Thermal Performance of Silica-Coated Wood Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wood Particles
2.2. Silica Treatment of Wood Particles
2.3. Morphology and Characterization of Wood Particles
2.4. Thermal Analysis
2.5. Powder X-Ray Diffraction
3. Results and Discussion
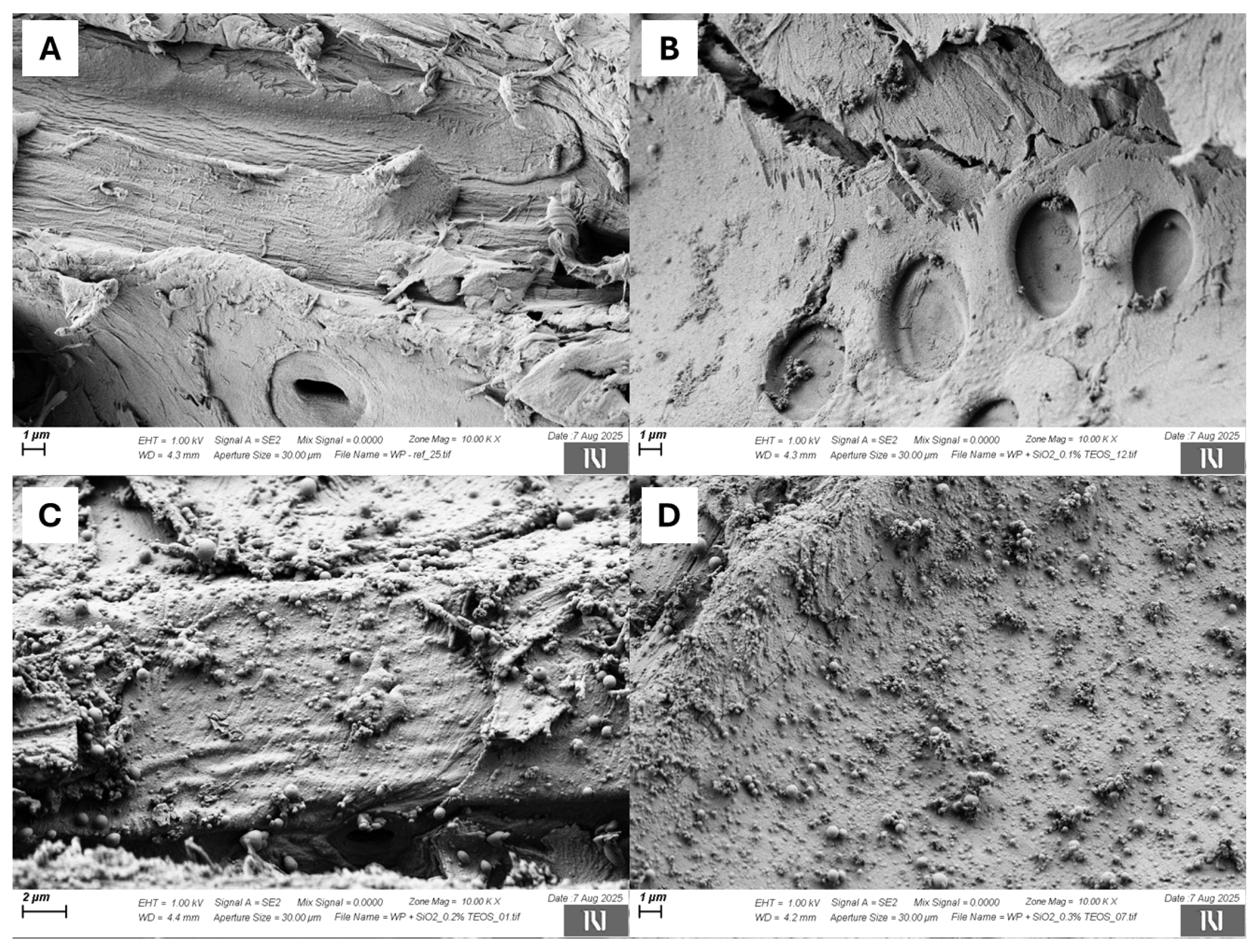
3.1. Morphology and Characterization
