Abstract
Like other proteins, the natural silk fibroin (SF) extracted from domesticated silkworms can adsorb at the air/water interface and stabilize foam due to its amphiphilic character and surface activity. At the interface, the adsorbed SF molecules experience structural reorganization and form water-insoluble viscoelastic films, which protect foam bubbles from coalescence and rupture. The solution conditions, such as protein concentration, pH, and additives, have significant influences on the molecular adsorption, layer thickness, interfacial mechanical strength, and, thus, on the foaming properties of SF. The understanding of the relationship between the interfacial adsorption, surface viscoelasticity, and foaming properties of SF is very important for the design, preparation, and application of SF foams in different fields.
1. Introduction
Foam is a gas-in-liquid dispersion with gas bubbles separated by thin liquid films. These thin liquid films are thermodynamically instable and will rupture eventually due to drainage and van der Waals attractions, thus leading to foam collapse. Foam can be stabilized by amphiphilic proteins or low-molecular-weight surfactants, which can adsorb at the air/water interface and protect the gas bubbles against coalescence. Compared with surfactants, proteins usually form thicker adsorbed layers and endow the foam with higher stability, although they adsorb more slowly and result in larger bubble size [1]. Generally, the foaming properties can be quantified in terms of foamability and foam stability. Foamability is defined as the capacity of the continuous phase to entrap gas and depends on the rate of diffusion and interfacial adsorption of surface-active molecules [2]. Foam stability is the ability to retain the gas for a certain period of time, and relates to the thickness, mechanical strength, and molecular interactions of the adsorbed layers [3]. The mechanical resistance of the surface films to shear and dilatational deformations counteracts bubble coalescence caused by film drainage and rupture. Therefore, understanding the relationships between the adsorption, surface viscoelasticity, and foaming properties of proteins at the air/water interface is very important for the design, preparation, and stability control of foams stabilized by proteins.
It is commonly agreed that not only the intrinsic molecular properties but also the solution conditions such as protein concentration, pH, and additives remarkably affect the interfacial adsorption, film formation, and thus the foam stability [4,5]. High protein concentrations can lead to the formation of a multilayer of globular proteins and, thus, enhance the foam stability [6]. At pH near the isoelectric point (pI), proteins usually show poor foaming properties because of their strong hydrophobic interactions in the formed surface films [4,7,8]. Acidic pH can help some proteins adsorb much faster and give a higher elastic modulus by dissociating into small subunits with better flexibility [4,9]. Even at the same pH, different proteins exhibit different foamability due to the difference in adsorption and unfolding rates [10]. The charge of proteins also plays an important role in their adsorption and foaming properties [11,12], and reduced electrostatic repulsion between molecules at the interface can improve the foam stability [2,13]. Salts with different ions can alter the effective surface charge of proteins by interacting with the amino acids, and then change the conformation and molecular interactions of proteins and the formation and stability of surface films [5]. Increasing ion valence or concentration in a certain range can enhance the protein adsorption and the foam stability, due to the decrease in net surface charge, the promotion of protein–protein interactions and the increase in surface dilatational elasticity [5,11,14]. For example, lysozyme in its native state forms a fragile monolayer film, but the addition of NaNO3 leads to a thick and strongly viscoelastic film, in which lysozyme transforms its secondary structure from helix to β sheet [15]. Similar to salts, surfactants can also accelerate the interfacial adsorption and enhance the foamability of proteins. However, a competitive adsorption exists between proteins and surfactants, which may result in the decrease in the interfacial modulus and foam stability [16,17,18]. Different surfactants exhibit different competitive adsorption effects on some proteins [19]. The displacement of β-lactoglobulin (β-LG) by the anionic sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) can be described by the nucleation of surfactant domains at the foam bubble surfaces without significant domain growth. In contrast, the displacement of β-LG by nonionic Tween 20 surfactants includes both nucleation and growth of surfactant domains, with the rupture of protein networks and the disappearance of shear elasticity [18,20]. Although Tween 20 decreases the surface dilatational modulus of soy globulins because of competitive adsorption, it accelerates their interfacial adsorption and improves the foamability and foam stability [16,17]. The interfacial interactions between proteins and surfactants are driven not only by their surface activity, but also by the abilities of proteins to form networks [16].
Silk fibroin (SF), a natural protein extracted from domesticated silkworms, has attracted great attention in various biomedical fields due to its unique mechanical properties, excellent biocompatibility, and low immunogenicity [21,22,23]. As a kind of fibrous structural protein with the components of amino acids glycine, alanine, and serine, SF can arrange into different forms of random coil, α-helix, and crystalline β-sheet [23], and can be processed into different forms of film, gel, membrane, powder, and porous sponge as well [24,25]. Due to the existence of highly repetitive amino acid sequences with alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic blocks along the molecular chains, SF exhibits an amphiphilic character and can adsorb at interfaces between water and hydrophobic media (such as air or oil) to form stable viscoelastic films [26]. Using a combination of transmission electron microscopy and electron diffraction techniques, it was found that SF at the air/water interface exhibits a silk Ⅲ conformation, an approximately hexagonal packing of protein molecules in a left-handed threefold helical chain conformation [27].
Like other proteins, SF can also form viscoelastic protective films at the air/water interface and stabilize foam. SF foams were successfully utilized to prepare some special and functional materials for creative investigations and biomedical applications. SF foam can produce single crystals of SF in the metastable silk Ⅰ polymorph after being dried and sonicated [28]. The injectable SF foams fabricated by using low-pressure nitrous oxide gas or freeze-processing techniques allow SF to support tissue regeneration as a porous bioactive degradable filler [29,30]. It was demonstrated that the freeze-dried microporous SF foams are useful for constructing long-term controlled drug release systems [31,32]. Through a new method of compressing the SF foams, the porous SF membranes can be obtained for tissue scaffolding applications [33]. The production of stable SF foams is very important for their applications. As mentioned above, the foamability and foam stability of SF are closely related to its interfacial adsorption and the mechanical resistance of its interfacial films. In this review, we present a summary about the state of the art on the adsorption, surface viscoelasticity, and foaming properties of SF at the air/water interface with the effects of different solution conditions. The techniques of dynamic surface tension measurements as well as surface dilatational and interfacial shear rheology provide a lot of important information on the molecular interactions during adsorption, the mechanical strength of adsorbed layers, and the long-term foam stability [1]. The insights gained can provide a basis for the design, preparation, and application of biocompatible SF foams.
