Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles Using Cleistocalyx operculatus Leaf Extract and Their Acute Oral Toxicity Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization of Selenium Nanoparticles
2.4. Acute Toxicity
2.5. Anti-Bacterial Activity
3. Results and Discussion
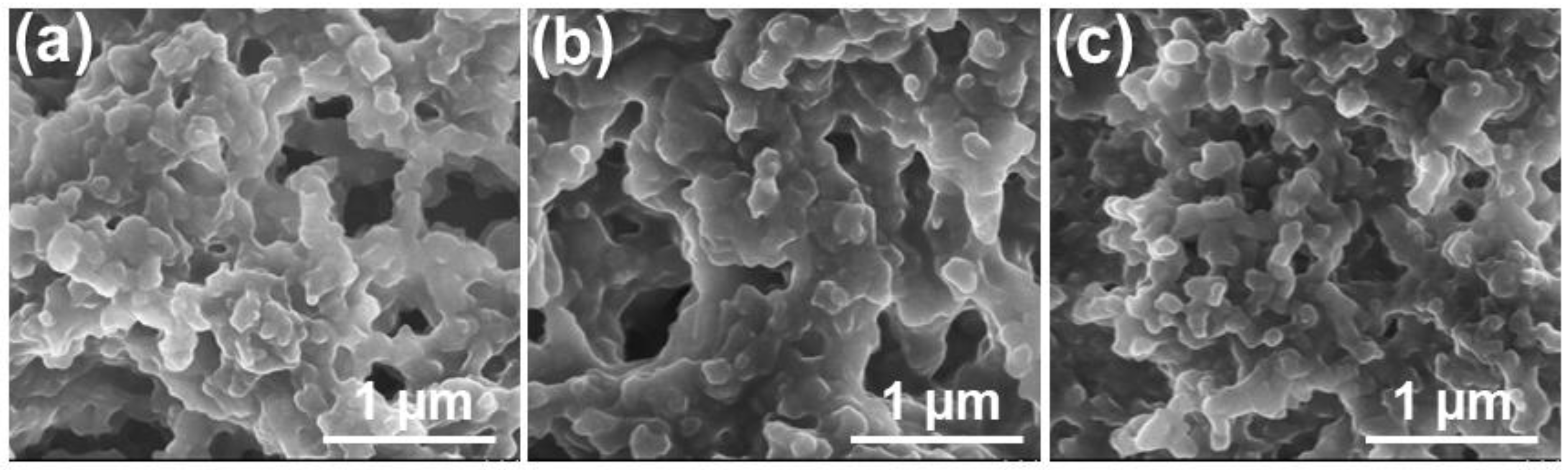
3.1. Effect of the Stirring Methods
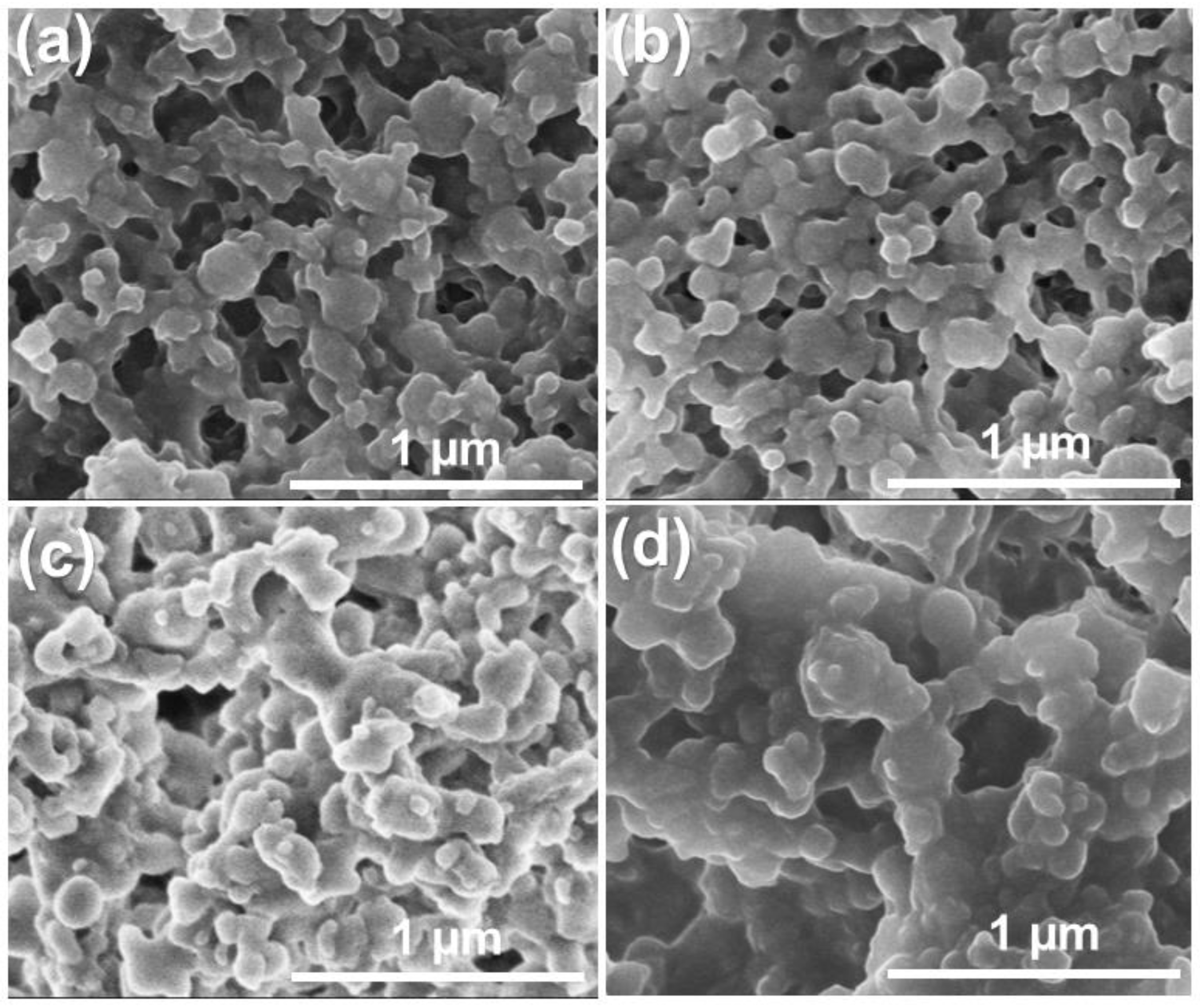
3.2. Effect of the Se4+/CO Volume Ratios
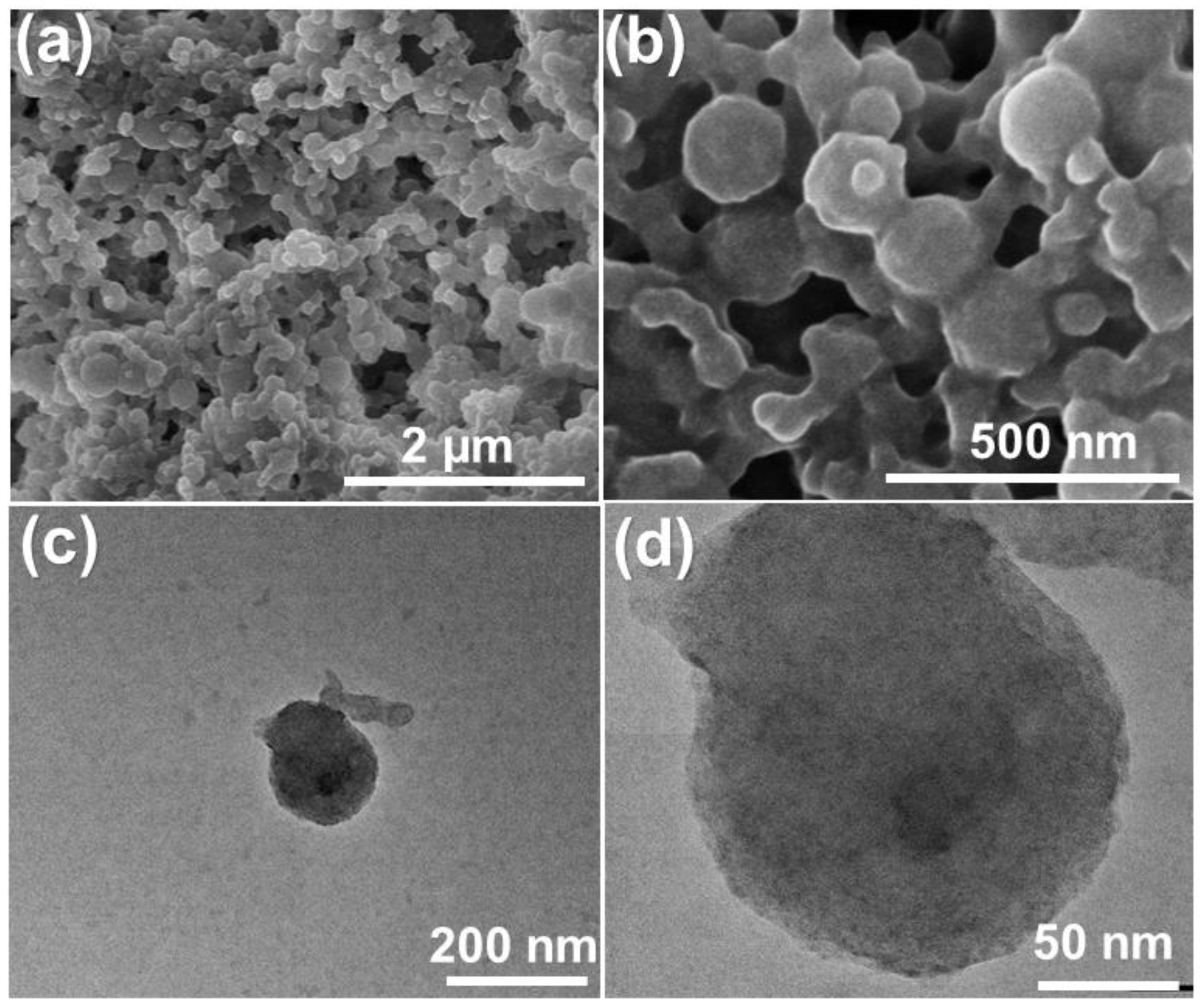
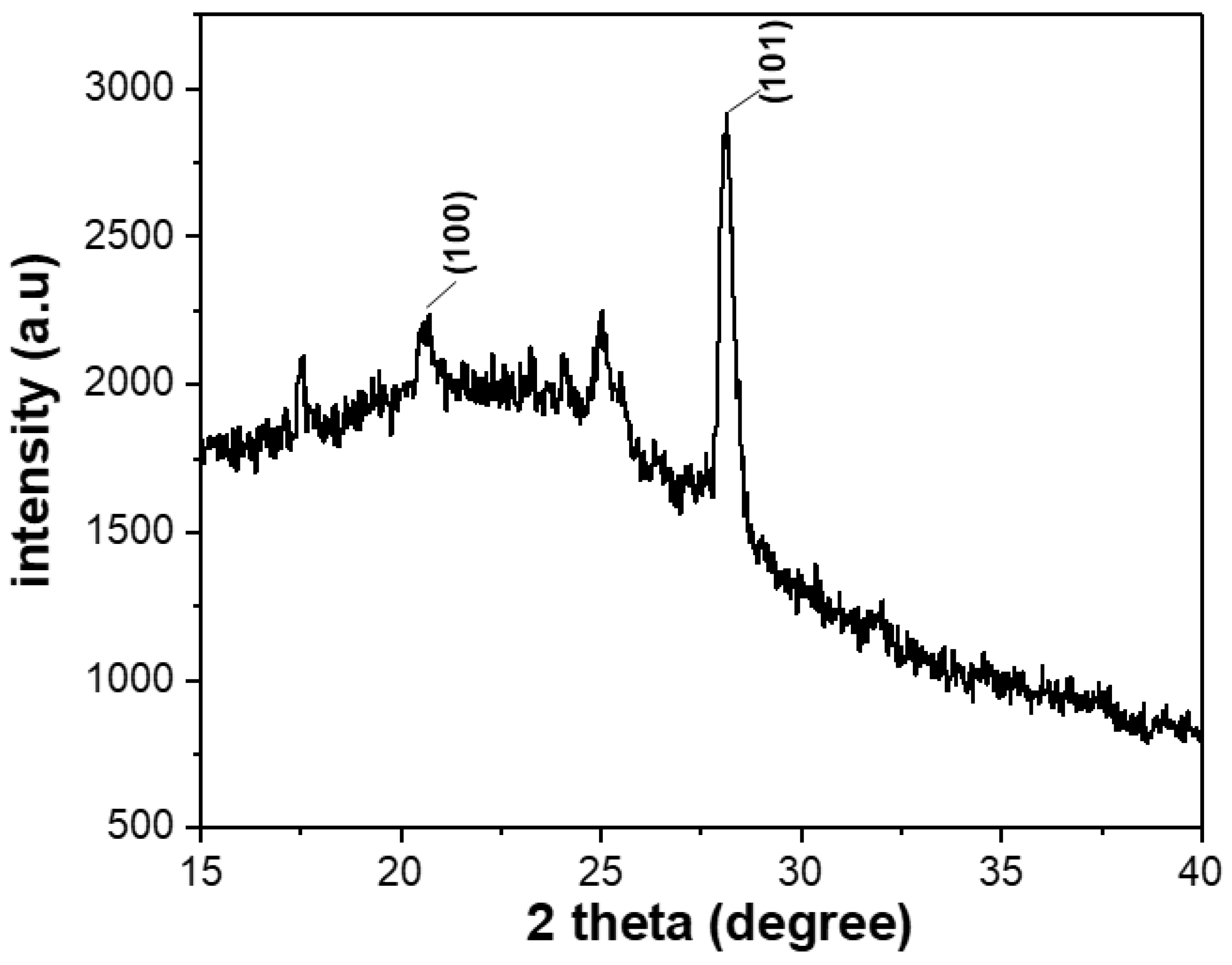
3.3. Characterization of Se NPs
3.4. Antimicrobial Activity
3.5. Acute Oral Toxicity and Lethal Concentration (LC50) of Se NPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baer, D.R.; Amonette, J.E.; Engelhard, M.; Gaspar, D.; Karakoti, A.; Kuchibhatla, S.; Nachimuthu, P.; Nurmi, J.T.; Qiang, Y.; Sarathy, V.; et al. Characterization challenges for nanomaterials. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lines, M. Nanomaterials for practical functional uses. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 449, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, N.; Butsen, A.; Nevar, E.; Savastenko, N. Synthesis of nanosized particles during laser ablation of gold in water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 4439–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoun, S.; Arif, R.; Jangid, N.K.; Meena, R.K. Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 19, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, G.; Rai, P.; Pandey, A. Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles: A Greener Approach for a Cleaner Future. In Green Synthesis, Characterization and Applications of Nanoparticles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayano, H.; Miyake, M.; Terasawa, K.; Kuroda, M.; Soda, S.; Sakaguchi, T.; Ike, M. Isolation of a selenite-reducing and cadmium-resistant bacterium Pseudomonas sp. strain RB for microbial synthesis of CdSe nanoparticles. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 117, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.; Kon, K.; Kratošová, G.; Durán, N.; Ingle, A.P.; Rai, M. Fungi as an efficient mycosystem for the synthesis of metal nanoparticles: Progress and key aspects of research. Biotechnol. Lett. 2015, 37, 2099–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.; Faraz, M.; Pandey, R.; Shakir, M.; Fatma, T.; Varma, A.; Barman, I.; Prasad, R. Facile Algae-Derived Route to Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Antibacterial, and Photocatalytic Properties. Langmuir 2015, 31, 11605–11612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Green chemistry for nanoparticle synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5778–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.T.; Dang, T.