The Performance of Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) Tools Machined by Abrasive Grinding and Electrical Discharge Grinding (EDG) in High-Speed Turning
Abstract
1. Introduction
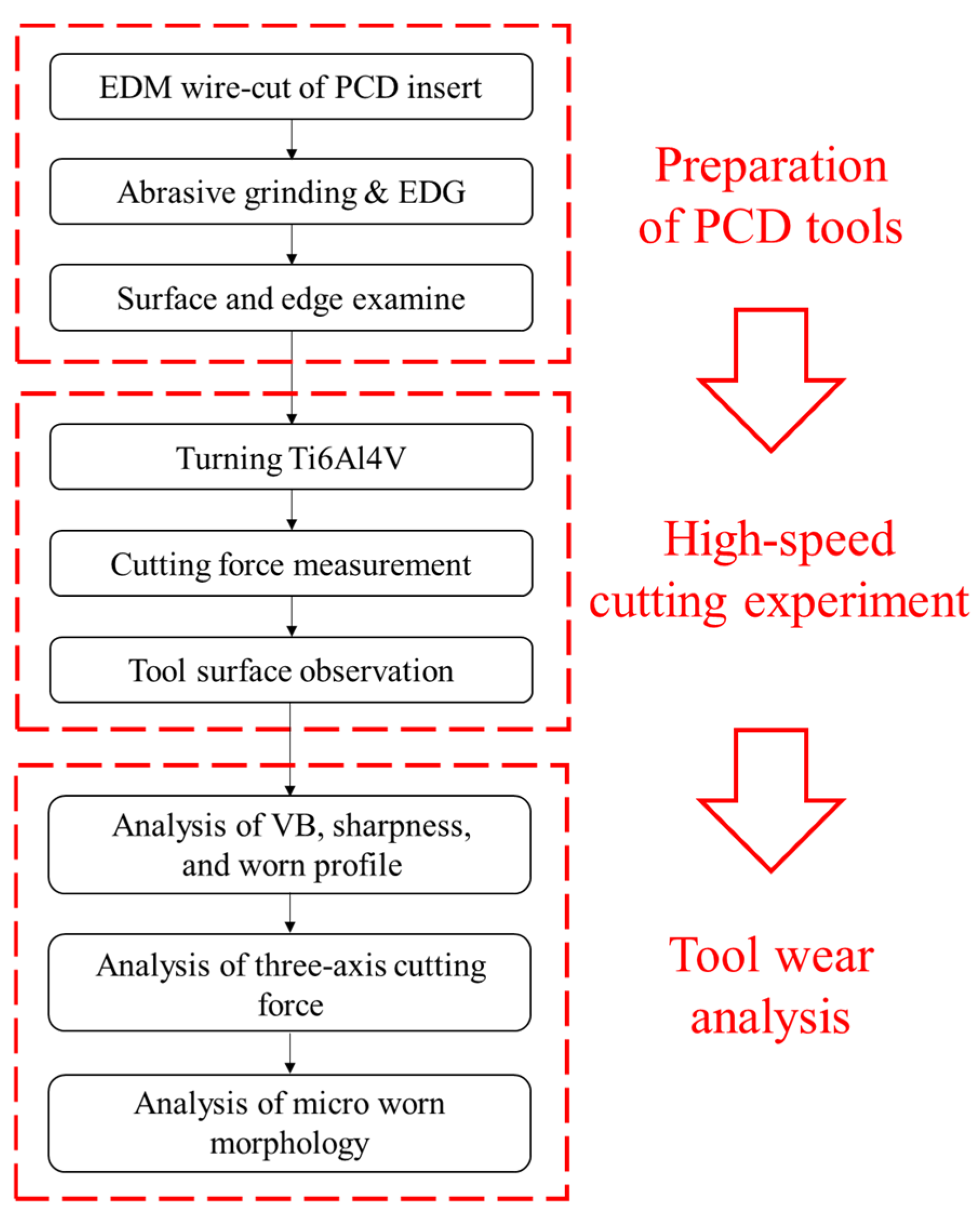
