Oil-In-Water Microemulsions for Thymol Solubilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Microemulsion Preparation
2.3. Determination of the Microemulsion Region
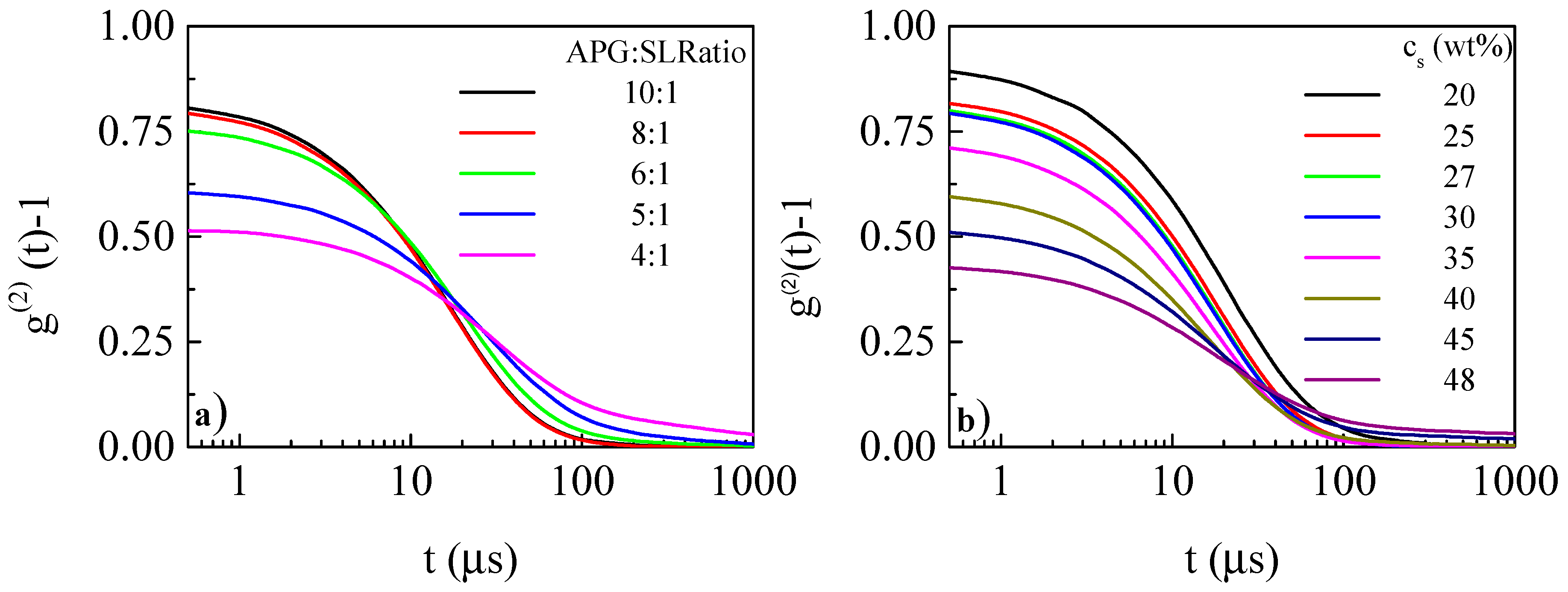
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering
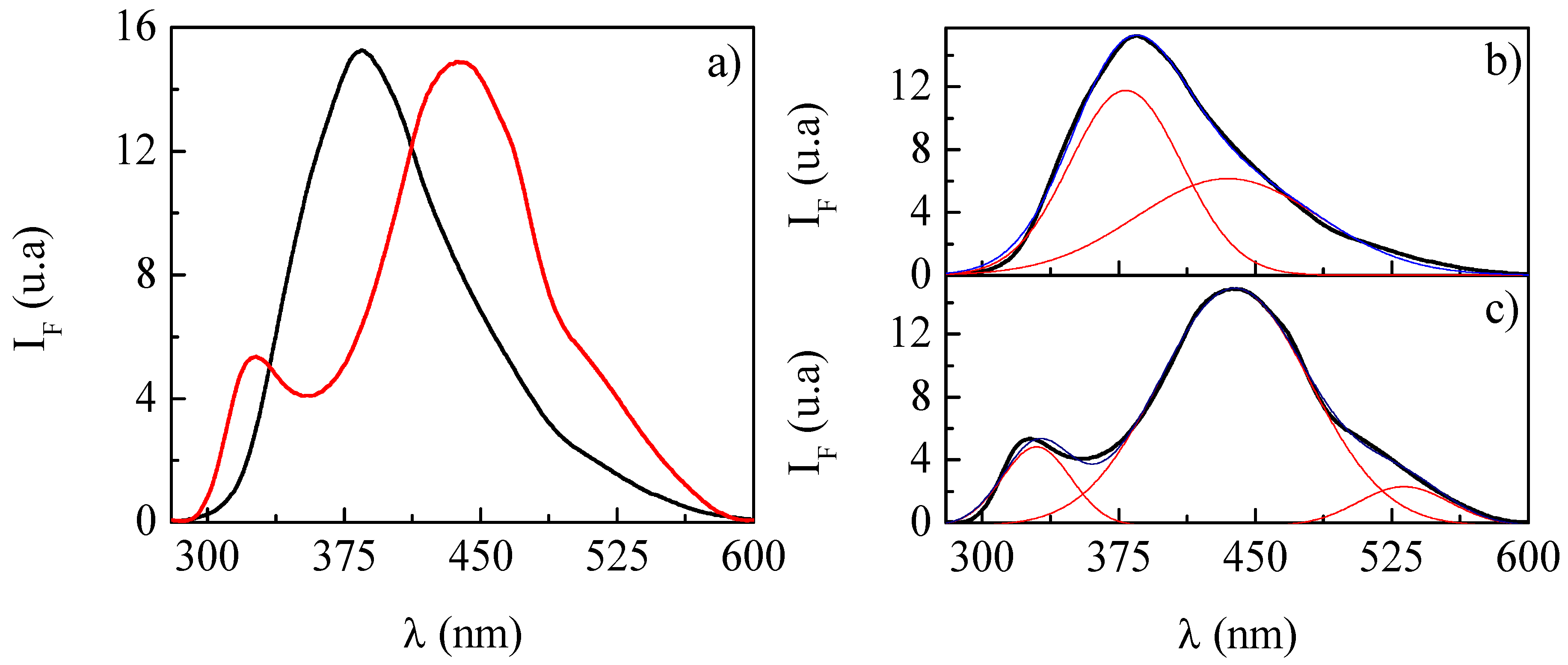
2.5. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
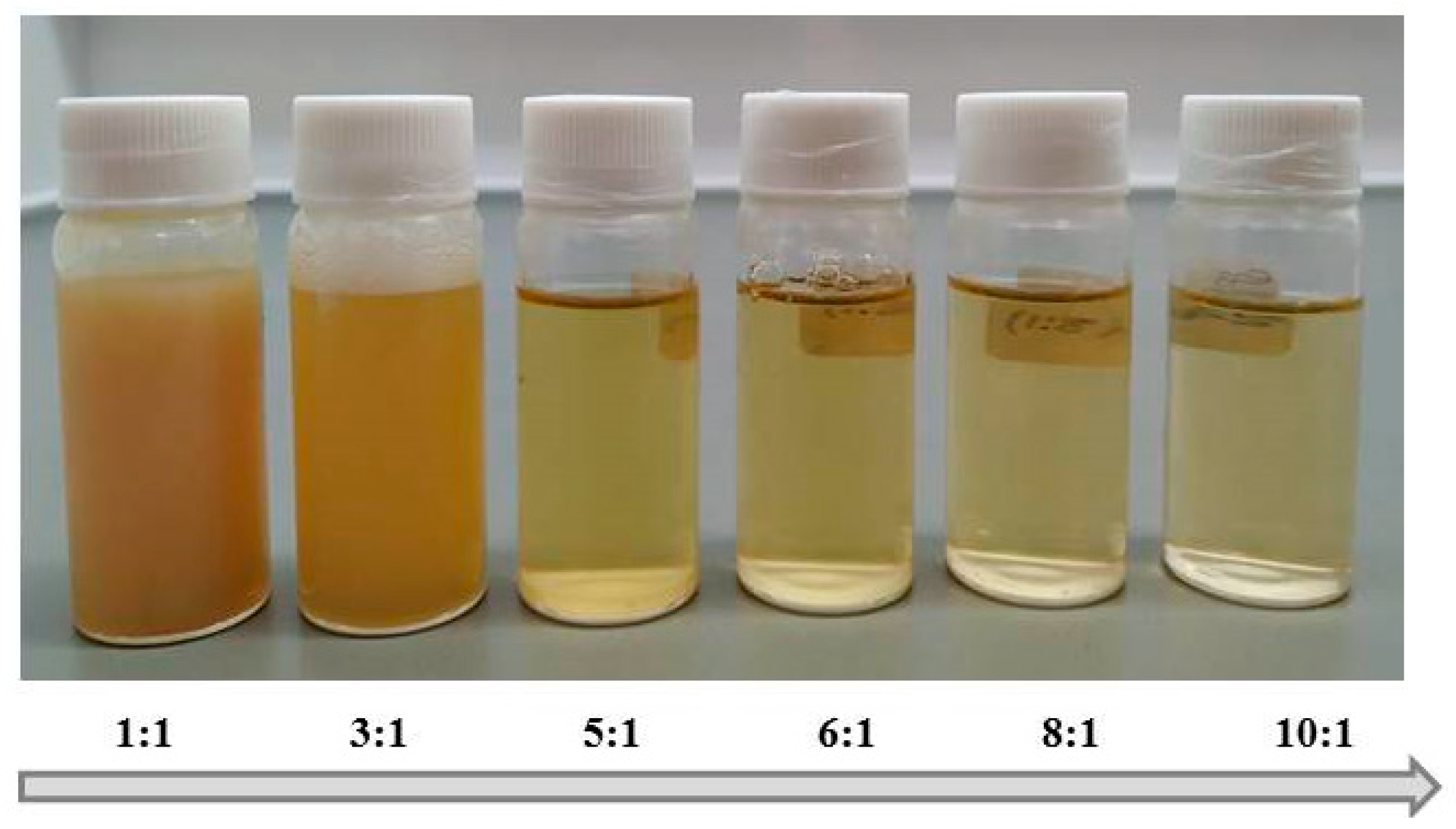
3.1. Determination of Oil-In-Water Microemulsion Region
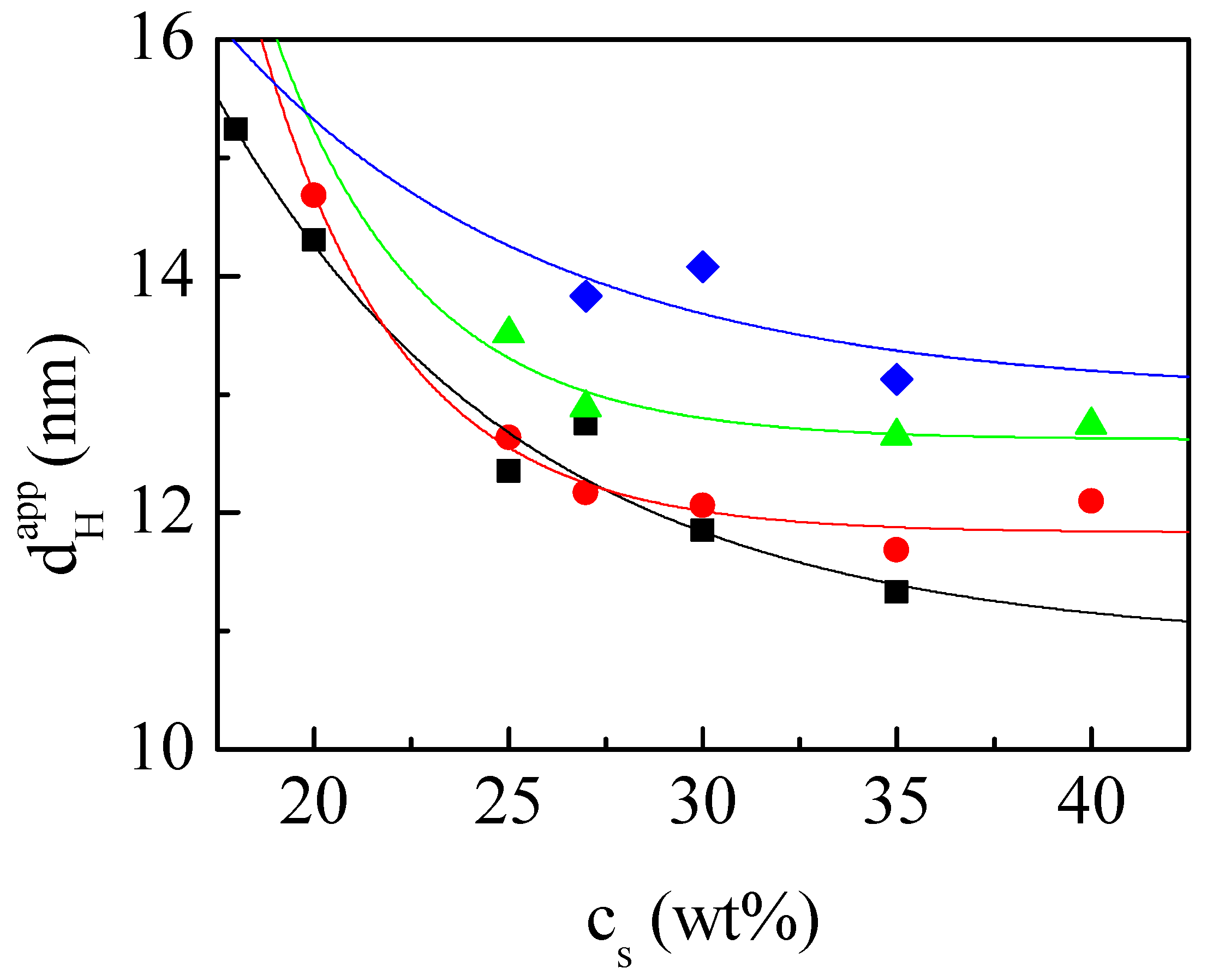
3.2. Characterization of the Droplet Size
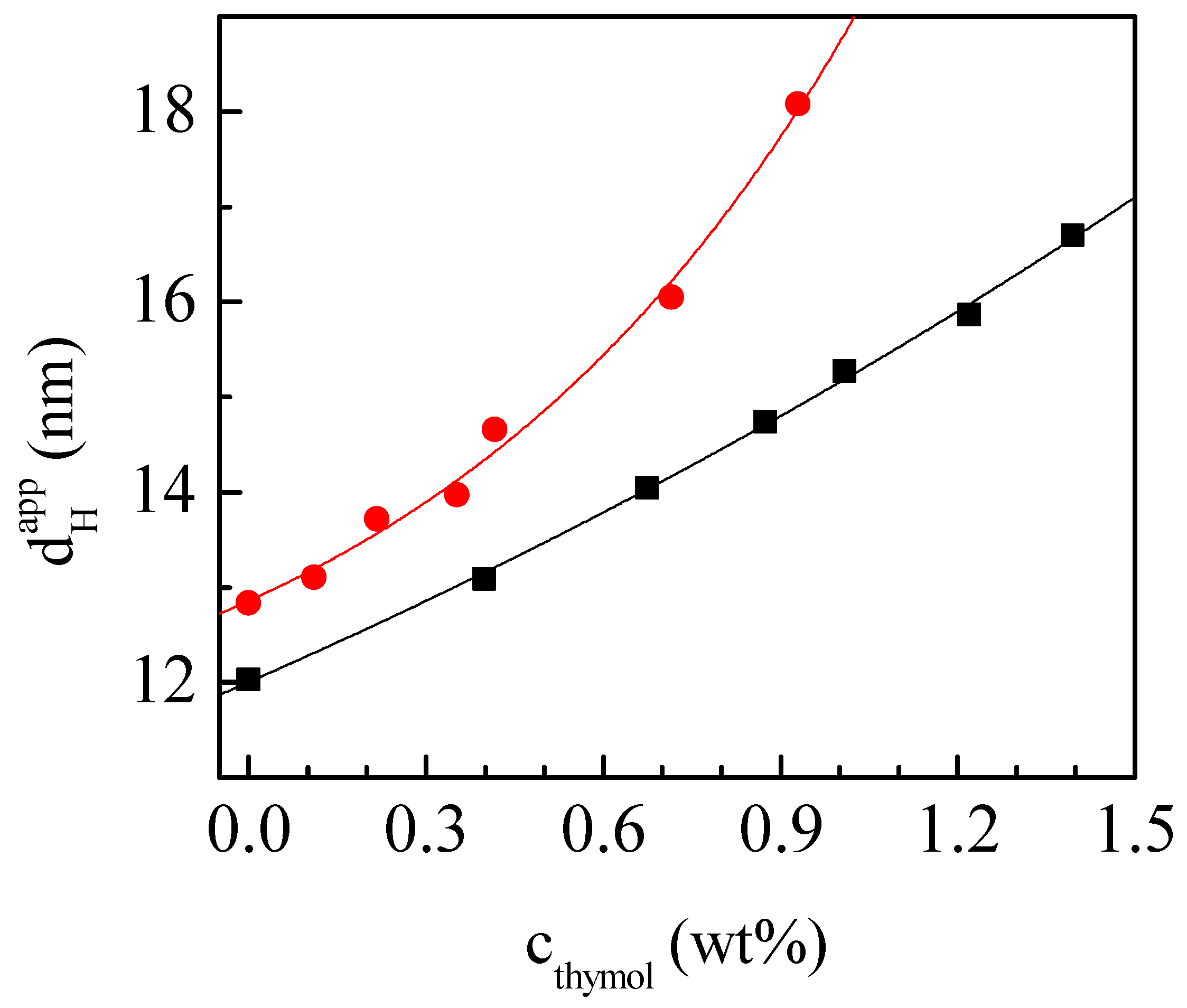
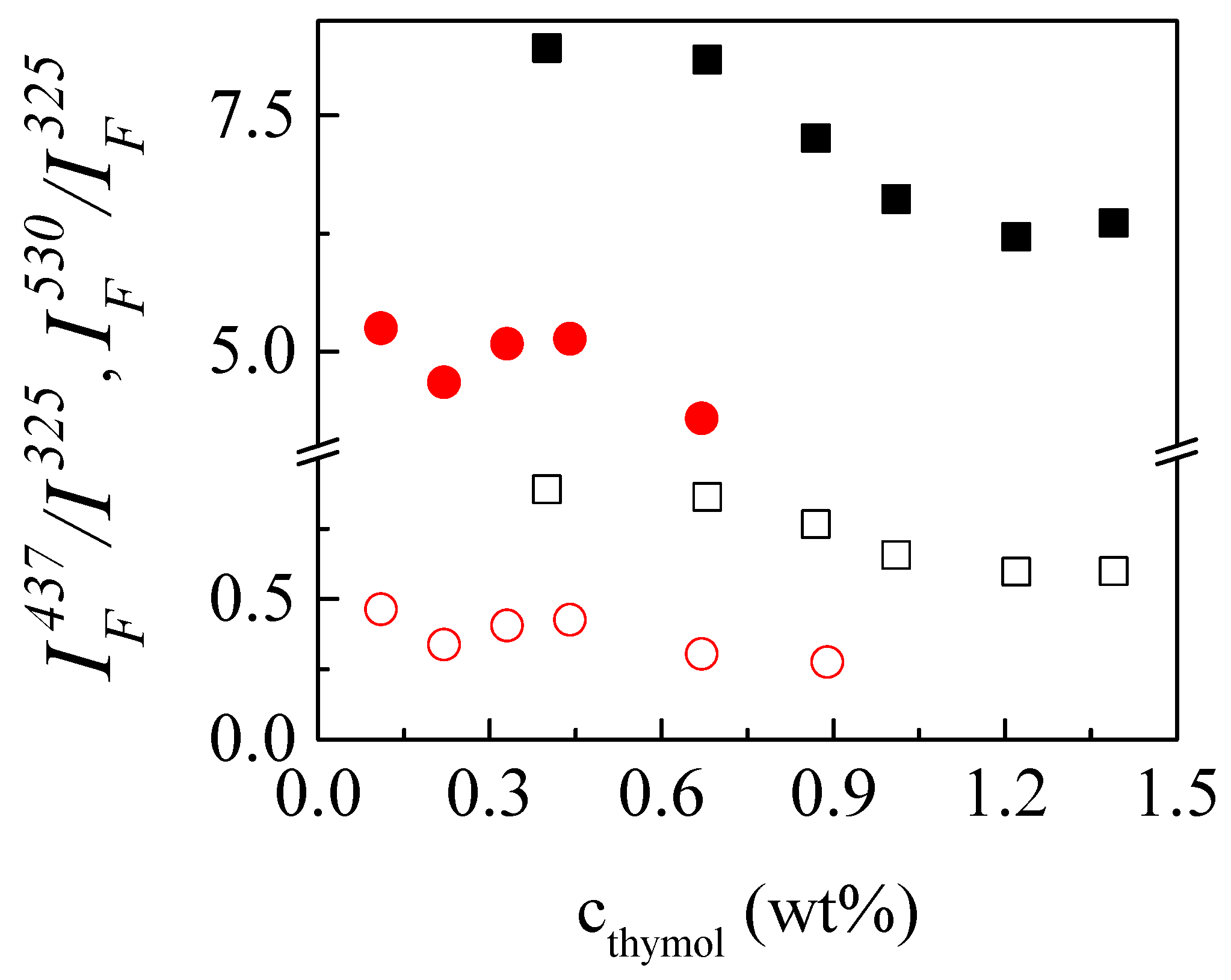
3.3. Microemulsions for Thymol Solubilization
3.4. Understanding the Solubilization Process of Thymol
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breuer, E.; Chorghadez, M.S.; Fischer, J.; Golomb, G. Glossary of Terms related to Pharmaceutics. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 971–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.D.; Tran, P.H.L. Nanoconjugation and Encapsulation Strategies for Improving Drug Delivery and Therapeutic Efficacy of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wais, U.; Jackson, A.W.; He, T.; Zhang, H. Nanoformulation and encapsulation approaches for poorly water-soluble drug nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 1746–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán, E.; Mateos-Maroto, A.; Ruano, M.