Experimental Factors Affecting Anisotropic Electrical Conductivity in Carbon/Epoxy Laminates Using a Solid Electrode-Based Two-Probe Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Carbon/Epoxy Specimens and Preparations
2.2. Determination of Fibre Volume Fraction Using Burn-Off Methods
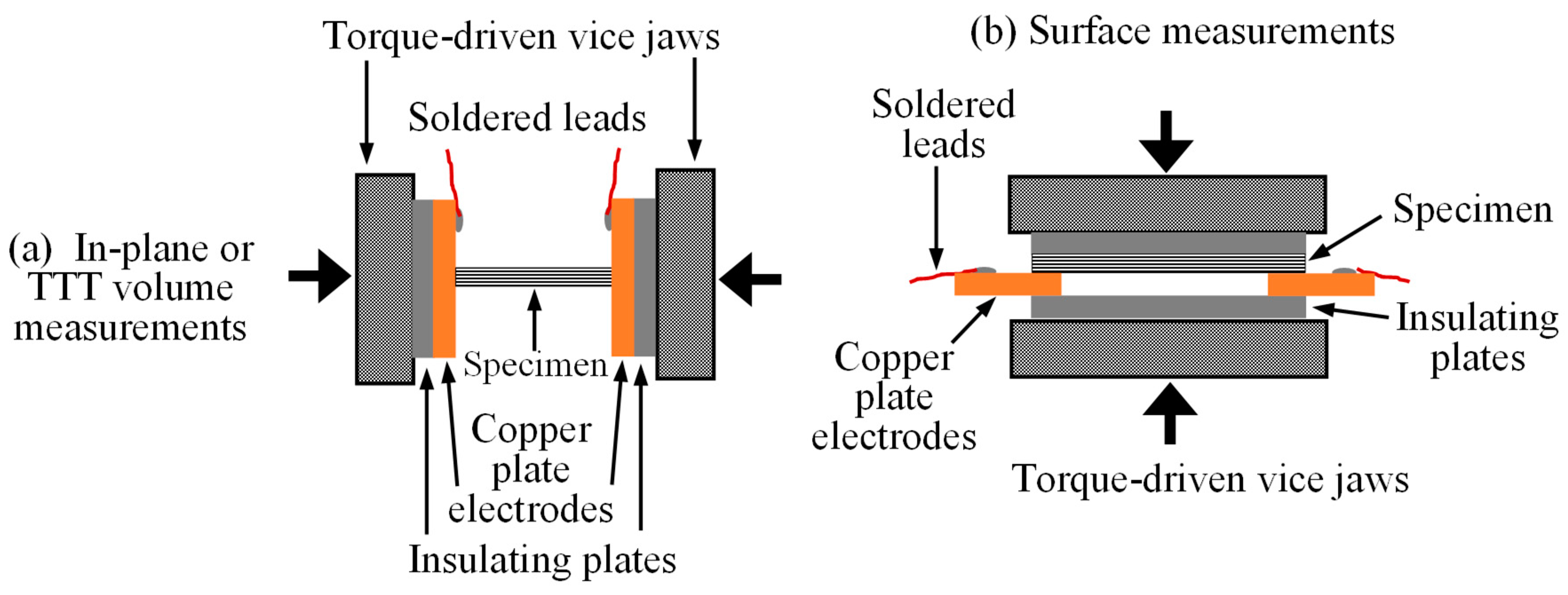
2.3. Method Development for Surface and Volume Electrical Conduction Measurement
2.4. Experimental Set-Up for Electrical Conduction Measurement
2.5. Rule of Mixtures for Electrical Conductivity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Contact Resistance in In-Plane Volume Electrical Conduction
3.2. Anisotropic Volume Electrical Conduction in UD Laminates
3.3. Surface Electrical Conduction
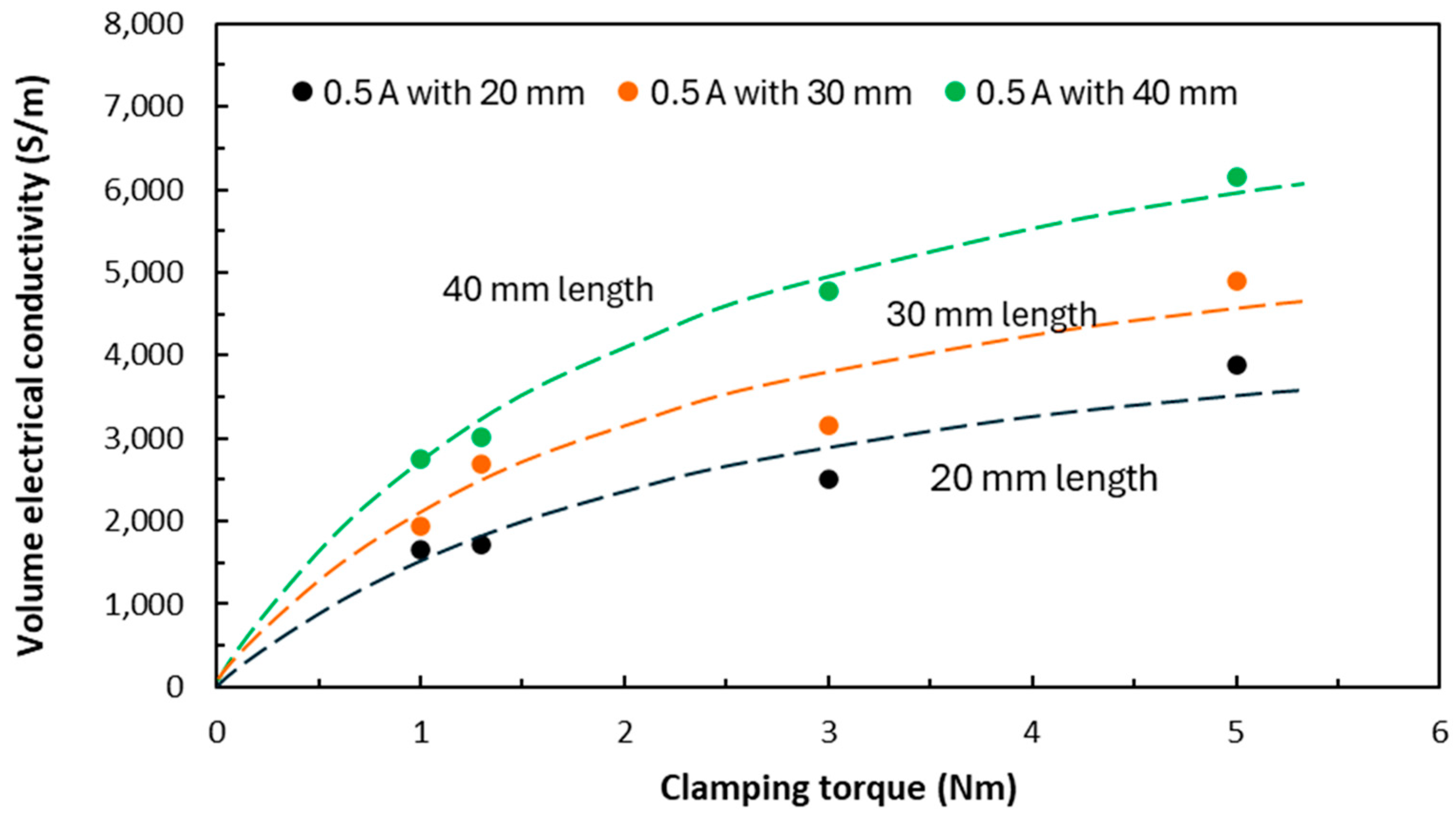
3.4. Effect of Clamping Torque on Volume Electrical Conduction
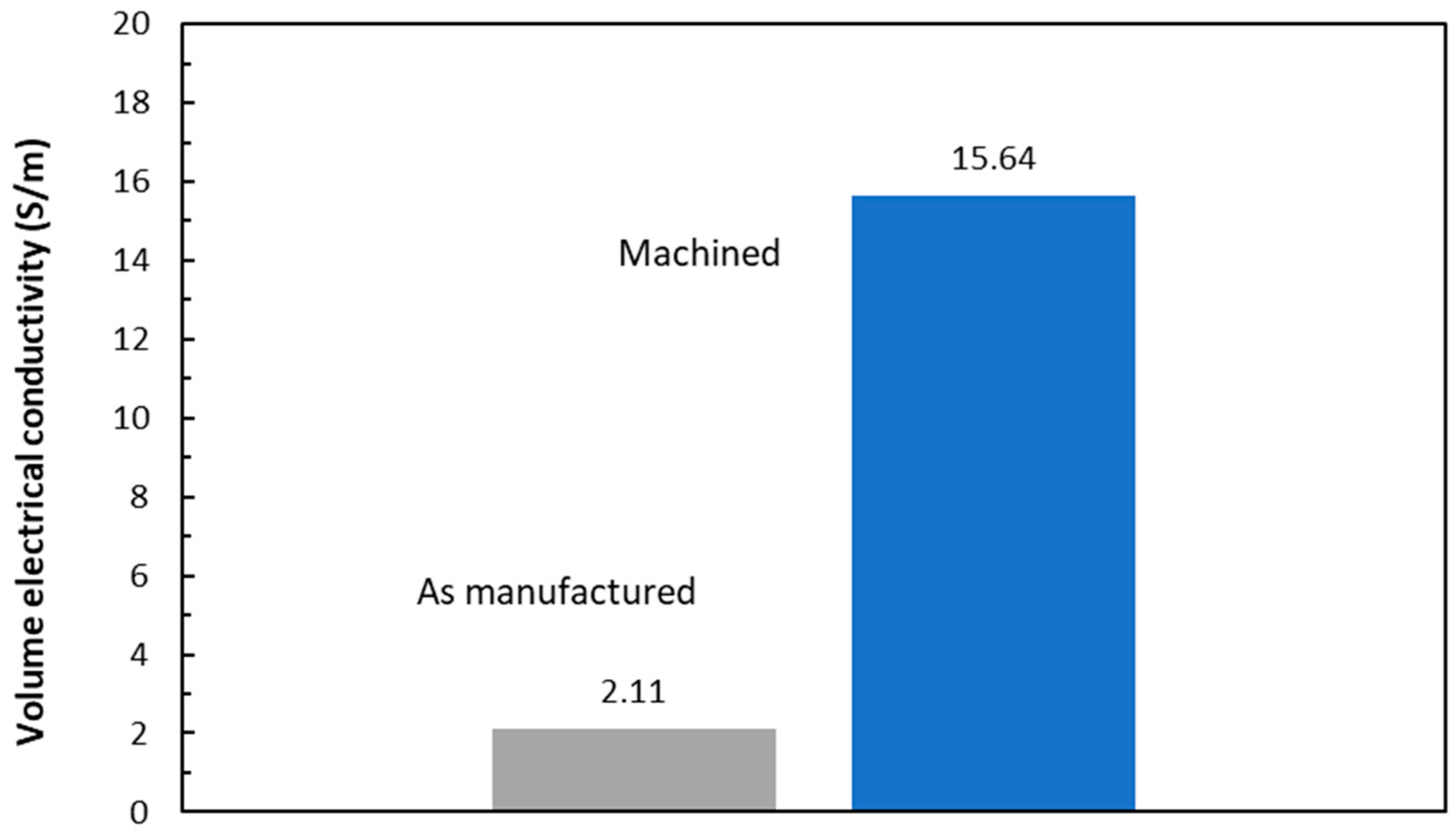
