2]. The widely accepted approach involves a crown prosthesis supported by a post and core build-up [3]. However, the intra-radicular posts weaken the tooth structure and increase the incidence of root failure [4]. Furthermore, several studies have considered luting cement to be a critical point since it is thick and has a tendency to acquire flaws and stresses that jeopardize the adhesive union between the post and substrate [5,6]. With growing emphasis on minimally invasive approaches and current advancements in adhesive technology, endocrown has emerged as a viable alternative for rehabilitating ETT [7,8]. An endocrown is a monolithic prosthesis that is retained by utilizing the pulp chamber and remaining coronal tooth structure [9,10]. This treatment modality is characterized by supragingival butt joint preparation, thus facilitating impression acquisition, maintaining gingival health, and preserving the maximum enamel collar, which improves adhesion [11,12,13]. Compared to post-core retained crowns, which present a smaller material volume in the occlusal area and concentrate stresses in their thinner portion, endocrowns have a large material volume in this area, which offers optimal fracture resistance and promising clinical performance [8,14]. Furthermore, endocrowns enable the effective sealing of the root canal system and reduce the risk of recontamination, which could possibly affect the favorable long-term prognosis of ETT [11,15].
Endocrown design remains in dispute regarding the restoration of ETT. The form of the finish line (circumferential butt joint margin or chamfer finish line) and the depth and shape of the pulp chamber are diverse tested preparation designs that can change the biomechanical behavior of the endocrowns [10,16,17,18]. Research has indicated that margin forms play a crucial role in the biomechanical performance of ETT restored with post-retained crowns [10]. To determine whether margin design has a comparable impact on endocrown behavior, further investigation is needed. Typically, the butt joint margin was employed in endocrown research and was often compared with ferrule and curved surface designs [19,20]. Curved preparations have the advantage of maximum preservation of the tooth structure [20], and ferrule-incorporated endocrowns provide increased fracture resistance; however, finite element analysis (FEA) has shown greater stress concentrations in such margins [21,22,23]. To date, limited studies are available to definitively determine which margin design is more effective in restoring ETT. Additionally, occlusal coverage extent could be another critical factor that might influence the fracture behavior of the endocrown. Studies have found that conservative indirect onlay preparations preserved the tooth structure to a greater extent, as well as improving stress distribution [24,25]. Thus, from a minimally invasive standpoint, the following question arises: could conventional complete occlusal coverage endocrowns be modified into a defect-driven preparation? Furthermore, the suitability of a butt-margin-designed endocrown remains questionable due to the complex occlusal morphology of the natural tooth crown [8,26]. Thus, in light of these factors, we established six models of ETT restored using different modified endocrown restorations.
A wide variety of ceramic materials are available for the fabrication of endocrowns. Lithium disilicate glass ceramic is one such material due to its biomechanical properties [27]. The material possesses approximately 70 vol% and small needle-shaped crystals (3–6 μm × 0.8 μm) embedded in a glass matrix, thus showing valuable mechanical characteristics with a flexural strength of 350 MPa [28,29,30]. Lithium disilicate exhibits very good esthetic features and is considered an acid-sensitive ceramic, so high adhesion capacity to the substrate is expected, thus making it ideal for use in inlays, onlays, and endocrowns [31,32,33].
FEA has been widely used in dental biomechanical research to assess the stress distribution generated by masticatory loads in ETT and to predict the clinical performance of restorative material [34,35]. Such analysis is able to detect stress concentration regions that might undergo clinical failure. Usually, the failure origin consists of points of greater stress concentration previously evidenced by FEA [9,20]. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the influences of margin design and the extent of crown coverage on the biomechanical behavior of endocrowns made from lithium disilicate material using FEA.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of the 3D Geometrical Model
An intact mandibular third molar was extracted based on routine clinical indications and scanned using cone beam computed tomography imaging (NewTom Giano HR Cefla, Imola, Italy). The obtained data were imported into an interactive medical image control system (Mimics ver.21.0; Materialise Leuven, Belgium) in a “Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine” (DICOM) format. The three-point clouds (enamel, dentin, and pulp) were separated according to the different pixel densities. The contour for each portion was then generated using software (Geomagic Studio 10, Geomagic, Inc., Research Triangle Park, NC, USA). A solid 3D model was then reconstructed with a computer-aided design software program (SolidWorks 2014; Dassault Systems,,Vélizy-Villacoublay, France). To simulate an ETT, the pulp in the root canal space was replaced with gutta percha [36].
2.2. Endocrown Designs
To compare the stress distribution of the proposed endocrowns, six models were created using the software Solid Works® 2014 (Figure 1). Model A: The coronal tooth structure was reduced perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth, approximately 2.0 mm below the buccal groove, which was considered a cutting reference for all simulated models. Model B: A 2.0 mm vertical reduction was performed, following the anatomy and fissure direction. Model C: A 2.0 mm occlusal reduction was designed while preserving the distal cusps, using both lingual and buccal grooves as an indicator for partial occlusal cutting. Model D: A 2.0 mm partial occlusal reduction was prepared, preserving the original morphological features of the partially reduced occlusal surface. Model E: The same protocol as Model C was followed with the incorporation of a mesial cavity. The mesio-occlusal (MO) class II cavity was designed by preparing an interproximal box 0.5 mm above the cementoenamel junction with an isthmus measuring one third of the buccolingual dimension (3.0 mm) at the greatest width and 2.0 mm at the cervical area. The box had a butt joint preparation and a rounded internal line angle transition. Model F: A 2.0 mm reduction was obtained following fissure directions, and a mesial proximal box was integrated, similar to Model E. All models received lithium disilicate ceramic (IPS e. max CAD; Ivoclar Vivadent, Schaan, Liechtenstein) endocrowns with a 2.0 mm occlusal thickness at the buccal groove region and a 4.0 mm central retainer depth. The vertical walls exhibited an internal tapering of 6° to 8° with smooth internal transitions [31]. The restorations were cemented using self-adhesive resin cement (RelyX Unicem 2, 3M ESPE, Seefeld, Germany). The cement layer between the endocrown and bonding surfaces of the teeth was modeled to be 80 μm in thickness [9].