2. Preparation and Features of Aqueous Silk Fibroin Solution
Aqueous SF solutions are typically prepared from fresh domestic Bombyx mori cocoon shells by sericin extraction, cocoon fiber dissolution, and solution dialysis. They are then diluted with the solutions at different solution conditions to the desired concentration (CSF) [34,35,36,37]. The pI of SF, at which the zeta potential vanishes, was determined to be 4.2 [7]. This means that SF should be negatively charged in aqueous solution at neutral state. The average hydrodynamic diameter (Dhyd) of SF shows a minimum at pH 7 and a maximum at pH 4 (Figure 1). When the solution pH changes from neutral to acidic values, the neutralization of side chain carboxyl groups via protonation [38] leads to the decrease in electrostatic repulsion and solubility, thus promoting the formation of large SF aggregates. At pH 4 close to the pI, SF exhibits the lowest solubility and the largest aggregates [35].
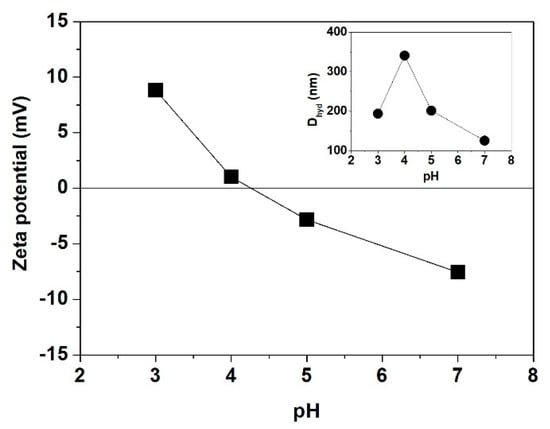
Figure 1.
Dependence of the Zeta potential of SF on pH. The inset plot shows the hydrodynamic diameter (Dhyd) of SF aggregates at different pH (taken from [35]).
3. The Adsorption of Silk Fibroin at the Air/Water Interface
3.1. Ellipsometry
The thickness of the adsorbed layers formed at the air/water interface can be determined by ellipsometry. The adsorption of proteins usually experiences several steps, including diffusion to the interface, surface adsorption, structural reorganization, and spreading at the surface [39]. During adsorption, the layer thickness of SF gradually increases and then becomes steady when saturation is reached. Clearly, the amphiphilic SF adsorbs to the air/water interface and forms surface layers. The thickness of SF layers is much higher than that of soy protein isolates [40], but slightly lower than that of soy protein fibrils (SPF) [41]. Variations in the equilibrium thickness (δe) (Figure 2) arise from a subtle balance between molecular size, shape, surface charge, and surface hydrophobicity [41].
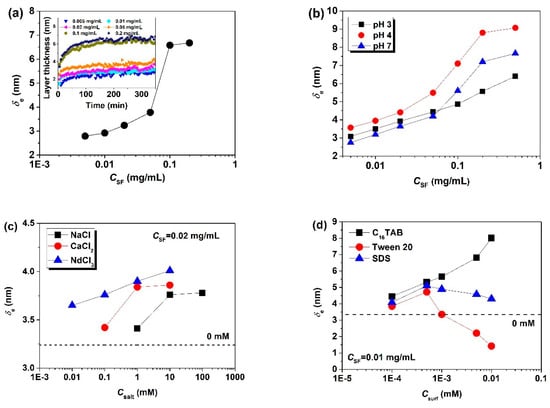
Figure 2.
Influences of solution conditions on the equilibrium thickness (δe) of the adsorbed layers formed by SF at the air/water interface: (a) influence of CSF; (b) influence of pH; (c) influence of salts; (d) influence of surfactants (taken from [34,35,36,37]).
Irrespective of the pH, δe is larger at higher CSF. High CSF helps to promote the packing density, but at small or saturated adsorption the effect of CSF weakens [34]. In addition, δe is higher at pH 4 than at pH 3 and pH 7, due to the lack of electrostatic repulsion near the pI and the resulting denser accumulation of SF molecules at the interface [35]. δe depends not only on the electrostatic repulsion but also on the protein conformation and flexibility, especially at high CSF. At pH 7, the smaller aggregate size and higher molecular flexibility make SF reorganize and pack at the interface more efficiently than at pH 3. When salt is added, δe becomes thicker and increases with the salt concentration (Csalt) and the ion valence from NaCl to NdCl3 [36]. SF in aqueous solution is negatively charged at neutral pH, and the counter-ion screening effect of salt significantly reduces the electrostatic repulsion between SF molecules, thus causing a gradual molecular aggregation in the bulk and at the interface. In addition, the increasing ion valence further enhances the molecular interactions within the layers and, thus, the thickness of adsorbed layers. The incorporated surfactants remarkably enhance the surface activity of SF: δe increases much more strongly and attains equilibrium at much lower CSF. Moreover, δe exhibits different dependence on the surfactant concentration (CSurf) for different surfactant types within the studied range, increasing with CSurf for C16TAB, but exhibiting a non-monotonic behavior for Tween 20 and SDS [37]. Due to electrostatic attraction, the cationic C16TAB and negatively charged SF can form complexes which co-adsorb in a very dense way and maximize the adsorbed amount. However, due to electrostatic repulsion, the anionic SDS can merely fill up SF-free defects and increase δe only slightly. The adsorbed layers formed by surfactants are usually thinner than those formed by proteins. Therefore, when CSurf exceeds a critical value, SDS and Tween 20 make the interfacial layers become thinner due to increasing competition in the adsorption layer, the growth of surfactant domains and the breakage of protein networks. The faster decline in δe for Tween 20-mixed solutions should be attributed to the higher surface activity and stronger competition of Tween 20 (its critical micelle concentration (~0.05 mM [42]) is much lower than that of SDS (~8 mM [43]).
