KGEARSRG: Kernel Graph Embedding on Attributed Relational SIFT-Based Regions Graph
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Kernel Graph Embedding on Attributed Relational SIFT-Based Regions Graph (KGEARSRG)
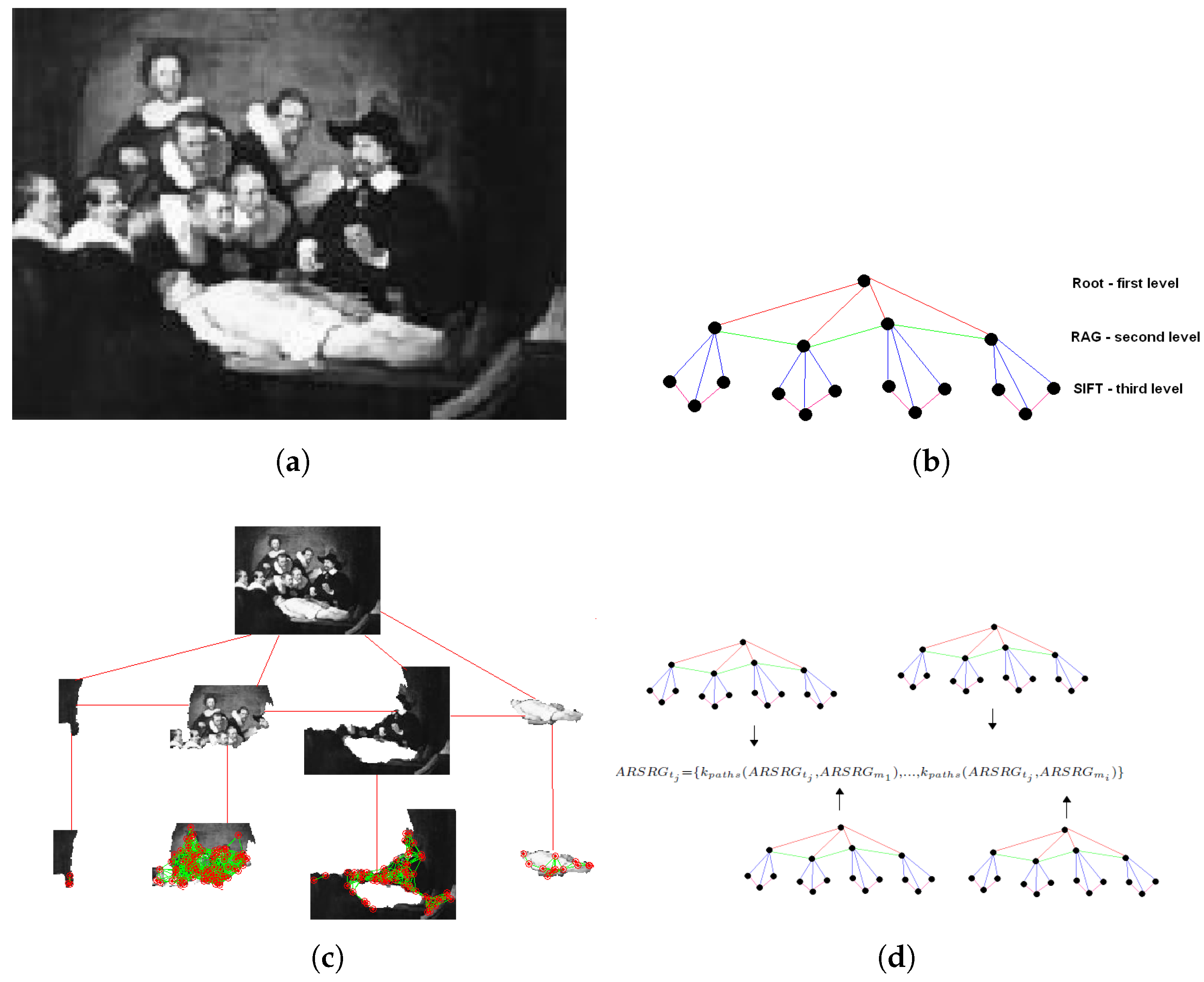
3.1. Graph-Based Image Representation
3.2. Graph Embedding
3.3. Kernel Graph Embedding
- is the set of nodes associated to SIFT keypoints;
- is the set of edges.
Computational Cost
- The computational cost for extracting SNNG pairs between image regions through SIFT match with graph matching.
- Kernel graph computation involves:
- (a)
- The direct product graph upper bounded by , where n is the number of nodes.
- (b)
- The inversion of the adjacency matrix of this direct product graph; standard algorithms for the inversion of an matrix require time.