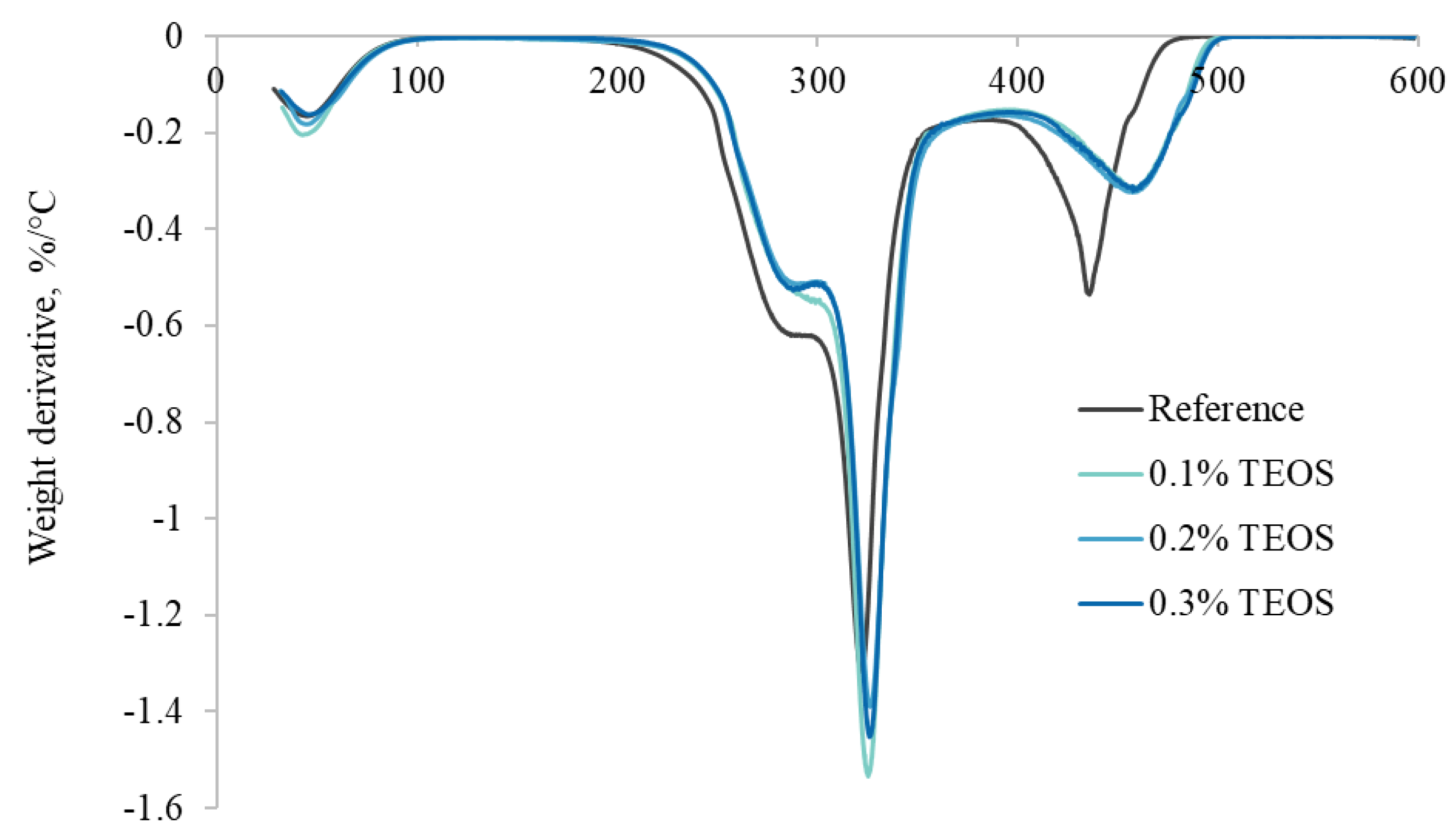
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
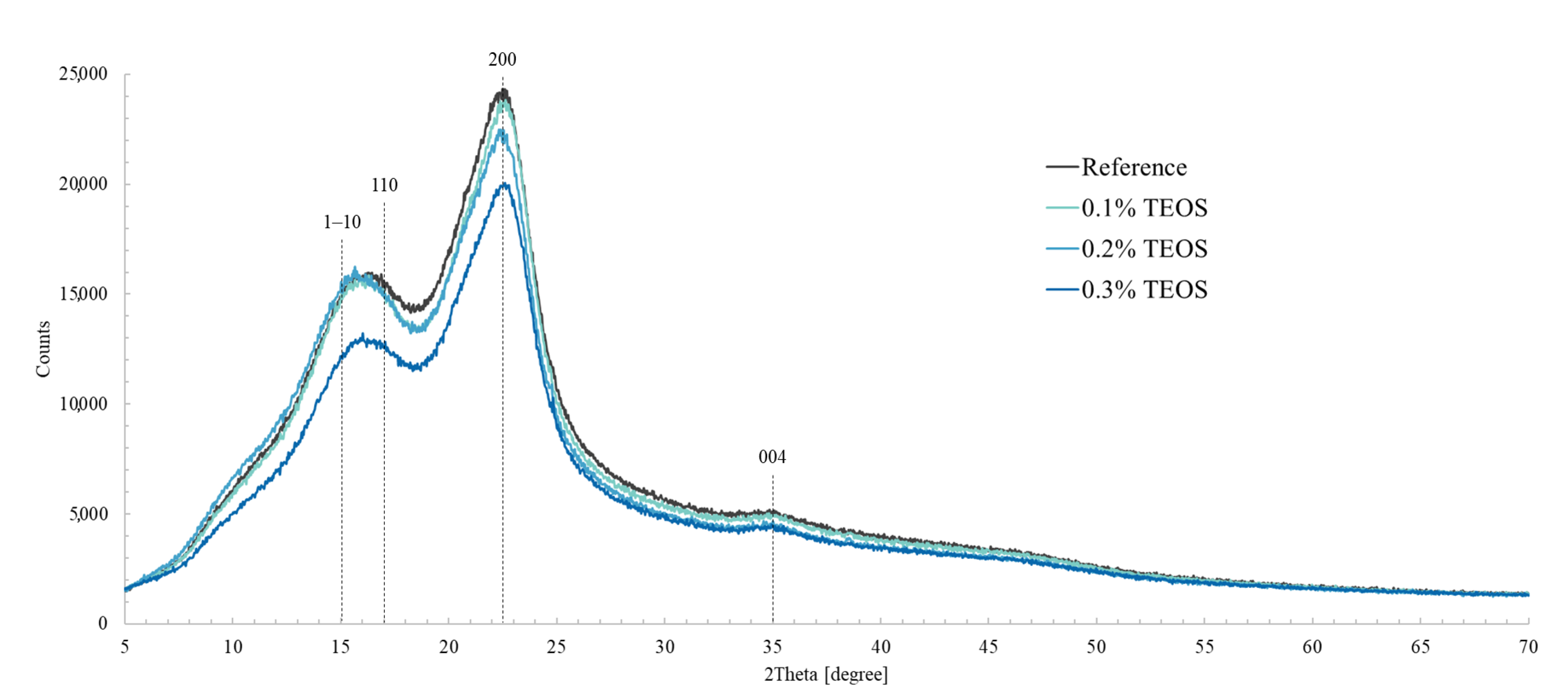
3.3. XRD Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schellnhuber, H.J. Bauhaus Earth: Sustainable Use of Wood in the Construction Sector. In 3 Degrees More: The Impending Hot Season and How Nature Can Help Us Prevent It; Wiegandt, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 147–177. ISBN 9783031581441. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission: Directorate-General for Research and Innovation. European Green Deal—Research & Innovation Call; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021; Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2777/33415 (accessed on 7 October 2025).