2. Experiment and Methodology
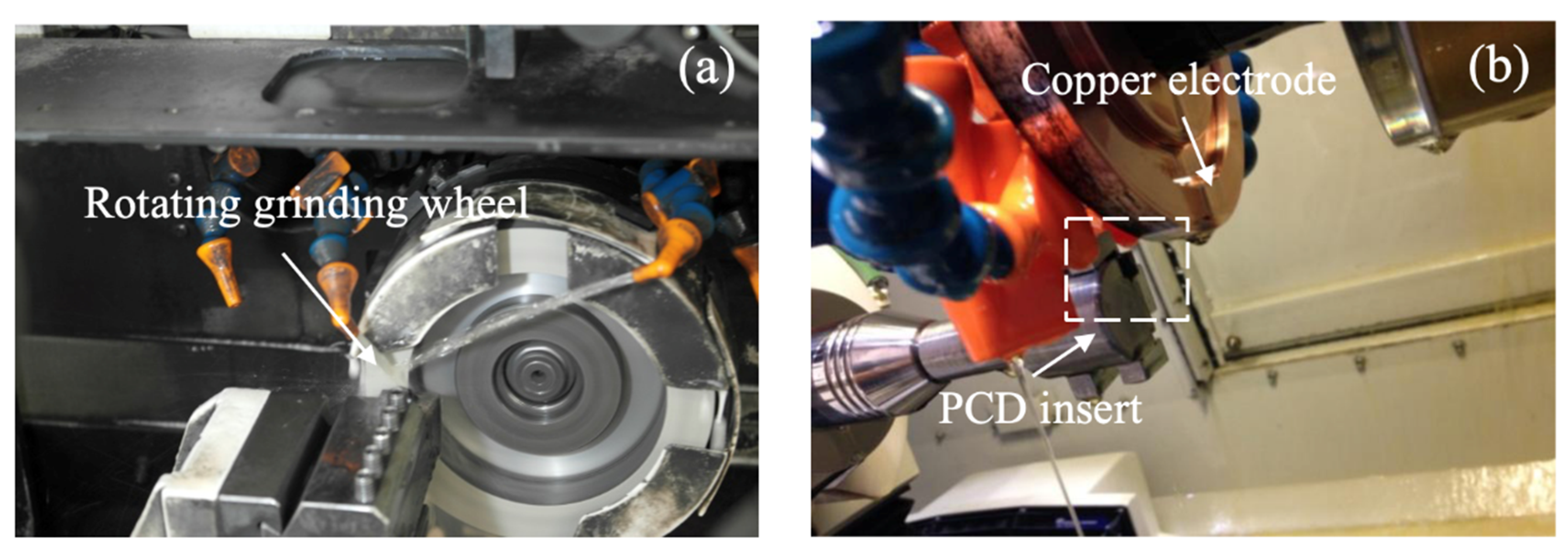
2.1. Preparation of Cutting Tools
2.2. Turning Experiments
