Influence of Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate on Surface Properties of Dispersions of Oat Globulin Fibrils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surface Tension and Dynamic Surface Elasticity
2.2. Ellipsometry
2.3. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calamai, M.; Kumita, J.R.; Mifsud, J.; Parrini, C.; Ramazzotti, M.; Ramponi, G.; Taddei, N.; Chiti, F.; Dobson, C.M. Nature and Significance of the Interactions between Amyloid Fibrils and Biological Polyelectrolytes. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 12806–12815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenyuk, P.; Kurochkina, L.; Barinova, K.; Muronetz, V. Alpha-Synuclein Amyloid Aggregation Is Inhibited by Sulfated Aromatic Polymers and Pyridinium Polycation. Polymers 2020, 12, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Argueta, E.; Wojcikiewicz, E.P.; Du, D. Effects of Charged Polyelectrolytes on Amyloid Fibril Formation of a Tau Fragment. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 3034–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makshakova, O.; Bogdanova, L.; Faizullin, D.; Khaibrakhmanova, D.; Ziganshina, S.; Ermakova, E.; Zuev, Y.; Sedov, I. The Ability of Some Polysaccharides to Disaggregate Lysozyme Amyloid Fibrils and Renature the Protein. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nian, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hu, B. Protein Fibrillation and Hybridization with Polysaccharides Enhance Strength, Toughness, and Gas Selectivity of Bioplastic Packaging. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 9884–9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuelli, M.; Germerdonk, T.; Cao, Y.; Peydayesh, M.; Bagnani, M.; Handschin, S.; Nyström, G.; Mezzenga, R. Polysaccharide-Reinforced Amyloid Fibril Hydrogels and Aerogels. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 12534–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-H.; Li, X.-Y.; Huang, C.-L.; Liu, P.; Zeng, Q.-Z.; Yang, X.-Q.; Yuan, Y. Development and Mechanical Properties of Soy Protein Isolate-Chitin Nanofibers Complex Gel: The Role of High-Pressure Homogenization. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 2021, 150, 112090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Solin, N. Protein-Based Flexible Conductive Aerogels for Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 3360–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Yu, X.-H.; Zhang, J.-W.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Chen, H.