Strategic Management Knowledge Map via BERTopic (1980–2025): Evolution, Integration, and Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
1.2. Brief Literature Context
1.3. Methodological Background
1.4. Objectives and Contributions
- O1 (Topic discovery and quality): Identify latent topics in a domain-bounded corpus (RBV, KBV, DCV, CA) and retain high-quality topics based on coherence (C_V, C_NPMI [32]).
- O3 (Temporal structure): Provide a time-sliced view of topic configurations to describe shifts in emphasis across strategic traditions (1980–2025).
- C3 (Practical): Providing a reproducible basis for topic labeling, construct classification, and time-aware knowledge mapping useful to both scholars and managers, with a managerial translation via Balanced Scorecard [33].
2. Literature Review
2.1. Scientific Knowledge Evolution Analysis
2.2. Knowledge Structure
2.2.1. Main Path Analysis in Citation Networks
2.2.2. Topic Extraction and the Mechanism of Evolutionary Pathways
2.2.3. Applications and Advantages of BERT and BERTopic in Topic Extraction
2.2.4. Textual Data Collection and BERT-Based Topic Modeling in Strategic Management
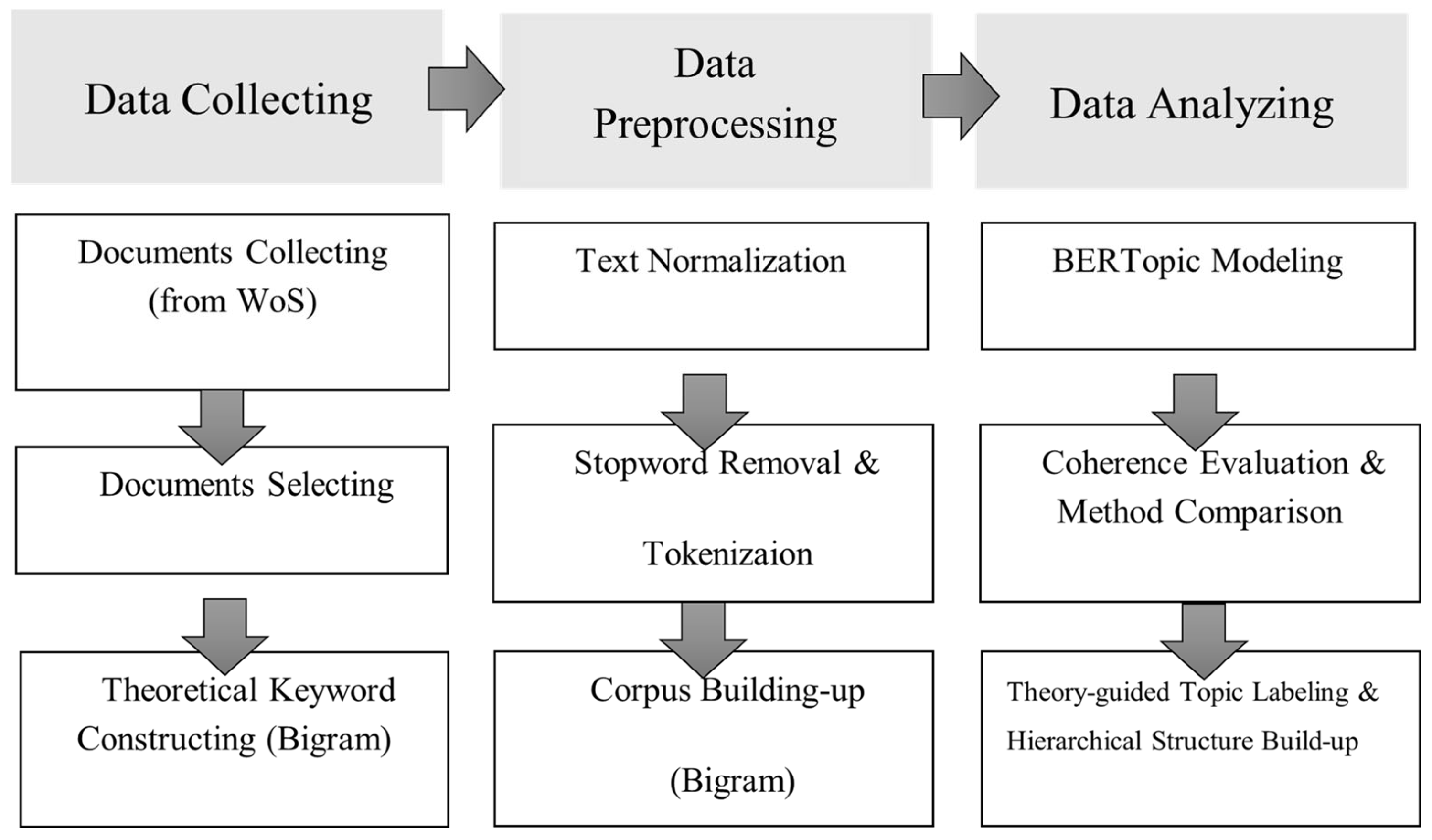
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Data Collection and Literature Screening
3.2. Data Preprocessing
Construction of Text Corpus
3.3. Semantic Topic Modeling with BERTopic
3.3.1. BERTopic Topic Modeling
| Algorithm 1. BERTopic-based topic modeling. |
| Corpus D (Title/Abstract/Keywords composites; n = 25,907). Require: Corpus D; parameters embedding_model, vectorizer Ensure: Topics T, probabilities P, keyword sets K 1: Normalize text; tokenize; remove stopwords. 2: Embed with Sentence-BERT. 3: Reduce with UMAP; cluster with HDBSCAN. 4: Extract keywords via c-TF–IDF; compute C_V, C_NPMI. 5: return (T, P, K) |
3.3.2. Topic Coherence Evaluation
| Algorithm 2. Topic score calculation. |
| Corpus D (Title/Abstract/Keywords composites; n = 25,907). Input: Structured dataset from topic-modeling results (full text or tokenized) Output: Coherence score C_V for topic coherence Extract topic words and keywords 1: topic_words ← GETTOPICSANDWORDS() Prepare text format for coherence calculation 2: (texts, dictionary, corpus) ← PREPARECOHERENCEDATA(df) Set number of keywords per topic 3: topn_words ← 10 Generate topic–term sets 4: topic_terms ← GETTOPICTERMS(topic_words, topn_words) Calculate coherence score 5: coherence_score ← EVALUATECOHERENCESCORE(topic_terms, texts, dictionary) 6: return coherence_score ▷ C_V |
