Evaluation of Mechanical, Thermal, and Tribological Properties of 3D-Printed Nylon (PA6) Hybrid Composites Reinforced with MWCNTs and Carbon Fibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Experimental Characterizations
2.1. Nylon, MWCNTs and CF Specifications
2.2. Filament Extrusion and Specimen Fabrication
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4. Tensile Test
2.5. Flexural Test
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscope (FTIR)
2.7. Surface Morphology (Scanning Electron Microscopy)
2.8. Tribological Analysis
2.8.1. Wear Characterization
2.8.2. Scratch Test
2.8.3. Hardness Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. DSC Test Results
3.2. Tensile Test Results
3.3. Flexural Test Results
3.4. FTIR Analysis
3.5. Tribological Analysis
3.5.1. Wear Rate Analysis
3.5.2. Coefficient of Friction (COF)
3.5.3. Scratch Test
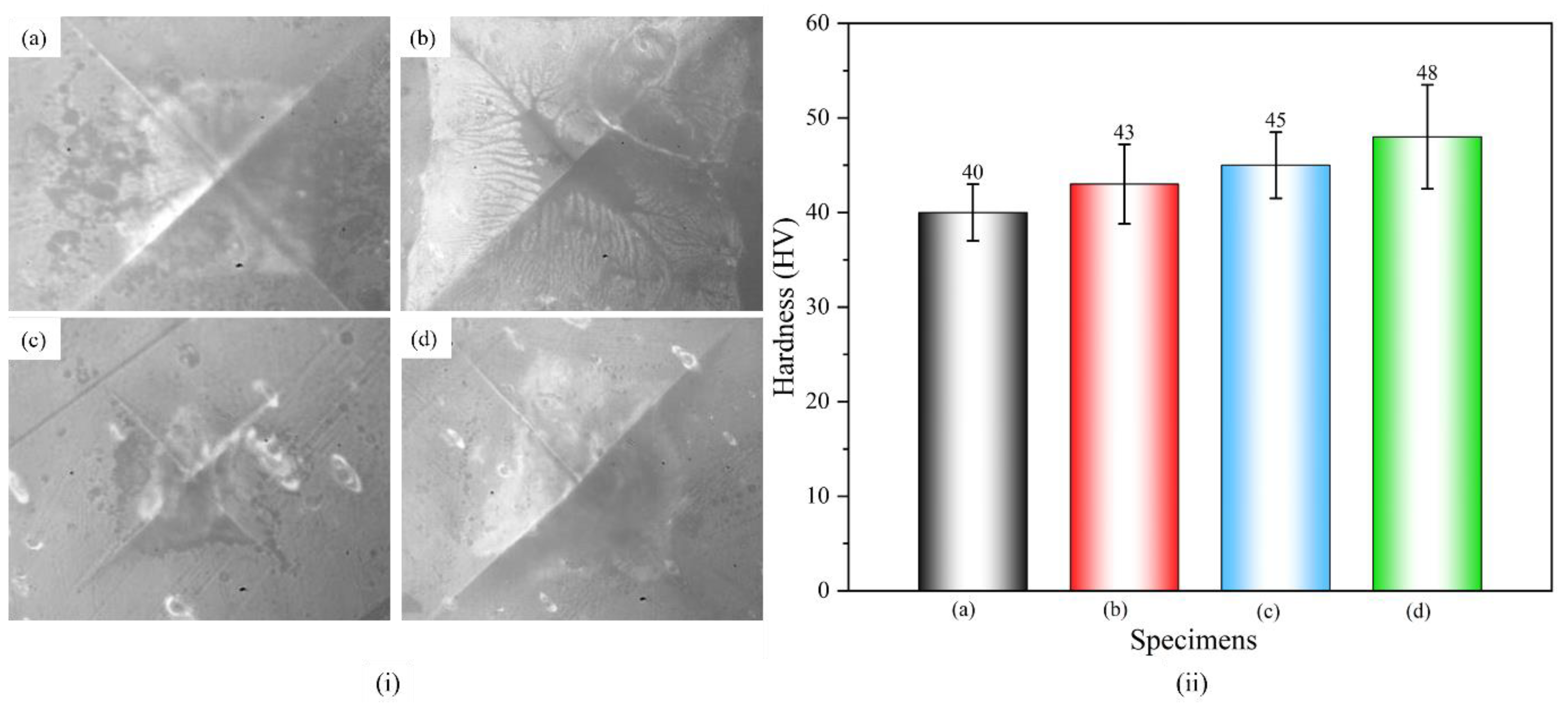
3.5.4. Hardness Test
4. Conclusions
- Mechanical properties improved due to the synergistic effect of MWCNTs and CFs. The hybrid reinforcement (0.5 wt.% MWCNTs and 15 wt.% CF) significantly enhanced tensile and flexural properties through proper alignment and even distribution within the polymer matrix.