- (c)
- The shortest-path kernel requires a Floyd-transformation algorithm which can be performed in time. The number of edges in the transformed graph is when the original graph is connected. Pairwise comparison of all edges in both transformed graphs is required to determine the kernel value. pairs of edges are considered, which results in a total runtime of .
4. Experimental Results
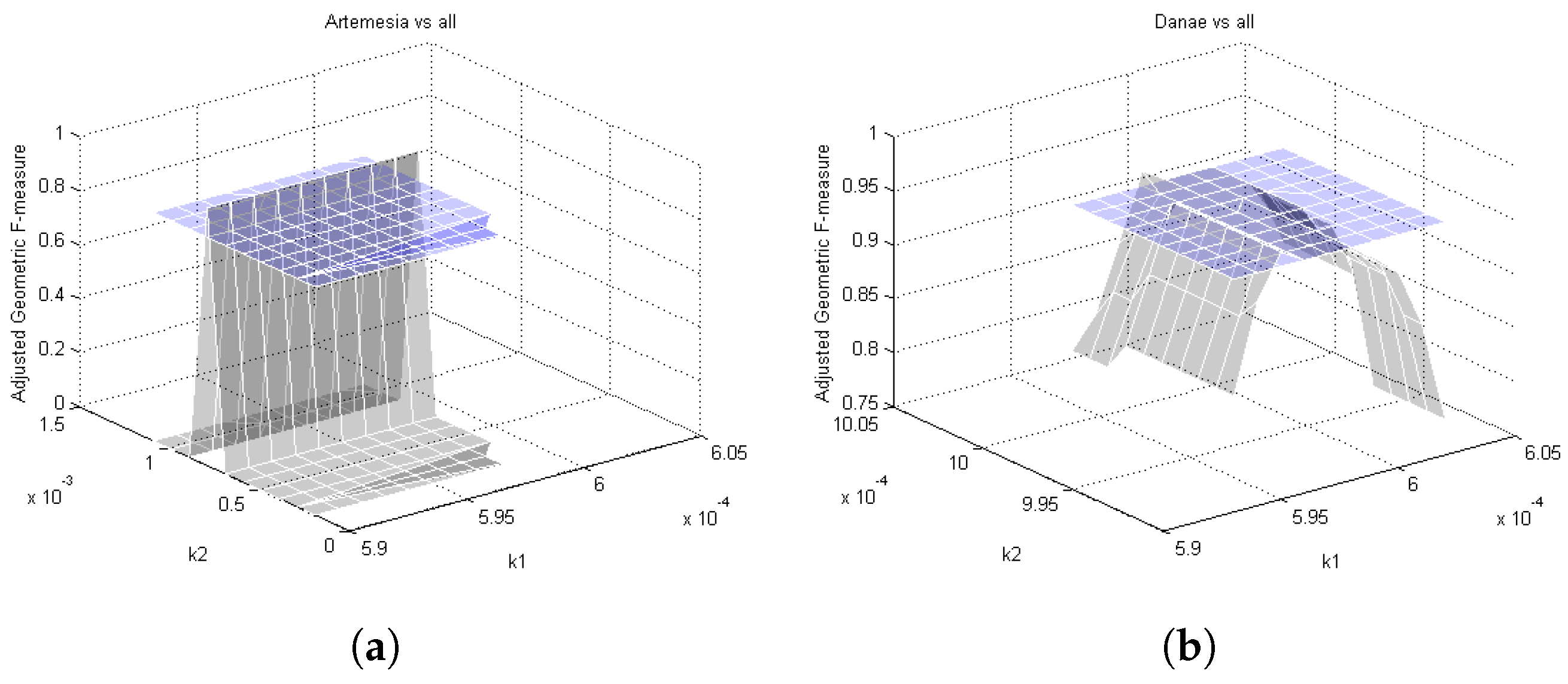
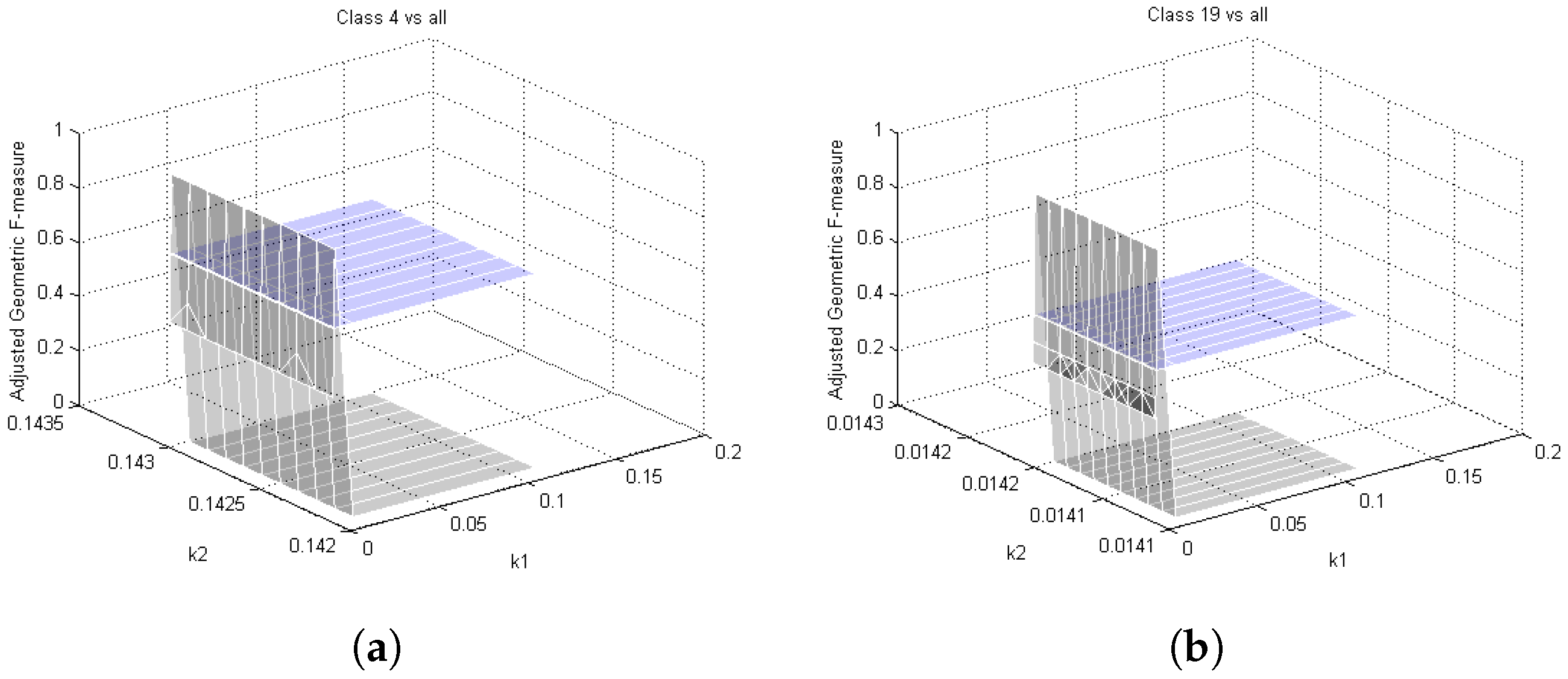
4.1. Asymmetric Kernel Scaling (AKS) for Support Vector Machines
4.2. OvA Classification Setting
4.3. Datasets
4.4. AKS vs. SVM
4.5. Comparison Results
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vapnik, V. Statistical Learning Theory; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, T.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Mori, G. Image retrieval with structured object queries using latent ranking SVM. In Proceedings of the European Conference Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012; pp. 129–142. [Google Scholar]
- Hajj, N.; Awad, M. Isolated handwriting recognition via multi-stage Support Vector Machines. In Proceedings of the International Conference in Intelligent Systems, Sofia, Bulgaria, 6–8 September 2012; pp. 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, L.; Cheng, X.; Kang, L.; Li, D.; Li, D.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y. A SVM-Based Text Classification System for Knowledge Organization Method of Crop Cultivation. In Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture V; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 318–324. [Google Scholar]
- Manzo, M.; Petrosino, A. Attributed Relational Sift-based Regions Graph for art painting retrieval. In Proceedings of the ICIAP 2013, Naples, Italy, 9–13 September 2013; pp. 833–842. [Google Scholar]
- Maratea, A.; Petrosino, A.; Manzo, M. Adjusted F-measure and Kernel Scaling for Imbalanced Data Learning. Inf. Sci. 2014, 257, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulos, D.N.; Tsihrintzis, G.A. Artificial Immune System-based Classification in Class-Imbalanced Image Classification Problems. In Proceedings of the 2012 Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, Piraeus-Athens, Greece, 18–20 July 2012; pp. 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, A.; Mendonça, A.; Campilho, A. The class imbalance problem in TLC image classification. In Proceedings of the Image Analysis and Recognition, Póvoa de Varzim, Portugal, 18–20 September 2006; pp. 513–523. [Google Scholar]
