Determination of the Rate of Salt-Induced Rapid Coagulation of Polystyrene Latex Particles in Turbulent Flow Using Small Stirred Vessel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Rate of Coagulation in Turbulent Flow
2.1. Rate of Coagulation during Turbulent Mixing
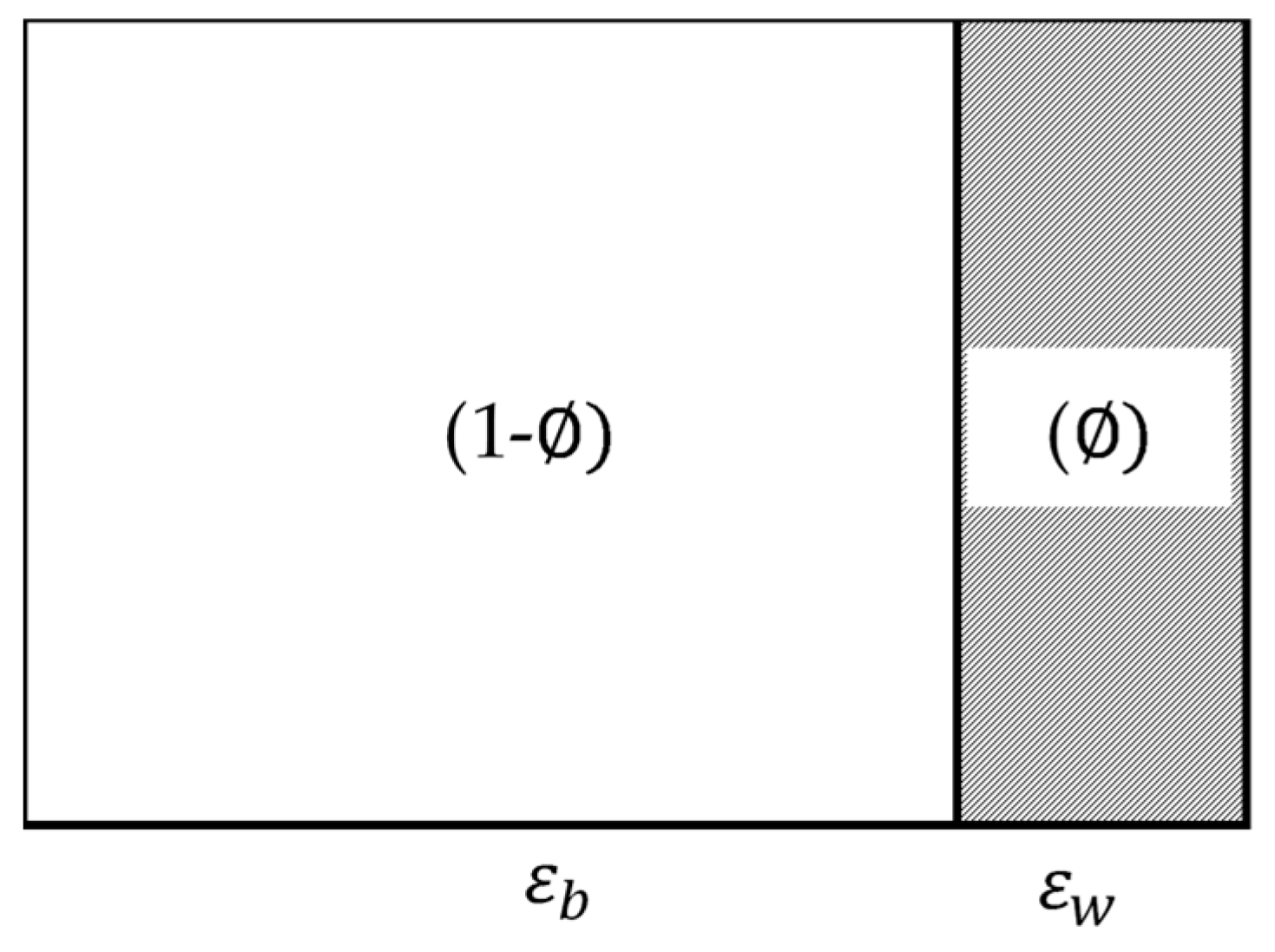
2.2. Deviations in the Case of the System Corresponding to a Low-Mixing Intensity in a Small Vessel
3. Materials and Methods
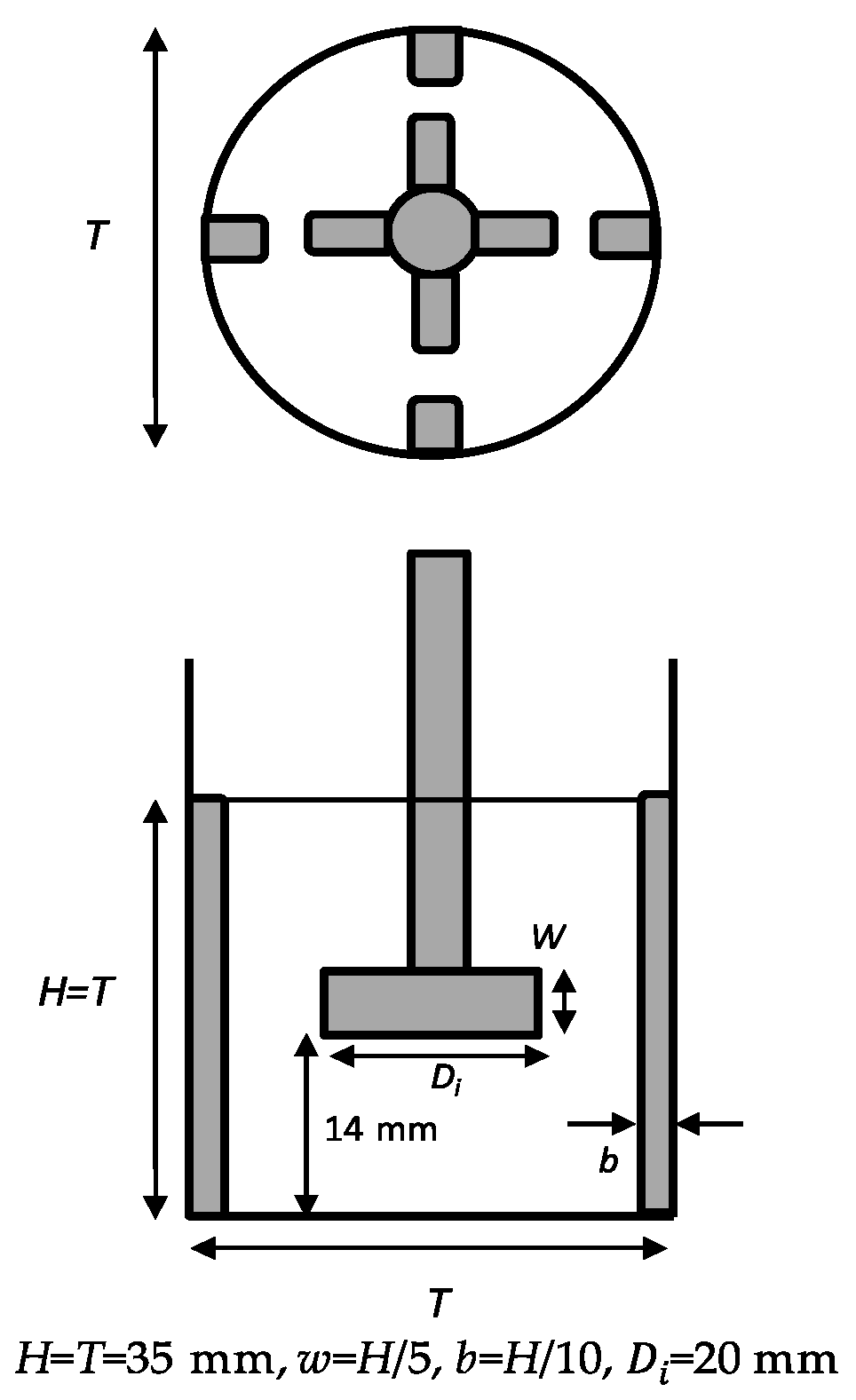
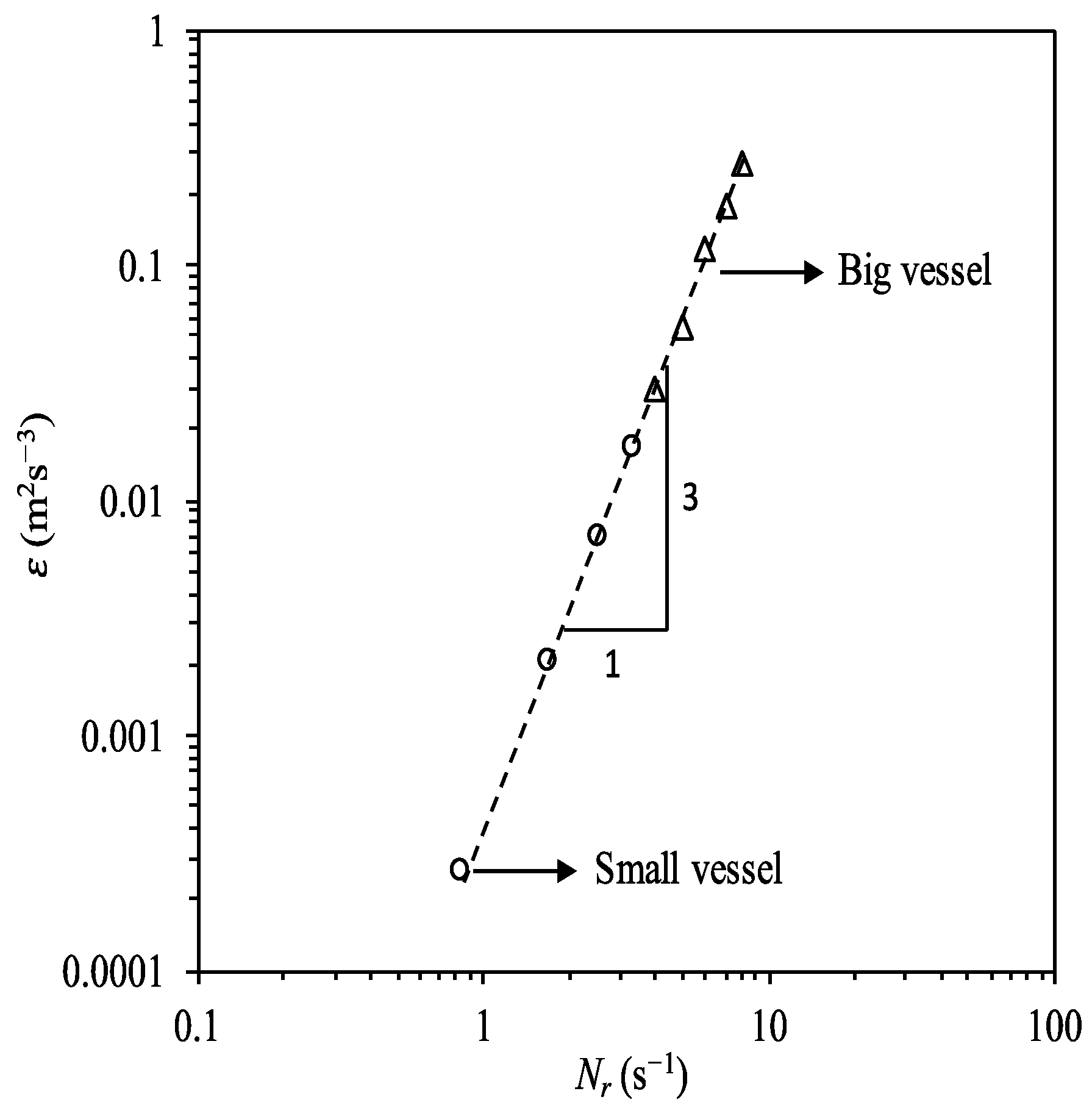
3.1. Mixing Vessel Used
3.2. Materials Used
3.3. Procedure
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of Rate of Coagulation
4.2. Analyses of Wall and Coupling Effects for Low Peclet Numbers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McAnally, W.H.; Mehta, A.J. Collisional Aggregation of Fine Estuarine Sediments. In Coastal and Estuarine Fine Sediment Processes; McAnally, W.H., Mehta, A.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2000; pp. 19–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, G.A. Coagulation Theory and Models of Oceanic Plankton Aggregation. In Flocculation in Natural and Engineered Environmental Systems; Droppo, I.G., Leppard, G.G., Liss, S.N., Milligan, T.G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Farrow, J.B.; Swift, J.D. A new procedure for assessing the performance of flocculants. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1996, 46, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, O.J.; Hubbe, M.A. The dispersion science of papermaking. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2005, 25, 713–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Vepsäläinen, M.; Sillanpää, M. Natural organic matter removal by coagulation during drinking water treatment: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 159, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higahshitani, K.; Yamauchi, Y.; Matsuno, Y.; Hosokawa, G. Turbulent coagulation of particles dispersed in a viscous fluid. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1983, 16, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, Y.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; Fokkink, R. Kinetics of turbulent coagulation studied by means end-over-end rotation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 165, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusters, K.A.; Wijers, J.G.; Thoenes, D. Aggregation kinetics of small particles in agitated vessel. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1997, 52, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrl, L.; Soos, M.; Morbidelli, M.; Bäbler, M.U. Dependence of initial cluster aggregation kinetics on shear rate for particles of different sizes under turbulence. AIChE J. 2009, 55, 3076–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Adachi, Y.; Ooi, S. Breakup of fractal flocs in a turbulent flow. Langmuir 1999, 15, 4351–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, L.; Coufort-Saudejaud, C.; Liné, A.; Frances, C. Dynamics of aggregate size and shape properties under sequenced flocculation in a turbulent Taylor-Couette reactor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 491, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachin, K.; Sauze, N.L.; Raimondi, N.D.M.; Aubin, J.; Gourdon, C.; Cabassud, M. Aggregation and breakup of acrylic latex particles inside millimetric scale reactors. Chem. Eng. Process. 2017, 113, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. The local structure of turbulence in incompressible viscous fluid for very large Reynolds numbers. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1941, 30, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoluchowski, M.V. Versuch einer mathematischen theorie der koagulationskinetik kolloider lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1918, 92, 129–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, D.L.; Friedlander, S.K. The coagulation of hydrosols by Brownian motion and laminar shear flow. J. Colloid Sci. 1964, 19, 621–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feke, D.L.; Schowalter, W.R. The Effect of Brownian Diffusion on Shear-Induced Coagulation of Colloidal Dispersions. J. Fluid Mech. 1983, 133, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feke, D.L.; Schowalter, W.R. The influence of Brownian diffusion on binary flow-induced collision rates in colloidal dispersions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1985, 106, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Ven, T.G.M.; Mason, S.G. The microrheology of colloidal dispersions VIII. Effect of shear on perikinetic doublet formation. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1977, 255, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffman, P.G.; Turner, J.S. On the Collision of Drops in Turbulent Clouds. J. Fluid Mech. 1956, 1, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, Y. Dynamic aspect of coagulation and flocculation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1995, 56, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Stuart, M.C.; Adachi, Y. Dynamics of polyelectrolyte adsorption and colloidal flocculation upon mixing studied using mono-dispersed polystyrene latex particles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 226, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Adachi, Y. Break-up Strength of Flocs Analyzed Using Orifice Converging Flow. Available online: https://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10029817970 (accessed on 17 December 2018).
