Tuning the Carbonation Resistance of Metakaolin–Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers: The Dual Role of Reactive MgO in Microstructure and Degradation Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Programs
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Experimental Design and Specimen Preparation
2.3. Accelerated Carbonation Procedure
2.4. Testing Methods
2.4.1. Compressive Strength
2.4.2. Carbonation Depth
2.4.3. Material Alkalinity
2.4.4. MIP, XRD, and FTIR Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
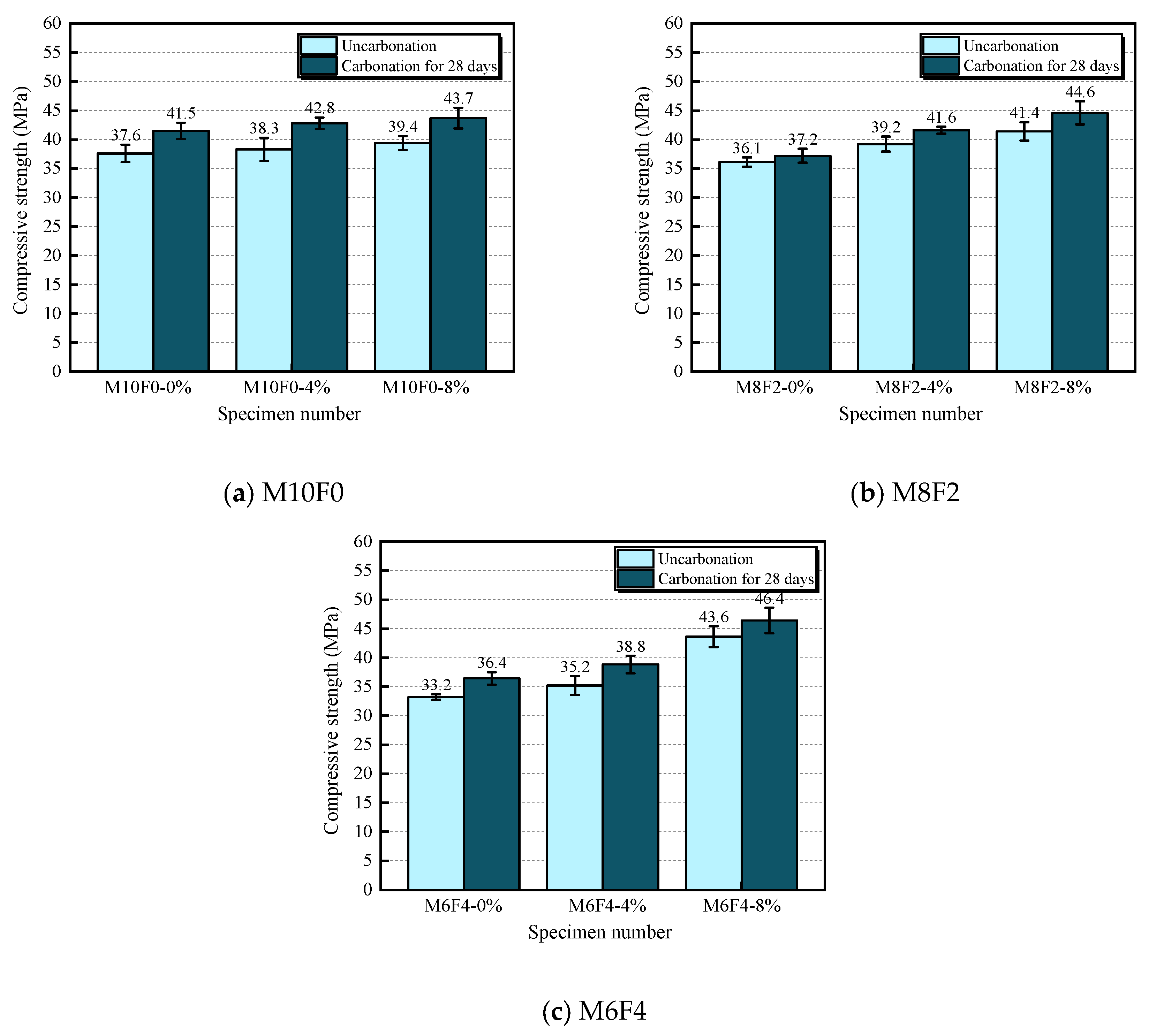
3.1. Compressive Strength
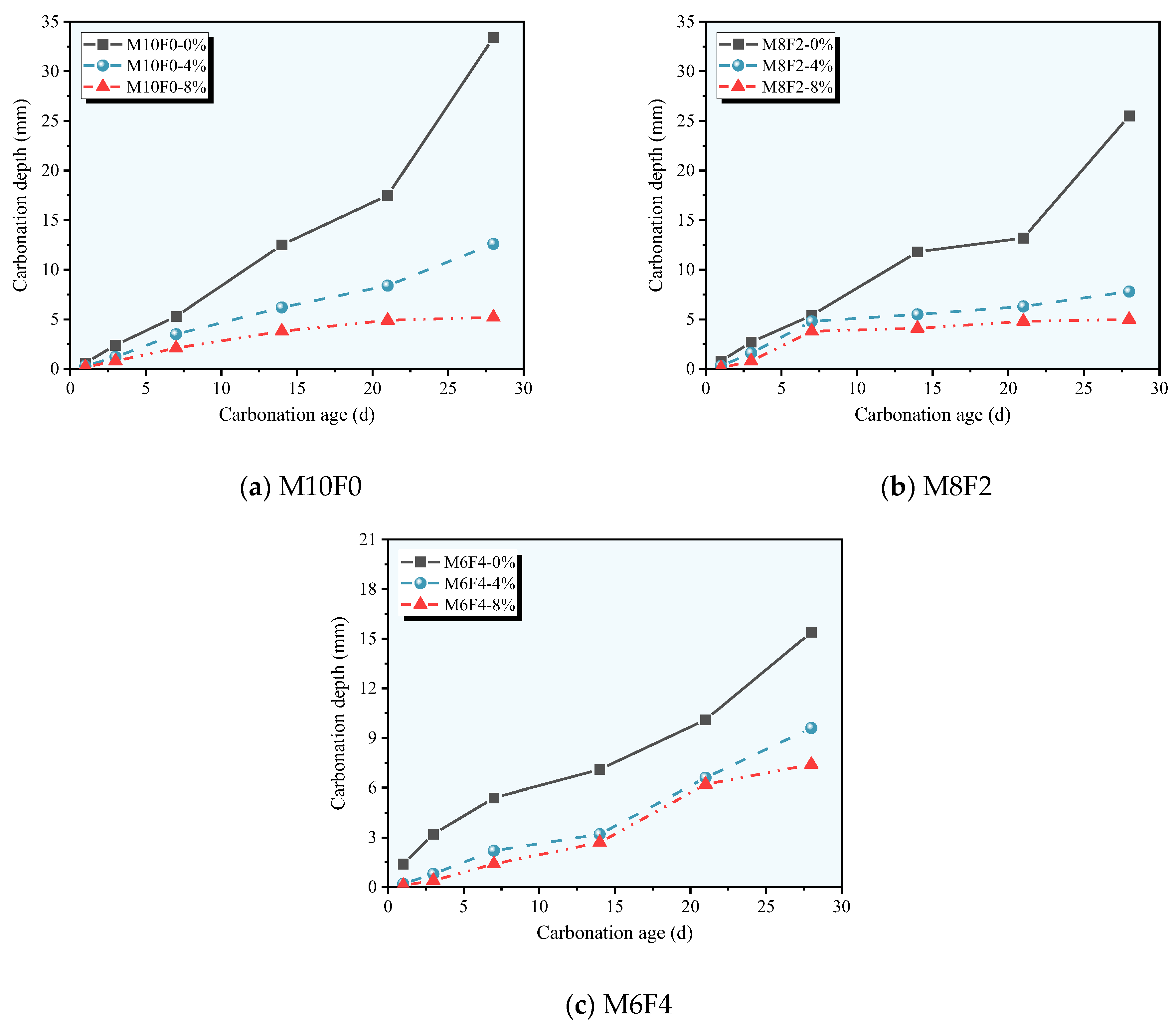
3.2. Carbonation Depth
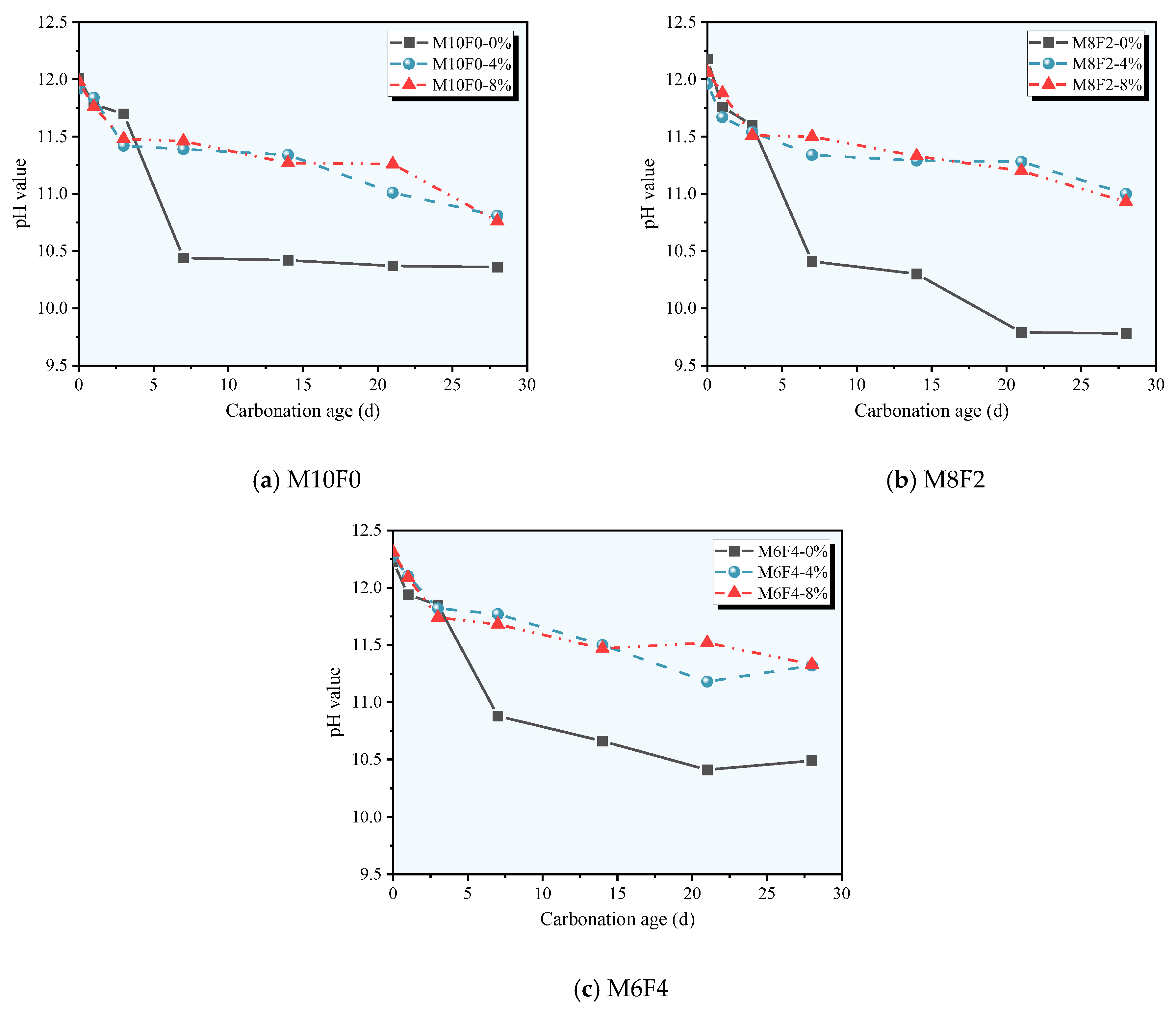
3.3. pH Value
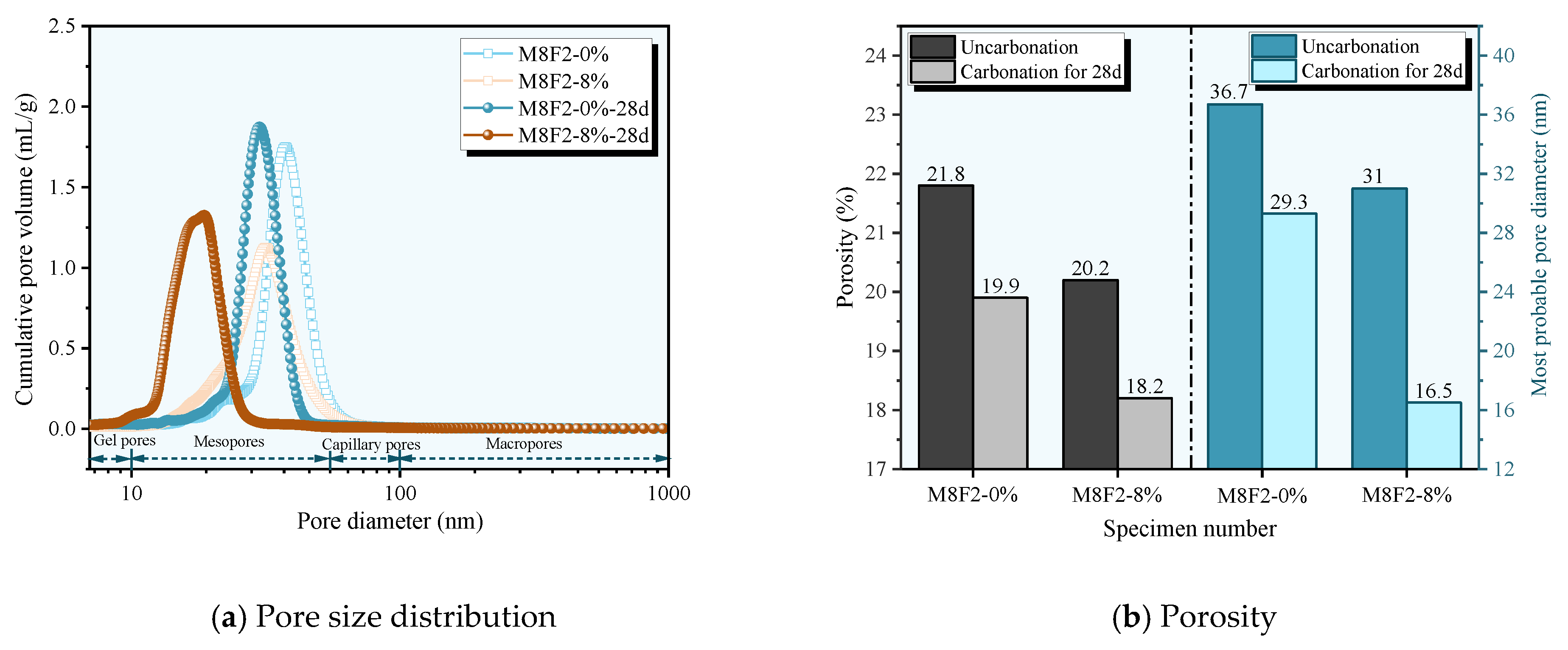
3.4. Pore Structure
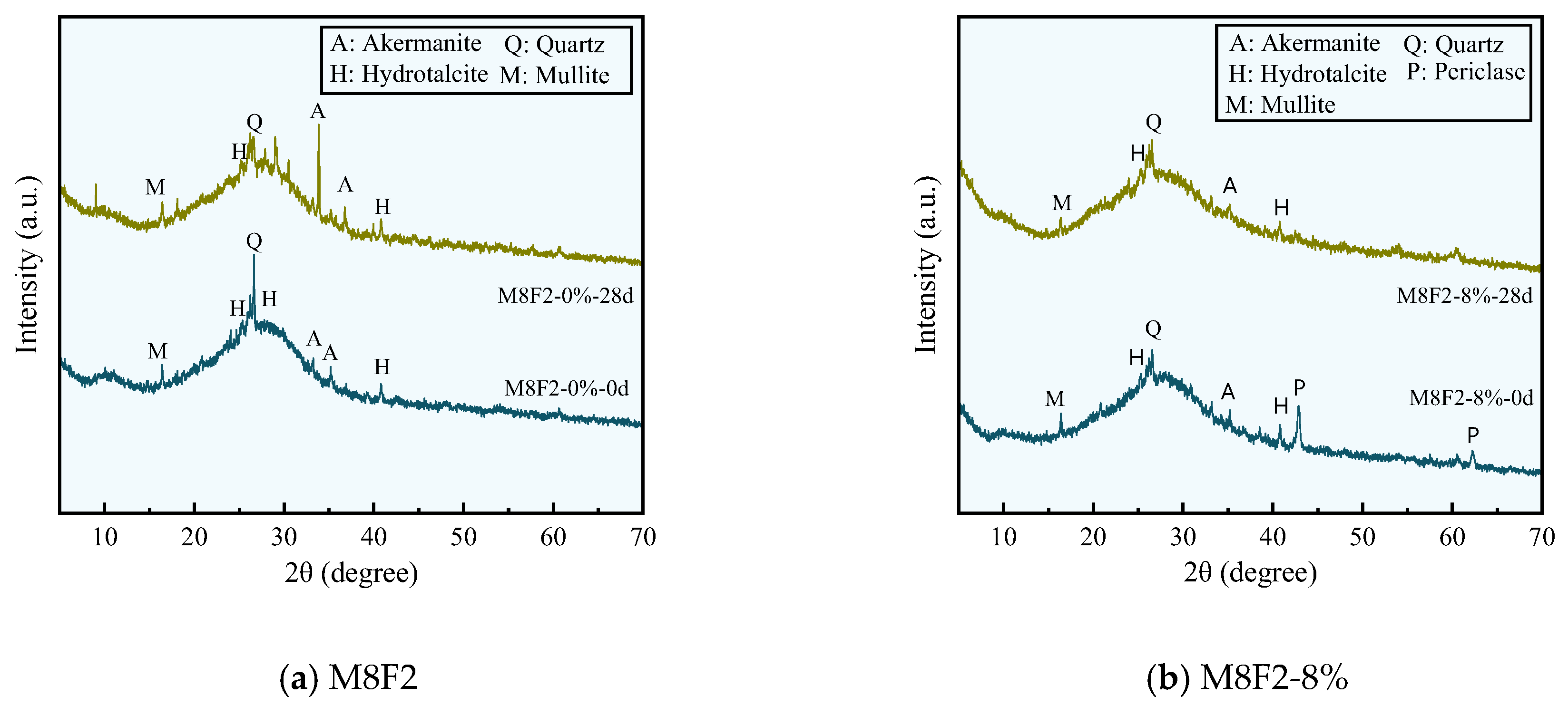
3.5. XRD Analysis
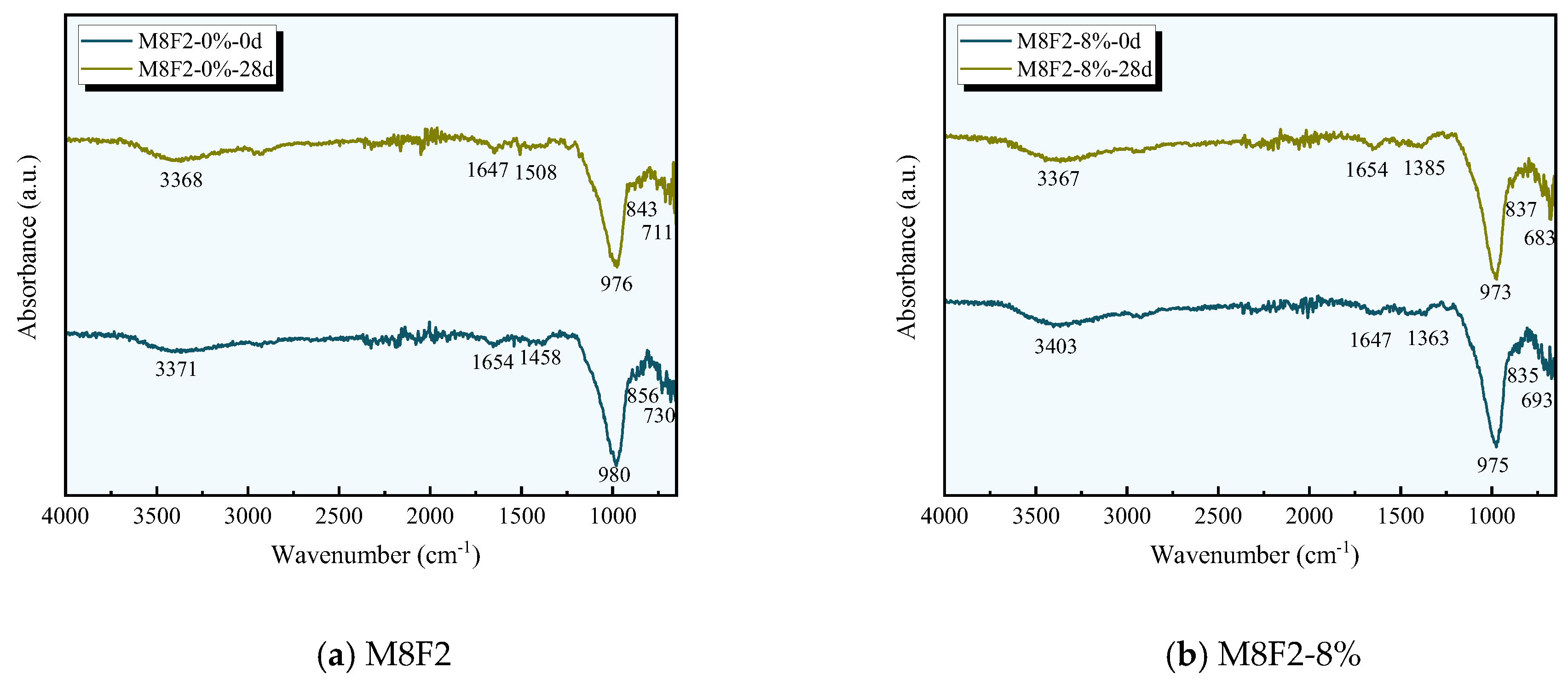
3.6. FT-IR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhao, X.; Bu, M.; Yuan, Q.; Niu, D. The microstructure and durability of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete: A review. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 29550–29566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, K.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Ling, Y. Fabrication and engineering properties of concretes based on geopolymers/alkali-activated binders—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y. Durability properties of sustainable alkali-activated cementitious materials as marine engineering material: A review. Mater. Today Sustain. 2022, 17, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skariah Thomas, B.; Yang, J.; Bahurudeen, A.; Chinnu, S.N.; Abdalla, J.A.; Hawileh, R.A. Geopolymer concrete incorporating recycled aggregates: A comprehensive review. Clean. Mater. 