Assessment of Long-Term Water Absorption on Thermal, Morphological, and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene-Based Composites with Agro-Waste Fillers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Specimens’ Manufacture
2.2.2. Water Absorption Tests
2.2.3. Thermal Analysis
2.2.4. Morphology Assessment
2.2.5. Tensile and Flexural Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Long-Term Water Absorption Tests
3.2. Thermal Properties
3.2.1. Oxidation Induction Time
3.2.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) and Derivative Thermogravimetry (DTG)
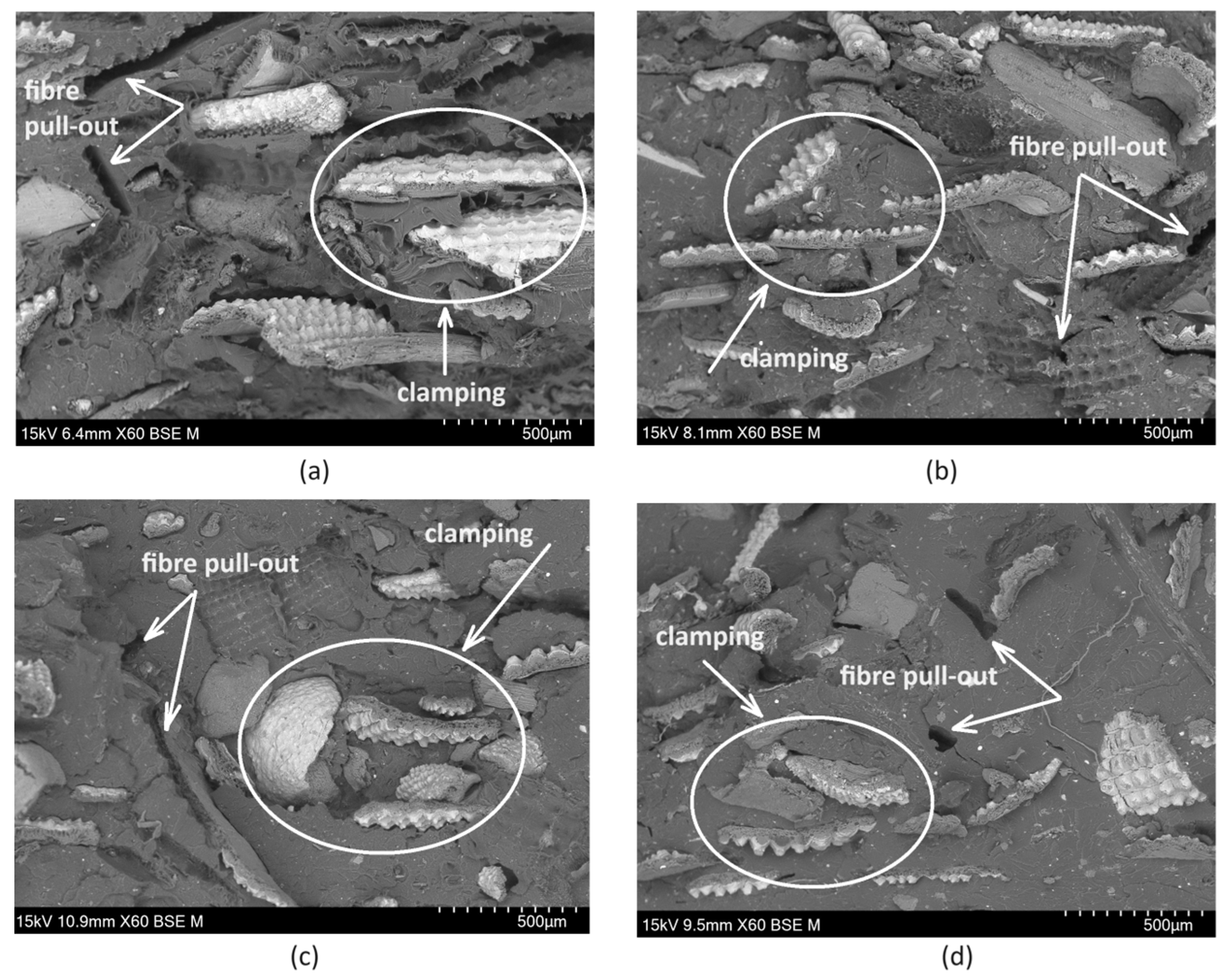
3.3. Morphology Assessment
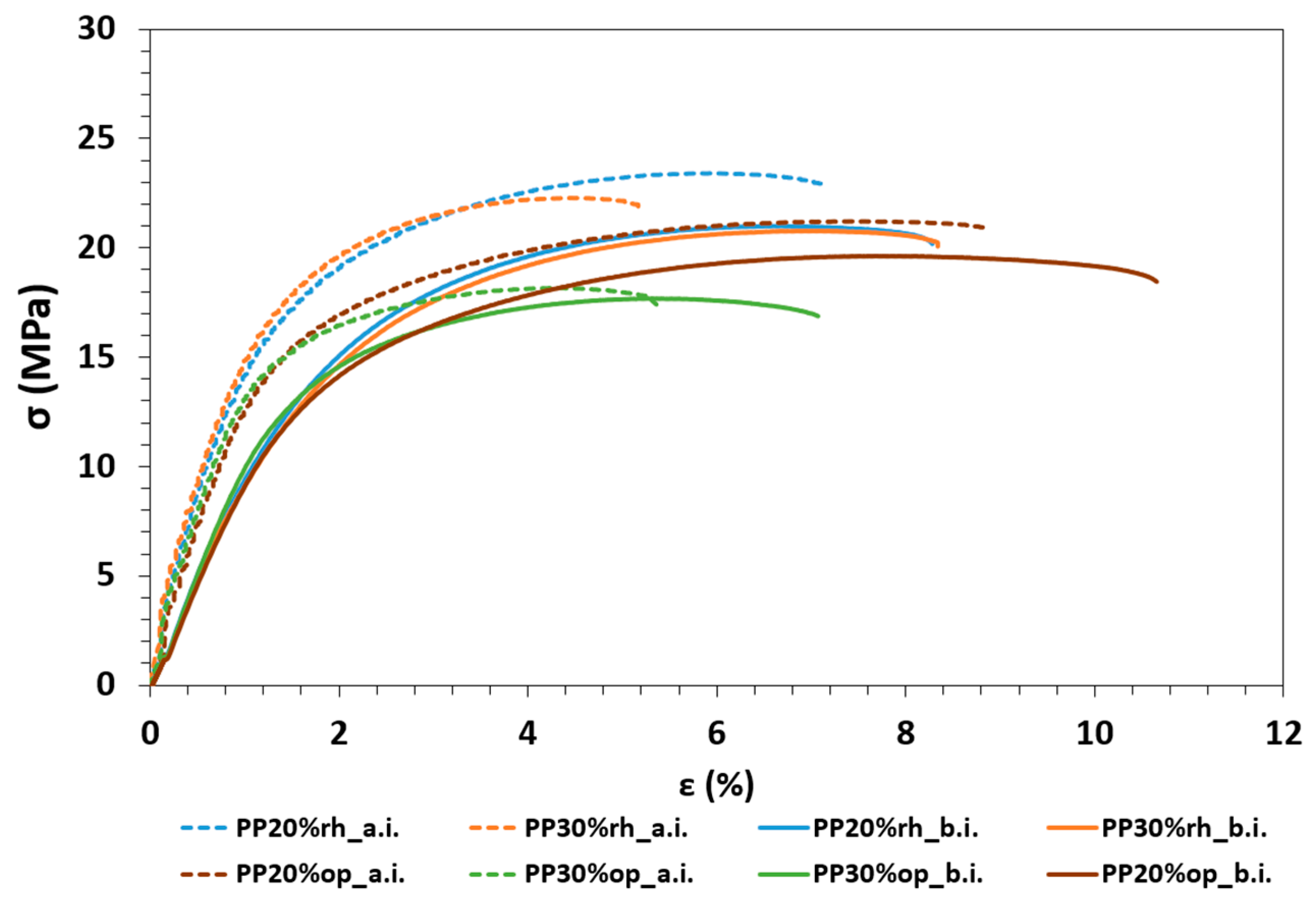
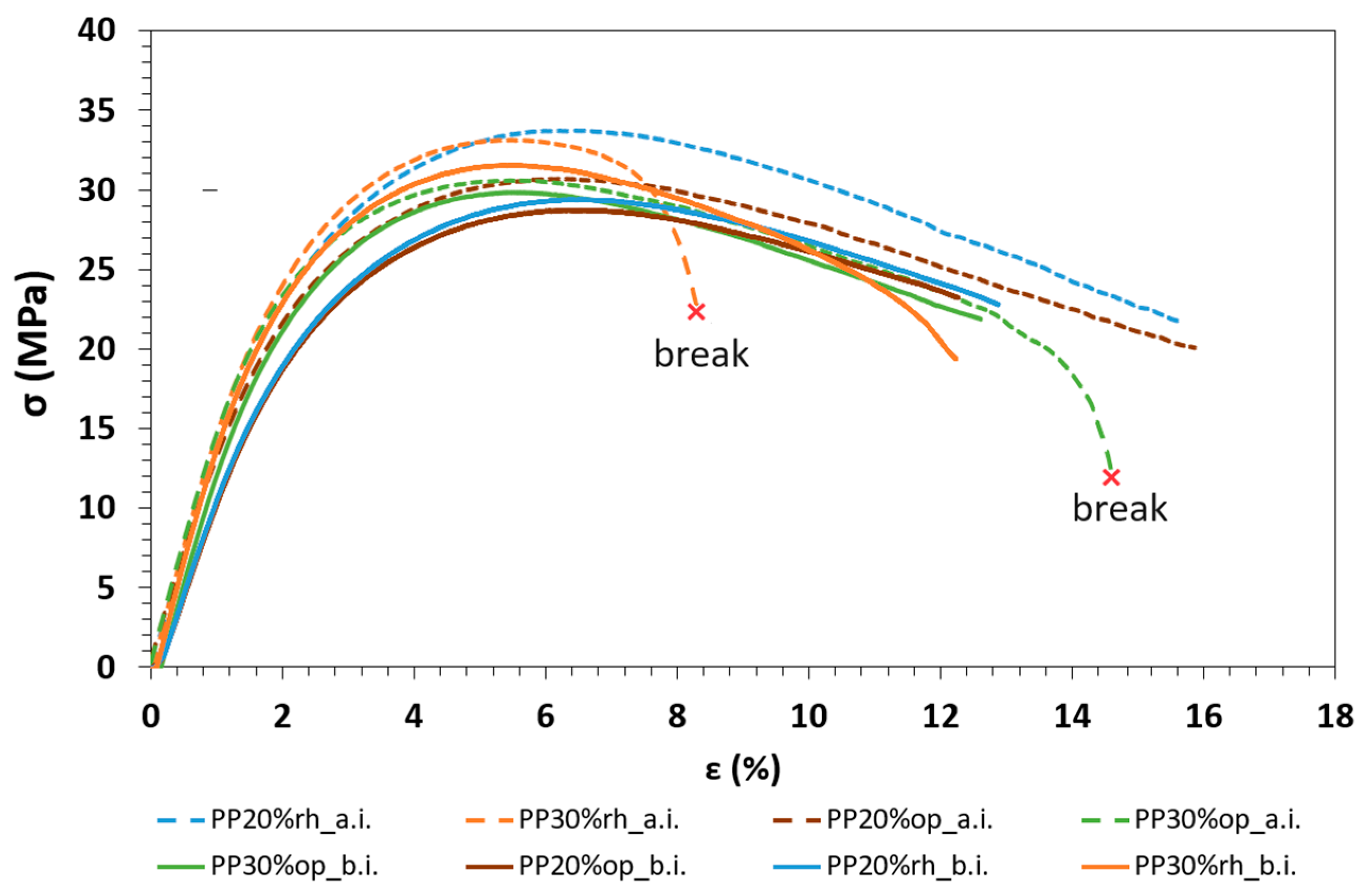
3.4. Influence of Water Absorption on the Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission, Directorate-General for Climate Action. Going Climate-Neutral by 2050—A Strategic Long-Term Vision for a Prosperous, Modern, Competitive and Climate-Neutral Eu Economy; Publications Office of the European Union (OP): Luxembourg, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsollahi, Z.; Partovinia, A. Recent Advances on Pollutants Removal by Rice Husk as a Bio-Based Adsorbent: A Critical Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Made in EU Rice. Sustainable EU Rice. Available online: https://www.sustainableeurice.eu/sustainable-rice/ (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- dos Santos, F.F.M. PORDATA, the Database of Contemporary Portugal. Available online: https://www.pordata.pt/en/portugal/olive+production+–+mainland+portugal-3362 (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Valvez, S.; Maceiras, A.; Santos, P.; Reis, P.N.B. Olive Stones as Filler for Polymer-Based Composites: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, P.; Gupta, M.K. Water absorption behavior of cellulosic fibres polymer composites: A review on its effects and remedies. J. Ind. Text. 2020, 51 (Suppl. S5), 7480S–7512S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, T.P.; Navaneethakrishnan, P.; Shankar, S.; Rajasekar, R.; Rajini, N. Characterization of natural fiber and composites—A review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2013, 32, 1457–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azwa, Z.N.; Yousif, B.F.; Manalo, A.C.; Karunasena, W. A review on the degradability of polymeric composites based on natural fibres. