Using 3D Density-Gradient Vectors in Evolutionary Topology Optimization to Find the Build Direction for Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Topology Optimization
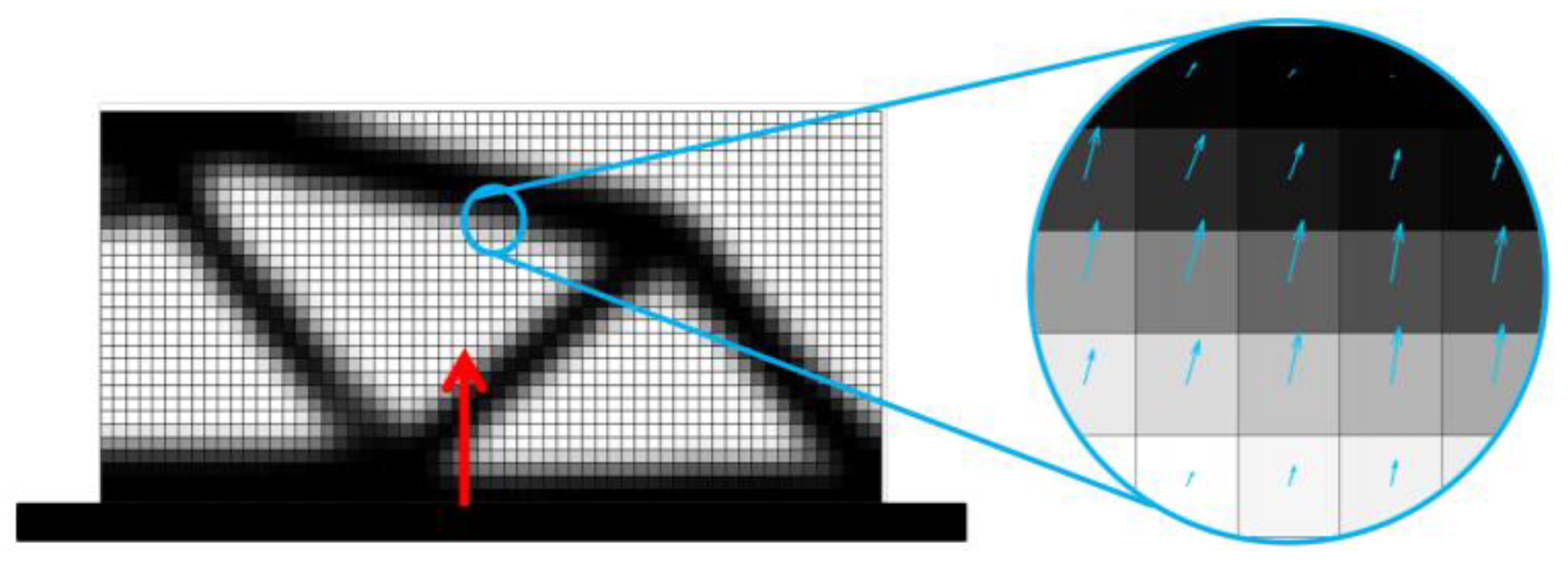
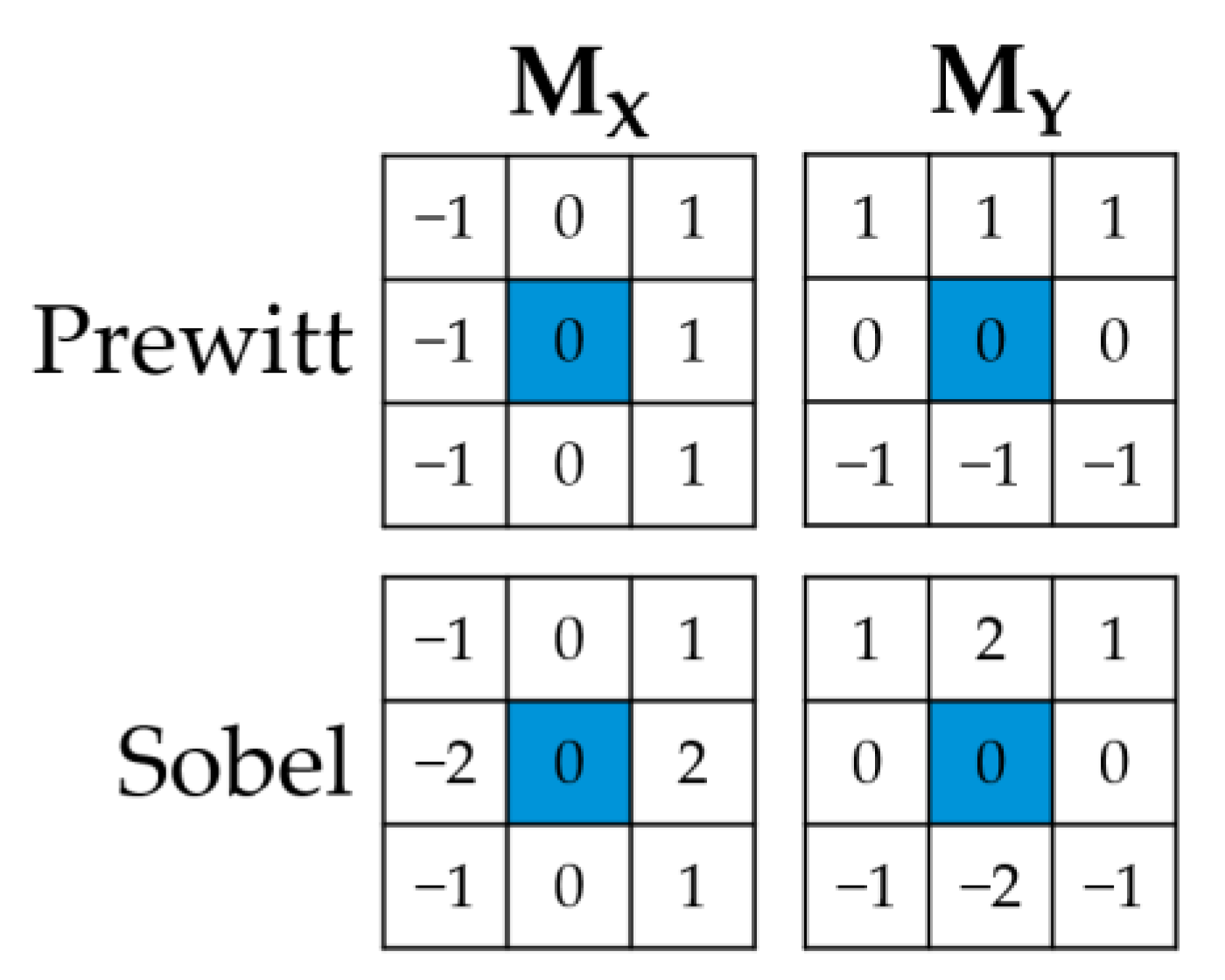
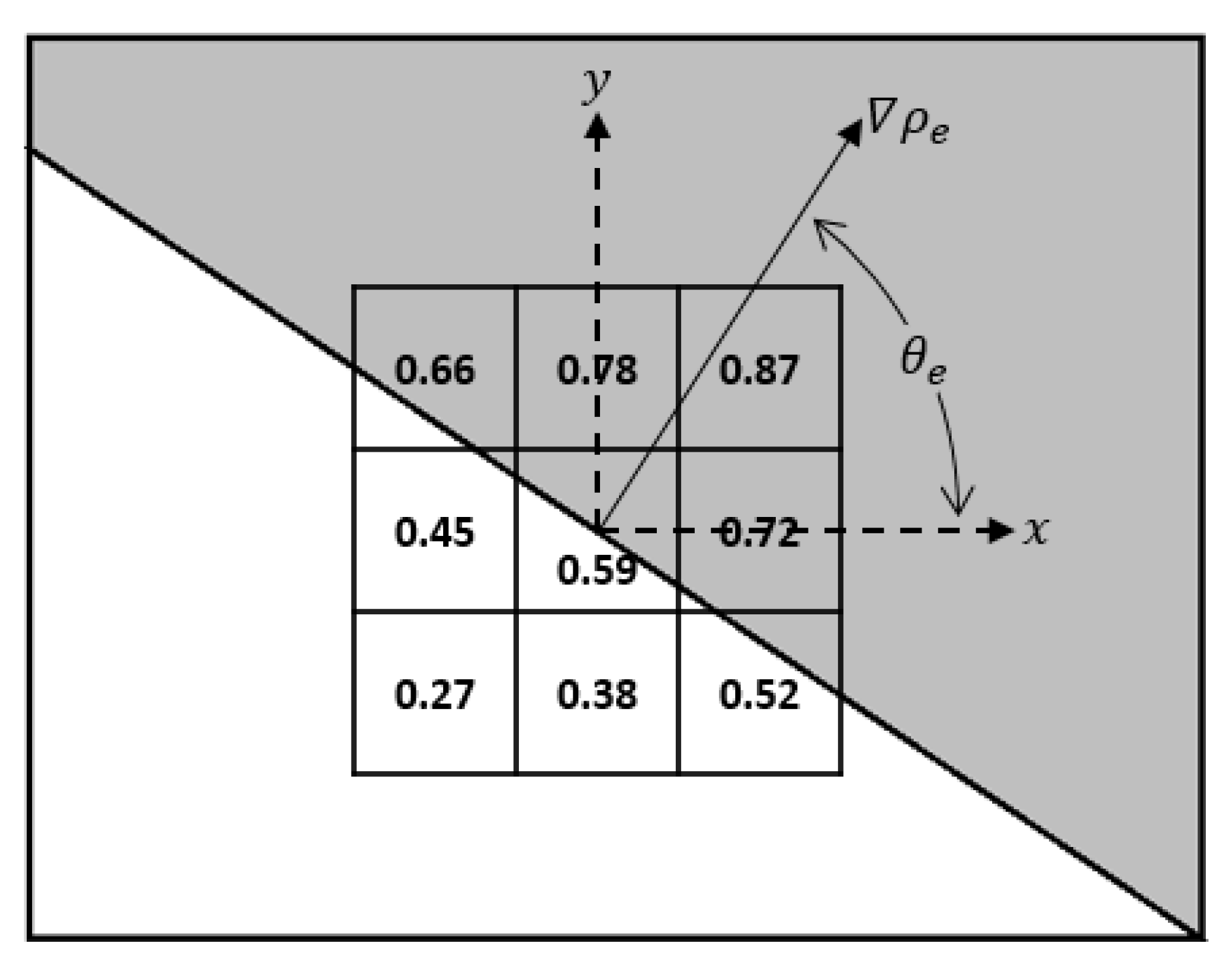
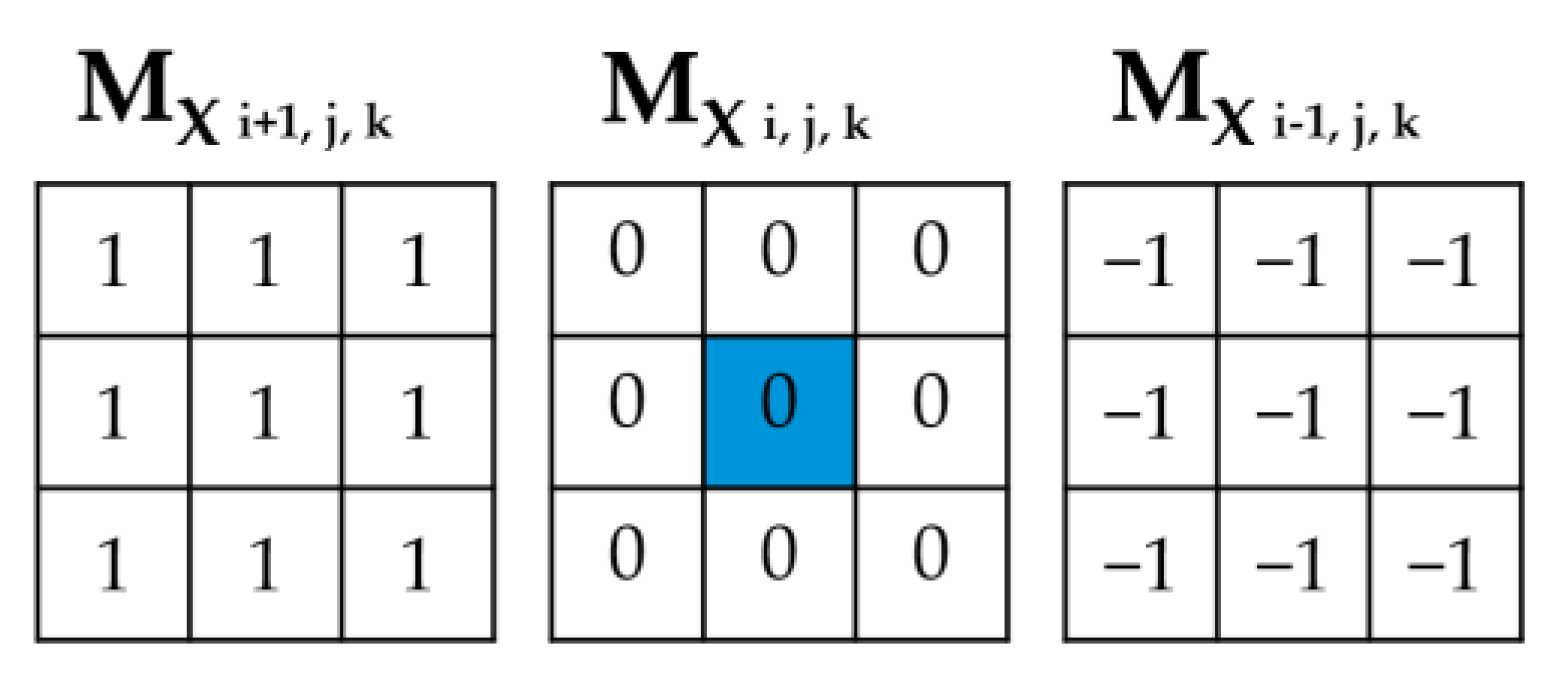
2.2. Two-Dimensional Density Gradient
2.3. Limitations of the Gradient Vector’s Ability to Approximate Overhanging Angles
2.4. Support Slimming
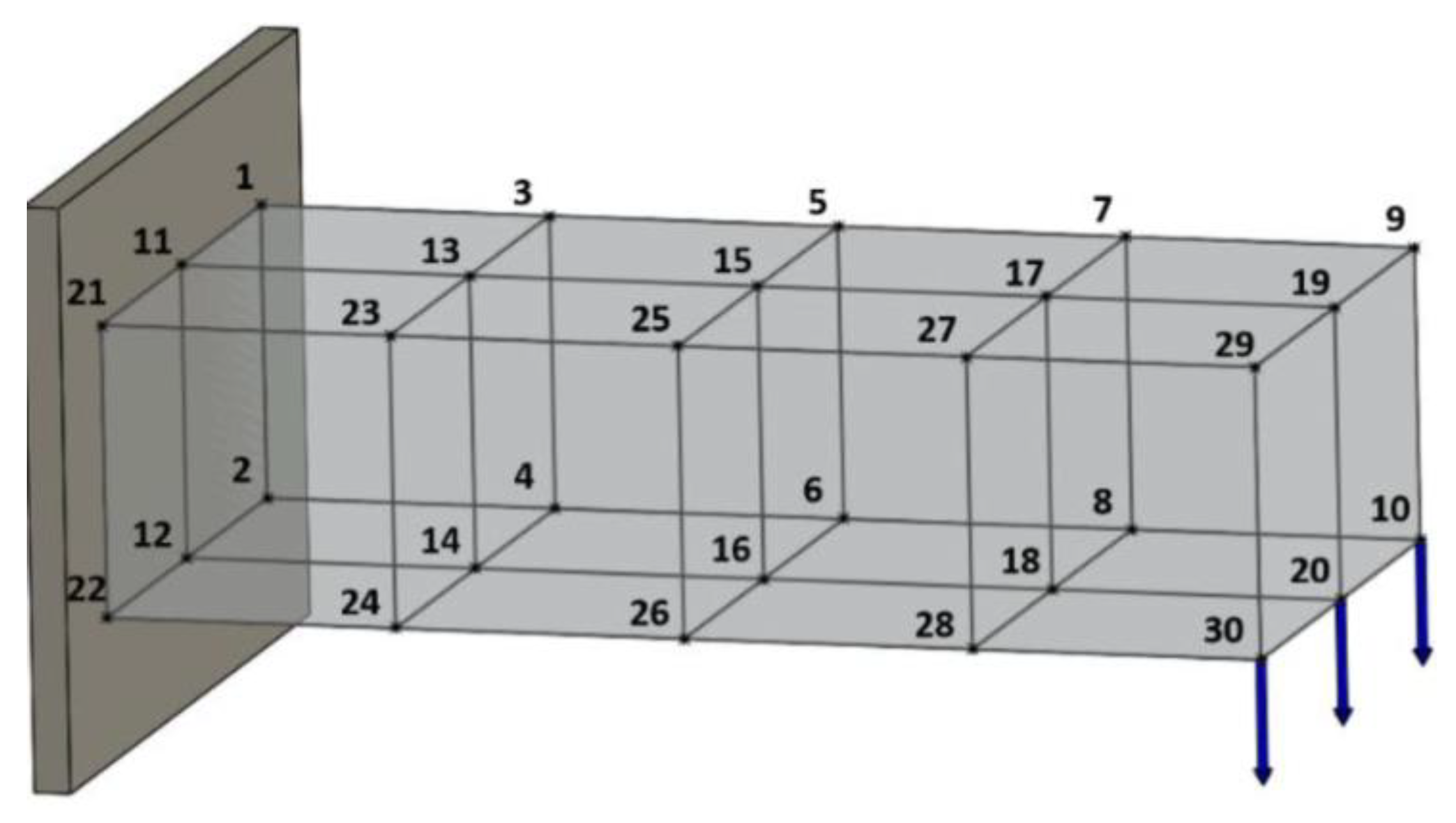
3. Developed Methodology
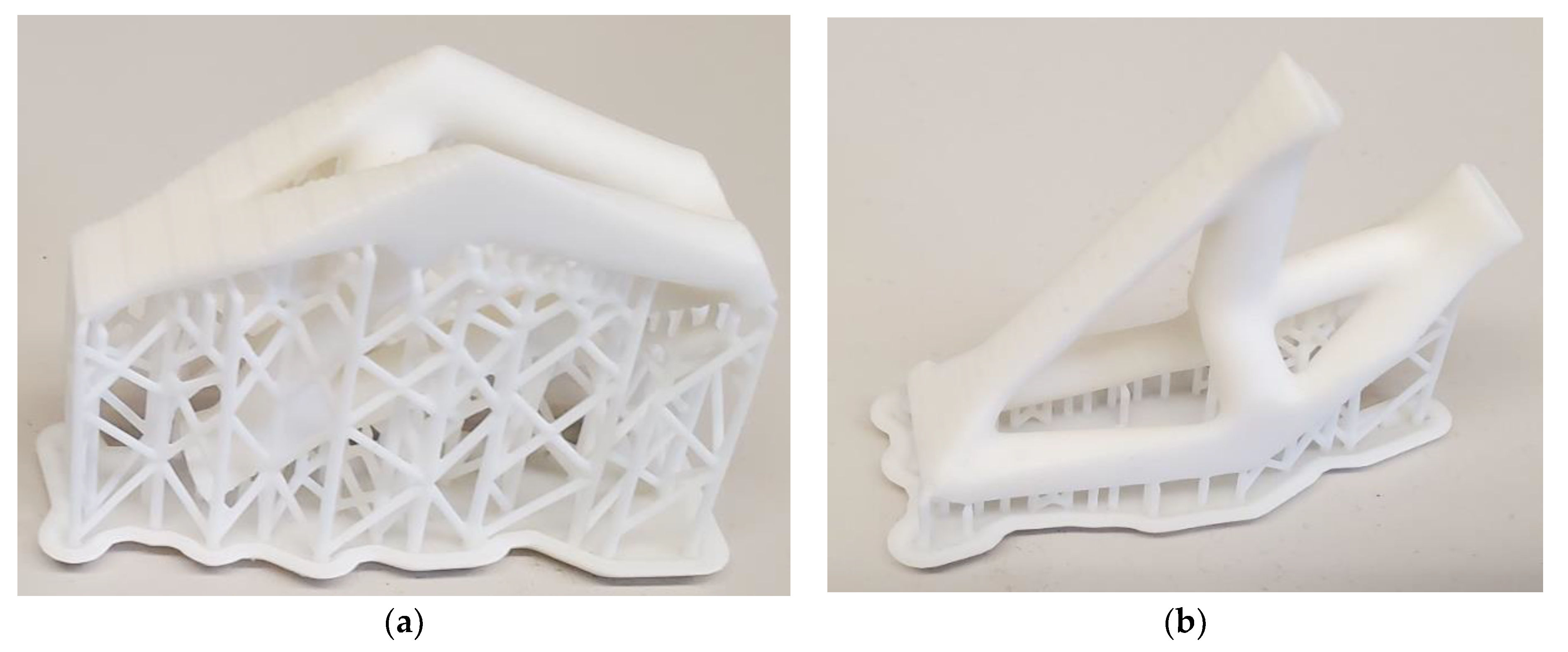
4. Implementation and Results
5. Replication of the Results
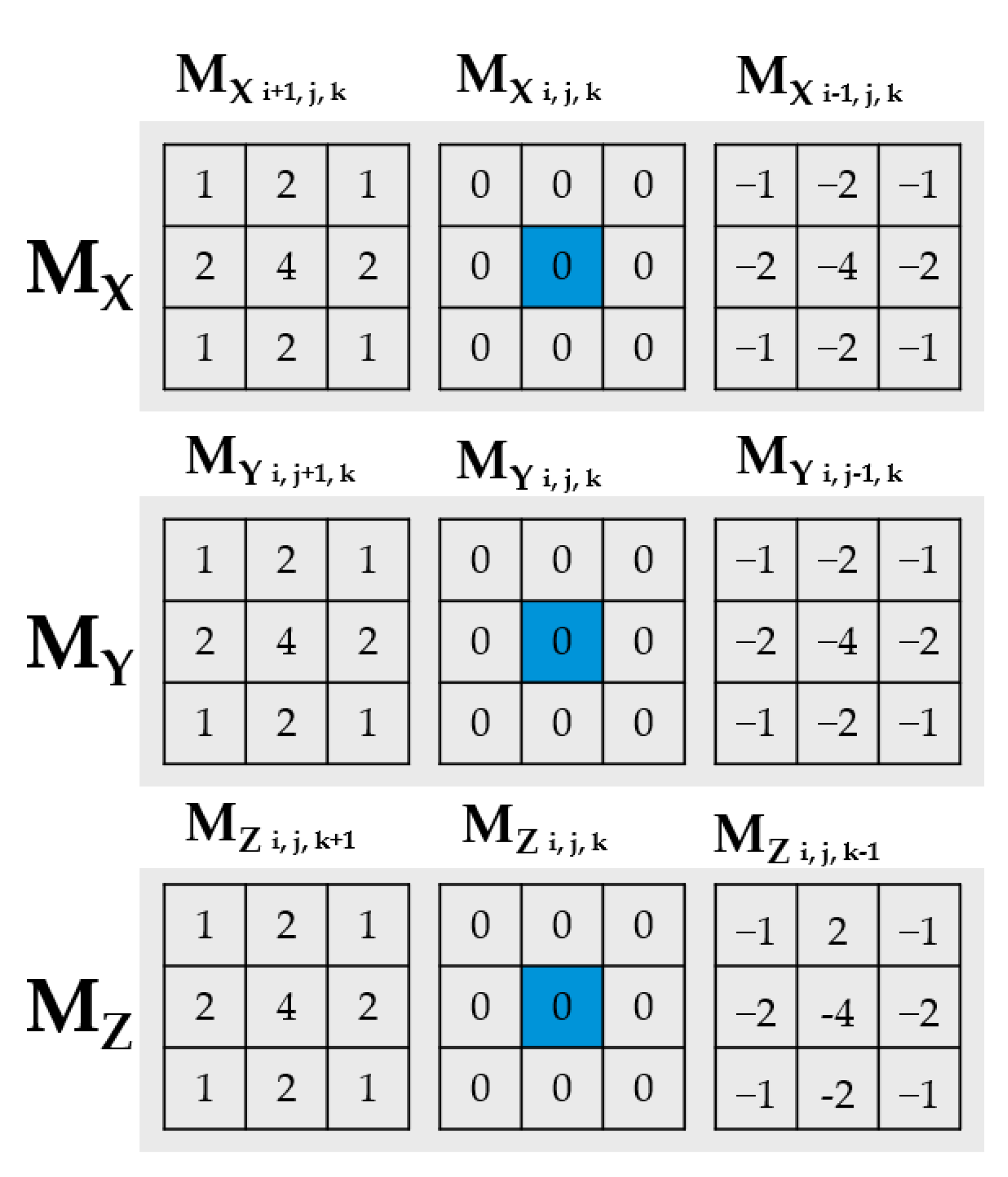
6. Filter Approach for Density Gradient Vectors
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. MATLAB Program Density Gradient


References
- Huang, X.; Xie, M. Evolutionary Topology Optimization of Continuum Structures: Methods and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund, O.; Maute, K. Topology optimization approaches. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 2013, 48, 1031–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, E.; Iuliano, L.; Marchiandi, G.; Minetola, P.; Salmi, A.; Bassoli, E.; Denti, L.; Gatto, A. Additive manufacturing as a cost-effective way to produce metal parts. In High Value Manufacturing: Advanced Research in Virtual and Rapid Prototyping, Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advanced Research and Rapid Prototyping, VR@ P, Leiria, Portugal, 1–5 October 