2022, 3, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.G.; Selvam, R.; Govindaraj, V. Durability assessment of blended slag-fly ash geopolymer concrete in field conditions after 5 years. J. Sustain. Cem.-Based Mater. 2024, 13, 1770–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L. Durability of alkali- activated materials: Progress and perspectives. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Durability of low-carbon geopolymer concrete: A critical review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 40, e00882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Peng, H. Behavior of BFRP-confined geopolymer-based coral aggregate concrete columns under axial compression: Effects of specimen sizes. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundra, S.; Criado, M.; Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L. Chloride-induced corrosion of steel rebars in simulated pore solutions of alkali-activated concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 100, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, M.S.; Kupwade-Patil, K.; Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L.; Allouche, E.N. Corrosion of steel bars induced by accelerated carbonation in low and high calcium fly ash geopolymer concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 61, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupathy, K.; Sanjayan, J.; Rajeev, P. Evaluation of alkalinity changes and carbonation of geopolymer concrete exposed to wetting and drying. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 35, 102029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, H.M.; Al-Attar, A.; Beddu, S.; Askar, M.K.; Yousif, S.T.; Majdi, A. Impact of rice husk ash on geopolymer concrete: A literature review and future directions. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanoni, M.; Angst, U.; Elsener, B. Corrosion rate of carbon steel in carbonated concrete—A critical review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 103, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, H.; Shi, L.; Hou, X.; Kong, X.; Yu, B. Corrosion resistance of polymer-modified hardened cement paste and phosphoric acid-activated metakaolin geopolymer in carbonic acid solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 445, 137950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L.; Brice, D.G.; Kilcullen, A.; Duxson, P.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Accelerated carbonation testing of alkali-activated binders significantly underestimates service life: The role of pore solution chemistry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Long, K.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Long, W.J. Carbonation and chloride ions’ penetration of alkali-activated materials: A review. Molecules 2020, 25, 5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, H.; Yang, Z.; Dong, Y.R. BFRP bars reinforced geopolymer-based coral aggregate concrete beams with sustainable and high seawater erosion resistance: Flexural durability, economic, and ecological analysis. Eng. Struct. 2025, 330, 119910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Qiao, J.; Han, W.; Pan, B.; Jin, X.; Peng, H. Modification effect of Ca(OH)2 on the carbonation resistance of fly ash-metakaolin-based geopolymer. Materials 2023, 16, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.B.