Abstract
Corn stalks (CS) were modified by a cationic surfactant, cetylpyridinium bromide (CPB), and used as an adsorbent (CS-CP) to remove anionic dyes [Acid Red (AR) and Acid Orange (AO)] from aqueous solutions. The FTIR analysis and the obtained calculations based on the determination of the adsorption capacity of CS towards CPB confirmed that the cationic surfactant had been adsorbed on the surface of corn stalks. Adsorption of the anionic dyes on modified corn stalks was investigated in a series of batch adsorption experiments at 303–328 K. The adsorption data were analyzed using Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin models. The Langmuir model was found to be more suitable for the experimental data of the anionic dyes on CS-CP than other adsorption models. Kinetic studies revealed that the pseudo-second order model showed the best fit to the experimental data. The thermodynamic parameters indicated that the adsorption process was spontaneous and exothermic. Mechanisms involving ion exchange and chemisorption might be responsible for the uptake of the anionic dyes on CS-CP. Obtained results imply that CS-CP could be applied as an effective adsorbent to remove anionic dyes from aqueous solutions.
1. Introduction
Various kinds of synthetic dyes (anionic, cationic, and non-ionic) have been widely used in different industries (textile, paper and pulp, leather, fur, printing, rubber, plastics, pharmaceutical, cosmetics, and food), to color their products [1,2,3,4]. Among these industries, the textile industry ranks first in usage of anionic dyes and generates a large volume of colored wastewater that emanates from the spent dye bathes and washing stages. According to Zaharia and Suteu [3], 10–25% of textile dyes are lost during the dyeing process, and 2–20% of textile dyes are directly discharged as aqueous effluents in different environmental components that can lead to serious environmental problems. This is due to the fact that most anionic dyes exhibit toxic, mutagenic, allergenic, and carcinogenic effects towards human beings and animals [2].
It should be kept in mind that the complex aromatic structures of dyes make them stable and difficult to be removed from the wastewater. There are several traditional methods for dye removal from industrial effluents: biological treatment, coagulation, flocculation, flotation, electrochemical destruction, ozonation, and adsorption [1,2,3]. Many listed methods are often ineffective in the removal of dyes or they are very expensive. The adsorption method is considered a better alternative in wastewater treatment due to high effectiveness, simplicity of design, and ease of operation. However, today, the most commonly adopted adsorbents are the activated carbons, which have high costs and high regeneration costs after being exhausted. The disadvantages of active carbons have led to the search for new low-cost adsorbents.
Over time, several literature reviews concerning the use of low-cost adsorbents based on the agricultural plant waste for wastewater treatment have been published [2,4]. The reviews have shown that use of the untreated plant waste does not give a good effect in removing anionic dyes. A number of studies focused on such plant waste as wood sawdust, barley and wheat straw, Jerusalem artichoke stalks, peanut husk, pineapple leaf, and coir pith modified by cationic surfactants (сetylpyridinium bromide or chloride and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide) that are capable of removing anionic dyes from wastewater [1,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. Modification of agricultural plant waste by cationic surfactants substantially increases their adsorption capacity, thus such modified materials allow the effective removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions. However, more recent literature data about corn stalks (CS) modified by cetylpyridinium bromide (CPB) as adsorbents towards anionic dyes are not available.
The aim of this paper is to evaluate the adsorption potential of corn stalks modified by cetylpyridinium bromide for the removal of anionic dyes from aqueous media and to study the equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics of the adsorption process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
All used chemicals were analytical reagent grades. They were used without further purification. Chemical reagents as C21H38NBr, NaOH, HCl, KBr, and C2H5OH were obtained from Cherkassy State Chemical Plant (Cherkassy, Ukraine). Anionic dyes [Acid Red (AR) and Acid Orange (AO)] were purchased from the Ukraine company, “Fine organic synthesis plant ‘Barva AG’” (Yamnytsia, Ukraine). The dye solutions were prepared by dissolving accurately weighed dyes in distilled water.
Dye characteristics are presented in Table 1. Van der Waals areas of dye molecules were calculated using a software package ChemAxon Marvin 5.2 (ChemAxon, Budapest, Hungary).