2013; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; Volume 2013, pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, T.R.; Laherta, R.D.; Silva, E.C.N.; Tsuzuki, M.D.S.G.; Martins, T.D.C.; Barari, A.; Wood, I. Topologically optimized diesel engine support manufactured with additive manufacturing. In IFAC Symposium on Information Control Problems in Manufacturing; Elsevier: Bergamo, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Doubrovski, Z.; Verlinden, J.C.; Geraedts, J.M. Optimal design for additive manufacturing: Opportunities and challenges. In Proceedings of the ASME 2011 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 28–31 August 2011; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 635–646. [Google Scholar]
- Brackett, D.; Ashcroft, I.; Hague, R. Topology optimization for additive manufacturing. In Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 8–10 August 2011; Volume 1, pp. 348–362. [Google Scholar]
- Lalehpour, A.; Barari, A. Post processing for Fused Deposition Modeling Parts with Acetone Vapour Bath. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalehpour, A.; Barari, A. A more accurate analytical formulation of surface roughness in layer-based additive manufacturing to enhance the product’s precision. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 3793–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikder, S.; Barari, A.; Kishawy, H.A. Effect of adaptive slicing on surface integrity in additive manufacturing. In Proceedings of the ASME 2014 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Buffalo, NY, USA, 17–20 August 2014; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. V01AT02A052. [Google Scholar]