-D.; Binh, K.H.; Nguyen, T.M.; Xuan, T.N.; La, D.D.; Nadda, A.K.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D. Green synthesis of highly stable zero-valent iron nanoparticles for organic dye treatment using Cleistocalyx operculatus leaf extract. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 25, 100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onitsuka, S.; Hamada, T.; Okamura, H. Preparation of antimicrobial gold and silver nanoparticles from tea leaf extracts. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 173, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, S.; Ghamsari, M.S.; Lee, C.; Han, W.; Park, H.-H.; Tafreshi, M.J.; Afarideh, H.; Ara, M.H.M. Preparation and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Sambucus ebulus. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginting, B.; Maulana, I.; Karnila, I. Biosynthesis Copper Nanoparticles using Blumea balsamifera Leaf Extracts: Characterization of its Antioxidant and Cytotoxicity Activities. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 21, 100799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Bano, I.; Zare, H. A Comprehensive Review on Selenium and Its Effects on Human Health and Distribution in Middle Eastern Countries. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2021, 200, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, D.F.; da Silva, M.D.C.S.; de Paula Alves, M.; Fuentes, D.P.; Porto, L.E.O.; de Oliveira, P.V.; Kasuya, M.C.M.; Eller, M.R. By-Products as Substrates for Production of Selenium-Enriched Pleurotus ostreatus Mushrooms. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2021, 13, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Yan, X.; Zhang, L. Comparison of short-term toxicity between Nano-Se and selenite in mice. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, T.J.; Tran, P. Selenium nanoparticles inhibit Staphylococcus aureus growth. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wong, Y.-S.; Zheng, W.; Bai, Y.; Huang, L. Selenium nanoparticles fabricated in Undaria pinnatifida polysaccharide solutions induce mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in A375 human melanoma cells. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 67, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, C.; Sampath, K.S.; Arunkumar, P.; Kumar, M.S.; Sujatha, V.; Premkumar, K.; Thirunavukkarasu, C. Green synthesis and characterization of selenium nanoparticles and its augmented cytotoxicity with doxorubicin on cancer cells. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 36, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H. Elemental selenium at nano size possesses lower toxicity without compromising the fundamental effect on selenoenzymes: Comparison with selenomethionine in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidi, H.; Barabadi, H.; Saravanan, M. Emerging Selenium Nanoparticles to Combat Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Clust. Sci. 2019, 31, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.A.; Sarin, L.; Hurt, R.H.; Webster, T.J. Opportunities for nanotechnology-enabled bioactive bone implants. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 2653–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.; Chen, Z.; Tai, R.-Z.; Shen, H.-M.; Martin, F.L.; Zhu, Y.-G. Selenite-Induced Toxicity in Cancer Cells Is Mediated by Metabolic Generation of Endogenous Selenium Nanoparticles. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Tran, P.A.; Norello, R.; Simpson, D.A.; O’Connor, A.J.; Tomljenovic-Hanic, S. Intrinsic fluorescence of selenium nanoparticles for cellular imaging applications. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3376–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Y.; Langrock, A.; Wang, C. Selenium@ Mesoporous Carbon Composite with Superior Lithium and Sodium Storage Capacity. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8003–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Mehta, S.K. Selenium Nanomaterials: Applications in Electronics, Catalysis and Sensors. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 1658–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Gao, B.; Fu, J.; Xiao, S.; Huo, K.; Chu, P.K. Reduced graphene oxide encapsulated selenium nanoparticles for high-power lithium–selenium battery cathode. J. Power Sources 2015, 288, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Brockgreitens, J.; Xu, K.; Abbas, A. Sponge-supported synthesis of colloidal selenium nanospheres. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 465601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, C.P.; Dwivedi, C.; Singh, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Bajaj, P.N. Riley oxidation: A forgotten name reaction for synthesis of selenium nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2010, 45, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamnev, A.A.; Mamchenkova, P.V.; Dyatlova, Y.A.; Tugarova, A.V. FTIR spectroscopic studies of selenite reduction by cells of the rhizobacterium Azospirillum brasilense Sp7 and the formation of selenium nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1140, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, M.; Haro-Poniatowski, E.; Morales, J.; Batina, N. Synthesis of selenium nanoparticles by pulsed laser ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 195, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Bai, Y. Electrochemical synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and formation of sea urchin-like selenium nanoparticles by electrostatic assembly. Mater. Lett. 2017, 196, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionin, A.; Ivanova, A.; Khmel’Nitskii, R.; Klevkov, Y.; Kudryashov, S.; Mel’Nik, N.; Nastulyavichus, A.; Rudenko, A.; Saraeva, I.; Smirnov, N.; et al. Milligram-per-second femtosecond laser production of Se nanoparticle inks and ink-jet printing of nanophotonic 2D-patterns. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 436, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.T.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Le, H.T.; Nguyen, D.D.; La, D.D. One-Step Solution Plasma-Mediated Preparation of Se Nanoplarticles and Evaluating Their Acute Oral Toxicity in Mice. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagesan, V.; Venugopal, S. Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticle Using Leaves Extract of Withania somnifera and Its Biological Applications and Photocatalytic Activities. BioNanoScience 2018, 9, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokila, K.; Elavarasan, N.; Sujatha, V. Diospyros montana leaf extract-mediated synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and their biological applications. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 7481–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardsadegh, B.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Aloe vera leaf extract mediated green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and assessment of their In vitro antimicrobial activity against spoilage fungi and pathogenic bacteria strains. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhlou, K.; Allahyari, S.; Sabouri, S.; Najian, Y.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Walnut leaf extract-based green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles via microwave irradiation and their characteristics assessment. Open Agric. 2020, 5, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anu, K.; Devanesan, S.; Prasanth, R.; Al Salhi, M.S.; Ajithkumar, S.; Singaravelu, G. Biogenesis of selenium nanoparticles and their anti-leukemia activity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 2520–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalishwaralal, K.; Jeyabharathi, S.; Sundar, K.; Muthukumaran, A. A novel one-pot green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and evaluation of its toxicity in zebrafish embryos. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2014, 44, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardsadegh, B.; Vaghari, H.; Mohammad-Jafari, R.; Najian, Y.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities assessment of fabricated selenium nanoparticles using Pelargonium zonale leaf extract. Green Process. Synth. 2018, 8, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrzynska, K.; Sentkowska, A. Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using plant extracts. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2021, 12, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, P.; Ghotekar, S.; Pagar, T.; Pansambal, S.; Oza, R.; Mane, D. Plant extract assisted eco-benevolent synthesis of selenium nanoparticles-a review on plant parts involved, characterization and their recent applications. J. Chem. Rev. 2020, 2, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Mukhopadhyay, M. Green synthesis and structural characterization of selenium nanoparticles and assessment of their antimicrobial property. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Fouda, A.; Awad, M.A.; Al-Olayan, E.M.; Allam, A.A.; Shaheen, T.I. Antibacterial, Cytotoxicity and Larvicidal Activity of Green Synthesized Selenium Nanoparticles Using Penicillium corylophilum. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 32, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Tang, Q.; Zhong, X.; Bai, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W. Surface decoration by Spirulina polysaccharide enhances the cellular uptake and anticancer efficacy of selenium nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Hoang, N.H.; Van Tran, C.; Nguyen, P.; Dang, T.