Table 1.
Characteristics of the anionic dyes.
Corn stalks were obtained from the Izmail district of the Odessa region in 2016, dried at room temperature, milled in the electrical universal grinder, and sieved to retain the fraction <250 μm. This fraction was used for preparing unmodified and modified adsorbents.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Adsorbent
The processing of corn stalks before their modification was executed as follows: milled corn stalks were treated with NaOH solution (0.1 M) at the ratio 1:20 (w/v) for 2 h, then washed with distilled water until the produced filtrate was free of color and turbidity, then the stalks were dried at 323 K until the constant weight. Corn stalks after this preparation were designated as CS.
Corn stalks are lignocellulose materials and their ester linkages and glycosidic side chains are cleaved under alkaline treatments. In addition to delignification, this treatment also results in partial hydrolysis of hemicelluloses, cellulose swelling, cellulose decrystallization, lower degree polymerization of cellulose, increased internal area and porosity—essentially required for adsorption application [12].
Our preliminary studies have shown that treatment of the corn stalks by alkaline solution increased adsorption of CPB about 1.6 times with respect to the case without this treatment. These studies are in good agreement with the data in [13], where adsorption of CPB on barley straw treated by NaOH solution was also higher than adsorption of CPB on barley straw without this treatment.
Regarding the modified corn stalks, 10 g of CS was added to 200 cm3 of C21H38NBr (CPB) solution (2.5 mmol L−1), and the mixture was kept for 24 h at 293 K. The concentration of CPB was set above the CMC level in order to ensure the formation of admicelle on the solid surface [14]. Then, the liquid was separated from the solid phase using a Buchner funnel. The modified corn stalks were washed with distilled water to get the negative bromide test that had been obtained with 0.1 M AgNO3 and then dried at 323 K up to the constant weight. Corn stalks after modification were designated as CS-CP.
The characteristics of CS and CS-CP are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Characteristics of corn stalks (CS) before and after modification by cationic surfactant.
In Table 2, specific surface area (S) was calculated using the Langmuir adsorption isotherm of AR; the pH of point zero charge (pHPZC) and bulk density (Δ) were determined as described in [15].
2.2.2. Infrared Analysis
Samples of the adsorbents (CS and CS-CP) were characterized by recording their FTIR spectra (Perkin-Elmer Spectrometer, Waltham, MA, USA) in the 4000–400 cm−1 range. In each case, 2.0 mg of the dried sample and 400 mg of KBr were homogenized using a mortar and pestle and thereafter pressed into a tablet.
2.2.3. Batch Experiments
Adsorption of anionic dyes was carried out using batch experiments in 100 cm3 Erlenmeyer flasks. The mixtures of the adsorbent (0.1 g) with 10 cm3 aqueous solutions of dyes (50–1000 mg L−1) at pH = 3 were shaken at 150 rpm at different temperatures (303, 313, and 328 K). At the end of each established contact time for kinetic studies, and after equilibrium time for equilibrium studies, the dye solutions were analyzed for residual dye concentration. The concentrations of the dyes before and after adsorption were determined at maximum wavelengths 490 nm using an UV-VIS spectrophotometer (SF-56, Spectral, LOMO, S.-Peterburg, Russia).
Our preliminary results showed that adsorption of anionic dyes on CS-CP had maximum values at pH = 2–3, while at higher pH values the adsorption of anionic dyes on CS-CP had decreased (the figure is not shown). Therefore, all of the next adsorption experiments for dye removal using CS-CP adsorbent were carried out at the pH value of 3. This pH value is in line with the studies reported on the removal of Methyl Orange on wheat straw modified by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide [8] and pineapple leaf modified by hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide [10].
The amount of the dye on the adsorbent, which represents the dye uptake, was calculated from the difference in dye concentration in the aqueous phase before and after adsorption, according to Equation (1):
where Co is the initial dye concentration; C is the dye concentration after adsorption at time t; m is the mass of adsorbent; V is the volume of the dye solution.