- Molinara, M.; Ricamato, M.T.; Tortorella, F. Facing imbalanced classes through aggregation of classifiers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, Modena, Italy, 10–14 September 2007; pp. 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bhowan, U.; Zhang, M.; Johnston, M. Genetic programming for image classification with unbalanced data. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Image and Vision Computing New Zealand, Wellington, New Zealand, 23–25 November 2009; pp. 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- Celebi, M.E.; Kingravi, H.A.; Uddin, B.; Iyatomi, H.; Aslandogan, Y.A.; Stoecker, W.V.; Moss, R.H. A methodological approach to the classification of dermoscopy images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2007, 31, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, B.; Yeshaya, J.; Koushnir, L. On the classification of a small imbalanced cytogenetic image database. Trans. Comput. Bioinform. 2007, 4, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malof, M.; Mazurowski, M.A.; Tourassi, G.D. The effect of class imbalance on case selection for case-based classifiers: An empirical study in the context of medical decision support. Neural Netw. 2012, 25, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremeau, A.; Colantoni, P. Regions adjacency graph applied to color image segmentation. Trans. Image Process. 2000, 9, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgwardt, K.M.; Kriegel, H.P. Shortest-path kernels on graphs. In Proceedings of the Fifth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM’05), Houston, TX, USA, 27–30 November 2005; pp. 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Culjak, M.; Mikus, B.; Jez, K.; Hadjic, S. Classification of art paintings by genre. In Proceedings of the MIPRO 34th International Convention, Opatija, Croatia, 23–27 May 2011; pp. 1634–1639. [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, J.R. C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers: San Mateo, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, W.W. Fast effective rule induction. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference in Machine Learning, Tahoe City, CA, USA, 9–12 July 1995; Morgan Kaufmann: San Mateo, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Boser, B.E.; Guyon, I.M.; Vapnik, V.N. A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual Workshop on Computational Learning Theory, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 27–29 July 1992; pp. 