- The addition of MWCNTs and CFs to the nylon interferes with the orderly packing of the polymer chains, leading to an increase in crystallinity and, consequently, a higher melting temperature
- The synergistic effect of MWCNTs and CF contributes to the maximum hardness enhancement in nylon composites. The improvements in hardness result from the enhanced load-bearing capacity and improved interfacial bonding. This could result in enhanced creep resistance and reduced plastic deformation.
- The presence of MWCNT and CF has considerably lowered the wear during the run-in phase thereby marking a lower static coefficient of friction and subsequently a lower kinetic friction coefficient.
- Tangential force during scratching is lowered, which reduces the plastic deformation and thereby enhances the composites’ performance. The penetration depth and plastic deformation of the composite samples were observed to be reduced due to increased scratch hardness.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| N | Nylon |
| PA6 | Polyamide |
| MWCNT | Multi-walled carbon nanotubes |
| CF | Carbon nanofiber |
| Hs | Scratch hardness |
| Tm | Melting point |
References
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, K.; Liu, Z. Synthesis of high molecular weight nylon 46 in supercritical carbon dioxide. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meincke, O.; Kaempfer, D.; Weickmann, H.; Friedrich, C.; Vathauer, M.; Warth, H. Mechanical properties and electrical conductivity of carbon-nanotube filled polyamide-6 and its blends with acrylonitrile/butadiene/styrene. Polymer 2003, 45, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchelli, A.; Focarete, M.L.; Gualandi, C.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanofibers for enhancing structural performance of composite materials. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.; Llorca, J. Mechanical behavior of unidirectional fiber-reinforced polymers under transverse compression: Microscopic mechanisms and modeling. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 2795–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Sun, X. Effects of interphase properties in unidirectional fiber reinforced composite materials. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3486–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei, S.H.R.; Popescu, D. 3D-printed carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites: A systematic review. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasel, U.; Keidel, D.; Baumann, L.; Cavolina, G.; Eichenhofer, M.; Ermanni, P. Composite additive manufacturing of morphing aerospace structures. Manuf. Lett. 2020, 23, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, S.; Khandelwal, A.; Raj, A.; Ahmad, G. Fabrication of FFF 3D-printed surfaces for PMMA-based biomedical device employing the pre-processing optimization to eliminate the post-processing steps. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 9, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Werken, N.; Hurley, J.; Khanbolouki, P.; Sarvestani, A.N.; Tamijani, A.Y.; Tehrani, M. Design considerations and modeling of fiber reinforced 3D printed parts. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 160, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Werken, N.; Tekinalp, H.; Khanbolouki, P.; Ozcan, S.; Williams, A.; Tehrani, M. Additively manufactured carbon fiber-reinforced composites: State of the art and perspective. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 31, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarifi, I.M. A performance evaluation study of 3d printed nylon/glass fiber and nylon/carbon fiber composite materials. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, B.; Niu, J.; Yang, C.; Sun, C.; Wang, L.; Li, D. Effect of fiber content on mechanical properties of carbon fiber-reinforced polyether-ether-ketone composites prepared using screw extrusion-based online mixing 3D printing. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 80, 103976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Baxevanakis, K.P.; Silberschmidt, V.V. Mechanical characterisation of AM nylon-matrix carbon-fibre-reinforced composite in tension. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 70, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Palaniappan, A.K.; Krishnan, R.K.; Vasanaperumal, P.; Rajendiran, K. Analysis of the Mechanical Characteristics and Properties of a Carbon Fiber–Nylon Composite Influence of the Factors of the Fused Deposition Modeling. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024, 33, 12976–12989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, H.; Kurita, D.; Nakakubo, S.; Yamaguchi, A.; Yamane, M.; Kawabe, K.; Tanoue, S. Mechanical behavior of unidirectional carbon fiber-reinforced polyamide 6 composites under transverse tension and the structure of polyamide 6 among carbon fibers. Polym. J. 2020, 52, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.; Singh, S.P.; Behera, B.K. Mechanical, thermal, and microstructural analysis of 3D printed short carbon fiber-reinforced nylon composites across diverse infill patterns. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 10, 1671–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SV, L.S.; Karthick, A.; Dinesh, C. Evaluation of mechanical properties of 3D printed PETG and Polyamide (6) polymers. Chem. Phys. Impact 2024, 8, 100491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Mubarak, S.; Zhang, G.; Peng, K.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; Wang, J. Fused-Deposition Modeling 3D Printing of Short-Cut Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced PA6 Composites for Strengthening, Toughening, and Light Weighting. Polymers 2023, 15, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y. Evaluating tensile properties of 3d printed continuous fiber reinforced nylon 6 nanocomposites. In Proceedings of the International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, College Station, TX, USA, 18–22 June 2018; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 51357, p. V001T01A031. [Google Scholar]
- Al Rashid, A.; Ikram, H.; Koç, M. Additive manufacturing and mechanical performance of carbon fiber reinforced Polyamide-6 composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 6359–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustika, D.K.; Mercuriani, I.; Purnomo, C.W.; Hartono, S.; Triyana, K.; Iliescu, D.D.; Leeson, M.S. Fourier transform infrared spectrum pre-processing technique selection for detecting PYLCV-infected chilli plants. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 278, 121339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Vanga, S.; Ariese, F.; Umapathy, S. Review of multidimensional data processing approaches for Raman and infrared spectroscopy. EPJ Tech. Instrum. 2015, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phang, I.Y.; Ma, J.; Shen, L.; Liu, T.; Zhang, W.D. Crystallization and melting behavior of multi-walled carbon nanotube-reinforced nylon-6 composites. Polym. Int. 2006, 55, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihi, M.; Shojaei, A.; Bagheri, R. Characterization of polyamide 6/carbon nanotube composites prepared by melt mixing-effect of matrix molecular weight and structure. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 78, 50–64. [Google Scholar]
- Chafidz, A.; Latief, F.H.; Al-Fatesh, A.S.; Kaavessina, M. Crystallization and thermal stability of polypropylene/multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2016, 96, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, L.; Yang, D.; Liang, J.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, Z. Effects of Carbon Fiber Content on the Crystallization and Rheological Properties of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polyamide 6. Polymers 2024, 16, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, F.S.; Luna, C.B.; da Silva Barbosa Ferreira, E.; de Matos Costa, A.R.; Wellen, R.M.; Araújo, E.M. Polyamide 6 (PA6)/carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) nanocomposites for antistatic application: Tailoring mechanical and electrical properties for electronic product protection. J. Polym. 2024, 31, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Rwei, S.-P.; Ranganathan, P.; Lee, Y.-H. Isothermal crystallization kinetics study of fully aliphatic PA6 copolyamides: Effect of novel long-chain polyamide salt as a comonomer. Polymers 2019, 11, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namathoti, S.; Paladugu, S.R.; Barick, A.K.; Sreekanth, P.R. Shape recovery behavior and mechanical performance of 4D printed Polyurethane/MWCNT nanocomposites under γ-irradiation. Polymer 2025, 317, 127932. [Google Scholar]
