Moisture Absorption and Its Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Biopolymers Reinforced by Curauá Fiber and Montmorillonite Clay: A Transient Experimental Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Reinforcement Preparation
2.3. Samples Preparation
2.4. Mechanical Characterization After Water Sorption
2.5. Water Sorption Tests
2.6. The Studied Cases
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mechanical Properties at the Wet Condition
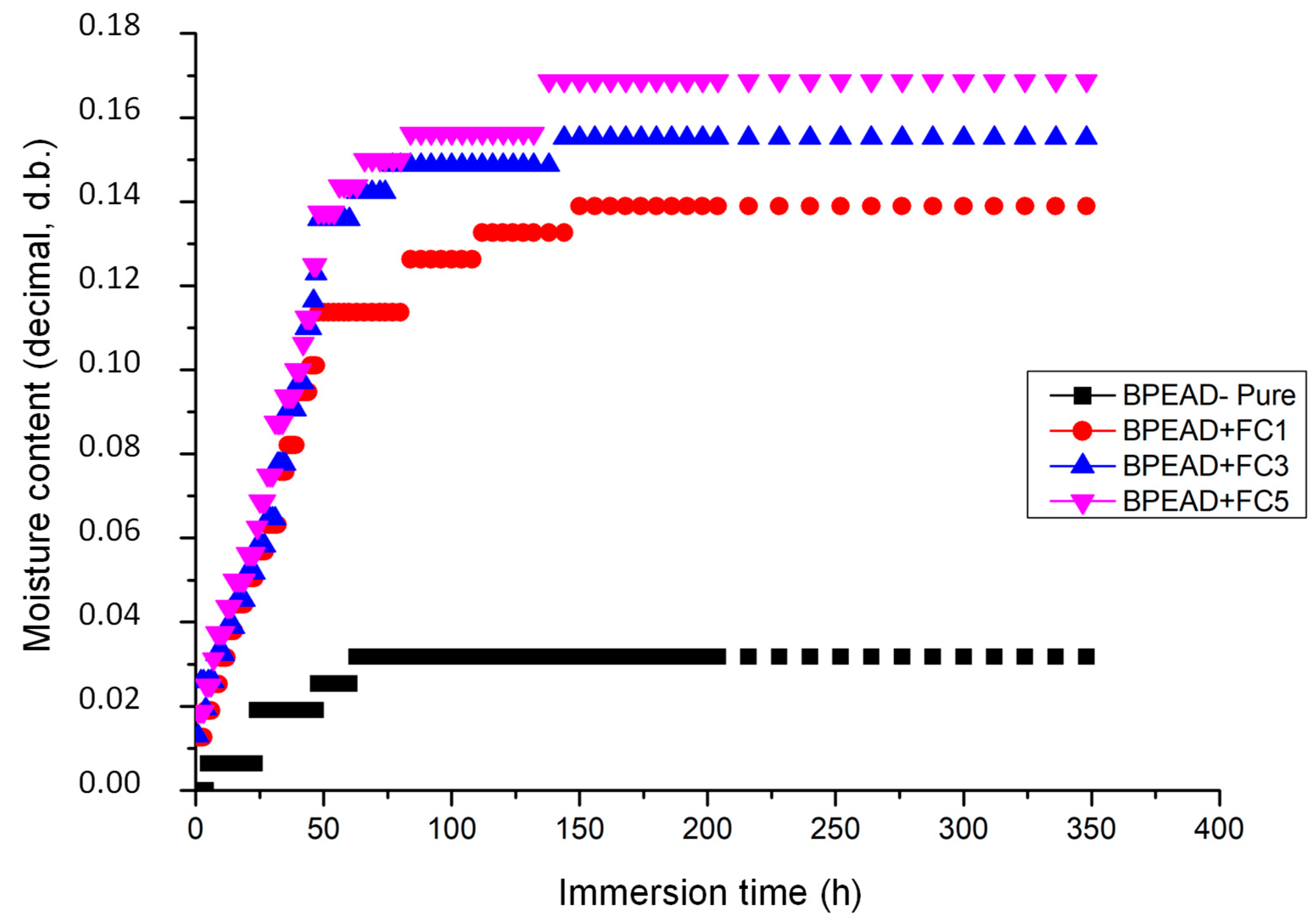
3.2. Water Sorption Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colangelo, S. Reducing the environmental footprint of glass manufacturing. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2024, 15, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raquez, J.-M.; Habibi, Y.; Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. Polylactide (PLA)-based nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1504–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.R.; Rorrer, N.A.; Carpenter, A.C.; Beckham, G.T. Manufacturing energy and greenhouse gas emissions associated with plastics consumption. Joule 2021, 5, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, T.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. A review of the recent developments in biocomposites based on natural fibres and their application perspectives. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manufact. 2015, 77, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherrafi, A.; Garza-Reyes, J.A.; Kumar, V.; Mishra, N.; Ghobadian, A.; Elfezazi, S. Lean, green practices and process innovation: A model for green supply chain performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 206, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzopoulou, Z.N.