- Vallejos, J.R.; Kostov, Y.; Ram, A.; French, J.A.; Marten, M.R.; Rao, G. Optical analysis of liquid mixing in a minibioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 93, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamping, S.R.; Zhang, W.; Allen, B.; Shamlou, P.A. Design of a prototype miniature bioreactor for high throughput automated bioprocessing. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, D.M.; Lindsey, E.E. An approach to characterizing agitation by dispersion particle size. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1962, 1, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Statistical theory of turbulence. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1935, 151, 421–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, A.A. The Measurement of Double and Triple Correlation Derivatives in Isotropic Turbulence. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1947, 43, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Ven, T.G.M.; Mason, S.G. The microrheology of colloidal dispersions VII. Orthokinetic doublet formation of spheres. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1977, 255, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeichner, G.R.; Schowalter, W.R. Use of trajectory analysis to study stability of colloidal dispersions in flow fields. AIChE J. 1977, 23, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng-Hua, X.; Zhi-Wei, S.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.T. Coupling effect of Brownian motion and laminar shear flow on colloid coagulation: A Brownian dynamic simulation study. Chin. Phys. B 2012, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, S.; Verduyn, M.; Storti, G.; Morbidelli, M.; Bałdyga, J. Effect of fluid motion on the aggregation of small particles subject to interaction forces. AIChE J. 1999, 45, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinchenko, A.Z.; Davis, R.H. Collision rates of spherical drops or particles in a shear flow at arbitrary Peclet numbers. Phys. Fluids 1995, 7, 2310–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. Mass Transfer from Small Particles Suspended in Turbulent Fluid. J. Fluid Mech. 1980, 98, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, J.W.; Hearn, J.; Ho, C.C.; Ottewill, R.H. Studies on the preparation and characterisation of monodisperse polystyrene lattice III. Preparation without added surface active agents. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1974, 252, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Adachi, Y. Kinetics of polyelectrolyte adsorption onto polystyrene latex particle studied using electrophoresis: Effects of molecular weight and ionic strength. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 300, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutter, L.A. Flow and turbulence in a stirred tank. AIChE J. 1966, 12, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.; Yianneskis, M. Observations on the distribution of energy dissipation in stirred vessels. Trans IChemE A. 2000, 78, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Kresta, S.M. Distribution of energy between convective and turbulent flow for three frequently used impellers. Trans IChemE A. 1996, 74, 379–389. [Google Scholar]
