Effect of Amplitude on the Surface Dilational Visco-Elasticity of Protein Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Theory
3.1. Adsorption Layer Model
3.2. Effect of Oscillation Amplitude
- The dynamic contribution due to inertia of the liquid can disturb the ideal Laplace shape of the drop. The inertia contribution is proportional to ρv², where ρ is the density, and v is the velocity of the liquid, i.e., this contribution is proportional to the squared velocity and, therefore, to the squared amplitude. Hence, it should decrease fast with the amplitude decrease and, in the linear regimes, it can be neglected.
- Non-uniformity of the surface expansion during the oscillations—the surface can expand stronger near the drop apex and much less near its base (wetting perimeter). This leads to tangential flows at the surface (Marangoni flows). The corresponding contribution to the surfactant balance equation is proportional to the product ΔΓ⋅vs, where vs is the tangential velocity of the liquid at the surface, and ΔΓ is the difference of the surface concentrations in different points. Both vs and ΔΓ are proportional to the amplitude and, therefore, the effect is proportional to the squared amplitude. In linear regimes, we assume the surface concentration Γ to be constant over the surface.
- The convective surfactant transfer in the bulk of a solution can overlap with the diffusional transport. The convective term in the convective diffusion equation is proportional to the product v⋅Δc, where v is the velocity of the liquid and Δc is the concentration difference in the bulk. Here, again both multipliers are proportional to the amplitude and, therefore, the effect is proportional to the squared amplitude. The respective term can be neglected by a linearization of the equation.