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Papadopoulou, E.; Athanassiadou, E.; Alexopoulou, E.; Bikiaris, D.N. Green composites prepared from aliphatic polyesters and bast fibers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 68, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annie Paul, S.; Boudenne, A.; Ibos, L.; Candau, Y.; Joseph, K.; Thomas, S. Effect of fiber loading and chemical treatments on thermophysical properties of banana fiber/polypropylene commingled composite materials. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manufact. 2008, 39, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodzic, A.; Shanks, R. Natural Fibre Composites: Materials, Processes and Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, M.C.; Rosa, P.T.V.; De Paoli, M.-A.; Felisberti, M.L. Biocomposites based on cellulose acetate and short Curaua fibers treated with supercritical CO2. Polimeros 2012, 22, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, D.O.; Frollini, E.; Marini, J.; Ruvolo-Filho, A. Preparation and characterization of biocomposites based on curaua fibers, high-density biopolyethylene (HDBPE) and liquid hydroxylated polybutadiene (LHPB). Polímeros 2013, 23, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, M.; Vallejos, M.; Opedal, M.T.; Area, M.C.; Chinga-Carrasco, G. Lignocellulosics as sustainable resources for production of bioplastics—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 646–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.A., Jr.; Thiré, R.M.S.M.; Lima, E.M.B.; Racca, L.M.; Silva, A.L.N. Mechanical and thermal properties of environment friendly composite based on mango’s seed shell and high-density polyethylene. Macromol. Symp. 2018, 381, 1800125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, P.J.P.; Alves, T.S.; Barbosa, R. Development and characterization of green polyethylene/clay/antimicrobial additive nanocomposites. Polímeros 2022, 32, e2022022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalho, G.H.A.; Nascimento, J.J.S.; Silva, L.B.; Gomez, R.S.; Farias, D.O.; Diniz, D.D.S.; Santos, R.S.; Figueiredo, M.J.; Lima, A.G.B. Bio-Polyethylene Composites Based on Sugar Cane and Curauá Fiber: An Experimental Study. Polymers 