The Contact Angle Hysteresis Puzzle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
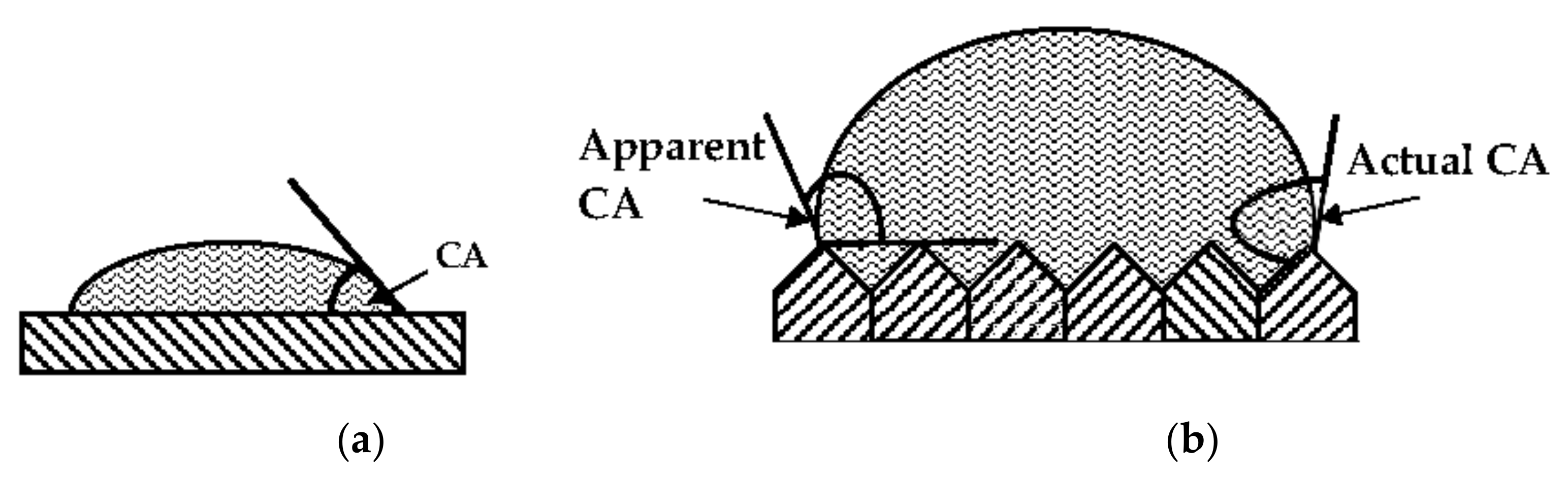
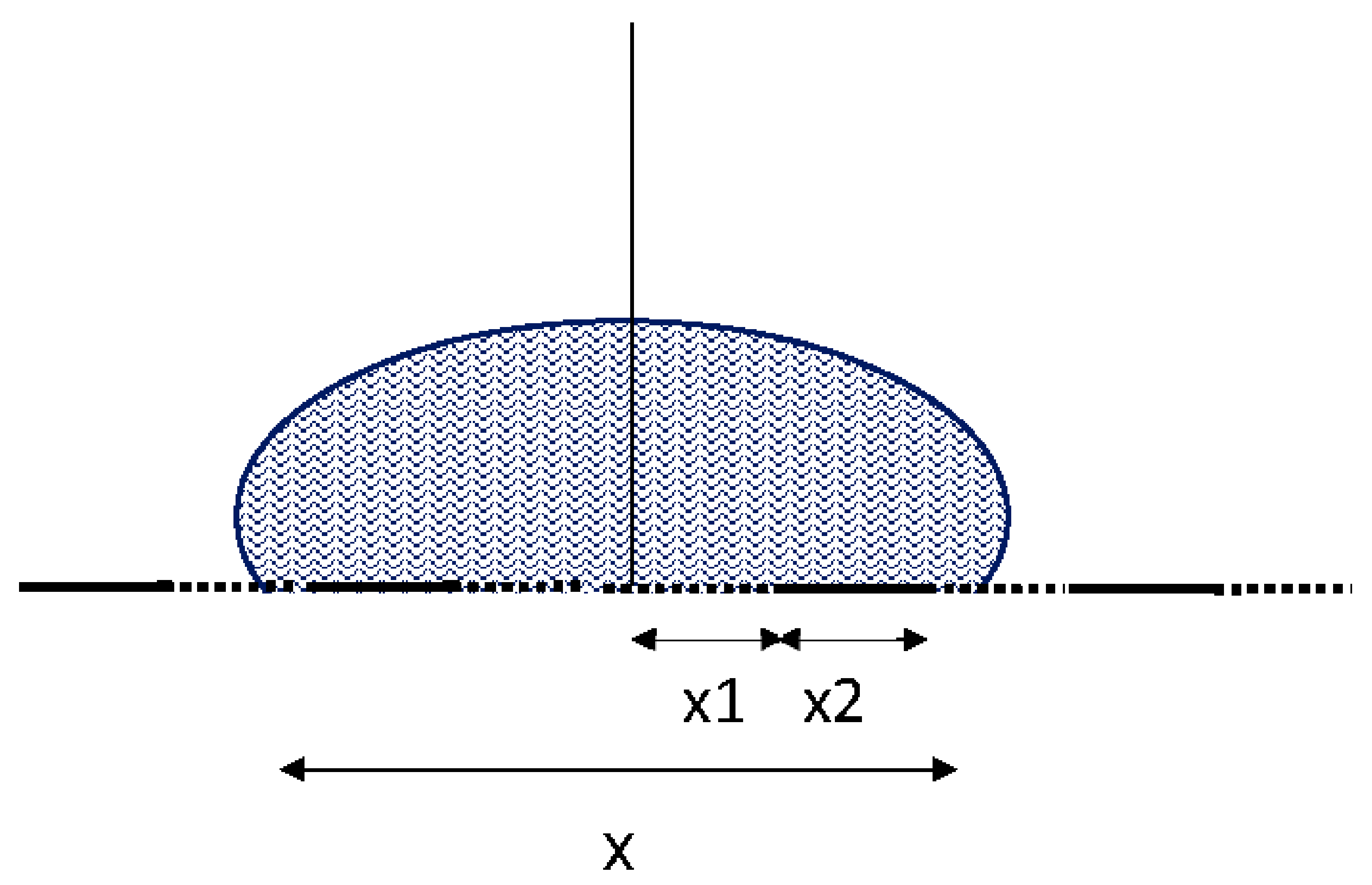
2. A Very Simple Model of a Real Surface
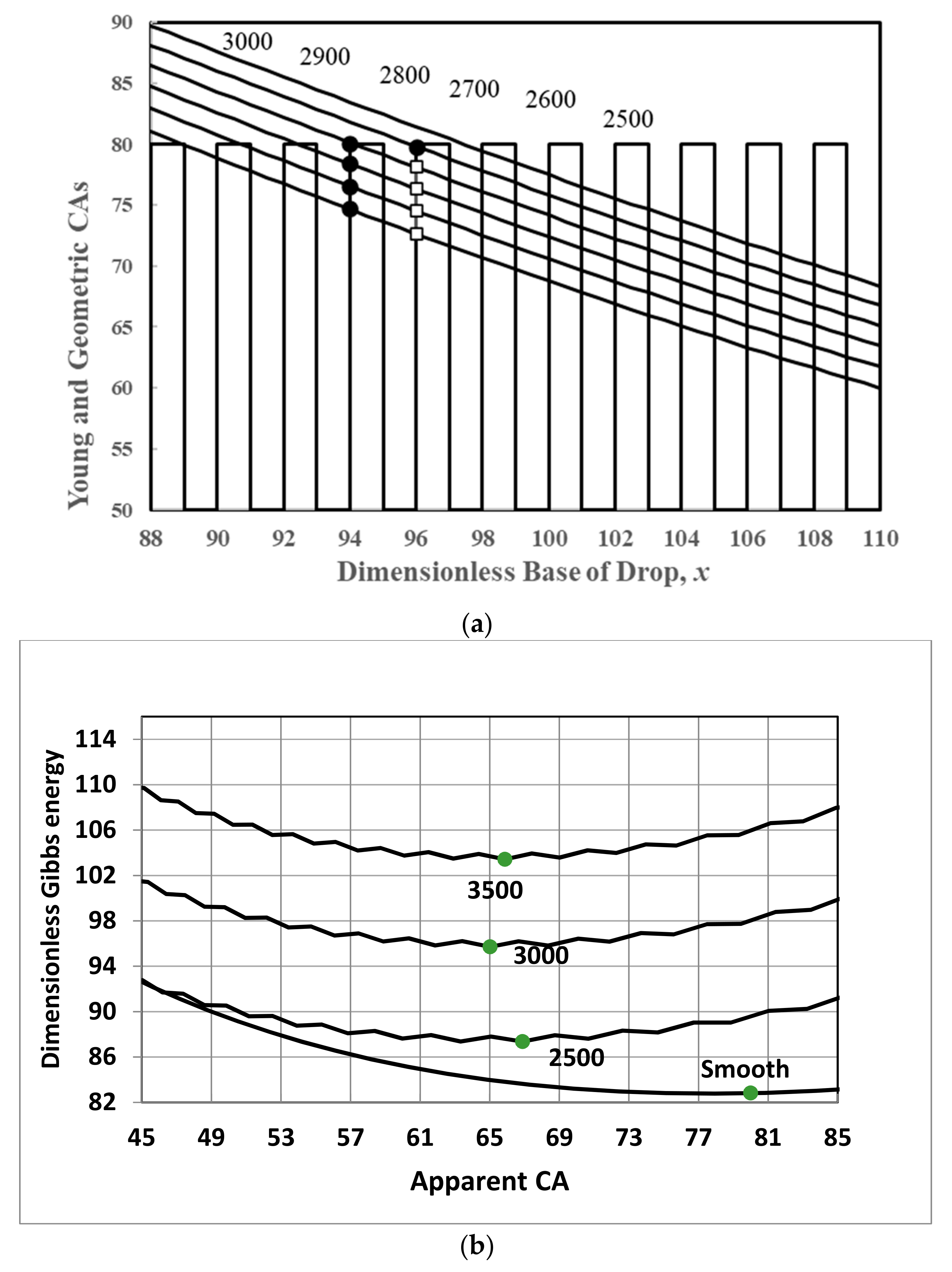
3. The Cause of CAH
4. Effect of CAH on Measurement and Interpretation of CAs
5. Conclusions
- The concepts of advancing and receding CAs are not yet sufficiently well defined, because they depend on the method of measurement as well as on the level of environmental vibrations that cause vibrations of the measuring instrument.