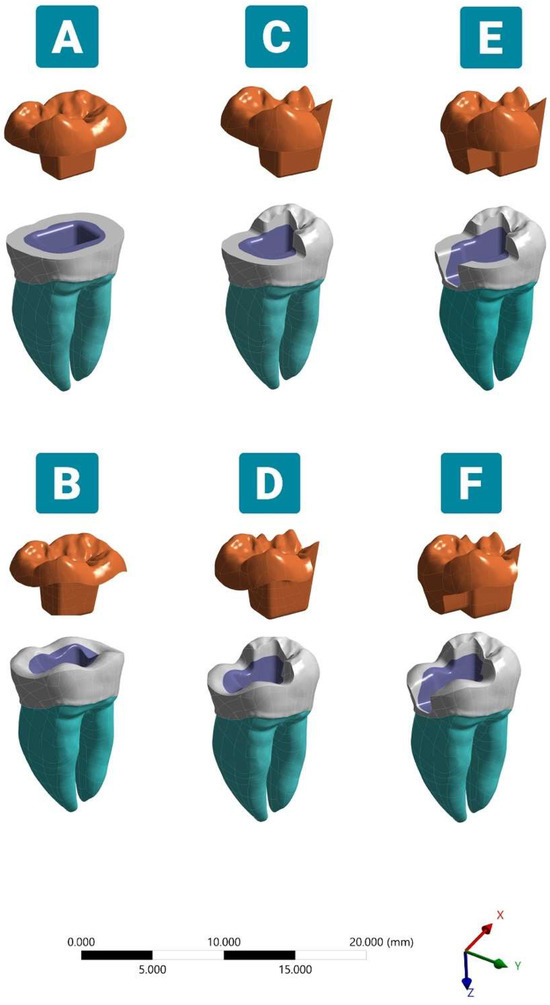
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of different modified endocrowns. (A) Complete flat butt joint. (B) Complete anatomic margin. (C) Partial flat butt joint. (D) Partial anatomic margin. (E) Partial flat butt joint with MO class II cavity. (F) Partial anatomic margin with MO class II cavity. The endocrown was modeled with a 2.0 mm occlusal thickness and a 4.0 mm pulp chamber extension depth.
The model was embedded in a 14 × 20 mm (diameter × height) polystyrene resin cylinder, keeping 2.0 mm of the cervical root exposed below the cementoenamel junction to simulate the alveolar bone level. This tooth–resin cylinder base compliance was maintained during both vertical and oblique load applications. After the modeling process, each geometry was established as a volumetric solid with seven layers (polystyrene resin cylinder, cementum, dentin, enamel, gutta-percha, resin cement, and restorative material).
2.3. Finite Element Analysis
All of the geometries were imported in the “Standard for the Exchange of Product Data” format for the ANSYS software (ANSYS 19.2, ANSYS Inc., Houston, TX, USA). The geometries were divided into meshes composed of nodes and tetrahedral elements. A convergence test of 10% mesh control was used to determine the number of elements and nodes needed to generate six models. Each model was meshed to elements for FE simulations using a 10-node 3D tetrahedral structural solid with 3 degrees of freedom per node that showed a quadratic displacement behavior appropriate for irregular and complex geometries. The total number of nodes and elements is listed in Table 1. The mechanical properties of the dental tissues and all materials were obtained from previously published data (Table 2). All structures were set as linearly elastic, isotropic, and homogeneous.

Table 1.
Number of elements and nodes in the six models.

Table 2.
Mechanical characteristics of materials and dental tissues.
Perfectly bonded contacts were considered between all model interfaces in which the target and contact surfaces were tied for the remainder of the analysis without sliding permission [13]. For all models, the fixation occurred at the base of the polystyrene cylinder with fixed zero nodal displacements. By ensuring only the movement constraint on the z-axis, the deformation generated in all directions could be computed [40].
Two different static loadings were simulated. The first was a vertical load of 300 N applied on the central fossa parallel to the longitudinal axis of the tooth, acting like a normal loading (simulating a compressive load), according to test parameters used in FEA and experimental studies. The second was an oblique load of 250 N at 45° to the long axis of the tooth, applied to the lingually inclined planes of the buccal cusps (based on the working cusp contacts) to stimulate the force acting on the mandibular molar during the closing phase of the mastication cycle [13,31,33].
The maximum VMS was adopted to evaluate the stress distribution patterns for the endocrown, tooth remnants, and cement layer in all tested models [7,36,41]. For all dental models, the adhesive area of the tooth structure was calculated using the ANSYS software program.
3. Results
The results of the stress distributions are presented in contour graphics with a color scale in megapascal (MPa), with the maximum VMS in each dental model component with two different loading directions being illustrated in Table 3 and Table 4 and Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7.