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, R.E.; Chang, K.W.; Hsieh, C.J.; Wang, X.R.; Lin, C.J. LIBLINEAR: A library for large linear classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 1871–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Dazeley, R.; Warner, P.; Johnson, S.; Vamplew, P. The Ballarat Incremental Knowledge Engine. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Knowledge Management and Acquisition for Smart Systems and Services, Daegue, Korea, 20 August–3 September 2010; pp. 195–207. [Google Scholar]
- Amari, S.; Wu, S. Improving svm classifiers by modifying kernel functions. Neural Netw. 1999, 12, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haladová, Z.; Šikudová, E. Limitations of the SIFT/SURF based methods in the classifications of fine art paintings. Internet J. Comput. Graph. Geom. 2010, 12, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
| Problem | Classification Problem | (%min,%maj) | IR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Artemisia vs. all | (3.00,97.00) | 32.33 |
| 2 | Bathsheba vs. all | (3.00,97.00) | 32.33 |
| 3 | Danae vs. all | (12.00,88.00) | 7.33 |
| 4 | Doctor_Nicolaes vs. all | (3.00,97.00) | 32.33 |
| 5 | HollyFamilly vs. all | (2.00,98.00) | 49.00 |
| 6 | PortraitOfMariaTrip vs. all | (3.00,97.00) | 32.33 |
| 7 | PortraitOfSaskia vs. all | (1.00,99.00) | 99.00 |
| 8 | RembrandtXXPortrai vs. all | (2.00,98.00) | 49.00 |
| 9 | SaskiaAsFlora vs. all | (3.00,97.00) | 32.33 |
| 10 | SelfportraitAsStPaul vs. all | (8.00,92.00) | 11.50 |
| 11 | TheJewishBride vs. all | (4.00,96.00) | 24.00 |
| 12 | TheNightWatch vs. all | (9.00,91.00) | 10.11 |
| 13 | TheProphetJeremiah vs all | (7.00,93.00) | 13.28 |
| 14 | TheReturnOfTheProdigalSon vs. all | (9.00,91.00) | 10.11 |
| 15 | TheSyndicsoftheClothmakersGuild vs. all | (5.00,95.00) | 19.00 |
| 16 | Other vs. all | (26.00,74.00) | 2.84 |
| Problem | Classification Problem | (%min,%maj) | IR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Class 4 vs. all | (1.00,9.00) | 9.00 |
| 2 | Class 7 vs. all | (1.00,9.00) | 9.00 |
| 3 | Class 8 vs. all | (1.00,9.00) | 9.00 |
| 4 | Class 13 vs. all | (1.00,9.00) | 9.00 |
| 5 | Class 15 vs. all | (1.00,9.00) | 9.00 |
| 6 | Class 19 vs. all | (1.00,9.00) | 9.00 |
| 7 | Class 21 vs. all | (1.00,9.00) | 9.00 |
| 8 | Class 27 vs. all | (1.00,9.00) | 9.00 |
| 9 | Class 30 vs. all | (1.00,9.00) | 9.00 |
| 10 | Class 33 vs. all | (1.00,9.00) | 9.00 |
| AGF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Problem | AKS | C4.5 | RIPPER | L2-L SVM | L2 RLR | RDR |
| 1 | 0.9414 | 0.5614 | 0.8234 | 0.6500 | 0.5456 | 0.8987 |