3.2. Surface Tension
The dynamics of adsorption of SF at the air/water interface can be investigated by measurements of the surface tension (σ) as a function of the adsorption time (tad) under different solution conditions (Figure 3). When CSF ≤ 0.002 mg/mL, there is no obvious adsorption of SF and σ shows a plateau value close to that of pure water [34]. At sufficiently low CSF and short tad, changes in the adsorbed amounts usually do not directly lead to changes in σ, and this time range of negligible σ changes is called induction period (tind) [44]. When CSF exceeds 0.002 mg/mL, σ begins to decrease immediately until the equilibrium surface tension (σeq) is reached [34,35,36]. The initial rapid decrease in σ is related to the adsorption of SF, and the following slow change of σ is more related to the structure formation of adsorption layers. The time for σ to reach equilibrium is around 6 h for SF [34], much longer than that for β-LG [5], gliadin nanoparticles (GNPs) [8], or amaranth protein isolates [4] at comparable bulk concentrations, indicating that SF needs more time to complete the structural reorganization into gelled β-sheets during the formation of water-insoluble films [45]. SF shows a lower σeq and a much shorter tind [35,36] than ovalbumin (OVA) with its more compact and rigid structure [10,46], but a higher σeq than the highly hydrophobic bovine serum albumin (BSA) and the more deformable wheat protein fractions [46]. Obviously molecular size, structure, and hydrophobicity of proteins significantly influence their adsorption characteristics at interfaces. A lower degree of ordering, higher hydrophobicity, and stronger molecular flexibility can increase the surface activity of proteins and accelerate their adsorption.
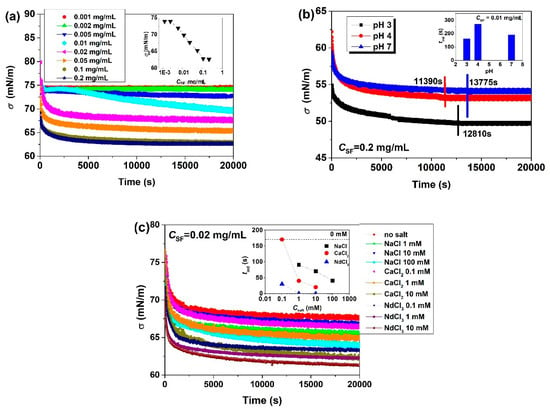
Figure 3.
Influences of solution conditions on the surface tension (σ) of SF solutions at the air/water interface: (a) influences of CSF; (b) influences of pH; (c) influences of salts. The inset plots are the effects of CSF, pH and Csalt on the equilibrium surface tension (σeq) and induction time (tind) (taken from [34,35,36]).
Increasing CSF leads to lower σeq and faster establishment of equilibrium, but σeq shows no further decrease at CSF ≥ 0.1 mg/mL when adsorption saturation is reached [34]. Therefore, the surface can only accommodate a limited number of SF molecules. Increasing CSF also causes a decrease in tind. The initial adsorption of SF at the interface is controlled by diffusion and thus by the aggregate size, while the consecutive steps are controlled by intermolecular interactions at the interface. With that, both molecular flexibility and surface charge are of great importance for this later adsorption stage. σ and tind show the same ranking of pH 4 > pH 7 > pH 3 [35]. At pH 4, the large aggregate size decelerates the diffusion, thus resulting in a longer tind and slower decrease in σ. At pH 7, although the size of SF aggregates is smaller than at pH 3, the electrostatic barrier interferes with the interfacial adsorption [47,48] and then causes a slower decrease in σ as compared to pH 3. The addition of salt effectively reduces the electrostatic repulsion between SF molecules and, thus, the energy barrier to SF adsorption. As a consequence, both σ and tind decrease with increasing Csalt and ion valence [36]. Obviously, the surface activity of SF is remarkably promoted in the presence of salt, and salt addition not only accelerates the diffusion but also enhances the interfacial adsorption of SF molecules.
4. The Surface Viscoelasticity of Silk Fibroin Adsorption Layers at the Air/Water Interface
The mechanical surface properties of adsorbed SF layers at the aqueous solution/air interface are subject to compression/expansion as well as to shear deformations. Both types of surface perturbations provide important information on the mechanical behavior of the SF adsorption layers in the process of foam formation and against foam destabilization. A general introduction into the surface viscoelasticity of adsorbed layers was given in Ref. [49].
4.1. Surface Dilatational Rheology
E’ of SF (Figure 4) is much larger than that of β-LG [14], whey globular proteins [50] and soy globulins [51], revealing that the adsorbed SF layers formed by densely packed β-sheets [52] possess stronger mechanical strength than those of other proteins. The dependence of E’ on CSF is insensitive to frequency, and E’ exhibits a maximum at CSF = 0.02~0.05 mg/mL [34]. Additionally, human serum albumin (HSA) [53], β-casein (BCS) [53], and alkaline protease [54] exhibit such non-monotonic-behavior-featuring maxima. High CSF enhances surface adsorption and increases E’. Nevertheless, when CSF exceeds a critical value, interfacial SF molecules reach a jamming state and can no longer reorganize well into ordered elastic networks [55], thus leading to a decrease in E’ [34]. At high CSF, E’ is larger at pH 7 and decreases with CSF at pH 3 and especially at pH 4 [35]. It seems that neutral pH is advantageous for forming strong interfacial networks [56]. At pH 7, due to electrostatic repulsion, SF molecules adsorb gradually and have more space for the conformational rearrangements required to form strong networks. In contrast, at pH 4, due to the strong hydrophobic interactions, a jamming state is rapidly reached, and the formation of a rigid network does not occur. In the presence of salt, E’ remarkably increases with Csalt at CSF ≤ 0.01 mg/mL, but begins to decrease with Csalt and ion valence for CSF ≥ 0.02 mg/mL [36]. Obviously, the added salts strengthen the molecular interactions and increase E’ by screening electrostatic repulsion [57]. However, the reduction in electrostatic repulsion concurrently enhances the hydrophobic interactions and causes possible SF aggregation, similar to the results observed at pH near pI. Therefore, with the increase in the ionic strength, the enhanced SF accumulation at the air/water interface leads to thicker adsorbed layers and higher E’ at low CSF, but to weaker networks and lower E’ at high CSF because of the imperfect molecular reorganization at the crowded interface [55]. To conclude, at high CSF, low ionic strength is beneficial for the SF molecules to form stronger interfacial networks.