When time is equal to the equilibrium time (te), the amount of the dye on the adsorbent at equilibrium time (qe) was calculated using Equation (1).
2.2.4. Desorption Studies
CS-CP (1 g) was added to 100 cm3 of the dye solution (200 mg L−1) and left for 2.5 h at pH = 3 and 303 K. Dye-loaded adsorbent was washed with distilled water to remove any unadsorbed dye and dried at 323 K according to [6,8,10].
Desorption of the dye from CS-CP was carried out using one cycle by immersing 0.1 g of the dye-loaded adsorbent into 10 cm3 distilled H2O, 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M NaOH, and 95% C2H5OH, respectively, for 3 h at 303 K.
The efficiency of dye desorption removal was calculated by Equation (2):
where qe is the equilibrium amount of dye adsorbed on the adsorbent; Cd is the dye concentration in solution after desorption; Vd is the volume of the eluent.
2.2.5. Adsorption Isotherms
The analysis of the adsorption isotherm data by fitting them to different isotherm models is an important step to finding the suitable model [2,10] that can be used for design purposes. In the present study, the two-parameter models of Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin were used to examine the relationship between the amount of adsorbed dye and its equilibrium concentration. The linear forms of the Langmuir [Equation (3)], Freundlich [Equation (4)] and Temkin [Equation (5)] isotherms are given below:
where Ce is the equilibrium dye concentration in solution; KF is the Freundlich constant related to the adsorption capacity; 1/n is the adsorption intensity; qm is the monolayer capacity of the adsorbent; KL is the Langmuir constant that relates to energy of adsorption; KT is the Temkin equilibrium constant corresponding to the maximum binding energy; b is the heat of adsorption.
2.2.6. Kinetic Studies
Kinetics data help to describe dye uptake rates, which control the residence time of adsorbate at the solid–liquid interface and provide useful information for adsorption process designing [8]. Experimental kinetic curves can be evaluated using different kinetic models [2,9]. In this paper, the applicability of the pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, Elovich, and Weber-Morris (intra-particle diffusion) kinetic models was tested for modelling the adsorption kinetics of the anionic dyes on CS-CP.
The linear form of pseudo-first order [Equation (6)], pseudo-second order [Equation (7)], Elovich [Equation (8)], and Weber-Morris [Equation (9)] kinetic model equations can be expressed as:
where qe and q are the amount of the dye on the adsorbent at equilibrium and various time t, respectively; k1 is the adsorption rate constant of pseudo-first order model; k2 is the adsorption rate constant of pseudo-second order model; α is initial adsorption rate; β is the desorption constant; kid is the adsorption rate constant of the intra-particle diffusion model; I is the constant, which gives an idea about the boundary layer thickness.
2.2.7. Adsorption Thermodynamics
The results of thermodynamic studies make it possible to understand the feasibility of the adsorption process and to obtain useful information about fundamental thermodynamic parameters of adsorption, such as standard free energy change (ΔGo), standard enthalpy change (ΔHo), and standard entropy change (ΔSo).
If the experimental adsorption isotherms are adequately described by the Langmuir equation, thermodynamic parameters can be calculated by Equations (10)–(12):
where K is the adsorption constant; γ is the amount solvent in 1 kg of its weight (for water γ = 55.5 mol kg−1); so and s are areas of solvent and dye molecules occupied on the surface of the adsorbent (for water, so = 0.0959 nm2; for dyes, Van der Waals areas of dye molecules are listed in Table 1); R is the universal gas constant; T is the absolute temperature.
2.2.8. Error Analysis
In this study, standard error (SE) and Chi-square test (χ2) were employed to find out the best-fit model for the experimental kinetic and equilibrium data.