| 2 | 0.9356 | 0.8256 | 0.6600 | 0.8356 | 0.8078 | 0.7245 |
| 3 | 0.9678 | 0.8462 | 0.8651 | 0.4909 | 0.6123 | 0.7654 |
| 4 | 0.9746 | 0.8083 | 0.6600 | 0.4790 | 0.4104 | 0.6693 |
| 5 | 0.9654 | 0.7129 | 0.9861 | 0.8456 | 0.4432 | 0.6134 |
| 6 | 0.9342 | 0.5714 | 0.9525 | 0.8434 | 0.9525 | 0.5554 |
| 7 | 0.9567 | 0.6151 | 0.7423 | 0.5357 | 0.4799 | 0.6151 |
| 8 | 0.8345 | 0.4123 | 0.3563 | 0.7431 | 0.5124 | 0.7124 |
| 9 | 0.9435 | 0.9456 | 0.9456 | 0.8345 | 0.6600 | 0.6600 |
| 10 | 0.8456 | 0.4839 | 0.5345 | 0.4123 | 0.4009 | 0.5456 |
| 11 | 0.9457 | 0.9167 | 0.9088 | 0.9220 | 0.8666 | 0.9132 |
| 12 | 0.6028 | 0.5875 | 0.5239 | 0.4124 | 0.4934 | 0.5234 |
| 13 | 0.8847 | 0.7357 | 0.6836 | 0.7436 | 0.7013 | 0.5712 |
| 14 | 0.9376 | 0.9376 | 0.8562 | 0.8945 | 0.8722 | 0.8320 |
| 15 | 0.9765 | 0.8630 | 0.8897 | 0.8225 | 0.7440 | 0.8630 |
| 16 | 0.7142 | 0.5833 | 0.3893 | 0.4323 | 0.5455 | 0.5111 |
| AGF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Problem | AKS | C4.5 | RIPPER | L2-L SVM | L2 RLR | RDR |
| 1 | 0.9822 | 0.6967 | 0.5122 | 0.4232 | 0.4322 | 0.6121 |
| 2 | 0.9143 | 0.5132 | 0.4323 | 0.4121 | 0.4212 | 0.5323 |
| 3 | 0.9641 | 0.4121 | 0.4211 | 0.4213 | 0.3221 | 0.4323 |
| 4 | 0.9454 | 0.4332 | 0.1888 | 0.4583 | 0.3810 | 0.3810 |
| 5 | 0.9554 | 0.3810 | 0.2575 | 0.5595 | 0.3162 | 0.6967 |
| 6 | 0.9624 | 0.3001 | 0.1888 | 0.1312 | 0.3456 | 0.3121 |
| 7 | 0.9344 | 0.3810 | 0.5566 | 0.4122 | 0.4455 | 0.2234 |
| 8 | 0.9225 | 0.4333 | 0.1112 | 0.2575 | 0.1888 | 0.1888 |
| 9 | 0.9443 | 0.6322 | 0.1888 | 0.1888 | 0.6122 | 0.6641 |
| 10 | 0.9653 | 0.1897 | 0.5234 | 0.6956 | 0.1888 | 0.1121 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manzo, M. KGEARSRG: Kernel Graph Embedding on Attributed Relational SIFT-Based Regions Graph. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2019, 1, 962-973. https://doi.org/10.3390/make1030055
Manzo M. KGEARSRG: Kernel Graph Embedding on Attributed Relational SIFT-Based Regions Graph. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction. 2019; 1(3):962-973. https://doi.org/10.3390/make1030055
Chicago/Turabian StyleManzo, Mario. 2019. "KGEARSRG: Kernel Graph Embedding on Attributed Relational SIFT-Based Regions Graph" Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 1, no. 3: 962-973. https://doi.org/10.3390/make1030055
APA StyleManzo, M. (2019). KGEARSRG: Kernel Graph Embedding on Attributed Relational SIFT-Based Regions Graph. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, 1(3), 962-973. https://doi.org/10.3390/make1030055