3.5. Effect of Conductive Paint on Volume Electrical Conduction
3.6. Effect of Lay-Ups on Volume Electrical Conduction
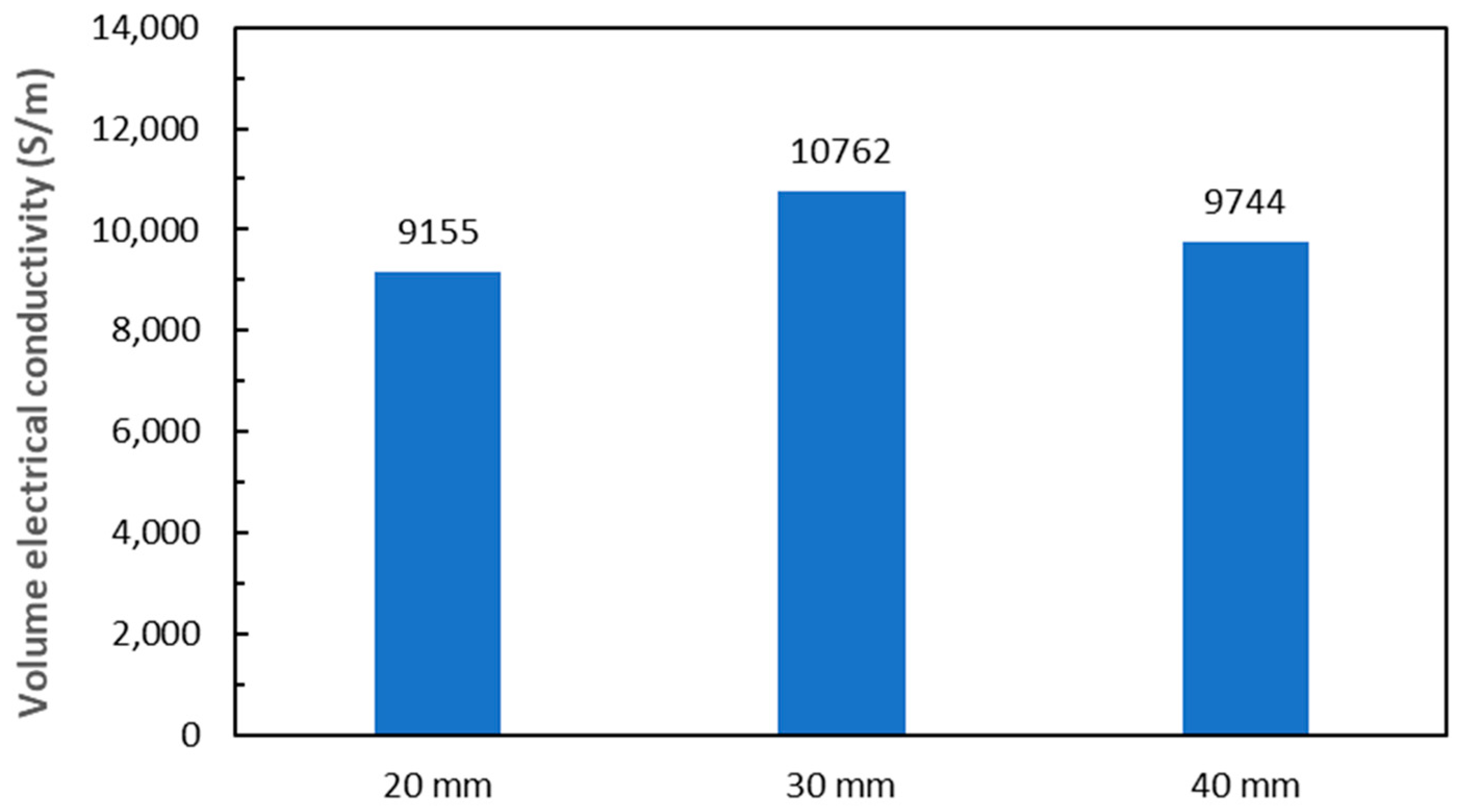
3.7. Effect of Specimen Sizes on Volume Electrical Conduction
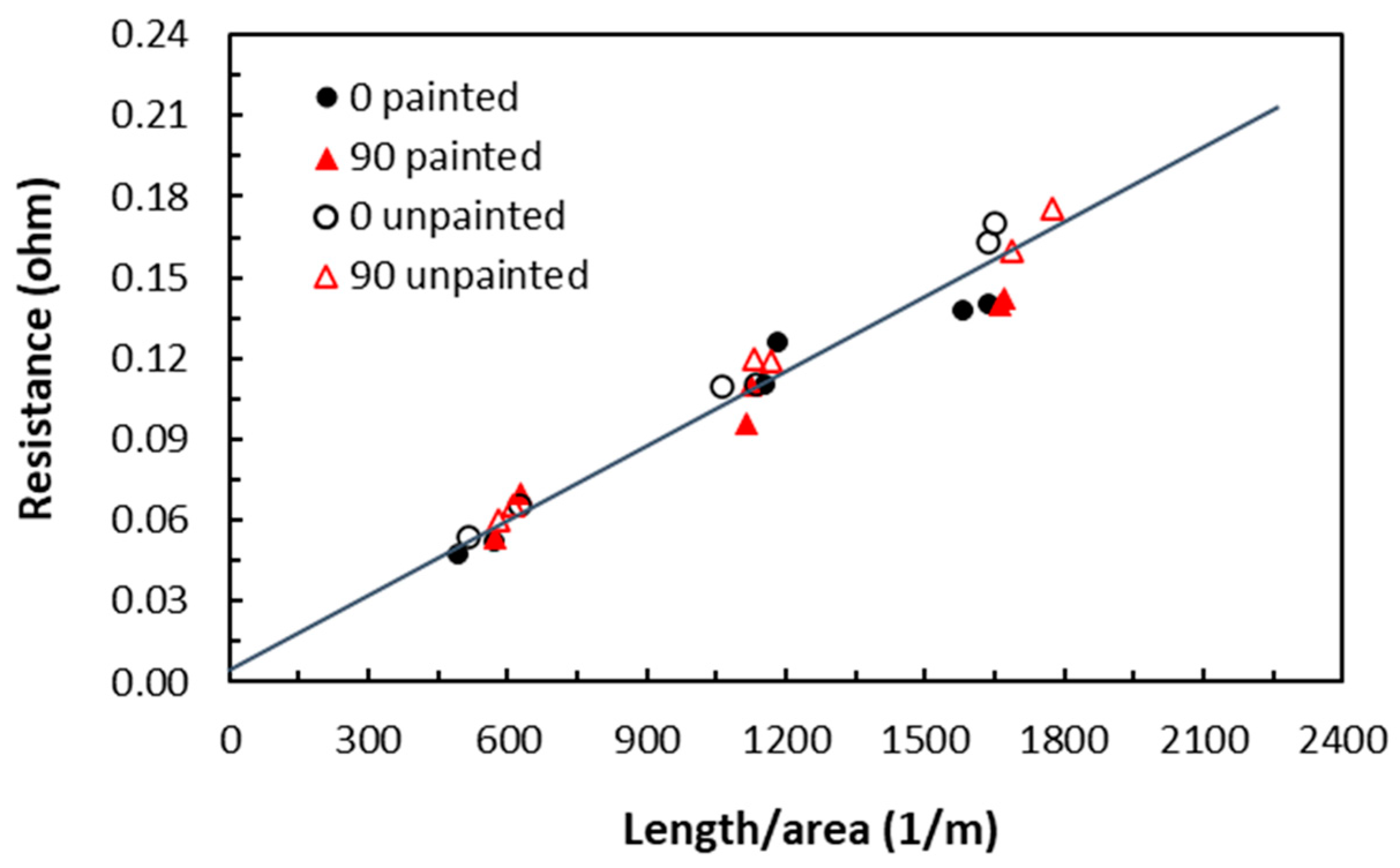
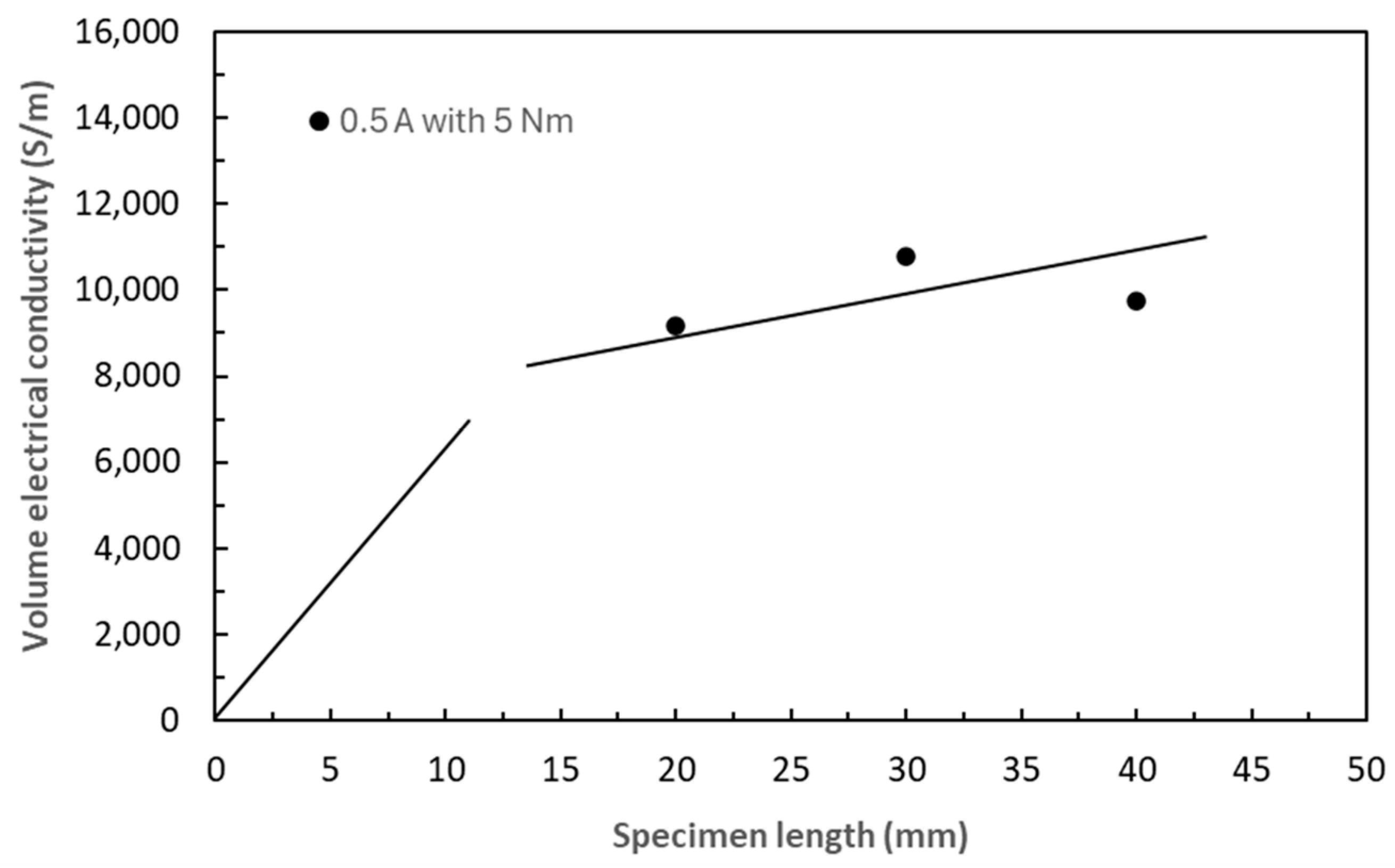
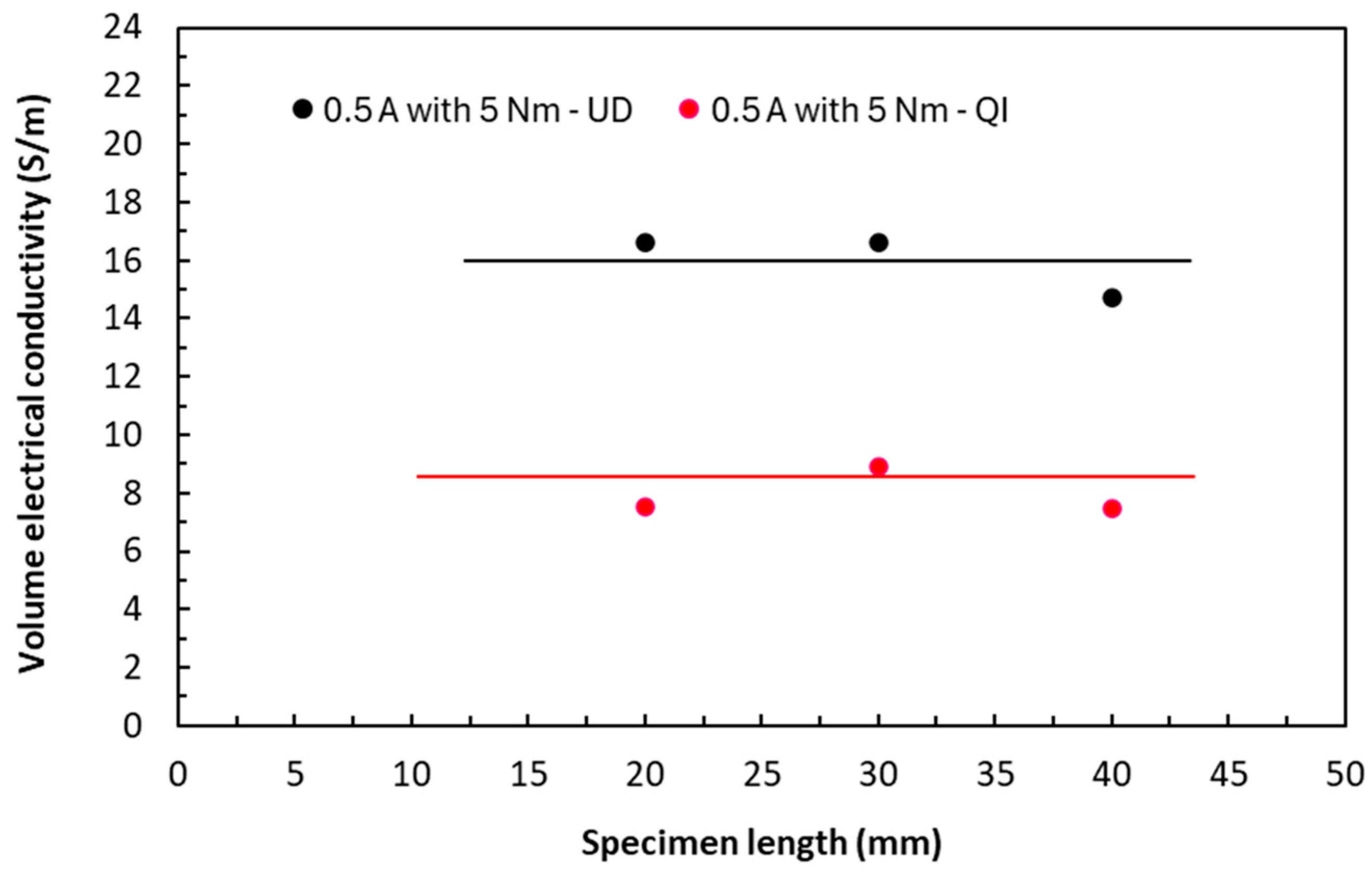
3.7.1. Length Effect on In-Plane Electrical Conductivities
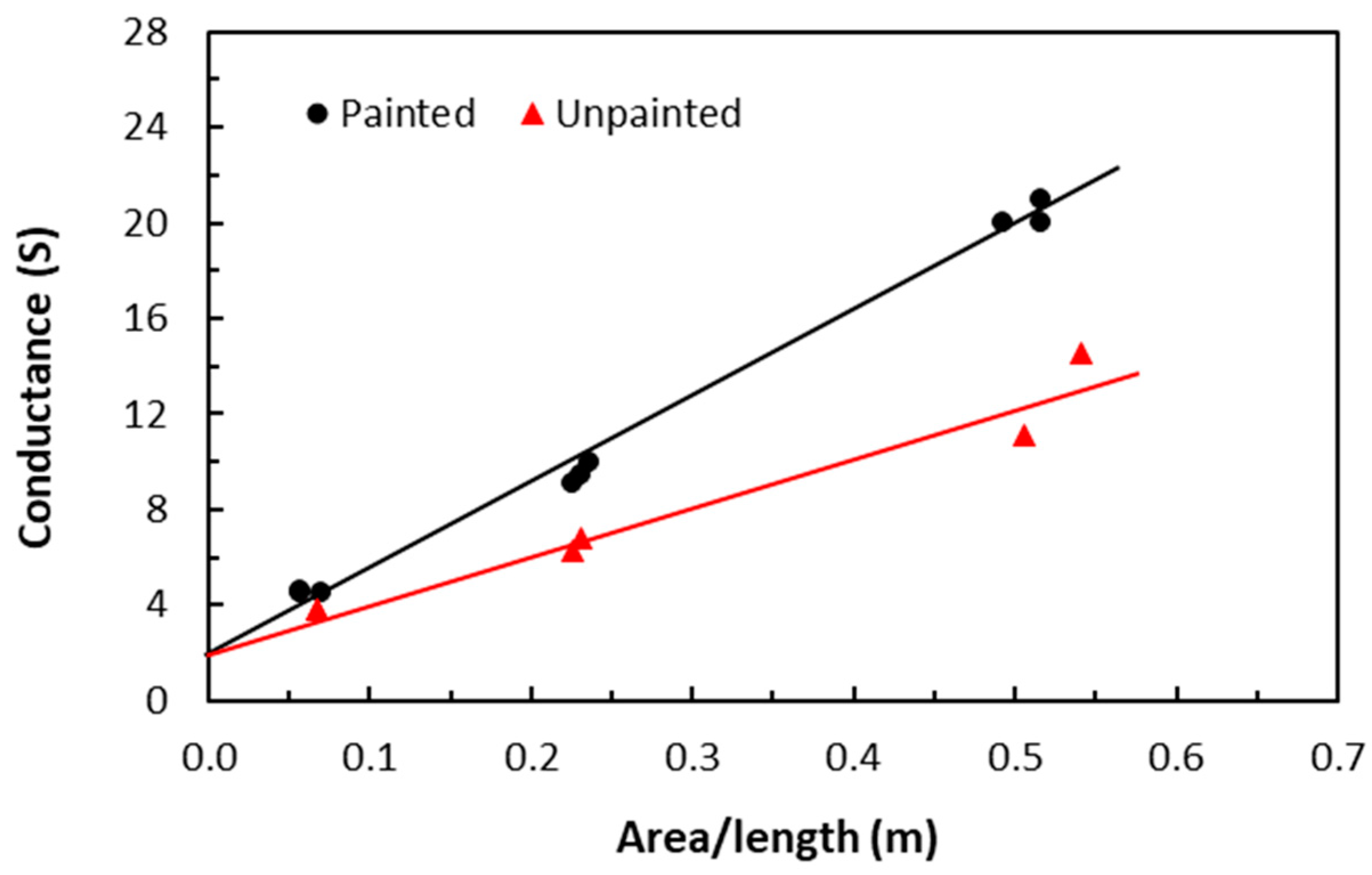
3.7.2. Area Effects on TTT Electrical Conductivities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, X.; Chung, D. Electromagnetic interference shielding using continuous carbon-fibre carbon-matrix and polymer-matrix composites. Compos. Part B 1999, 30, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualli, D.; Dimitrakis, G.; Chronopoulos, D.; Greedy, S.; Long, A. Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of carbon fibre reinforced composites. Compos. Part B 2019, 173, 106906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinquin, J.; Heinrich, C.; Balland, E.; Pons, F.; Gaztelumendi, I.; Vavouliotis, A.; Kostopoulos, V.; Kostagiannakopoulou, C. Volume electrical conductivity measurement on organic composite material. In Proceedings of the SETEC13 Conference, Wuppertal, Germany, 11–12 September 2013; pp. 192–204. [Google Scholar]
- Russello, M.; Diamanti, E.; Catalanotti, G.; Ohlsson, F.; Hawkins, S.; Falzon, B. Enhancing the electrical conductivity of carbon fibre thin ply laminates with directly grown aligned carbon nanotubes. Compos. Struct. 2018, 206, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.B.; Smith, A.C.; Tuohy, P.M.; Gresil, M.; Soutis, C.; Lambourne, A. Experimental electrical characterisation of carbon fibre composites for use in future aircraft applications. IET-Sci. Meas. Technol. 2019, 13, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, P.; Thiagarajan, C. Fatigue damage characterization in carbon fibre composite materials using an electrical potential technique. Smart Mater. Struct. 1998, 7, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abry, J.; Bochard, S.; Chateauminois, A.; Salvia, M.; Giraud, G. In situ detection of damage in CFRP laminates by electrical resistance measurements. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1999, 59, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, M.; Joshi, S.; Brockman, W. An experimental investigation of through-thickness electrical resistivity of CFRP laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoroki, A.; Yoshida, J. Electrical resistance change of unidirectional CFRP due to applied