3.1. Stress Distribution under Vertical Load
3.1.1. Endocrown Restoration
The highest stress was observed close to the load application area on the occlusal surface of the restoration, with a gradual reduction toward the central retainer in all tested models. The anatomic-based Models B and F showed the highest peak VMS, with an approximate value of 50 MPa, followed by flat butt joint Models A, C, and E with an average VMS of 47.3 MPa. The lowest stress was exhibited by Model D when subjected to a vertical load (Figure 2).
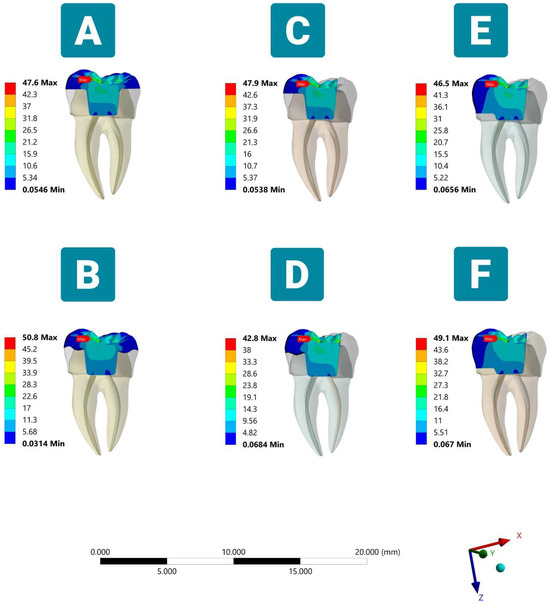
Figure 2.
Distribution of the stresses (MPa) according to different margin design and occlusal coverage extent endocrowns under vertical load (sectioned lingual side view). (A) Complete flat butt joint. (B) Complete anatomic margin. (C) Partial flat butt joint. (D) Partial anatomic margin. (E) Partial flat butt joint with MO class II cavity. (F) Partial anatomic margin with MO class II cavity.
3.1.2. Tooth Structure
Regarding enamel, the VMS was mainly concentrated in the mesial and distal sides of the cervical region of all simulated models (Figure 3). The lowest stress peak concentration was recorded for the Model B compared with the other tested models. The highest stress value of 20.2 MPa was noticed with the presence of more red, green, and yellow fringes accumulated in the same region when Model D was applied. For the remnant dentin structure, the VMS was concentrated on the mesio-lingual and disto-lingual sides of the roots and accumulated in the furcation area, tooth cervix, and bucco-pulpal line angle of the pulp chamber (Figure 3). Although the stress concentration values between anatomic and butt joint margins are typically subtle regarding dentin, a more homogeneous stress dissipation pattern could be noticed in the anatomically driven preparation designs, specifically in the pulp chamber floor and the lingual aspect of the crown.
3.1.3. Cement Layer
In the resin luting cement, the peak stresses were different, and the position of the maximum stress is clinically crucial to deciding the type of failure in the luting cement layer. The maximum VMS was observed in the region of the angle between the axial and pulpal walls of Models A, B, D, and F, while the maximum VMS was concentrated at the endocrown-unreduced occlusal tooth tissue interface for the partial coverage butt margin simulations C and E. In addition, the integration of mesial class II generated slightly higher stresses (12 MPa) in the cement layer compared to other tested models (Figure 4).

Table 3.
Peak von Mises stress values (MPa) for all tested models under vertical loading.
Table 3.
Peak von Mises stress values (MPa) for all tested models under vertical loading.
| Model Preparation Design | Endocrown Restoration | Cement Layer | Tooth Structure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enamel | Dentin | |||
| Model A | 47.6 | 11.3 | 12.3 | 11.5 |
| Model B | 50.8 | 11.0 | 11.4 | 12.7 |
| Model C | 47.9 | 11.4 | 18.4 | 11.5 |
| Model D | 42.7 | 11.2 | 20.2 | 12.8 |
| Model E | 46.5 | 12 | 17.2 | 10.8 |
| Model F | 49.0 | 12.1 | 14.2 | 11.6 |
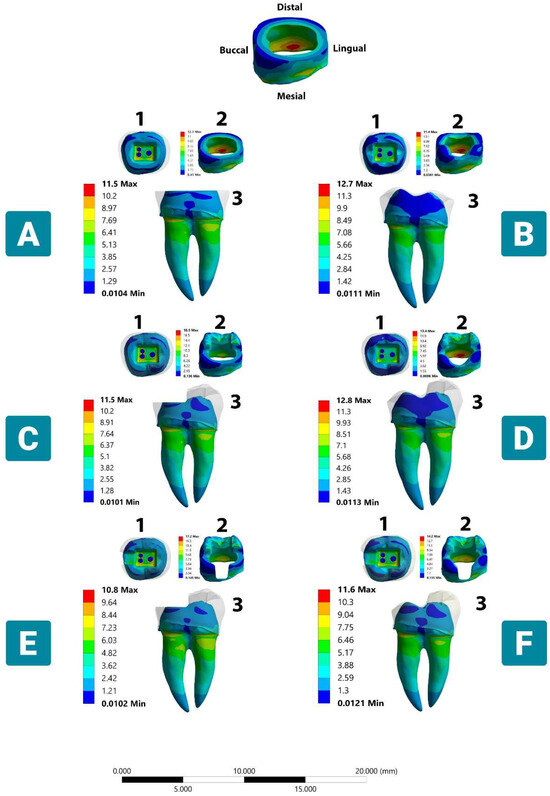
Figure 3.
