Hybrid Magneto-Responsive Composites Made from Recyclable Components: Tunable Electrical Properties Under Magnetic and Mechanical Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of MMPs + Lard Mixture and hMRCs
2.3. Structural Properties of hMRCs
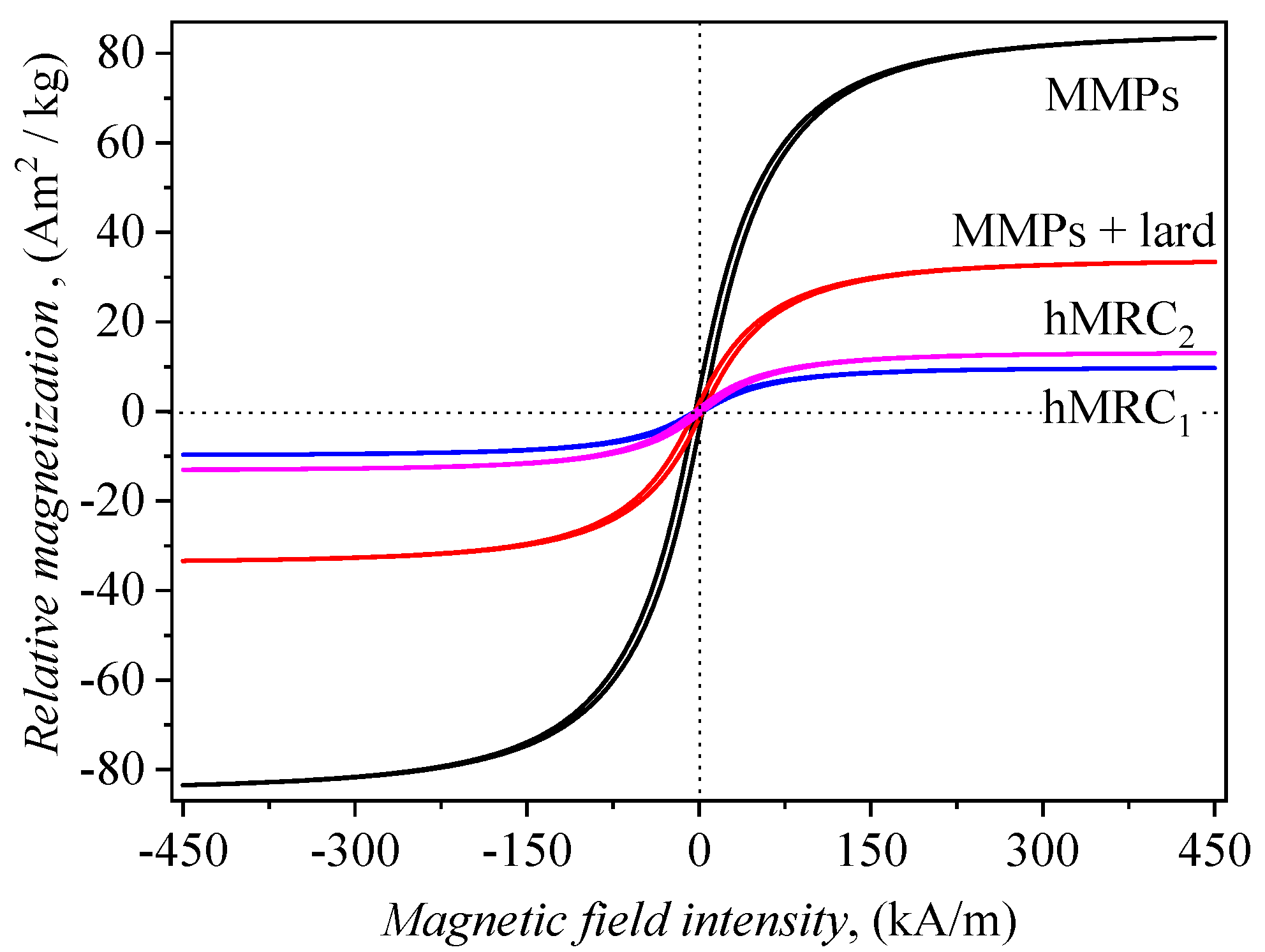
2.4. Magnetic Properties of hMRCs
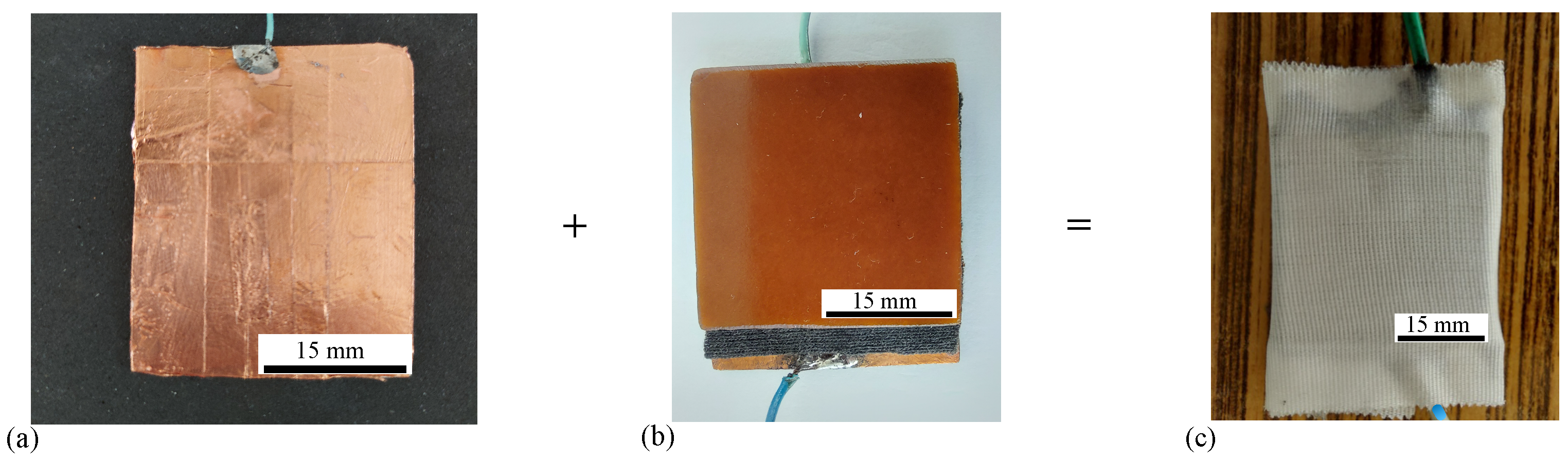
2.5. Manufacturing of FC
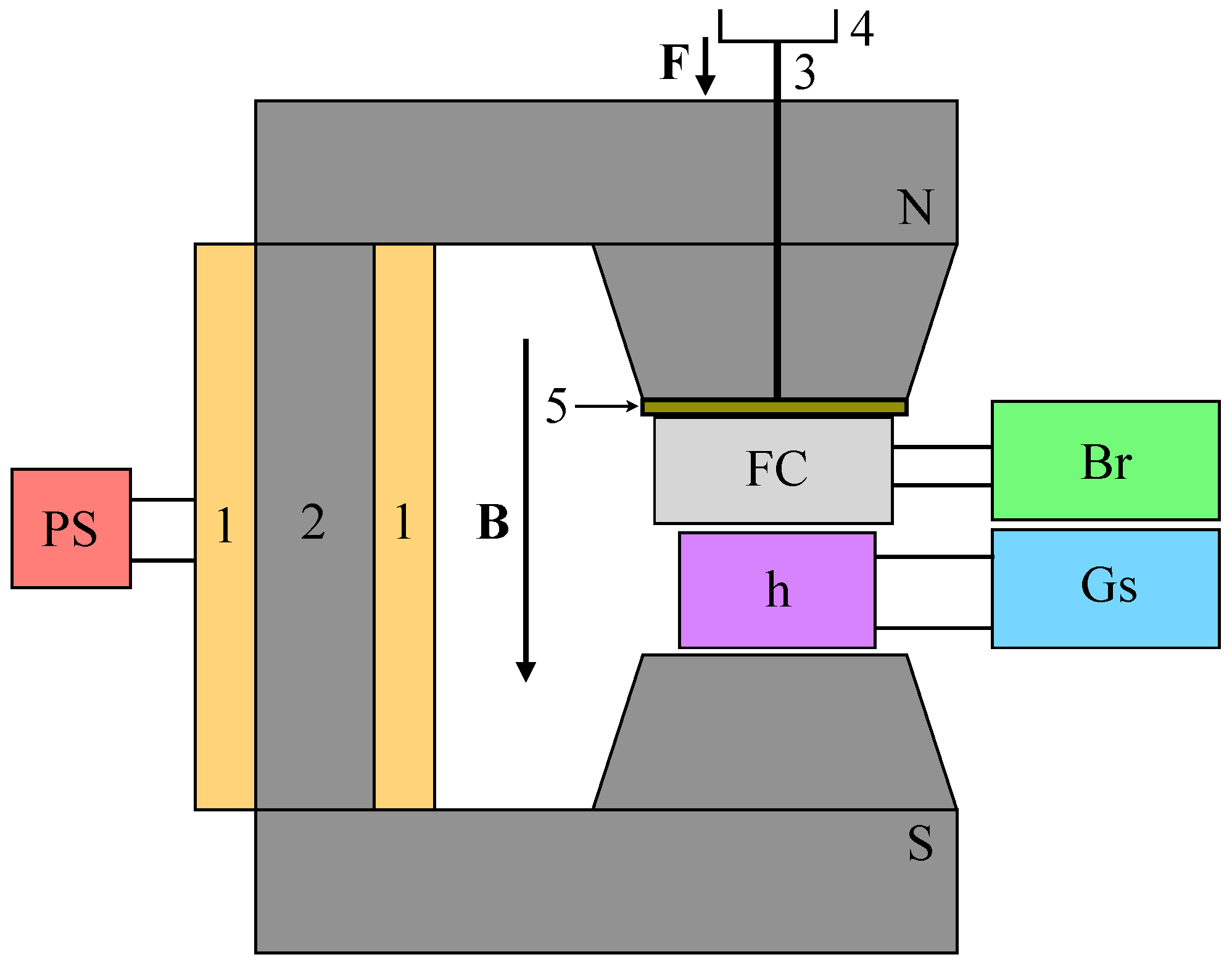
2.6. Experimental Setup for Measuring the Electrical Properties of FC
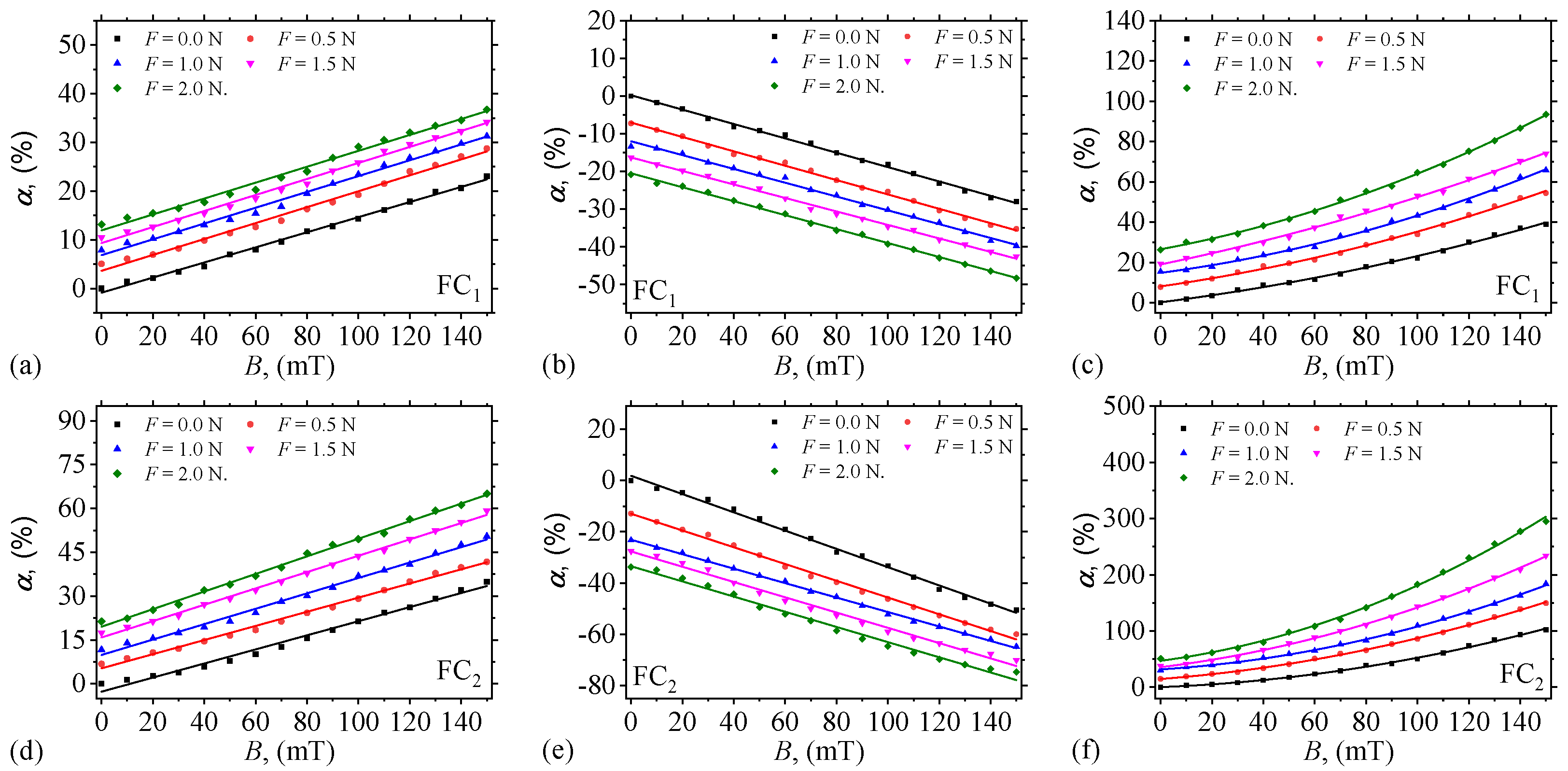
3. Electrical Properties of FC
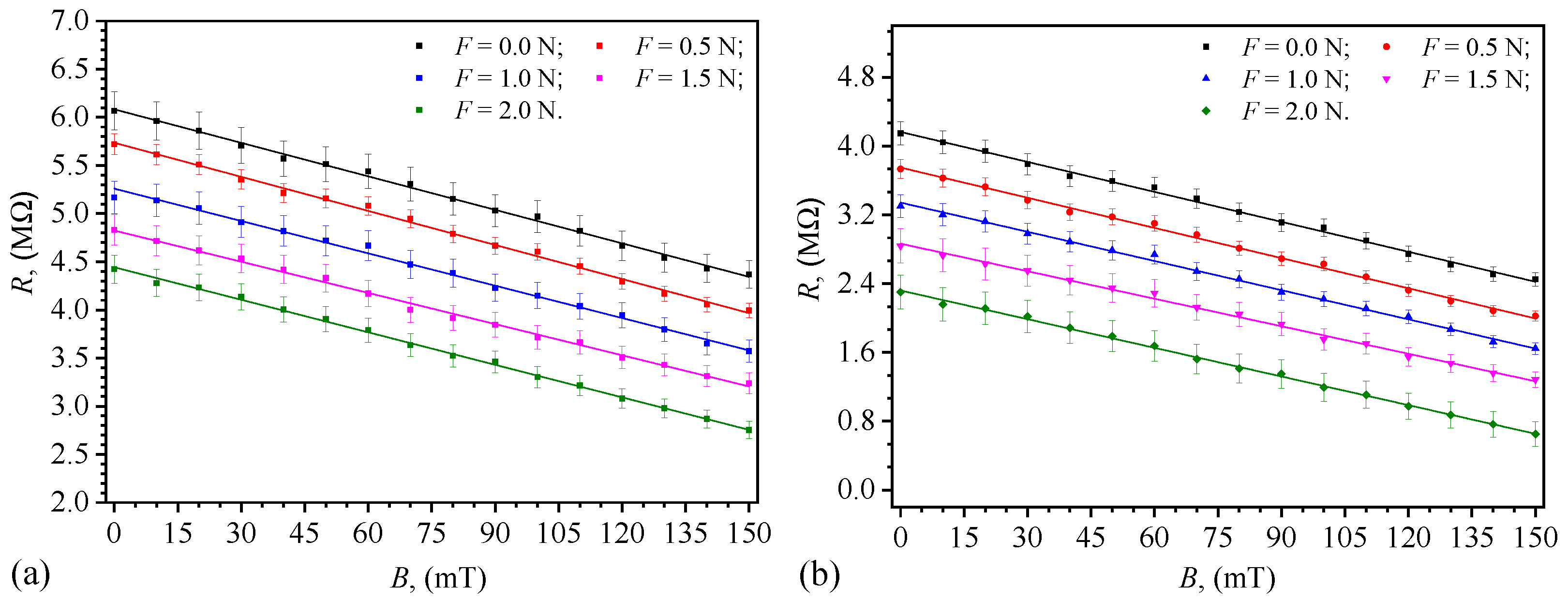
3.1. Electrical Capacitance and Resistance
3.2. Relative Dielectric Permittivity
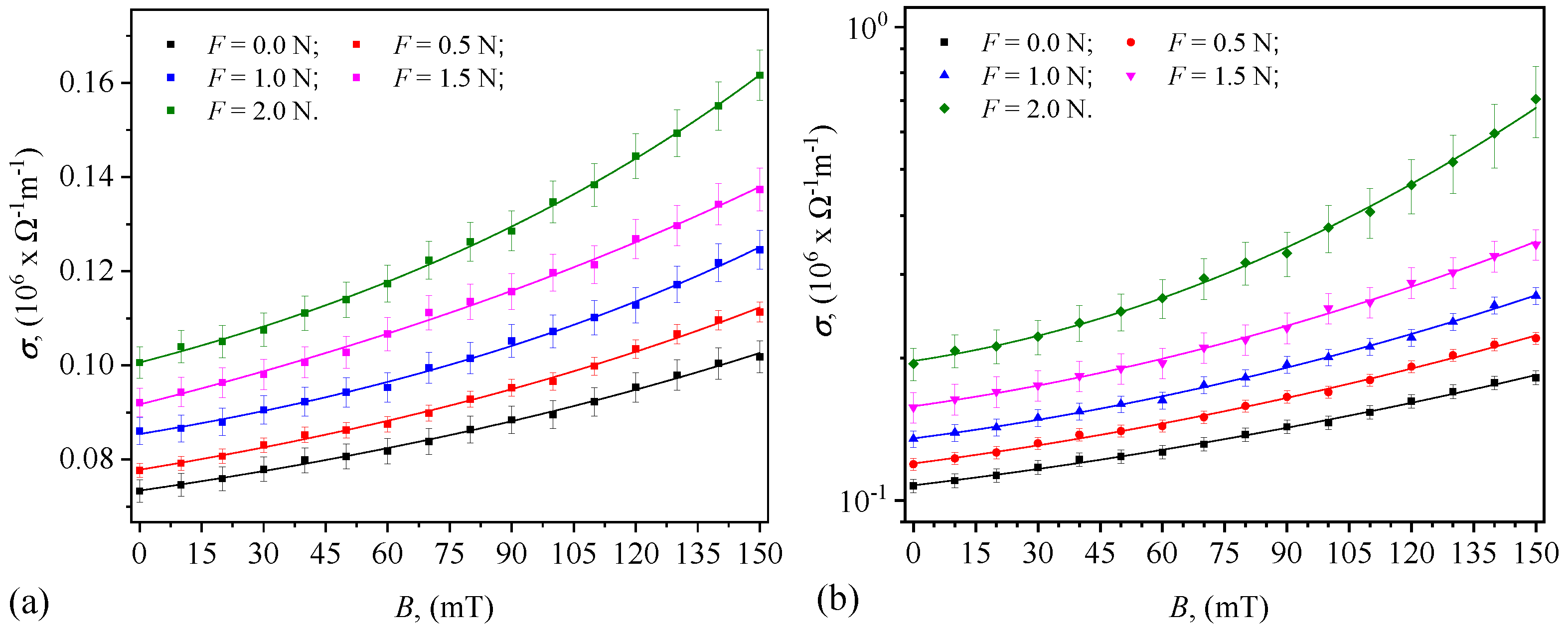
3.3. Electrical Conductivity
3.4. Quantification of the Contribution of Magnetic and Compression Fields on C, R, and
4. Discussions
4.1. Scalability and Process Optimization of Plasma-Synthesized MMPs
4.2. Comparison with Conventional ER/MR Materials and Limitations
4.3. Future Directions for Large-Scale Implementations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
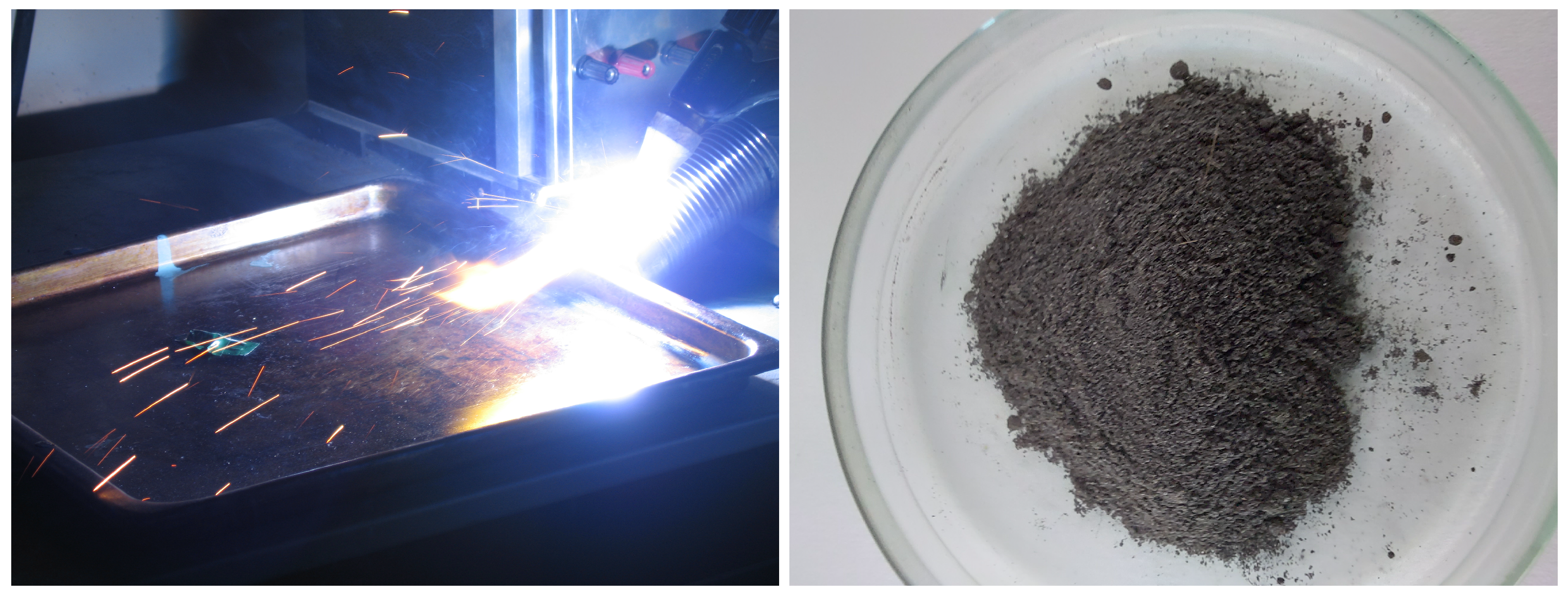
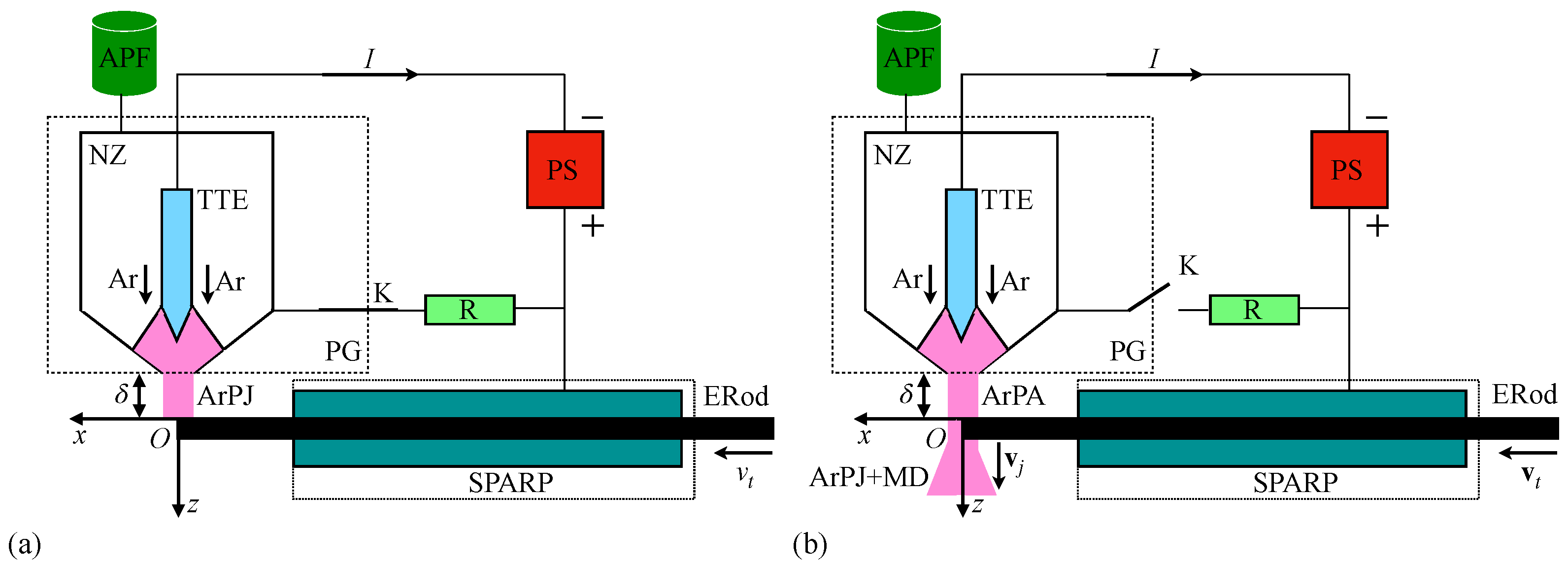
Appendix A. Setup for Producing MMPs

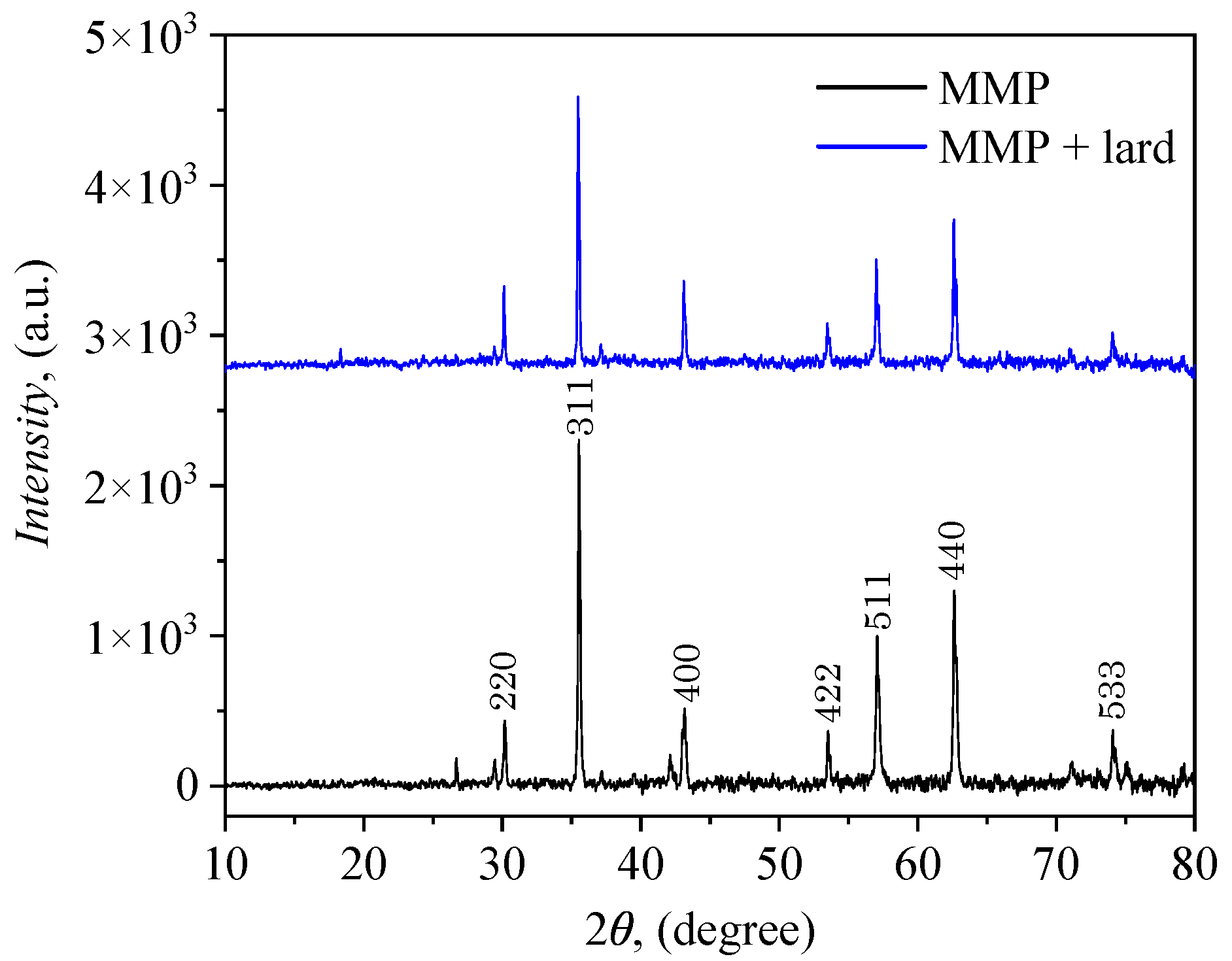
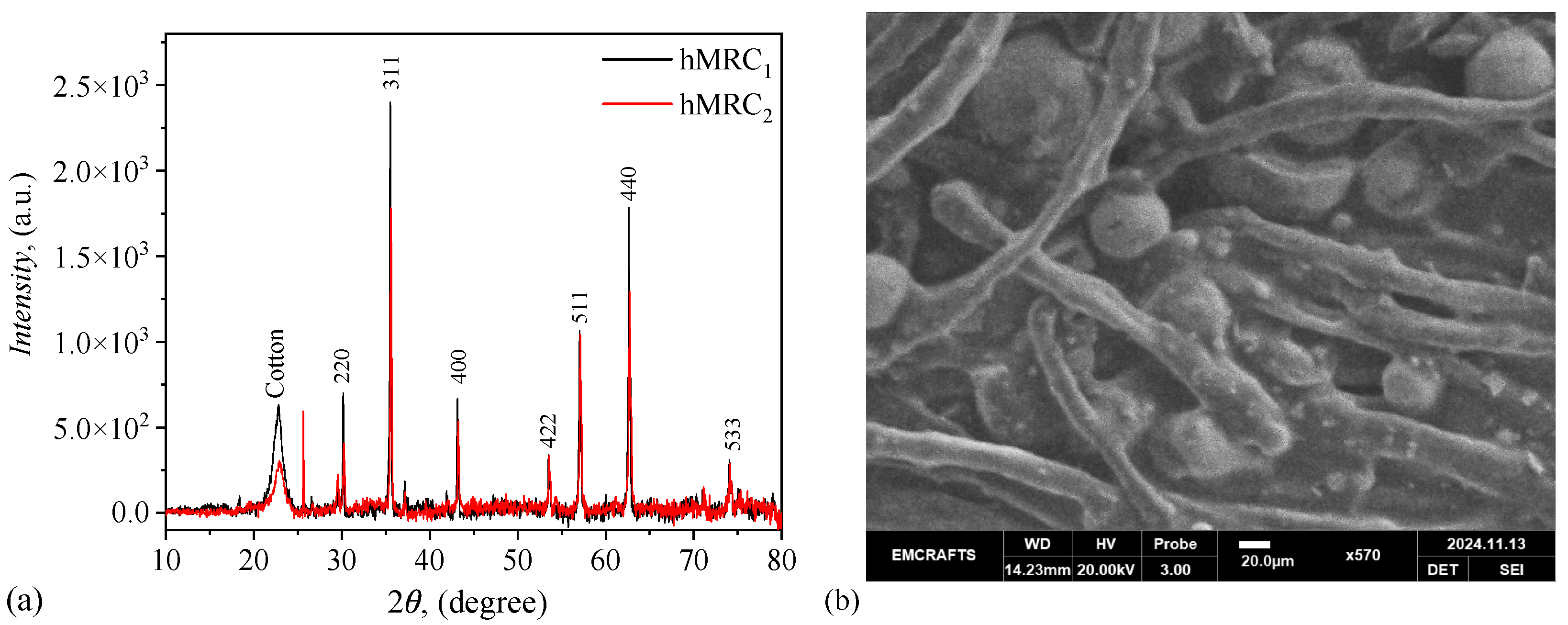
Appendix B. XRD and SEM Measurements

Appendix C. Components of FC

Appendix D. Measurement of Electrical Properties
References
- Yildirim, M.; Candan, Z. Smart materials: The next generation in science and engineering. Mater. Today 2023, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lee, T.L.; Qin, Y. Advances in Smart Materials and Structures. Materials 2023, 16, 7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xiang, Y.; Yu, J.; Yang, L. Development