These error functions are given as:
where qi,calc is the theoretical amount of the dye adsorbed on the adsorbent, which was calculated from one of the isotherm or kinetic model equations; qi,exp is the experimental amount of the dye adsorbed on the adsorbent; N is the number of the data points.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Adsorbent
FTIR analysis was performed to determine the properties of the functional groups involved in the adsorption process. It is seen from Figure 1 that the spectra of CS and CS-CPS displayed many absorption peaks. The strong and broad peak at 3401 cm−1 was originated from the O–H stretching vibration, and this indicates significant hydrogen-bond interactions in CS. The strong and broad peak at 3369 cm−1 was found from the O–H stretching vibration for CS-CPS. The C–H stretching vibrations at 2921 cm−1 from the methylene group were found for CS. The peak located at 1736 cm−1 was contributed to the stretching vibration of carbonyl groups in hemicelluloses of CS. The peak at 1631 cm−1 was related to the deformation vibration for H-O-H bonds of the physically adsorbed water in CS. The appearance of the strong sharp peak ranging from 2921 cm−1 can be ascribed to the C–H stretching vibration in cellulose and hemicelluloses in CS. The C–H stretching vibrations at 2919 cm−1 from the methylene group were found for CS-CP, and a shoulder peak near 2855 cm−1 was slightly resolved. This was due to the increase in the aliphatic carbon content from CPB in CS-CP [7,9].
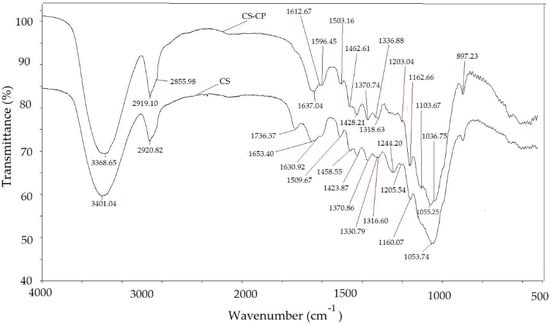
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra for unmodified and modified CS.
As seen from Figure 1, FTIR analysis implied that the cationic surfactant CPB had been adsorbed on the surface of the corn stalks. Obtained results are in line with the FTIR spectra of barley straw modified by cetylpyridinium chloride [6], wheat straw modified by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide [8], peanut husk modified by hexadecylpyridinum bromide [9], and pineapple leaf powder modified by hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide [10].
Our calculations were based on the determination of the adsorption capacity of CS towards CPB using the Langmuir adsorption isotherm (the figure is not shown), and confirmed that the cationic surfactant was loaded on corn stalks [0.2 mmol g−1 (76.8 mg g−1)].
3.2. Equilibrium Studies
The experimental adsorption isotherm describes how solutes interact with an adsorbent and help research in an adsorbent choosing. It is also important to pick up adsorption isotherm equations for the experimental adsorption isotherms and to find the most appropriate correlation of the equilibrium data [7].
In this study, experimental adsorption isotherms were used to describe the adsorption equilibrium between the CS-CP and the anionic dyes. As seen in Figure 2, increasing the temperature from 303 K to 328 K reduced the adsorption capacity of CS-CP, and the adsorption process of anionic dyes on CS-CP was exothermic. The increasing temperature decreased the adsorptive forces between the dyes and the active sites on the adsorbent surface as a result of the decreasing adsorption capacity [16].
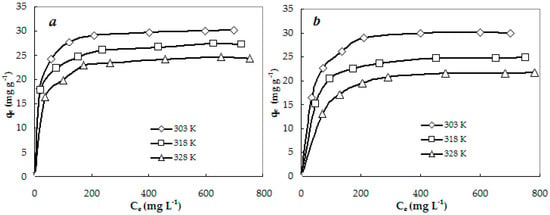
Figure 2.
Adsorption isotherms of Acid Red (AR) (a) and Acid Orange (AO) (b) on CS-CP at different temperatures.
Similar results have been observed by Su et al. [8] and Zhao et al. [9], where the increasing temperature was not beneficial for the adsorption of Methyl Orange on wheat straw modified by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide from 303 K to 323 K or Light Green on peanut husk modified by hexadecylpyridinium bromide from 293 K to 313 K.
In this work, Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin models are used to describe the equilibrium between the anionic dyes adsorbed on CS-CP and the anionic dyes in the solution. Accepted different isotherm models for the adsorption can be characterized by two common validity tests [7,8,17]: (i) a high correlation coefficient (R2), indicating the applicability and reliability of a given model; and (ii) the model must have conformity between experimental data and the model-predicted qe values expressed by the least error values.
