Fabrication and Characterization of Quinary High Entropy-Ultra-High Temperature Diborides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Processing of HEBs
2.2. Characterization of HEBs
| KIC= 0.0824 | (Evans and Charles, E&C) |
| KIC= 0.0515 | (Lawn and Fuller, L&F) |
| KIC= 0.079 | (Evans and Wilshaw, E&W) |
| KIC= 0.0363 | (Lankford, L) |
3. Results and Discussion
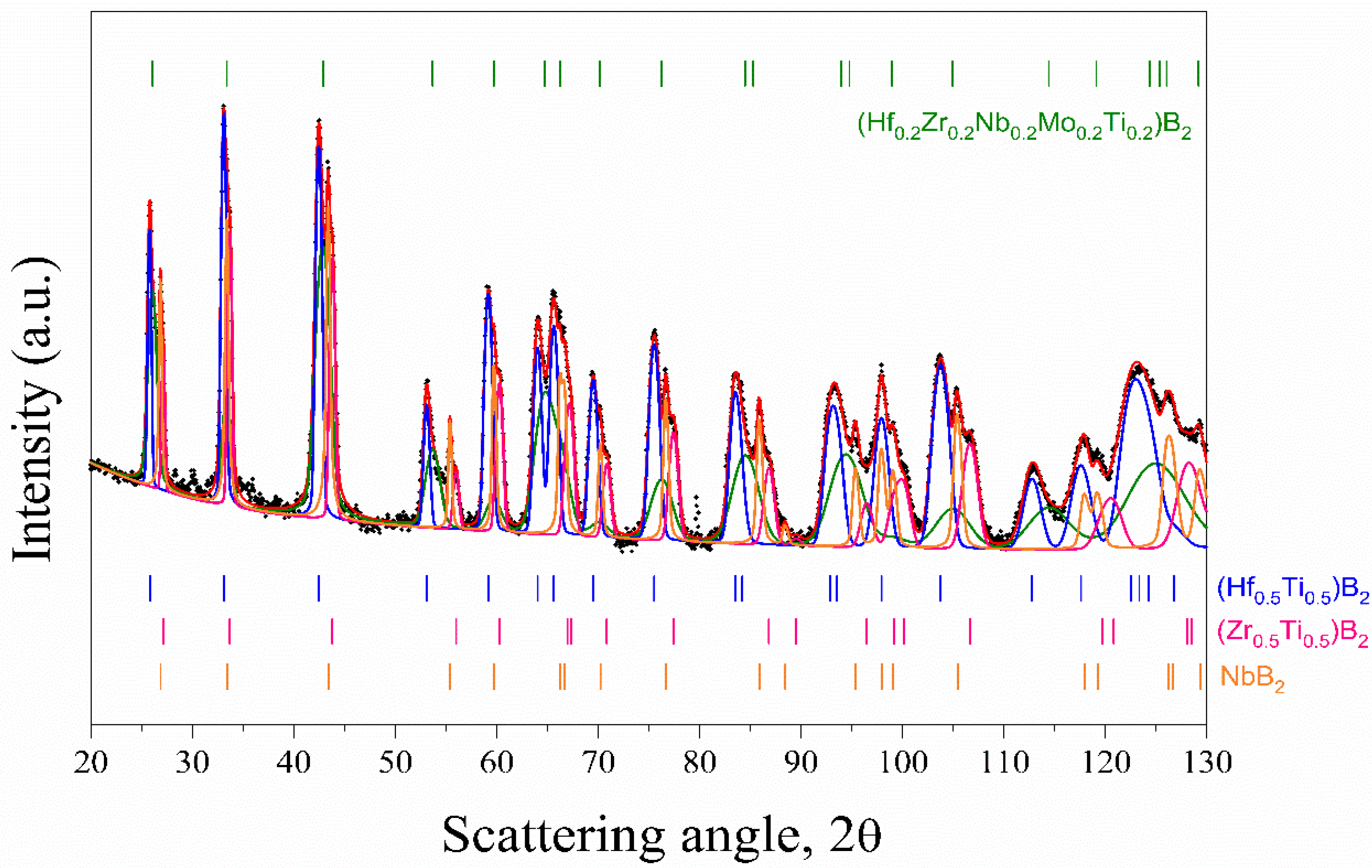
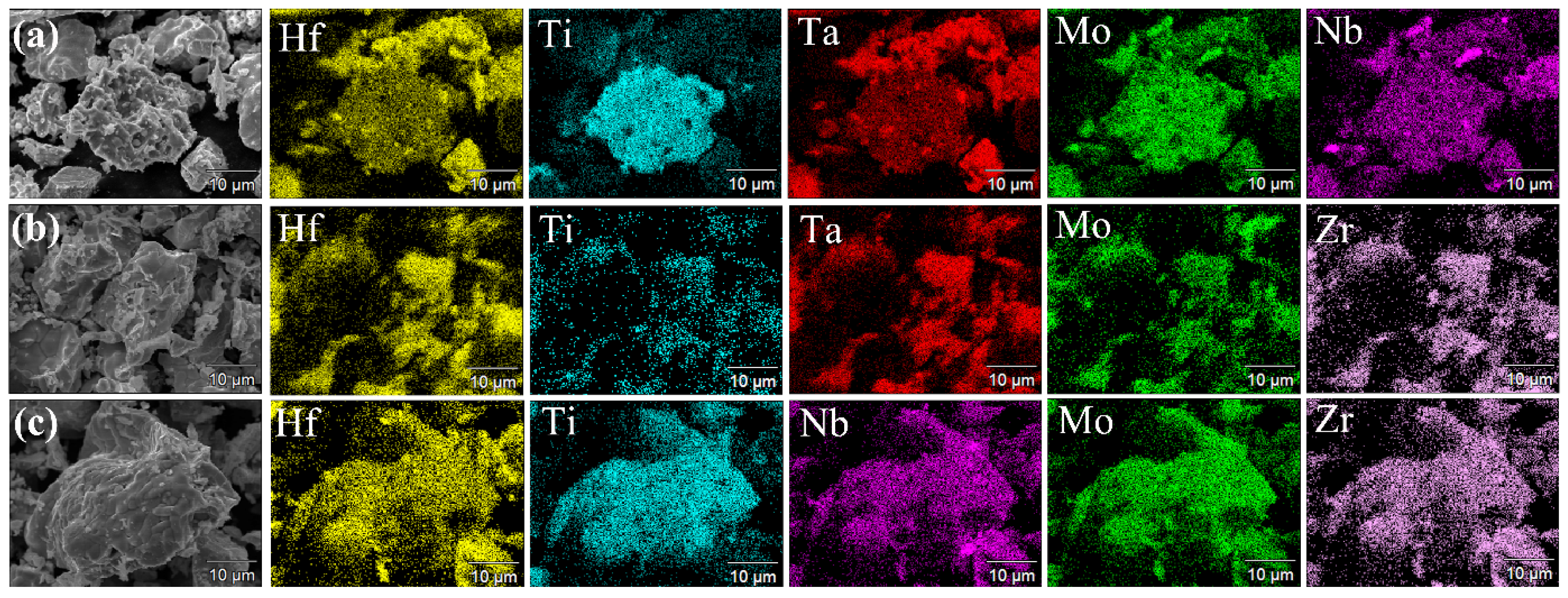
3.1. Powders Synthesis and Characterization
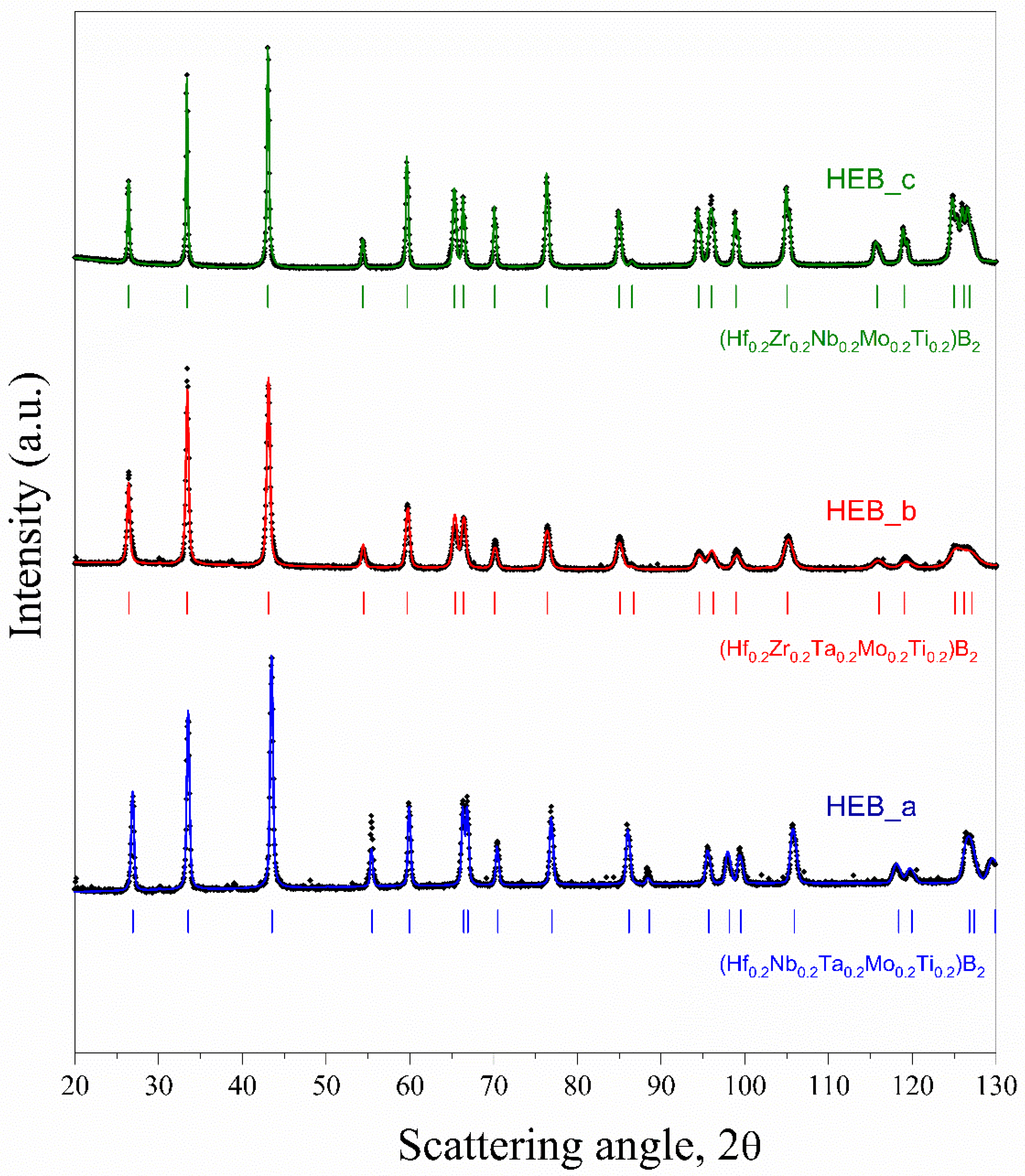
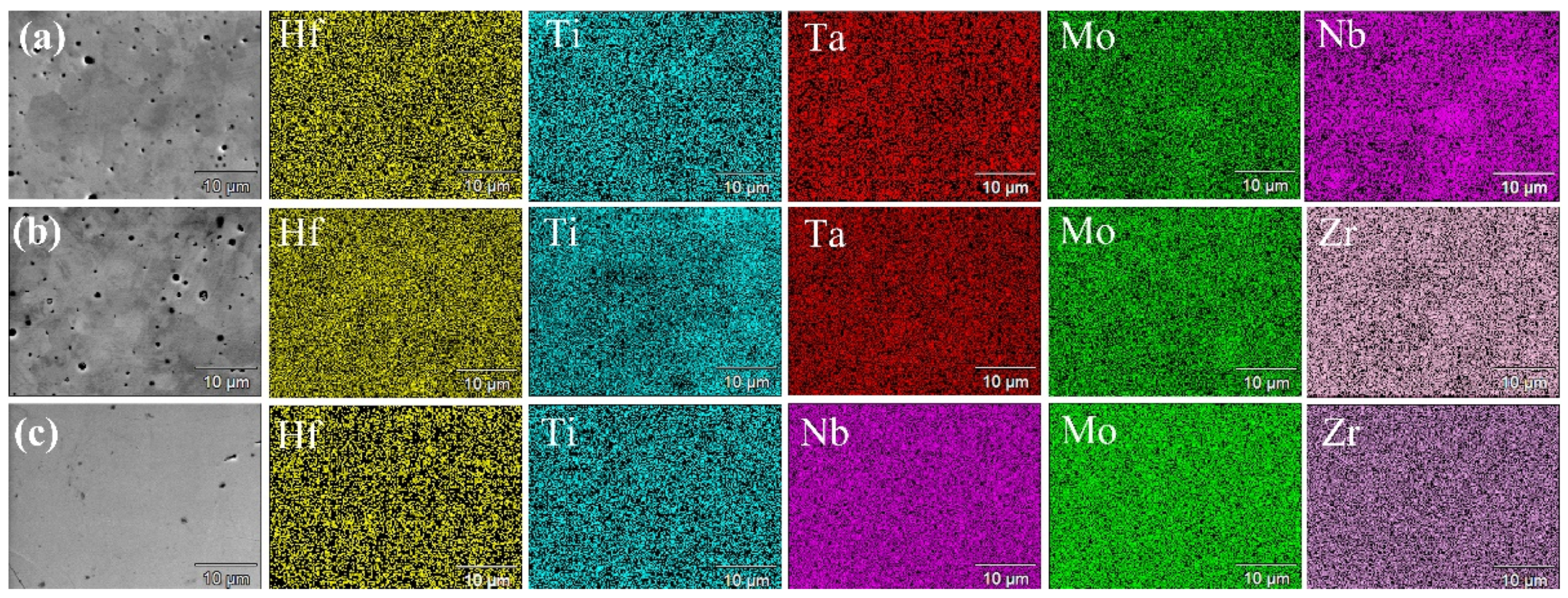
3.2. Spark Plasma Sintering and Structural Characterization of Dense Products
3.3. Mechanical Properties of Sintered Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gild, J.; Zhang, Y.; Harrington, T.; Jiang, S.; Hu, T.; Quinn, M.C.; Mellor, W.M.; Zhou, N.; Vecchio, K.; Luo, J. High-Entropy Metal Diborides: A New Class of High-Entropy Materials and a New Type of Ultrahigh Temperature Ceramics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W. High-Entropy Alloys: A Critical Review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gild, J.; Kaufmann, K.; Vecchio, K.; Luo, J. Reactive Flash Spark Plasma Sintering of High-Entropy Ultrahigh Temperature Ceramics. Scr. Mater. 2019, 170, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.F.; Zou, J.; Sun, S.K.; Wang, H.; Yu, S.Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Fu, Z. Dense And Pure High-Entropy Metal Diboride Ceramics Sintered from Self-Synthesized Powders via Boro/Carbothermal Reduction Approach. Sci. China Mater. 2019, 62, 1898–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallarita, G.; Licheri, R.; Garroni, S.; Orrù, R.; Cao, G. Novel Processing Route for the Fabrication of Bulk High-Entropy Metal Diborides. Scr. Mater. 2019, 158, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, W.M.; Jiang, Z.B.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Sun, S.K.; You, Y.; Plucknett, K.; Lin, H.T. Dense High-Entropy Boride Ceramics with Ultra-High Hardness. Scr. Mater. 2019, 164, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.B.; Sun, S.K.; Guo, W.M.; Chen, Q.S.; Qiu, J.X.; Plucknett, K.; Lin, H.T. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of High-Entropy Borides Derived from Boro/Carbothermal Reduction. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 3920–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarossa, S.; Orrù, R.; Garroni, S.; Licheri, R.; Cao, G. Ultra High Temperature High-Entropy Borides: Effect of Graphite Addition on Oxides Removal and Densification Behavior. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 6220–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Fahrenholtz, W.G.; Hilmas, G.E. Processing of Dense High-Entropy Boride Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 3815–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gild, J.; Wright, A.; Quiambao-Tomko, K.; Qin, M.; Tomko, J.A.; Md Shafkat bin, H.; Braun, J.L.; Bloomfield, B.; Martinez, D.; Harrington, T.; et al. Thermal Conductivity and Hardness of Three Single-Phase High-Entropy Metal Diborides Fabricated by Borocarbothermal Reduction and Spark Plasma Sintering. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 6906–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Gild, J.; Wang, H.; Harrington, T.; Vecchio, K.S.; Luo, J. Dissolving and Stabilizing Soft WB2 and MoB2 Phases into High-Entropy Borides Via Boron-Metals Reactive Sintering to Attain Higher Hardness. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 4348–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Gild, J.; Hu, C.; Wang, H.; Hoque, M.S.B.; Braun, J.L.; Harrington, T.J.; Hopkins, P.E.; Vecchio, K.S.; Luo, J. Dual-Phase High-Entropy Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 5037–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallarita, G.; Licheri, R.; Garroni, S.; Barbarossa, S.; Orrù, R.; Cao, G. High-Entropy Transition Metal Diborides by Reactive and Non-Reactive Spark Plasma Sintering: A Comparative Investigation. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.K.; Zhang, W.; You, Y.; Guo, W.M.; Chen, Z.W.; Yuan, J.H.; Lin, H.T. Improved Densification and Hardness of High Entropy Diboride Ceramics from Fine Powders Synthesized via Borothermal Reduction Process. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 14299–14303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Fahrenholtz, W.G.; Hilmas, G.E.; Monteverde, F. Effect of Nb Content on the Phase Composition, Densification, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties of High-Entropy Boride Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.K.; Guo, W.M.; Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Yuan, J.H.; Guan, D.K.; Wang, D.W.; You, Y.; Lin, H.T. Fabrication of Textured (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Cr0.2Ti0.2)B2 High-Entropy Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Orrù, R.; Licheri, R.; Locci, A.M.; Cincotti, A.; Cao, G. Consolidation/Synthesis of Materials by Electric Current Activated/Assisted Sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2009, 63, 127–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.; Das, S.; Pathak, L.C. Defect Structures in Zirconium Diboride Powder Prepared by Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 364, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licheri, R.; Orrù, R.; Musa, C.; Cao, G. Combination of SHS and SPS Techniques for Fabrication of Fully Dense ZrB2-ZrC-SiC Composites. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, C.; Orrù, R.; Sciti, D.; Silvestroni, L.; Cao, G. Synthesis, Consolidation and Characterization of Monolithic and SiC Whiskers Reinforced Hfb2 Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licheri, R.; Musa, C.; Orrù, R.; Cao, G.; Sciti, D.; Silvestroni, L. Bulk Monolithic Zirconium and Tantalum Diborides by Reactive and Non-Reactive Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Alloy Compd. 2016, 663, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İpekçi, M.; Acar, S.; Elmadağlı, M.; Hennicke, J.; Balcı, Ö.; Somer, M. Production of TiB2 by SHS and HCl Leaching at Different Temperatures: Characterization and Investigation of Sintering Behavior by SPS. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 2039–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, E.; Meucci, M.; Mercatelli, L.; Balbo, A.; Musa, C.; Licheri, R.; Orrù, R.; Cao, G. Titanium Diboride Ceramics for Solar Thermal Absorbers. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 169, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licheri, R.; Musa, C.; Locci, A.M.; Montinaro, S.; Orrù, R.; Cao, G.; Silvestroni, L.; Mercatelli, L.; Sani, E. Ultra-High Temperature Porous Graded Ceramics for Solar Energy Applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbatkina, V.V.; Patsera, E.I.; Smirnov, D.V.; Levashov, E.A.; Vorotilo, S.; Timofeev, A.N. Part 2. Structure, Mechanical and Thermophysical Properties Of Consolidated Ceramics Based on (Hf,Ta)B2. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 4076–4083. [Google Scholar]