- Zaldua, N.; Maiz, J.; de la Calle, A.; García-Arrieta, S.; Elizetxea, C.; Harismendy, I.; Tercjak, A.; Müller, A.J. Nucleation and Crystallization of PA6 Composites Prepared by T-RTM: Effects of Carbon and Glass Fiber Loading. Polymers 2019, 11, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athokpam, B.; Ramesh, S.G.; McKenzie, R.H. Effect of hydrogen bonding on the infrared absorption intensity of OH stretch vibrations. Chem. Phys. 2017, 488–489, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, I.S.; Liu, X.; Jin, Y.; Sun, J.; Lee, Y.J. Stoichiometric analysis of competing intermolecular hydrogen bonds using infrared spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 23481–23488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S. Comprehensive analysis of 3D printed PA6. 6 and fiber-reinforced variants: Revealing mechanical properties and adhesive wear behavior. Polym. Compos 2024, 45, 1446–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Xia, Y.C. The reinforcement effect of carbon fiber on the friction and wear properties of carbon fiber reinforced PA6 composites. Fibers Polym. 2009, 10, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khun, N.W.; Cheng, H.K.F.; Li, L.; Liu, E. Thermal, mechanical and tribological properties of polyamide 6 matrix composites containing different carbon nanofillers. J. Polym. Eng. 2015, 35, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Gu, P.; Zhang, Z. Indentation and scratch behavior of nano-SiO2/polycarbonate composite coating at the micro/nano-scale. Wear. 2010, 269, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Rybnicek, J.; Lach, R.; Dominguez, S.R.; Tondl, D.; Valek, R.; Grellmann, W. Scratch resistance of PA6 nanocomposites. Rubber Fibres Plast. Int. 2013, 8, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo, L.F.; Brostow, W.; Devaux, E.; López, B.L.; Pérez, L.D. Scratch and wear resistance of polyamide 6 reinforced with multiwall carbon nanotubes. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 3176–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Z.; Wan, B.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Chang, L. Experimental and numerical study on scratch performance of additively manufactured continuous carbon fibre reinforced polyamide 6 composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 230, 109314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Purity (%) | ~99 |
| NH2 ratio (%) | 2–5 |
| Length (μm) | >10 |
| Outer dia. (nm) | 10–20 |
| Inner dia. (nm) | 5–10 |
| Printing Parameters | Nylon/MWCNT | Nylon/CF and Nylon/MWCNTs/CF |
|---|---|---|
| Height of layer | 0.2 mm | 0.2 mm |
| Nozzle diameter | 0.4 mm | 0.8 mm |
| Fill density | 100% | 100% |
| Print speed | 35 mm/s | 35 mm/s |
| Temperature of nozzle | 260 °C | 270 °C |
| Temperature of print bed | 60 °C | 60 °C |
| Orientation of layer | 45° and 135° | 45° and 135° |
| Material/Reinforcement | Tm /°C | Tc/°C | ∆Hm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon (N) | 215.2 | 178.2 | 54.82 |
| N+0.5% MWCNT | 218.3 | 179.3 | 61.48 |
| N+15% CF | 219.3 | 180.1 | 64.78 |
| N+0.5% MWCNT+15%CF | 221.2 | 181.5 | 67.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siddikali, P.; Sreekanth, P.S.R. Evaluation of Mechanical, Thermal, and Tribological Properties of 3D-Printed Nylon (PA6) Hybrid Composites Reinforced with MWCNTs and Carbon Fibers. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9040155
Siddikali P, Sreekanth PSR. Evaluation of Mechanical, Thermal, and Tribological Properties of 3D-Printed Nylon (PA6) Hybrid Composites Reinforced with MWCNTs and Carbon Fibers. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(4):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9040155
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiddikali, Palaiam, and P. S. Rama Sreekanth. 2025. "Evaluation of Mechanical, Thermal, and Tribological Properties of 3D-Printed Nylon (PA6) Hybrid Composites Reinforced with MWCNTs and Carbon Fibers" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 4: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9040155
APA StyleSiddikali, P., & Sreekanth, P. S. R. (2025). Evaluation of Mechanical, Thermal, and Tribological Properties of 3D-Printed Nylon (PA6) Hybrid Composites Reinforced with MWCNTs and Carbon Fibers. Journal of Composites Science, 9(4), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9040155