The isotherm constants, correlation coefficient (R2), and error values (SE, χ2) of these models for the adsorption of the anionic dyes on CS-CP at different temperatures are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Comparison of the isotherm models.
As listed in Table 3, the Langmuir model exhibited a very good fit to the experimental adsorption data of the anionic dyes on CS-CP at all investigated temperatures since the R2 values were more than 0.9995. The results showed that with the increase in temperature, the qm and KL values decreased due to the lower interaction between the anionic dye ions with the adsorbent’s surface.
The experimental adsorption isotherms were further analyzed using the Freundlich isotherm. The results indicated that the Freundlich model fit the experimental data less than Langmuir model since the R2 values were 0.8673–0.8916 for AR and 0.9029–0.9521 for AO (Table 3). Nevertheless, these coefficient correlation values show a good linearity. The constant parameters of the Freundlich isotherm 1/n and KF decreased with the increase in temperature. The values 1/n below one also reflected favorable adsorption of anionic dyes on CS-CP.
Temkin studied the heat of adsorption and the adsorbent–adsorbate interactions on the surfaces of adsorbents [18]. According to the Temkin model, there is a linear decrease in the heat of adsorption of the molecules in the layer, which is due to the adsorbate–adsorbate interactions. As listed in Table 3, the correlation coefficients for the Temkin model were high (R2 = 0.9526–0.9709) and showed good linearity (Table 3). The good linear fitting of the Temkin isotherm to experimental data is an indication of the strong interaction between the anionic dyes and CS-CP. The results in Table 3 indicate that the values of constants KT decreased and b increased with the increase in temperature. The constants bT were positive for both anionic dyes, which indicates that the adsorption process is exothermic. The experimental equilibrium curves of anionic dyes on CS-CP were close to those predicted by the Temkin model.
Comparing the values of R2 and errors showed that the linear fits using three equations of adsorption isotherms were good for studying the adsorption of the anionic dyes on CS-CP within the used concentration range, but the fit with the ones of the Langmuir isotherm equation was better.
Su et al. [7] found that the Langmuir, Temkin, and Freundlich models fitted equilibrium data of Light Green on wheat straw modified by hexadecylpyridinium bromide and R2 value were 0.951, 0.910, and 0.824, respectively, while the values of sum of squares error became larger in such on order as Langmuir, Temkin, and Freundlich models with 16.48, 30.11, and 58.88, respectively.
3.3. Kinetics Studies
The experimental kinetic curves of the anionic dyes on CS-CP are presented in Figure 3. The adsorption process of the anionic dyes on CS-CP can be divided into two sections: (i) an initial rapid stage (to 60 min) where adsorption rate is fast; and (ii) a slower second stage where the adsorption rate becomes lower (60–150 min). It is evident from Figure 3 that the equilibrium time of the anionic dyes was 150 min at 303–328 K, but the adsorption rate was faster at 303 K than at 328 K.
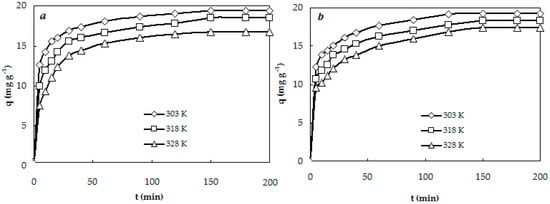
Figure 3.
Kinetic adsorption curves of anionic dyes AR (a) and AO (b) on CS-CP at different temperatures.
The adsorption kinetic curves of the anionic dyes on CS-CP were analyzed by kinetic models for a better understanding of the adsorption process. Table 4 summarizes the kinetic parameters of four kinetic models: pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, Elovich, and Weber-Morris.

Table 4.
Comparison of the kinetic models.
The pseudo-first and pseudo-second models were compared for their fitness for the anionic dyes uptake by CS-CP. Accepted kinetic models for the adsorption can be characterized by three common validity tests [7,8,19]: (i) a high correlation coefficient (R2), indicating the applicability and reliability of a given model; (ii) a close agreement between the calculated and experimental qe values; and (iii) the model must have conformity between the experimental data and the calculated (model-predicted) q values expressed by the least error values.