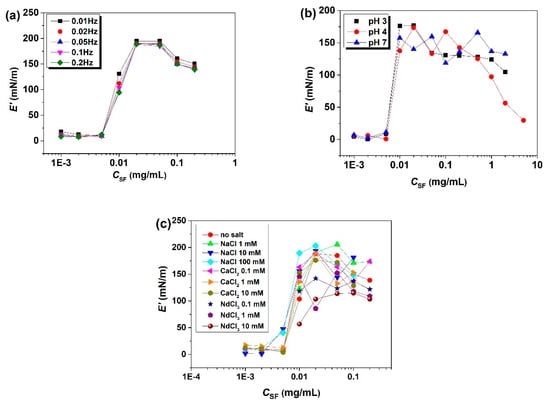
Figure 4.
Influences of the solution conditions on the surface dilatational elastic modulus (E’) of the SF layers formed at the air/water interface after reaching adsorption equilibrium: (a) influences of CSF; (b) influences of pH at 0.1 Hz; (c) influences of salts at 0.1 Hz (taken from [34,35,36]).
4.2. Surface Shear Rheology
Through surface shear rheology measurements, the time dependence of the viscoelastic parameters of storage modulus (G’) and loss modulus (G”) can be obtained and utilized to analyze the formation and stability of interfacial layers (Figure 5). The values of G’ of SF layers increases first rapidly and then gradually with the adsorption time and cannot attain a steady state even after 24 h [34]. As for SF, the structural reorganization and network formation are remarkably slower than the molecular diffusion and adsorption, thus making G’ increase slowly and reach equilibrium with more difficulty at a later stage. However, in the presence of salts and surfactants, the surface activity of SF is significantly enhanced, and G’ reaches a plateau rapidly, especially in the presence of salts within 3 h [36,37]. As mentioned above, the presence of salt remarkably decreases the electrostatic repulsion and accelerates the molecular diffusion, adsorption, and structural reorganization of SF at the interface [36]. Due to their low molecular weight, the added surfactant molecules can diffuse, adsorb, and reorganize much faster than the SF molecules at the interface, thus greatly shortening the time to establish adsorption equilibrium [37]. Compared with the proteins of bovine serum albumin (BSA) and bovine gamma globulin (BGG), SF needs much more time to form stable surface networks and shows almost one order of magnitude higher G’ values [16]. Hence, the viscoelastic networks formed by fibrous SF are much stronger than those formed by globular BSA and BGG, and the surface layers of SF can be expected to be more resistant against external perturbations and contribute to a higher foam stability. For all solution conditions, the magnitude of G’ is significantly larger than that of G”, implying that the SF molecules can form elastic surface gels at the interface by physical crosslinks [34,36,37]. With the increase in CSF, the rapid increase in G’ at low CSF changes to a slow increase at high CSF, which indicates that high CSF helps to increase both the surface coverage and the mechanical strength of the adsorbed layers [34]. Similar to the equilibrium of E’, the equilibrium value of G’ (Ge’) gradually decreases with increasing Csalt [36]. At high CSF, although added salt enhances the hydrophobic interactions and interfacial adsorption of SF, the more crowded adsorbed SF molecules are unable to establish highly ordered and tight networks, thus resulting in a decrease in Ge’. The competitive adsorption of surfactants also interferes with the structural reorganization and interfacial gel formation of SF [37]. The rapid arrangement of surfactants at the interface, termed as the “orogenic” displacement mechanism [16], will preempt the formation of robust SF networks. The cationic C16TAB remarkably reduces the surface charge and promotes the aggregation of SF, such that it cannot form tightly packed networks, leading to an initial fast decrease in Ge’. However, with the charge neutralization and upon approaching the pI, the cross-linked SF networks become stronger [58] and prevent the adsorption of C16TAB, which, therefore, has only a weak impact [37]. When Csurf is above 0.001 mM, the decrease in Ge’ in the presence of the nonionic Tween 20 exceeds that of C16TAB [37]. The anionic SDS shows a weak ability to replace SF, and the possibly formed SF-SDS complexes make the mixture more hydrophilic and less surface active [59].
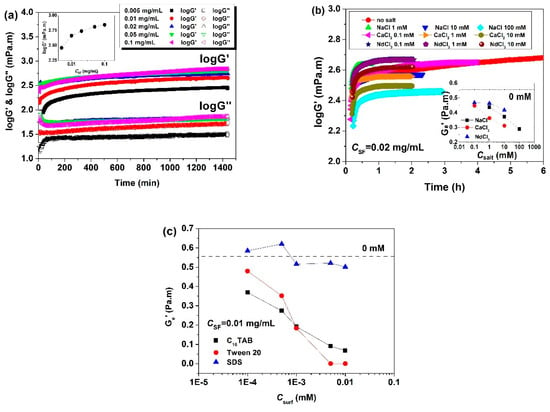
Figure 5.
Influences of the solution conditions on the (equilibrium) surface shear moduli of adsorbed SF layers at the air/water interface: (a) influences of CSF; (b) influences of salts; (c) influences of surfactants. G’ in the inset plot of (a) is obtained after 24 h, and the dashed horizontal line in the inset plots of (b) and (c) indicates the value for a pure SF solution without any added surfactant (taken from [34,36,37]).
4.3. Nonlinear Fracture of SF Surface Layers
Strain (γ) sweeps are useful for evaluating the nonlinear fracture of SF layers formed at the air/water interface (Figure 6). During the strain sweeps, interfacial SF layers exhibit a linear behaviour with a constant G’ at low γ, and then a nonlinear behaviour is observed with a continuous decrease in G’ with increasing γ due to the structural fracture [34]. The degree of structure fracture (ηf) can be calculated via ηf = (G’0 − G’γ)/G’0 × 100%, where G’γ represents the elastic modulus at a certain γ and G’0 represents the initial constant elastic modulus at low γ [32]. High CSF enhances the elasticity of interfacial layers and their abilities to resist against nonlinear breakage, and ηf decreases with increasing CSF. However, this enhancement effect declines with the increase in γ, and all SF layers are fully broken at γ ≥ 15% [34]. In the presence of salts, ηf increases with γ and decreases with Csalt, and the adsorbed SF layers are still partially intact even at γ = 25% [36]. Obviously, the added salt indeed improves the interfacial toughness of SF layers, although it decreases the interfacial strength of SF layers in terms of E’. The increase in interfacial toughness may be attributed to the binding of ions to the functional groups of SF and the resultant enhanced molecular interconnection. However, high-valent ions cause an increase in the brittleness of SF layers, and ηf is lower for NaCl than for CaCl2 and NdCl3 [36]. As mentioned above, interfaces covered by surfactant molecules are more expandable than those covered by protein molecules, and the incorporated surfactants endow the SF layers with better toughness and markedly decrease ηf. Nevertheless, at high Csurf, the excessive interfacial adsorption of surfactant molecules reduces the bond density of SF networks, resulting in a decreasing ηf with Csurf [37]. Different from Tween 20 and SDS, C16TAB promotes SF aggregation by charge neutralization, and large SF aggregates cannot pack tightly to form strong interfacial SF networks, which makes ηf exceed that of pure SF when Csurf ≥ 0.001 mM [37]. Among the three surfactants, SDS shows the lowest ηf and inconspicuous sacrifice of strength, and it appears to be a promising additive to improve the foaming properties of SF solutions.