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G. Layer-by-Layer polyelectrolyte assemblies for encapsulation and release of active compounds. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudo, P.G.; Guzmán, E.; Lucia, A.; Rubio, R.G.; Ortega, F. Preparation and Application in Drug Storage and Delivery of Agarose Nanoparticles. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018, 7823587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbahani, A.E.; Miladi, K.; Badri, W.; Sala, M.; Addi, E.H.A.; Casabianca, H.; Mousadik, A.E.; Hartmann, D.; Jilale, A.; Renaud, F.N.R.; et al. Essential oils: From extraction to encapsulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 483, 220–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T.F. (Ed.) Emulsion Science and Technology; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.: Weinheim, Germanuy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Donsì, F.; Ferrari, G. Essential oil nanoemulsions as antimicrobial agents in food. J. Biotech. 2016, 233, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M. (Ed.) Handbook of Encapsulation and Controlled Release; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanun, M. Colloids in Drug Delivery; Taylor and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fanun, M. Microemulsions Properties and Applications; Taylor and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fanun, M. Microemulsions as delivery systems. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 17, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, M.; Domínguez, J.A.; Pascual-Pineda, L.A.; Azuara, E.; Beristain, C.I. Elaboration and characterization of O/W cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum) and black pepper (Piper nigrum) emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzidaki, M.D.; Balkiza, F.; Gad, E.; Alexandraki, V.; Avramiotis, S.; Georgalaki, M.; Papadimitriou, V.; Tsakalidou, E.; Papadimitriou, K.; Xenakis, A. Reverse micelles as nano-carriers of nisin against foodborne pathogens. Part II: The case of essential oils. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayaud, L.; Carricajo, A.; Zhiri, A.; Aubert, G. Comparison of bacteriostatic and bactericidal activity of 13 essential oils against strains with varying sensitivity to antibiotics. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 47, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, S. Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucia, A.; Toloza, A.C.; Guzmán, E.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G. Novel polymeric micelles for insect pest control: Encapsulation of essential oil monoterpenes inside a triblock copolymer shell for head lice control. Peer J. 2017, 5, e3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dima, C.; Dima, S. Essential oils in foods: Extraction, stabilization, and toxicity. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 5, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingan, K. A Review on Major Constituents of Various Essential Oils and its Application. Transl. Med. 2018, 8, 1000201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, Z.A.A.; Nasir, H.M.; Ahmad, A.; Setapar, S.H.M.; Ahmad, H.; Noor, M.H.M.; Rafatullah, M.; Khatoon, A.; Kausar, M.A.; Ahmad, I.; et al. Enrichment of Eucalyptus oil nanoemulsion by micellar nanotechnology: Transdermal analgesic activity using hot plate test in rats’ assay. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Godoi, S.N.; Quatrin, P.M.; Sagrillo, M.R.; Nascimento, K.; Wagner, R.; Klein, B.; Santos, R.C.V.; Ourique, A.F. Evaluation of Stability and In Vitro Security of Nanoemulsions Containing Eucalyptus globulus Oil. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2723418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, Z.; Gharib, R.; Fourmentin, S.; Elaissari, A.; Greige-Gerges, H. New findings on the incorporation of essential oil components into liposomes composed of lipoid S100 and cholesterol. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 561, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppasansatorn, P.; Nimmannit, U.; Conway, B.R.; Du, L.; Wang, Y. Microemulsions as topical delivery vehicles for the anti-melanoma prodrug, temozolomide hexyl ester (TMZA-HE). J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathout, R.M.; Woodman, T.J.; Mansour, S.; Mortada, N.D.; Geneidi, A.S.; Guy, R.H. Microemulsion formulations for the transdermal delivery of testosterone. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 40, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yu, A.; Wang, W.; Dong, R.; Wu, J.; Zhai, G. Formulation design of microemulsion for dermal delivery of penciclovir. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 360, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.A.; Arias, J.L.; Gallardo, V. Skin Creams Made with Olive Oil. In Olives and Olive Oil in Health and Disease Prevention; Preedy, V.R., Watson, R.R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berne, B.J.; Pecora, R. Dynamic Light Scattering: With Applications to Chemistry, Biology, and Physics; Dover Publications Inc.: Mineola, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.B.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xiao, X.; Jin, D.; Zhao, N.J.; Yin, G.F.; Guo, L.Q.; Liu, W.Q.. Excitation-emission fluorescence characterization study of the three phenolic compounds. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal 2010, 30, 1271–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isailović, T.M.; Todosijević, M.N.; Đorđević, a.M.; Savić, S.D. Natural Surfactants-Based Micro/Nanoemulsion Systems for NSAIDs—Practical Formulation Approach, Physicochemical and Biopharmaceutical Characteristics/Performances. In Microsized and Nanosized Carriers for Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Formulation Challenges and Potential Benefits; Čalija, B., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 179–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolman, R.C. The Effect of Droplet Size on Surface Tension. J. Chem. Phys. 1949, 17, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeran, M.F.N.; Javed, H.; Taee, H.A.; Azimullah, S.; Ojha, S.K. Pharmacological Properties and Molecular Mechanisms of Thymol: Prospects for Its Therapeutic Potential and Pharmaceutical Development. Front. Pharm. 2017, 8, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, M.; Hofkens, J.; Enderlein, J. Handbook of Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Imaging; Wiley VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tchaikovskaya, O.N.; Sokolova, I.V.; Kuznetsova, R.T.; Swetlitchnyi, V.A.; Kopylova, T.N.; Mayer, G.V. Fluorescence Investigations of Phenol Phototransformation in Aqueous Solutions. J. Fluoresc. 2000, 10, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Chen, H.; Davidson, P.M.; Zhong, Q. Thymol Nanoencapsulated by Sodium Caseinate: Physical and Antilisterial Properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, A.; Sengupta, P.; Pal, U.; Senapati, S.; Ahsan, M.; Roy, S.; Das, U.; Sen, K. Encapsulation of Thymol in cyclodextrin nano-cavities: A multispectroscopic and theoretical study. Spectrochim. Acta A 2019, 208, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollamby, M.J.; Danks, A.E.; Schnepp, Z.; Rogers, S.E.; Hart, S.R.; Nakanishi, T. Fluorescent liquid pyrene derivative-in-water microemulsions. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 7344–7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| cs/wt% | APG:SL Ratio | ϕ/wt% |
|---|---|---|
| 18 | 8:1 | 0.0 |
| 25 | 8:1 | 0.9 |
| 30 | 8:1 | 1.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Peña, L.; Gutiérrez-Muro, S.; Guzmán, E.; Lucia, A.; Ortega, F.; G. Rubio, R. Oil-In-Water Microemulsions for Thymol Solubilization. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3040064
Fernández-Peña L, Gutiérrez-Muro S, Guzmán E, Lucia A, Ortega F, G. Rubio R. Oil-In-Water Microemulsions for Thymol Solubilization. Colloids and Interfaces. 2019; 3(4):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3040064
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Peña, Laura, Sonia Gutiérrez-Muro, Eduardo Guzmán, Alejandro Lucia, Francisco Ortega, and Ramón G. Rubio. 2019. "Oil-In-Water Microemulsions for Thymol Solubilization" Colloids and Interfaces 3, no. 4: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3040064
APA StyleFernández-Peña, L., Gutiérrez-Muro, S., Guzmán, E., Lucia, A., Ortega, F., & G. Rubio, R. (2019). Oil-In-Water Microemulsions for Thymol Solubilization. Colloids and Interfaces, 3(4), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3040064









