Construction of pH-Responsive Drug Carrier Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Controlled Capecitabine Release
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of BMSN@MIP and BMSN@MIP/CAPE
2.2. Optimization of Imprinting Time in Synthesis of BMSN@MIP
2.3. Evaluation of Encapsulation Efficiency
2.4. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
3. Results and Discussion
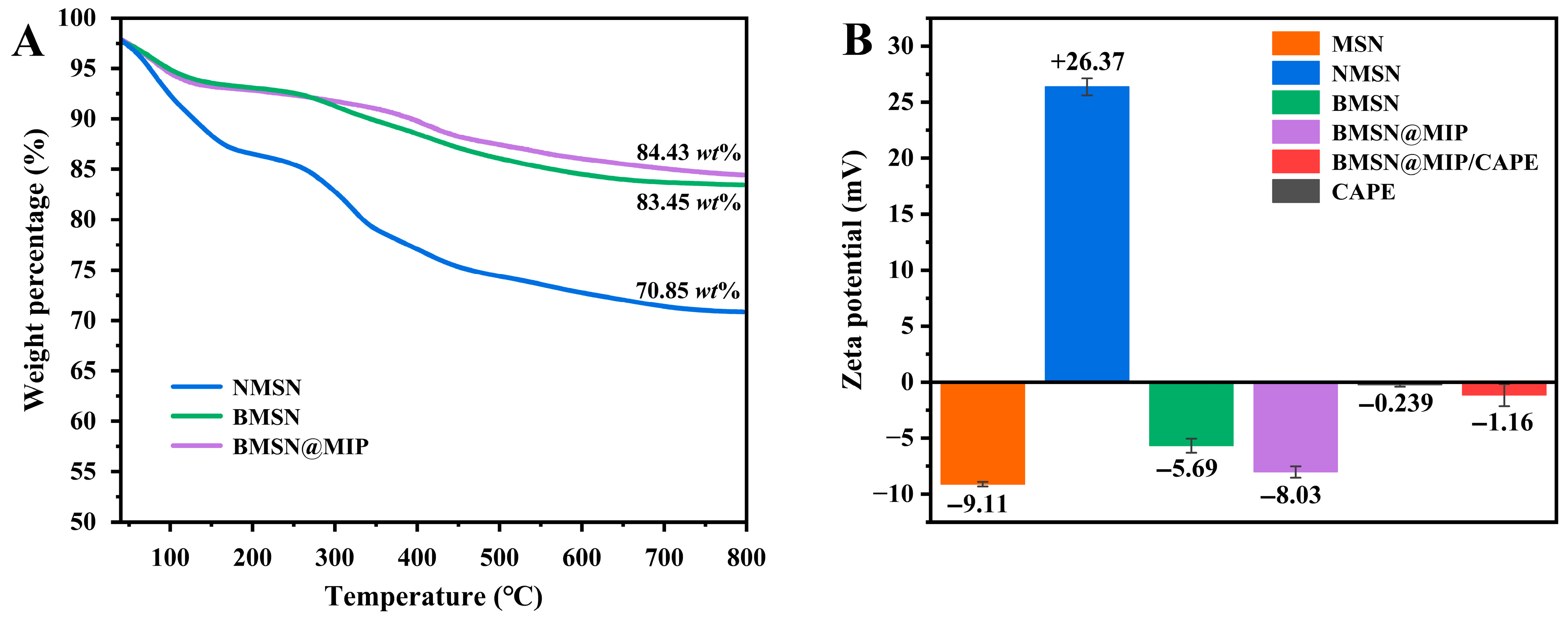
3.1. Characterization
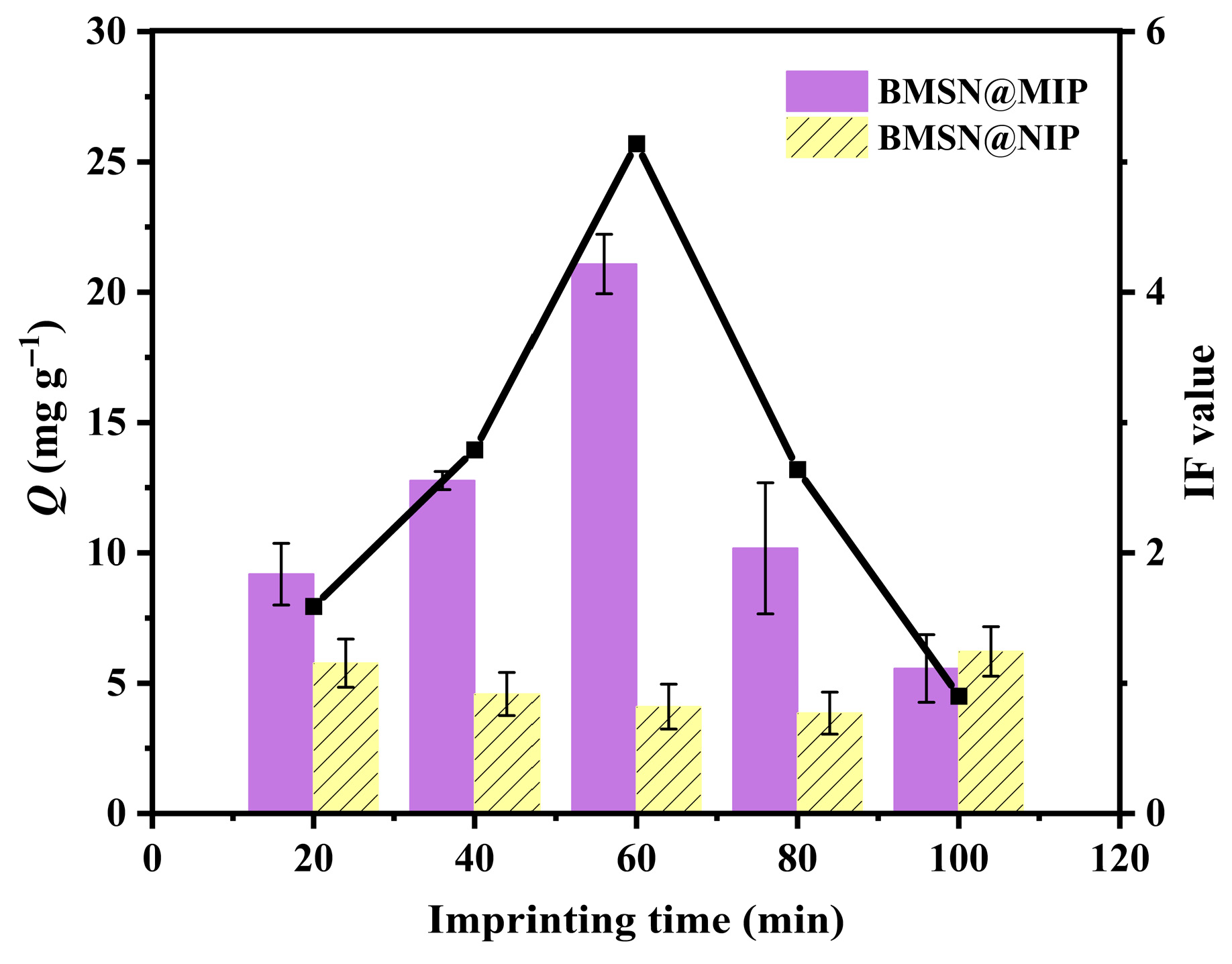
3.2. Optimization of Imprinting Time in Synthesis of BMSN@MIP
3.3. Evaluation of Encapsulation Efficiency
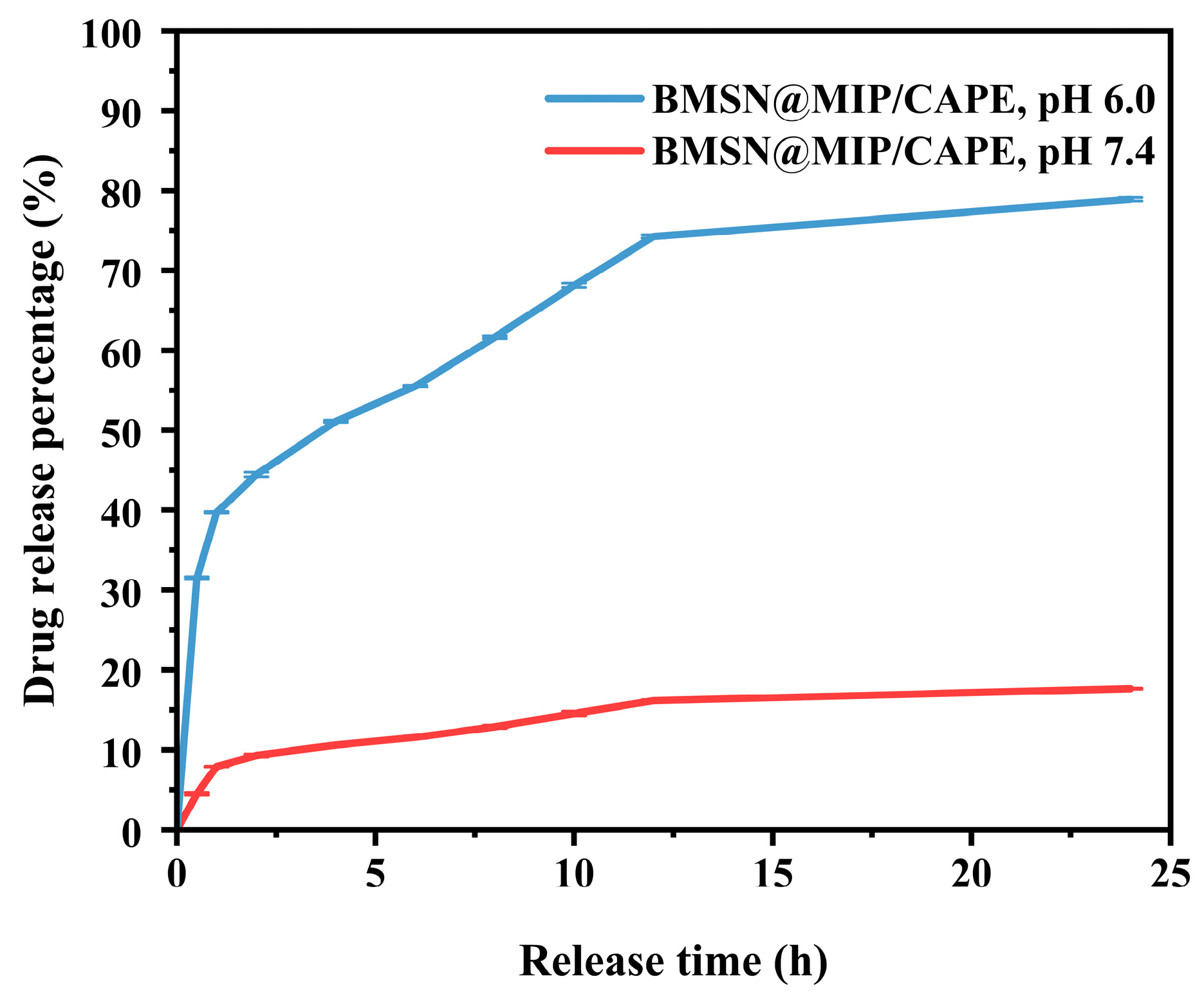
3.4. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotech. 2007, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.L.; Bendayan, R.; Rauth, A.M.; Li, Y.Q.; Wu, X.Y. Chemotherapy with anticancer drugs encapsulated in solid lipid nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2007, 59, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, J.D.G.; Arias, J.L.; Gallardo, V.; Delgado, A.V. Magnetic colloids as drug vehicles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2948–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, J.L. Novel strategies to improve the anticancer action of 5-fluorouracil by using drug delivery systems. Molecules 2008, 13, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.M.; Xu, W.H.; Xu, G.X.; Jia, Q. An updated overview of MOF@MIP in drug carrier and drug analysis: Construction, application and prospective. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.F.; Liu, Z. Glycan-specific molecularly imprinted polymers towards cancer diagnostics: Merits, applications, and future perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 1870–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Kitayama, Y.; Sasao, R.; Yamada, T.; Toh, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kataoka, K. Molecularly imprinted nanogels acquire stealth in situ by cloaking themselves with native dysopsonic proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7088–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.X.; He, H.; Liu, Z. Molecularly imprinted nanogels acquire stealth in situ by cloaking themselves with native dysopsonic proteins. Chemisity 2022, 40, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.R.; Wang, S.S.; Bie, Z.Y.; He, H.; Liu, Z. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers specific to glycoproteins, glycans and monosaccharides via boronate affinity controllable-oriented surface imprinting. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 964–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Song, Y.Z.; Liu, S.W.; Zhao, L.; Sun, R.N. Dual responsive molecularly imprinted polymers based on UiO-66-DOX for selective targeting tumor cells and controlled drug release. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 171, 111219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowing, I.I.; Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Wu, C.W.; Lin, V.S.Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2008, 60, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkiliopoulos, D.; Bikiaris, D.; Efstathiadis, D.; Triantafyllidis, K. Glassy and rubbery epoxy composites with mesoporous silica. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.X.; Wang, L.S.; Liu, Z. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles: An emerging versatile platform for cancer therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3858–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Boronate affinity materials for separation and molecular recognition: Structure, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8097–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, H. Synthesis and applications of boronate affinity materials: From class selectivity to biomimetic specificity. Accounts Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2185–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.J.; Ji, J.Y.; Shi, Y.Y.; Li, N.; Yan, Z.C.; Du, Q.Z. Recent advances in composite materials integrating molecularly imprinted polymers for targeted drug delivery systems. Eur. Polym. J. 2025, 228, 113825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.P.; Mo, C.E.; Huang, Y.P.; Liu, Z.S. Preparation of liquid crystalline molecularly imprinted polymer coated metal organic framework for capecitabine delivery. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2019, 36, 1800355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C.E.; Chai, M.H.; Zhang, L.P.; Ran, R.X.; Huang, Y.P.; Liu, Z.S. Floating molecularly imprinted polymers based on liquid crystalline and polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes for capecitabine sustained release. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2019, 557, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.F.; Zhang, R.R.; Ma, X.L.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y.P.; Liu, Z.S. Cooperation effect of 4-vinylbenzeneboronic acid/methacrylic acid on affinity of capecitabine imprinted polymer for drug carrier. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 154, 105476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.M.; Zheng, H.J.; Ma, J.T.; Xu, G.X.; Jia, Q. Design of pH-responsive molecularly imprinted polymer as a carrier for controlled and sustainable capecitabine release. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2024, 1317, 342881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; He, M.F.; Wang, X.M.; Fan, H.; Wei, Y.M. Facile preparation of boronic acid-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles with a high capacity and their use in the enrichment of cis-diol-containing compounds from plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, S.