As listed in Table 4, the low correlation coefficients (R2 = 0.8363 at 303 K and R2 = 0.8251 at 328 K for AR; R2 = 0.7911 at 328 K for AO), different values of calculated and experimental equilibrium adsorption capacities of CS-CP toward the anionic dyes, and higher error values imply the non-applicability of the pseudo-first order kinetics model. On the other hand, the high correlation coefficients (R2 > 0.9988), close values of calculated and experimental equilibrium adsorption capacities of CS-CP toward the anionic dyes, and low error values imply the applicability of the pseudo-second order kinetics model. The pseudo-second order equation also generated the best agreement with experimental data for adsorption of Acid Green and Acid Red on sawdust modified by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide [1].
According to [20], the pseudo-second order model implies that two reactions, either in a series or in parallel, occur; the first one is fast and rapidly reaches the equilibrium, while the second one is a slower reaction that continues for a long period of time. The pseudo-second order kinetic model also indicates that chemical adsorption is the rate determining stage [21]. This means that the rate limiting step in the process is the chemical adsorption between the adsorbate and the active sites of the adsorbent.
As seen in Table 4, the correlation coefficients for the Elovich equation changed in the range of 0.9501–0.9902. These results show that the experimental kinetic data of anionic dyes on CS-CP agree with the Elovich model, and the constants in the Elovich equation (initial adsorption rates and desorption constants) decrease with the increase in temperature. Su et al. [8] also reported that kinetics of Methyl Orange on wheat straw modified by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide can be predicted well by the Elovich equation.
The Elovich model is successfully used to describe the adsorption kinetics of ion exchange systems [9]. Therefore, it can be concluded that the adsorption of the anionic dyes on CS-CP is a chemical process, especially an ion exchange process.
As listed in Table 4, the values of R2 obtained from the pseudo-second order and Elovich model were higher, while the error values were lower than the pseudo-first order model.
The kinetic data of the anionic dyes on CS-CP were also analyzed using the intraparticle diffusion model of Weber and Morris. When adsorbate molecules in solution are mixed with the adsorbent, there occurs a transport of the adsorbate into the pores of particles from the solution through the interface between the solution and the adsorbent. According to the intraparticle diffusion model, adsorption transpires in three distinct phases [20]: (i) adsorbate molecules transfer from the soluble phase to the adsorbent surface (penetration process); (ii) molecules are transported to porous locations in the adsorbent (influence on porosity); and (iii) the particles attach to the surface of the adsorbent and are absorbed.
As seen from Table 4, plots of the adsorbed amount of the anionic dyes on CS-CP versus t1/2 at different temperatures were linear (R2 = 0.8058–0.9355) over the whole time range, but they did not pass through the origin of the coordinates. Our results indicate that intraparticle diffusion is not the only rate-limiting step of the studied adsorption process, and film diffusion control may be involved in the adsorption process. From Table 4, it is observed that values of kid increased with increasing temperatures for both anionic dyes on CS-CP. Values of constants I were nonzero and they decreased in increasing temperature.
The intraparticle diffusion model of Weber and Morris is successfully used to describe experimental data for adsorption of Methyl Orange [8] and Reactive Blue [22] on wheat straw modified by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide.
3.4. Thermodynamic Study
The free energy change, enthalpy change, and entropy change for adsorption of the anionic dyes on CS-CP were calculated according to the equilibrium data, and their values are listed in Table 5. The negative values of ΔGo at all studied temperatures indicate the spontaneous adsorption process, reflecting the affinity of CS-CP towards the anionic dyes. The negative value of ΔHo confirms the exothermic nature of the adsorption process. The positive value of ΔSo for the adsorption of the anionic dyes on CS-CP indicates an increase in the randomness of the adsorption and affinity of the modified adsorbent for anionic dyes.

Table 5.
Thermodynamical parameters of adsorption of anionic dyes on CS-CP.