2023, 15, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalho, G.H.A.; Nascimento, J.J.S.; Silva, L.B.; Delgado, J.M.P.Q.; Simões, J.N.B.; Oliveira, V.A.B.; Santos, L.E.A.; Figueiredo, M.J.; Chaves, F.S.; Lima, A.G.B. Sugarcane-Based Polyethylene Biocomposite Reinforced with Organophilic Montmorillonite Clay: Experimental Characterization and Performance Evaluation. Polymers 2024, 16, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azwaz, Y.B.; Manalo, A.; Karunasena, W. A review on the degradability of polymeric composites based on natural fibres. Mater. Design 2013, 47, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.H.; Canedo, E.L.; Farias Neto, S.R.; Lima, A.G.B.; Silva, C.J. Moisture Transport Process in Vegetable Fiber Composites: Theory and Analysis for Technological Applications. In Industrial and Technological Applications of Transport in Porous Materials; Delgado, J., Ed.; Advanced Structured Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 36, pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, T.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, J.; Song, G.; Liu, S. Recent Progress on Moisture Absorption Aging of Plant Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbalho, G.H.A.; Delgado, J.M.P.Q.; Barbosa de Lima, W.C.P.; Lima, A.G.B.; Santos Júnior, V.A.; Oliveira Neto, G.L.; Macedo Neto, M.C.; Oliveira, V.A.V.; Santos Júnior, Z.J.; Almeida Neto, D.L.; et al. Advanced Mathematical Modeling of Moisture Transport in Polymer Composite Materials: State-of-the-Art and Numerical Computation. In State of the Art and Future Trends in Materials Modelling 2; Altenbach, H., Öchsner, A., Eds.; Advanced Structured Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijuan, J.; Xin, W.; Xiao, C.; Yinzhi, Z.; Yongzhan, Y. A review of moisture absorption and corrosion resistance performance of FRTP in marine environments. Polym. Test. 2025, 145, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Hasan, B. An overview of the effects of water and moisture absorption on the performance of hemp fiber and its composites. SPE Polym. 