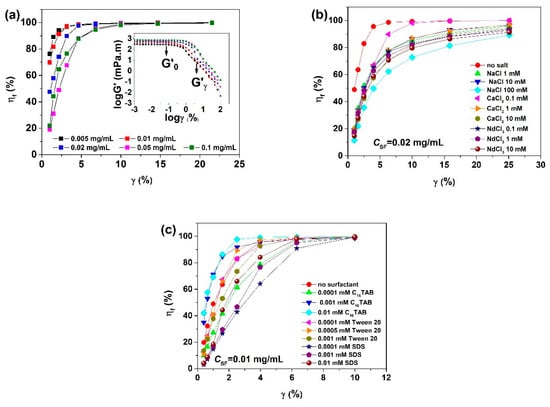
Figure 6.
Change of the degree of structure fracture (ηf) with strain (γ) for equilibrium adsorbed SF layers formed at the air/water interface under different solution conditions: (a) influences of CSF; (b) influences of salts; (c) influences of surfactants. The inset in (a) is the double-logarithmic plot of the interfacial shear storage modulus (G’) versus shear strain (γ) (taken from [34,36,37]).
5. The Foaming Properties of Aqueous Silk Fibroin Solutions
5.1. Foamability
SF foams can be easily prepared by the bubbling method through injection of air into different SF solutions through a porous glass frit. The minimum protein concentration required to generate foam with aqueous SF solutions is 0.1 mg/mL [34], 100 times lower than that for rigid globular ovalbumin and glycinin (above 10 mg/mL) [10]. This indicates the superior foamability of SF with its high flexibility and fast molecular adsorption. Foams are thermodynamically unstable systems. It is clear that SF can be a stabilizer for foams although the final “stable” volume fraction is not very large. The surface activity promotes SF to generate the foam, and the adsorbed SF layers with a high G’ help maintain the foam structure through mechanical protection against bubble coalescence and rupture. The foamability of SF was quantified in terms of the foaming rate (Kf) by dividing the foam height by the time at a constant air flow (Figure 7). Kf is around 140 mm/min when CSF < 0.2 mg/mL, and then decreases to approximately 120 mm/min for CSF = 1 mg/mL [34]. Moreover, Kf is lower at pH 4 than at pH 3 and pH 7 [35]. Just as mentioned above, the SF molecules need more time to reach equilibrium when forming surface layers at high CSF, and the larger aggregate size at pH 4 may slow down the diffusion and adsorption of SF molecules at the interface and then the formation of the foam. The incorporated surfactant obviously accelerates the foaming of SF solutions [37], because small surfactant molecules can diffuse and adsorb to the interface much faster than the big protein molecules [3]. However, the cationic C16TAB induces SF aggregation, slows down the SF adsorption, disturbs the SF network formation, and then decreases the foamability. As the concentration of C16TAB reaches 0.005 mM, the foam decays while being generated, and cannot completely fill up the glass cylinder [37].
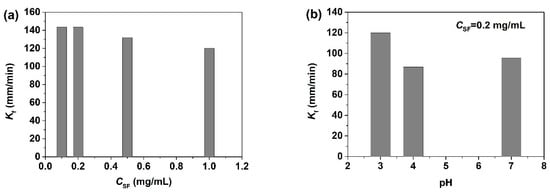
Figure 7.
Change of the foaming rate of SF solutions under different solution conditions: (a) the influence of CSF, (b) the influence of pH (taken from [34,35]).
5.2. Foam Stability
After the air injection was stopped, the SF foam started to collapse until reaching a steady state without any obvious changes in volume (Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10). During collapse, greatly different from GNPs [8] and β-LG fibrils [4], SF foam does not have a flat surface and even collapses from inside, which makes it difficult to quantify the accurate volume of SF foam at different times. In addition, some elastic fiber meshes with filamentous structures appear and adhere to the cylinder wall due to the favorable interactions between SF and glass [34]. This phenomenon implies that even when the gas diffuses out, some SF layers do not break and still retain their strong interconnected network structures with weak mobility. Nevertheless, with the increasing addition of C16TAB and Tween 20, the SF fiber meshes gradually decrease, and even visually disappear when Csurf is above 0.005 and 0.01 mM, respectively [37]. The fracture of interfacial SF networks should be attributed to the SF aggregation caused by the electric screening effect of C16TAB and the displacement of SF by growing Tween 20 domains.
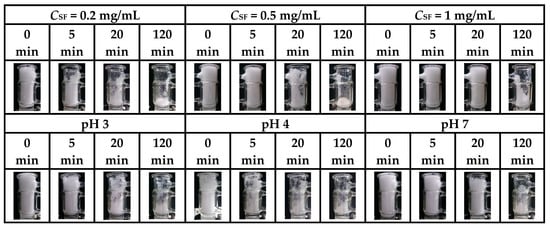
Figure 8.
Photographs of foams fabricated by SF aqueous solutions with different CSF and by 0.2 mg/mL SF buffer solutions at different pH taken at different times immediately after foam preparation (taken from [34,35]).