3.4. Theory-Informed Knowledge Map: Definition and Assembly
3.5. Topic Labels and Disciplinary Provenance
4. Result Analysis
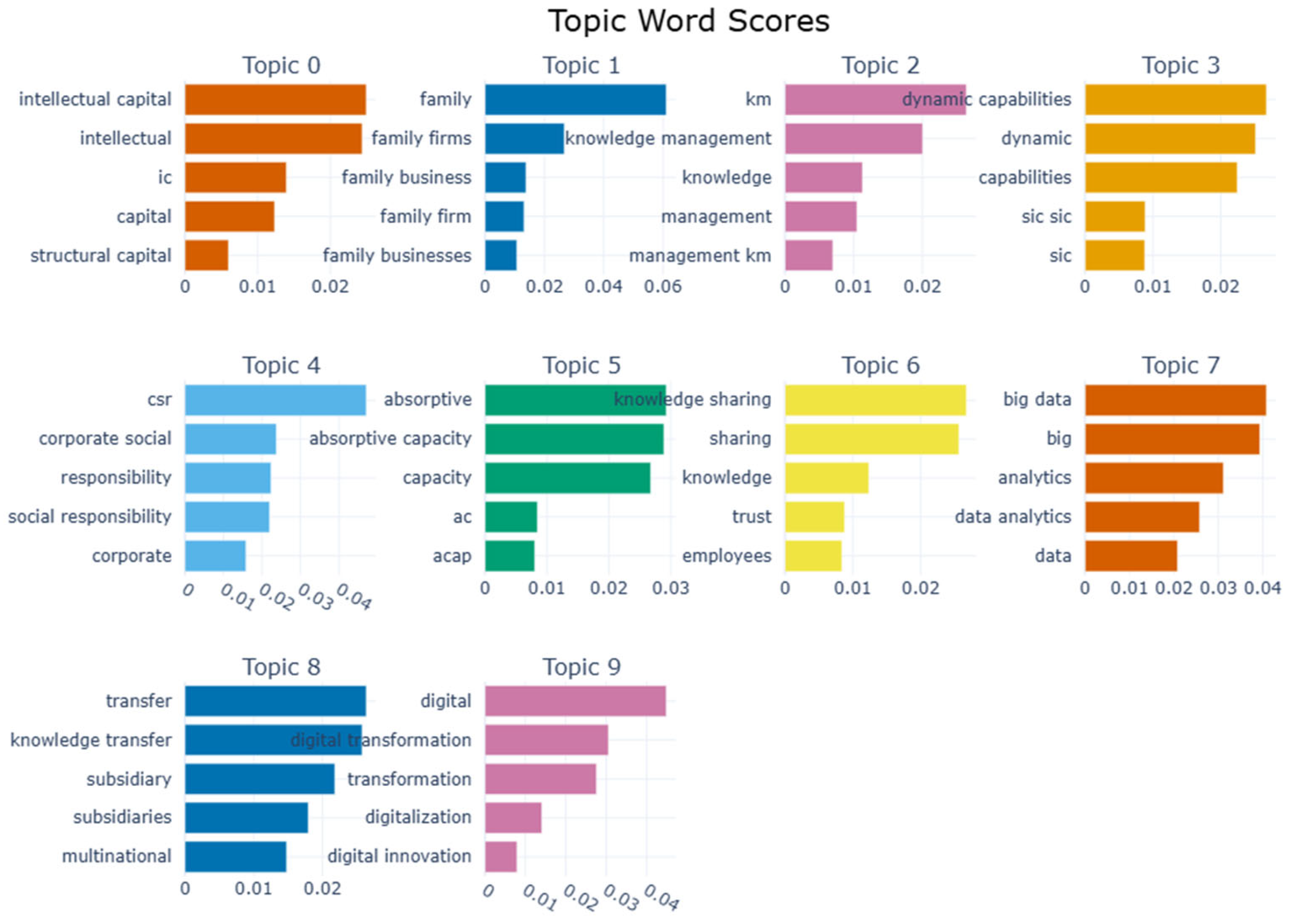
4.1. Topic Modeling Results Based on BERTopic
- Topic 0 emphasizes intellectual capital and knowledge assets, highlighting concepts such as “intellectual capital” and “structural capital,” central to knowledge-based views of competitive advantage.
- Topic 1 focuses on family business and organizational capital, characterized by terms like “family firms” and “family business,” suggesting a stream of research centered on governance, succession, and performance in family-owned firms.
- Topic 2 addresses knowledge management and resource configuration, incorporating phrases like “knowledge management” and “management KM,” reflecting discussions around dynamic knowledge capabilities and organizational learning.
- Topic 3 covers dynamic capabilities and market responsiveness, with strong associations with terms like “dynamic capabilities” and “capabilities,” aligned with the dynamic capabilities framework in the strategy literature.
- Topic 4 relates to corporate social responsibility and sustainable advantage, evidenced by terms such as “CSR” and “corporate responsibility,” capturing the intersection of ethics, legitimacy, and long-term performance.
- Topic 5 centers on absorptive capacity and innovation potential, including keywords like “absorptive capacity” and “innovation,” indicating a focus on external knowledge assimilation and innovation performance.
- Topic 6 highlights knowledge sharing and organizational trust, drawing on terms like “trust” and “employees,” and pointing toward collaboration, knowledge diffusion, and intraorganizational dynamics.
- Topic 7 involves big data and analytics-driven decision-making, showing strong signals of “data analytics” and “big data,” aligning with the rise of data-driven strategies.
- Topic 8 reflects knowledge transfer and multinational coordination, with terms such as “subsidiaries” and “multinational,” revealing insights into international strategy and global knowledge flow.
- Topic 9 focuses on digital transformation and innovation governance, combining terms like “digital transformation” and “innovation” to capture the evolution of strategic responses in the digital era.