- Z axis: 0.56 mv/N.
- X and Y axes: 2.25 mv/N.
2.3. Wear Analysis
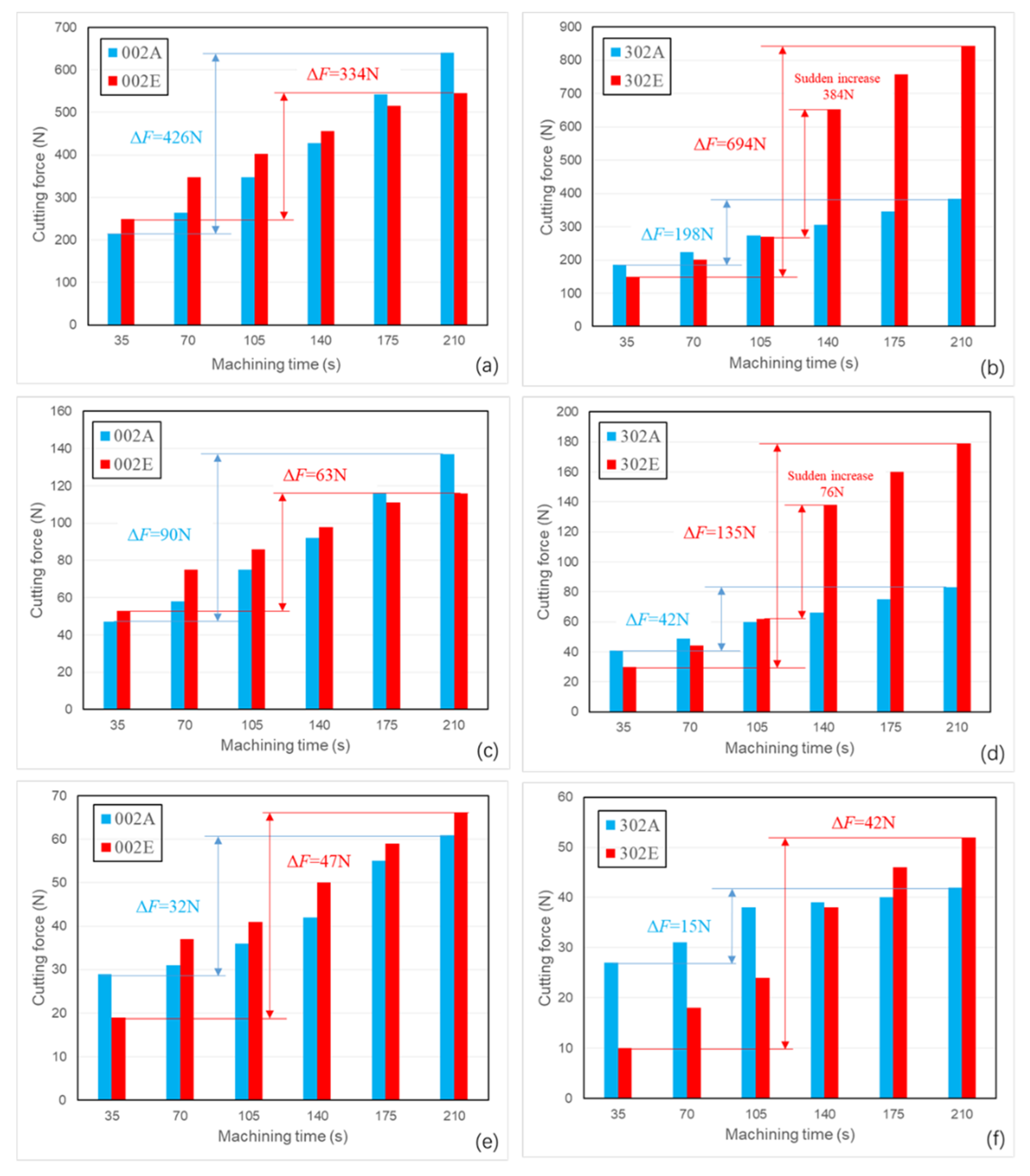
3. Results