2025, 6, e10167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, K.; Jakubowska, P.; Romańska, P.; Kuciel, S. Green high density polyethylene (HDPE) reinforced with basalt fiber and agricultural fillers for technical applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 202, 108399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladaci, N.; Saadia, A.; Belaadi, A.; Boumaaza, M.; Chai, B.X.; Abdullah, M.M.S.; Al-Khawlani, A.; Ghernaout, D. ANN and RSM Prediction of Water Uptake of Recycled HDPE Biocomposite Reinforced with Treated Palm Waste W. filifera. J. Nat. Fibers 2024, 21, 2356697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.M.; Gowrishankar, M.C.; Shettar, M. Water-soaking effect and influence of nanoclay on mechanical properties of bamboo/glass fiber reinforced epoxy hybrid composites. Cogent Eng. 2024, 11, 2338160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scida, D.; Assarar, M.; Poilâne, C.; Ayad, R. Influence of hygrothermal ageing on the damage mechanisms of flax-fibre reinforced epoxy composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 48, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Li, X.; Wu, C.; Du, L.; Du, X.; Tafsirojjaman, T. Effect of Hydrothermal Environment on Mechanical Properties and Electrical Response Behavior of Continuous Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Composite Plates. Polymers 2022, 14, 4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM D256; Standard Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- ASTM D790; Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM D638; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- ASTM D570; Standard Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Chen, J.; Yan, N. Mechanical properties and dimensional stability of organo-nanoclay modified biofiber polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 47, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, O.; Varley, R.J.; Simon, G.P. Thermal stability and water uptake of high performance epoxy layered silicate nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, R.K.Y. Effect of water absorption on the mechanical and dielectric properties of nano-alumina filled epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manufact. 2008, 39, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, P.; Prasad, B.D.; Narayana, K.L. Influence of montmorillonite clay content on thermal, mechanical, water absorption and biodegradability properties of treated kenaf fiber/PLA-hybrid biocomposites. Silicon 2021, 13, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, H.; Low, I.M. Effect of water absorption on the mechanical properties of nano-filler reinforced epoxy nanocomposites. Mater. Design 2012, 42, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Miao, M.; Ding, X. Influence of moisture absorption on the interfacial strength of bamboo/vinyl ester composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manufact. 2009, 40, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsina, O.L.S.; Carvalho, L.H.; Ramos Filho, F.G.; d’Almeida, J.R.M. Immersion temperature effects on the water absorption behavior of hybrid lignocellulosic fiber reinforced-polyester matrix composites. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2007, 46, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abacha, N.; Kubouchi, M.; Tsuda, K.; Sakai, T. Performance of epoxy-nanocomposite under corrosive environment. Express Polym. Lett. 2007, 1, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.J.; Lima, A.G.B.; Silva, E.G.; Andrade, T.H.F.; Melo, R.Q.C. Water Absorption in Caroá-Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composite at Different Temperatures: A Theoretical Investigation. Diffus. Found. 2017, 10, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes dos Santos, D.; Lima, A.G.B.; Costa, P.S.; Lima, E.S.; Moreira, G.; Nascimento, J.J.S. Water Absorption in Sisal Fiber Reinforced-Polymeric Matrix Composites: Three-Dimensional Simulations and Experiments. Diffus. Found. 