and Prospect of Smart Materials and Structures for Aerospace Sensing Systems and Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Tang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Huang, M.; Wan, Y.; Cheng, P.; Wang, G. Photo- and magneto-responsive highly graphitized carbon based phase change composites for energy conversion and storage. Mater. Today Nano 2022, 19, 100234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Hao, L.; Mao, H. Magneto-responsive biocomposites in wound healing: From characteristics to functions. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 7463–7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccola, S.; Bakhshi, H.; Sanchez Sifuentes, M.; Lloyd, P.; Tinsley, L.J.; Macdonald, J.; Bacchetti, A.; Cespedes, O.; Chandler, J.H.; Valdastri, P.; et al. Dual-Material Aerosol Jet Printing of Magneto-Responsive Polymers with In-Process Tailorable Composition for Small-Scale Soft Robotics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2400463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lesage, K.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Van Tittelboom, K.; De Schutter, G. A comparison of magneto-responsive particles and testing protocols for active rheology control of cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 146, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I.; Liu, Y.D.; Choi, H.J. Physical characteristics of magnetorheological suspensions and their applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem 2013, 19, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Choi, J.; Seo, Y.P.; Park, I.J.; Choi, H.J.; Seo, Y. High-Performance Magnetorheological Suspensions of Pickering-Emulsion-Polymerized Polystyrene/Fe3O4 Particles with Enhanced Stability. Langmuir 2018, 34, 2807–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, N.; Kovaleva, V.; Belousov, S.; Chvalun, S. Electrorheological fluids: From historical retrospective to recent trends. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Hu, X.; Zhao, X.; Yin, J. Electrorheological Effect of Suspensions of Polyaniline Nanoparticles with Different Morphologies. Polymers 2023, 15, 4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunoiu, O.M.; Bica, I.; Anitas, E.M.; Chirigiu, L.M.E. Magnetodielectric and Rheological Effects in Magnetorheological Suspensions Based on Lard, Gelatin and Carbonyl Iron Microparticles. Materials 2024, 17, 3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Ren, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, J.; Wen, W. Highly stable and efficient electrorheological suspensions with hydrophobic interaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 564, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, H.; Sun, W.; Wang, B.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Strong nano size effect of titanium silicalite (TS-1) zeolites for electrorheological fluid. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ning, D.; Sun, S.; Zheng, J.; Lu, H.; Nakano, M.; Zhang, S.; Du, H.; Li, W. A semi-active suspension using a magnetorheological damper with nonlinear negative-stiffness component. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 147, 107071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, S.; Koh, A.S. Performance and Stability of Magnetorheological Fluids—A Detailed Review of the State of the Art. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2001458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sehgal, R.; Wani, M.; Sharma, M.D. Stabilization and tribological properties of magnetorheological (MR) fluids: A review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 538, 168295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.B. Sedimentation Stability of Magnetorheological Fluids: The State of the Art and Challenging Issues. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, P.; Dong, X.; Wu, Z.; Qi, M. Improved Magnetorheological Properties by Using Ionic Liquid as Carrier Liquid of Magnetorheological Fluids. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 659998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Tao, M.; Li, D. Rheological properties and suspension stability of magnetorheological fluid based on Fe3O4 hollow spheres. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2024, 589, 171227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, O.; Karatayeva, U.; Faul, C.F.J. Electrorheological Fluids Based on Porous Carboxyl-Functionalized Polytriphenylamines. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2025, 7, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ji, X.; Yan, H.; Wang, L.; Lin, Y.; Wang, B.; Hao, C. Preparation of layered carbon nitride/titanium-based metal skeleton materials and study on their electrorheological properties. Soft Matter 2025, 21, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitas, E.M.; Munteanu, A.; Sedlacik, M.; Bica, I.; Munteanu, L.; Stejskal, J. Magnetic and electric effects in magnetorheological suspensions based on silicone oil and polypyrrole nanotubes decorated with magnetite nanoparticles. Results Phys. 2024, 61, 107768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I.; Mircea