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Preparation of glycan-oriented imprinted polymer coating Gd-doped silicon nanoparticles for targeting cancer Tn antigens and dual-modal cell imaging via boronate-affinity surface imprinting. Talanta 2020, 223, 121706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.D.; Tian, M.F.; Ahmad, N.; Xie, Y.X.; Xu, C.G.; Liu, J.; Zhao, C.J.; Li, C.Y. A surface multiple imprinting layers membrane with well-oriented recognition sites for selective separation of chlorogenic acid from Ficus carica L. Food Chem. 2024, 433, 137347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.F.; Xu, S.X.; Guo, Z.C.; Zhao, M.H.; Liu, Z. Redox-responsive molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for targeted intracellular delivery of protein toward cancer therapy. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18214–18225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Rasuli, H.; Mohammadi, R. Facile preparation of pH-sensitive biocompatible alginate beads havening layered double hydroxide supported metal-organic framework for controlled release from doxorubicin to breast cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Lobo, J.M.S. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, U.; Sarfraz, R.M.; Mahmood, A.; Akbar, S.; Altyar, A.E.; Khinkar, R.M.; Gad, H.A. pH-Responsive hydrogels for the delivery of capecitabine: Development, optimization and pharmacokinetic studies. Gels 2022, 8, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, S.; Murthy, P.N.; Nath, L.; Chowdhury, P. Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Erdem, B.; Azko, Ç. B-SBA-15-SO3H: A versatile mesoporous catalyst. J. Porous Mater. 2017, 24, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’ Souza, L.; Devi, P.; Divya Shridhar, M.P.; Naik, C.G. Use of fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy to study cadmium-induced changes in padina tetrastromatica (hauck). Anal. Chem. Insights 2008, 3, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipurković, A.; Horozić, E.; Ljubijankić, N.; Odobašić, A.; Galijašević, S.; Saletović, M. Synthesis and spectral characterization of Fe (II) and Mn (II) complexes with oral fluorouracil prodrug capecitabine. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Ashraf, N.; Zohuri, G.H. A smart electrochemical sensor based upon hydrophilic core–shell molecularly imprinted polymer for determination of L-tryptophan. Microchem. J. 2023, 185, 108260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.Y.; Gao, F.; Komarneni, S.; Mallouk, T.E. Ordered SBA-15 nanorod arrays inside a porous alumina membrane mallouk. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8650–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Gadag, S.; Cheruku, S.P.; Raichur, A.M.; Day, C.M.; Garg, S.; Manandhar, S.; Pai, K.S.R.; Suresh, A.; Mehta, C.H.; et al. Chitosan-glucuronic acid conjugate coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A smart pH-responsive and receptor-targeted system for colorectal cancer therapy. Carbohyd. Polym. 