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, N.T.; Shen, Y.; Hao, X.K. Comparative analysis of time-dependent CO2 uptake in cement and geopolymer concretes via diffusion-induced carbonation. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bu, Y.; Guo, S.; Lu, C.; Liu, H.; Guo, X. Experimental and thermodynamic analysis of the carbonation of geopolymer under geologic CO2 sequestration conditions. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 043356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Peng, H.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Z.; Pan, H.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X. Basalt fiber-reinforced seawater sea-sand geopolymer composites for offshore engineering constructions: Mechanical performance, microstructure, enhanced mechanisms and sustainability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 493, 143129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhaleem, K.N.; Hamada, H.M.; Osman, A.I.; Yousif, S.T.; Humada, A.M.; Majdi, A. A comprehensive review of sustainable geopolymer concrete using palm oil clinker: Environmental and engineering aspects. Energy Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 958–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Huseien, G.F.; Shah, K.W. Shrinkage mechanisms and shrinkage-mitigating strategies of alkali-activated slag composites: A critical review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 125993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Farzadnia, N.; Shi, C. Microstructural changes in alkali-activated slag mortars induced by accelerated carbonation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 100, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalqader, A.; Jin, F.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Performance of magnesia-modified sodium carbonate-activated slag/fly ash concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 103, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Nedeljković, M.; Ye, G. Pore solution composition of alkali-activated slag/fly ash pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 115, 230–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robayo-Salazar, R.A.; Aguirre-Guerrero, A.M.; Mejía de Gutiérrez, R. Carbonation-induced corrosion of alkali-activated binary concrete based on natural volcanic pozzolan. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakharev, T.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Cheng, Y.B. Resistance of alkali-activated slag concrete to carbonation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Z.; Peng, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Xu, X. State-of-the-art review of geopolymer concrete carbonation: From impact analysis to model establishment. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhag, A.B.; Selmi, A.; Ahmad, Z.; Ghazouani, N. Enhancing mechanical properties and microstructural integrity of silica fume-based self-compacting geopolymer concrete through municipal solid waste incineration fly ash incorporation. Mater. Lett. 2025, 392, 138541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Tang, H.; Sun, Y.; Bu, C.; Zhang, J. Improving the carbonation resistance of alkali-activated slag mortars by MgO with different reactivity. Mater. Struct. 2025, 58, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.A.; San Nicolas, R.; Myers, R.J.; Mejía de Gutiérrez, R.; Puertas, F.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. MgO content of slag controls phase evolution and structural changes induced by accelerated carbonation in alkali-activated binders. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 57, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Pan, B.; Han, W.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J. Carbonation resistance of fly ash-metakaolin-based geopolymer pastes regulated by slag and carbide slag. J. Sustain. Cem.-Based Mater. 2024, 13, 1538–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Hu, S.; Ling, Y. Properties of fresh and hardened fly ash/slag based geopolymer concrete: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, E.U.; Padmanabhan, S.K.; Licciulli, A. In-situ carbonation of alkali activated fly ash geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamaa, G.; Duarte, A.P.C.; Silva, R.V.; De Brito, J. Carbonation of alkali-activated materials: A review. Materials 2023, 16, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Cai, R.; Tian, Z. Natural carbonation-induced phase and molecular evolution of alkali-activated slag: Effect of activator composition and curing temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 248, 118726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Lv, Q. The influence of reactive MgO on the hydration and carbonation performance of slag-rich cement system. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 77, 107477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podnar, T.M.; Knez, Z.; Kravanja, G. Enhancing strength and CO2 uptake in lignite-based fly ash geopolymer mortar through supercritical carbonation. J. Supercrit. Fluid. 2025, 225, 106695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, R.; Peng, B.; Celik, K. Filler effects of CaCO3 polymorphs derived from limestone and seashell on hydration and carbonation of reactive magnesium oxide (MgO) cement (RMC). Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 164, 107040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Kamseu, E.; Leonelli, C.; Palomo, A. Binder chemistry—Low-calcium alkali-activated materials. In Alkali Activated Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, M.U.; Moro, C. Microstructural insights of geopolymer mortar containing cenosphere: Effects on fresh properties and durability. Mater. Struct. 2025, 58, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfadaly, E.; Othman, A.M.; Aly, M.H.; Elgarhy, W.A.; Abdellatief, M. Assessing performance and environmental benefits of high-performance geopolymer mortar incorporating pumice and rice straw ash. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2025, 44, 101918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Sirivivatnanon, V.; Nezhad, A.; Zhao, Q. Comparisons of alkali-activated binder concrete (ABC) with OPC concrete-A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 135, 104851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.K.; Koh, K.T.; Kim, M.O.; An, G.H.; Ryu, G.S. Physicochemical changes caused by reactive MgO in alkali-activated fly ash/slag blends under accelerated carbonation. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 12490–12496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.; Sun, R.; Guan, Y.; Fang, C.; Ge, Z.; Ran, Y. Effect of white mud on carbonation resistance of alkali activated slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 137207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | MgO | K2O | Na2O | SO3 | TiO2 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metakaolin | 53.80 | 43.20 | - | 1.10 | 0.82 | 0.45 | 0.18 | - | - | 0.45 |