-Q. The Complex of Arachin Amyloid-like Fibrils Formed with Ultrasound Treatment and Chitosan: A Potential Vehicle for Betanin and Curcumin with Improved Chemical Stability and Slow Release In Vitro. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 166, 111272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Z.; Dong, X.; Ding, X.; Zhou, X.; Cui, P. Novel Fava Bean 11S Nanofiber Gels for Sustained Ergothioneine Delivery: A Calcium Ion and κ-Carrageenan Approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 169, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhou, J.; Peydayesh, M.; Yao, Y.; Bagnani, M.; Kutzli, I.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Mezzenga, R. Plant Protein Amyloid Fibrils for Multifunctional Sustainable Materials. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2023, 7, 2200414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydayesh, M.; Bagnani, M.; Soon, W.L.; Mezzenga, R. Turning Food Protein Waste into Sustainable Technologies. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 2112–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Tang, M.; Wang, D.; Xie, Q.; Xu, X. Exploring the Self-Assembly Journey of Oat Globulin Fibrils: From Structural Evolution to Modified Functionality. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 149, 109587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; He, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J. Plant-Based Protein Amyloid Fibrils: Origins, Formation, Extraction, Applications, and Safety. Food Chem. 2025, 469, 142559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Yang, X.; Sagis, L.M.C. Nonlinear Surface Dilatational Rheology and Foaming Behavior of Protein and Protein Fibrillar Aggregates in the Presence of Natural Surfactant. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3679–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noskov, B.; Loglio, G.; Miller, R.; Milyaeva, O.; Panaeva, M.; Bykov, A. Dynamic Surface Properties of α-Lactalbumin Fibril Dispersions. Polymers 2023, 15, 3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milyaeva, O.Y.; Akentiev, A.V.; Bykov, A.G.; Loglio, G.; Miller, R.; Portnaya, I.; Rafikova, A.R.; Noskov, B.A. Dynamic Properties of Adsorption Layers of κ-Casein Fibrils. Langmuir 2023, 39, 15268–15274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboroceanu, D.; Wang, L.; Magner, E.; Auty, M.A.E. Fibrillization of Whey Proteins Improves Foaming Capacity and Foam Stability at Low Protein Concentrations. J. Food Eng. 2014, 121, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Simon, J.R.; Venema, P.; van der Linden, E. Protein Fibrils Induce Emulsion Stabilization. Langmuir 2016, 32, 2164–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveday, S.M.; Anema, S.G.; Singh, H. β-Lactoglobulin Nanofibrils: The Long and the Short of it. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 67, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Tang, C.; Li, B. Foams Stabilized by β-Lactoglobulin Amyloid Fibrils: Effect of PH. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10658–10665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, R.A.; de Figueiredo Furtado, G.; Netto, F.M.; Cunha, R.L. Assessing the Potential of Whey Protein Fibril as Emulsifier. J. Food Eng. 2018, 223, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Nishinari, K.; Phillips, G.O.; Fang, Y. Comparative Study on Foaming and Emulsifying Properties of Different Beta-Lactoglobulin Aggregates. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5922–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Pan, Y.; Peng, D.; Huang, W.; Shen, W.; Jin, W.; Huang, Q. Tunable Self-Assemblies of Whey Protein Isolate Fibrils for Pickering Emulsions Structure Regulation. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhu, L.; Karrar, E.; Qi, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, G. Pickering Foams Stabilized by Protein-Based Particles: A Review of Characterization, Stabilization, and Application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 133, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyst, A.M.R.; Van der Meeren, P.; Housmans, J.A.J.; Monge-Morera, M.; Rousseau, F.; Schymkowitz, J.; Delcour, J.A. Improved Coalescence and Creaming Stability of Structured Oil-in-Water Emulsions and Emulsion Gels Containing Ovalbumin Amyloid-like Fibrils Produced by Heat and Enzymatic Treatments. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; Xu, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, Z.; Tong, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Exploring the Interfacial Behavior and Foam Characteristics of Various Soy Protein Aggregates: Insights of Morphology and Conformational Flexibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 166, 111362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Yu, X.; Fu, L.; Tang, X.; Feng, X. Enhance Quinoa Protein Foaming Properties through Amyloid-like Fibrillation and 2S Albumin Blending. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 164, 111154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskov, B.A.; Akentiev, A.V.; Bykov, A.G.; Loglio, G.; Miller, R.; Milyaeva, O.Y. Spread and Adsorbed Layers of Protein Fibrils at Water –Air Interface. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 220, 112942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydayesh, M.; Kistler, S.; Zhou, J.; Lutz-Bueno, V.; Victorelli, F.D.; Meneguin, A.B.; Spósito, L.; Bauab, T.M.; Chorilli, M.; Mezzenga, R. Amyloid-Polysaccharide Interfacial Coacervates as Therapeutic Materials. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bykov, A.G.; Loglio, G.; Miller, R.; Tsyganov, E.A.; Wan, Z.; Noskov, B.A. Mixed Adsorption Mono- and Multilayers of ß-Lactoglobulin Fibrils and Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate. Colloids Interfaces 2024, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, T.; Peydayesh, M.; Usuelli, M.; Lutz-Bueno, V.; Teng, J.; Wang, L.; Mezzenga, R. Oat Plant Amyloids for Sustainable Functional Materials. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khrebina, A.D.; Akentiev, A.V.; Wan, Z.; Noskov, B.A. Dynamic Surface Properties of Oat Protein Dispersions. Mendeleev Commun. 2025, 35, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tang, M.; Xu, X. Effect of Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Fibrillization of Oat Globulins: Aggregation Kinetics, Structural Evolution, and Core Composition. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 165, 111233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskov, B.A.; Krycki, M.M. Formation of Protein/Surfactant Adsorption Layer as Studied by Dilational Surface Rheology. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 247, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motschmann, H.; Teppner, R. Ellipsometry in Interface Science. In Novel Methods to Study Interfacial Layers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 11, pp. 2–42. [Google Scholar]
- Akentiev, A.; Lin, S.-Y.; Loglio, G.; Miller, R.; Noskov, B. Surface Properties of Aqueous Dispersions of Bovine Serum Albumin Fibrils. Colloids Interfaces 2023, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskov, B.A.; Nuzhnov, S.N.; Loglio, G.; Miller, R. Dynamic Surface Properties of Sodium Poly(Styrenesulfonate) Solutions. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 2519–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivard, S.; Jacomine, L.; Kratz, F.S.; Foussat, C.; Lamps, J.