-D.; Chung, W.J.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Kumar, P.S.; La, D.D. Green synthesis of a photocatalyst Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite using Cleistocalyx operculatus leaf extract for degradation of organic dyes. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, H.P.N.; Thi, K.T.P.; Thi, L.N.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, P.T.; Vu, T.T.; Le, H.T.; Dang, T.-D.; Huynh, D.C.; Mai, H.T.; et al. Green synthesis of an Ag nanoparticle-decorated graphene nanoplatelet nanocomposite by using Cleistocalyx operculatus leaf extract for antibacterial applications. Nano-Struct. Nano-Obj. 2021, 29, 100810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakibaie, M.; Shahverdi, A.R.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Hassanzadeh, G.R.; Rahimi, H.R.; Sabzevari, O. Acute and subacute toxicity of novel biogenic selenium nanoparticles in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 51, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vu, T.T.; Nguyen, P.T.M.; Pham, N.H.; Le, T.H.; Nguyen, T.H.; Do, D.T.; La, D.D. Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles Using Cleistocalyx operculatus Leaf Extract and Their Acute Oral Toxicity Study. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6100307
Vu TT, Nguyen PTM, Pham NH, Le TH, Nguyen TH, Do DT, La DD. Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles Using Cleistocalyx operculatus Leaf Extract and Their Acute Oral Toxicity Study. Journal of Composites Science. 2022; 6(10):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6100307
Chicago/Turabian StyleVu, Tri Thien, Phuong Thi Mai Nguyen, Ngan Hanh Pham, Thanh Huu Le, Tran Hung Nguyen, Dinh Trung Do, and Duong Duc La. 2022. "Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles Using Cleistocalyx operculatus Leaf Extract and Their Acute Oral Toxicity Study" Journal of Composites Science 6, no. 10: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6100307
APA StyleVu, T. T., Nguyen, P. T. M., Pham, N. H., Le, T. H., Nguyen, T. H., Do, D. T., & La, D. D. (2022). Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles Using Cleistocalyx operculatus Leaf Extract and Their Acute Oral Toxicity Study. Journal of Composites Science, 6(10), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6100307