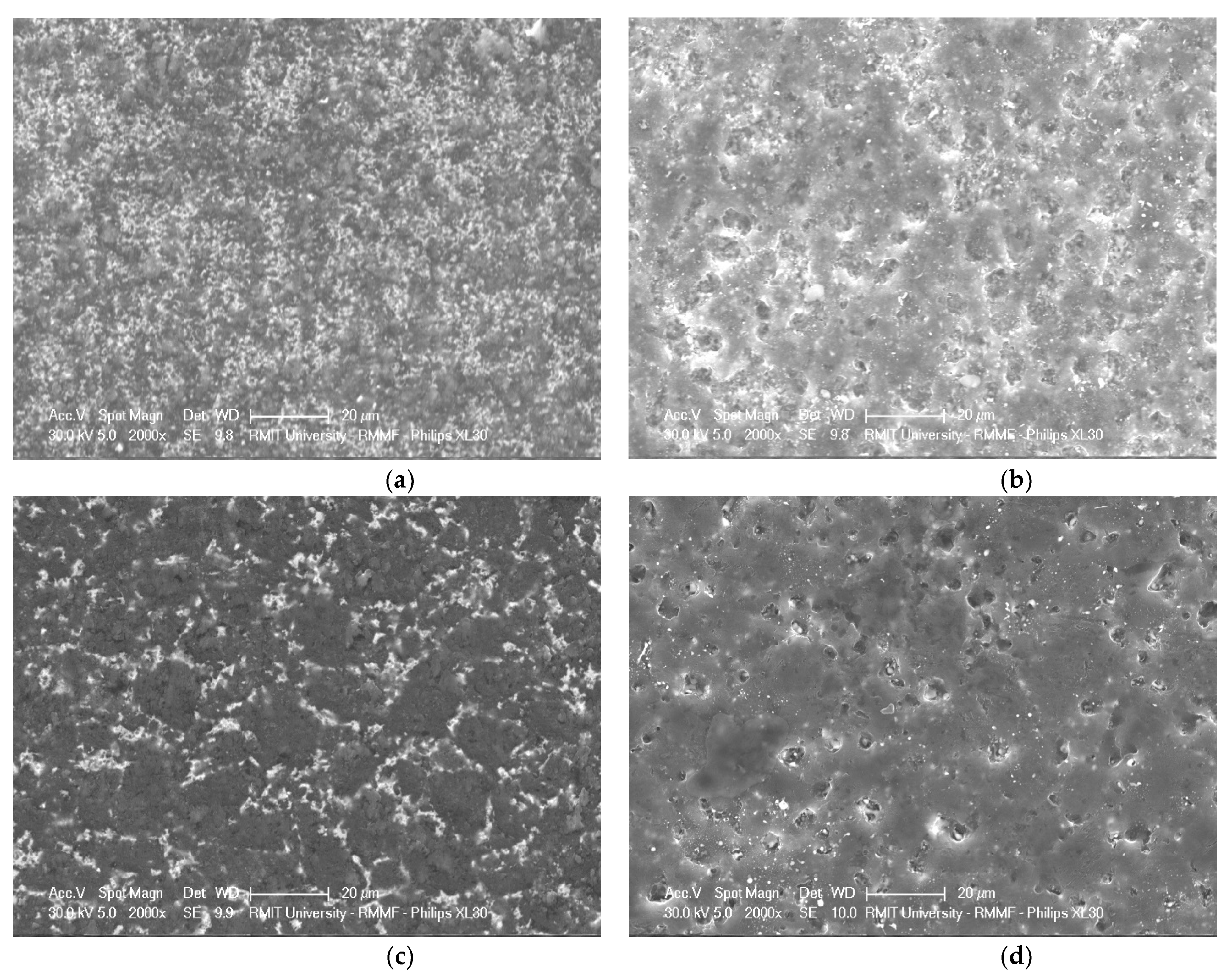
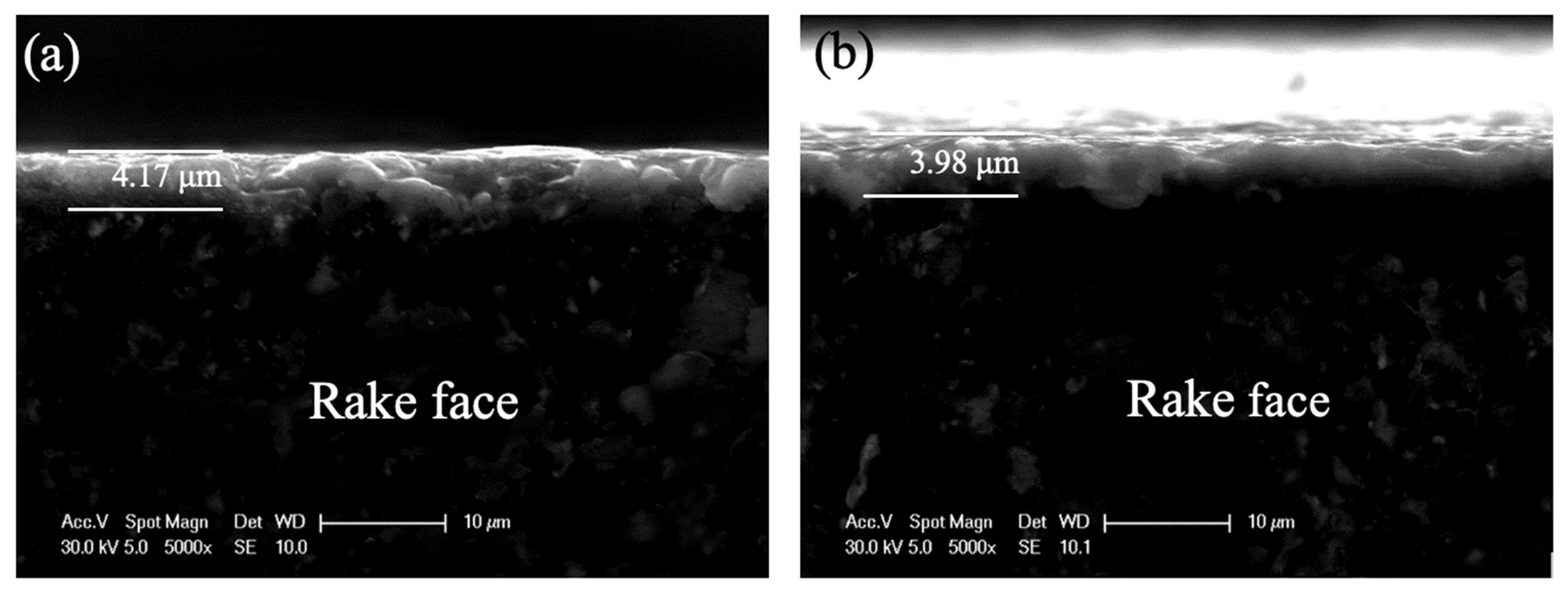
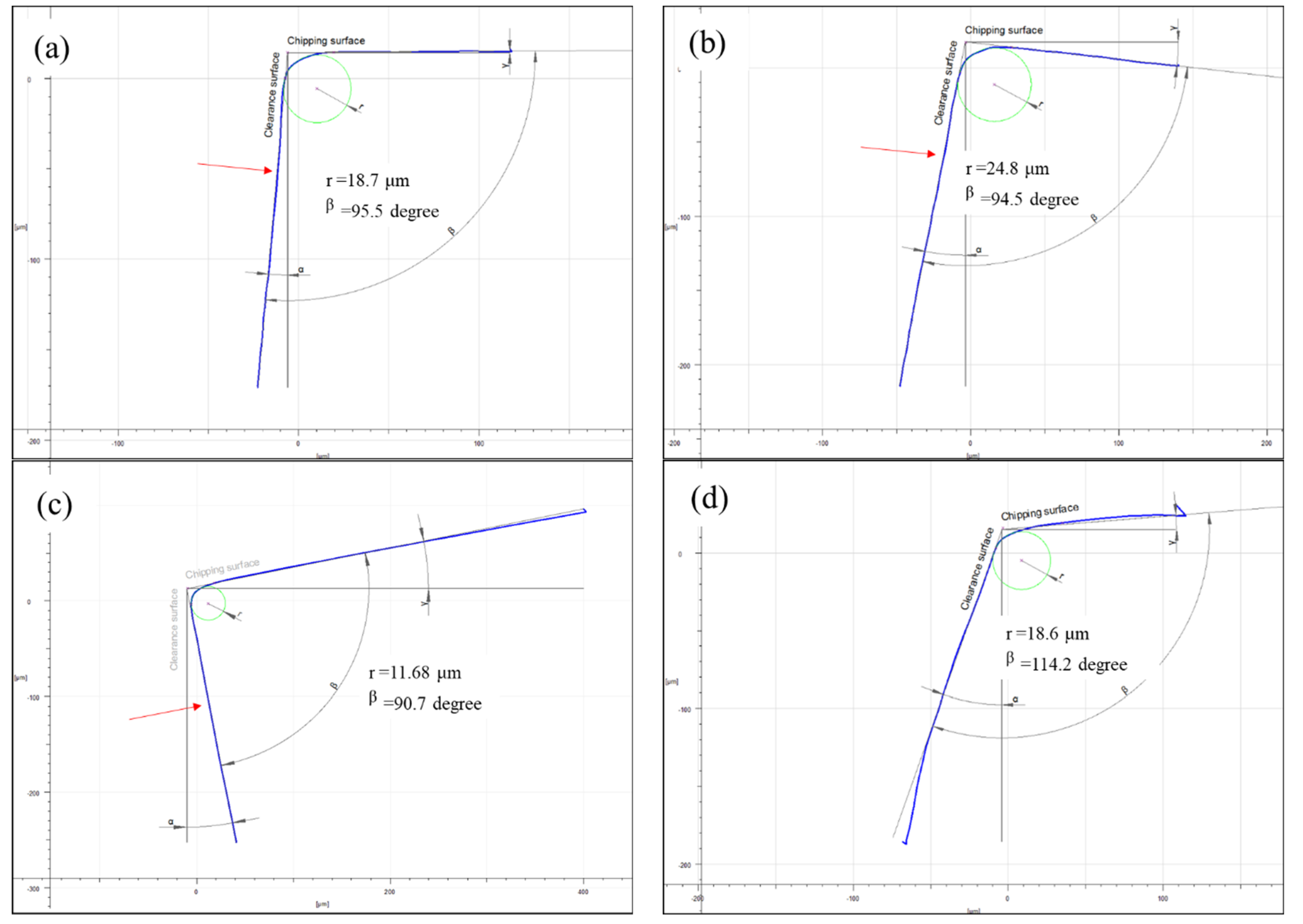