- Cincotti, A.; Licheri, R.; Locci, A.M.; Orrù, R.; Cao, G. A Review on Combustion Synthesis of Novel Materials: Recent Experimental and Modeling Results. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2003, 78, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutterotti, L.; Ceccato, R.; Dal Maschio, R.; Pagani, E. Quantitative Analysis of Silicate Glass in Ceramic Materials by the Rietveld method. Mater. Sci. Forum 1998, 87, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.; Pharr, G. An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus Using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation Experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponton, C.B.; Rawlings, R.D. Vickers Indentation Fracture Toughness Test. Part 1: Review of Literature and Formulation of Standardised Indentation Toughness Equations. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1989, 5, 865–872. [Google Scholar]
- Ponton, C.B.; Rawlings, R.D. Vickers Indentation Fracture Tough-Ness Test. Part 2: Application and Critical Evaluation of Standardised Indentation Toughness Equations. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1989, 5, 961–976. [Google Scholar]
- Barin, I. Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances; VHC: Weinheim, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, J.T.; Blumenthal, H.; Sindeband, S.J. Structures of Diborides of Titanium, Zirconium, Columbium, Tantalum and Vanadium. JOM 1949, 185, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, F.W.; Post, B.; Moskowitz, D. Transition Metal Diborides. Acta Met. 1954, 2, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
| Systems | Raw Powders | Method/Conditions for Powders Synthesis/Activation | SPS Conditions (TD/tH/tD/P) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Mo0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Zr0.2Mo0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2) (Hf0.2Mo0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Mo0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Zr0.2W0.2Mo0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Cr0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Individual metal borides | HEBM (CR= n.r./6 h) | (2000 °C/~20 min/ 5 min/30 MPa) | [1] |