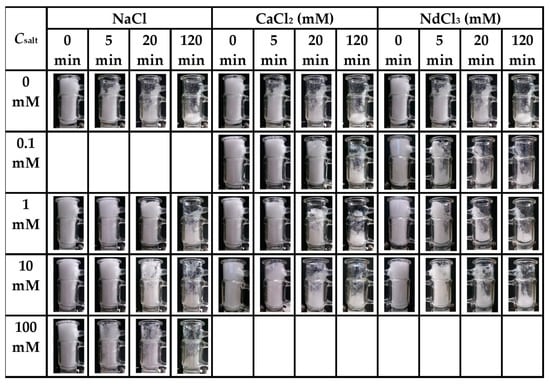
Figure 9.
Digital photographs of foams fabricated from 0.2 mg/mL SF solutions in presence of different salt types and concentrations taken at various times after the foaming process was terminated (taken from [36]).

Figure 10.
Digital photographs of foams generated from 0.2 mg/mL SF solutions in absence and presence of various types and amounts of surfactants taken at different times immediately after foam preparation (taken from [37]).
Increasing CSF helps to stabilize the foam, with slower foam collapse and larger stable foam fraction [34]. The foamability strongly depends on the diffusion and adsorption of proteins to the interface, while the foam stability strongly depends on the elasticity of the surface films. At higher CSF, although Kf is slightly lower, the intermolecular interactions become stronger and more tightly packed networks form at the interface, which significantly enhance the mechanical strength of the surface films and, thus, the foam stability. The foams prepared at pH 3 and pH 7 exhibit a denser structure and a larger stable volume fraction than those prepared at pH 4 [35], similar to sodium caseinate (Na-cas) showing higher foam stability at neutral pH than at pI [60]. At pH 4, which is near the pI, the lower solubility and enhanced aggregation prevent SF from forming fine, homogeneous, and stable bubbles, while at pH 7, higher solubility, thicker layers, and stronger interfacial elasticity endow SF foams with the best stability with the slowest foam decay and the largest stable volume fraction [35]. This conclusion is proven by the fact that the SF layers show the smallest ηf at pH 7 and the largest ηf at pH 4 under the same γ. The possible increase in the crystallinity of SF at acidic pH may decrease the flexibility of interfacial films [45] and then further decrease the foam stability of SF at pH 3.
In the presence of salt, the foam stability of SF solutions increases due to the screening of surface charge and the promotion of protein–protein interactions (except for NdCl3, which is generally found to impede SF foam stability) [5], just as was reported for the effects of Ca2+ on β-LG [14] and of Na+ on glycinin [51]. However, with increasing CSF and ion valence, the distance between the protein-stabilized bubble surfaces is reduced, thus facilitating bubble coalescence and decreasing the foam stability with the loosening and rapid collapse of foam during decay [36]. Moreover, as mentioned before, salt-induced protein aggregation can also interfere with the interfacial network formation and, thereby, further destabilize the foam. E’ of SF layers becomes larger in the presence of NaCl and CaCl2 but smaller in the presence of NdCl3, and the strengthening of interfacial elasticity certainly contributes to protect SF foam against bubble coalescence and film rupture [36]. Similarly, the presence of surfactants also improves the foam stability of SF, except for C16TAB at Csurf ≥ 0.0005 mM. The foam height of SF at the same standing time decreases with increasing Csurf for C16TAB, but exhibits a maximum at Csurf = 0.0005 mM for Tween 20 and increases with Csurf for SDS [37]. In general, surfactants tend to form thin, mobile, and elastic films at the interface, while proteins tend to form thick, immobile, and rigid films. It seems that the expandable surfactant layers can transfer the external stress from the interfacial SF networks to improve the foam stability, especially for SDS [37]. C16TAB leads to a strong SF aggregation due to the charge neutralization effect, and it is difficult for these large SF aggregates to form tight networks, thus resulting in a weak foam stability at high Csurf. SDS exhibits a less pronounced SF displacement than Tween 20, and increasing SDS addition does not bring obvious negative effects to the foam stability.
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Similar to other proteins, the amphiphilic SF can form protective films at the air/water interface to suppress bubble coalescence and stabilize aqueous foams, thus making SF become a novel natural foam stabilizer. The solution conditions, such as protein concentration, pH, and concentrations of added salts or surfactants, have significant influences on the adsorption, surface rheology, and foaming properties of SF solutions.
Higher CSF leads to thicker adsorbed layers, accelerates the interfacial adsorption and increases the viscoelastic moduli at the interface. However, the increase in the dilatational elastic modulus is limited due to the finite surface coverage by SF molecules, and it even decreases when CSF exceeds a critical value. Faster adsorption and foaming are found for pH 3, larger SF aggregates, thicker adsorbed layers, and slower foaming are found for pH 4, and denser and more stable foams can be generated at pH 7. At pH 7, smaller aggregate size and higher molecular flexibility help SF form more ordered and stable viscoelastic networks at the interface, which are beneficial for the interfacial films to resist deformation breakage. Both salts and surfactants can substantially increase the surface activity of SF, but the type and concentration of additives cause great differences in the molecular adsorption, layer thickness, interfacial mechanical strength, and, thus, the foaming properties of SF solutions. The incorporated salt reduces the electrostatic repulsion between SF molecules, thus accelerating the diffusion, adsorption and reorganization of SF molecules and increasing the thickness and toughness of interfacial layers. Low ionic strength is beneficial for foam stability, while high ionic strength reduces the foam stability by impeding the formation of rigid interfacial networks due to possible SF aggregation. The surfactants improve the toughness of interfacial networks and, thus, the foam stability of SF solutions, especially the anionic surfactant SDS. However, at high Csurf, the enhanced competition adsorption of surfactant leads to the destruction of interfacial SF networks, thus resulting in a decrease in the foam stability of SF. The negative effect of nonionic Tween 20 and anionic SDS comes from the displacement of surfactant domains, while that of the cationic C16TAB comes from the SF aggregation caused by the electric screening effect of surfactant.
The understanding of the relationship between the interfacial adsorption, surface viscoelasticity, and foaming properties of SF is very important for the design, preparation, and application of SF foams in different fields. Smaller molecular size and higher surface activity fasten the molecular diffusion and interfacial adsorption, and the greater mechanical strength of adsorbed layers helps to stabilize the foam by resisting against external deformation breakage and bubble rupture and coalescence. Until now, the molecular diffusion and adsorption and the interfacial structure, morphology, and viscoelasticity of SF at the air/water interface have been less reported. The microstructural rearrangements and interfacial morphology changes of SF layers under different solution conditions need to be further explored with the help of advanced characterization techniques. The influences of temperature and other additives on the adsorption, surface rheology, and foaming properties of SF need to be further studied in future work. In addition, the molecular interactions between SF and additives and their mechanisms also need to be deeply investigated and described. There may be a global optimum in the foamability with regard to all the parameters including SF concentration, salt type/concentration, pH, and surfactant type/concentration.