load. JSME Int. J. 2004, 47, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Hwang, T.; Kim, H.; Doh, Y. Experimental and numerical study of the electrical anisotropy in unidirectional carbon fibre reinforced polymer composites. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sawi, I.; Olivier, P.; Demont, P.; Bougherara, H. Processing and electrical characterization of a unidirectional CFRP composite filled with double walled carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 73, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Falzon, B.; Hawkins, S.; Tsantzalis, S. Aligned carbon nanotube webs embedded in a composite laminate: A route towards a highly tunable electro-thermal system. Carbon 2018, 129, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galehdar, A.; Rowe, W.; Ghorbani, K.; Callus, P.; John, S.; Wang, C. The effect of ply orientation on the performance of antennas in or on carbon fiber composites. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2011, 116, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; Yi, R. Analyses on electromagnetic and temperature fields of super high-speed permanent-magnet generator with different sleeve materials. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3056–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zantout, A.; Zhupanska, O. On the electrical resistance of carbon fiber polymer matrix composites. Compos. Part A 2010, 41, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, R. Electrical Characterisation of Aerospace Grade Carbon-Fibre-Reinforced Polymers. Ph.D. Thesis, Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Mikinka, E.; Bao, X.; Sun, W. Electrical conduction investigation of pre-stressed carbon/epoxy fabric laminates heated by ampere-level currents. Funct. Compos. Mater. 2023, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Hahn, H.T. Investigation of temperature dependency of electrical resistance changes for structural management of graphite/polymer composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 2603–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.; Eddib, A. Effect of fiber lay-up configuration on the electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of continuous carbon fiber polymer-matrix composite. Carbon 2019, 141, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3171-15; Standard Test Methods for Constituent Content of Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- ASTM E1131-08; Standard Test Method for Compositional Analysis by Thermogravimetry. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008.