4.2. Topic Distribution and Topic Coherence Evaluation (BERTopic Modeling vs. LDA Topic Modeling)
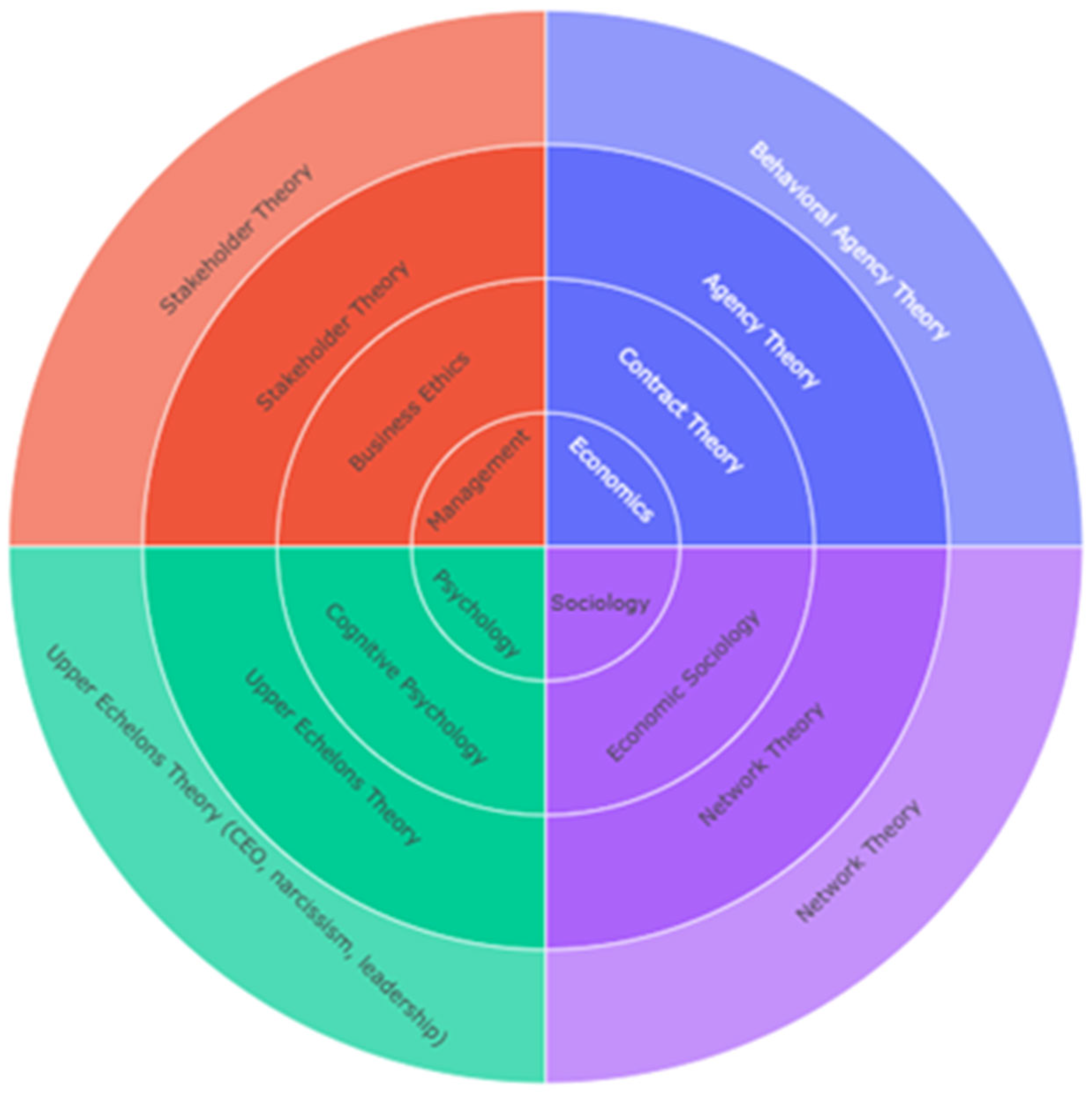
4.3. Theoretical Hierarchy of Strategic Management
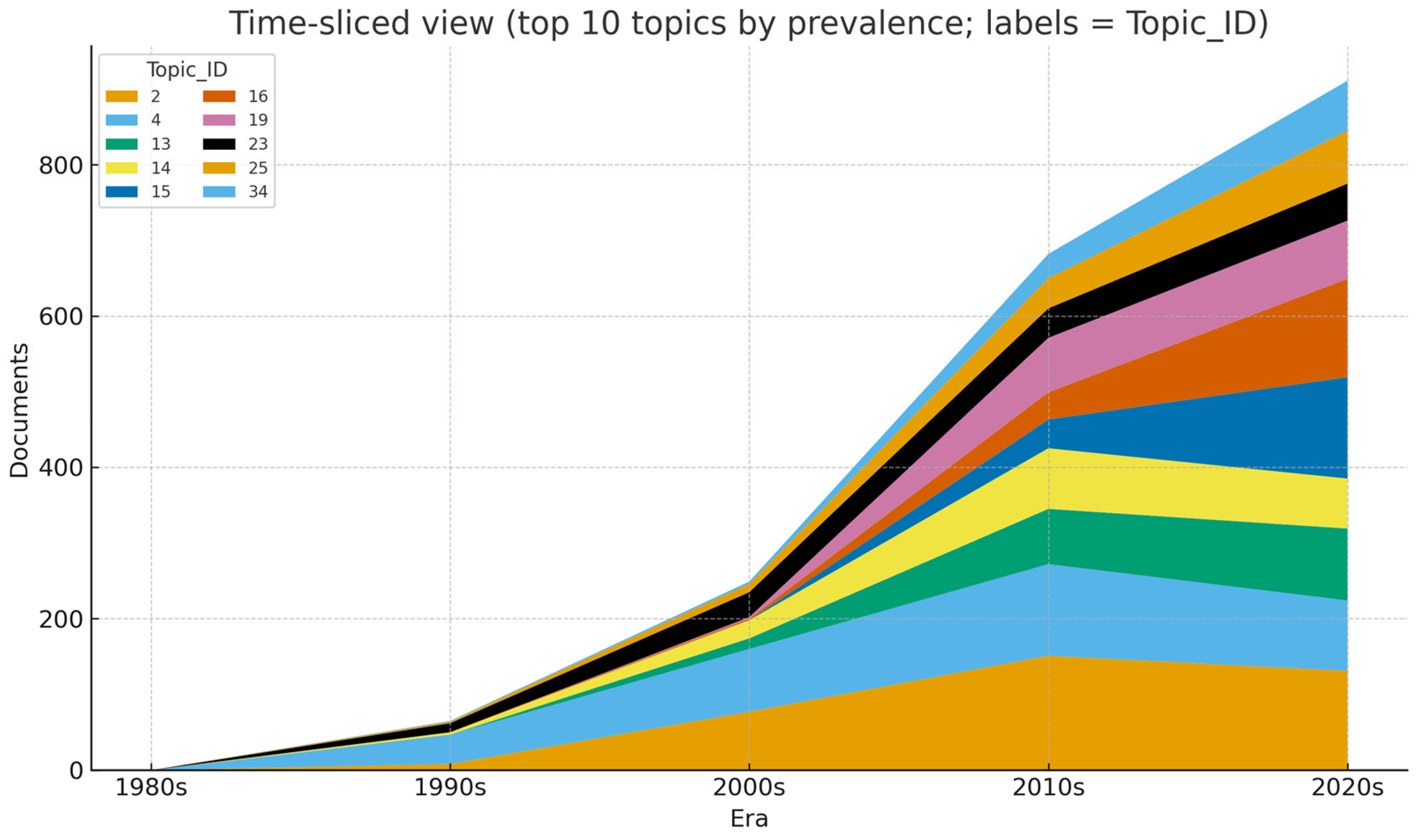
4.4. Knowledge Map and Per-Topic Metrics
4.5. Conclusions
5. Discussion
5.1. Unveiling the Semantic Landscape of Strategic Management: From Core Theories to Emerging Themes
5.2. Theoretical Anchoring Through Multidisciplinary Mapping
5.3. Advancing Semantic Precision and Theoretical Differentiation Through BERTopic
5.4. Contribution to Understanding Strategic Theory Evolution
- Structural Validation: The successful mapping of semantic topics to theoretical layers confirms that strategic management is not merely a fragmented field, but one with identifiable, structured, and evolving knowledge domains.
