Design Guide for Hybrid-Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718 Combining PBF-LB/M and In Situ High-Speed Milling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
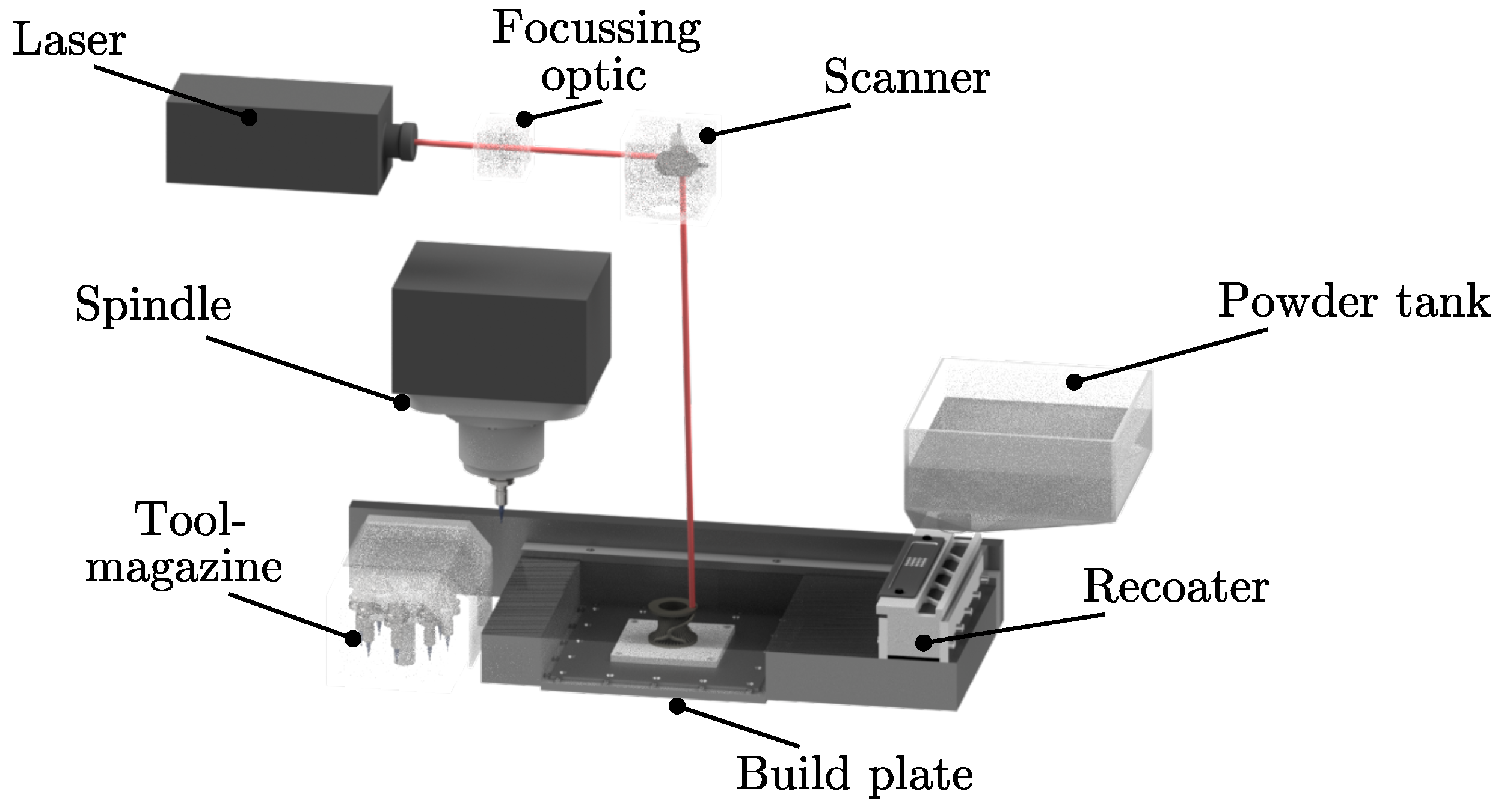
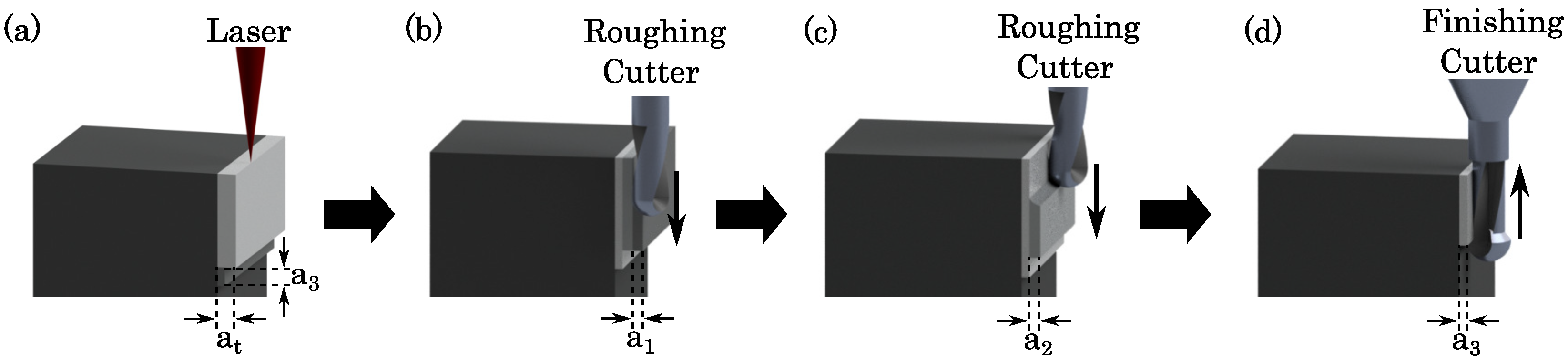
2.1. Machine and Process
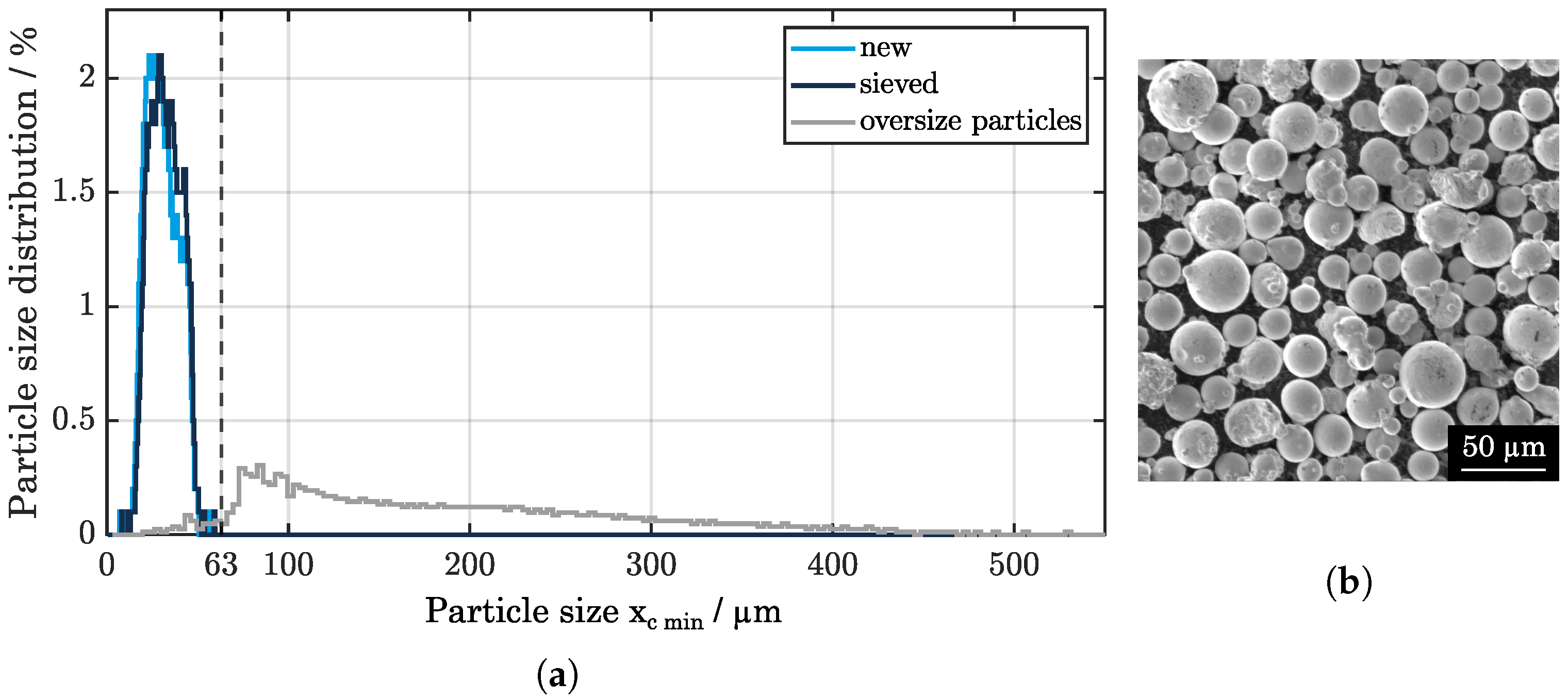
2.2. Powder Characterization
2.3. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Powder Distribution
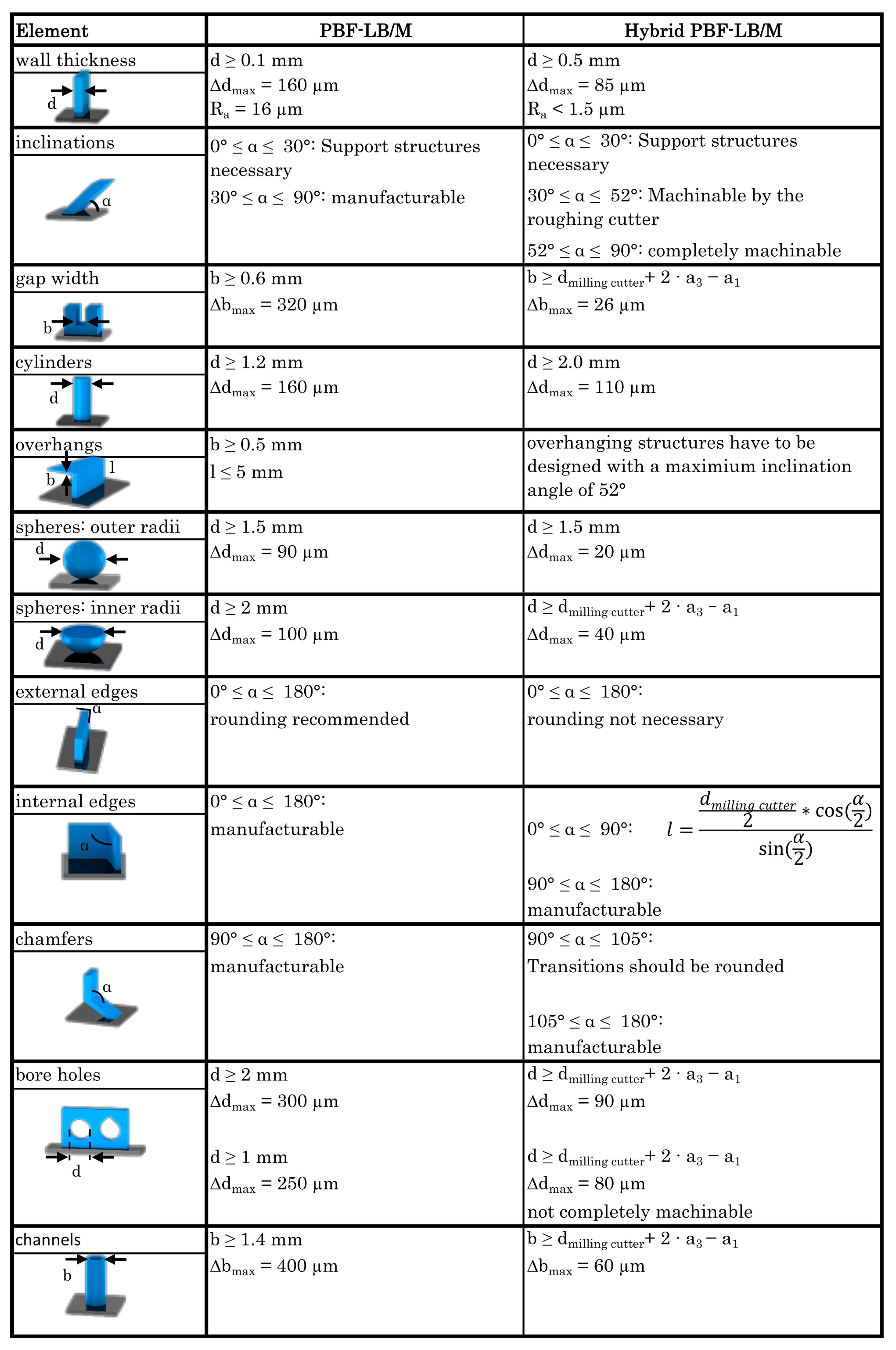
3.2. Design Guidelines
3.2.1. Minimum Wall Thickness
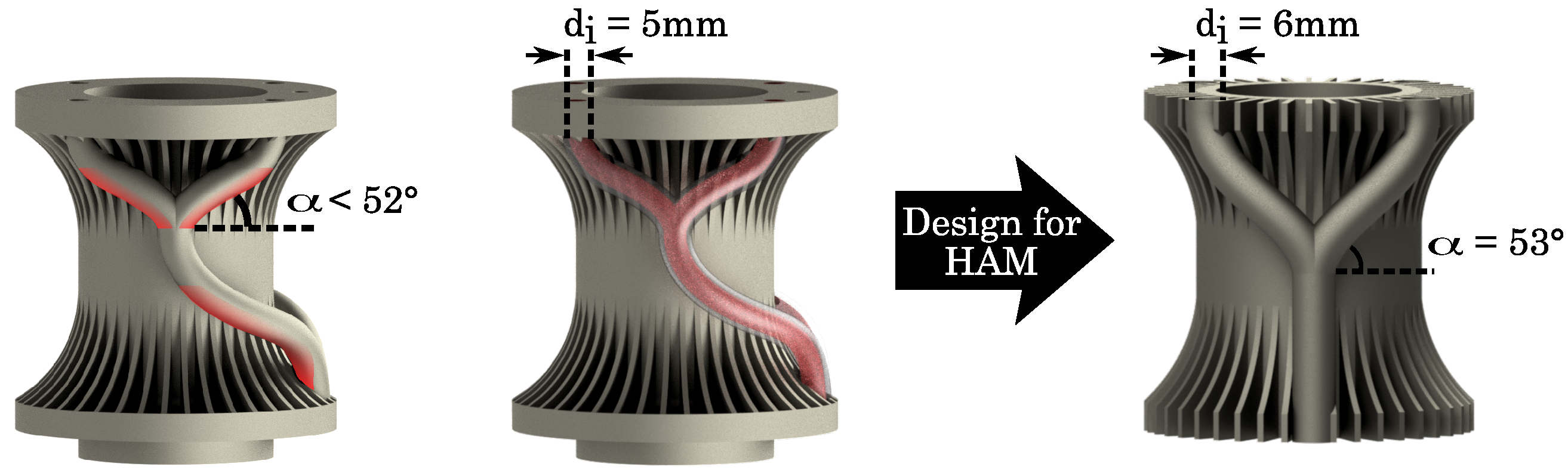
3.2.2. Inclinations
3.2.3. Gap Width
3.2.4. Extension to Further Structures
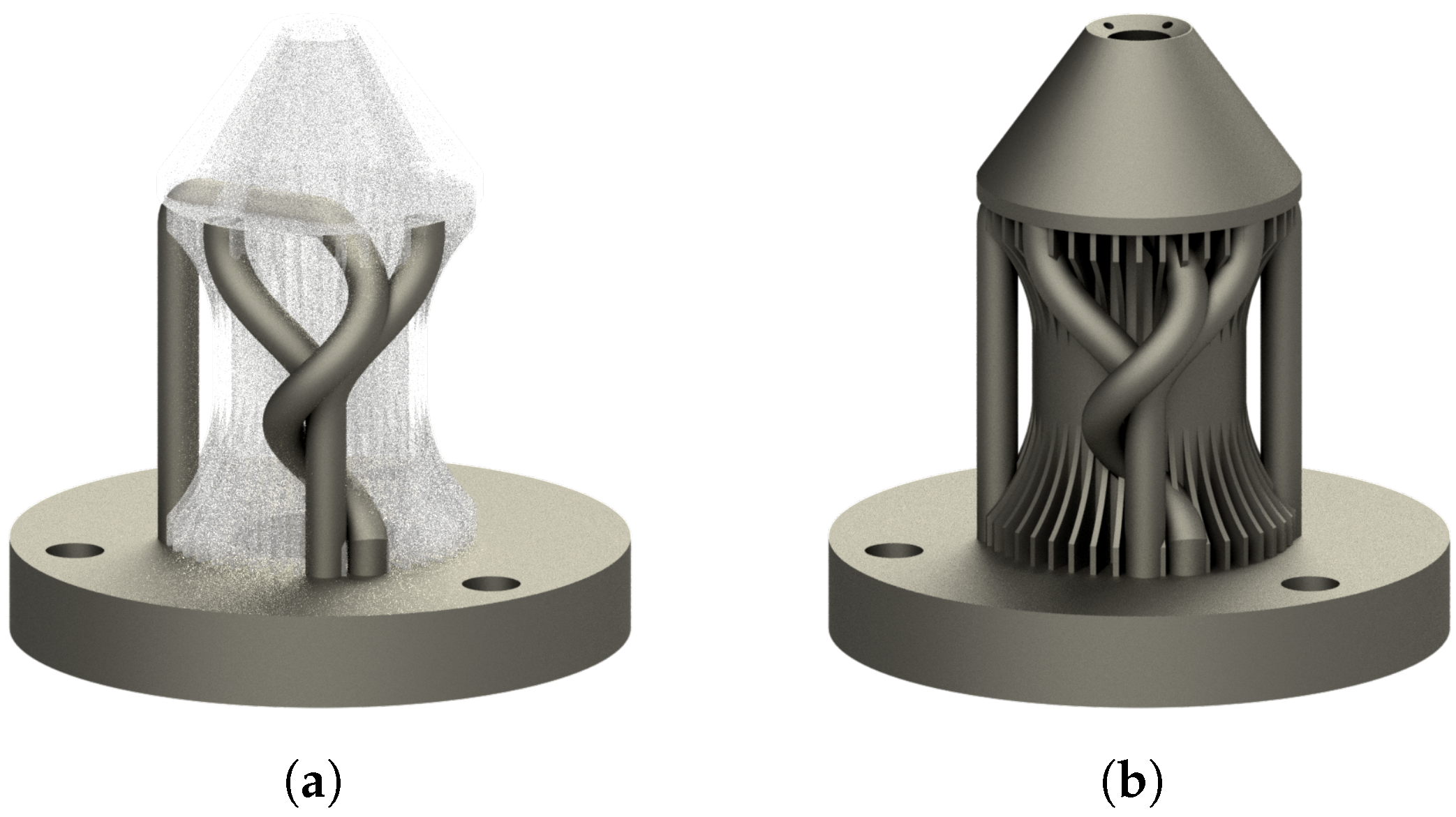
3.3. Redesign of the Powder Nozzle
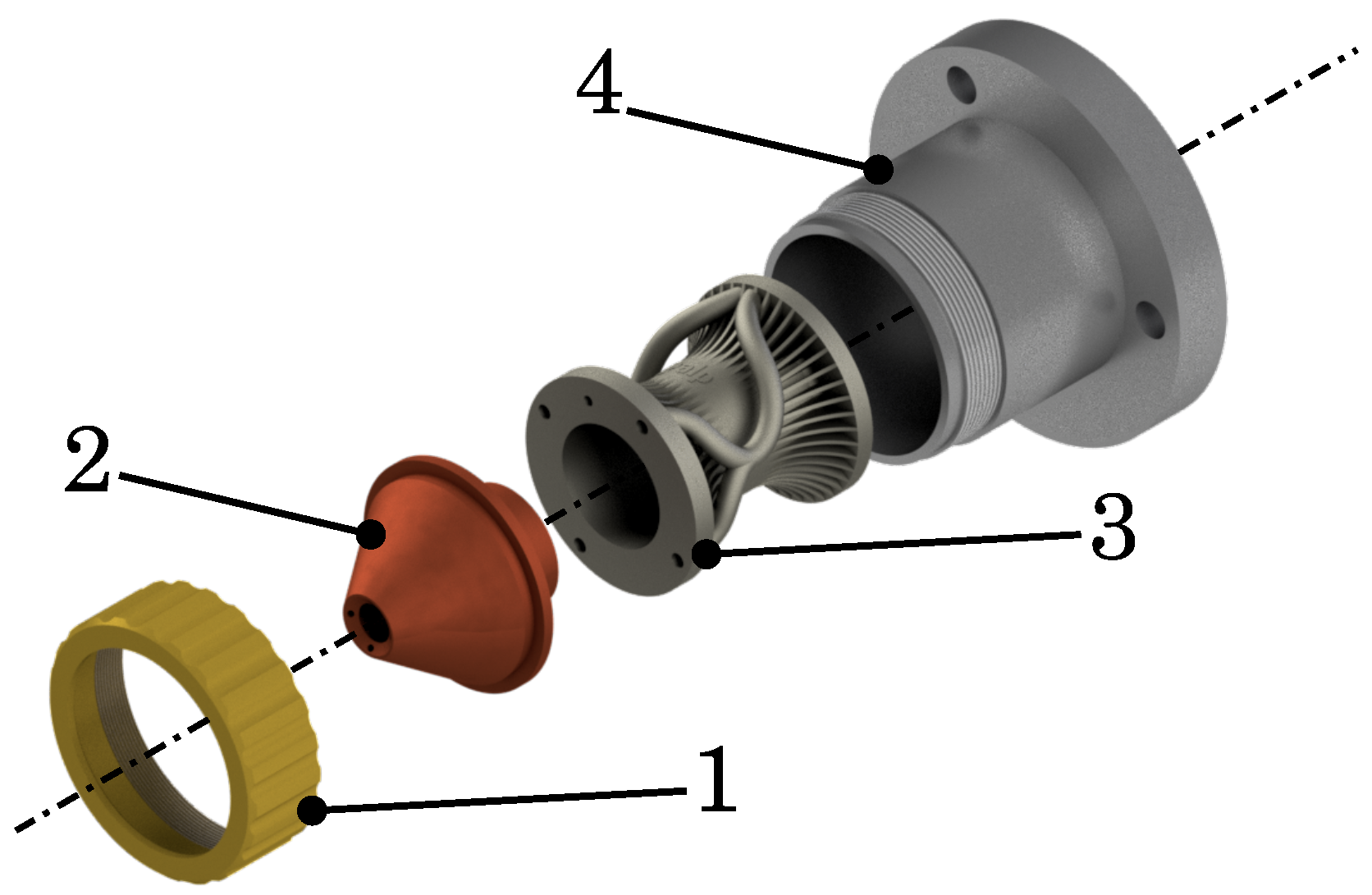
3.3.1. The Nozzle
3.3.2. Scope
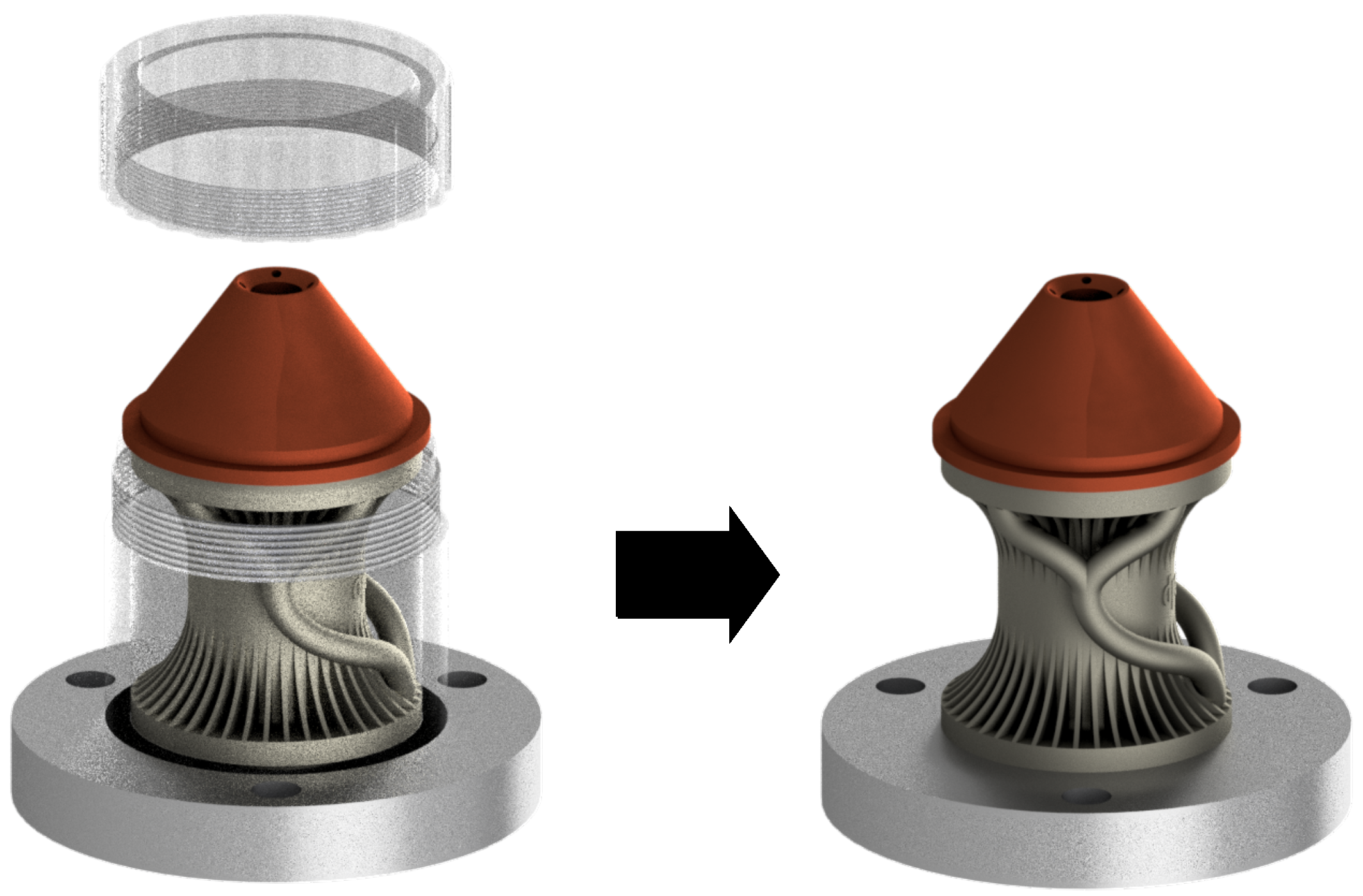
3.3.3. Orientation and Redundant Parts
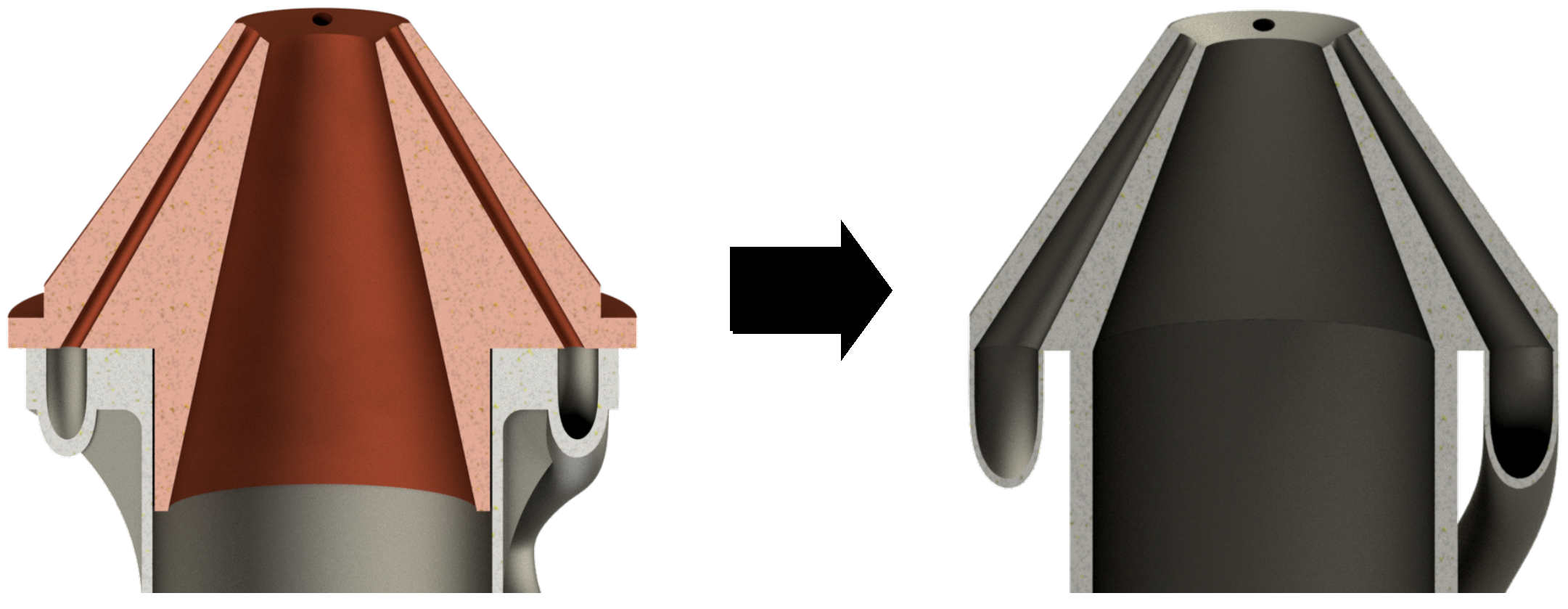
3.3.4. Analysis and Redesign
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Construction Rules
References
- Du, W.; Bai, Q.; Zhang, B. A Novel Method for Additive/Subtractive Hybrid Manufacturing of Metallic Parts. Procedia Manuf. 2016, 5, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, R.B.; Lachmayer, R. Bionic inspired infill structures for a light-weight design by using SLM. In Proceedings of the DS 84: DESIGN 2016 14th International Design Conference, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 16–19 May 2016; pp. 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Seabra, M.; Azevedo, J.; Araújo, A.; Reis, L.; Pinto, E.; Alves, N.; Santos, R.; Pedro Mortágua, J. Selective laser melting (SLM) and topology optimization for lighter aerospace componentes. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2016, 1, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortina, M.; Arrizubieta, J.I.; Ruiz, J.E.; Ukar, E.; Lamikiz, A. Latest Developments in Industrial Hybrid Machine Tools that Combine Additive and Subtractive Operations. Materials 2018, 11, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilberoglu, U.M.; Gharehpapagh, B.; Yaman, U.; Dolen, M. Current trends and research opportunities in hybrid additive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 113, 623–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.M.; Shokrani, A.; Newman, S.T.; Dhokia, V. Hybrid additive and subtractive machine tools – Research and industrial developments. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2016, 101, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, K.A.; Jones, J.B.; Wimpenny, D.I.; Jackson, M.R. A review of hybrid manufacturing. In Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication, Austin, TX, USA, 10–12 August 2015; pp. 96–108. [Google Scholar]
- Manogharan, G.; Wysk, R.A.; Harrysson, O.L. Additive manufacturing–integrated hybrid manufacturing and subtractive processes economic model and analysis. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2016, 29, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Jiang, L.J.; Baldacchini, T.; Lu, Y.F. Laser additive manufacturing using nanofabrication by integrated two-photon polymerization and multiphoton ablation. In Laser Additive Manufacturing; Brandt, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.P.; Zhang, Z.J.; Jin, X.; Xiao, M.Z.; Su, J.Z. Study