Stress distribution in dental tissue remnants according to different margin designs and occlusal coverage extent under vertical load. (A) Complete flat butt joint. (B) Complete anatomic margin. (C) Partial flat butt joint. (D) Partial anatomic margin. (E) Partial flat butt joint with MO class II cavity. (F) Partial anatomic margin with MO class II cavity. (1) Occlusal dentinal side view. (2) Mesio-occlusal side view (enamel). (3) Lingual dentinal side view. The color scale with red to blue colors corresponds to high- to low-stress areas. The top figure shows the enamel layer orientation.
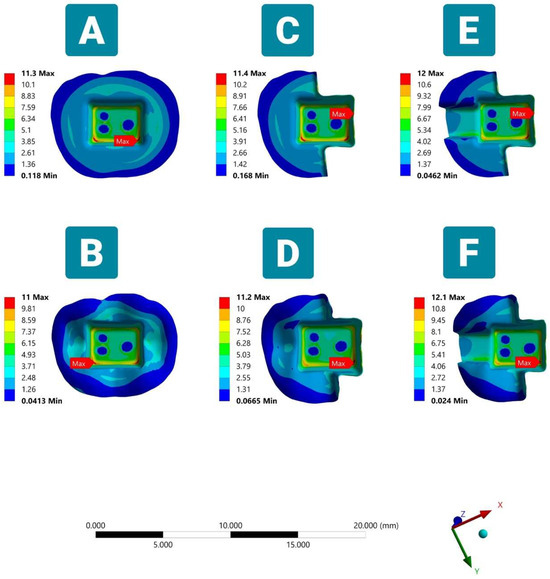
Figure 4.
Von Mises stresses (VMS) in the cement layer in six FEA models under vertical load (occlusal side view). Showing maximum VMS at the pulp chamber floor in models (A,B,D,F) and at the interface of the endocrown margin and unreduced occlusal dental surface in partial coverage butt joint margin design models (C,E).
3.2. Stress Distribution under the Oblique Load
3.2.1. Lithium Disilicate Restoration
The maximum VMS values from the oblique direction were obviously much higher than those under the vertical load on all endocrown restorations. In general, all of the tested models showed symmetric behaviors regarding the distribution of stress, which was particularly concentrated on the loading area (Figure 5). The average peak value was 79.6 MPa for Models B, C, and F, followed by Models A and E with 77.1 MPa, and only 73.2 MPa was recorded for Model D.

Figure 5.
Distribution of the stresses (MPa) according to different margin designs and occlusal-coverage-extended endocrowns under oblique load (sectioned lingual side view). (A) Complete flat butt joint. (B) Complete anatomic margin. (C) Partial flat butt joint. (D) Partial anatomic margin. (E) Partial flat butt joint with MO class II cavity. (F) Partial anatomic margin with MO class II cavity.
3.2.2. Tooth Structure
Under the oblique loading, although the trend of the stress distribution in dentin was similar to that under the vertical load, the region where VMS was concentrated in the enamel was in the buccal cervical region, which extended to the buccal-prepared tooth margin. Regardless of the margin type and coverage extent, the VMS remained concentrated in these parts of the enamel for Models A, C, E, and F, with an average stress value of 56.6 MPa, but the VMS achieved a value of 59.1 MPa in Model B, which was considered the highest recorded value among all tested models. On the contrary, the VMS did not exceed 52.8 MPa in Model D, which exhibited a more homogeneous stress distribution in the remaining enamel, with a reduced stress concentration being observed on the buccal anatomic-prepared margin (Figure 6).
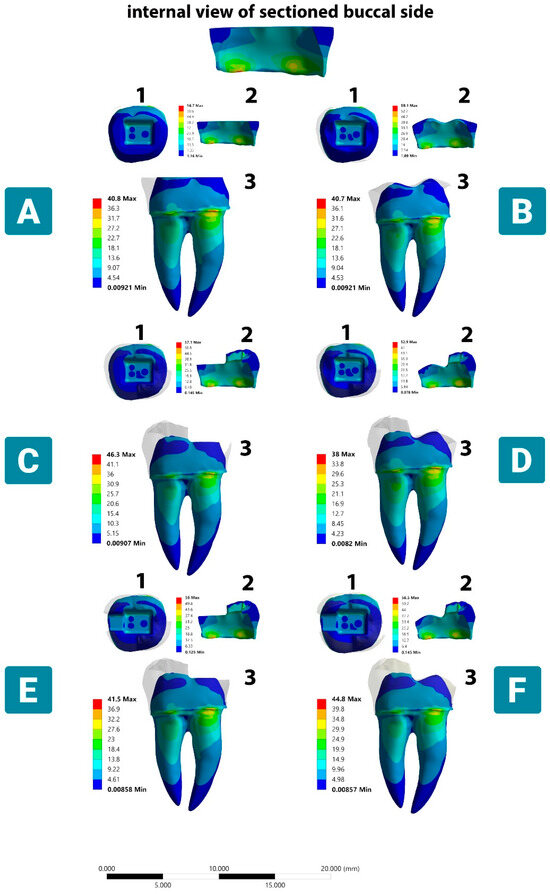
Figure 6.
Stress distribution in dental tissue remnants according to different margin and occlusal reduction designs under oblique load. (A) Complete flat butt joint. (B) Complete anatomic margin. (C) Partial flat butt joint. (D) Partial anatomic margin. (E) Partial flat butt joint with MO class II cavity. (F) Partial anatomic margin with MO class II cavity. (1) Occlusal dentinal side view. (2) Internal side of buccal enamel side view. (3) buccal dentinal side view. The color scale with red to blue colors corresponds to high- to low-stress areas. The top figure shows the enamel layer orientation.