| (Hf0.2Mo0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Metal powders, B | SHS (few secs) + HEBM (CR = 2/20–60 min) | (1950 °C/10 min/ 20 min/20 MPa) | [5,13] |
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Cr0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Mo0.2Zr0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Mo0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Metal oxides, B | BR (1600 °C/60 min) | (2000 °C/~13 min/ 10 min/30 MPa) | [6] |
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Zr0.2Mo0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Mo0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Metal oxides, B4C, graphite | BCR (1600 °C/60 min) | (2000 °C/~13 min/ 10 min/30 MPa) | [7] |
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Individual metal borides, graphite | Pre-sintering by SPS (1600 °C/5 min/30 MPa) | FSPS (30%Pw,max/120 s+ 50% Pw,max/30 s + 100% Pw,max/90 s) | [3] |
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Metal oxides, B4C, graphite | BCR by SPS (1700 °C/10 min) | (2000 °C/~20 min/ 5 min/50 MPa) | [4] |
| (Hf0.2Mo0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Metal powders, B | None | RSPS (1950 °C/10 min/ 20 min/20–70 MPa) | [13] |
| (Hf0.2Mo0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Mo0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Metal powders, B, graphite | SHS (few seconds) + HEBM (CR = 2, 60 min) | (1950 °C/10 min/ 20 min/20 MPa) | [8] |
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Zr0.2Mo0.2W0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Metal oxides, B | BR (1600 °C/60 min) | (2000 °C/n.r./ 10 min/30 MPa) | [14] |
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Mo0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Zr0.2W0.2Mo0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Cr0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Metal oxides, B4C, C | BCR (1550 °C/90 min) | (2000 °C/~20 min/ 30 min/80 MPa) | [10] |
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Metal oxides, B4C, C | BCR (1650 °C/3.5 h) | (2000–2200 °C/~23 min/ 10 min/50 MPa) | [9] |