-P.; Legros, M.; Boulmedais, F.; Kierfeld, J.; Schosseler, F.; Drenckhan, W. Interfacial Rheology of Linearly Growing Polyelectrolyte Multilayers at the Water–Air Interface: From Liquid to Solid Viscoelasticity. Soft Matter 2024, 20, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safouane, M.; Miller, R.; Möhwald, H. Surface Viscoelastic Properties of Floating Polyelectrolyte Multilayers Films: A Capillary Wave Study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 292, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, A.D.; Dong, W.-F.; Benbow, N.L.; Webber, J.L.; Krasowska, M.; Beattie, D.A.; Ferri, J.K. The Influence of Polyanion Molecular Weight on Polyelectrolyte Multilayers at Surfaces: Elasticity and Susceptibility to Saloplasticity of Strongly Dissociated Synthetic Polymers at Fluid–Fluid Interfaces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 23781–23789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
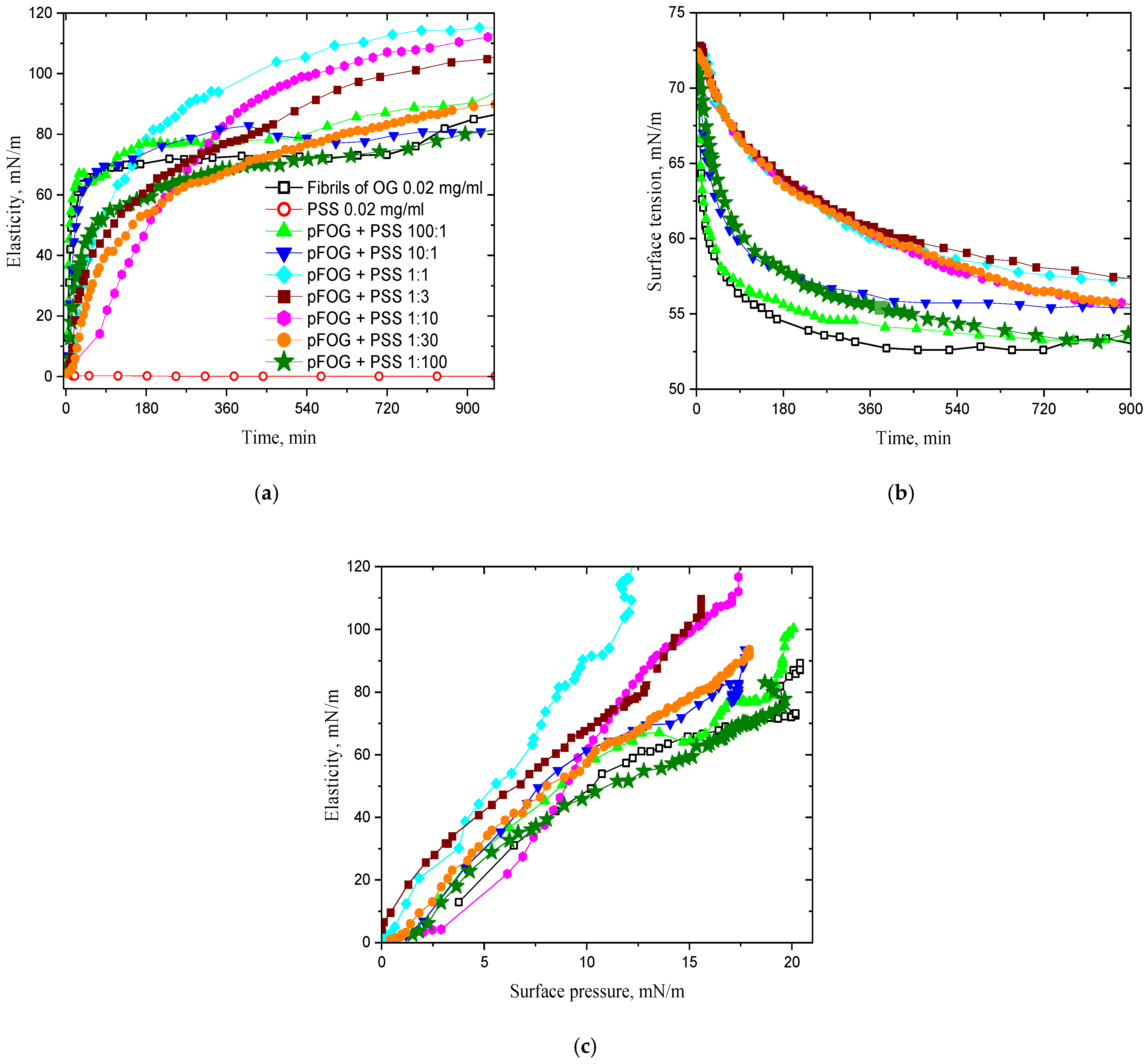

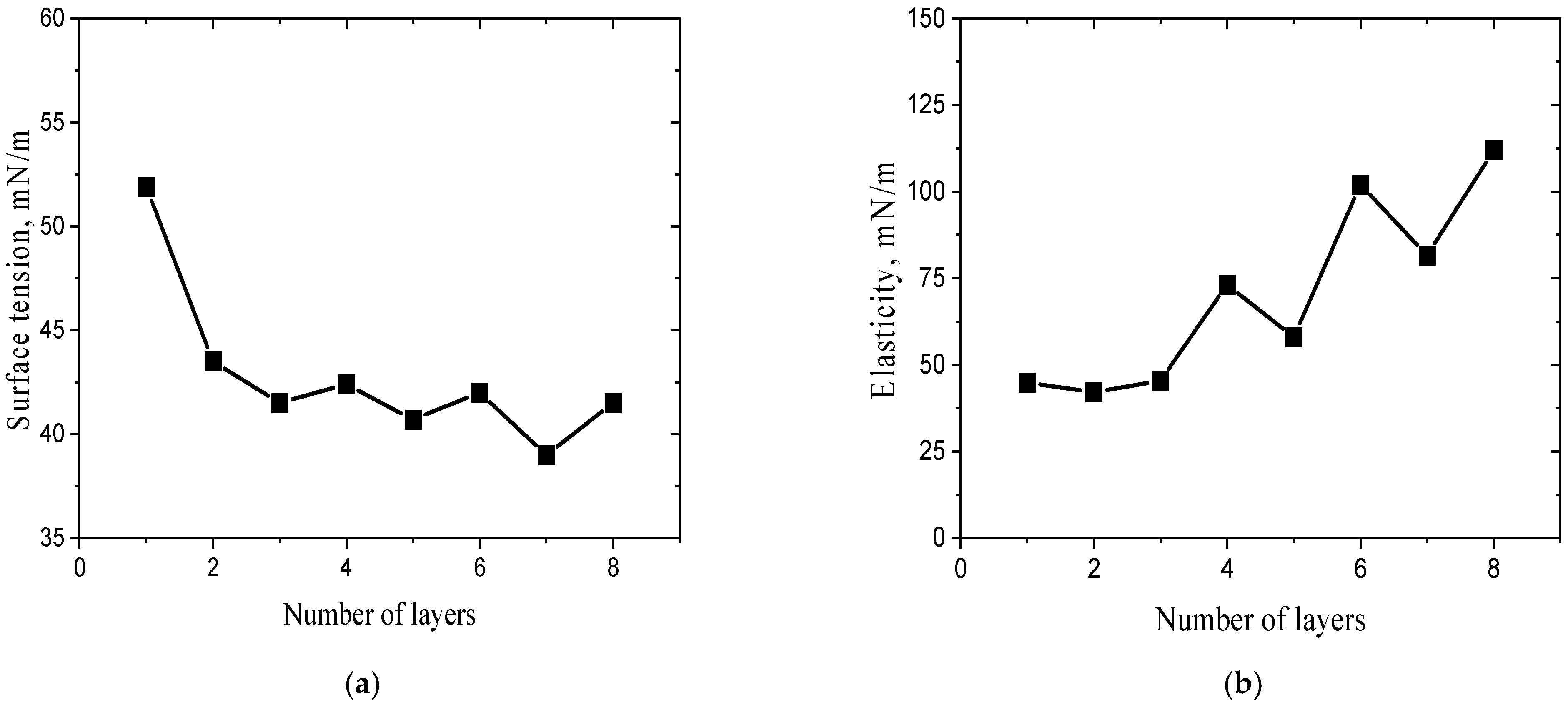
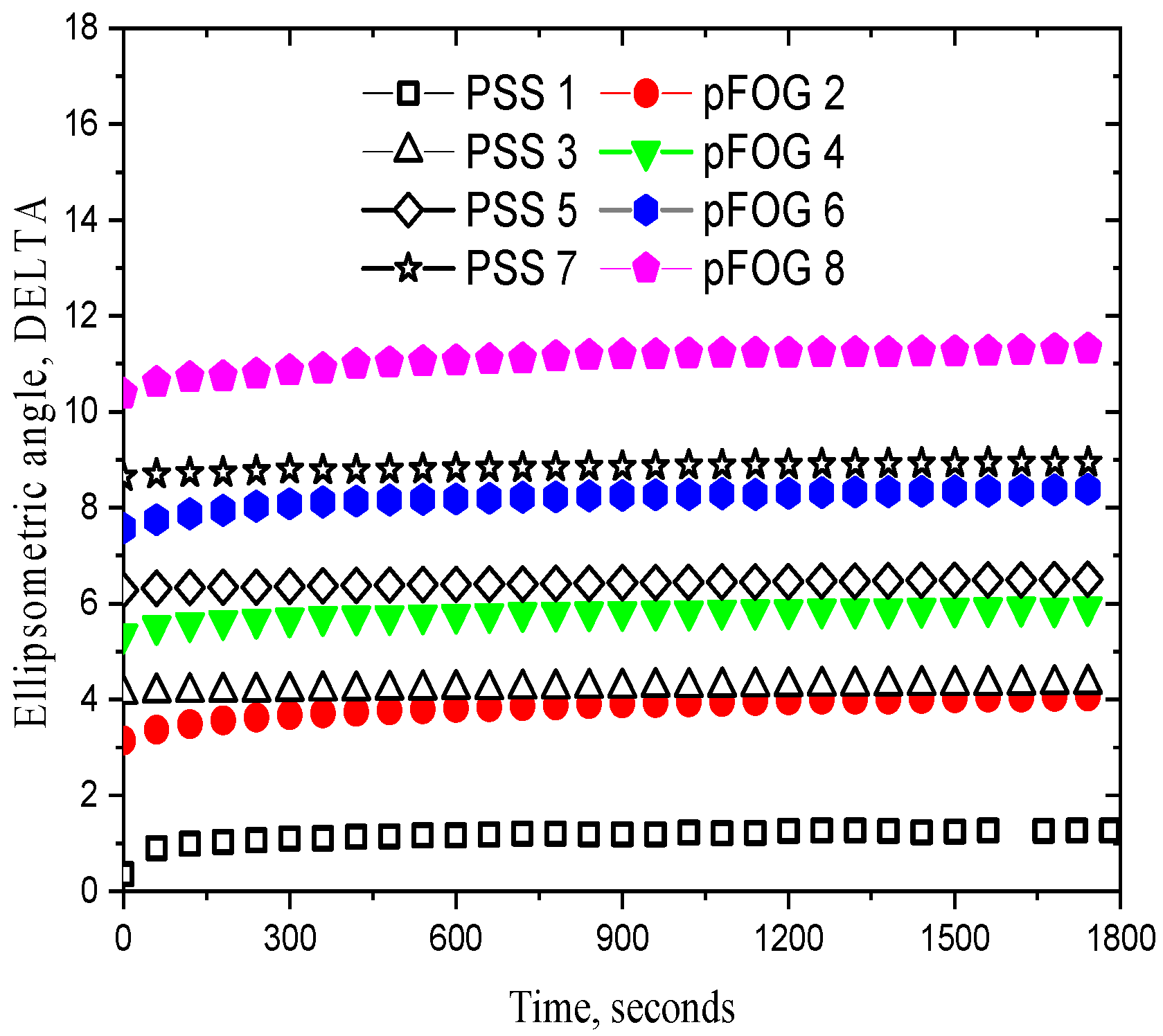

| Concentration Ratio Fibrils/PSS (Fibril Concentration Is Constant and Equals 20 mg/L) | ζ, mV |
|---|---|
| Only fibrils | 36.7 |
| 100:1 | 38.5 |
| 10:1 | 18.9 |
| 1:1 | −40.8 |
| 1:10 | −48.2 |
| 1:100 | −56.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noskov, B.A.; Bykov, A.G.; Khrebina, A.D.; Levchuk, E.A.; Loglio, G.; Miller, R.; Tsyganov, E.A. Influence of Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate on Surface Properties of Dispersions of Oat Globulin Fibrils. Colloids Interfaces 2025, 9, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9060089
Noskov BA, Bykov AG, Khrebina AD, Levchuk EA, Loglio G, Miller R, Tsyganov EA. Influence of Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate on Surface Properties of Dispersions of Oat Globulin Fibrils. Colloids and Interfaces. 2025; 9(6):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9060089
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoskov, Boris A., Alexey G. Bykov, Alexandra D. Khrebina, Evlaliya A. Levchuk, Giuseppe Loglio, Reinhard Miller, and Egor A. Tsyganov. 2025. "Influence of Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate on Surface Properties of Dispersions of Oat Globulin Fibrils" Colloids and Interfaces 9, no. 6: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9060089
APA StyleNoskov, B. A., Bykov, A. G., Khrebina, A. D., Levchuk, E. A., Loglio, G., Miller, R., & Tsyganov, E. A. (2025). Influence of Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate on Surface Properties of Dispersions of Oat Globulin Fibrils. Colloids and Interfaces, 9(6), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9060089