Author Contributions
The manuscript was written through the contributions of all authors. X.Q.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. R.M.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—review and editing. E.S.: Project administration, Resources, Writing—review and editing. K.S.: Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation (grant number: CHN/1150450).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not available.
Informed Consent Statement
Not available.
Data Availability Statement
Not available.
Acknowledgments
Reproduced from Ref. [35] with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry. Reproduced from Refs. [34,36,37] with permission from Elsevier.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Narsimhan, G.; Xiang, N. Role of proteins on formation, drainage, and stability of liquid food foams. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lech, F.J.; Steltenpool, P.; Meinders, M.B.J.; Sforza, S.; Gruppen, H.; Wierenga, P.A. Identifying changes in chemical, interfacial and foam properties of β-lactoglobulin-sodium dodecyl sulphate mixtures. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 462, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Xu, G.Y.; Liu, T.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.W. Foam and interfacial properties of Tween 20-bovine serum albumin systems. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 416, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.F.; Yang, J.C.; Li, J.; Tang, C.; Li, B. Foams stabilized by β-Lactoglobulin amyloid fibrils: Effect of pH. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10658–10665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, J.; Gschwendtner, M.; Saalfeld, D.; Kulozik, U. Salt-dependent interaction behavior of β-Lactoglobulin molecules in relation, to their surface and foaming properties. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 558, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, S. Functional properties. In Food Proteins: Properties and Characterization; VCH Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 167–234. [Google Scholar]
- Wilde, P.J. Interfaces: Their role in foam and emulsion behaviour. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 5, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüchner-Gühmann, M.; Heiden-Hecht, T.; Sözer, N.; Drusch, S. Foaming characteristics of oat protein and modification by partial hydrolysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 2095–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.H.; Bos, M.A.; van Vliet, T. Interfacial rheology properties and conformational aspects of soy glycinin at the air/water interface. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.H.; Grolle, K.; Bos, M.A.; Stuart, M.A.C.; van Vliet, T. Network forming properties of various proteins adsorbed at the air/water interface in relation to foam stability. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2002, 254, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, J.; Gschwendtner, M.; Kulozik, U. Evaluation of structural characteristics determining surface and foaming properties of β-lactoglobulin aggregates. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 516, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, J.; Johler, F.; Warncke, M.; Kulozik, U. Correlation between bulk characteristics of aggregated β-lactoglobulin and its surface and foaming properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, K.; Lexis, M.; Gochev, G.; Konnerth, C.; Miller, R.; Willenbacher, N.; Peukert, W.; Braunschweig, B. pH effects on the molecular structure of β-lactoglobulin modified air-water interfaces and its impact on foam rheology. Langmuir 2013, 29, 11646–11655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunschweig, B.; Schulze-Zachau, F.; Nagel, E.; Engelhardt, K.; Stoyanov, S.; Gochev, G.; Khristov, K.; Mileva, E.; Exerowa, D.; Miller, R.; et al. Specific effects of Ca2+ ions and molecular structure of β-lactoglobulin interfacial layers that drive macroscopic foam stability. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 5995–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaganathan, M.; Dhathathreyan, A.; Selvaraju, C.; Miller, R. Jones-Ray effect on the organization of lysozyme in the presence of NaNO3 at an air/water interface: Is it a cause or consequence? RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 100638–100645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Henestrosa, V.P.; Sánchez, C.C.; Patino, J.M.R. Adsorption and foaming characteristics of soy globulins and Tween 20 mixed systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 2876–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Henestrosa, V.P.; Sánchez, C.C.; Patino, J.M.R. Formulation engineering can improve the interfacial and foaming properties of soy globulins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6339–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunning, P.A.; Mackie, A.R.; Gunning, A.P.; Woodward, N.C.; Wilde, P.J.; Morris, V.J. Effect of surfactant type on surfactant-protein interactions at the air-water interface. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahverdjieva, V.S.; Grigoriev, D.O.; Fainerman, V.B.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Miller, R.; Möhwald, H. Competitive adsorption from mixed hen egg-white lysozyme/surfactant solutions at the air-water interface studied by tensiometry, ellipsometry, and surface dilational rheology. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 2136–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkov, J.T.; Gurkov, T.D.; Campbell, B.E.; Borwankar, R.P. Dilatational and shear elasticity of gel-like protein layers on air/water interface. Langmuir 2000, 16, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, N.; Hu, R.Q.; Pi, Y.P.; Feng, J.Q.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, W.L.; Yang, H.J. Wet spinning of bletilla striata polysaccharide/silk fibroin hybrid fibers. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, A.; Azadi, M.; Emadi, R.; Lari, J.; Chermahini, A.N. Preparation, characterization, degradation and biocompatibility of different silk fibroin based composite scaffolds prepared by freeze-drying method for tissue engineering application. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 121, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangkert, S.; Meesane, J.; Kamonmattayakul, S.; Chai, W.L. Modified silk fibroin scaffolds with collagen/decellularized pulp for bone tissue engineering in cleft palate: Morphological structures and biofunctionalities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, R.; Michelson, C.D.; Perera, A.L.; Brunner, T.F.; Harsono, M.; Leisk, G.G.; Kugel, G.; Kaplan, D.L. Electrodeposited silk coatings for bone implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 103, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, T.Y.; Jiang, Z.J.; Wang, P.; Bie, S.Y.; Zhang, F.; Zuo, B.Q. Silk fibroin/copolymer composite hydrogels for the controlled and sustained release of hydrophobic/hydrophilic drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.H.; Dicko, C.; Bain, C.D.; Gong, Z.G.; Jacobs, R.M.J.; Shao, Z.Z.; Terry, A.E.; Vollrath, F. Behavior of silk protein at the air-water interface. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 9705–9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valluzzi, R.; Gido, S.P.; Muller, W.; Kaplan, D.L. Orientation of silk III at the air-water interface. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 24, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.J.; Valluzzi, R.; Gido, S.P. SilkⅠStructure in Bombyx Mori Silk Foams. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 24, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniglio, D.; Bonani, W.; Migliaresi, C.; Motta, A. Silk fibroin porous scaffolds by N2O foaming. J. Biomat. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, E.; Lo, T.J.; Fournier, E.P.; Brown, J.E.; Abbott, R.D.; Gil, E.S.; Marra, K.G.; Rubin, J.P.; Leisk, G.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Injectable silk foams for soft tissue regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Pereira, R.F.P.; Coradin, T.; Bermudez, V.; Fernandes, F.M. Biomimetic silk macroporous materials for drug delivery obtained via ice-templating. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 2556–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambre, L.; Parker, R.N.; Allardyce, B.J.; Valente, F.; Rajkhowa, R.; Dilley, R.J.; Wang, X.; Kaplan, D.L. Tunable biodegradable silk-based memory foams with controlled release of antibiotics. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, G.M.; Weska, R.F.; Vieira, W.C., Jr.; Polakiewicz, B.; Rodas, A.C.D.; Higa, O.Z.; Beppu, M.M. A new method to prepare porous silk fibroin membranes suitable for tissue scaffolding applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.Y.; Miller, R.; Schneck, E.; Sun, K. Foaming properties and the dynamics of adsorption and surface rheology of silk fibroin at the air/water interface. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 591, 124553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.Y.; Miller, R.; Schneck, E.; Sun, K. Influence of pH on the surface and foaming properties of aqueous silk fibroin solutions. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 3695–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.Y.; Miller, R.; Schneck, E.; Sun, K. Influence of salt addition on the surface and foaming properties of silk fibroin. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 609, 125621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.Y.; Miller, R.; Schneck, E.; Sun, K. Influence of surfactant charge and concentration on the surface and foaming properties of biocompatible silk fibroin. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 281, 125920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Chen, J.S.; Collette, A.L.; Kim, U.K.; Altman, G.H.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Mechanisms of silk fibroin sol-gel transitions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 21630–21638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitropoulos, V.; Mütze, A.; Fischer, P. Mechanical properties of protein adsorption layers at the air/water and oil/waer interface: A comparison in light of the thermodynamical stability of proteins. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, L.; Auser, N.D.; Gigli, J.; Windhab, E.J.; Fischer, P. Interfacial rheology of soy proteins-high methoxyl pectin films. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.L.; Yang, X.Q.; Sagis, L.M.C. Contribution of long fibrils and peptides to surface and foaming behavior of soy protein fibril system. Langmuir 2016, 32, 8092–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.E.; Al-Koofee, D.A.F. Effect of temperature changes on critical micelle concentration for tween series surfactant. Glob. J. Sci. Front. Res. Chem. 2013, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Fuguet, E.; Ràfols, C.; Rosés, M.; Bosch, E. Critical micelle concentration of surfactants in aqueous buffered and unbuffered systems. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 548, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.; Fainerman, V.B.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Leser, M.E.; Michel, M. Dynamic surface tension and adsorption kinetics of β-casein at the solution/air interface. Langmuir 2004, 20, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, E.R.; Miyagi, Y.; Chuah, J.A.; Numata, K.; Serban, M.A. Interplay between silk fibroin’s structure and its adhesive properties. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 2815–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, K.; Horváth-Szanics, E.; Hajós, G.; Kiss, É. Surface and interfacial properties of water-soluble wheat proteins. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 319, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.B.; Damodaran, S. Influence of electrostatic forces on the adsorption of succinylated beta-lactoglobulin at the air-water interface. Langmuir 1991, 7, 2737–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaganathan, V.; Retzlaff, I.; Won, J.Y.; Gochev, G.; Gehin-Delval, C.; Leser, M.; Noskov, B.A.; Miller, R. β-Lactoglobulin adsorption layers at the water/air surface: 1. Adsorption kinetics and surface pressure isotherm: Effect of pH and ionic strength. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 519, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.; Ferri, J.K.; Javadi, A.; Krägel, J.; Mucic, N.; Wüstneck, R. Rheology of interfacial layers. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, N.; Gaillard, C.; Boué, F.; Axelos, M.A.V.; Riaublanc, A. Self-similar assemblies of globular whey proteins at the air-water interface: Effect of the structure. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2010, 345, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Henestrosa, V.P.; Sánchez, C.C.; Escobar, M.D.M.Y.; Jiménez, J.J.P.; Rodríguez, F.M.; Patino, J.M.R. Interfacial and foaming characteristics of soy globulins as a function of pH and ionic strength. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 309, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Xu, W.; Lu, Q.; Han, H.; Zhu, H. Controllable transition of silk fibroin nanostructures: An insight into in vitro silk self-assembly process. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7806–7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fainerman, V.B.; Kovalchuk, V.I.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Zinkovych, I.I.; Makievski, A.V.; Nikolenko, M.V.; Miller, R. Dilational viscoelasticity of proteins solutions in dynamic conditions. Langmuir 2018, 34, 6678–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Interfacial behavior of alkaline protease at the air-water and oil-water interfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 433, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühs, P.A.; Scheuble, N.; Windhab, E.J.; Fischer, P. Protein adsorption and interfacial rheology interfering in dilational experiment. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2013, 222, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lech, F.J.; Delahaije, R.J.; Meinders, M.B.J.; Gruppen, H.; Wierenga, P.A. Identification of critical concentrations determining foam ability and stability of β-lactoglobulin. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lexis, M.; Willenbacher, N. Relating foam and interfacial rheological properties of β-lactoglobulin solutions. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 9626–9636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, S.; Murray, B.S.; Dickinson, E. Interfacial shear rheology of aged and heat-treated β-lactoglobulin films: Displacement by nonionic surfactant. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, K.; Weichsel, U.; Kraft, E.; Segets, D.; Peukert, W.; Braunschweig, B. Mixed layers of β-lactoglobulin and SDS at air-water interfaces with tunable intermolecular interactions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 4098–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinova, K.G.; Basheva, E.S.; Nenova, B.; Temelska, M.; Mirarefi, A.Y.; Campbell, B.; Ivanov, I.B. Physico-chemical factors controlling the foamability and foam stability of milk proteins: Sodium caseinate and whey protein concentrates. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1864–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).