- Mechanisms of Evolution: The observed topic dynamics—such as convergence of digital strategy with organizational learning, or differentiation within governance models—mirror the evolution mechanisms discussed in Section 2, namely theoretical convergence, differentiation, and regeneration.
- Clarifying Theoretical Ambiguity: By exposing overlapping topics and hybrid constructs, the findings offer tools for resolving ambiguities in the field’s theoretical core. For instance, the separation of platform strategy from traditional resource-based themes reflects an emerging shift toward ecosystemic thinking.
- Future Synthesis: The identified topic clusters and their temporal trajectories provide a data-driven basis for future synthesis, allowing scholars to track theoretical lineage, anticipate convergence points, and identify gaps in conceptual coverage.
5.5. Application for Empirical Decision-Making (BSC Translation)
- Learning and Growth: Build board governance capability.
- 2.
- Internal Process: strengthen monitoring and control routines.
- 3.
- Customer (capital market): increase investor confidence and governance signals.
- 4.
- Financial: reduce agency costs and stabilize earnings.
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Abbreviation | Expanded Form | In-Context Usage (English; Citation Numbers Match Your Draft) | Definition/Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers | Section 1.3: background on NLP, LDA [22], BERT/Sentence-BERT [25,26], and BERTopic [27], including UMAP [28], HDBSCAN [29], and c-TF-IDF; coherence metrics C_V/C_NPMI [30]. | Transformer model that encodes text into context-aware vectors. |
| HDBSCAN | Hierarchical Density-Based Clustering | Section 1.3: used after UMAP [28] within the BERTopic pipeline [27] to cluster documents; details and coherence checks in Section 3 [30]. | Density-based clustering; detects groups and labels noise (−1). |
| IDF | Inverse Document Frequency | Section 1.3: appears in class-based TF-IDF within BERTopic [27] (with UMAP [28] and HDBSCAN [29]); coherence evaluated in [30]. | Weights rare terms higher in TF–IDF to highlight informative words. |
| UMAP | Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection | Section 1.3: dimensionality reduction before HDBSCAN [29] in the BERTopic workflow [27]; see [28]. | Reduces dimensions while preserving structure for clustering/plots. |
| BSC | managerial implications and demonstrates a Balanced Scorecard | Section 1.4 and Section 5: managerial translation via Balanced Scorecard (BSC) strategy maps and KPIs [41,42]. | Strategy map with four perspectives for translating topics to KPIs. |
| MPA | Main Path Analysis | Section 2.1: citation-based tracing of knowledge backbones; Section 2.2.1 links to historiography maps and main path extraction (see the citations given there). | Traces main knowledge flows in citation networks. |
| IO | Industrial Organization | Section 2.2.4: listed with RBV and TCE as core theoretical backgrounds in strategic management. | Field on industry structure and competition among firms. |
| JMMT | Joint Multi-Scale Multimodal Transformer | Section 2.2.4: cited as a recent multi-scale multimodal Transformer illustrating embedding-centric advances [31]. | Neural model fusing multiple modalities/scales for prediction. |
| QA | Question Answering | Section 2.2.4: medical QA example showing knowledge-embedding gains prior to generation [30]. | Automated question answering from text. |
| TCE | Transaction Cost Economics | Section 2.2.4: paired with IO and RBV as an economics-rooted perspective for theory mapping. | Explains make-vs-buy via transaction cost minimization. |
| CA | Competitive Advantage | Section 3.1: one of the inclusion boundaries for the corpus (with RBV, KBV, DCV). | A firm’s performance edge over rivals. |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses | Section 3.1: flow follows PRISMA stages (Identification → Screening → Eligibility → Inclusion) for transparency in retrieval/screening. | Reporting guideline for systematic reviews/meta-analyses. |
| TI | The query was executed within the title | Section 3.1: ritle (TI) field used to increase topical specificity and reduce semantic noise in the initial search. | Title field used to narrow database searches. |
| VRIO | Value, Rarity, Imitability, Organization | Section 3.1: referenced in the strategy lexicon/codebook to align RBV constructs with topic labels. | Checklist to test if resources yield sustained advantage. |
| LSA | traditional methods such as Latent Semantic Analysis | Section 3.3: listed alongside LDA [22] as traditional baselines contrasted with the semantic BERTopic approach [27]. | Matrix factorization method for capturing term–document relations. |
| ARI | Adjusted Rand Index | Section 3.3.2: used to assess clustering stability on overlapping documents in sensitivity checks (Adjusted Rand Index). | Similarity score for clustering stability (0–1; higher = more similar). |
| CSR | Market Adaptation Topic 4 Corporate Social Responsibility | Section 4.1: appears within a CSR/sustainability-related topic illustrating ethics/legitimacy and long-term advantage. | Corporate social/environmental responsibility and disclosure. |
| ERP | Enterprise Resource Planning | Section 4.2: example application within Dynamic Capabilities (ERP implementation) topics/processes. | Integrated system linking finance, supply, production, HR, etc. |
| ESG | Environmental, Social, and Governance | Section 4.2: part of stakeholder/disclosure themes illustrating cross-disciplinary integration. | Environmental, social, and governance indicators of firm practices. |
| HPWS | High-Performance Work Systems | Section 4.2: under Behavioral Theory/Human Resources topics as high-performance work systems. | Bundles of HR practices to boost employee and firm performance. |
| HR | Human Resources | Section 4.2: appears within behavioral/HR topics as people and capability signals. | People operations and workforce management. |
| HRM | Human Resource Management | Section 4.2: policy/process layer within HR-related topics. | Policies/processes for staffing, pay, training, and evaluation. |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization | Section 4.2: under Institutional Theory (ISO legitimacy strategy) to illustrate institutional pressure/legitimacy. | International standards (e.g., quality, environment). |
| SEW | Socioemotional Wealth | Section 4.2: Socioemotional Wealth in family-owned firm topics (non-financial goals, governance tensions). | Family-owned firm non-financial goals (identity, control, legacy). |
| TMT | Top Management Team | Section 4.2: Top management team variables in Upper Echelons topics. | Top management team (senior executives). |