3.2.3. Cement Layer
In the evaluation of the cement layer, the visual maps shown in Figure 7 demonstrated that the VMS with an average value of 17.5 MPa was accumulated in the region of the bucco-pulpal and linguo-pulpal line angles of the complete coverage designs (Models A and B). The stress was distributed further and extended to the buccal margin of the endocrown in all groups. The stress value in the cement layer was increased in the partial anatomic margin Model D, which reached the highest peak of 42.2 MPa (Table 4). In all partial coverage endocrowns, regardless of the design, it can be observed that the stress peaks exhibit a notable increase, approximately doubling in magnitude when compared to those found in complete coverage simulations, and are concentrated at the endocrown/unreduced tooth structure interface. It is worth mentioning that the anatomic-driven preparations demonstrated a higher degree of stress dissipation, characterized by a more uniform and consistent dispersion of stress.

Table 4.
Peak von Mises stress values (MPa) for all tested models under oblique loading.
Table 4.
Peak von Mises stress values (MPa) for all tested models under oblique loading.
| Model Preparation Design | Endocrown Restoration | Cement Layer | Tooth Structure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enamel | Dentin | |||
| Model A | 77.6 | 17.8 | 56.7 | 40.8 |
| Model B | 79.4 | 17.3 | 59.1 | 40.6 |
| Model C | 80.2 | 34.7 | 57.1 | 46.2 |
| Model D | 73.1 | 42.2 | 52.8 | 37.9 |
| Model E | 76.7 | 32.3 | 56.2 | 41.5 |
| Model F | 79.3 | 30.0 | 56.5 | 44.7 |
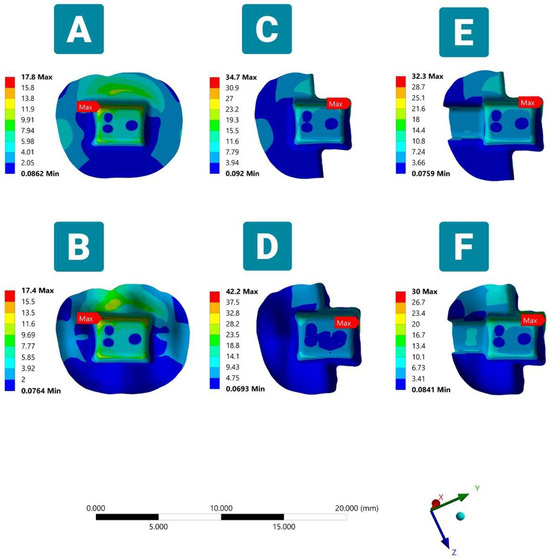
Figure 7.
Von Mises stresses (VMS) in the cement layer in six FEA models under oblique load (occlusal side view). Showing maximum VMS at the pulp chamber floor in complete coverage endocrown simulation models (A,B) and at the interface between the occlusal endocrown margin and the unreduced occlusal dental surface in partial coverage butt joint margin design models (C–F).
The adhesive areas of the remnant tooth structure in all tested designs are listed in Table 5. It was observed that the anatomically reduced surfaces offered a greater bonding area compared to the simulations featuring flat butt joint margins.

Table 5.
Adhesive area of the remaining tooth structure in all tested models.
4. Discussion
The development of an accurate tooth preparation strategy for endocrown margins remains a clinical challenge for dentists. Few research have considered the influence of margin design on endocrowns [7,9,13]. Thus, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of “coverage extent” and “margin design” on the stress distribution of ETT restored using endocrown restorations. Through the FEA methodology, it was possible to show that both factors influenced the biomechanical behavior as a function of the endocrown restorations.
In FEA studies, functional loads have a significant impact on the stress distribution within the restoration. In earlier research, the load was applied to the occlusal surface following the tripoidism concept [8,9,12], which concentrated stresses primarily on the loading points and intaglio surface of the prosthesis. Clinically, functional contacts during the chewing cycle occur regionally rather than at individual points [42,43,44]. Consequently, in the present study, the load was applied to an occlusal area rather than points. Observing the FEA results, the stress maps corroborated previous studies, with stress peaks mainly occurring on the crown surface [9,10]. However, regarding the intaglio surface, the results of this study are in contrast to earlier findings [9,10], as it was shown that no critical stresses were transmitted to the bonded surface of the endocrown in any of the tested designs. This highlights that loading on an area rather than points can improve stress concentration and impair stress transmission to the surrounding structure during vertical and oblique loading. Furthermore, the anatomic-driven designs showed more homogeneous stress dissipation throughout the restoration compared to the flat margin endocrowns when a vertical load was experienced. It is crucial to consider the impact of oblique load conditions on the biomechanical behavior of endocrowns. Although the stress peaks observed in all endocrown restorations were approximately 63.82% higher than the maximum VMS accumulated under vertical load, it was not sufficient to reach the fracture resistance threshold of lithium disilicate material [9].
