Inverse Cellular Lattices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Cellular Lattice Design
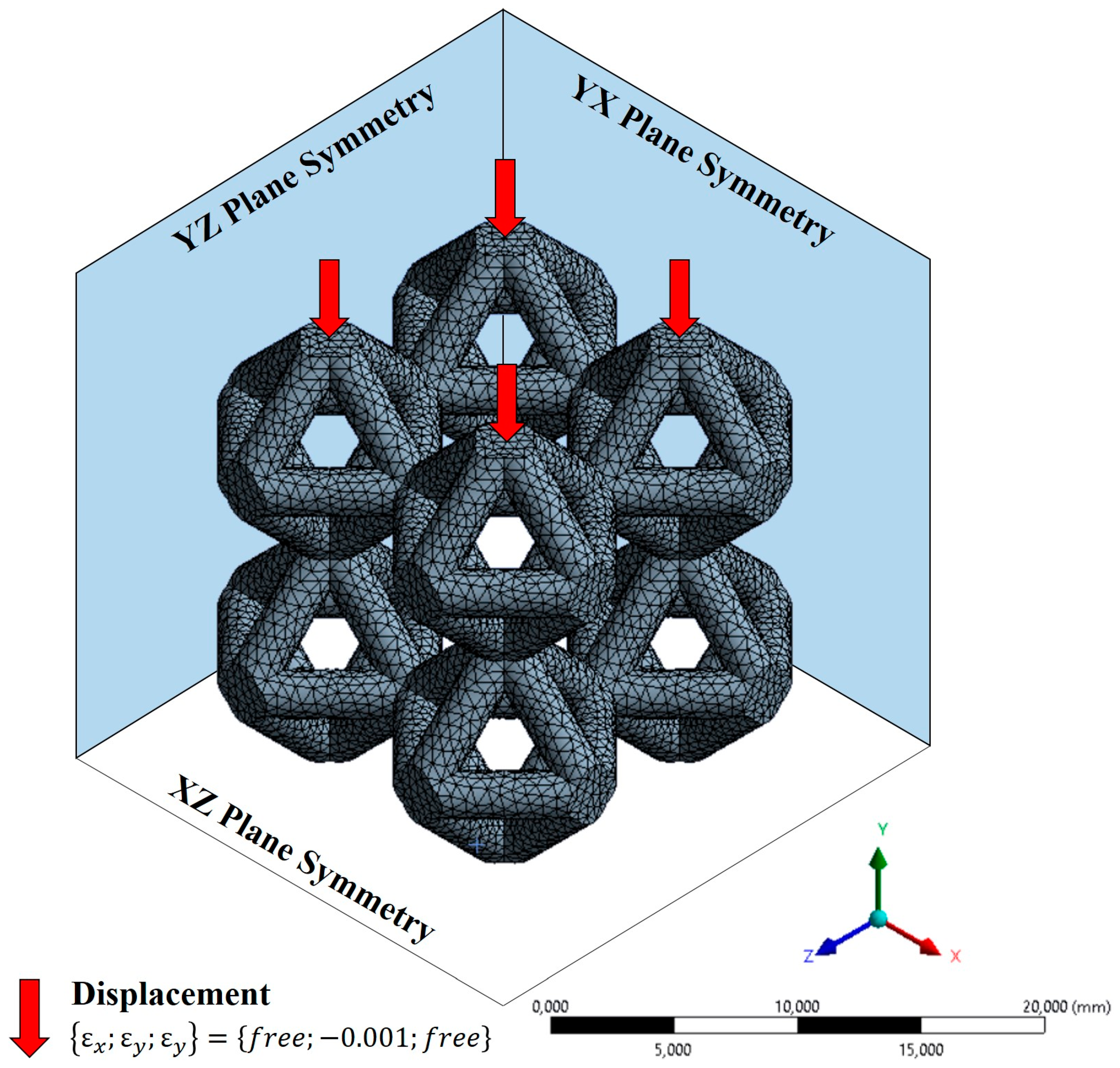
2.2. Static Structural Simulation
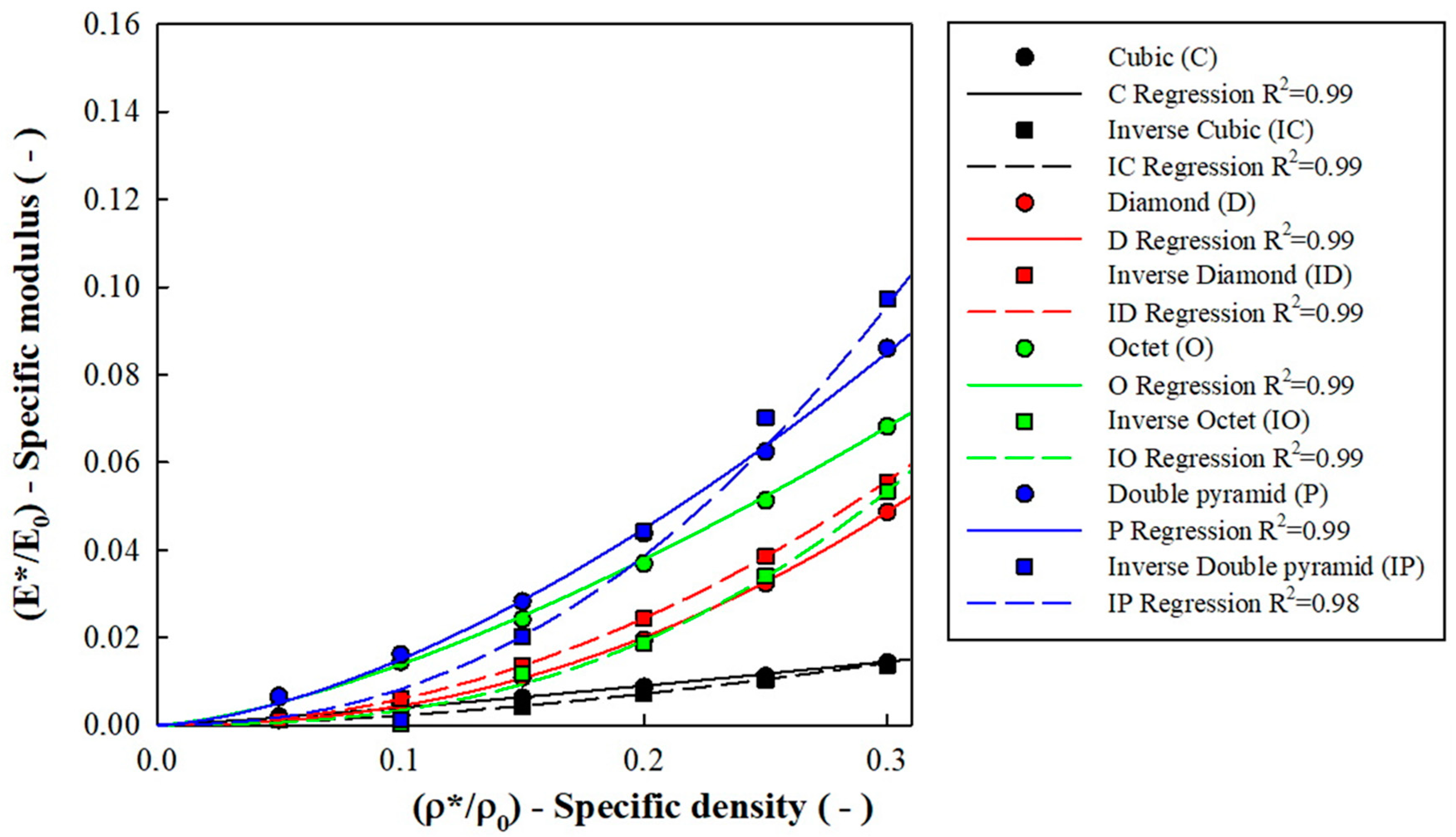
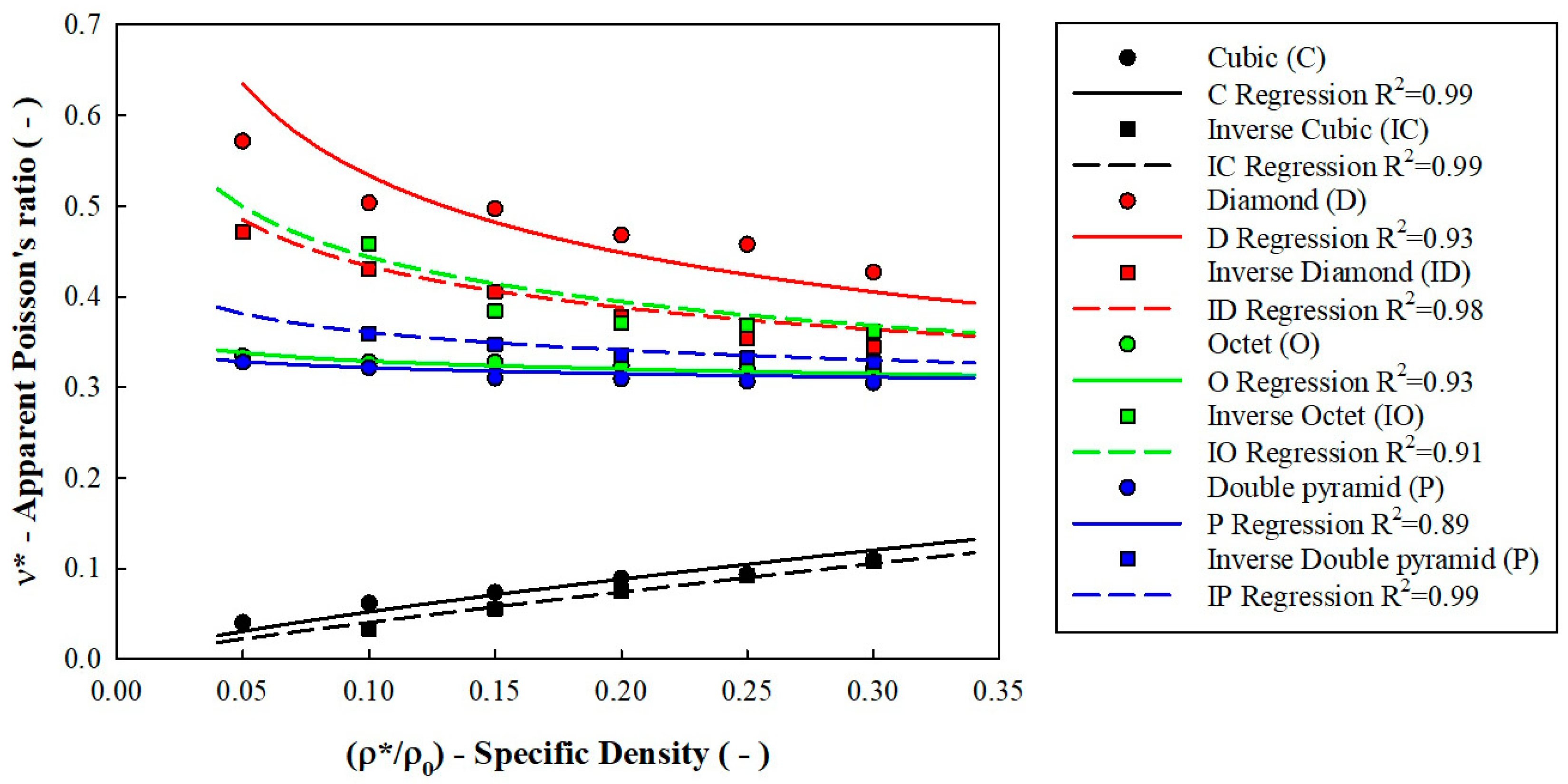
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FEA | Finite Element Analysis |
References
- Bari, K. Design, Simulation, and Mechanical Testing of 3D-Printed Titanium Lattice Structures. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, B.; Berthel, J.; Frecker, M.; Simpson, T.W. Mechanical Properties of Additively Manufactured Metal Lattice Structures: Data Review and Design Interface. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, V.; Tsongas, K.; Mansour, M.T.; Tzetzis, D.; Mansour, G. Mechanical Properties and Vibrational Behavior of 3D-Printed Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polyphenylene Sulfide and Polyamide-6 Composites with Different Infill Types. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.O.; Borges, J.P.; Velhinho, A. Structural Metamaterials with Negative Mechanical/Thermomechanical Indices: A Review. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2021, 31, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F.; Harley, B.A. Cellular Materials in Nature and Medicine; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; ISBN 0-521-19544-6. [Google Scholar]
- Le Barbenchon, L.; Girardot, J.; Kopp, J.-B.; Viot, P. Multi-Scale Foam: 3D Structure/Compressive Behaviour Relationship of Agglomerated Cork. Materialia 2019, 5, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Hiremath, S.S. Bio-Inspired Repeatable Lattice Structures for Energy Absorption: Experimental and Finite Element Study. Compos. Struct. 2022, 283, 115102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. 3D-Printed Bioinspired Cage Lattices with Defect-Tolerant Mechanical Properties. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 82, 104036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Feng, D.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; Wang, C.C.L. Topology Optimization of Self-Supporting Lattice Structure. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 67, 103507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Yu, G.; Qin, B.; Xiao, L. Mechanical Behavior of Topology-Optimized Lattice Structures Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2025, 18, 3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gongora, A.E.; Friedman, C.; Newton, D.K.; Yee, T.D.; Doorenbos, Z.; Giera, B.; Duoss, E.B.; Han, T.Y.-J.; Sullivan, K.; Rodriguez, J.N. Accelerating the Design of Lattice Structures Using Machine Learning. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Panesar, A. Machine Learning Based Lattice Generation Method Derived from Topology Optimisation. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 60, 103238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Luo, J.; Zhong, J.; Xu, Y.; Wan, B.; Huang, W.; Fang, J.; Steven, G.P.; Sun, G.; Li, Q. Topology