- Non-linearity of the surface equation of state and the adsorption isotherm. All usually-used adsorption isotherms are non-linear, except the Henry isotherm. In linear regimes of surface oscillations, the derivatives dΠ/dΓ and dΓ/dc are assumed to be constant. However, in non-linear regimes, these derivatives can change due to large deviations from the equilibrium. When the equations for surface visco-elasticity are derived, one usually expands the functions Π(Γ) and Γ(c) in series, and only the leading terms are retained. At higher amplitudes, the contribution of the neglected higher order terms can be significant.
4. Results and Discussion
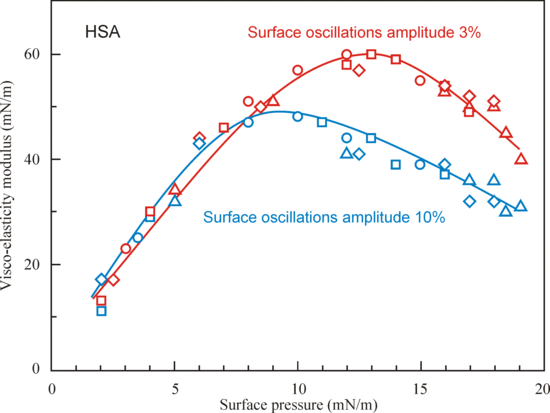
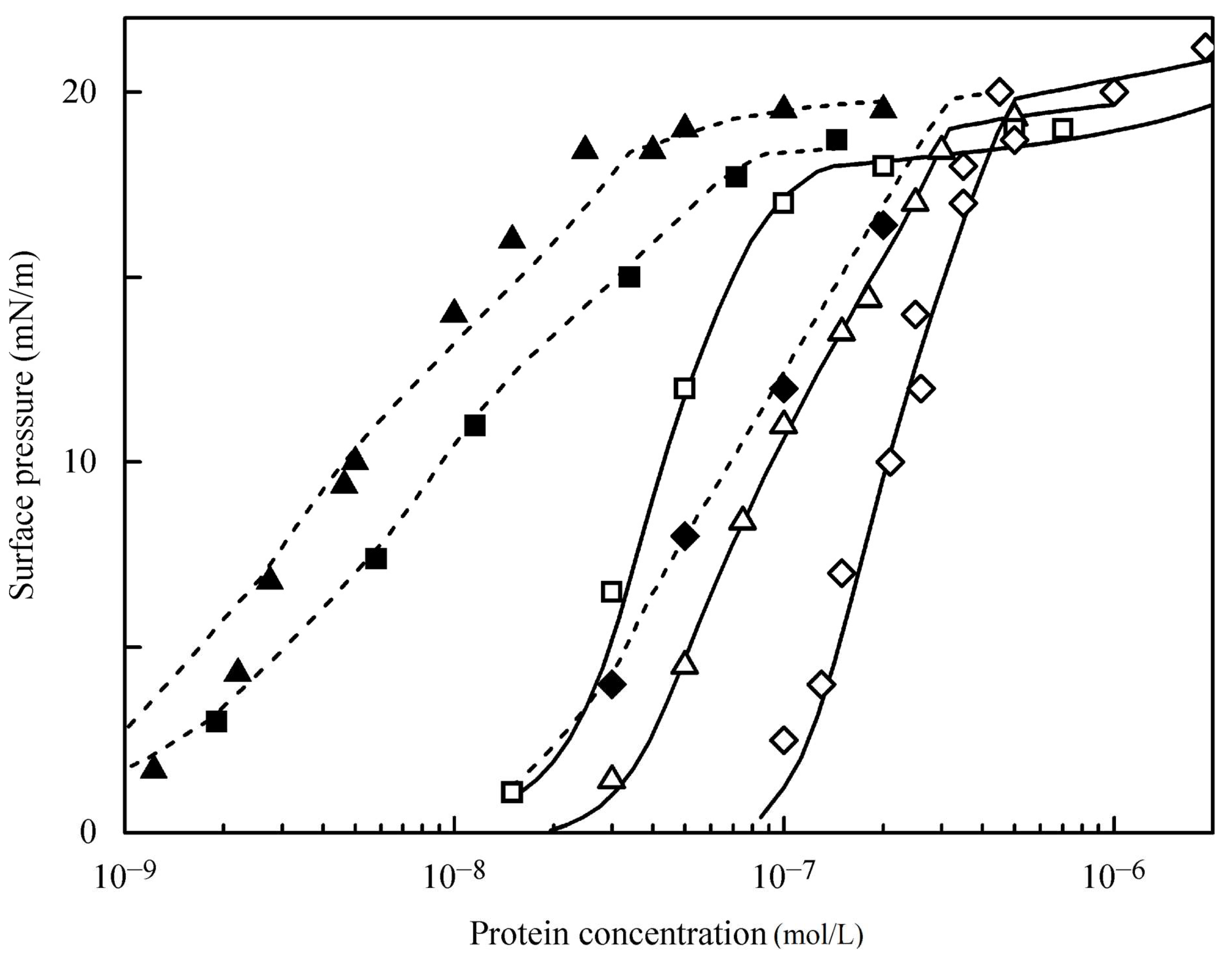
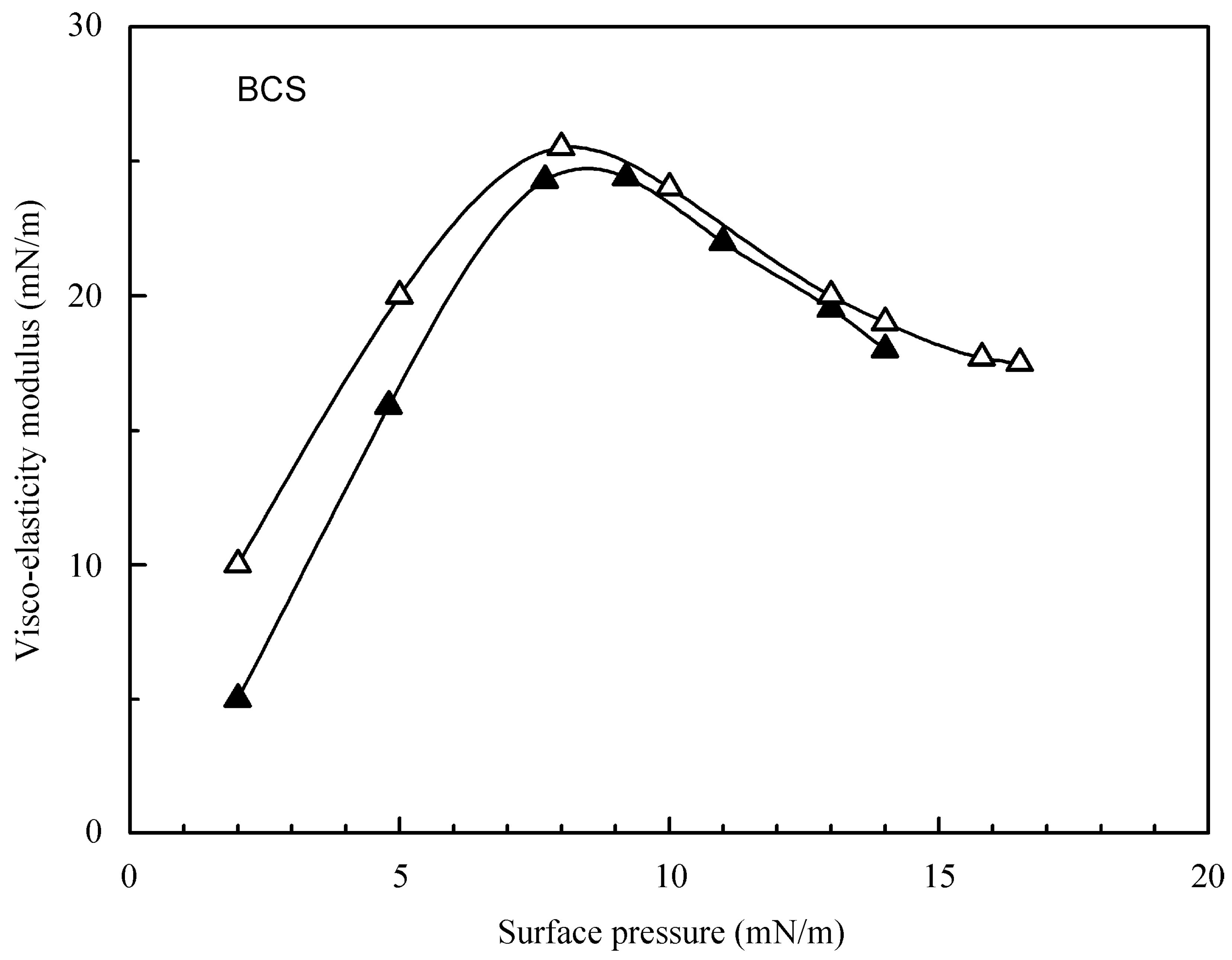
4.1. Experimental Results for the Studied Proteins
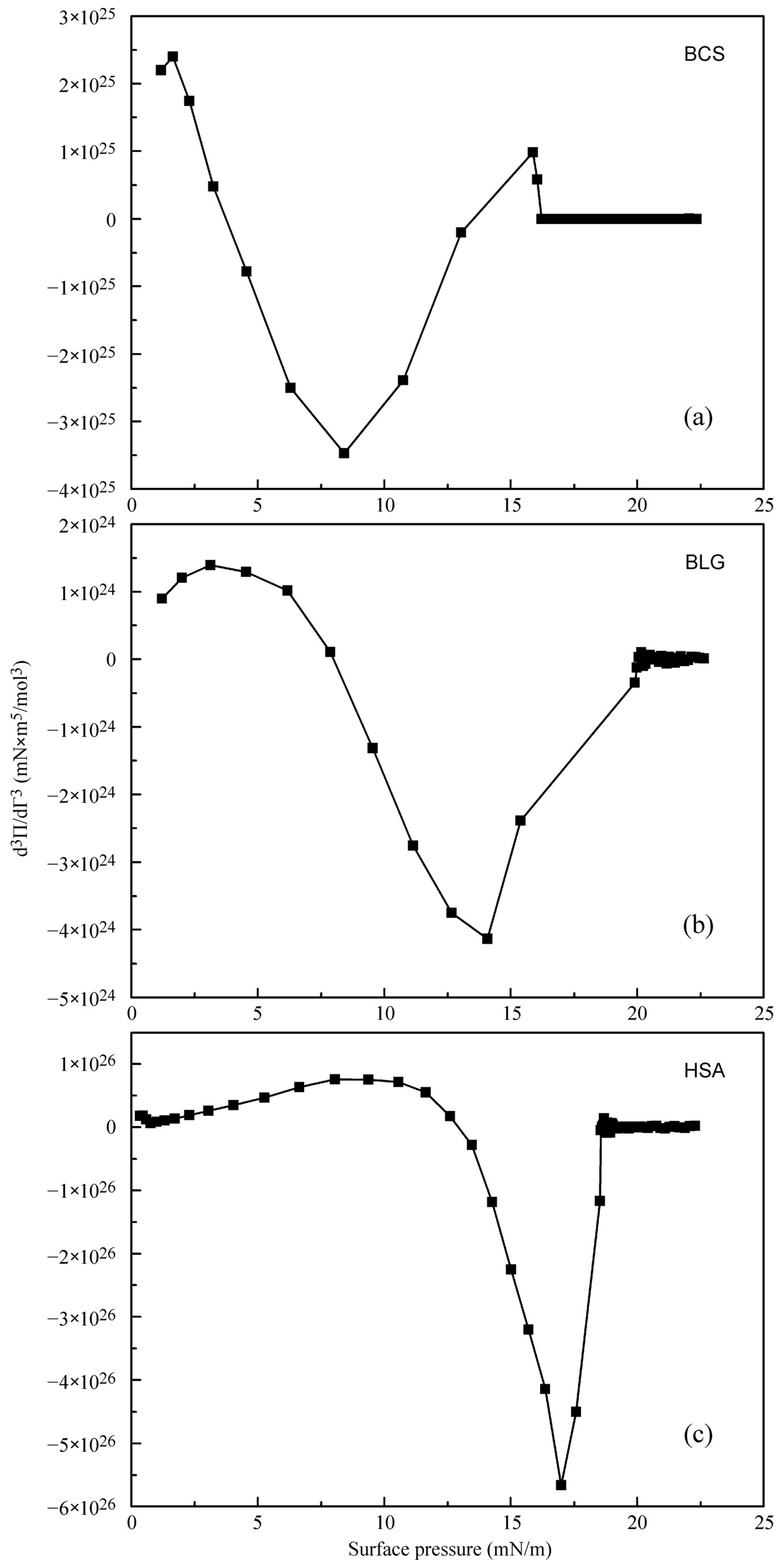
4.2. Evaluation of the Effect of Oscillation Amplitude for the Studied Proteins
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Cascao-Pereira, L.G.; Theodoly, O.; Blanch, H.W.; Radke, C.J. Dilatational rheology of BSA conformers at the air/water interface. Langmuir 2003, 19, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freer, E.M.; Yim, K.S.; Fuller, G.G.; Radke, C.J. Shear and dilatational relaxation mechanisms of globular and flexible proteins at the hexadecane/water interface. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10159–10167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freer, E.M.; Yim, K.S.; Fuller, G.G.; Radke, C.J. Interfacial rheology of globular and flexible proteins at the hexadecane/water interface: Comparison of shear and dilatation deformation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 3835–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamins, J.; Lyklema, J.; Lucassen-Reynders, E.H. Compression/expansion rheology of oil/water interfaces with adsorbed proteins. Comparison with the air/water surface. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6181–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgieva, D.; Cagna, A.; Langevin, D. Link between surface elasticity and foam stability. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucassen-Reynders, E.H.; Benjamins, J.; Fainerman, V.B. Dilational rheology of protein films adsorbed at fluid interfaces. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüstneck, R.; Fainerman, V.B.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Kotsmar, C.; Pradines, V.; Krägel, J.; Miller, R. Surface dilatational behavior of β-casein at the solution/air interface at different pH values. Colloids Surf. A 2012, 404, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühs, P.; Scheuble, N.; Windhab, E.; Fischer, P. Protein adsorption and interfacial rheology interfering in dilatational experiment. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2013, 222, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, A.; Wüstneck, R.; Krägel, J.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Fainerman, V.B.; Miller, R. Interfacial adsorption and rheological behavior of β-casein at the water/hexane interface at different pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 34, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskov, B.A. Protein conformational transitions at the liquid–gas interface as studied by dilational surface rheology. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noskov, B.A. Dilational surface rheology of polymer and polymer/surfactant solutions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilles, H.; Monroy, F.; Bonales, L.J.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G. Fourier-transform rheology of polymer Langmuir monolayers: Analysis of the non-linear and plastic behaviors. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 122, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erni, P.; Parker, A. Nonlinear viscoelasticity and shear localization at complex fluid interfaces. Langmuir 2012, 28, 7757–7767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fainerman, V.B.; Lucassen-Reynders, E.H.; Miller, R. Description of the adsorption behaviour of proteins at water/fluid interfaces in the framework of a two-dimensional solution model. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 106, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainerman, V.B.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Krägel, J.; Miller, R. Thermodynamics, interfacial pressure isotherms and dilational rheology of mixed protein-surfactant adsorption layers. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 233, 200–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulaganathan, V.; Retzlaff, I.; Won, J.Y.; Gochev, G.; Gunes, D.Z.; Gehin-Delval, C.; Leser, M.; Noskov, B.A.; Miller, R. β-Lactoglobulin adsorption layers at the water/air surface: 2. Dilational rheology: Effect of pH and ionic strength. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 521, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskov, B.A.; Loglio, G.; Miller, R. Dilational surface visco-elasticity of polyelectrolyte/surfactant solutions: Formation of heterogeneous adsorption layers. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 168, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bykov, A.G.; Liggieri, L.; Noskov, B.A.; Pandolfini, P.; Ravera, F.; Loglio, G. Surface dilational rheological properties in the nonlinear domain. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagis, L.M.C. Rheology of interfaces stabilized by a 2D suspension of anisotropic particles: A classical irreversible thermodynamics theory. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 7727–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Yang, X.; Sagis, L.M.C. Nonlinear Surface Dilatational Rheology and Foaming Behavior of Protein and Protein Fibrillar Aggregates in the Presence of Natural Surfactant. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3679–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagis, L.M. Dynamic properties of interfaces in soft matter: Experiments and theory. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2011, 83, 1367–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagis, L.M.; Scholten, E. Complex interfaces in food: Structure and mechanical properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kempen, S.E.; Schols, H.A.; van der Linden, E.; Sagis, L.M. Non-linear surface dilatational rheology as a tool for understanding microstructures of air/water interfaces stabilized by oligofructose fatty acid esters. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 9579–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fainerman, V.B.; Kovalchuk, V.I.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Zinkovych, I.I.; Makievski, A.V.; Nikolenko, M.V.; Miller, R. Dilational viscoelasticity of proteins solutions in dynamic conditions. Langmuir 2018, 34, 6678–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kairaliyeva, T.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Mucic, N.; Makievski, A.V.; Fainerman, V.B.; Miller, R. Surface tension and adsorption studies by drop profile analysis tensiometry. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2017, 20, 1225–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zholob, S.A.; Makievski, A.V.; Miller, R.; Fainerman, V.B. Optimisation of calculation methods for determination of surface tensions by drop profile analysis tensiometry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 134-135, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joos, P. Dynamic Surface Phenomena; VSP: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; ISBN 90-6764-300-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fainerman, V.B.; Lylyk, S.V.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Makievski, A.V.; Ravera, F.; Petkov, J.T.; Yorke, J.; Miller, R. Adsorption layer characteristics of Tritons surfactants. 3. Dilational visco-elasticity. Colloids Surf. A 2009, 334, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucassen, J. Dynamic dilational properties of composite surfaces. Colloids Surf. 1992, 65, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leser, M.E.; Acquistapace, S.; Cagna, A.; Makievski, A.V.; Miller, R. Limits of oscillation frequencies in drop and bubble shape tensiometry. Colloids Surf. A 2005, 261, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainerman, V.B.; Miller, R.; Kovalchuk, V.I. Influence of the compressibility of adsorbed layers on the surface dilational elasticity. Langmuir 2002, 18, 7748–7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainerman, V.B.; Miller, R.; Kovalchuk, V.I. Influence of the two-dimensional compressibility on the surface pressure isotherm and dilational elasticity of dodecyldimethylphosphine oxide. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 6119–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, V.I.; Loglio, G.; Fainerman, V.B.; Miller, R. Interpretation of surface dilational elasticity data based on an intrinsic two-dimensional interfacial compressibility model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 270, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fainerman, V.B.; Kovalchuk, V.I.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Michel, M.; Leser, M.E.; Miller, R. Models of two-dimensional solution assuming the internal compressibility of adsorbed molecules: A comparative analysis. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 13700–13705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainerman, V.B.; Lylyk, S.V.; Makievski, A.V.; Miller, R. Interfacial tensiometry as a novel methodology for the determination of surfactant adsorption at a liquid surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.E.; Phillips, M.C. Proteins at liquid interfaces II: Adsorption isotherms. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1979, 70, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.E.; Phillips, M.C. Proteins at liquid interfaces III: Molecular structure of adsorbed films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1979, 70, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
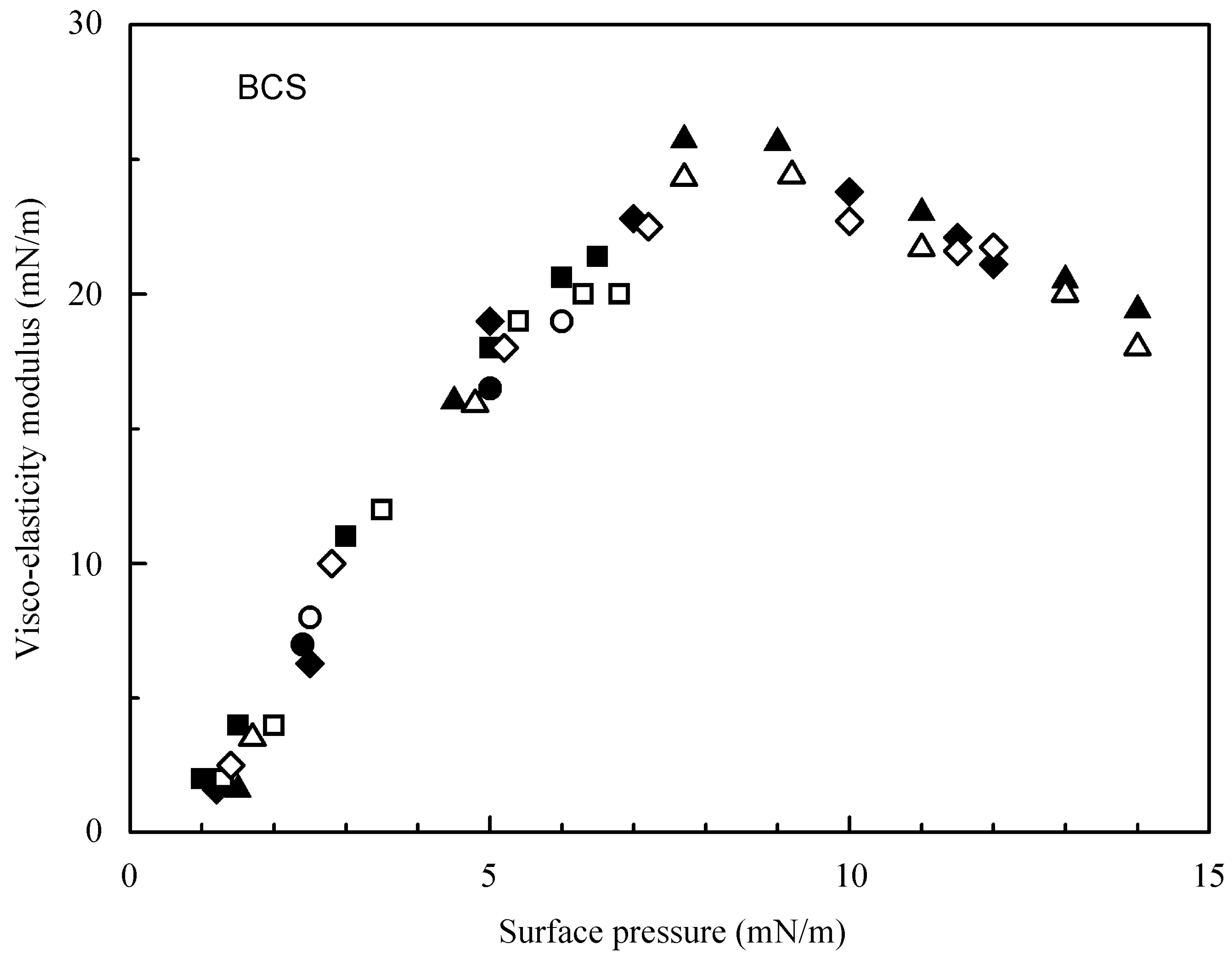

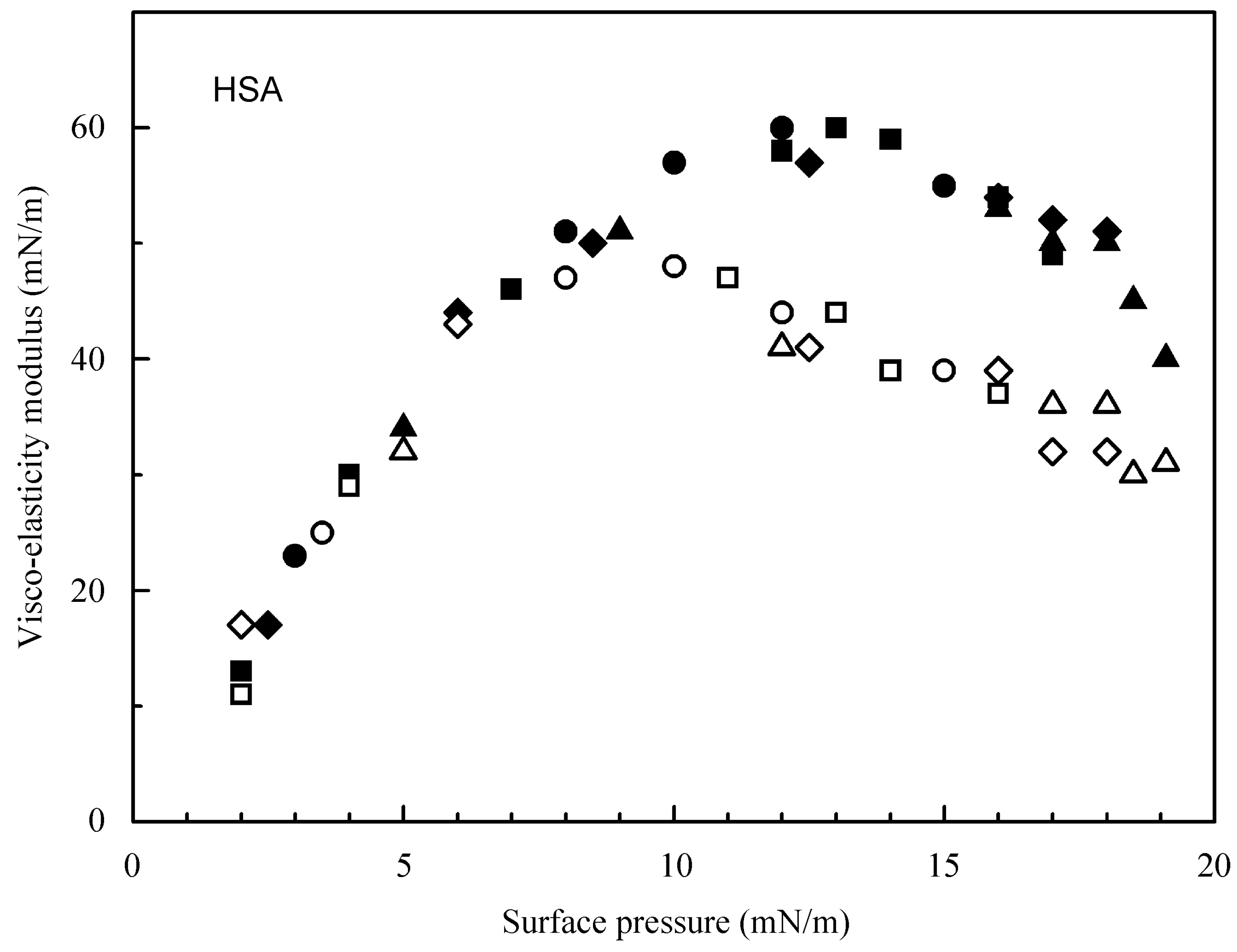

| Parameters | BLG | BLG [24] | BCS | BCS [24] | HSA | HSA [24] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| a | 2.1 | 2.1 | 0.55 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| ω0 (105 m2/mol) | 3.1 | 3.1 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3.6 | 3.5 |
| ωmin (106 m2/mol) | 6.0 | 6.0 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 35 | 36 |
| ωmax (107 m2/mol) | 1.5 | 1.5 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 7.8 | 7.5 |
| na | 3 | 4 | 10 | 10 | 3 | 3 |
