Evaluating Raw Albizia amara Plant Powder as a Plant-Derived Surface-Active Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AA Suspension Preparation and Thermal Stability Assessment
2.2. AA Suspension Stability
2.2.1. pH and Sensory Evaluation
2.2.2. Particle Size Distribution
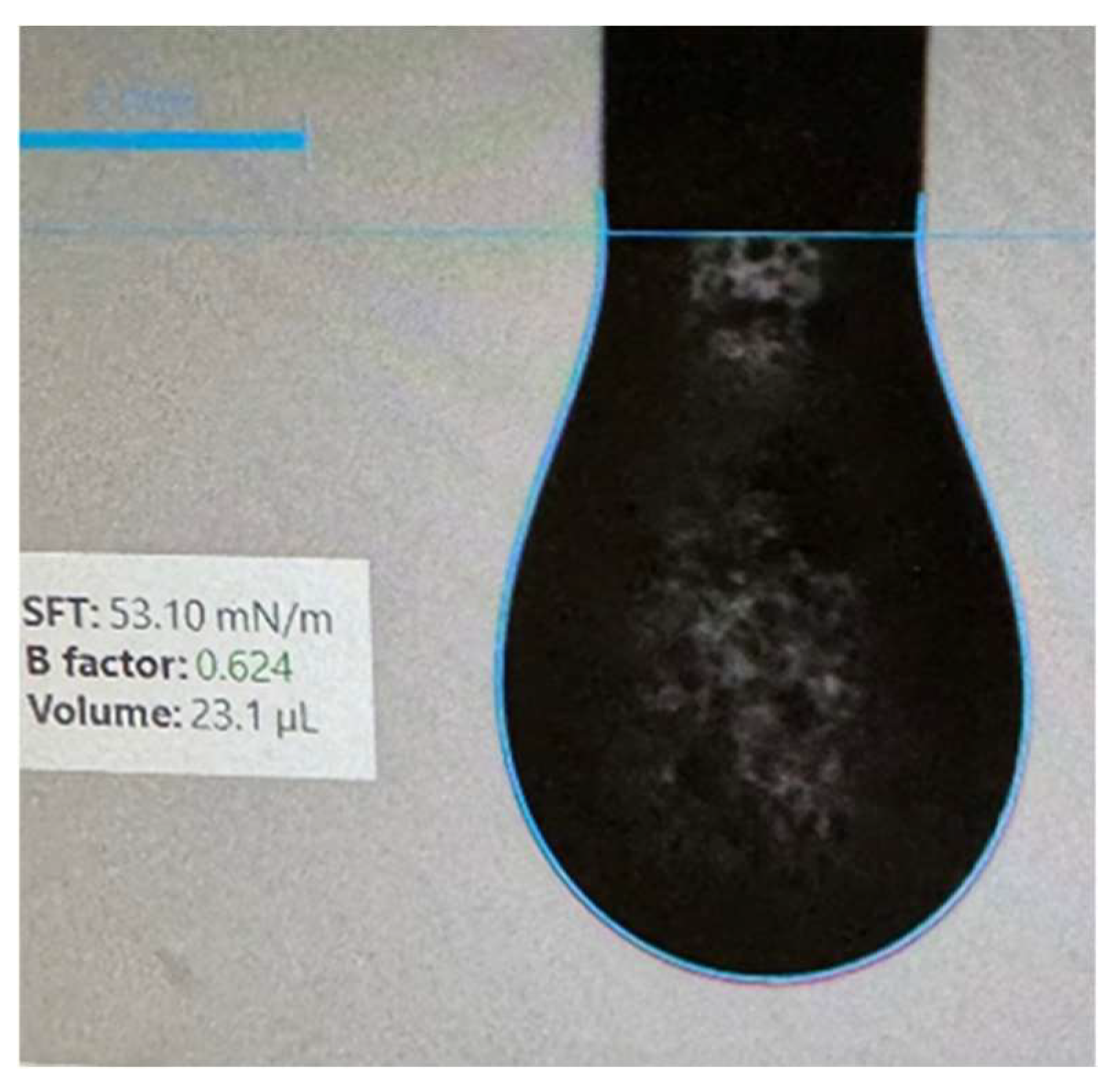
2.3. Apparent Surface Tension Measurement
2.4. Emulsification—Oil-in-Water Emulsion
2.5. Emulsion Capacity (EC) and Emulsion Stability (ES)
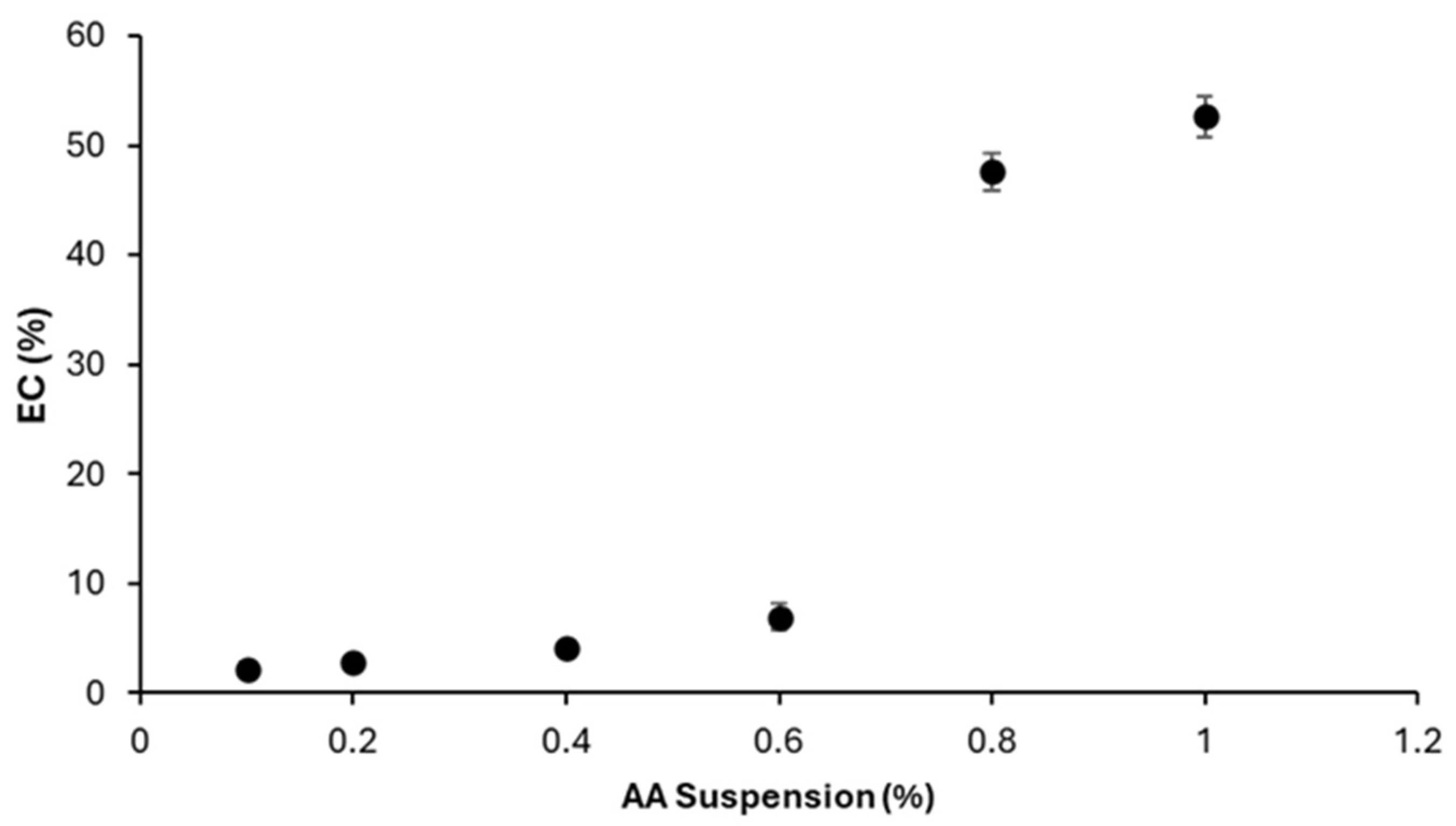
3. Results and Discussion
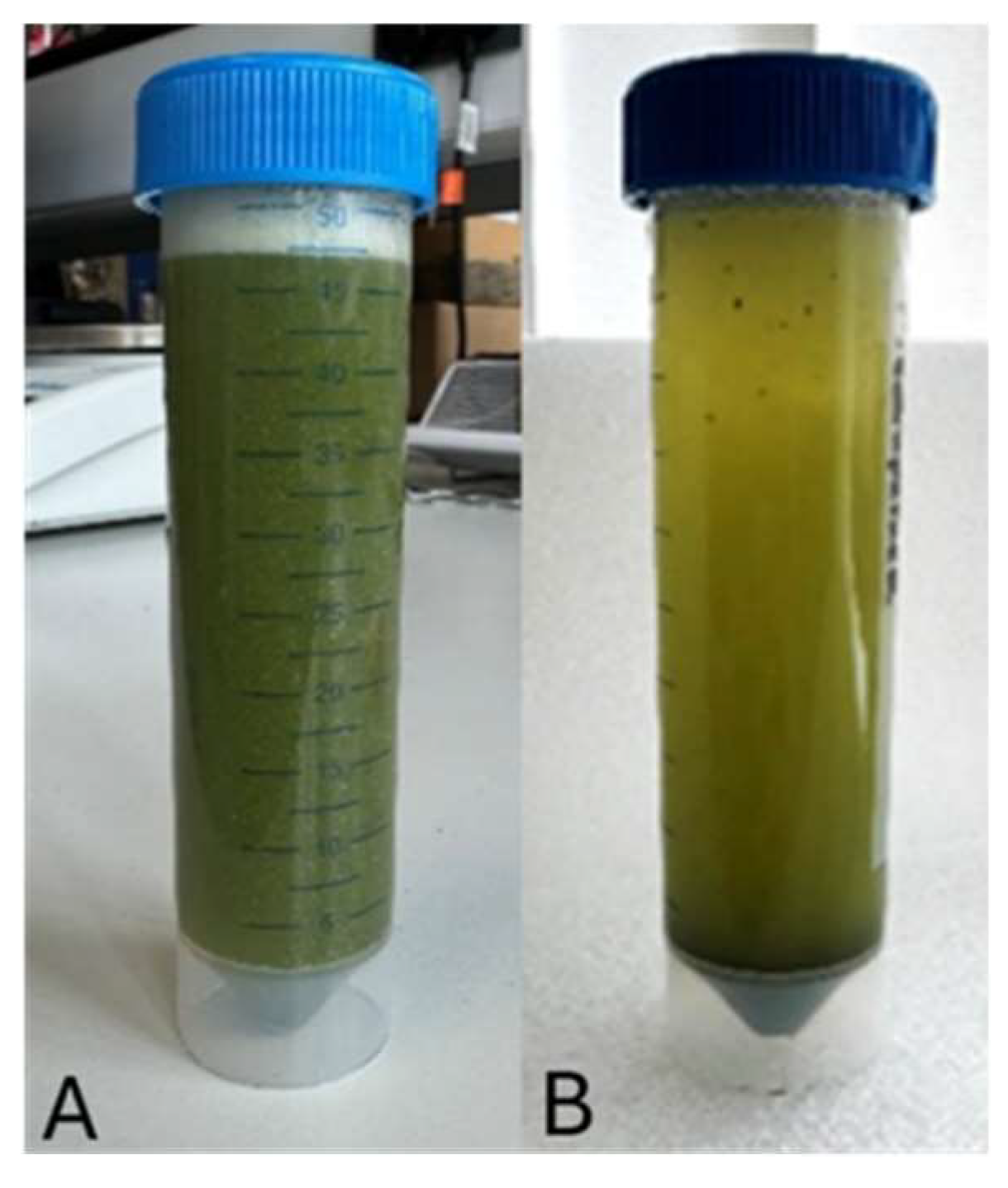
3.1. Stability of Albizia amara Suspension
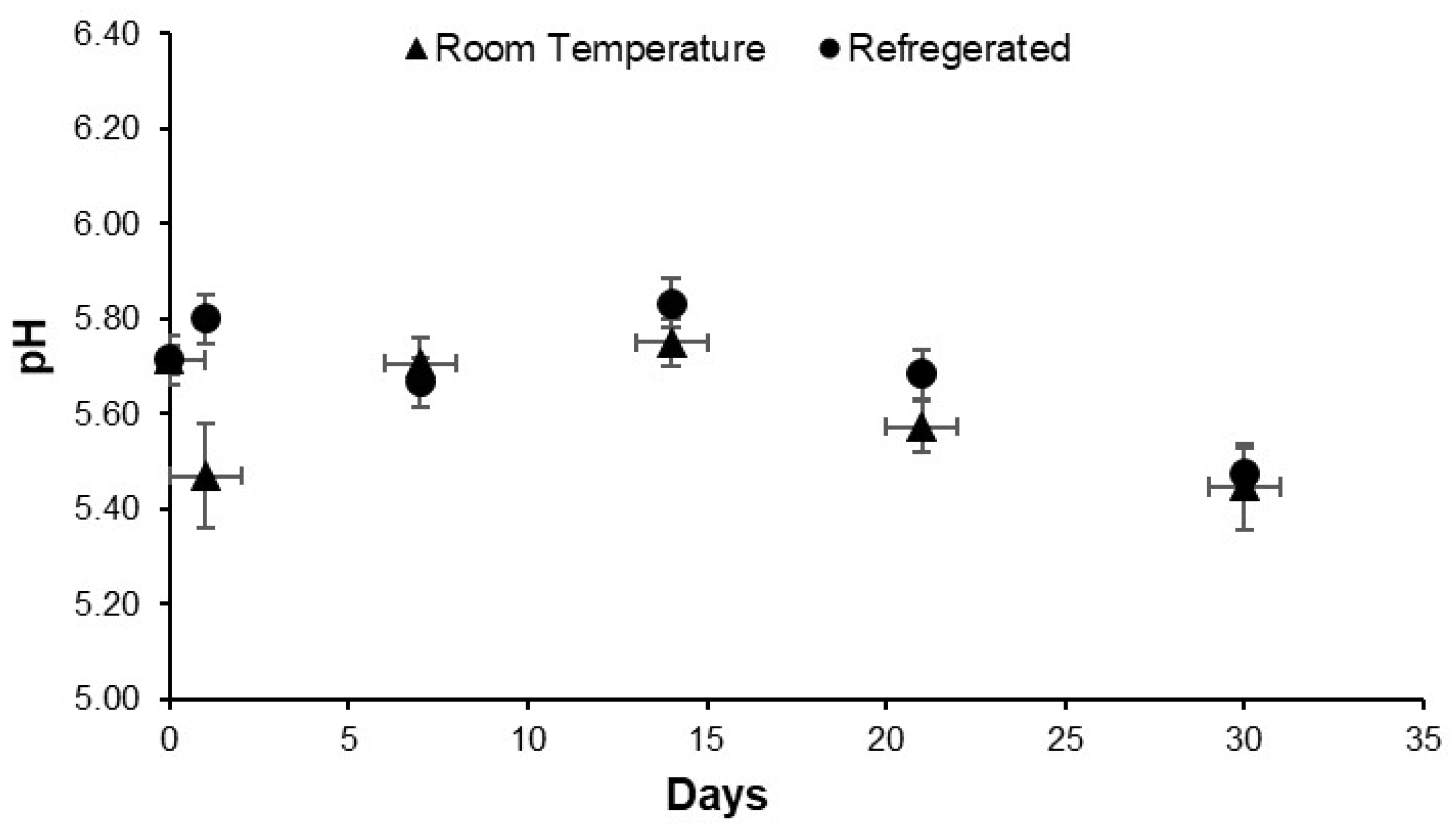
3.2. pH Measurements and Sensory Evaluation
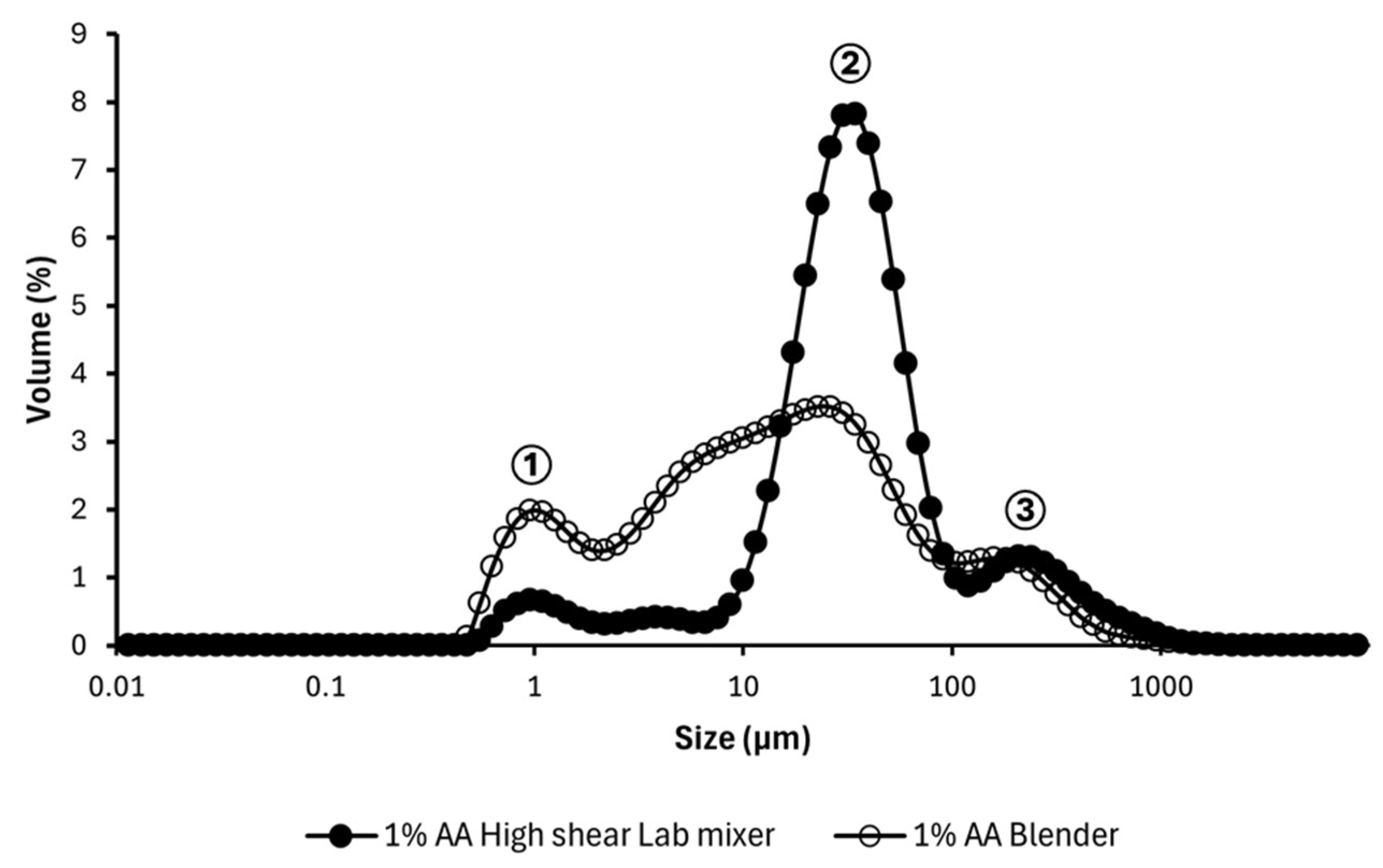
3.3. Particle Size Measurement
3.4. Apparent Surface Tension
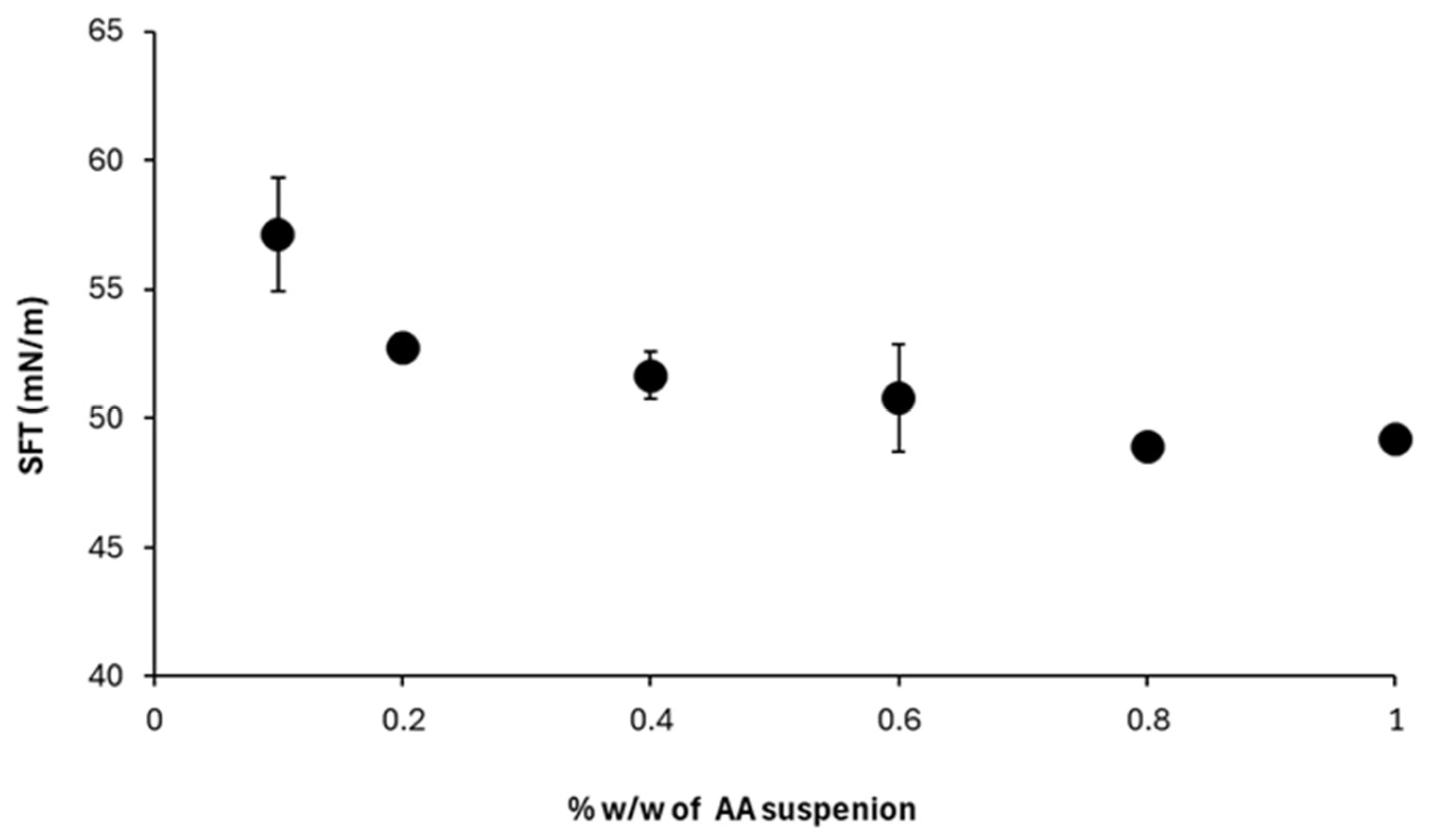
3.4.1. Apparent Surface Tension of AA Suspension vs. AA Mass Concentration
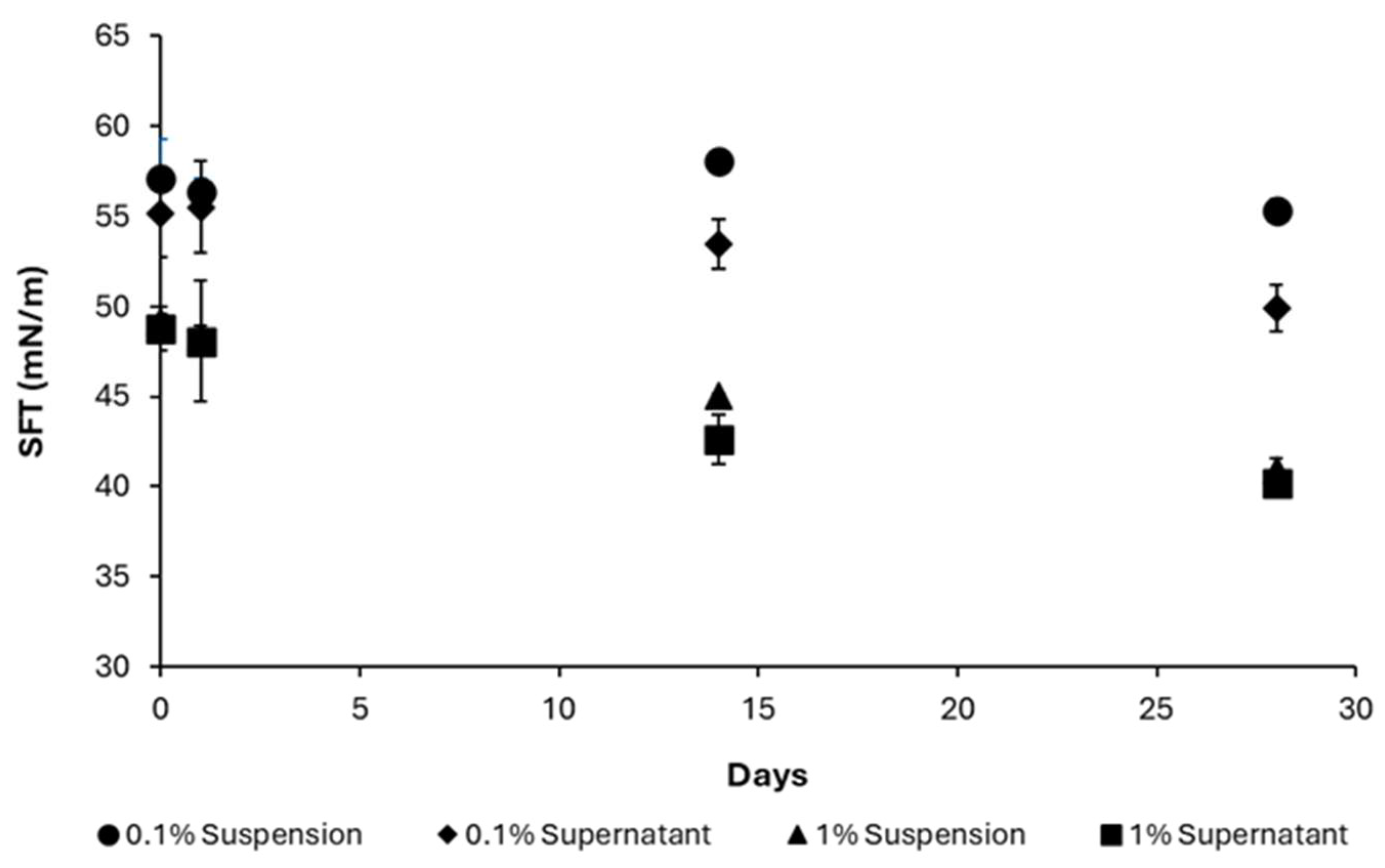
3.4.2. Stability of Apparent Surface Tension of AA Suspension
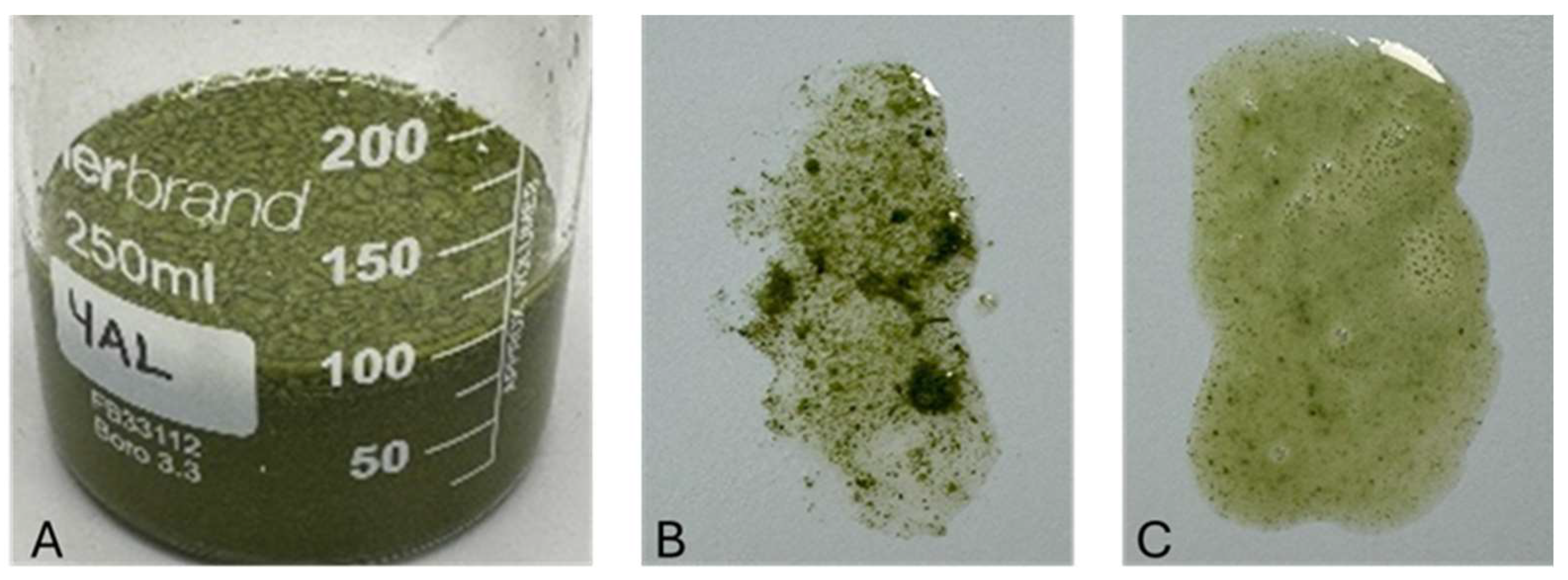
3.5. AA Emulsion
3.5.1. Emulsification Methods
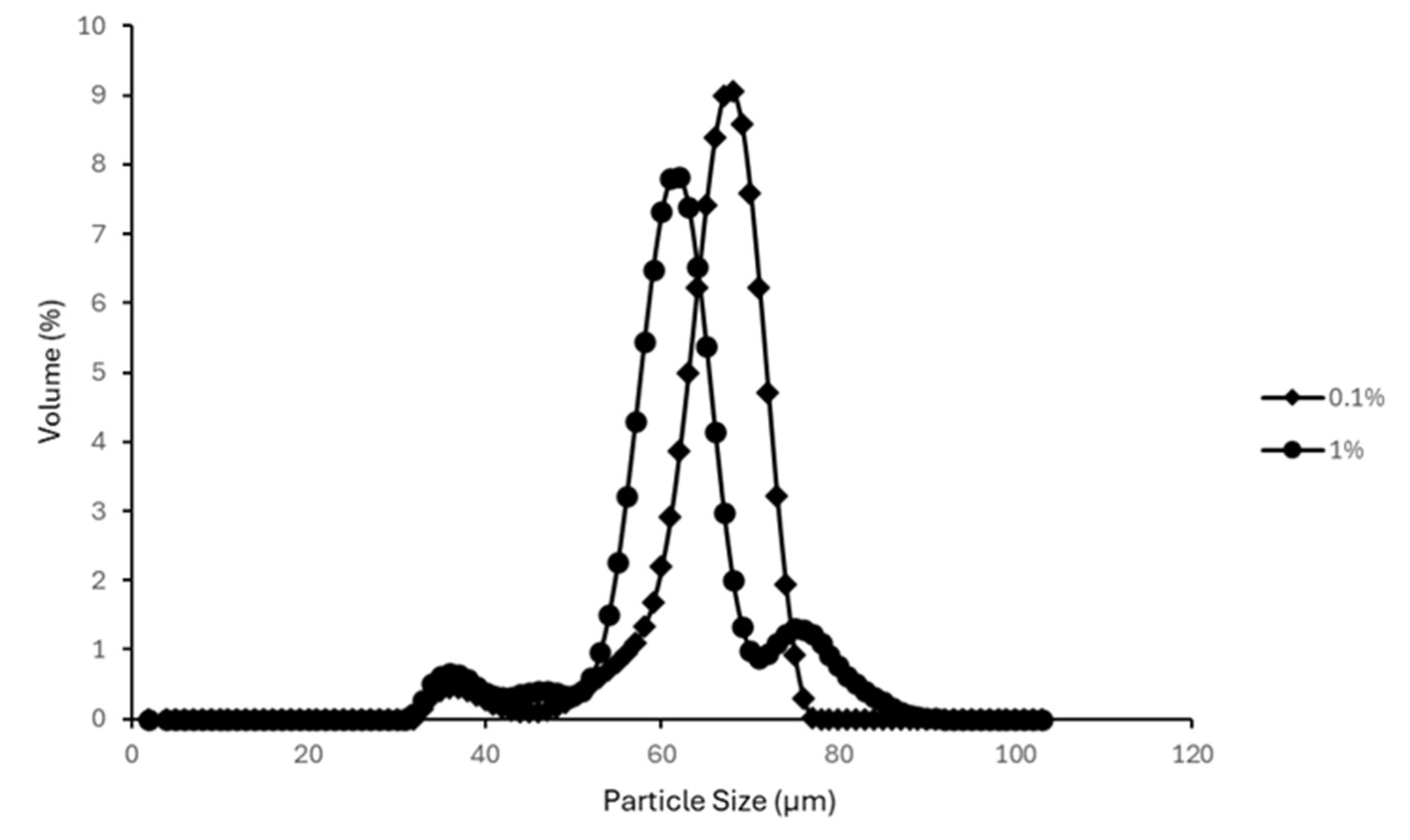
3.5.2. Oil-in-Water Emulsion Droplet Size vs. AA Suspension Amount
3.6. Microscopy of Oil-in-Water Emulsion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | Albizia amara |
| MADLS | Multiangle dynamic light scattering |
| RT | Room Temperature |
References
- Aguirre-Ramírez, M.; Silva-Jiménez, H.; Banat, I.M.; Diaz De Rienzo, M.A. Surfactants: Physicochemical interactions with biological macromolecules. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 43, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordor Intelligence. Surfactants Market Size—Industry Report on Share, Growth Trends & Forecasts Analysis (2025–2030). 2025. Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/surfactants-market (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Pradhan, A.; Bhattacharyya, A. Quest for an eco-friendly alternative surfactant: Surface and foam characteristics of natural surfactants. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 150, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asio, J.R.; Garcia, J.S.; Antonatos, C.; Sevilla-Nastor, J.B.; Trinidad, L.C. Sodium lauryl sulfate and its potential impacts on organisms and the environment: A thematic analysis. Emerg. Contam. 2023, 9, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J. Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: A rapidly increasing, long-term threat. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suran, M. A planet too rich in fibre: Microfibre pollution may have major consequences on the environment and human health. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19, e46701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, M.S.; Alvarado, J.G.; Zambrano, F.; Marquez, R. Surfactants produced from carbohydrate derivatives: A review of the biobased building blocks used in their synthesis. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2022, 25, 147–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagtode, V.S.; Cardoza, C.; Yasin, H.K.A.; Mali, S.N.; Tambe, S.M.; Roy, P.; Singh, K.; Goel, A.; Amin, P.D.; Thorat, B.R.; et al. Green Surfactants (Biosurfactants): A Petroleum-Free Substitute for Sustainability—Comparison, Applications, Market, and Future Prospects. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 11674–11699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, R.; Varsani, V.; Mehta, D.; Dudhagara, D.; Gamit, S.; Nandaniya, N.; Chaun, D.; Vala, A.; Patel, A.; Vyas, S. Biosurfactants production from plant-based saponin: Extraction and innovative applications & sustainable aspect for future commercialization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 219, 115838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.; Miyamoto, T.; Laurens, V.; Lacaille-Dubois, M.