3.5. Desorption Studies
To make the adsorption process more economical, it was expedient to regenerate the used adsorbent and dyes, which could be recycled further [11]. The desorption studies are also important to understanding the adsorption mechanism of an adsorbate onto an adsorbent. Desorption of the anionic dyes from CS-CP by different eluents is presented in Figure 4.
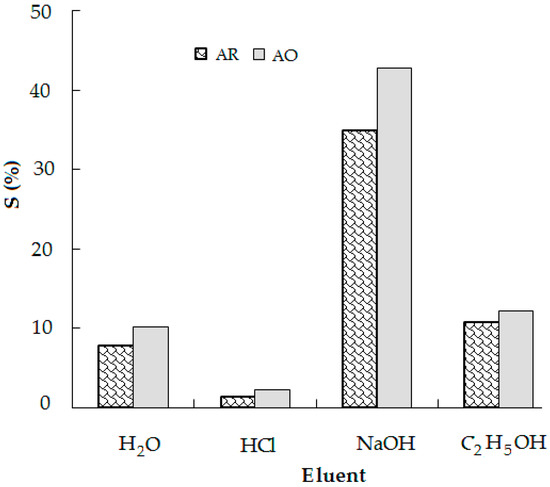
Figure 4.
Desorption of the anionic dyes on CS-CP by different eluents.
The desorption percentage of the anionic dyes from CS-CP using H2O or C2H5OH was found to be about 10%. Desorption of the anionic dyes from the surface of CS-CP was insignificant (3%) when HCl solution was used and higher (35% AR and 43% AO) when NaOH solution was used. Thus, the reduction in positively charged adsorption sites in alkaline solution led to the electrostatic repulsion of the anionic dyes from the surface of CS-CP. The low percentage of desorption suggests that anionic dyes were chemisorbed onto the surface of cationic surfactant-modified adsorbents [10].
According to [8], if alkali solution desorbs the dye, it may be possible that the attachment of the dye onto the adsorbent is through the ion exchange or electrostatic attraction. If an organic solvent, such as alcohol, desorbs the dye, it may be possible that the adsorption of the dye onto the adsorbent is due to chemisorption.
3.6. Adsorption Mechanism
In an aqueous solution, some groups in corn stalks—such as lignin and cellulose—lose hydrogen ions and form a potential negative surface. Thus, CPB may interact with corn stalks by the electrostatic attraction. On the other hand, the non-polar portion of CPB may interact with corn stalks through hydrophobic bonding and the polar (positively charged) head group directed towards the bulk of the solution. Therefore, there is a positive charge onto the surface of CS-CP, and the adsorption mechanism of anionic dyes onto CS may include electrostatic interaction, ion-exchange, and chemisorption.
4. Conclusions
Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies were carried out for the adsorption of the anionic dyes (AR and AO) from aqueous media on corn stalks modified by cetylpyridinium bromide at 303, 318, and 328 K. Equilibrium adsorption values of both anionic dyes decreased with the increase in temperature, which signifies the exothermic adsorption process of the anionic dyes on CS-CP.
The equilibrium data were analyzed using Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin isotherms. The constants for each isotherm, related correlation coefficients, and error functions were determined. The data are better simulated by the adsorption models in the following order: Langmuir > Temkin > Freundlich.
The suitability of kinetic models such as the pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, Elovich, and Weber-Morris equations for the adsorption of the anionic dyes on CS-CP was discussed. The results of the Weber-Morris model suggest that intraparticle diffusion is not the only rate controlling step. The classification of the kinetic models according to the simulation of the adsorption study is: pseudo-second order > Elovich > Weber-Morris > pseudo-first order.
The spontaneity and feasibility of the adsorption process are insinuated by the negative values of free energy change. The positive value of the entropy change for the adsorption of the anionic dyes indicates an increase in the randomness of the adsorption and affinity of the modified corn stalks for the anionic dyes.
It may be concluded that CS-CP can be an effective low-cost adsorbent for the removal of the anionic dyes present in the waste effluents. Further study should be devoted to practical wastewater’s treatment.