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.S.S.; de Queiroz, H.F.M.; Aguiar, R.A.A.; Banea, M.D. A Review on the Thermal Characterisation of Natural and Hybrid Fiber Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfaleh, I.; Abbassi, F.; Habibi, M.; Ahmad, F.; Guedri, M.; Nasri, M.; Garnier, C. A comprehensive review of natural fibers and their composites: An eco-friendly alternative to conventional materials. Results Eng. 2023, 19, 101271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Calado, V.; Rodriguez, R.J.S.; Margem, F.M. Thermogravimetric behavior of natural fibers reinforced polymer composites—An overview. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 557, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.C.M.; Abenojar, J.; Martínez, M.Á. Recent progress in hybrid biocomposites: Mechanical properties, water absorption, and flame retardancy. Materials 2020, 13, 5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, H.; Wang, H.; Pattarachaiyakoop, N.; Trada, M. A review on the tensile properties of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos. B Eng. 2011, 42, 856–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espert, A.; Vilaplana, F.; Karlsson, S. Comparison of water absorption in natural cellulosic fibres from wood and one-year crops in polypropylene composites and its influence on their mechanical properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajvidi, M.; Takemura, A. Thermal Degradation of Natural Fiber-reinforced Polypropylene Composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2009, 23, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, J.; Rodrigue, D. Effect of fiber treatment on the water absorption and mechanical properties of hemp fiber/polyethylene composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotouh, A.; Wolodko, J.; Lipsett, M.G. Isotherm moisture absorption kinetics in natural-fiber-reinforced polymer under immersion conditions. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 49, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, E.; Garcia-Manrique, J. Water Absorption Behaviour and Its Effect on the Mechanical Properties of Flax Fibre Reinforced Bioepoxy Composites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 390275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kord, B. Assessment of long-term water absorption in natural fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites influenced by filler rate and compatibilizer treatment. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2013, 26, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.I.; Ishak, Z.A.M. Effect of fiber loading on mechanical and water absorption capacity of Polylactic acid/Polyhydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyhexanoate/Kenaf composite. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 368, 12014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghmouchi, I.; Mutjé, P.; Boufi, S. Polyvinyl chloride composites filled with olive stone flour: Mechanical, thermal, and water absorption properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 41083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, Z.A.M.; Yow, B.N.; Ng, B.L.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Rozman, H.D. Hygrothermal aging and tensile behavior of injection-molded rice husk-filled polypropylene composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 81, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Seixas, G.B.; de Queiroz, H.F.M.; Neto, J.S.S.; Banea, M.D. Effect of water on the mechanical and thermal properties of natural fibre reinforced hybrid composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2023, 57, 1941–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiltsova, T.; Campos, J.; Costa, A.; Oliveira, M.S.A. Sustainable Polypropylene-Based Composites with Agro-Waste Fillers: Thermal, Morphological, Mechanical Properties and Dimensional Stability. Materials 2024, 17, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 527-1:2019; Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 1: General Principles. ISO Copyright Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- ISO 178:2019; Plastics Determination of Flexural Properties. ISO Copyright Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- D5229/D5229M−20; Standard Test Method for Moisture Absorption Properties and Equilibrium Conditioning of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Springer, G.S. Environmental Effects. In Engineering Mechanics of Fibre Reinforced Polymers and Composite Structures; Hult, J., Rammerstorfer, F.G., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1994; pp. 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-H.; Springer, G.S. Moisture absorption and desorption of composite materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D3895−19; Standard Test Method for Oxidative-Induction Time of Polyolefins by Differential Scanning Calorimetry. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- E2550-11; Standard Test Method for Thermal Stability by Thermogravimetry. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.F.A.; Althobaiti, I.O.; El-Rafey, E.; Gad, E.S. Wooden Polymer Composites of Poly(vinyl chloride), Olive Pits Flour, and Precipitated Bio-Calcium Carbonate. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 23924–23933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Song, P.; Liu, X. 19—Thermal and flame retardancy properties of thermoplastics/natural fiber biocomposites. In Advanced High Strength Natural Fibre Composites in Construction; Fan, M., Fu, F., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Shaston, UK, 2017; pp. 479–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyosov, A.A. Wood-Plastic Composites; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; Available online: https://books.google.pt/books?id=KmuK4w_D7UUC (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Chun, K.S.; Husseinsyah, S.; Syazwani, N.F. Properties of kapok husk-filled linear low-density polyethylene ecocomposites: Effect of polyethylene-grafted acrylic acid. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2016, 29, 1641–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlaczek, P.; Sinn, G.; Peter, P.; Wan-Wendner, R.; Lichtenegger, H.C. Characterization of moisture uptake and diffusion mechanisms in particle-filled composites. Polymer 2022, 249, 124799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeevi, S.; Shanmugam, V.; Kumar, S.; Ganesan, V.; Sas, G.; Johnson, D.J.; Shanmugam, M.; Ayyanar, A.; Naresh, K.; Neisiany, R.E.; et al. Effects of water absorption on the mechanical properties of hybrid natural fibre/phenol formaldehyde composites. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başboğa, İ.H.; Atar, İ.; Karakuş, K.; Mengeloğlu, F. Determination of Some Technological Properties of Injection Molded Pulverized-HDPE Based Composites Reinforced with Micronized Waste Tire Powder and Red Pine Wood Wastes. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 1776–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.S.; Ahmad, S.; Gan, S.; Tarawneh, M.A. High loading rice husk green composites: Dimensional stability, tensile behavior and prediction, and combustion properties. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2020, 33, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regazzi, A.; Léger, R.; Corn, S.; Ienny, P. Modeling of hydrothermal aging of short flax fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 90, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genieva, S.D.; Turmanova, S.C. Utilization of Rice Husks and the Products of Its Thermal Degradation as Fillers in Polymer Composites. In Cellulose Fibers: Bio- and Nano-Polymer Composites: Green Chemistry and Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 345–377. Available online: https://books.google.pt/books?id=HZa-Ljm7iwgC (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Gregorová, A.; Cibulková, Z.; Košíková, B.; Šimon, P. Stabilization effect of lignin in polypropylene and recycled polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 89, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schoors, L.; Minerbe, M.G.; Moscardelli, S.; Rabii, H.; Davies, P. Antioxidant properties of flax fibers in polyethylene matrix composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 126, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, S.; Adnot, A.; Roy, D. Hydrolytic aging of polypropylene studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 3830–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.M.; van Vuure, A.W. Effects of water immersion, natural ageing in sunlight and natural ageing under the shade on non-dry flax fibre reinforced composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 216, 118655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudood, A.; Rahman, A.; Öchsner, A.; Islam, M.; Francucci, G. Flax fiber and its composites: An overview of water and moisture absorption impact on their performance. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2019, 38, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Salazar, M.A.; Salinas, E. Mechanical, thermal, viscoelastic performance and product application of PP-rice husk Colombian biocomposites. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 176, 107135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.J.; Yang, H.S. Thermal properties of bio-flour-filled polyolefin composites with different compatibilizing agent type and content. Thermochim. Acta 2006, 451, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khraisha, Y.H. Thermal Decomposition of Olive-Solid Waste by TGA: Characterization and Devolatilization Kinetics under Nitrogen and Oxygen Atmospheres. J. Power Energy Eng. 2024, 12, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janković, B.; Radojević, M.B.; Balać, M.M.; Stojiljković, D.D.; Manić, N.G. thermogravimetric study on the pyrolysis kinetic mechanism of waste biomass from fruit processing industry. Therm. Sci. 2020, 24 Pt B, 4221–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, A.A.; Kareem, M.A. Chemical composition and physical characteristics of rice husk ash blended cement. Int. J. Eng. Res. Afr. 2017, 32, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandola, B.K.; Mistik, S.I.; Pornwannachai, W.; Horrocks, A.R. Effects of Water and Chemical Solutions Ageing on the Physical, Mechanical, Thermal and Flammability Properties of Natural Fibre-Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites. Molecules 2021, 26, 4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, H.N.