- Ramage, M.H.; Burridge, H.; Busse-Wicher, M.; Fereday, G.; Reynolds, T.; Shah, D.U.; Wu, G.; Yu, L.; Fleming, P.; Densley-Tingley, D.; et al. The Wood from the Trees: The Use of Timber in Construction. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 333–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.W.; Kolya, H.; Jang, E.S.; Zhu, S.; Choi, B.S. Steam Exploded Wood Cell Walls Reveals Improved Gas Permeability and Sound Absorption Capability. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 179, 108049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, Y.; Song, T.; Bao, M.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, Y. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Magnetic Sawdust for Effective Oil/Water Separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 120058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowden, L.A.; Hull, T.R. Flammability Behaviour of Wood and a Review of the Methods for Its Reduction. Fire Sci. Rev. 2013, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östman, B.; Tsantaridis, L.; Mikkola, E.; Hakkarainen, T.; Belloni, K.; Brumer, H.; Piispanen, P. Innovative Eco-Efficient High Fire Performance Wood Products for Demanding Applications: Final Report for Vinnova-Tekes Project InnoFireWood; SP Rapport No. 30; SP Technical Research Institute of Sweden: Boras, Sweeden, 2006; Available online: https://cris.vtt.fi/en/publications/innovative-eco-efficient-high-fire-performance-wood-products-for- (accessed on 7 October 2025).
- Oneil, E.; Bergman, R.; Han, H.; Eastin, I. Comparative Life-Cycle Assessment of California Redwood Decking; CORRIM: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Forest Products Laboratory. Wood Handbook: Wood as an Engineering Material; Ross, R.J., Ed.; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory: Madison, WI, USA, 2010; ISBN 1892529025. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaeva, M.; Kärki, T. A Review of Fire Retardant Processes and Chemistry, with Discussion of the Case of Wood-Plastic Composites. Balt. For. 2011, 17, 314–326. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.J.; Yang, H.S. Thermal Properties of Bio-Flour-Filled Polyolefin Composites with Different Compatibilizing Agent Type and Content. Thermochim. Acta 2006, 451, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.L.; Hassabo, A.G. Flame Retardant of Cellulosic Materials and Their Composites. In Engineering Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 247–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.H.; Stark, N.M.; Ayrilmis, N. Recent Activities in Flame Retardancy of Wood-Plastic Composites at the Forest Products Laboratory. In Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Conference on Recent Advances in Flame Retardancy of Polymeric Materials 2011, Stamford, CT, USA, 23–25 May 2011; BCC Research: Wellesley, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 303–310, ISBN 9781618394699/161839469X . [Google Scholar]
- El Hajam, M.; Kandri, N.I.; Zerouale, A.; Wang, X.; Gustafsson, J.; Wang, L.; Mäkilä, E.; Hupa, L.; Xu, C. Lignocellulosic Nanocrystals from Sawmill Waste as Biotemplates for Free-Surfactant Synthesis of Photocatalytically Active Porous Silica. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 19547–19560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Xu, W. The Influence of Different Impregnation Factors on Mechanical Properties of Silica Sol-Modified Populus Tomentosa. Wood Fiber Sci. 2024, 56, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Chang, H.; Liu, J. Sol-Gel Deposition of TiO2 Nanocoatings on Wood Surfaces with Enhanced Hydrophobicity and Photostability. Wood Fiber Sci. 2014, 46, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.Z. A Review on Flame Retardant Technology in China. Part I: Development of Flame Retardants. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2010, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübert, T.; Mahr, M.S. Wood (Sol–Gel) Composites for Fire Retardancy. In Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology; Klein, L., Aparicio, M., Jitianu, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alongi, J.; Ciobanu, M.; Malucelli, G. Sol-Gel Treatments for Enhancing Flame Retardancy and Thermal Stability of Cotton Fabrics: Optimisation of the Process and Evaluation of the Durability. Cellulose 2011, 18, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malucelli, G. Sol-Gel and Layer-by-Layer Coatings for Flame-Retardant Cotton Fabrics: Recent Advances. Coatings 2020, 10, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Piao, C. From Hydrophilicity to Hydrophobicity: A Critical Review—Part II: Hydrophobic Conversion. Wood Fiber Sci. 2011, 43, 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- Hribernik, S.; Smole, M.S.; Kleinschek, K.S.; Bele, M.; Jamnik, J.; Gaberscek, M. Flame Retardant Activity of SiO2-Coated Regenerated Cellulose Fibres. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.P.; Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Kumar, R.; Mishra, G.; Sharma, U.; Singh, G.; Ahalawat, S. Sol-Gel Processing of Silica Nanoparticles and Their Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 214, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled Growth of Monodisperse Silica Spheres in the Micron Size Range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Baker, J.O.; Himmel, M.E.; Parilla, P.A.; Johnson, D.K. Cellulose Crystallinity Index: Measurement Techniques and Their Impact on Interpreting Cellulase Performance. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2010, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, M.; Molnár, F.; Rákosa, R.; Németh, Z.; Németh, R. Dimensional Stabilization of Wood by Microporous Silica Aerogel Using In-Situ Polymerization. Wood Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 1353–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, J.; Paz dos Santos, L.; Henrique Soares Del Menezzi, C.; Henrique Denzin Tonoli, G. Effect of Nano-Silica Deposition on Cellulose Fibers on the Initial Hydration of the Portland Cement. Bioresources 2018, 13, 3525–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.-X.; Cai, Y.-T.; Xu, G.-Y.; Xu, W. Mechanical and Optical Properties of Waterborne UV Curing Coating Modified by Silica. In Proceedings of the 4th 2016 International Conference on Material Science and Engineering (ICMSE 2016), Guangdong, China, 17–19 June 2016; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, Y.; Asoh, T.A.; Uyama, H. Hierarchical Silica Monolith Prepared Using Cellulose Monolith as Template. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 177, 109164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, V.; Odile, B.; Céline, R. FTIR Spectroscopy of Woods: A New Approach to Study the Weathering of the Carving Face of a Sculpture. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazari, M.; Elmi, F. Structural Study of Coated Wood with Superhydrophobic Chitosan/Silica Hybrid Nanocomposite in Seawater. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 186, 108076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, N.; He, Y. Quantitative Visualization of Lignocellulose Components in Transverse Sections of Moso Bamboo Based on Ftir Macro- and Micro-Spectroscopy Coupled with Chemometrics. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Yu, J.; Tesso, T.; Dowell, F.; Wang, D. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass Using Infrared Techniques: A Mini-Review. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sills, D.L.; Gossett, J.M. Using FTIR to Predict Saccharification from Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Alkali-Pretreated Biomasses. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herth, E.; Zeggari, R.; Rauch, J.Y.; Remy-Martin, F.; Boireau, W. Investigation of Amorphous SiOx Layer on Gold Surface for Surface Plasmon Resonance Measurements. Microelectron. Eng. 2016, 163, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, H.; Li, Y.; Qiu, J. Using Nanoimprint Lithography to Create Robust, Buoyant, Superhydrophobic PVB/SiO2 Coatings on Wood Surfaces Inspired by Red Roses Petal. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liodakis, S.; Bakirtzis, D.; Dimitrakopoulos, A. Ignition Characteristics of Forest Species in Relation to Thermal Analysis Data. Thermochim. Acta 2002, 390, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, T.; Larnøy, E.; Volkmer, T. Thermal Behavior and Reaction to Fire of European Beech (Fagus sylvatica) Treated with Various Salts and Mineralization Formulations. Fire Saf. J. 2024, 144, 104088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grønli, M.G.; Várhegyi, G.; Di Blasi, C. Thermogravimetric Analysis and Devolatilization Kinetics of Wood. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 4201–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anca-Couce, A.; Tsekos, C.; Retschitzegger, S.; Zimbardi, F.; Funke, A.; Banks, S.; Kraia, T.; Marques, P.; Scharler, R.; de Jong, W.; et al. Biomass Pyrolysis TGA Assessment with an International Round Robin. Fuel 2020, 276, 118002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brebu, M.; Vasile, C. Thermal Degradation of Lignin—A Review. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2010, 44, 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Vargun, E.; Baysal, E.; Turkoglu, T.; Yuksel, M.; Toker, H. Thermal Degradation of Oriental Beech Wood Impregnated with Different Inorganic Salts. Maderas Cienc. Tecnol. 2019, 21, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykhnazari, S.; Tabarsa, T.; Ashori, A.; Ghanbari, A. Bacterial Cellulose Composites Loaded with SiO2 Nanoparticles: Dynamic-Mechanical and Thermal Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.D. Idealized Powder Diffraction Patterns for Cellulose Polymorphs. Cellulose 2014, 21, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment | D10 [µm] | D90 [µm] | Median [µm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 322.9 | 496.7 | 404.8 |
| 0.1% TEOS | 322.4 | 510.2 | 407.1 |
| 0.2% TEOS | 325.1 | 514.9 | 413.3 |
| 0.3% TEOS | 323.5 | 513.6 | 410.5 |
| Treatment | SSA, m2/g | µSA, m2/g | TPV, cc/g | µPV, cc/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 3.14 | 48.65 | 0.007 | 0.018 |
| 0.1% TEOS | 3.40 | 92.32 | 0.009 | 0.035 |
| 0.2% TEOS | 2.32 | 76.71 | 0.013 | 0.029 |
| 0.3% TEOS | 6.86 | 96.06 | 0.011 | 0.035 |
| Treatment | Tonset, °C | Tmax, °C | Tendset, °C | T10%, °C | T50%, °C | Ash, wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 300 ± 1 | 324 ± 1 | 363 ± 2 | 251.7 ± 9 | 319.0 ± 5 | 0.8 ± 6 |
| 0.1% TEOS | 316 ± 3 | 327 ± 4 | 360 ± 1 | 255.9 ± 2 | 323.1 ± 6 | 1.2 ± 8 |
| 0.2% TEOS | 316 ± 4 | 326 ± 3 | 363 ± 2 | 254.8 ± 1 | 322.0 ± 7 | 2.8 ± 2 |
| 0.3% TEOS | 316 ± 6 | 326 ± 2 | 358 ± 7 | 255.5 ± 7 | 322.8 ± 4 | 4.3 ± 3 |
| Treatment | CI % |
|---|---|
| Reference | 69.5 |
| 0.1% TEOS | 69.5 |
| 0.2% TEOS | 67.1 |
| 0.3% TEOS | 61.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yurttaş, E.; Zouari, M.; Hribernik, S.; Schwarzkopf, M. Thermal Performance of Silica-Coated Wood Particles. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100556
Yurttaş E, Zouari M, Hribernik S, Schwarzkopf M. Thermal Performance of Silica-Coated Wood Particles. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(10):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100556
Chicago/Turabian StyleYurttaş, Elif, Mariem Zouari, Silvo Hribernik, and Matthew Schwarzkopf. 2025. "Thermal Performance of Silica-Coated Wood Particles" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 10: 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100556
APA StyleYurttaş, E., Zouari, M., Hribernik, S., & Schwarzkopf, M. (2025). Thermal Performance of Silica-Coated Wood Particles. Journal of Composites Science, 9(10), 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100556