Anitas, E.; Sedlacik, M.; Munteanu, A.; Munteanu, L.; Marina Elisabeth Chirigiu, L. Electrorheological and magnetorheological properties of liquid composites based on polypyrrole nanotubes/magnetite nanoparticles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2024, 33, 065007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I.; Anitas, E.M.; Sedlacik, M.; Munteanu, A.; Munteanu, L.; Chirigiu, L.M.E.; Jurca, M. Electromagnetic modulation of conductance and susceptance in electrical devices based on silicone oil with polypyrrole–magnetite particle composites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 13596–13608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sang, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, S.; Wang, Y.; Gong, X. Conductive magnetorheological fluid (cMRF)-based flexible sensor with adjustable stiffness for magneto-mechanical dual-response and soft actuator. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 489, 151229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.N.; Kumar, V.; Jo, C.R.; Ryu, S.R.; Lee, D.J.; Park, S.S. Mechanical and magneto-mechanical properties of styrene-butadiene-rubber-based magnetorheological elastomers conferred by novel filler-polymer interactions. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 229, 109669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Sapurina, I.; Vilčáková, J.; Plachý, T.; Sedlačík, M.; Bubulinca, C.; Gořalík, M.; Trchová, M.; Kolská, Z.; Prokeš, J. Conducting and Magnetic Composites Polypyrrole Nanotubes/Magnetite Nanoparticles: Application in Magnetorheology. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 2247–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurca, M.; Vilcakova, J.; Kazantseva, N.E.; Munteanu, A.; Munteanu, L.; Sedlacik, M.; Stejskal, J.; Trchova, M.; Prokes, J. Conducting and Magnetic Hybrid Polypyrrole/Nickel Composites and Their Application in Magnetorheology. Materials 2024, 17, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso-Santana, S.; Fleitas-Salazar, N. Ionotropic gelation method in the synthesis of nanoparticles/microparticles for biomedical purposes. Polym. Int. 2020, 69, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, N.; Meghwal, M.; Das, K. Microencapsulation: An overview on concepts, methods, properties and applications in foods. Food Front. 2021, 2, 426–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I.; Anitas, E.M.; Choi, H.J.; Sfirloaga, P. Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of iron oxide microfibers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 6159–6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, B.; Lu, Q.; Xiao, L.; Ma, X.; Feng, Y.; Qian, Y. Fabrication of Fe3O4 nanoparticles by using cathode glow discharge electrolysis plasma and its electrochemical properties. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 427, 140843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovane, P.; Borriello, C.; Pandolfi, G.; Portofino, S.; Rametta, G.; Tammaro, L.; Fedele, N.; Galvagno, S. Thermal Plasma Spheroidization and Characterization of Stainless Steel Powders Using Direct Current Plasma Technology. Plasma 2024, 7, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaneetha Pandiyaraj, K.; Karuppusamy, M.; Jayamurugan, P.; Chaturvedi Misra, V.; Ghorui, S.; Saravanan, P.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Gopinath, P.; Pichumani, M.; et al. Iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) synthesized via a novel non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma-assisted electrolysis: Physicochemical characterization and cytocompatibility evaluation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2024, 35, 104441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.; El-khateeb, M.A.; Sobhy, N.A.; Hefny, M.M.; Abdel-Haleem, F.M. Green Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles Using Waste Natural Materials and Its Application for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 25, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulistyaningsih, T.; Sari, D.A.; Widiarti, N.; Astuti, W.; Wulandari, R.; Harjunowibowo, D. Green synthesis of gaharu leaf extract-modified magnetite as an adsorbent for methyl orange textile dyes. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 2, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I. Steady current plasma macro-nanotechnologies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2009, 15, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, K.; Yang, H.; Yue, K.; Liu, R.; Bi, Y.; Ma, C. Characterization of lard from different adipose tissues: Physicochemical properties, thermodynamics characteristics and crystallization behaviors. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 115, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercuta, A. Sensitive AC Hysteresigraph of Extended Driving Field Capability. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, S. Synthesis and Properties of Magnetorheological (MR) Fluids. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2002. Available online: https://d-scholarship.pitt.edu/8924/ (accessed on 23 February 2025).