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Richardson, M.O.W. Effect of water absorption on the mechanical properties of hemp fibre reinforced unsaturated polyester composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
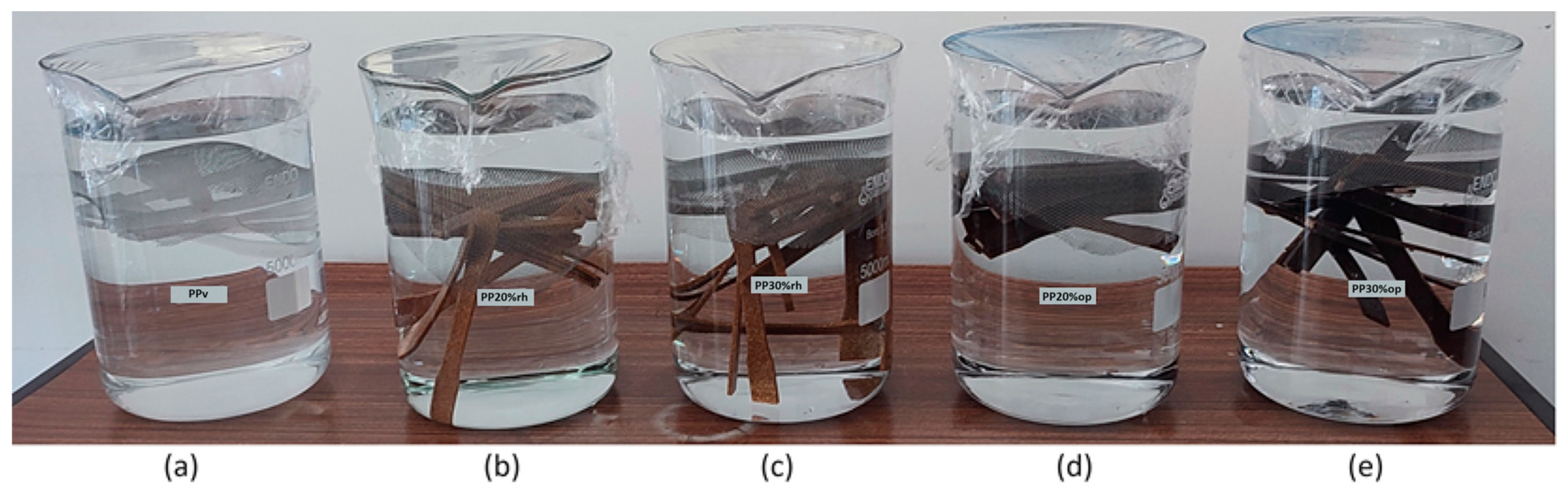







| Designation | Composition (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP 1 | Rice Husk | Olive Pits | PPMA 2 | |
| PPv | 100 | - | - | - |
| PP20%rh | 79 | 20 | - | 1 |
| PP30%rh | 69 | 30 | - | 1 |
| PP20%op | 79 | - | 20 | 1 |
| PP30%op | 69 | - | 30 | 1 |
| Property | Specimen Type | PP20%rh | PP30%rh | PP20%op | PP30%op |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture saturation content − Mm (%) | TS 1 | 1.47 | 2.38 | 1.13 | 1.59 |
| FS 1 | 1.01 | 1.63 | 0.80 | 1.11 | |
| Diffusion coefficient − Dc (× 10−7) (mm2/s) | TS | 1.153 | 1.147 | 1.216 | 1.166 |
| FS | 2.764 | 3.134 | 2.798 | 2.572 | |
| Time to saturation (days) | TS | 232 | 232 | 232 | 232 |
| FS | 232 | 232 | 232 | 232 |
| Material | OIT (s) | OIT↓ (%) 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before Immersion | After Immersion | ||
| PPv | 17.8 ± 2.5 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 75 |
| PP20%rh | 10.2 ± 0.5 | 5.9 ± 0.6 | 42 |
| PP30%rh | 10.4 ± 0.8 | 8.0 ± 0.8 | 23 |
| PP20%op | 14.3 ± 0.1 | 8.6 ± 0.6 | 40 |
| PP30%op | 19.6 ± 1.8 | 12.2 ± 1.1 | 38 |
| Material | 1st Stage | 2nd Stage | Ash Residue 5 (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ts 1–Te 2 (°C) | TDTG 1st.peak (°C) | Weight Loss 3 (%) | Ts–Te (°C) | TDTG 2nd.peak (°C) | Weight Loss 4 (%) | ||
| PPv | ― | ― | ― | 313.7–486.3 | 448.2 | 99.2 | 0.8 |
| PP20%rh | 233.7–372.1 | ― | 9.8 | 372.1–494.1 | 455.1 | 92.2 | 6.9 |
| PP30%rh | 219.2–373.9 | 348.9 | 14.4 | 373.9–498.0 | 457.1 | 89.1 | 10.2 |
| PP20%op | 234.1–376.5 | 348.5 | 12.4 | 376.5–496.4 | 457.1 | 94.2 | 5.3 |
| PP30%op | 221.5–376.3 | 348.6 | 19.0 | 376.3–497.7 | 457.0 | 91.1 | 8.0 |
| Material | F.C. (%) 1 | A.R. (%) 2 | A.R./F.C. | A.C.R. 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP20%rh | 20 | 6.9 | 0.35 | 1.5 |
| PP30%rh | 30 | 10.2 | 0.34 | |
| PP20%op | 20 | 5.3 | 0.27 | 1.5 |
| PP30%op | 30 | 8.0 | 0.27 |