- Yu, H.; Heider, D.; Advani, S. A 3D microstructure based resistor network model for the electrical resistivity of unidirectional carbon composites. Compos. Struct. 2015, 134, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakassides, A.; Karakassides, A.; Konstantinidou, M.; Paipetis, A.S.; Papakonstantinou, P. Enhanced out of plane electrical conductivity in polymer composites induced by co2 laser irradiation of carbon fibers. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coste, J.; Pechery, P. Influence of surface profile in polymer-metal contact charging. J. Electrost. 1981, 10, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, K.W.; Moyer, C.A.; Arajs, S. Electrical conductivity of graphite fiber-epoxy resin composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1981, 49, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knibbs, R.; Morris, J. The effects of fibre orientation on the physical properties of composites. Composites 1974, 5, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, B. Engineering Composite Materials, 2nd ed.; Institute of Materials Communications: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, R.J.; Zhupanska, O.I. The role of electrical anisotropy and effective conducting thickness in understanding and interpreting static resistance measurements in CFRP composite laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 2020, 54, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupke, M.; Schulte, K.; Schüler, R. Non-destructive testing of FRP by D.C. and A.C. electrical methods. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, H.O. Handbook of Carbon, Graphite, Diamond, and Fullerenes: Properties, Processing, and Applications; Noyes Publications: Park Ridge, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]









| Thickness | Dimensions | Lay-Up | Electrical Conductivity | Lay-Up | Electrical Conductivity | Diff. from UD | Lay-Up | Electrical Conductivity | Diff. from UD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | mm × mm | - | S/m ± S.D. | - | S/m ± S.D. | % | - | S/m ± S.D. | % |
| 2 | 10 × 10 | UD | 10,544 ± 2236 | - | - | - | QI | 6357 ± 1107 | +60.8 |
| 20 × 10 | 11,815 ± 1447 | - | - | - | 8128 ± 892 | +83.5 | |||
| 30 × 10 | 11,780 ± 964 | - | - | - | 11,074 ± 1081 | +150.7 | |||
| 40 × 10 | 18,978 ± 3099 | - | - | - | 13,035 ± 1117 | +83.2 | |||
| 4 | 20 × 10 | UD | 9155 ± 1614 | CP | 4877 ± 1024 | +6.5 | QI | 3892 ± 492 | +13.4 |
| 30 × 10 | 10,762 ± 2133 | 5773 ± 528 | +7.3 | 4888 ± 731 | +21.1 | ||||
| 40 × 10 | 9744 ± 3470 | 7016 ± 1092 | +44.0 | 6151 ± 624 | +68.3 |
| Thickness | Dimensions | Lay-Up | Electrical Conductivity | Lay-Up | Electrical Conductivity | Lay-Up | Electrical Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | mm × mm | - | S/m ± S.D. | - | S/m ± S.D. | - | S/m ± S.D. |
| 2 | 10 × 10 | UD | 9.75 ± 5.82 | - | - | QI | 12.0 ± 4.98 |
| 20 × 10 | 6.23 ± 2.79 | - | - | 4.15 ± 1.04 | |||
| 30 × 10 | 2.22 ± 0.96 | - | - | 3.98 ± 1.81 | |||
| 40 × 10 | 1.36 ± 0.58 | - | - | 3.18 ± 0.82 | |||
| 4 | 20 × 10 | UD | 16.6 ± 7.50 | CP | - | QI | 7.54 ± 0.14 |
| 30 × 10 | 16.6 ± 4.99 | 6.87 ± 0.10 | 8.93 ± 1.47 | ||||
| 40 × 10 | 14.7 ± 5.09 | 5.12 ± 0.08 | 7.48 ± 0.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, G.; Sun, W. Experimental Factors Affecting Anisotropic Electrical Conductivity in Carbon/Epoxy Laminates Using a Solid Electrode-Based Two-Probe Method. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050212
Zhou G, Sun W. Experimental Factors Affecting Anisotropic Electrical Conductivity in Carbon/Epoxy Laminates Using a Solid Electrode-Based Two-Probe Method. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(5):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050212
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Gang, and Weiwei Sun. 2025. "Experimental Factors Affecting Anisotropic Electrical Conductivity in Carbon/Epoxy Laminates Using a Solid Electrode-Based Two-Probe Method" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 5: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050212
APA StyleZhou, G., & Sun, W. (2025). Experimental Factors Affecting Anisotropic Electrical Conductivity in Carbon/Epoxy Laminates Using a Solid Electrode-Based Two-Probe Method. Journal of Composites Science, 9(5), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9050212