Optimisation for Design and Additive Manufacturing of Functionally Graded Lattice Structures Using Derivative-Aware Machine Learning Algorithms. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 78, 103833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, L.; Wei, S.; Zhang, Z.; Choi, S.-K.; Song, B.; Shi, Y. A Review of Additive Manufacturing of Metamaterials and Developing Trends. Mater. Today 2021, 50, 303–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, V.; Puga, H.; Barbosa, J.; Teixeira, J.C. Effect of Yttria Mould Coating on the Investment Casting of AZ91D-1 Wt% CaO Magnesium Alloy. Int. J. Met. 2020, 14, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Morales, P.; Echeverrí, L.; Fandiño, E.M.; Zuleta Gil, A.A. Replication Casting and Additive Manufacturing for Fabrication of Cellular Aluminum with Periodic Topology: Optimization by CFD Simulation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.F. The Properties of Foams and Lattices. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 364, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejripour, F.; Salam, M.A.; Bowlin, G.L.; Asadi, E. Laser-Based Powder-Bed Fusion Strategies for the Fabrication of Cellular Structures with a Fine Resolution. Materialia 2020, 13, 100829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maconachie, T.; Leary, M.; Lozanovski, B.; Zhang, X.; Qian, M.; Faruque, O.; Brandt, M. SLM Lattice Structures: Properties, Performance, Applications and Challenges. Mater. Des. 2019, 183, 108137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.; du Plessis, A.; Ritchie, R.O.; Dallago, M.; Razavi, S.M.J.; Berto, F. Architected Cellular Materials: A Review on Their Mechanical Properties towards Fatigue-Tolerant Design and Fabrication. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2021, 144, 100606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arretche, I.; Matlack, K.H. On the Interrelationship Between Static and Vibration Mitigation Properties of Architected Metastructures. Front. Mater. 