2018, 20, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Designation | Curauá Fiber (%) | Montmorillonite Clay (%) | PE-g-MA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| B-HDPE | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| B-HDPE/PE-g-MA/FC1 | 1 | 0 | 10 |
| B-HDPE/PE-g-MA/FC3 | 3 | 0 | 10 |
| B-HDPE/PE-g-MA/FC5 | 5 | 0 | 10 |
| B-HDPE/PE-g-MA/OMMT1 | 0 | 1 | 10 |
| B-HDPE/PE-g-MA/OMMT3 | 0 | 3 | 10 |
| B-HDPE/PE-g-MA/OMMT5 | 0 | 5 | 10 |
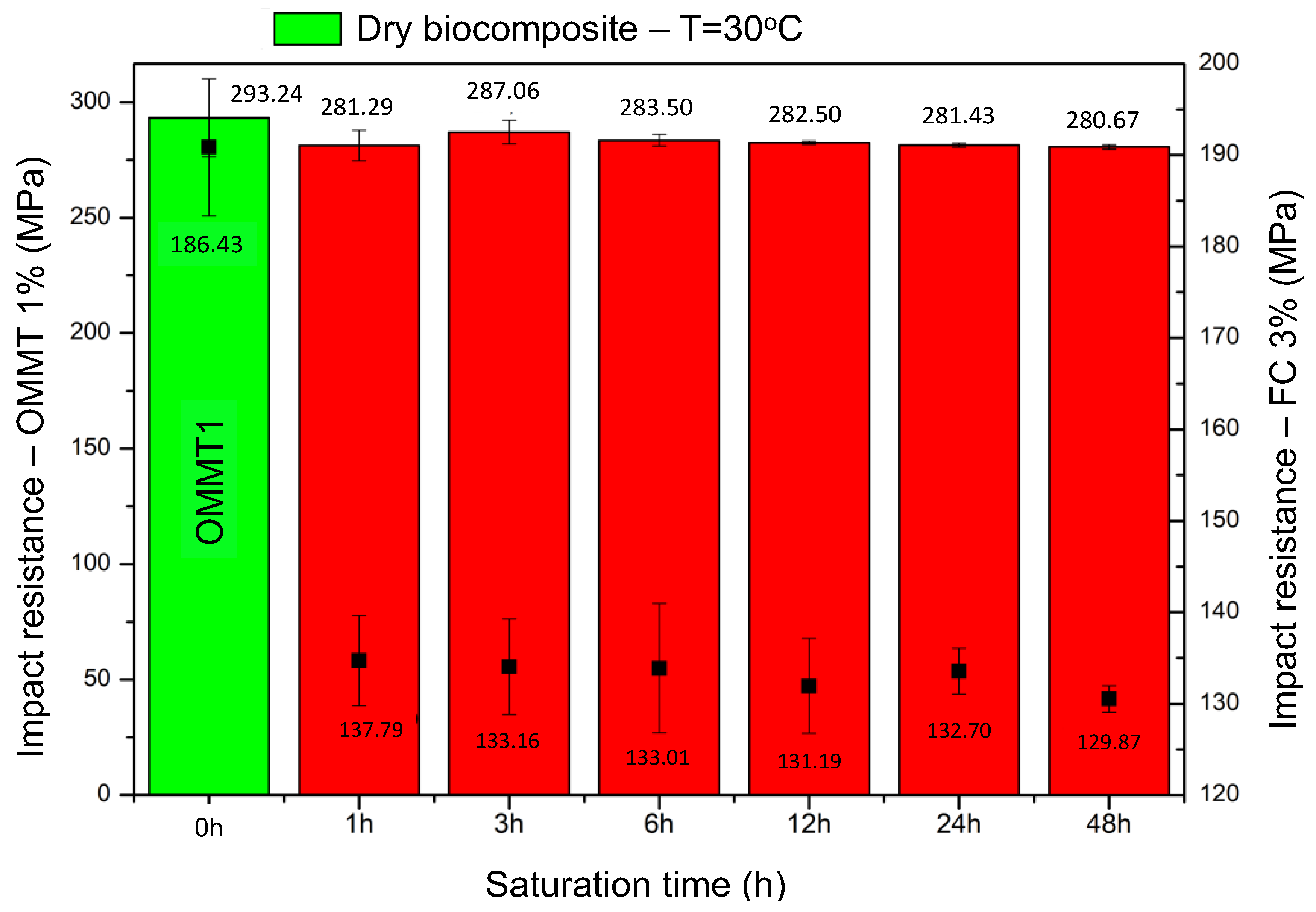
| Impact Resistance (MPa) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Wet | |||||
| Saturation Time (h) | Water at 30 °C | Water at 70 °C | ||||
| OMMT1 | FC3 | OMMT1 | FC3 | OMMT1 | FC3 | |
| 293.24 ± 16.86 | 186.43 ± 9.03 | 1 | 291.29 ± 6.67 | 133.79 ± 4.61 | 280.45 ± 0.34 | 137.79 ± 0.35 |
| 3 | 287.06 ± 5.15 | 133.16 ± 4.90 | 286.62 ± 1.36 | 132.95 ± 0.37 | ||
| 6 | 283.50 ± 2.44 | 133.01 ± 8.64 | 283.58 ± 0.37 | 131.99 ± 0.38 | ||
| 12 | 282.50 ± 2.38 | 131.19 ± 4.86 | 282.63 ± 0.38 | 131.91 ± 2.90 | ||
| 24 | 281.43 ± 8.39 | 132.70 ± 2.34 | 281.21 ± 10.39 | 130.71 ± 2.40 | ||
| 48 | 280.67 ± 7.35 | 129.87 ± 0.34 | 279.67 ± 1.34 | 128.45 ± 1.35 | ||
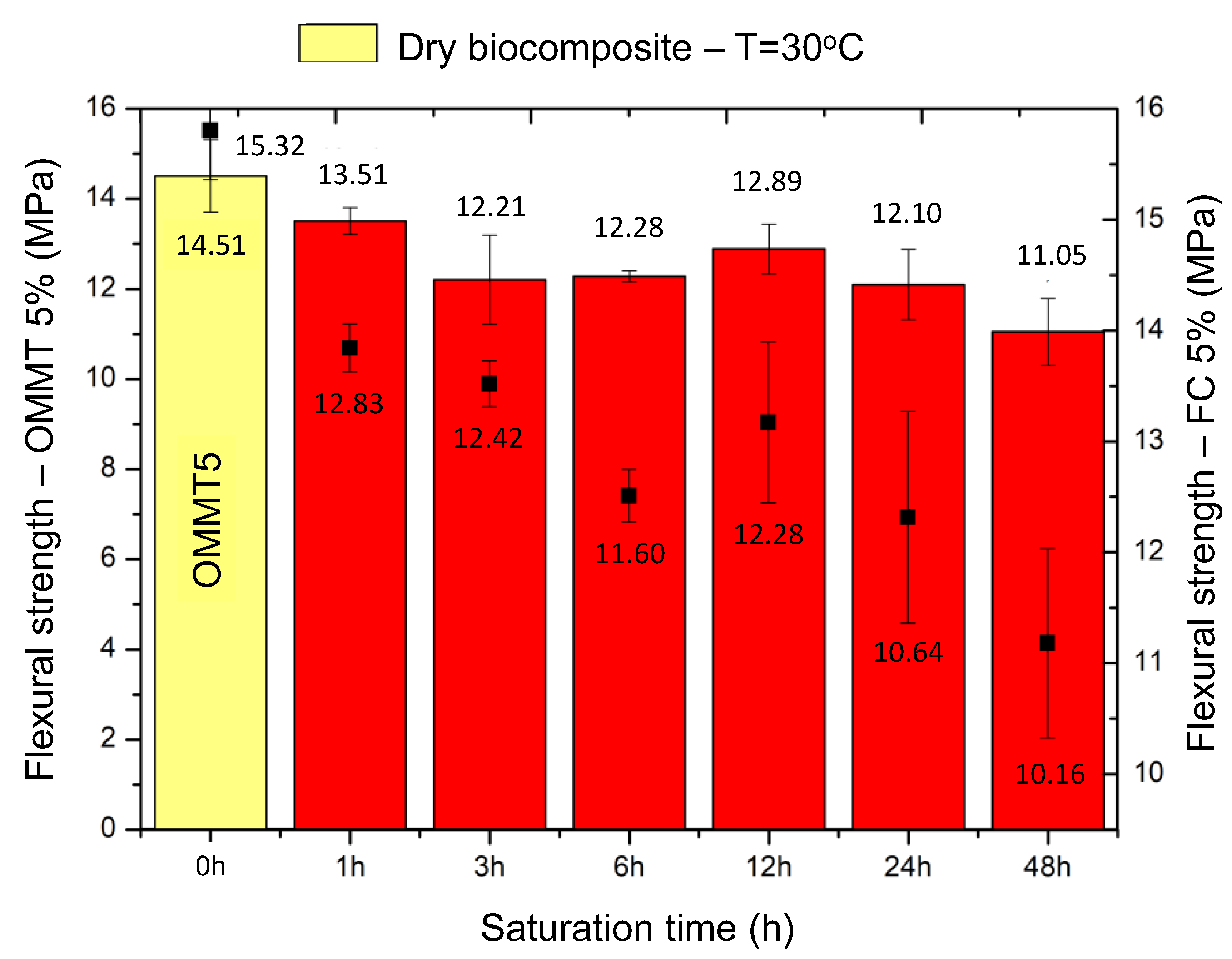
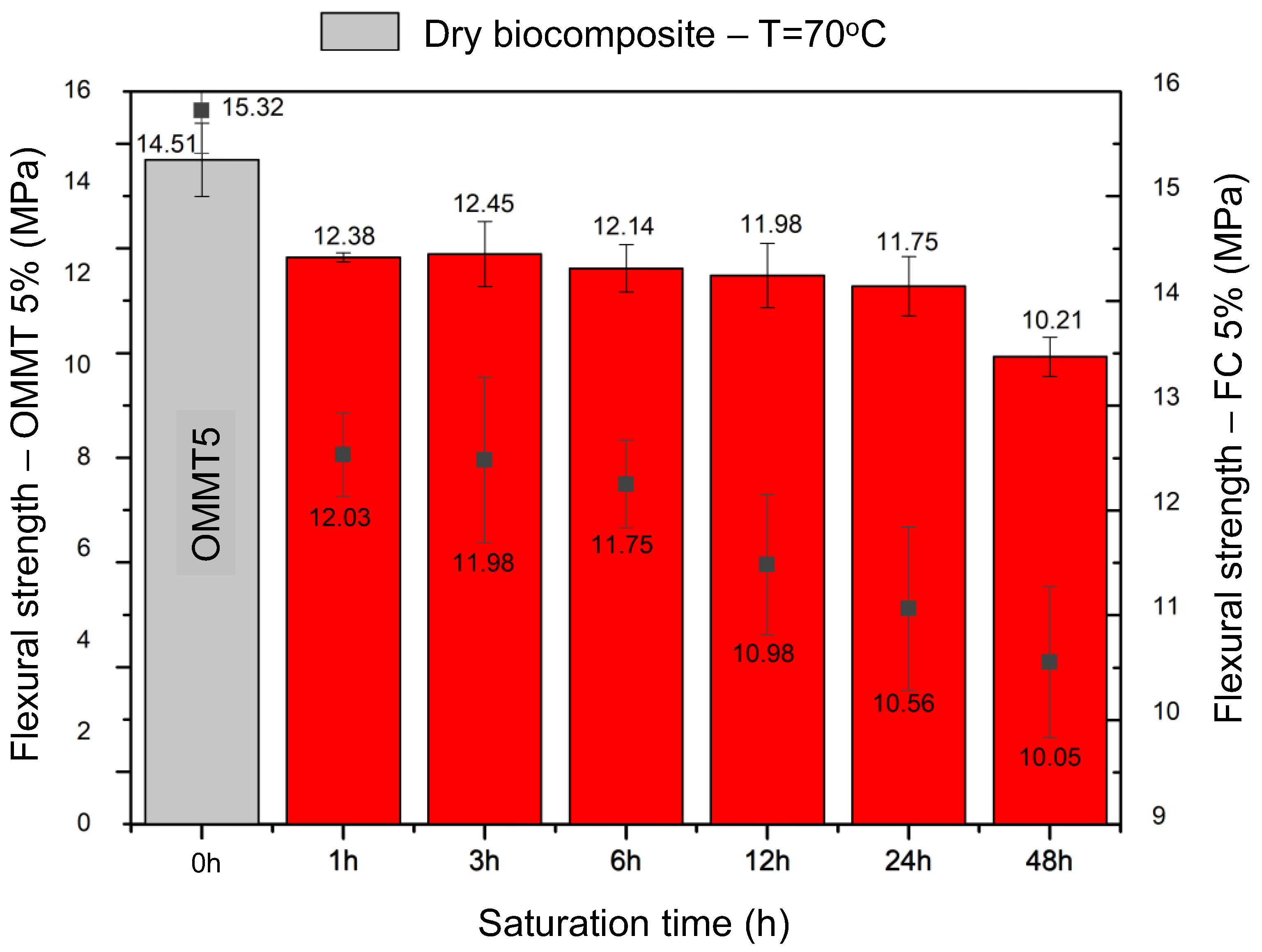
| Flexural Strength (MPa) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Biocomposite | Wet Biocomposite | |||||
| Saturation Time (h) | Water at 30 °C | Water at 70 °C | ||||
| OMMT5 | FC5 | OMMT5 | FC5 | OMMT5 | FC5 | |
| 14.51 ± 0.80 | 15.32 ± 0.41 | 1 | 13.51 ± 0.30 | 12.83 ± 0.20 | 12.38 ± 0.10 | 12.03 ± 0.40 |
| 3 | 13.21 ± 0.99 | 12.42 ± 0.19 | 12.45 ± 0.71 | 11.98 ± 0.79 | ||
| 6 | 12.28 ± 0.12 | 12.28 ± 0.22 | 12.14 ± 0.52 | 11.75 ± 0.42 | ||
| 12 | 12.89 ± 0.55 | 11.60 ± 0.67 | 11.98 ± 0.70 | 10.98 ± 0.67 | ||
| 24 | 12.10 ± 0.78 | 10.64 ± 0.88 | 11.75 ± 0.65 | 10.56 ± 0.78 | ||