2021, 261, 117893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, M.; Trendafilova, I.; Zgureva, D.; Kalvachev, Y.; Boycheva, S.; Tušar, N.N.; Szegedi, A. Polymer-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled release of the prodrug sulfasalazine. J. Drug Deliver. Sci. Tec. 2018, 44, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpiano, G.R.; Casula, M.F.; Piludu, M.; Corpino, R.; Ricci, P.C.; María, V.R.; Sanjust, E.; Monduzzi, M.; Salis, A. Assembly of multicomponent nano-bioconjugates composed of mesoporous silica nanoparticles, proteins, and gold nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 11044–11052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.J.; Yu, K.; Li, L.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Guo, L.P.; Zhang, Z.L.; Lu, Y.X.; Li, L. Fabrication of dual-template molecularly imprinted mesoporous silica for simultaneous rapid and efficient detection of bisphenol A and diethylstilbestrol in environmental water samples. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 4761–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.S.; Qin, Y.T.; Zhuang, J.; Ma, Y.J.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Mitochondria-targeted thymidylate synthase inhibitor based on fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymers for tumor antimetabolic therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 31139–31149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapino, S.; Ugazio, E.; Gastaldi, L.; Miletto, I.; Berlier, G.; Zonari, D.; Oliaro-Bosso, S. Mesoporous silica as topical nanocarriers for quercetin: Characterization and in vitro studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 89, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, M.D.; Szegedi, Á.; Kolev, I.N.; Mihály, J.; Tzankov, B.S.; Momekov, G.T.; Lambov, N.G.; Yoncheva, K.P. Carboxylic modified spherical mesoporous silicas as drug delivery carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.T.; Peng, H.L.; Luo, M.; Yu, N.X.; Xiong, H.; Wang, R.H.; Li, Y.B. Zipper-like magnetic molecularly imprinted microspheres for on/off-switchable recognition and extraction of 17β-estradiol from food samples. Food Chem. 2018, 261, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Lu, W.H.; Wu, X.Q.; Li, J.H. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwi, H.; Fuad, M.K.A.; Khairul, A.; Parsaoran, S.; Meida, M.S. In vitro evaluation of curcumin encapsulation in gum arabic dispersions under different environments. Molecules 2022, 27, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.J.; Zhao, H.Q.; Ma, Q.Y.; Cheng, D.W.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, W.X.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.F. Development of chitosan/potato peel polyphenols nanoparticles driven extended-release antioxidant films based on potato starch. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 31, 100793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roya, S.; Somayeh, A.; Bahareh, H. pH-sensitive molecularly imprinted polymer based on graphene oxide for stimuli actuated controlled release of curcumin. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 857, 157603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.K.; He, Y.; Zhang, H.T.; Zhang, Y.X.; Gao, T.B.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, S.L. Zwitterion-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhancing oral delivery of protein drugs by overcoming multiple gastrointestinal barriers. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 582, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Yang, Y.; O’Brien, J.; Brezan, D.; Nimesh, S.; Bernatchez, S.; Hill, M.; Sayari, A.; Vincent, R.; Kumarathasan, P. Synthesis and physicochemical characterization of mesoporous SiO2 nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.C.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Z. Probing the interactions between boronic acids and cis-diol-containing biomolecules by affinity capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2361–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Imprinting Time (min) | IF |
|---|---|
| 20 | 1.59 |
| 40 | 2.79 |
| 60 | 5.14 |
| 80 | 2.64 |
| 100 | 0.90 |
| Drug Release Kinetic Models | Parameters | BMSN@MIP/CAPE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| at pH 6.0 | at pH 7.4 | ||
| Higuchi | kH (h−1) | 20.69 | 4.15 |
| R2 | 0.69 | 0.97 | |
| Korsmeyer-Peppas | kK-P (h−n) | 37.94 | 5.26 |
| n | 0.24 | 0.41 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; He, T.; Lou, Y.; Xu, G.; Jia, Q. Construction of pH-Responsive Drug Carrier Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Controlled Capecitabine Release. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9080421
Guo Z, He T, Lou Y, Xu G, Jia Q. Construction of pH-Responsive Drug Carrier Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Controlled Capecitabine Release. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(8):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9080421
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zimeng, Tianxiao He, Yuqi Lou, Guoxing Xu, and Qiong Jia. 2025. "Construction of pH-Responsive Drug Carrier Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Controlled Capecitabine Release" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 8: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9080421
APA StyleGuo, Z., He, T., Lou, Y., Xu, G., & Jia, Q. (2025). Construction of pH-Responsive Drug Carrier Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Controlled Capecitabine Release. Journal of Composites Science, 9(8), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9080421