of hybrid additive manufacturing based on pulse laser wire depositing and milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 88, 2237–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merklein, M.; Junker, D.; Schaub, A.; Neubauer, F. Hybrid Additive Manufacturing Technologies – An Analysis Regarding Potentials and Applications. Phys. Procedia 2016, 83, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Zhao, X.; Yu, X.; Hu, A.; Vukelic, S.; Jun, M.B.G.; Joe, H.E.; Yao, Y.L.; Shin, Y.C. Ultrafast Laser Applications in Manufacturing Processes: A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2020, 142, 031005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, G.; Missell, F.; Zeilmann, R. Surface quality in milling of hardened H13 steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 49, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafan, S.; Wanjara, P.; Gholipour, J.; Bernier, F.; Osman, M.; Sikan, F.; Molavi-Zarandi, M.; Soost, J.; Brochu, M. Evaluation of Maraging Steel Produced Using Hybrid Additive/Subtractive Manufacturing. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, D.; Götzendorfer, B.; Esen, C.; Hellmann, R. Design Rules for Hybrid Additive Manufacturing Combining Selective Laser Melting and Micromilling. Materials 2021, 14, 5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Gu, D.; Xia, M.; Cao, S.; Rong, T. Effects of laser processing parameters on thermal behavior and melting/solidification mechanism during selective laser melting of TiC/Inconel 718 composites. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 84, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yang, F.; Li, P.; Zheng, B.; Fan, H. Design and additive manufacturing of a modified face-centered cubic lattice with enhanced energy absorption capability. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2021, 47, 101358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann Becker, T.; Dimitrov, D. The achievable mechanical properties of SLM produced Maraging Steel 300 components. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2016, 22, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasa, E.; Kempen, K.; Kruth, J.P. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Maraging Steel 300 After Selective Laser Melting. In Proceedings of the International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 9–11 August 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, S.; Bai, Y.; Lin, H.; Yang, Y.; Song, C. Characteristics of typical geometrical features shaped by selective laser melting. J. Laser Appl. 2017, 29, 022007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslantas, K.; Alatrushi, L.K.H. Experimental Study on the Effect of Cutting Tool Geometry in Micro-Milling of Inconel 718. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 2327–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Gupta, M.K.; Song, Q.; Cai, W.; Zheng, T.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Pimenov, D.Y. Microstructure and machinability evaluation in micro milling of selective laser melted Inconel 718 alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.R.; Zheng, J.Y.; Kuo, P.C.; Huang, C.D.; Fung, C.P. Process Optimization of Inconel 718 Alloy Produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Metals 2022, 12, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbaa, M.; Mekhiel, S.; Elbestawi, M.; McIsaac, J. On selective laser melting of Inconel 718: Densification, surface roughness, and residual stresses. Mater. Des. 2020, 193, 108818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, D.; Hornung, S.; Esen, C.; Hellmann, R. Surface roughness optimization of hybrid PBF-LB/M-built Inconel 718 using in situ high-speed milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 132, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüst, P.; Edelmann, A.; Hellmann, R. Areal Surface Roughness Optimization of Maraging Steel Parts Produced by Hybrid Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2020, 13, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, D.; Esen, C.; Hellmann, R. Static and Dynamic Mechanical Behaviour of Hybrid-PBF-LB/M-Built and Hot Isostatic Pressed Lattice Structures. Materials 2023, 16, 3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez de Lacalle, L.N.; Angulo, C.; Lamikiz, A.; Sanchez, J.A. Experimental and numerical investigation of the effect of spray cutting fluids in high speed milling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 172, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh Kumar Reddy, N.; Venkateswara Rao, P. Experimental investigation to study the effect of solid lubricants on cutting forces and surface quality in end milling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Shrestha, S.; Chou, K. Stress and deformation evaluations of scanning strategy effect in selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2016, 12, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, M.; Leary, M.; Sun, S.; Vcelka, M.; Shidid, D.; Brandt, M. Deformation and failure behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V lattice structures manufactured by selective laser melting (SLM). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 84, 1391–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelkova, J.; Vanmunster, L.; Haitjema, H.; van Hooreweder, B. Texture of inclined up-facing surfaces in laser powder bed fusion of metals. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 42, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutiri, I.; Pessard, E.; Peyre, P.; Amlou, O.; de Terris, T. Influence of SLM process parameters on the surface finish, porosity rate and fatigue behavior of as-built Inconel 625 parts. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 255, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, M.; Mazur, M.; Williams, H.; Yang, E.; Alghamdi, A.; Lozanovski, B.; Zhang, X.; Shidid, D.; Farahbod-Sternahl, L.; Witt, G.; et al. Inconel 625 lattice structures manufactured by selective laser melting (SLM): Mechanical properties, deformation and failure modes. Mater. Des. 2018, 157, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, G.A.; Zimmer, D. Design for Additive Manufacturing—Element transitions and aggregated structures. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2014, 7, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, I.; Rosen, D.; Stucker, B.; Khorasani, M. (Eds.) Additive Manufacturing Technologies, 3rd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, C.Y.; Chua, C.K.; Dong, Z.