| VC | Venture Capital | Section 4.2: appears in RBV + Real Options topics to link capital markets and resource dynamics. | Venture capital funding for startups. |
| NRBV | Natural Resource-Based View | Section 4.3: Natural Resource-Based View topics (e.g., green/sustainable capabilities). | RBV extended to environmental resources/capabilities. |
| DCV | Dynamic Capabilities View | Section 1.1 and Section 3.1: a core theoretical axis for inclusion and mapping, alongside RBV/KBV. | Advantage via sensing, seizing, and reconfiguring capabilities. |
| KBV | Knowledge-Based View | Section 3.1: used with RBV/DCV to define the domain boundary and guide theory mapping. | Knowledge as the central strategic resource. |
| LDA | as citation analysis and Latent Dirichlet Allocation | Section 1.3 and Section 2.2.2: baseline topic model contrasted with BERTopic; cited in [22]. | Probabilistic topic model for text clustering. |
| RBV | theory-specific lexicon grounded in the Resource-Based View | Section 1.1 and Section 3.1: core theory for lexicon alignment and topic/theory mapping. | Advantage from valuable, rare, inimitable, and organized resources. |
References
- Taylor, F.W. The Principles of Scientific Management; NuVision Publications, LLC: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 1911. [Google Scholar]
- Fayol, H. General and Industrial Management; Ravenio Books: Osaka, Japan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.E. Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.E. The Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J.; Pisano, G.; Shuen, A. Dynamic capabilities and strategic management. Strateg. Manag. J. 1997, 18, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, A.; El Sawy, O.A.; Pavlou, P.A.; Venkatraman, N.v. Digital business strategy: Toward a next generation of insights. MIS Q. 2013, 37, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAfee, A.; Brynjolfsson, E.; Davenport, T.H.; Patil, D.; Barton, D. Big data: The management revolution. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2012, 90, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Adner, R. Match your innovation strategy to your innovation ecosystem. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2006, 84, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Gawer, A.; Cusumano, M.A. Industry platforms and ecosystem innovation. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2014, 31, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J. Dynamic Capabilities and Strategic Management: Organizing for Innovation and Growth; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Huutoniemi, K.; Klein, J.T.; Bruun, H.; Hukkinen, J. Analyzing interdisciplinarity: Typology and indicators. Res. Policy 2010, 39, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.T. Ethnocentrism of disciplines and the fish-scale model of omniscience. In Interdisciplinary Relationships in the Social Sciences; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 328–348. [Google Scholar]
- Baumol, W.J. Williamson’s the economic institutions of capitalism. Rand J. Econ. 1986, 17, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMaggio, P.J.; Powell, W.W. The iron cage revisited: Institutional isomorphism and collective rationality in organizational fields. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1983, 48, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, J.; Salancik, G. External control of organizations—Resource dependence perspective. In Organizational Behavior 2; Routledge: London, UK, 2015; pp. 355–370. [Google Scholar]
- Cyert, R.; March, J. Behavioral theory of the firm. In Organizational Behavior 2; Routledge: London, UK, 2015; pp. 60–77. [Google Scholar]
- Argyris, C.; Schön, D.A. Organizational learning: A theory of action perspective. Reis 1997, 77–78, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambrick, D.C.; Mason, P.A. Upper echelons: The organization as a reflection of its top managers. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1984, 9, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Rodríguez, A.R.; Ruíz-Navarro, J. Changes in the intellectual structure of strategic management research: A bibliometric study of the Strategic Management Journal, 1980–2000. Strateg. Manag. J. 2004, 25, 981–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernerfelt, B. A resource-based view of the firm. Strateg. Manag. J. 1984, 5, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, Z.S. Distributional structure. Word 1954, 10, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joachims, T. A probabilistic analysis of the Rocchio algorithm with TFIDF for text categorization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Nashville, TN, USA, 8–12 July 1997; pp. 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Mariani, M.; Borghi, M. Industry 4.0: A bibliometric review of its managerial intellectual structure and potential evolution in the service industries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 149, 119752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Suh, Y. Identifying convergence fields and technologies for industrial safety: LDA-based network analysis. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 138, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; Volume 1, pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, N.; Gurevych, I. Sentence-bert: Sentence embeddings using siamese bert-networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.10084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootendorst, M. BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with a class-based TF-IDF procedure. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.05794. [Google Scholar]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Melville, J. Umap: Uniform manifold approximation and projection for dimension reduction. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.03426. [Google Scholar]
- Campello, R.J.; Moulavi, D.; Sander, J. Density-based clustering based on hierarchical density estimates. In Proceedings of the Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Gold Coast, Australia, 14–17 April 2013; pp. 160–172. [Google Scholar]