| Material | S.C. 1 | E (MPa) | ∆ 2 E (%) | σu (MPa) | σu ↑ 3 (%) | εb (%) | εb ↓ 4 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP20%rh | b.i. | 1377.0 ± 198.2 | −0.8 | 19.7 ± 0.4 | 15.3 | 8.6 ± 1.2 | 15.5 |
| a.i. | 1366.6 ± 59.5 | 22.7 ± 0.4 | 7.2 ± 0.9 | ||||
| PP30%rh | b.i. | 1322.6 ± 170.63 | 6.9 | 19.6 ± 0.6 | 8.4 | 8.3 ± 1.4 | 38.9 |
| a.i. | 1413.73 ± 43.5 | 21.3 ± 0.2 | 5.1 ± 0.4 | ||||
| PP20%op | b.i. | 1305.8 ± 217.8 | −7.8 | 18.6 ± 0.5 | 11.4 | 10.0 ± 1.7 | 14.9 |
| a.i. | 1204.3 ± 34.1 | 20.7 ± 0.5 | 8.4 ± 0.9 | ||||
| PP30%op | b.i. | 1249.6 ± 239. 8 | 13.3 | 16.6 ± 0.3 | 8.1 | 6.8 ± 1.1 | 19.7 |
| a.i. | 1416.02 ± 106.1 | 17.9 ± 0.4 | 5.5 ± 1.0 |
| Material | S.C. 1 | Ef (MPa) | Ef ↑ 2 (%) | σf (MPa) | σf ↑ 2 (%) | σuf (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP20%rh | b.i. | 1263.4 ± 77.1 | 17.6 | 30.3 ± 0.8 | 11.3 | ― |
| a.i. | 1485.5 ± 16.0 | 33.7 ± 0.2 | ― | |||
| PP30%rh | b.i. | 1572.4 ± 67.0 | 3.3 | 31.4 ± 0.9 | 5.1 | ― |
| a.i. | 1624.1 ± 17.6 | 33.0 ± 0.3 | 22.7 ± 3.1 | |||
| PP20%op | b.i. | 1170.5 ± 47.3 | 17.2 | 28.6 ± 0.8 | 7.3 | ― |
| a.i. | 1371.7 ± 25.0 | 30.7 ± 0.3 | ― | |||
| PP30%op | b.i. | 1356.5 ± 95.5 | 13.9 | 29.0 ± 1.4 | 3.9 | ― |
| a.i. | 1544.8 ± 22.9 | 30.1 ± 0.3 | 11.3 ± 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhiltsova, T.; Costa, A.; Oliveira, M.S.A. Assessment of Long-Term Water Absorption on Thermal, Morphological, and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene-Based Composites with Agro-Waste Fillers. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs8080288
Zhiltsova T, Costa A, Oliveira MSA. Assessment of Long-Term Water Absorption on Thermal, Morphological, and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene-Based Composites with Agro-Waste Fillers. Journal of Composites Science. 2024; 8(8):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs8080288
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhiltsova, Tatiana, Andreia Costa, and Mónica S. A. Oliveira. 2024. "Assessment of Long-Term Water Absorption on Thermal, Morphological, and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene-Based Composites with Agro-Waste Fillers" Journal of Composites Science 8, no. 8: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs8080288
APA StyleZhiltsova, T., Costa, A., & Oliveira, M. S. A. (2024). Assessment of Long-Term Water Absorption on Thermal, Morphological, and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene-Based Composites with Agro-Waste Fillers. Journal of Composites Science, 8(8), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs8080288