| Fly ash | 57.96 | 31.14 | 3.02 | 3.86 | 0.52 | 2.03 | - | 0.64 | 0.52 | 0.31 |
| Serial Number | MgO Content (%) | MK (%) | FA (%) | Alkaline Content (%) | Water/Binder Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M10F0-0% | 0 | 100 | 0 | 10% | 0.63 |
| M8F2-0% | 80 | 20 | |||
| M6F4-0% | 60 | 40 | |||
| M10F0-4% | 4 | 100 | 0 | 10% | 0.63 |
| M8F2-4% | 80 | 20 | |||
| M6F4-4% | 60 | 40 | |||
| M10F0-8% | 8 | 100 | 0 | 10% | 0.63 |
| M8F2-8% | 80 | 20 | |||
| M6F4-8% | 60 | 40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Ji, D. Tuning the Carbonation Resistance of Metakaolin–Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers: The Dual Role of Reactive MgO in Microstructure and Degradation Mechanisms. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100549
Li S, Ji D. Tuning the Carbonation Resistance of Metakaolin–Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers: The Dual Role of Reactive MgO in Microstructure and Degradation Mechanisms. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(10):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100549
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuai, and Dongyu Ji. 2025. "Tuning the Carbonation Resistance of Metakaolin–Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers: The Dual Role of Reactive MgO in Microstructure and Degradation Mechanisms" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 10: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100549
APA StyleLi, S., & Ji, D. (2025). Tuning the Carbonation Resistance of Metakaolin–Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers: The Dual Role of Reactive MgO in Microstructure and Degradation Mechanisms. Journal of Composites Science, 9(10), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9100549