- Röder, M.; Both, A.; Hinneburg, A. Exploring the space of topic coherence measures. In Proceedings of the Eighth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Shanghai, China, 2–6 February 2015; pp. 399–408. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, R.S.; Norton, D.P. Using the balanced scorecard as a strategic management system. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1996, 74, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Garfield, E.; Merton, R.K. Citation Indexing: Its Theory and Application in Science, Technology, and Humanities; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Cheng, H. Research on the evolution of textile technological convergence in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Lu, L.Y.; Ho, M.H.-C. A few notes on main path analysis. Scientometrics 2019, 119, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ge, S.; Wang, N. Digital transformation: A systematic literature review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 162, 107774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, M.; Li, P.; Jiang, S.; Hu, W.; Guo, X.; Cao, M. Tracing knowledge development trajectories of the internet of things domain: A main path analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 6531–6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Science mapping: A systematic review of the literature. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2017, 2, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummon, N.P.; Dereian, P. Connectivity in a citation network: The development of DNA theory. Soc. Netw. 1989, 11, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Lu, L.Y. An integrated approach for main path analysis: Development of the Hirsch index as an example. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Guo, Y.; Porter, A.; Zhu, D. Identifying technology evolution pathways based on patent citation network and tech mining–illustrated for dye-sensitized solar cells. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Future-Oriented Technology Analysis (FTA), Brussels, Belgium, 27–28 November 2014; pp. 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, G. A semantic main path analysis method to identify multiple developmental trajectories. J. Informetr. 2022, 16, 101281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ibekwe-SanJuan, F.; Hou, J. The structure and dynamics of cocitation clusters: A multiple-perspective cocitation analysis. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1386–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Magee, C.L. Tracing technological development trajectories: A genetic knowledge persistence-based main path approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girvan, M.; Newman, M.E. Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7821–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, H. Visualizing science by citation mapping. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1999, 50, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsurai, M.; Ono, S. TrendNets: Mapping emerging research trends from dynamic co-word networks via sparse representation. Scientometrics 2019, 121, 1583–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdouline, I.; El Baz, J.; Jebli, F. Revisiting technological entrepreneurship research: An updated bibliometric analysis of the state of art. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 179, 121589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, F.; Xu, Z.D. Towards an integrated conceptual model of supply chain learning: An extended resource-based view. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2019, 24, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debao, D.; Yinxia, M.; Min, Z. Analysis of big data job requirements based on K-means text clustering in China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, R.; Yu, J. A topic modeling comparison between lda, nmf, top2vec, and bertopic to demystify twitter posts. Front. Sociol. 2022, 7, 886498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltagy, I.; Lo, K.; Cohan, A. SciBERT: A pretrained language model for scientific text. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yoon, W.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; So, C.H.; Kang, J. BioBERT: A pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.R.; Sánchez-Franco, M.J.; Tienda, M.d.l.S.R. Examining transaction-specific satisfaction and trust in Airbnb and hotels. An application of BERTopic and Zero-shot text classification. Tour. Manag. Stud. 2023, 19, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodeir, N.; Elghannam, F. Efficient topic identification for urgent MOOC Forum posts using BERTopic and traditional topic modeling techniques. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2025, 30, 5501–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelborn, H.; Berggren, J. Topic Modeling for Customer Insights: A Comparative Analysis of LDA and BERTopic in Categorizing Customer Calls. Master’s Thesis, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Khan, M.; Taleb-Ahmed, A.; Othmani, A. Advancing medical question answering with a knowledge embedding transformer. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0329606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Ahmad, J.; Gueaieb, W.; De Masi, G.; Karray, F.; El Saddik, A. Joint Multi-Scale Multimodal Transformer for Emotion Using Consumer Devices. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2025, 71, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, K.M.; Martin, J.A. Dynamic capabilities: What are they? Strateg. Manag. J. 2000, 21, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Jordan, J. Knowledge orientations and team effectiveness. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 1998, 16, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Constructs | Core Theory | Keywords |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge-Based View (KBV) | Knowledge-Based View | knowledge management, knowledge sharing, knowledge transfer, knowledge acquisition, knowledge integration, knowledge exploitation, knowledge exploration, knowledge capital |
| Intellectual Capital Theory | intellectual capital, human capital, structural capital, relational capital, social capital | |
| Organizational Learning Theory | organizational learning, learning capability, absorptive capacity, learning organization | |
| Knowledge-Based Innovation | knowledge-based innovation, knowledge integration capability, knowledge transformation, knowledge absorption, knowledge reconfiguration | |
| Resource-Based View (RBV) | Resource-Based View (RBV) | resource-based view, resource-based theory, resource advantage theory, firm resources, tangible resources, intangible resources, core competencies |
| VRIO Framework | VRIO framework, value, rarity, imitability, organization, valuable resources, rare resources, imitable resources, non-substitutable resources | |
| Strategic Resource Theory | strategic resources, competitive resources, strategic assets, firm-specific resources | |
| Resource Typology | human resources, organizational resources, technological resources, financial resources | |
| Dynamic Capabilities View (DCV) | Dynamic Capabilities View (DCV) | dynamic capabilities, DCV, dynamic capability view, sensing, seizing, transforming, strategic flexibility, organizational agility, adaptive capabilities, market responsiveness |