2018, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Design Approach | Cubic | Diamond | Octet | Double Pyramid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classic lattice | 2 × 2 × 2 CAD model for FEA (Scale bar: 20 mm) |  |  |  | 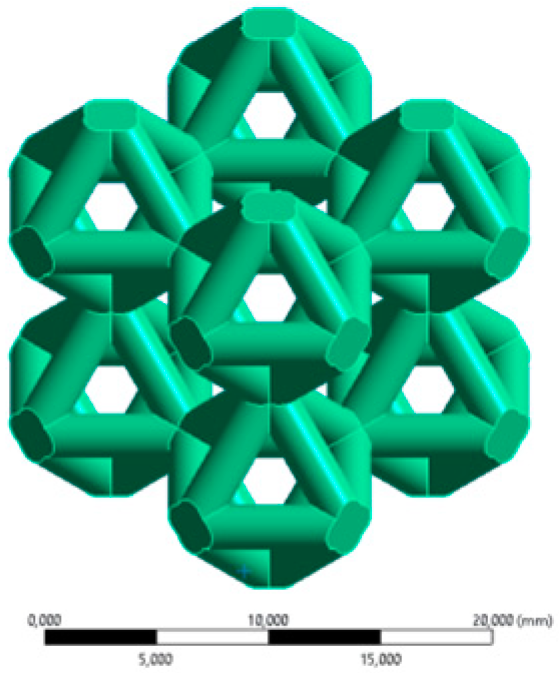 | |
| Single cell view (Scale bar: 10 mm) | Isometric |  |  |  |  | |
| Front |  | 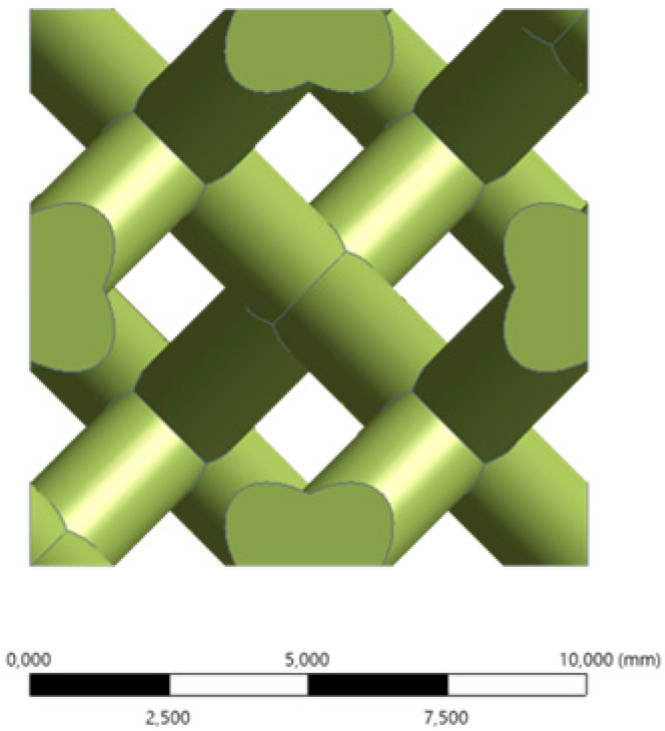 |  | 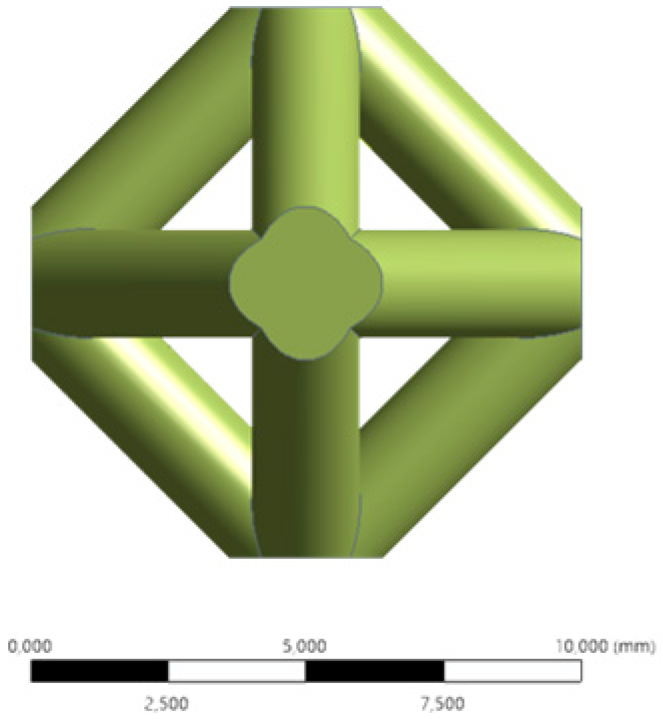 | ||
| Inverse lattice | 2 × 2 × 2 CAD model for FEA (Scale bar: 20 mm) |  | 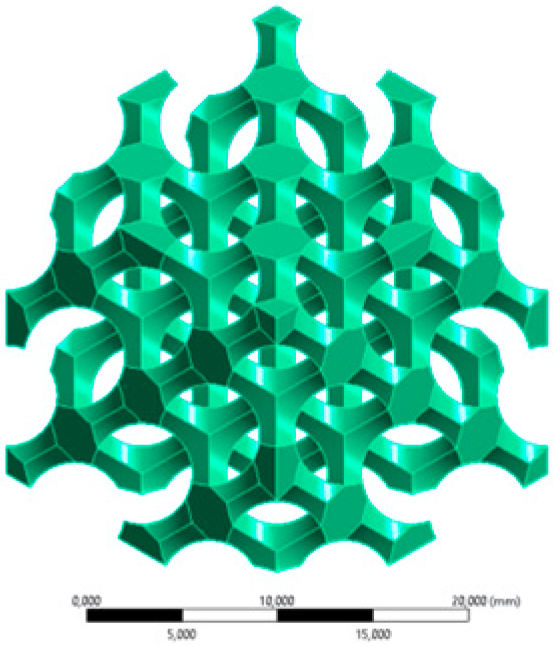 |  |  | |
| Single cell view (Scale bar: 10 mm) | Isometric | 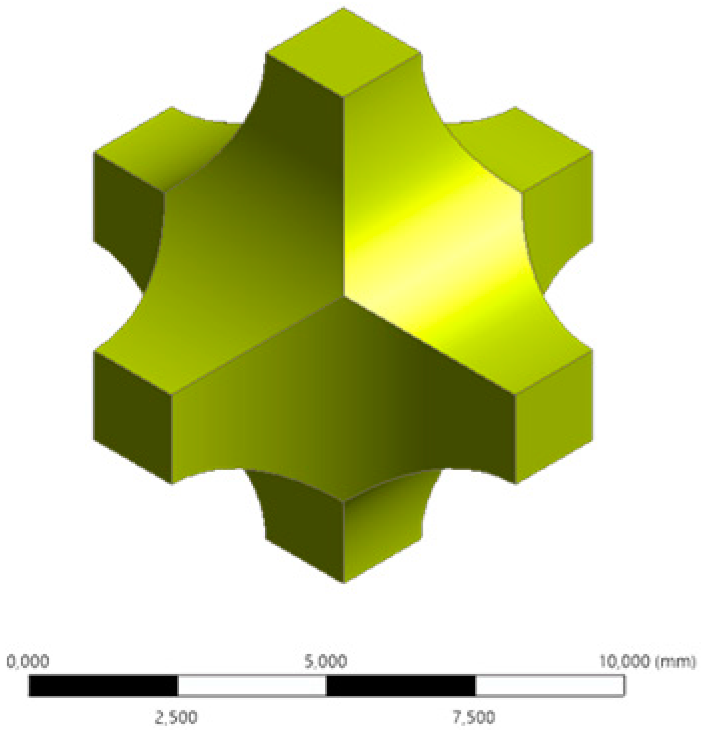 | 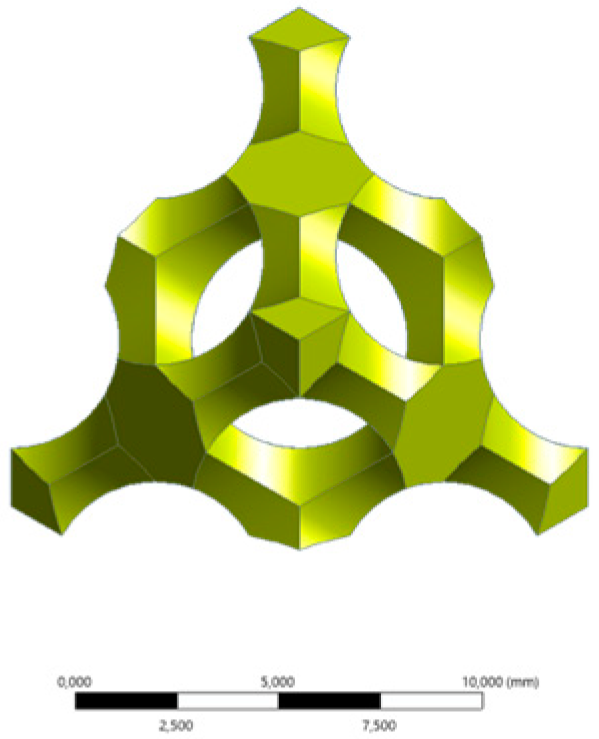 | 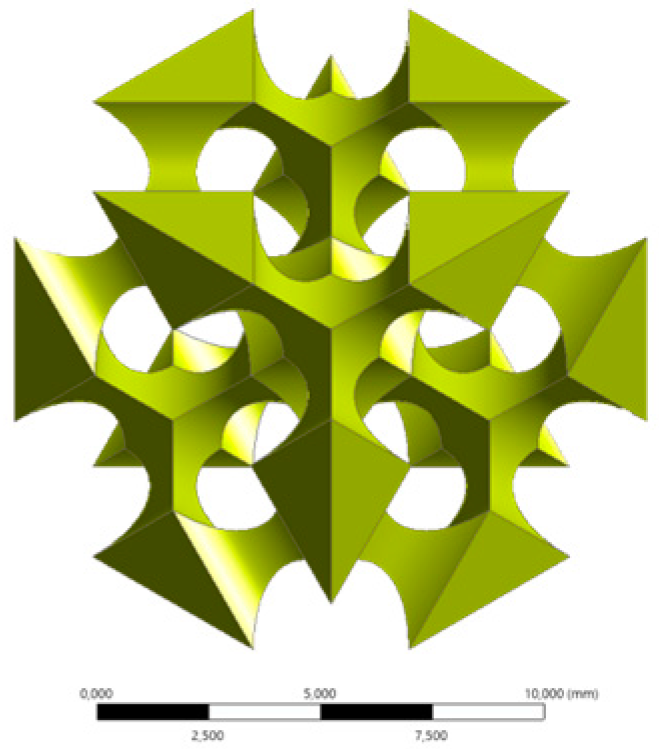 |  | |
| Front |  | 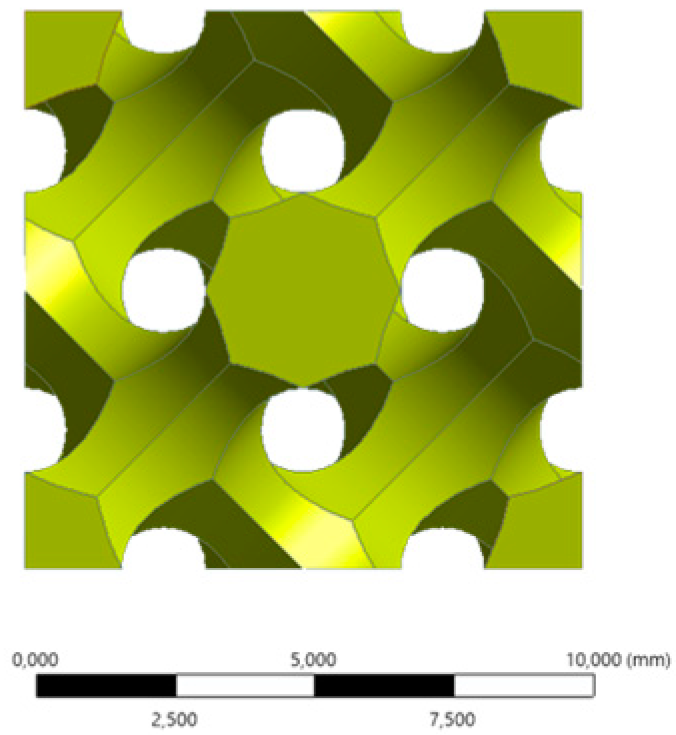 |  |  | ||