-A. Two New Biologically Active Triterpenoidal Saponins Acylated with Salicylic Acid from Albizia adianthifolia. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwa, C.; Mutua, A.; Kindt, R.; Jamnadass, R.; Simons, A. Agroforestree Database: A Tree Reference and Selection Guide Version 4.0. World Agroforestry Centre, Kenya. Available online: https://www.worldagroforestry.org/output/agroforestree-database (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Noté, O.P.; Simo, L.M.; Mbing, J.N.; Guillaume, D.; Muller, C.D.; Pegnyemb, D.E.; Lobstein, A. Structural determination of two new acacic acid-type saponins from the stem barks of Albizia zygia (DC.) J. F. Macbr. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 33, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Pan, G.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Gao, X.; Ma, B.; Kang, L. Rapid profiling and identification of triterpe-noid saponins in crude extracts from Albizia julibrissin Durazz. by ultra high-performance liquid chroma-tography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 55, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, F.A.; Simon, S.E.; Wei, Y.Y.; Woon, Y.P. Characteristic and optimized use of bioactive compounds from gloriosa superba and Albizia amara with apoptotic effect on hepatic and squamous skin carcinoma. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2018, 9, 1769. [Google Scholar]
- Tamilselvi, S.; Dharani, T.; Padmini, S.; Nivetha, S.; Sangeetha, M.; Das, A.; Balakrishnaraja, R. GC-MS Analysis of Albizia Amara and Phyla Nodiflora Ethanolic Leaf Extracts. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2018, 7, 466–473. [Google Scholar]