| 48 | 11.05 ± 0.74 | 10.16 ± 0.79 | 10.21 ± 0.43 | 10.05 ± 0.72 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbalho, G.H.A.; Nascimento, J.J.S.; Silva, L.B.; Delgado, J.M.P.Q.; Vilela, A.F.; Pereira, J.F.; Santos, I.B.; Luiz, M.R.; Pinheiro, L.S.S.; Silva, A.G.S.; et al. Moisture Absorption and Its Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Biopolymers Reinforced by Curauá Fiber and Montmorillonite Clay: A Transient Experimental Evaluation. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050248
Barbalho GHA, Nascimento JJS, Silva LB, Delgado JMPQ, Vilela AF, Pereira JF, Santos IB, Luiz MR, Pinheiro LSS, Silva AGS, et al. Moisture Absorption and Its Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Biopolymers Reinforced by Curauá Fiber and Montmorillonite Clay: A Transient Experimental Evaluation. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(5):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050248
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbalho, Gustavo H. A., José J. S. Nascimento, Lucineide B. Silva, João M. P. Q. Delgado, Anderson F. Vilela, Joseane F. Pereira, Ivonete B. Santos, Márcia R. Luiz, Larissa S. S. Pinheiro, Andressa G. S. Silva, and et al. 2025. "Moisture Absorption and Its Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Biopolymers Reinforced by Curauá Fiber and Montmorillonite Clay: A Transient Experimental Evaluation" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 5: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050248
APA StyleBarbalho, G. H. A., Nascimento, J. J. S., Silva, L. B., Delgado, J. M. P. Q., Vilela, A. F., Pereira, J. F., Santos, I. B., Luiz, M. R., Pinheiro, L. S. S., Silva, A. G. S., Faria, R. M., Chaves, F. S., & Lima, A. G. B. (2025). Moisture Absorption and Its Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Biopolymers Reinforced by Curauá Fiber and Montmorillonite Clay: A Transient Experimental Evaluation. Journal of Composites Science, 9(5), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050248