- Oktaviani, O.; Adachi, Y. Effect of mixing intensity on flocculation kinetics of polystyrene latex particles with high-charge density polyelectrolyte at various ionic strength. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

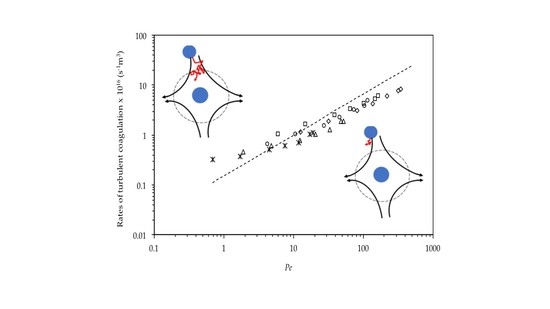
 ) [rpm]).
) [rpm]).
 ) [rpm]).
) [rpm]).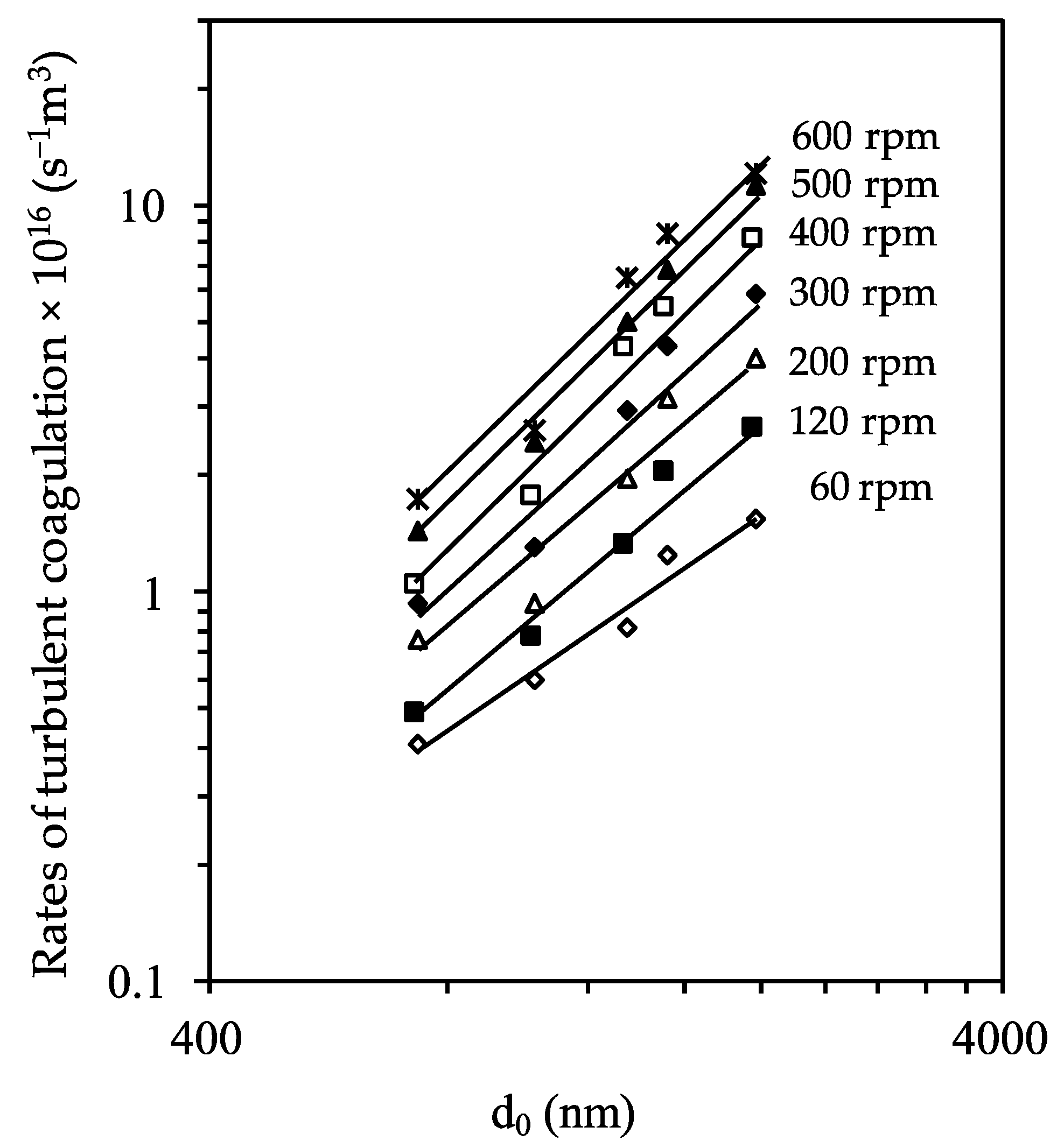
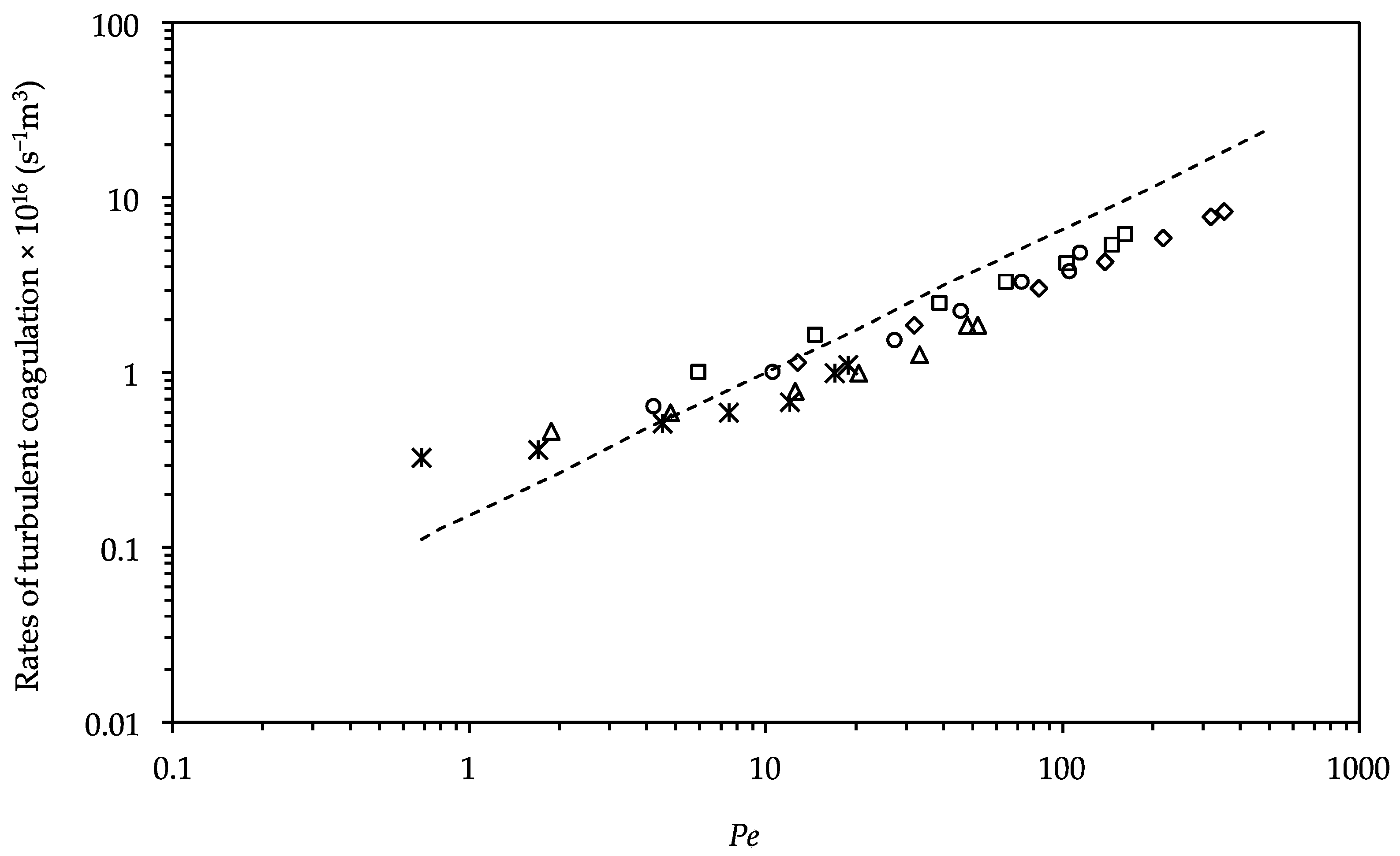
 ), 1040 nm (△), 1356 nm (○), 1520 nm (☐), and 1956 nm (◇)). Solid line (εi) is the energy dissipated per unit mass obtained using the torque meter, while dashed line (εd) is the energy used for coagulation in the case of an end-over-end mixing device as determined in a previous study [7].
), 1040 nm (△), 1356 nm (○), 1520 nm (☐), and 1956 nm (◇)). Solid line (εi) is the energy dissipated per unit mass obtained using the torque meter, while dashed line (εd) is the energy used for coagulation in the case of an end-over-end mixing device as determined in a previous study [7].
 ), 1040 nm (△), 1356 nm (○), 1520 nm (☐), and 1956 nm (◇)). Solid line (εi) is the energy dissipated per unit mass obtained using the torque meter, while dashed line (εd) is the energy used for coagulation in the case of an end-over-end mixing device as determined in a previous study [7].