- The main advantage of CAH measurements is their ability to indicate the existence of mechanical or chemical nonuniformity.
- The average of the advancing and receding CAs may serve as a rough approximation for the most stable CA, which enables in some cases (e.g., chemically uniform, rough surfaces) the estimation of the Young CA.
- The above discussed issues call for some standardization of CAH measurement, so consistent results may be universally achieved independently of the laboratory in which they are being measured.
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, T. An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1805, 95, 65–87. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, A.W. Wetting, Spreading and Adhesion; Padday, J.F., Ed.; Academic: London, NY, USA, 1978; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Wolansky, G.; Marmur, A. The Actual Contact Angle on a Heterogeneous Rough Surface in Three Dimensions. Langmuir 1998, 14, 5292–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, P.S.; Lipowsky, R. Contact angles on heterogeneous surfaces: A new look at Cassie’s and Wenzel’s laws. Langmuir 1998, 14, 6772–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, R.E., Jr.; Dettre, R.H.; Brandreth, M.D. Dynamic contact angle and contact angle hysteresis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1977, 62, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A. Solid-Surface Characterization by Wetting. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2009, 39, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, E.; Carmona, F.J.; Amirfazli, A. Understanding of sliding and contact angle results in tilted plate experiments. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 323, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasovitski, B.; Marmur, A. Drops down the hill: Theoretical study of limiting contact angles and the hysteresis range on a tilted plate. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3881–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neinhuis, C.; Barthlott, W. Characterization and distribution of water-repellent, self-cleaning plant surfaces. Ann. Bot. 1997, 79, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirasaki, G.J. Wettability: Fundamentals and Surface Forces. SPE Form. Eval. 1991, 6, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, D.H. A general approach to hysteresis 4. An alternative formulation of the domain model. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1955, 51, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, S.; Marmur, A. Simulation of Contact Angle Hysteresis on Chemically Heterogeneous Surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 183, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans-Jürgen Butt, H.-J.; Liu, J.; Koynov, K.; Straub, B.; Hinduja, C.; Roismann, I.; Berger, R.; Li, X.; Vollmer, D.; Steffen, W.; et al. Contact angle hysteresis. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 59, 101574. [Google Scholar]
- Makonen, L. A thermodynamic model of contact angle hysteresis. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 064703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eral, H.B.; Mannetje, D.J.C.M.’t.; Oh, J.M. Contact angle hysteresis: A review of fundamentals and applications. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A. Contact-angle hysteresis on heterogeneous smooth surfaces: Theoretical comparison of the captive bubble and drop methods. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 136, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittoun, E.; Marmur, A. Chemical Nano-Heterogeneities Detection by Contact Angle Hysteresis: Theoretical Feasibility. Langmuir 2010, 26, 15933–15937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A. Surface tension of an ideal solid: What does it mean? Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 51, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwikel, D.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.; Su, X.; Marmur, A. Comparing Contact Angle Measurements and Surface Tension Assessments of Solid Surfaces. Langmuir 2010, 26, 15289–15294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu, C.; Sykes, C.; Brochard, F. Average spreading parameter on heterogeneous surfaces. Langmuir 1994, 10, 2077–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, E.L.; Garoff, S. Using vibrational noise to probe energy barriers producing contact angle hysteresis. Langmuir 1996, 12, 2100–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A.; Dalal, D. Correlating Interfacial Tensions with Surface Tensions: A Gibbsian Approach. Langmuir 2010, 26, 5568–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marmur, A. The Contact Angle Hysteresis Puzzle. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6030039
Marmur A. The Contact Angle Hysteresis Puzzle. Colloids and Interfaces. 2022; 6(3):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6030039
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarmur, Abraham. 2022. "The Contact Angle Hysteresis Puzzle" Colloids and Interfaces 6, no. 3: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6030039
APA StyleMarmur, A. (2022). The Contact Angle Hysteresis Puzzle. Colloids and Interfaces, 6(3), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids6030039