- Sermakkani, M.; Indira Rani, S.; Elakkiya, V.; Kali Devi, K. Studies on preliminary phytochemical, fluorescences and mineral analysis of Albizia amara leaves. World J. Pharm. Life Sci. 2021, 10, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ramya Devi, D.; Sowmiya Lakshna, S.; Veena Parvathi, S.; Vedha Hari, B.N. Investigation of wound healing effect of topical gel of Albizia amara leaves extract. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2018, 119, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, G.; Singhal, P.; Chaturvedi, S. Food Processing for increasing consumption: The Case of Legumes. In Food Processing for Increased Quality and Consumption, Handbook of Food Bioengineering; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Böttger, S.; Hofmann, K.; Melzig, M.F. Saponins can perturb biologic membranes and reduce the surface tension of aqueous solutions: A correlation? Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 2822–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleszek, W.A. Chromatographic determination of plant saponins. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 967, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Shah, R.D.; Pallewar, S. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of athanolic extracts of Inularacemosa and Albizia amara. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2010, 3, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.S.; Sucheta, S.; Sudarshana, V.D.; Selvamani, P.; Latha, S. Antioxidant activity in some selected Indian medicinal plants. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 7, 1826–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Firebaugh, J.D.; Daubert, C.R. Emulsifying and foaming properties of a derivatized whey protein ingredient. Int. J. Food Prop. 2005, 8, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Potkule, J.; Reetu; Punia, S.; Dhakane-Lad, J.; Singh, S.; Dhumal, S.; Pradhan, P.C.; Bhushan, B.; et al. Functional characterization of plant-based protein to determine its quality for food applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 106986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhi, L.; Jiao, B.; Hu, H.; Ma, X.; Agyei, D.; Shi, A. Plant protein-based emulsifiers: Mechanisms, techniques for emulsification enhancement and applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 109008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.G.; Goldenberg, B.G. Surface-active agents from two Bacillus species. J. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, U. Overview of Downstream Processing in the Biomanufacturing Industry. In Comprehensive Biotechnology, 2nd ed.; Moo-Young, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 669–682. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, K.; Sharma, R.K.; Singh, A. A Detailed pharmacological approach on Albizia amara: A Review. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Appl. 2024, 4, 1658–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Ashok, P.K.; Upadhyaya, K. Tannins are astringent. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2012, 3, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lamkin-Kennard, K.A.; Popovic, M.B. Molecular and Cellular Level-Applications in Biotechnology and Medicine Addressing Molecular and Cellular Level. In Biomechatronics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 201–233. [Google Scholar]