| Resource Reconfiguration Theory | resource reconfiguration, technological adaptation, knowledge reconfiguration | |
| Innovation & Agility | innovation capability, learning agility, competitive agility, strategic adaptation, business model innovation | |
| Competitive Advantage (CA) | Competitive Advantage Theories | competitive advantage, sustainable competitive advantage, long-term competitive advantage, strategic positioning, cost leadership, differentiation strategy, focus strategy |
| Value Creation Theories | value creation, value co-creation, customer value | |
| Performance-Based Perspective | firm performance, strategic performance, innovation performance, financial performance, firm growth, business performance | |
| Market and Strategic Positioning | market competition, competitive positioning |
| Topic ID | Representative Keywords (Top 5) | Provisional Topic Label |
|---|---|---|
| Topic 0 | intellectual capital, capital, structural capital | Intellectual Capital and Knowledge Assets |
| Topic 1 | family, family firms, family business | Family Business and Organizational Capital |
| Topic 2 | km, knowledge management, management km | Knowledge Management and Resource Configuration |
| Topic 3 | dynamic capabilities, capabilities, sic | Dynamic Capabilities and Market Adaptation |
| Topic 4 | corporate social responsibility (CSR), corporate social responsibility, responsibility | Corporate Social Responsibility and Sustainable Advantage |
| Topic 5 | absorptive, absorptive capacity, innovation | Absorptive Capacity and Innovation Potential |
| Topic 6 | knowledge sharing, trust, employees | Knowledge Sharing and Organizational Trust |
| Topic 7 | big data, analytics, data analytics | Big Data and Analytics-Driven Strategy |
| Topic 8 | knowledge transfer, subsidiaries, multinational | Knowledge Transfer and Multinational Coordination |
| Topic 9 | digital transformation, transformation, innovation | Digital Transformation and Innovation Governance |
| Method | C_V Coherence Score | C_NPMI Score | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| BERTopic | 0.6620 | 0.1595 | High topic coherence; topics are semantically consistent and interpretable |
| LDA | 0.4359 | - | Moderate coherence; less semantic alignment among topic terms |
| Thematic Area | BERTopic (Separated) | LDA (Merged) | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agency Theory Subdomains | Board Governance (e.g., board, directors, CEO, governance) and Executive Compensation (e.g., compensation, incentives, CEO pay) | One broad “governance/compensation” topic | Distinguishes monitoring vs. incentive mechanisms |
| ESG/Stakeholder vs. Legitimacy/Disclosure | Stakeholder/ESG (e.g., ESG, governance, performance) and Legitimacy/IC Disclosure (e.g., disclosure, reporting, intellectual capital) | Single CSR/ESG/disclosure topic | Separates stakeholder salience from legitimacy signaling |
| Topic Id | Keywords | Topic Name |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | family, family firms, family firm, family business, ownership, family businesses, family involvement… | Socioemotional Wealth (SEW) |
| 4 | csr, corporate social, responsibility, social responsibility, corporate, social, responsibility csr… | Behavioral Agency Theory |
| 13 | hr, hrm, human resource, human, resource management, practices, resource, human resources, high perf… | Behavioral Theory of the Firm (HR, HRM, resource management, HPWS, human capital) |
| 14 | intellectual, intellectual capital, ic, capital, vaic, efficiency, capital efficiency, value added… | Resource-Based View (Intellectual Capital Efficiency) |
| 16 | board, directors, boards, ceo, corporate governance, governance, duality, director, busy, firm perfo… | Agency Theory (Board Governance) |
| 15 | gender, gender diversity, diversity, board, women, board gender, directors, female, boards, female d… | Behavioral Theory of the Firm (Board Gender Diversity) |
| 19 | compensation, pay, executive, ceo, executive compensation, ceo compensation, incentives, ceo pay, co… | Agency Theory (Executive Compensation) |
| 23 | corporate governance, governance, corporate, board, ownership, cg, firm performance, governance firm… | Agency Theory (corporate governance, board, ownership, agency) |
| 25 | disclosure, capital disclosure, icd, intellectual capital, intellectual, ic, reporting, capital, dis… | Legitimacy Theory |
| 34 | alliance, alliances, portfolio, alliance portfolio, partner, partners, portfolios, diversity, strate… | Network Theory |
| 37 | ceo, tmt, narcissism, ceos, leadership, upper, personality, ceo narcissism, upper echelons, echelons | Upper Echelons Theory (ceo, narcissism, upper echelons, leadership) |
| 48 | subsidiary, subsidiaries, reverse knowledge, reverse, transfer, knowledge transfer, rkt, multination… | Knowledge-Based View (KBV) |
| 51 | resilience, covid 19, covid, 19, pandemic, organizational resilience, 19 pandemic, crisis, disaster… | Dynamic Capabilities Theory (Crisis Resilience) |
| 54 | acquisitions, mergers, mergers acquisitions, border, cross border, merger, acquirers, acquirer, targ… | TCE (Cross-Border M&A Strategy) |
| 55 | ownership, shareholders, institutional, institutional investors, investors, governance, corporate go… | Agency Theory (ownership, investors, governance, performance) |
| 58 | diversity, tmt, diversity management, diversity firm, racial, gender, team, cultural diversity, gend… | Upper Echelons Theory (diversity, TMT, gender/cultural/age diversity) |
| 61 | esg, disclosure, environmental social, esg disclosure, social governance, governance esg, financial… | Stakeholder Theory |
| 67 | political, political connections, connections, lobbying, connected, politically connected, political… | Institutional Theory (Political Ties Strategy) |
| 70 | green, green supply, gscm, supply chain, supply, chain, chain management, environmental, gscm practi… | Natural Resource-Based View (Green Supply Chain) |
| 74 | islamic, islamic banks, banks, shariah, sharia, ibs, performance islamic, conventional, conventional… | Institutional Theory (Islamic Finance) |
| 75 | venture, venture capital, vc, cvc, corporate venture, backed, investors, vc backed, syndication, vcs | Resource-Based View + Real Options Theory (venture, VC) |
| 109 | exploration, exploitation, ambidexterity, exploration exploitation, exploitation exploration, ambide… | Ambidexterity Theory |
| 117 | franchising, franchise, franchisees, franchisor, franchisee, franchisors, transfer mechanisms, trans… | Agency Theory (franchising + knowledge transfer) |
| 127 | slack, slack resources, organizational slack, financial slack, slack firm, slack performance, hr sla… | Behavioral Theory of the Firm (slack, organizational) |