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, D.Q.; Loh, L.E.; Sing, S.L. Review of selective laser melting: Materials and applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 041101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13322-2; Particle Size Analysis-Image Analysis Methods-Dynamic Image Analysis Methods. International Organization for Standardization: London, UK, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Farah, J.; Akram, J.; Teng, C.; Ginn, J.; Misra, M. Influence of laser processing parameters on porosity in Inconel 718 during additive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, J.; Herzog, D.; Emmelmann, C. Design guidelines for laser additive manufacturing of lightweight structures in TiAl6V4. J. Laser Appl. 2015, 27, S14001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Ko, H.; Sprock, T.; Bernstein, W.Z.; Kwon, S. Part decomposition and evaluation based on standard design guidelines for additive manufacturability and assemblability. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 37, 101702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, G.A.O.; Zimmer, D. On design for additive manufacturing: Evaluating geometrical limitations. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2015, 21, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Laser Power PL/W | Scan Speed vs/(mm/min) | Hatch Distance dh/mm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area | 320 | 700 | 0.14 |
| Contour | 320 | 1400 | - |
| Support | 320 | 700 | 0.12 |
| Infeed an/μm | Z-Pitch ae,z/μm | Spindle Speed n/(1/min) | Feed Rate vc/(mm/min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roughing | 110 | 150 | 4800 | 240 |
| Semi-finishing | 110 | 100 | 4800 | 240 |
| Finishing | 30 | 80 | 9600 | 240 |
| Element | Ni | Cr | Nb | Mo | Ti | Al | C | Mn | Si | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt% | 50–55 | 17–21 | 4.8–5.5 | 2.8–3.3 | 0.7–1.2 | 0.2–0.8 | <0.1 | <0.4 | <0.4 | balance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sommer, D.; Hornung, S.; Esen, C.; Hellmann, R. Design Guide for Hybrid-Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718 Combining PBF-LB/M and In Situ High-Speed Milling. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9030088
Sommer D, Hornung S, Esen C, Hellmann R. Design Guide for Hybrid-Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718 Combining PBF-LB/M and In Situ High-Speed Milling. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2025; 9(3):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9030088
Chicago/Turabian StyleSommer, David, Simon Hornung, Cemal Esen, and Ralf Hellmann. 2025. "Design Guide for Hybrid-Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718 Combining PBF-LB/M and In Situ High-Speed Milling" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 9, no. 3: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9030088
APA StyleSommer, D., Hornung, S., Esen, C., & Hellmann, R. (2025). Design Guide for Hybrid-Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718 Combining PBF-LB/M and In Situ High-Speed Milling. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 9(3), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9030088