| Π* (mN/m) | 20 | 21 | 18.5 | 16.5 | 18.5 | 18.4 |
| b1 (103 m3/mol) | 0.57 | 0.68 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 37 | 37 |
| bX (m3/mol) | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 95 | 95 |
| L | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Protein | Π (mN/m) | Γ0 (10–8 mol/m2) | d3Π/dΓ3 (1024 mN⋅m5/mol3) | ΔE0(mN/m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSA | 17.0 | 2.3 | −566 | −0.77 | −8.61 |
| BLG | 14.1 | 9.1 | −4.13 | −0.35 | −3.89 |
| BLS | 8.4 | 2.1 | −34.7 | −0.036 | −0.40 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovalchuk, V.I.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Trukhin, D.V.; Makievski, A.V.; Fainerman, V.B.; Miller, R. Effect of Amplitude on the Surface Dilational Visco-Elasticity of Protein Solutions. Colloids Interfaces 2018, 2, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2040057
Kovalchuk VI, Aksenenko EV, Trukhin DV, Makievski AV, Fainerman VB, Miller R. Effect of Amplitude on the Surface Dilational Visco-Elasticity of Protein Solutions. Colloids and Interfaces. 2018; 2(4):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2040057
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovalchuk, Volodymyr I., Eugene V. Aksenenko, Dmytro V. Trukhin, Alexander V. Makievski, Valentin B. Fainerman, and Reinhard Miller. 2018. "Effect of Amplitude on the Surface Dilational Visco-Elasticity of Protein Solutions" Colloids and Interfaces 2, no. 4: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2040057
APA StyleKovalchuk, V. I., Aksenenko, E. V., Trukhin, D. V., Makievski, A. V., Fainerman, V. B., & Miller, R. (2018). Effect of Amplitude on the Surface Dilational Visco-Elasticity of Protein Solutions. Colloids and Interfaces, 2(4), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2040057