- Lu, Q.; Balasoiu, M.; Choi, H.J.; Anitas, E.M.; Bica, I.; Chirigiu, L.M.E. Magneto-dielectric and viscoelastic characteristics of iron oxide microfiber-based magnetoreological suspension. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 112, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarali, E.; Baniasadi, M.; Zolfagharian, A.; Chavoshi, M.; Arefi, F.; Hossain, M.; Bastola, A.; Ansari, M.; Foyouzat, A.; Dabbagh, A.; et al. Magneto-/electro-responsive polymers toward manufacturing, characterization, and biomedical/ soft robotic applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 26, 101306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza Filho, I.R.; Ma, Y.; Kulse, M.; Ponge, D.; Gault, B.; Springer, H.; Raabe, D. Sustainable steel through hydrogen plasma reduction of iron ore: Process, kinetics, microstructure, chemistry. Acta Mater. 2021, 213, 116971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R. Electro-Rheological Fluids and Magneto-Rheological Suspensions; World Scientific: Singapore, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I.; Anitas, E.M.; Iacobescu, G.E. Electrical Capacitors Based on Silicone Oil and Iron Oxide Microfibers: Effects of the Magnetic Field on the Electrical Susceptance and Conductance. Micromachines 2024, 15, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I.; Iacobescu, G.E. Composites Based on Cotton Microfibers Impregnated with Magnetic Liquid for Magneto-Tactile Sensors. Materials 2023, 16, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobescu, G.E.; Bunoiu, M.; Bica, I.; Sfirloaga, P.; Chirigiu, L.M.E. A Cotton Fabric Composite with Light Mineral Oil and Magnetite Nanoparticles: Effects of a Magnetic Field and Uniform Compressions on Electrical Conductivity. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Component | C, | D | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMPs | 45.50 | 0.1007 | 16.4255 | 1.6540 |
| Lard | 17.65 | 0.0209 | 6.3717 | 0.1332 |
| Cotton fabric | 19.22 | 0.1783 | 1.4473 | 0.2581 |
| Vlard (cm3) | VMMPs (cm3) | (% vol.) | (% vol.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 4 | 60 | 40 |
| Vlard (cm3) | VMMPs (cm3) | Vf (cm3) | (% vol.) | (% vol.) | (% vol.) | () | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hMR | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 42 | 29 | 29 | 9.68 |
| hMR | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 42 | 39 | 19 | 13.12 |
| Study | Matrix | Filler | , (m) | , (vol.%) | B, (mT) | F, (N) | Property |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This work | Lard + CF | Magnetite | ∼40.0 | 39 | 150 | 3.0 | C: +65% |
| R: −78% | |||||||
| : +300% | |||||||
| Ref. [46] | SO | Fe2O3 | ∼0.94 | 40 | 400 | 0.0 | C: +33% |
| R: −72% | |||||||
| : -% | |||||||
| Ref. [47] | CF | Magnetite | ∼0.01 | 4.4 | 400 | 8.0 | C: +16% |
| R: −20% | |||||||
| : +17.0% | |||||||
| Ref. [48] | MO + CF | Magnetite | ∼0.01 | 6.5 | 0.00 | 9.0 | C: - |
| R: −76% | |||||||
| : +620% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bica, I.; Anitas, E.M.; Sfirloaga, P.; Chirigiu, L.; Gavrilovici, A.M. Hybrid Magneto-Responsive Composites Made from Recyclable Components: Tunable Electrical Properties Under Magnetic and Mechanical Fields. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050219
Bica I, Anitas EM, Sfirloaga P, Chirigiu L, Gavrilovici AM. Hybrid Magneto-Responsive Composites Made from Recyclable Components: Tunable Electrical Properties Under Magnetic and Mechanical Fields. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(5):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050219
Chicago/Turabian StyleBica, Ioan, Eugen Mircea Anitas, Paula Sfirloaga, Liviu Chirigiu, and Andrei Mihai Gavrilovici. 2025. "Hybrid Magneto-Responsive Composites Made from Recyclable Components: Tunable Electrical Properties Under Magnetic and Mechanical Fields" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 5: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050219
APA StyleBica, I., Anitas, E. M., Sfirloaga, P., Chirigiu, L., & Gavrilovici, A. M. (2025). Hybrid Magneto-Responsive Composites Made from Recyclable Components: Tunable Electrical Properties Under Magnetic and Mechanical Fields. Journal of Composites Science, 9(5), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050219