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Zr0.2375Ta0.2375Nb0.05Ti0.2375)B2 | Metal oxides, B4C, C | BCR (1650 °C/3 h) | (2100 °C/~23 min/ 10 min/50 MPa) | [15] |
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Cr0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Metal oxides, B4C, C | BCR (1650 °C/1 h) | (2000 °C/~13 min/ 10 min/30 MPa) | [16] |
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Mo0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Hf0.2Zr0.2W0.2Mo0.2Ti0.2)B2 (Ti0.2Ta0.2Cr0.2Mo0.2W0.2)B2 (Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2W0.2)B2 (Zr0.225Hf0.225Ta0.225Mo0.225W0.1)B2 | Metal powders, B | HEBM (CR = 4, 50 min) | RSPS (2000 °C/~2 h/ 10 min/50 MPa) | [11] |
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Individual metal borides, graphite | HEBM (CR = 2.3, 100 min) | (2200 °C/~3 h/ 10 min/80 MPa) | [12] |
| Phase | Space Group | a (Å) | c (Å) | V(Å3) | Cryst. Size (Å) | R.m.s. Strain | Phase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Hf0.2Zr0.2Nb0.2Mo0.2Ti0.2)B2 | Hexagonal (P6/mmm) | 3.0975 | 3.4136 | 28.364 | 507 | 9.6*10−3 | 27 |
| (Hf0.5Ti0.5)B2 | Hexagonal (P6/mmm) | 3.1222 | 3.4488 | 29.115 | >2000 | 4.0*10−3 | 40 |
| (Zr0.5Ti0.5)B2 | Hexagonal (P6/mmm) | 3.0710 | 3.2840 | 26.822 | >2000 | 3.8*10−3 | 18 |
| NbB2 | Hexagonal (P6/mmm) | 3.0951 | 3.3158 | 27.508 | 1033 | 1.3*10−3 | 15 |
| System | d10 (μm) | d50 (μm) | d90 (μm) | dav (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEB_a | 0.16 | 1.13 | 11.69 | 3.69 |
| HEB_b | 0.25 | 1.29 | 8.49 | 2.93 |
| HEB_c | 0.19 | 1.29 | 10.84 | 3.46 |
| System | ρt (g/cm3) | ρ (%) | Lattice Parameters a(Ȧ), c(Ȧ) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEB_a | 8.67 | 97.4 ± 0.3 | 3.087, 3.316 | This work |
| 8.67 | 92.2 | 3.082, 3.279 | [1] | |
| 8.61 | 95.0 | 3.082, 3.307 | [6] | |
| 8.61 | 98.5 | 3.082, 3.281 | [7] | |
| HEB_b | 8.52 | 96.5 ± 0.7 | 3.092, 3.368 | This work |
| 8.52 | 92.4 | 3.080, 3.316 | [1] | |
| 8.37 | 99.9 | 3.092, 3.366 | [10] | |
| HEB_c | 7.37 | 98.2 ± 0.9 | 3.099, 3.374 | This work |
| 7.37 | 92.3 | 3.092, 3.345 | [1] | |
| 7.29 | 97.7 | 3.093, 3.353 | [6] |
| System | Conditions (Load, Loading Time, Loading/Unloading Rate) | Hv (GPa) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | KIC (MPa m1/2) Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEB_a | 0.25N, 15 s, 0.5 N/min | 28.1 ± 3.5 | 538.5 ± 49.9 | - | This work |