| Design | Cubic | Diamond | Octet | Double Pyramid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable C—Proportionality factor | ||||
| Classic lattice | 0.09 | 0.68 | 0.39 | 0.57 |
| Inverse lattice | 0.11 | 0.65 | 1.11 | 1.42 |
| Variable n—Growth factor | ||||
| Classic lattice | 1.18 1 | 2.19 3 | 1.15 1 | 1.58 2 |
| Inverse lattice | 1.70 2 | 1.99 3 | 2.52 3 | 2.24 3 |
| Cubic | Diamond | Octet | Double Pyramid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XX axis (lateral) |  |  |  |  |
| YY axis (vertical) | 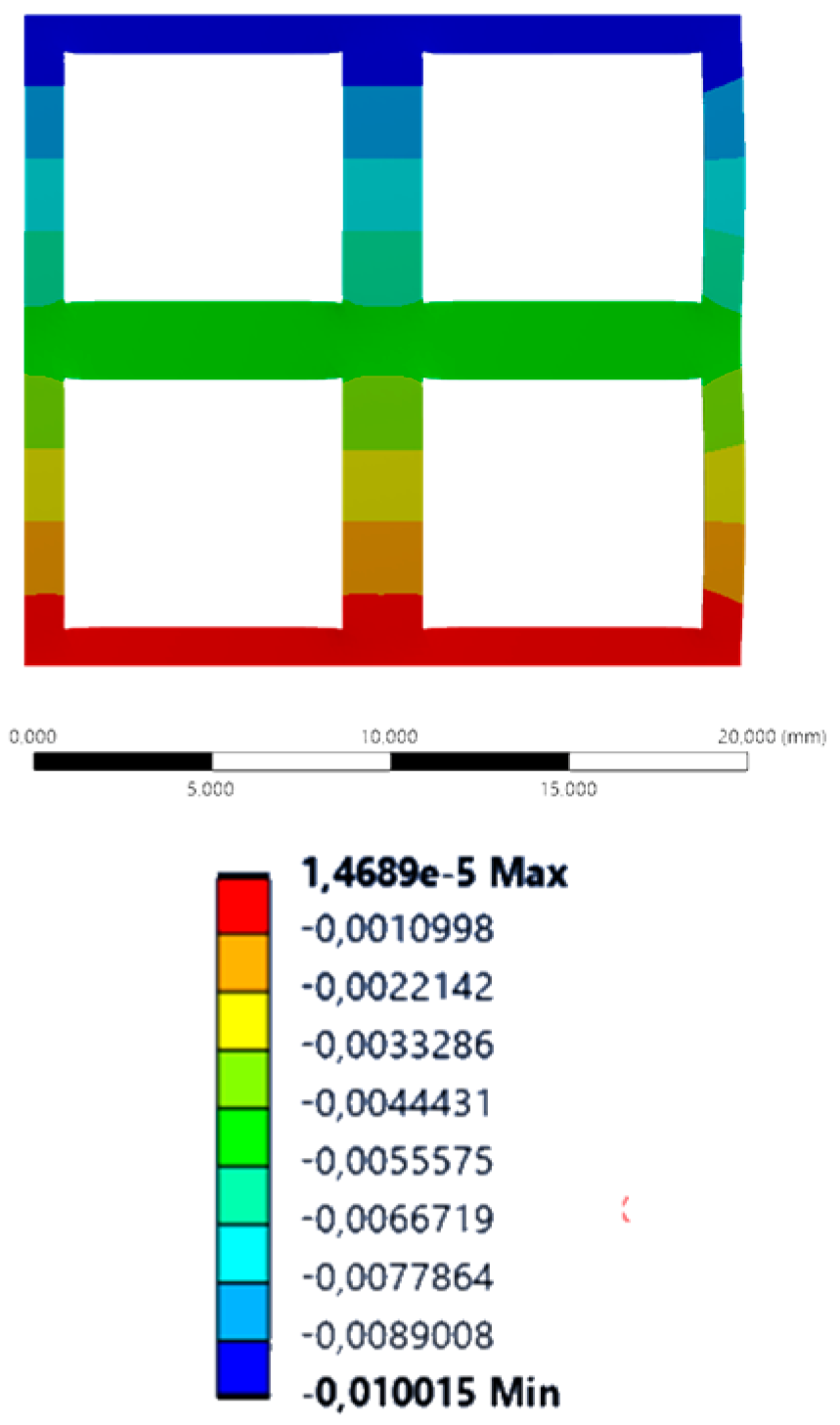 | 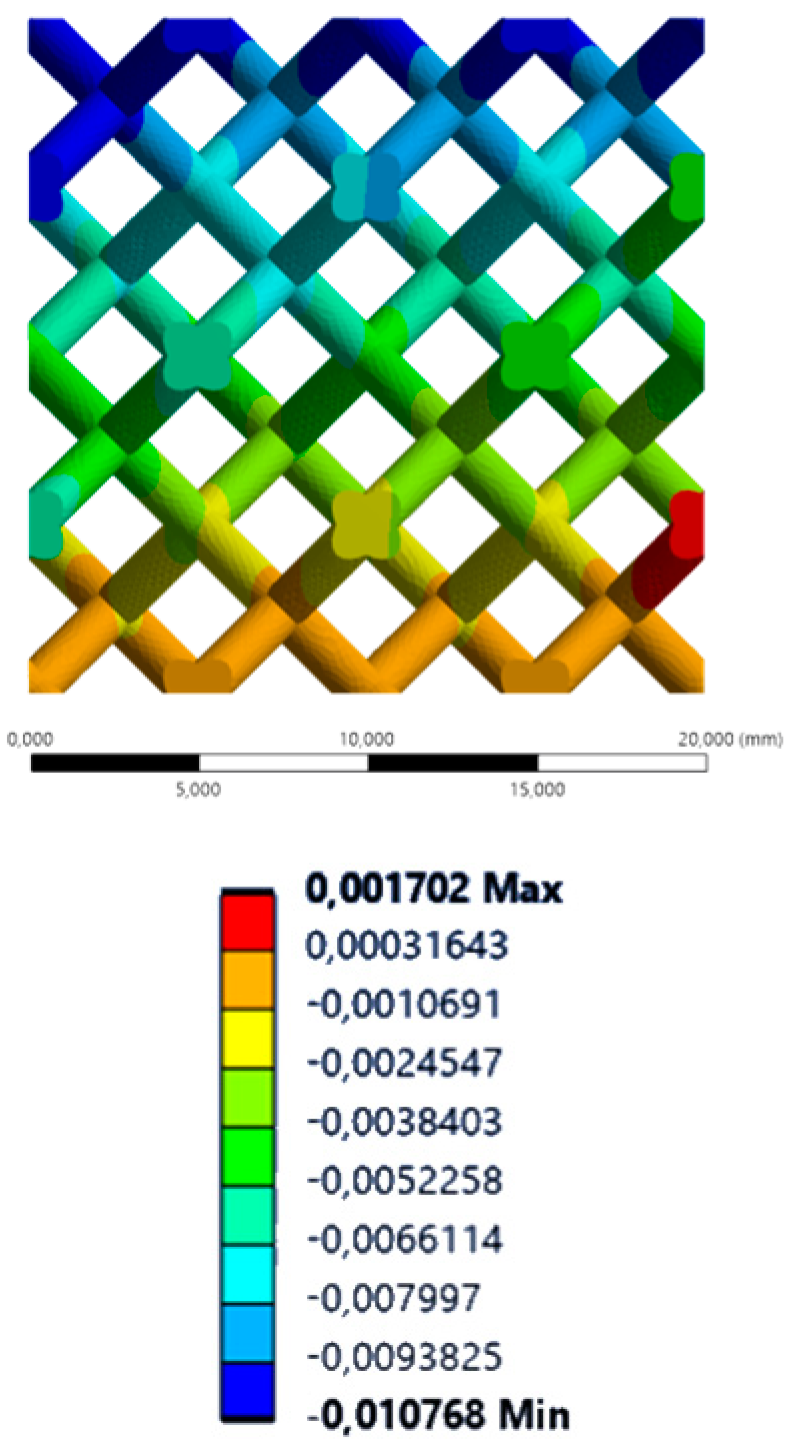 | 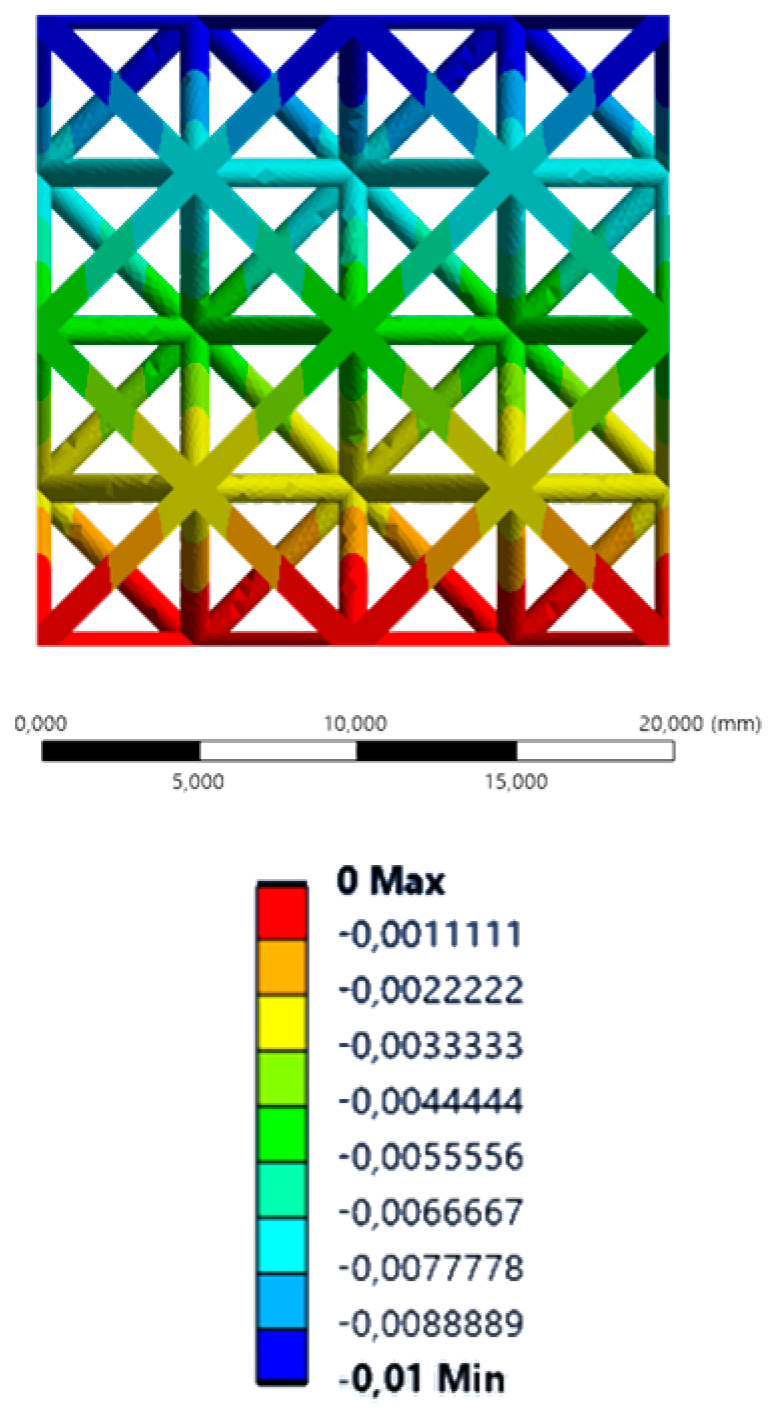 | 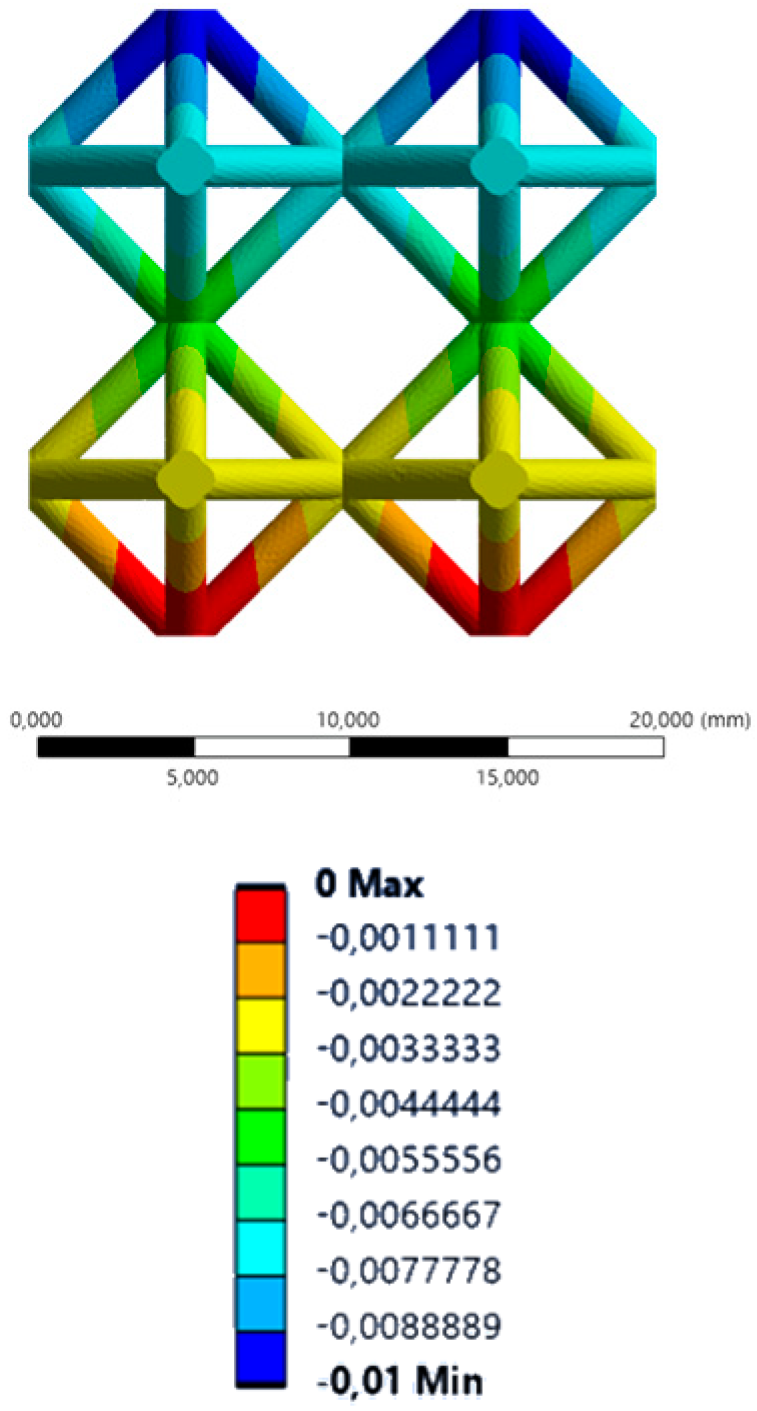 |
| Inverse Cubic | Inverse Diamond | Inverse Octet | Inverse Double Pyramid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XX axis (lateral) |  | 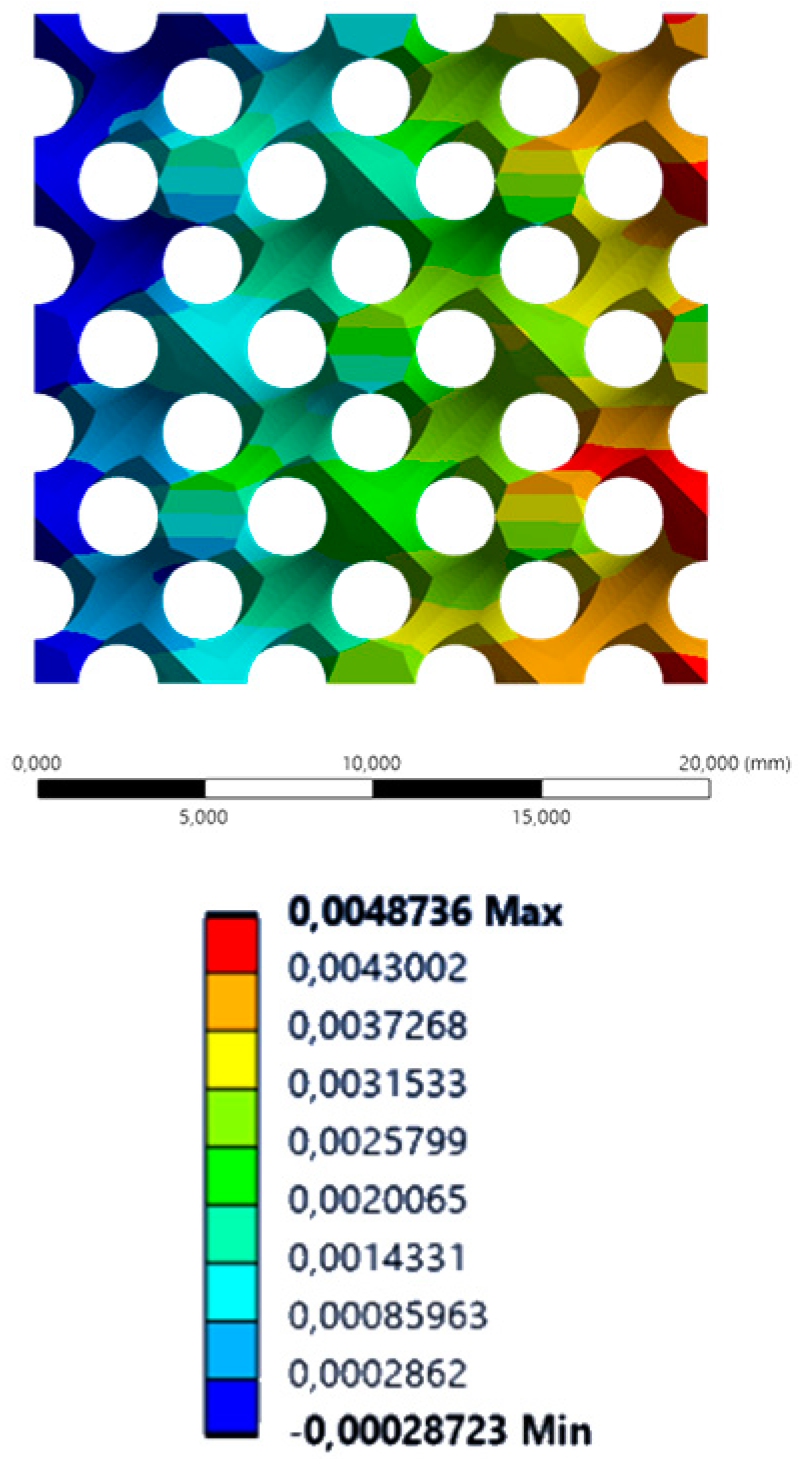 | 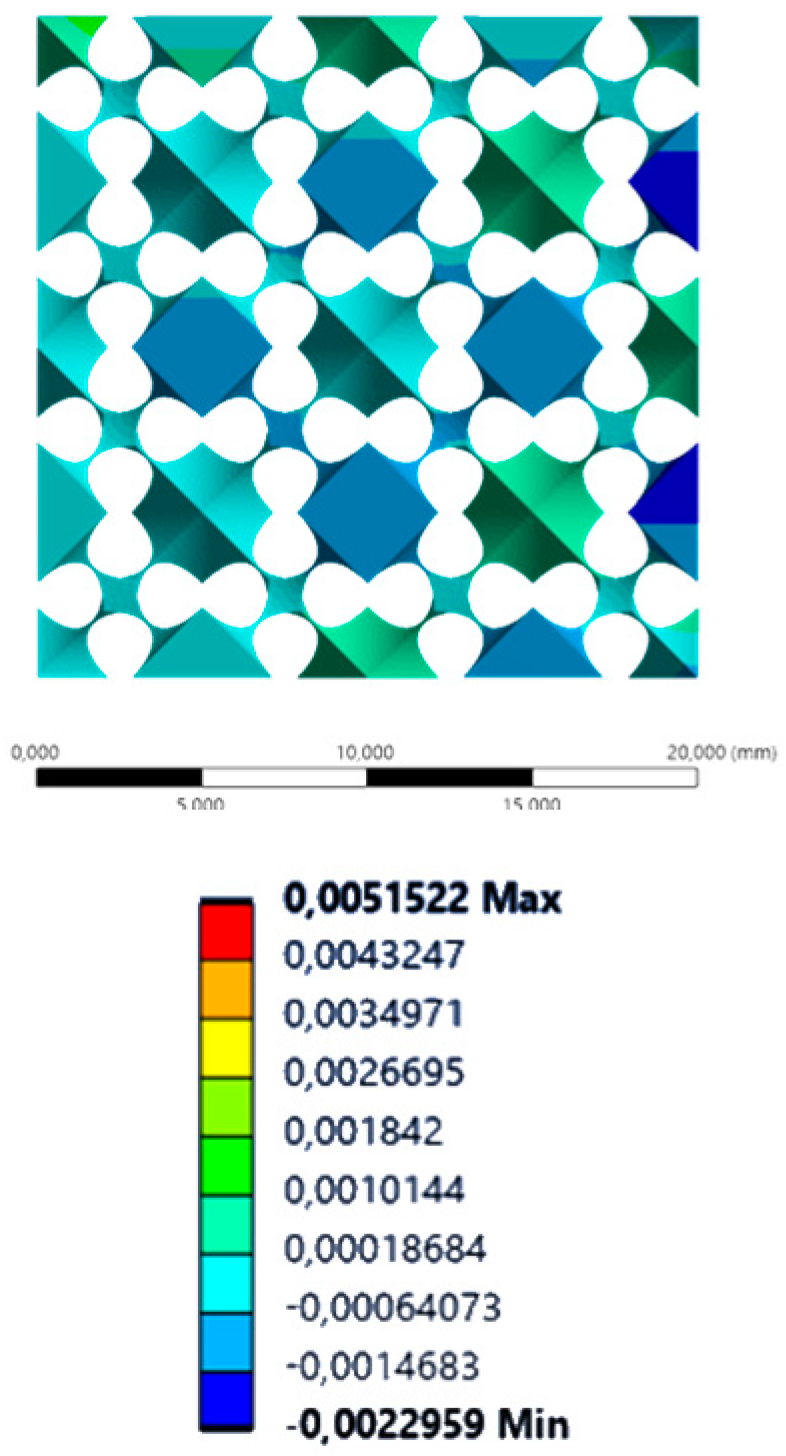 |  |
| YY axis (vertical) | 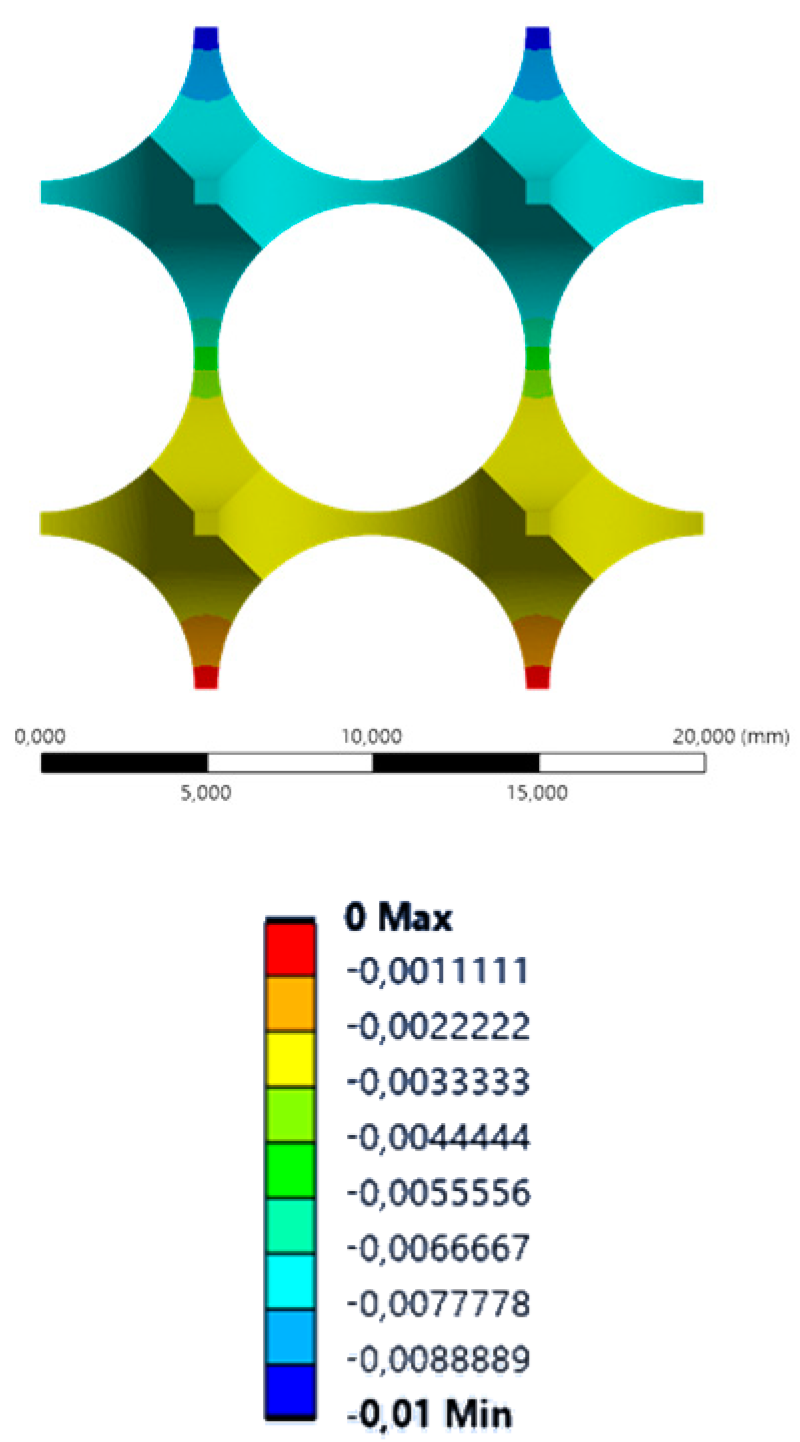 | 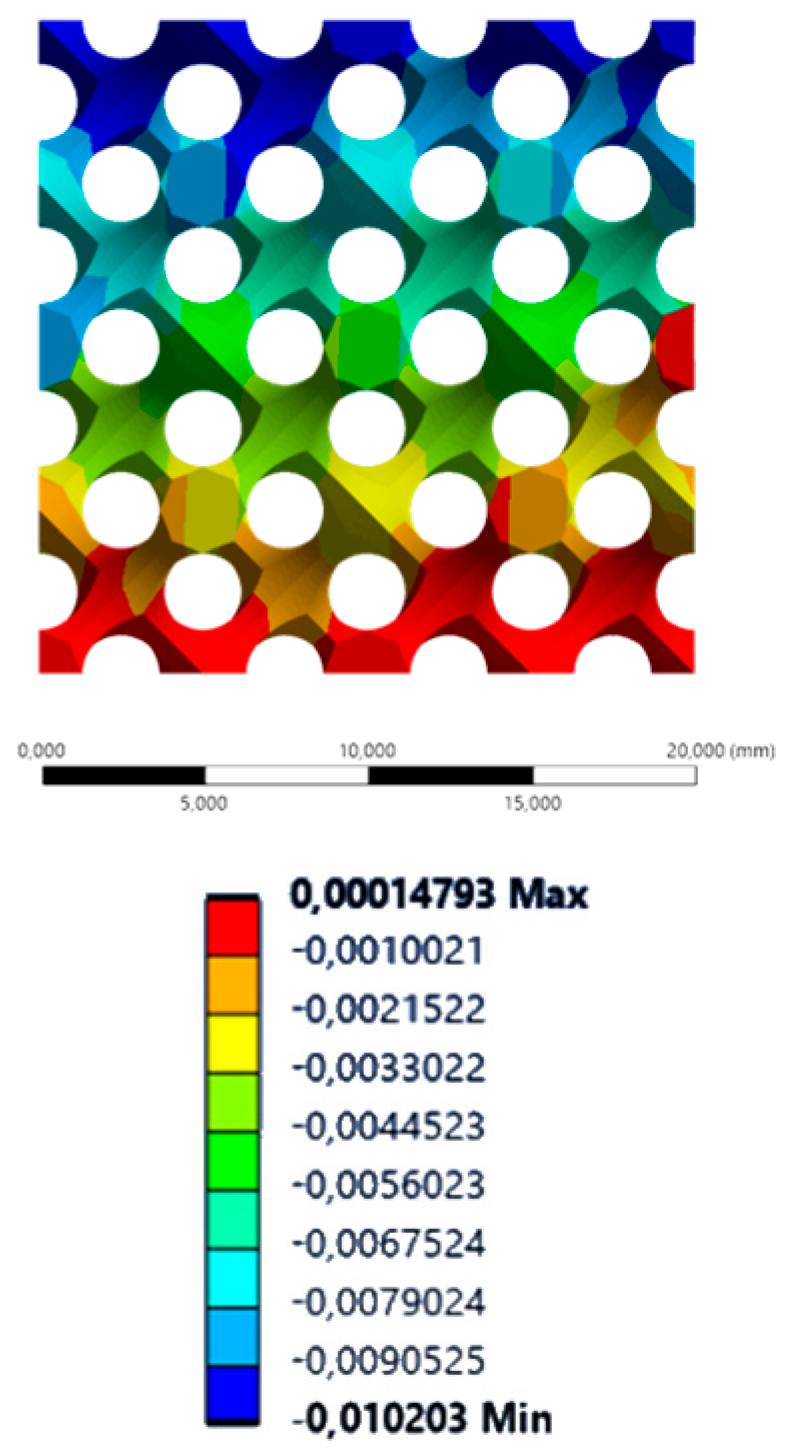 |  | 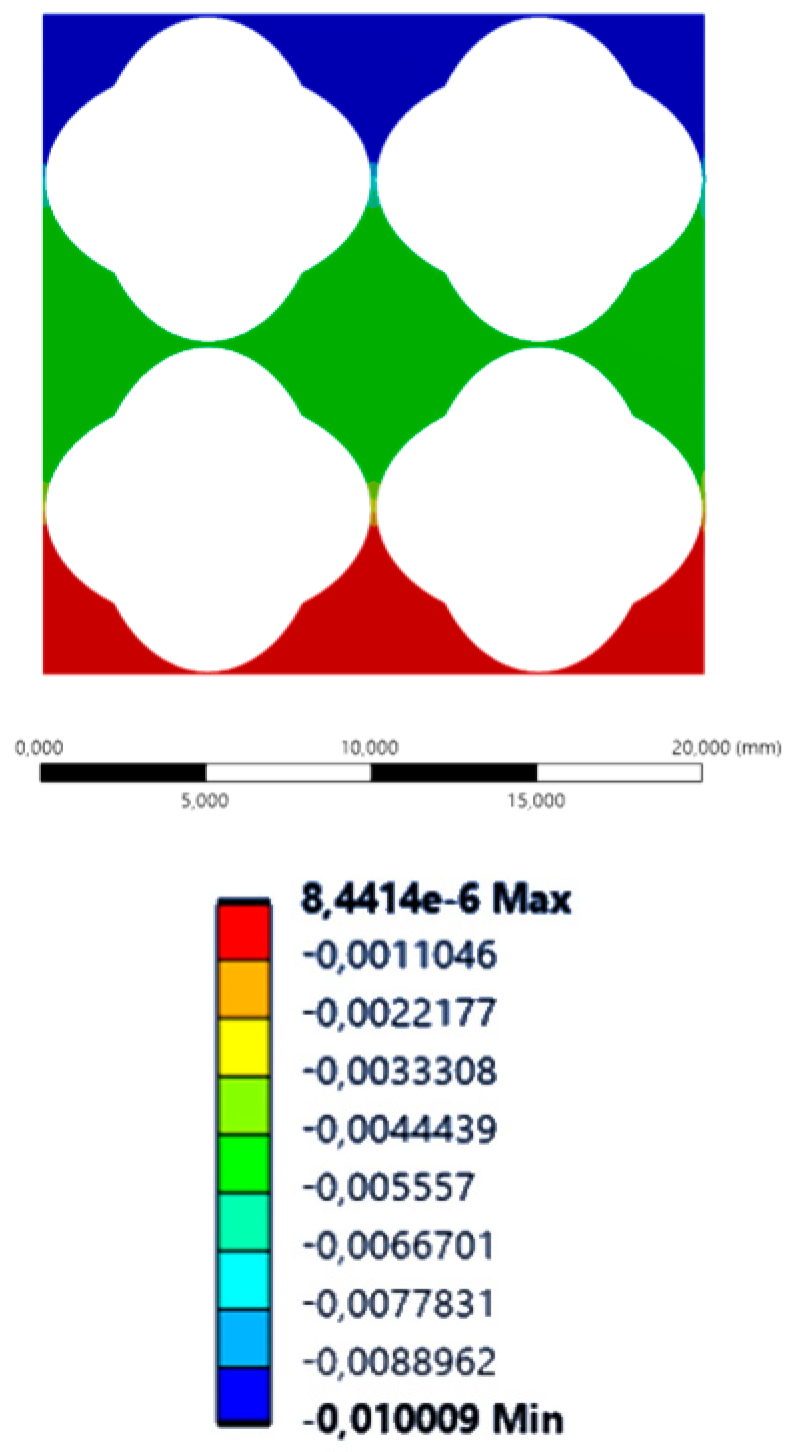 |
| Design | Cubic | Diamond | Octet | Double Pyramid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classic lattice | 0.76 | −0.25 | −0.02 | −0.03 |
| Inverse lattice | 0.87 | −0.16 | −0.17 | −0.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carneiro, V.H.; Puga, H. Inverse Cellular Lattices. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9110605
Carneiro VH, Puga H. Inverse Cellular Lattices. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(11):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9110605
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarneiro, Vitor H., and Hélder Puga. 2025. "Inverse Cellular Lattices" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 11: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9110605
APA StyleCarneiro, V. H., & Puga, H. (2025). Inverse Cellular Lattices. Journal of Composites Science, 9(11), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9110605