Regarding dental tissue remnants, the anatomic margin (complete and partial coverage) showed more uniform stress dissipation over the prepared margins and the pulp chamber floor compared with flat butt joints. This might explain the frequent clinical failures observed in cervical dentin when butt joint endocrowns are used, based on a previous meta-analysis [8]. This suggests that the anatomic margin provides a stable and uniform thickness through the entire prepared surface, which might better resist and disperse the stresses through the remaining tooth structure. This finding is in contrast with a previous study in which the researchers proposed that the addition of anatomic margin resulted in greater stress concentration [10]. This behavior could be explained by the fact that higher stress concentrations occurred more frequently in the irregular and sharp edges presented in the anatomical-driven preparation, while in the present study, the models were prepared in a dome shape and had no sharp edges. This implies that the well-rounded anatomical preparation may have improved the capacity to disperse compressive forces and moderate stress concentrations and might reduce the risk of fractures in ETT. Additionally, anatomic-based models provided a greater adhesive surface area, which facilitated better bonding of the endocrown prostheses; however, this might amplify the area exposed to the oral environment, thereby elevating the vulnerability to secondary caries. However, considering the clinical operability, endocrowns prepared with flat butt margins are more efficient and less technique-sensitive than those based on anatomic margins. During oblique loading, the stress concentration in the tooth remnant present in the cervical dentin and bucco/linguo-pulpal line angle in all tested modalities, i.e., this region, is the initiation point for crack propagation in brittle materials. To mitigate stress concentrations, it is recommended that any sharp line angles present in the pulp chamber floor be smoothed. The findings of this study demonstrated a noticeable alteration in the stress distribution within the cervical dentin when only a profound rounding of the central retainer was employed. Thus, we recommend the rounding of the central retainer to promote adequate load dissipation in this restoration modality, despite the increased risk of endocrown loosening [13].
The colorimetric stress map of the cement layer during oblique loading demonstrated an increased stress intensity due to the lever arm that is formed. This suggests a higher chance of adhesive failure, which might support the reported detachment failure of endocrown-restored teeth in a previous meta-analysis [8]. Within the inner cement line (between the endocrown and central retainer portion), the maximum VMS was observed at the axio-pulpal line angles. These areas do not come into contact with the oral environment; however, a crack can propagate internally when the stress intensity exceeds the fracture toughness of the cement layer, ultimately leading to adhesive failure. This is more critical when a partial coverage endocrown is applied, specifically in Models C and D, followed by E and F, regardless of the margin design, as they showed that the VMS values were doubled compared to a complete extension. This could be explained by the thickness of the restoration and its volume. This is supported by the results of the FEA, since Models E and F with class II demonstrated a slight reduction in the stress concentration in the remnant tooth structure and the cement line. As the increase in the thickness and volume of the restoration corresponds to a better pattern of stress distribution and less stress transferring to the adjacent structure, our finding is in line with the conclusions of previous studies [37,45]. Moreover, partial cusp coverage showed the highest VMS values, and this might be explained by the location of the loading points. In the partial coverage models, the loadings were partially applied to the enamel substrate, which exhibits a lower elastic modulus compared with the stiffer lithium disilicate; in complete coverage, they were applied to the entire restoration and absorbed most of the loads. Due to the stress location in partially covered endocrowns, debonding may be the potential failure in these types of restoration. The study also revealed that the outer cement layer (between the endocrown and prepared margin) accumulated stresses at the unprepared tooth/endocrown interface in the partial butt joint designs (C and E). The position and magnitude of the stress concentration are very important, as they determine the position of future crack progression in the cement layer and the type of failure [46,47]. Furthermore, from a clinical perspective, this part of the cement layer has a higher probability of coming into direct contact with the oral environment and, therefore, it can degrade, and there is an increased risk of secondary caries formation. Although increasing the future risk of adhesive failure is more critical under oblique loading, it is important to emphasize that incident loads on molars are predominantly axial; however, any alteration in the tooth anatomy or off-axis loading would alter the generated stress, which, in turn, could facilitate adhesion loss or tooth fracture, as previously reported [9].
From a minimally invasive perspective, the partial extended margin offered greater preservation of the tooth structure [24]. However, based on the FEA results, higher critical stress values were observed in the cement layer, particularly at the unprepared dental restoration interface of the butt joint margins under vertical load. Meanwhile, owing to this stress distribution pattern, there is a higher probability of microleakage around the affected restoration. Since cement polymerization shrinkage is a centrifugal contraction, the restoration margins may be more susceptible to leakage. However, thicker enamel was present in the occlusal surface of the partial coverage in comparison to the thinner enamel at the margin in the complete extended designed endocrowns, as it is known that enamel is responsible for greater bond strength in dental structures and its maintenance directly influences restoration longevity [9]. And, since the long-term adhesive stability in dentin is doubtful, it is not possible to assume adequate maintenance of complete coverage restorations in service, even if the generated stress is relatively lower in the cement layer [9].
The limitation of this study was the analysis of static-load-driven stress in the tooth–endocrown complex; however, the clinically adhesive failure of luting cement primarily occurs since the fatigue strength is lower than its ultimate strength [13]. Furthermore, the study exclusively utilized lithium disilicate ceramic as a restorative material. It is worth mentioning that the restorative material is a crucial factor that can impact restorative performance in FEA studies [20]. Therefore, further investigation is required to assess different types of restorative materials.
5. Conclusions
Considering the limitations of this study, it can be concluded that endocrowns based on an anatomical margin design may be a preferable preparation option for lithium disilicate endocrown prostheses. Though the maximum VMS values of the anatomic and flat butt margins were similar under axial loading, the former promotes a more uniform distribution of stress on the restoration–tooth structure, provides a larger adhesive surface area, and preserves the sound tooth structure. From a minimally invasive standpoint, the partial coverage endocrown exhibited the maximum preservation of the tooth structure; nevertheless, owing to such a stress distribution pattern in the cement layer under oblique loading, there is a greater probability of adhesive failure at the margin of the endocrown/unreduced tooth interface and leakage around the affected restoration and/or secondary caries formation.