| 0.5N, 15 s, 1 N/min | 27.8 ± 2.2 | 546.3 ± 20.1 | - | ||
| 1 N, 15 s, 2 N/min | - | - | 7.06 (E&C) 4.41 (L&F) 4.49 (E&W) 10.31 (L) | ||
| 1.96 N, 15 s, n.r. | 22.5 ± 1.7 | n.r. | n.r. | [1] | |
| 1.96 N, 15 s, n.r. | 25.9 ± 1.1 | n.r. | n.r. | [6] | |
| 1.96 N, 15 s, n.r. | 27.0 ± 0.4 | n.r. | 4.47 ± 0.40 (E&C) | [7] | |
| HEB_b | 0.25 N, 15 s, 0.5 N/min | 28.08 ± 1.6 | 498.1 ± 28.3 | - | This work |
| 0.5 N, 15 s, 1 N/min | 29.7 ± 1.9 | 514.8 ± 41.5 | - | ||
| 1 N, 15 s, 2 N/min | - | - | 4.31 (E&C) 2.69 (L&F) 3.82 (E&W) 5.84 (L) | ||
| 1.96 N, 15 s, n.r. | 19.1 ± 1.8 | n.r. | n.r. | [1] | |
| 1.96 N, 15 s, n.r. | 24.9 ± 1.0 | n.r. | n.r. | [10] | |
| HEB_c | 0.25 N, 15 s, 0.5 N/min | 25.1 ± 3.8 | 404.5 ± 57.8 | - | This work |
| 1 N, 15 s, 2 N/min | - | - | 8.84 (E&C) 5.53 (L&F) 5.12 (E&W) 12.0 (L) | ||
| 1.96 N, 15 s, n.r. | 21.9 ± 1.7 | n.r. | - | [1] | |
| 1.96 N, 15 s, n.r. | 26.3 ± 0.7 | n.r. | - | [6] | |
| 1.96 N, 15 s, n.r. | 26.3 ± 1.8 | n.r. | 3.64 ± 0.36 (E&C) | [7] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbarossa, S.; Orrù, R.; Cannillo, V.; Iacomini, A.; Garroni, S.; Murgia, M.; Cao, G. Fabrication and Characterization of Quinary High Entropy-Ultra-High Temperature Diborides. Ceramics 2021, 4, 108-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics4020010
Barbarossa S, Orrù R, Cannillo V, Iacomini A, Garroni S, Murgia M, Cao G. Fabrication and Characterization of Quinary High Entropy-Ultra-High Temperature Diborides. Ceramics. 2021; 4(2):108-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics4020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbarossa, Simone, Roberto Orrù, Valeria Cannillo, Antonio Iacomini, Sebastiano Garroni, Massimiliano Murgia, and Giacomo Cao. 2021. "Fabrication and Characterization of Quinary High Entropy-Ultra-High Temperature Diborides" Ceramics 4, no. 2: 108-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics4020010
APA StyleBarbarossa, S., Orrù, R., Cannillo, V., Iacomini, A., Garroni, S., Murgia, M., & Cao, G. (2021). Fabrication and Characterization of Quinary High Entropy-Ultra-High Temperature Diborides. Ceramics, 4(2), 108-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics4020010