| 124 | succession, ceo, ceo succession, interim, founder, ceos, successor, turnover, successions, ceo turno… | Upper Echelons Theory (CEO succession, turnover, founder, interim) |
| 132 | audit, audit committee, committee, internal audit, ac, audit quality, committee characteristics, ac… | Agency Theory (audit committee, internal audit, ac effectiveness, audit quality) |
| 138 | ijvs, ijv, international joint, joint, joint ventures, ventures, international, foreign, acquisition… | Transaction Cost Economics (TCE) + Resource-Based View (RBV) |
| 136 | erp, resource planning, enterprise resource, implementation, erp implementation, planning erp, plann… | Dynamic Capabilities Theory (ERP Implementation) |
| 155 | acquisitions, acquirer, takeover, acquirers, bidders, takeovers, acquiring, mergers, returns, deals | TCE (M&A Performance and Valuation) |
| 163 | food, sscm, supply, supply chain, sustainable supply, chain, sustainable, food supply, chain managem… | Natural Resource-Based View (Sustainable Supply Chain) |
| 183 | inventory, inventory management, leanness, relationship inventory, inventory leanness, turns matrix… | Resource-Based View (Inventory Leanness Strategy) |
| 184 | iso, certification, 9000, iso 9000, 9000 certification, certified, iso 9001, 9001, standards, 14,001 | Institutional Theory (ISO Legitimacy Strategy) |
| 207 | acquisitions, technological, acquiring, innovation performance, acquiring firms, cross border, borde… | Real Options Theory + Resource-Based View (RBV) |
| Topic_ID | Topic_Name | Size_Docs | Prevalence_pct | C_V | C_NPMI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Socioemotional Wealth (SEW) | 367 | 1.42 | 0.8543 | −0.0957 |
| 4 | Behavioral Agency Theory | 336 | 1.3 | 0.8673 | 0.2476 |
| 13 | Behavioral Theory of the Firm (HR, HRM, resource management, HPWS, human capital) | 182 | 0.7 | 0.8176 | −0.0523 |
| 14 | Resource-Based View (Intellectual Capital) | 173 | 0.67 | 0.8657 | 0.1039 |
| 15 | Upper Echelons Theory (Board Gender Diversity) | 172 | 0.66 | 0.9628 | 0.2071 |
| 16 | Agency Theory–Board Governance | 168 | 0.65 | 0.9151 | −0.1847 |
| 19 | Agency Theory–Executive Compensation | 151 | 0.58 | 0.8753 | −0.0783 |
| 23 | Agency Theory (corporate governance, board, ownership, agency) | 133 | 0.51 | 0.8788 | −0.2238 |
| 25 | Legitimacy Theory | 123 | 0.47 | 0.8555 | −0.0486 |
| 34 | Network Theory | 102 | 0.39 | 0.8328 | −0.1468 |
| 37 | Upper Echelons Theory (ceo, narcissism, upper echelons, leadership) | 98 | 0.38 | 0.8433 | −0.2219 |
| 48 | Knowledge-Based View | 71 | 0.27 | 0.9215 | 0.0797 |
| 51 | Dynamic Capabilities Theory (resilience, crisis, pandemic) | 67 | 0.26 | 0.8382 | 0.1486 |
| 54 | Transaction Cost Economics | 65 | 0.25 | 0.9259 | 0.1456 |
| 55 | Agency Theory (ownership, investors, governance, performance) | 63 | 0.24 | 0.8273 | −0.1454 |
| 58 | Upper Echelons Theory (diversity, TMT, gender/cultural/age diversity) | 61 | 0.24 | 0.8421 | 0.2838 |
| 61 | Stakeholder Theory | 59 | 0.23 | 0.8439 | 0.0003 |
| 67 | Institutional Theory (political connections, lobbying, government) | 56 | 0.22 | 0.8584 | 0.089 |
| 70 | Natural Resource-Based View | 55 | 0.21 | 0.8061 | −0.1319 |
| 74 | Institutional Theory (Islamic banks, shariah, compliant) | 49 | 0.19 | 0.8514 | −0.0891 |
| 75 | Resource-Based View + Real Options Theory (venture, VC, CVC, investors) | 49 | 0.19 | 0.8953 | 0.1155 |
| 109 | Ambidexterity Theory | 33 | 0.13 | 0.9471 | 0.5814 |
| 117 | Agency Theory (franchising + knowledge transfer) | 31 | 0.12 | 0.9265 | 0.4429 |
| 124 | Upper Echelons Theory (CEO succession, turnover, founder, interim) | 27 | 0.1 | 0.818 | −0.1646 |
| 127 | Behavioral Theory of the Firm (slack, organizational) | 26 | 0.1 | 0.863 | −0.1323 |
| 132 | Agency Theory (audit committee, internal audit, ac effectiveness, audit quality) | 25 | 0.1 | 0.8323 | −0.2171 |
| 136 | Dynamic Capabilities Theory (Enterprise Resource Planning, ERP) | 24 | 0.09 | 0.8138 | −0.1031 |
| 138 | Transaction Cost Economics (TCE) + Resource-Based View (RBV) | 24 | 0.09 | 0.8623 | −0.0441 |
| 155 | Transaction Cost Economics | 20 | 0.08 | 0.9138 | 0.1413 |
| 163 | Natural Resource-Based View (NRBV) | 18 | 0.07 | 0.8147 | −0.2133 |
| 183 | Resource-Based View (RBV, Inventory Management, Leanness) | 14 | 0.05 | 0.9509 | 0.3107 |
| 184 | Institutional Theory | 14 | 0.05 | 0.9493 | 0.3094 |
| 207 | Real Options Theory + RBV | 12 | 0.05 | 0.8156 | −0.0507 |
| Strategy Map | Economics | Management | Sociology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Perspective | Behavioral Agency Theory Agency Theory (Board Governance) Agency Theory (Executive Compensation) Agency Theory (ownership, investors, governance) Agency Theory (franchising and knowledge transfer) Agency Theory (Audit Committee Effectiveness) Agency Theory (corporate governance, board, ownership) TCE (Cross-Border M&A Strategy) TCE (M&A Performance and Valuation) | ||
| Customer Perspective | Stakeholder Theory | Institutional Theory (Political Ties Strategy) Institutional Theory (Islamic Finance) Legitimacy Theory Institutional Theory (ISO Legitimacy Strategy) | |
| Internal Process Perspective | Knowledge-Based View (KBV) Resource-Based View (Intellectual Capital Efficiency) Resource-Based View + Real Options Theory (venture, VC) TCE + RBV (M&A Strategy) Resource-Based View (Inventory Leanness Strategy) Real Options Theory + RBV (Investment Strategy) Natural Resource-Based View (Green Supply Chain) Natural Resource-Based View (Sustainable Supply Chain) | ||
| Learning and Growth Perspective | Dynamic Capabilities Theory (Crisis Resilience) Dynamic Capabilities Theory (ERP Implementation) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Institute of Knowledge Innovation and Invention. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, K.-K.; Hsiao, C.-W.; Hsu, Y.-J. Strategic Management Knowledge Map via BERTopic (1980–2025): Evolution, Integration, and Application. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2025, 8, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi8050142
Lai K-K, Hsiao C-W, Hsu Y-J. Strategic Management Knowledge Map via BERTopic (1980–2025): Evolution, Integration, and Application. Applied System Innovation. 2025; 8(5):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi8050142
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Kuei-Kuei, Chih-Wen Hsiao, and Yu-Jin Hsu. 2025. "Strategic Management Knowledge Map via BERTopic (1980–2025): Evolution, Integration, and Application" Applied System Innovation 8, no. 5: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi8050142
APA StyleLai, K.-K., Hsiao, C.-W., & Hsu, Y.-J. (2025). Strategic Management Knowledge Map via BERTopic (1980–2025): Evolution, Integration, and Application. Applied System Innovation, 8(5), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi8050142