- Sikder, S.; Barari, A.; Kishawy, H.A. Global adaptive slicing of NURBS based sculptured surface for minimum texture error in rapid prototyping. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2015, 21, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, H.; Kishawy, H.; Barari, A. Adaptive variable layer thickness and perimetral offset planning for layer-based additive manufacturing processes. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2021, 34, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Angelo, L.; Di Stefano, P.; Guardiani, E. Search for the Optimal Build Direction in Additive Manufacturing Technologies: A Review. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2020, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P. Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct. Optim. 1989, 1, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendøse, M.P.; Sigmund, O. Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; ISBN 3-540-42992-1. [Google Scholar]
- Barari, A.; ElMaraghy, H.A.; Orban, P. NURBS representation of actual machined surfaces. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2009, 22, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barari, A.; ElMaraghy, H.A.; Knopf, G.K. Evaluation of geometric deviations in sculptured surfaces using probability density estimation. In Models for Computer Aided Tolerancing in Design and Manufacturing: Selected Conference Papers from the 9th CIRP International Seminar on Computer-Aided Tolerancing; Springer Netherlands: Tempe, AZ, USA, 2007; pp. 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Barari, A.; Mordo, S. Effect of sampling strategy on uncertainty and precision of flatness inspection studied by dynamic minimum deviation zone evaluation. Int. J. Metrol. Qual. Eng. 2013, 4, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, H.; Berry, C.; Barari, A. A digital twin for integrated inspection system in digital manufacturing. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Yi, Z.; Su, X. Research on the fabricating quality optimization of the overhanging surface in SLM process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 65, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calignano, F. Design optimization of supports for overhanging structures in aluminum and titanium alloys by selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, W. A review of topology optimization for additive manufacturing: Status and challenges. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, M.; Merli, L.; Torti, F.; Mazur, M.; Brandt, M. Optimal topology for additive manufacture: A method for enabling additive manufacture of support-free optimal structures. Mater. Des. 2014, 63, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, A.M. Overhang Constraint in Topology Optimisation for Additive Manufacturing: A Density Gradient Based Approach; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Garaigordobil, A.; Ansola, R.; Santamaría, J.; de Bustos, I.F. A new overhang constraint for topology optimization of self-supporting structures in additive manufacturing. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2018, 58, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mass, Y.; Amir, O. Topology optimization for additive manufacturing: Accounting for overhang limitations using a virtual skeleton. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 18, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X. Undercut and overhang angle control in topology optimization: A density gradient based integral approach. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2017, 111, 247–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, D.; Barari, A. Overhanging Feature Analysis for the Additive Manufacturing of Topology Optimized Structures. In Proceedings of the ASME 2018 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 26–29 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, L.G.; Stockman, G.C. Computer Vision; Pearson: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jamiolahmadi, S.; Barari, A. Surface topography of additive manufacturing parts using a finite difference approach. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2014, 136, 061009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, H.; Barari, A.; Kishawy, H. Using Multistep Methods in Slicing 2 ½ Dimensional Parametric Surfaces for Additive Manufacturing Applications. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, H.; Barari, A.; Kishawy, H. An efficient methodology for slicing NURBS surfaces using multi-step methods. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 95, 3111–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, E.; Clausen, A.; Schevenels, M.; Lazarov, B.S.; Sigmund, O. Efficient topology optimization in MATLAB using 88 lines of code. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 2011, 43, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Tovar, A. An efficient 3D topology optimization code written in Matlab. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 2014, 50, 1175–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietz, A. Sufficiency of a finite exponent in SIMP (power law) methods. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 2001, 21, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Steven, G.P.; Xie, Y.M. A simple checkerboard suppression algorithm for evolutionary structural optimization. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 2001, 22, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gaynor, A.T.; Chen, S.; Kang, Z.; Suresh, K.; Takezawa, A.; Li, L.; Kato, J.; Tang, J.; Wang, C.C.; et al. Current and future trends in topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 2018, 57, 2457–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, M.J.; Querin, O.M.; Toropov, V. Rules, Precursors and Parameterisation Methodologies for Topology Optimised Structural Designs Realised through Additive Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 10th AIAA Multidisciplinary Design Optimization Conference, National Harbor, MD, USA, 13–17 January 2014; p. 0635. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, H.D.; Cherry, J.A.; Jonnalagadda, S.; Ewing, D.; Sienz, J. Part orientation optimisation for the additive layer manufacture of metal components. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 86, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, D. Integrated Topology Optimization Design and Process Planning for Additive Manufacturing; University of Ontario Institute of Technology: Oshawa, ON, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]


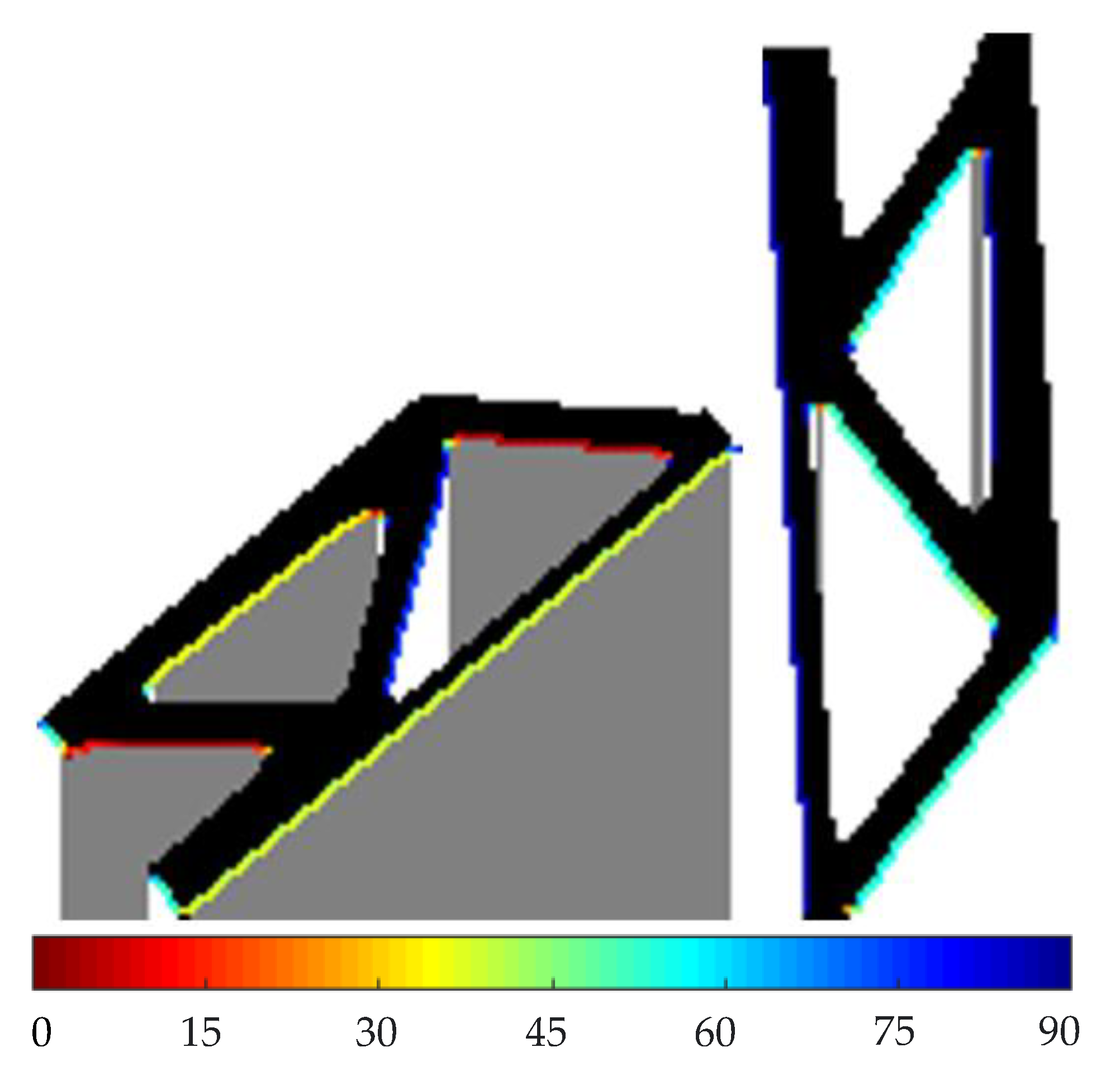

| Structural Design Problem and the Resulting Topology | Part Orientation Optimization Landscape | |
|---|---|---|
| Top. Opt. Software: Nelx: 70 Nely: 35 Nelz: 70 Two planes of symmetry |  |  |
| Top. Opt. Software: ANSYS 18.2 Nelx: 45 Nely: 67 Nelz: 70 One plane of symmetry |  |  |
| Top. Opt. Software: ANSYS 18.2 Nelx: 70 Nely: 35 Nelz: 70 No symmetry | 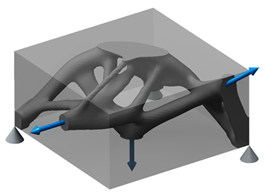 | 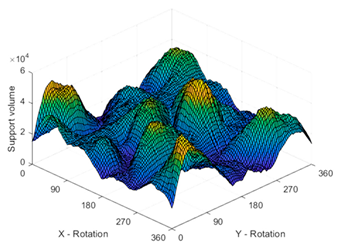 |
| Minimum RSV Orientation | Maximum RSV Orientation | Surface Overhang Angle w.r.t the Build Platform Visualization @ min Support Orientation |
|---|---|---|
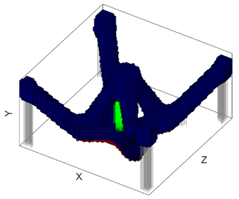 | 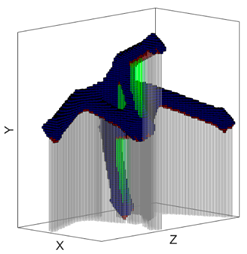 |  |
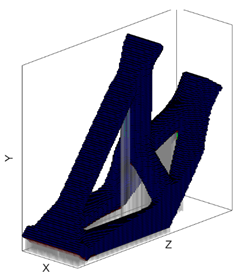 | 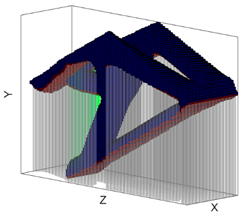 | 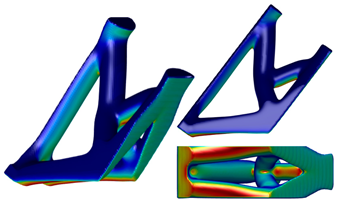 |
 | 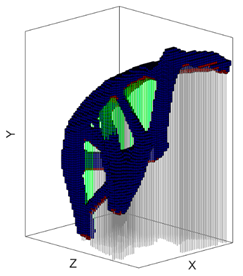 |  |
| Case Study | Theoretical Weight Difference between the Original Build Direction an Optimal Build Direction | Experimental Weight Difference between the Original Build Direction an Optimal Build Direction | Difference between Theoretical and Experimental Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Michell | 174.32% | 171.35% | 1.7% |
| Cantilever | 170.70% | 169.8% | 0.5% |
| Asymmetric | 148.02% | 145.7% | 1.5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bender, D.; Barari, A. Using 3D Density-Gradient Vectors in Evolutionary Topology Optimization to Find the Build Direction for Additive Manufacturing. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7010046
Bender D, Barari A. Using 3D Density-Gradient Vectors in Evolutionary Topology Optimization to Find the Build Direction for Additive Manufacturing. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2023; 7(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7010046
Chicago/Turabian StyleBender, Dylan, and Ahmad Barari. 2023. "Using 3D Density-Gradient Vectors in Evolutionary Topology Optimization to Find the Build Direction for Additive Manufacturing" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 7, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7010046
APA StyleBender, D., & Barari, A. (2023). Using 3D Density-Gradient Vectors in Evolutionary Topology Optimization to Find the Build Direction for Additive Manufacturing. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 7(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7010046