- Ravera, F.; Dziza, K.; Santini, E.; Cristofolini, L.; Liggieri, L. Emulsification and emulsion stability: The role of the interfacial properties. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 288, 102344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, D.; Hu, J. Effect of Surfactant molecular structure on emulsion stability investigated by interfacial dilatational rheology. Polymers 2021, 13, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachechen, L.S.; Silva, J.O.; Barbosa, L.R.S.; Itri, R.; Petri, D.F.S. Hofmeister effects on the colloidal stability of poly(ethylene glycol)-decorated nanoparticles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dossoki, F.I.; Gomaa, E.A.; Hamza, O.K. Solvation thermodynamic parameters for sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and sodium lauryl ether sulfate (SLES) surfactants in aqueous and alcoholic-aqueous solvents. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, K.G.O.; Silva, I.G.S.; Almeida, F.C.G.; Rufino, R.D.; Sarubbo, L.A. Plant-derived biosurfactants: Extraction, characteristics and properties for application in cosmetics. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 34, 102036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Basu, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Chowdhury, R. Optimization of evaporative extraction of natural emulsifier cum surfactant from Sapindus mukorossi—Characterization and cost analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 77, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routray, A.; Das, D.; Parhi, P.K.; Padhy, M.K. Characterization, stabilization, and study of mechanism of coal-water slurry using Sapindous mukorossi as an additive. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2018, 40, 2502–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhefian, E.A. Investigation on Some Properties of SDS Solutions. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2011, 5, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, S.; Cooke, M.; El-Hamouz, A.; Kowalski, A. Droplet break-up by in-line Silverson rotor–stator mixer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 2068–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiri, I.; Smith, P.; Norton, I.; Spyropoulos, F. Fabrication, characterisation and stability of oil-in-water emulsions stabilised by solid lipid particles: The role of particle characteristics and emulsion microstructure upon Pickering functionality. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, K.; Hanewald, A.; Vilgis, T.A. Milk Emulsions: Structure and Stability. Foods 2019, 8, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krog, N. Emulsifiers and Emulsions in Dairy Foods. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences; Roginski, H., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 891–900. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Mahto, V. Emulsification of Indian heavy crude oil using a novel surfactant for pipeline transportation. Pet. Sci. 2017, 14, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laben, A.B.; Kayiem, H.H.A.; Alameen, M.A.; Khan, J.A.; Belhaj, A.F.; Elraies, K.A. Experimental study on the performance of emulsions produced during ASP flooding. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2022, 12, 1797–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banat, M.; Makkar, R.S.; Cameotra, S.S. Potential commercial applications of microbial surfactants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 53, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerk, T.R.; Severino, P.; Jain, S. Biosurfactants: Properties and applications in drug delivery, Biotechnology and Ecotoxicology. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.W.; Gao, P. Emulsions and Microemulsions for Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery. In Handbook of Non-Invasive Drug Delivery Systems; Kulkarni, V.S., Ed.; Personal Care & Cosmetic Technology; William Andrew Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 59–94. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, R.J.; Godínez, L.A.; Robles, I. Waste Resources Utilization for Biosorbent Preparation, Sorption Studies, and Electrocatalytic Applications. In Valorization of Wastes for Sustainable Development; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 395–418. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Niu, Q.; Lan, Q.; Sun, D. Effect of dispersion pH on the formation and stability of pickering emulsions stabilized by layered double hydroxides particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 306, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fong, W.; Sadasivam, Y.; Belkhiri-Baines, A.; Pinfield, V.; Trybala, A. Evaluating Raw Albizia amara Plant Powder as a Plant-Derived Surface-Active Material. Colloids Interfaces 2025, 9, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9060081
Fong W, Sadasivam Y, Belkhiri-Baines A, Pinfield V, Trybala A. Evaluating Raw Albizia amara Plant Powder as a Plant-Derived Surface-Active Material. Colloids and Interfaces. 2025; 9(6):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9060081
Chicago/Turabian StyleFong, Wenghong, Yalini Sadasivam, Awatif Belkhiri-Baines, Valerie Pinfield, and Anna Trybala. 2025. "Evaluating Raw Albizia amara Plant Powder as a Plant-Derived Surface-Active Material" Colloids and Interfaces 9, no. 6: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9060081
APA StyleFong, W., Sadasivam, Y., Belkhiri-Baines, A., Pinfield, V., & Trybala, A. (2025). Evaluating Raw Albizia amara Plant Powder as a Plant-Derived Surface-Active Material. Colloids and Interfaces, 9(6), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9060081