Author Contributions
L.S. conceived the work; M.Z. designed the experiments and performed the experiments; L.S. and M.Z. analyzed and interpreted the data; M.Z. wrote the manuscript; L.S. contributed to critical revision of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was carried out with the support of the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ansari, R.; Seyghali, B. Application of wood sawdust modified with cationic surfactants for efficient removal of acidic dyes from aqueous solutions: Kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2013, 2, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, K.S.; Ramesh, S.T. Removal of dyes using agricultural waste as low-cost adsorbents: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 3, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, C.; Suteu, D. Textile organic dyes—Characteristics, polluting effects and separation/elimination procedures from industrial effluents—A critical overview. In Organic Pollutants Ten Years after the Stockholm Convention—Environmental and Analytical Update; Puzyn, T., Ed.; InTechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 55–86. ISBN 978-953-307-917-22. [Google Scholar]
- Gisi, S.D.; Lofrano, G.; Grassi, M.; Notarnicola, M. Characteristics and adsorption capacities of low-cost sorbents for wastewater treatment: A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2016, 9, 10–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatkina, L.M.; Zavrichko, M.A. Application of agriculture waste as biosorbents for dye removal from aqueous solution. Chemistry, Physics and Technology of Surface. Хімія, фізика та технoлoгія пoверхні 2013, 4, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oei, B.C.; Ibrahim, S.; Wang, S.; Ang, H.M. Surfactant modified barley straw for removal of acid and reactive dyes from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4292–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Zhao, B.; Xiao, W.; Han, R. Adsorption behavior of light green anionic dye using cationic surfactant-modified wheat straw in batch and column mode. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5558–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Dou, C.; Han, R. Biosorption of methyl orange from aqueous solutions using cationic surfactant-modified wheat straw in batch mode. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 6145–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Xiao, W.; Shang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Han, R. Adsorption of light green anionic dye using cationic surfactant-modified peanut husk in batch mode. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3595–S3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaru, A.A.; Sani, N.S.; Malek, N.A.N.N. Raw and surfactant-modified pineapple leaf as adsorbent for removal of methylene blue and methyl orange from aqueous solution. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, C.; Sureshkumar, M.V. Anionic Dye Adsorption Characteristics of Surfactant-Modified Coir Pith, a ‘Waste’ Lignocellulosic. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sharma, R.K.; Singh, A.P. Cellulose based grafted biosorbents-Journey from lignocellulose biomass to toxic metal ions sorption applications—A review. J. Mol. Liquids 2017, 232, 62–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.C. Treatment of Oily and Dye Wastewater with Modified Barley Straw. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11937/589 (accessed on 30 January 2017).
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, S.; Frank, C.; Israelachvili, J. Molecular mechanisms and kinetics during the self-assembly of surfactant layers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1992, 153, 244–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatkina, L.M.; Menchuk, V.V.; Zavrichko, M.A. Adsorption properties of polyaniline modified corn stalks. Herald ONU (Ukr). Chem. 2013, 18, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofomaja, A.E.; Ho, Y.-S. Equilibrium sorption of anionic dye from aqueous solution by palm kernel fibre as sorbent. Dyes Pigments 2007, 74, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khambhaty, Y.; Mody, K.; Basha, S.; Jha, B. Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies on biosorption of hexavalent chromium by dead fungal biomass of marine Aspergillus niger. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 145, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, H.N.; Safa, Y. Removal of anionic dyes by rice milling waste from synthetic effluents: Equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2012, 48, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itodo, A.U.; Itodo, H.U. Activation chemistry and kinetics of Shea nut shell biosorbents for textile waste water treatment. Acad. Arena 2010, 2, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Kermani, M.; Gholami, M.; Farzadkia, M. Kinetic and isotherm studies of adsorption and biosorption processes in the removal of phenolic compounds from aqueous solutions: Comparative study. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2013, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimvand, J.; Didehban, K.; Mirshokraie, S.A. Safranin-O removal from aqueous solutions using lignin nanoparticle-g-polyacrylic acid adsorbent: Synthesis, properties, and application. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 1422–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, K.M.; Taha, A.H. Adsorption of Reactive Blue Dye onto Natural and Modified Wheat Straw. Am. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).