Author Contributions
F.I.A.-n. was responsible for the methodology, analyzing the results, writing the paper, and was a corresponding author. B.J.S. was responsible for editing the manuscript and supervision. A.R.A.-z. was responsible for editing, original data, text preparation, language proofing and revision, and supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely acknowledge the College of Dentistry, University of Duhok, for supporting the project and the Alpha Dental Center for providing the CBCT scan with Mimics image processing software. Additionally, we extend our gratitude to Laith Sabri for his invaluable training on the FEA program and to Burhan Zaman for his guidance during the submission process.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dietschi, D.; Duc, O.; Krejci, I.; Sadan, A. Biomechanical considerations for the restoration of endodontically treated teeth: A systematic review of the literature, Part II (Evaluation of fatigue behavior, interfaces, and in vivo studies). Quintessence Int. 2008, 39, 117–129. [Google Scholar]
- Schestatsky, R.; Dartora, G.; Felberg, R.; Spazzin, A.O.; Sarkis-Onofre, R.; Bacchi, A.; Pereira, G.K.R. Do endodontic retreatment techniques influence the fracture strength of endodontically treated teeth? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 90, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, E.M.; do Nascimento, L.M.; Maia Filho, E.M.; Alves, C.M.C. The impact of post preparation on the residual dentin thickness of maxillary molars. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2011, 106, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phang, Z.Y.; Quek, S.H.Q.; Teoh, K.H.; Tan, K.B.C.; Tan, K. A Retrospective Study on the Success, Survival, and Incidence of Complications of Post-Retained Restorations in Premolars Supporting Fixed Dental Prostheses with a Mean of 7 Years in Function. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 33, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Piva, A.; Campos, F.; Alves, M.; Sousa, R.S.; Lima, J.; Souza, R. Influence of alveolar bone level on the pull-out bond strength of fiber-reinforced composite posts to root dentin. Gen Dent. 2016, 64, e5–e8. [Google Scholar]
- Dal Piva, A.M.d.O.; Tribst, J.P.M.; E Souza, R.O.d.A.; Borges, A.L.S. Influence of alveolar bone loss and cement layer thickness on the biomechanical behavior of endodontically treated maxillary incisors: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartora, N.R.; de Conto Ferreira, M.B.; Moris, I.C.M.; Brazão, E.H.; Spazin, A.O.; Sousa-Neto, M.D.; Silva-Sousa, Y.-T.; Gomes, E.A. Effect of intracoronal depth of teeth restored with endocrowns on fracture resistance: In vitro and 3-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedrez-Porto, J.A.; da Rosa, W.L.d.O.; Da Silva, A.F.; Münchow, E.A.; Pereira-Cenci, T. Endocrown restorations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2016, 52, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribst, J.P.M.; Dal Piva, A.M.d.O.; Madruga, C.F.L.; Valera, M.C.; Borges, A.L.S.; Bresciani, E.; de Melo, R.M. Endocrown restorations: Influence of dental remnant and restorative material on stress distribution. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Sun, J.; Jiang, L.; Wu, Y.; He, J.; Ruan, W.; Yan, W. Influence of margin design and restorative material on the stress distribution of endocrowns: A 3D finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedrez-Porto, J.A.; Münchow, E.A.; Cenci, M.S.; Pereira-Cenci, T. Which materials would account for a better mechanical behavior for direct endocrown restorations? J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 103, 103592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, Y.R.; Shiraguppi, V.L.; Deosarkar, B.; Tayeeb, S.M.; Pandey, A.; Shelke, U.R. Endocrowns: A Review. J. Interdiscip. Dent. Sci. 2020, 9, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, D.; Rong, Q.; Qian, J.; Wang, X. Effect of central retainer shape and abduction angle during preparation of teeth on dentin and cement layer stress distributions in endocrown-restored mandibular molars. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lin, Z.; Zheng, Z. Effect of different restorative crown design and materials on stress distribution in endodontically treated molars: A finite element analysis study. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, G.T.; Sedlakova, P.; Saratti, C.; Sedlacek, R.; Gregor, L.; Rizcalla, N.; Feilzer, A.J.; Krejci, I. Fatigue behavior of resin-modified monolithic CAD–CAM RNC crowns and endocrowns. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, e338–e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.; Duvall, N.; Wajdowicz, M.; Roberts, H. Effect of endocrown pulp chamber extension depth on molar fracture resistance. Oper. Dent. 2017, 42, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurpinar, B.; Tak, O. Effect of pulp chamber depth on the accuracy of endocrown scans made with different intraoral scanners versus an industrial scanner: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 127, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kuijper, M.C.; Cune, M.S.; Tromp, Y.; Gresnigt, M.M. Cyclic loading and load to failure of lithium disilicate endocrowns: Influence of the restoration extension in the pulp chamber and the enamel outline. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 105, 103670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einhorn, M.; DuVall, N.; Wajdowicz, M.; Brewster, J.; Roberts, H. Preparation ferrule design effect on endocrown failure resistance. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, e237–e242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lai, H.; Meng, Q.; Gong, Q.; Tong, Z. The synergetic effect of pulp chamber extension depth and occlusal thickness on stress distribution of molar endocrowns: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2022, 33, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralur, S.B.; Alamrey, A.A.; Alshehri, S.A.; Alzahrani, D.S.; Alfarsi, M. Effect of different preparation designs and all ceramic materials on fracture strength of molar endocrowns. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2020, 18, 2280800020947329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; He, Y.; Ruan, W.; Ling, Z.; Zheng, C.; Gai, Y.; Yan, W. Biomechanical behavior of endocrown restorations with different CAD-CAM materials: A 3D finite element and in vitro analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamajboor, A.; Dudley, J. The Influence of Ferrule on the Marginal Gap and Fracture Resistance of Zirconia Endocrowns. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 35, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianna, A.L.S.d.V.; Prado, C.J.d.; Bicalho, A.A.; Pereira, R.A.d.S.; Neves, F.D.d.; Soares, C.J. Effect of cavity preparation design and ceramic type on the stress distribution, strain and fracture resistance of CAD/CAM onlays in molars. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2018, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakeman, E.; Rego, N.; Chaiyabutr, Y.; Kois, J. Influence of ceramic thickness and ceramic materials on fracture resistance of posterior partial coverage restorations. Oper. Dent. 2015, 40, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dabbagh, R.A. Survival and success of endocrowns: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 415.e1–415.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Chen, C.; Yang, T.; Zhu, Z. Influence of Different Marginal Forms on Endodontically Treated Posterior Teeth Restored with Lithium Disilicate Glass-Ceramic Onlays: Two-Year Follow-up. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 33, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albakry, M.; Guazzato, M.; Swain, M.V. Influence of hot pressing on the microstructure and fracture toughness of two pressable dental glass–ceramics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2004, 71, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarone, F.; Di Mauro, M.I.; Ausiello, P.; Ruggiero, G.; Sorrentino, R. Current status on lithium disilicate and zirconia: A narrative review. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarone, F.; Ferrari, M.; Mangano, F.G.; Leone, R.; Sorrentino, R. “Digitally oriented materials”: Focus on lithium disilicate ceramics. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 2016, 9840594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo El Fadl, A.; Elsewify, T. Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Mandibular Molars Restored with Two Endocrown Designs (An In-Vitro Study). Egypt. Dent. J. 2019, 65, 3745–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Da Fonseca, G.F.; De Andrade, G.S.; Dal Piva, A.M.d.O.; Tribst, J.P.M.; Borges, A.L.S. Computer-aided design finite element modeling of different approaches to rehabilitate endodontically treated teeth. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2018, 18, 329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghoul, W.E.; Özcan, M.; Tribst, J.P.M.; Salameh, Z. Fracture resistance, failure mode and stress concentration in a modified endocrown design. Biomater. Investig. Dent. 2020, 7, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Rong, Q.; Wang, X.; Gao, X. Influence of remaining tooth structure and restorative material type on stress distribution in endodontically treated maxillary premolars: A finite element analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantó-Navés, O.; Marimon, X.; Ferrer, M.; Cabratosa-Termes, J. Comparison between experimental digital image processing and numerical methods for stress analysis in dental implants with different restorative materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 113, 104092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribst, J.P.M.; Dal Piva, A.M.d.O.; de Jager, N.; Bottino, M.A.; de Kok, P.; Kleverlaan, C.J. Full-Crown Versus Endocrown Approach: A 3D-Analysis of Both Restorations and the Effect of Ferrule and Restoration Material. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 30, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulec, L.; Ulusoy, N. Effect of endocrown restorations with different CAD/CAM materials: 3D finite element and weibull analyses. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 5638683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.N.; Al-Zahawi, A.R.; Sabri, L.A. Mechanical and thermal stress behavior of a conservative proposed veneer preparation design for restoring misaligned anterior teeth: A 3D finite element analysis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.O.; AL-Zahawi, A.R.; Sabri, L.A. Mechanical and thermal stress evaluation of PEEK prefabricated post with different head design in endodontically treated tooth: 3D-finite element analysis. Dent. Mater. J. 2021, 40, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartora, G.; Pereira, G.K.R.; de Carvalho, R.V.; Zucuni, C.P.; Valandro, L.F.; Cesar, P.F.; Caldas, R.A.; Bacchi, A. Comparison of endocrowns made of lithium disilicate glass-ceramic or polymer-infiltrated ceramic networks and direct composite resin restorations: Fatigue performance and stress distribution. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 100, 103401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejak, B.; Młotkowski, A. 3D-Finite element analysis of molars restored with endocrowns and posts during masticatory simulation. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, e309–e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausiello, P.; Ciaramella, S.; Di Rienzo, A.; Lanzotti, A.; Ventre, M.; Watts, D.C. Adhesive class I restorations in sound molar teeth incorporating combined resin-composite and glass ionomer materials: CAD-FE modeling and analysis. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausiello, P.; Ciaramella, S.; Fabianelli, A.; Gloria, A.; Martorelli, M.; Lanzotti, A.; Watts, D.C. Mechanical behavior of bulk direct composite versus block composite and lithium disilicate indirect Class II restorations by CAD-FEM modeling. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Piva, A.M.d.O.; Tribst, J.P.M.; Borges, A.L.S.; e Souza, R.O.d.A.; Bottino, M.A. CAD-FEA modeling and analysis of different full crown monolithic restorations. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, L.B.; Guimarães, J.C.; Monteiro Junior, S.; Baratieri, L.N. Effect of ceramic thickness and composite bases on stress distribution of inlays-a finite element analysis. Braz. Dent. J. 2015, 26, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, F.A.; Nathanson, D.; Morgano, S.M.; Baba, N.Z. Fracture resistance and failure mode of fatigued endodontically treated teeth restored with fiber-reinforced resin posts and metallic posts in vitro. Dent. Traumatol. 2014, 30, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Saidi, A.; Nassab, S.A.G.; Hashemipour, M.A. A three-dimensional finite element analysis of the effects of restorative materials and post geometry on stress distribution in mandibular molar tooth restored with post-core crown. Dent. Mater. J. 2012, 31, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).