), 1040 nm (△), 1356 nm (○), 1520 nm (☐), and 1956 nm (◇)). Solid line (εi) is the energy dissipated per unit mass obtained using the torque meter, while dashed line (εd) is the energy used for coagulation in the case of an end-over-end mixing device as determined in a previous study [7].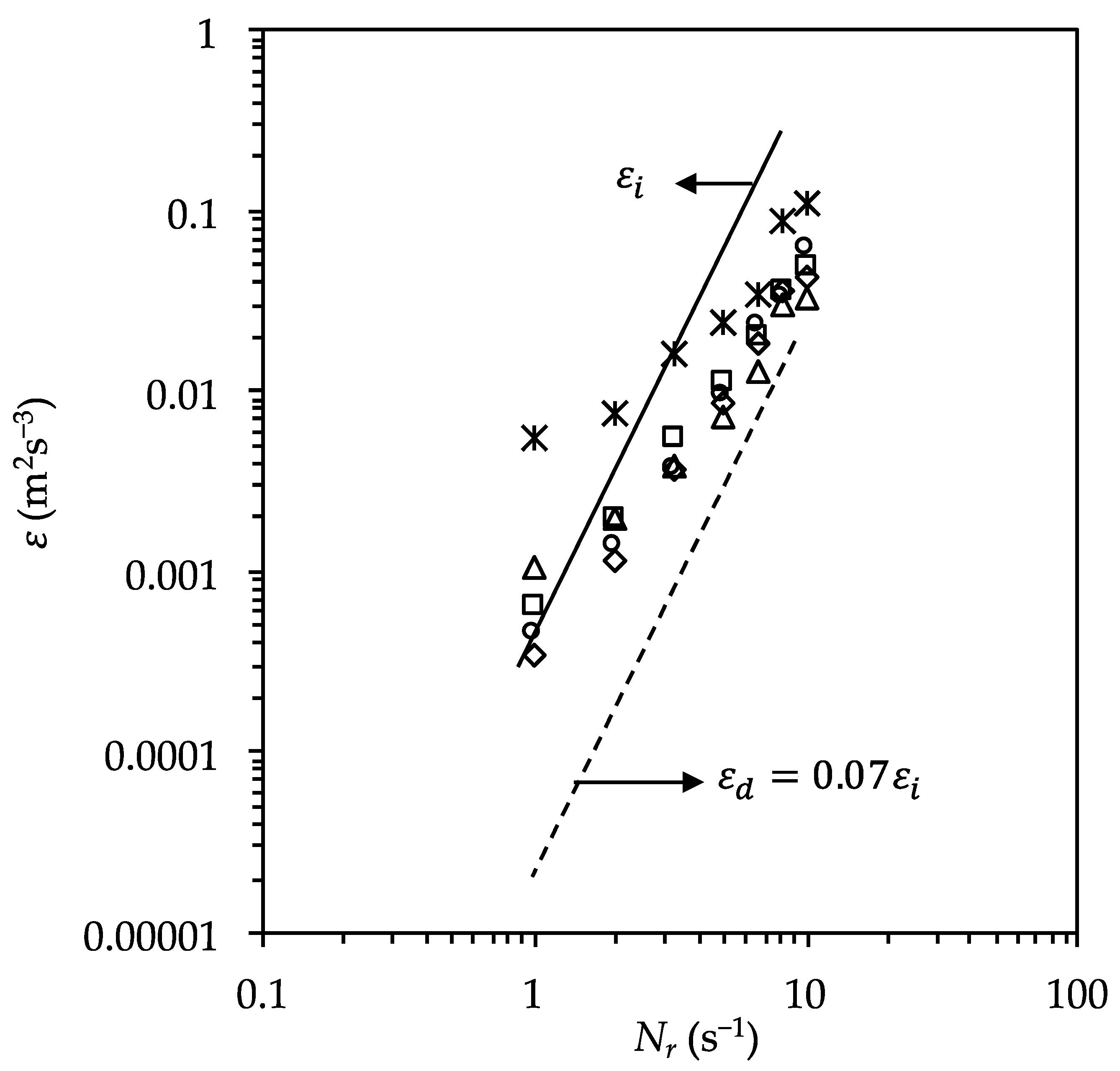
| Diameter (μm) | Number Concentration × 10−7 (cm−3) |
|---|---|
| 0.740 | 4.342 ± 0.016 |
| 1.040 | 5.284 ± 0.057 |
| 1.356 | 5.421 ± 0.041 |
| 1.520 | 5.578 ± 0.029 |
| 1.956 | 4.395 ± 0.017 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oktaviani, O.; Adachi, Y. Determination of the Rate of Salt-Induced Rapid Coagulation of Polystyrene Latex Particles in Turbulent Flow Using Small Stirred Vessel. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010005
Oktaviani O, Adachi Y. Determination of the Rate of Salt-Induced Rapid Coagulation of Polystyrene Latex Particles in Turbulent Flow Using Small Stirred Vessel. Colloids and Interfaces. 2019; 3(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleOktaviani, Oktaviani, and Yasuhisa Adachi. 2019. "Determination of the Rate of Salt-Induced Rapid Coagulation of Polystyrene Latex Particles in Turbulent Flow Using Small Stirred Vessel" Colloids and Interfaces 3, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010005
APA StyleOktaviani, O., & Adachi, Y. (2019). Determination of the Rate of Salt-Induced Rapid Coagulation of Polystyrene Latex Particles in Turbulent Flow Using Small Stirred Vessel. Colloids and Interfaces, 3(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010005