3.1. Geometric Characteristics of the PCD Tools
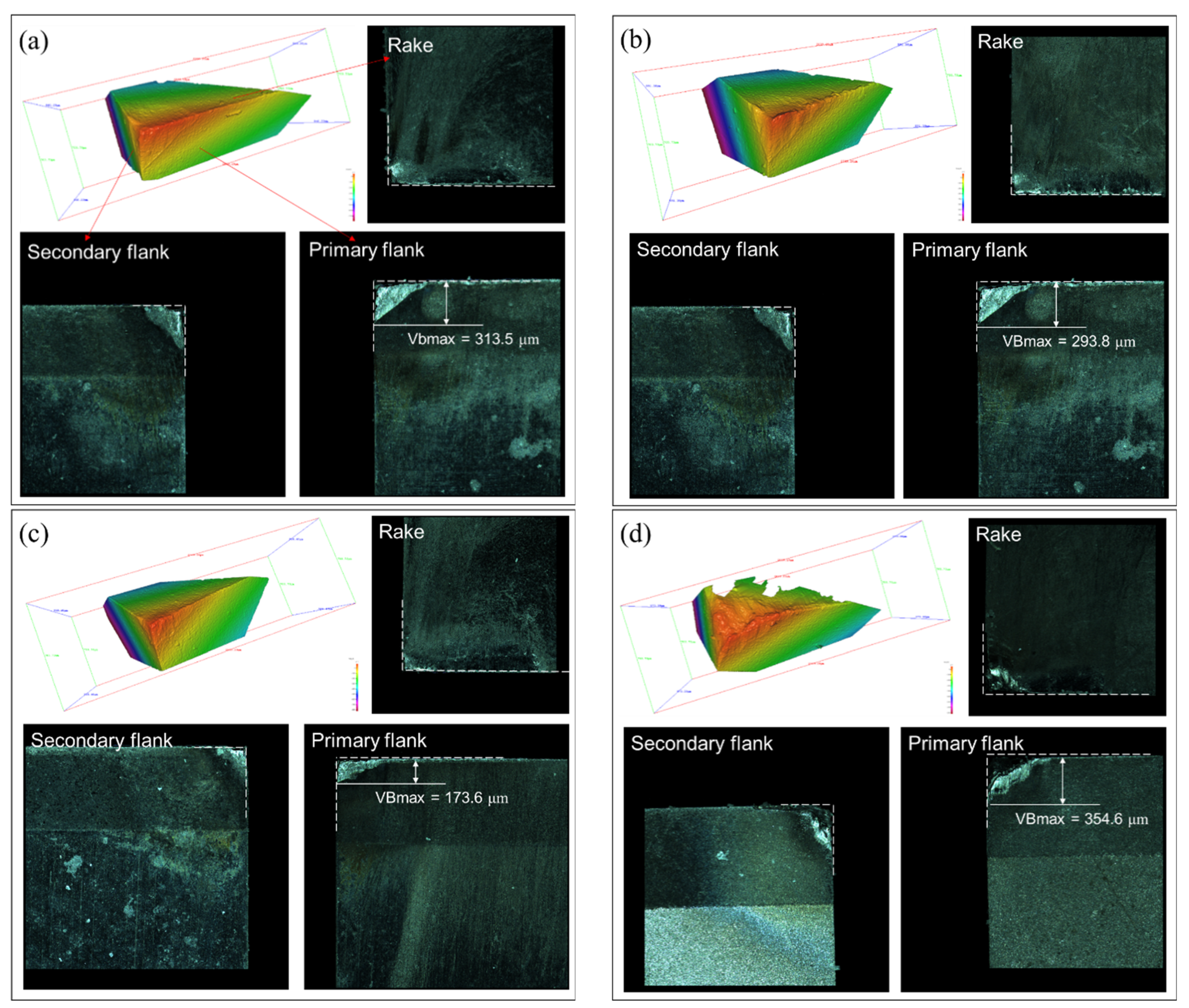
3.2. Flank Wear of the Cutting Tools
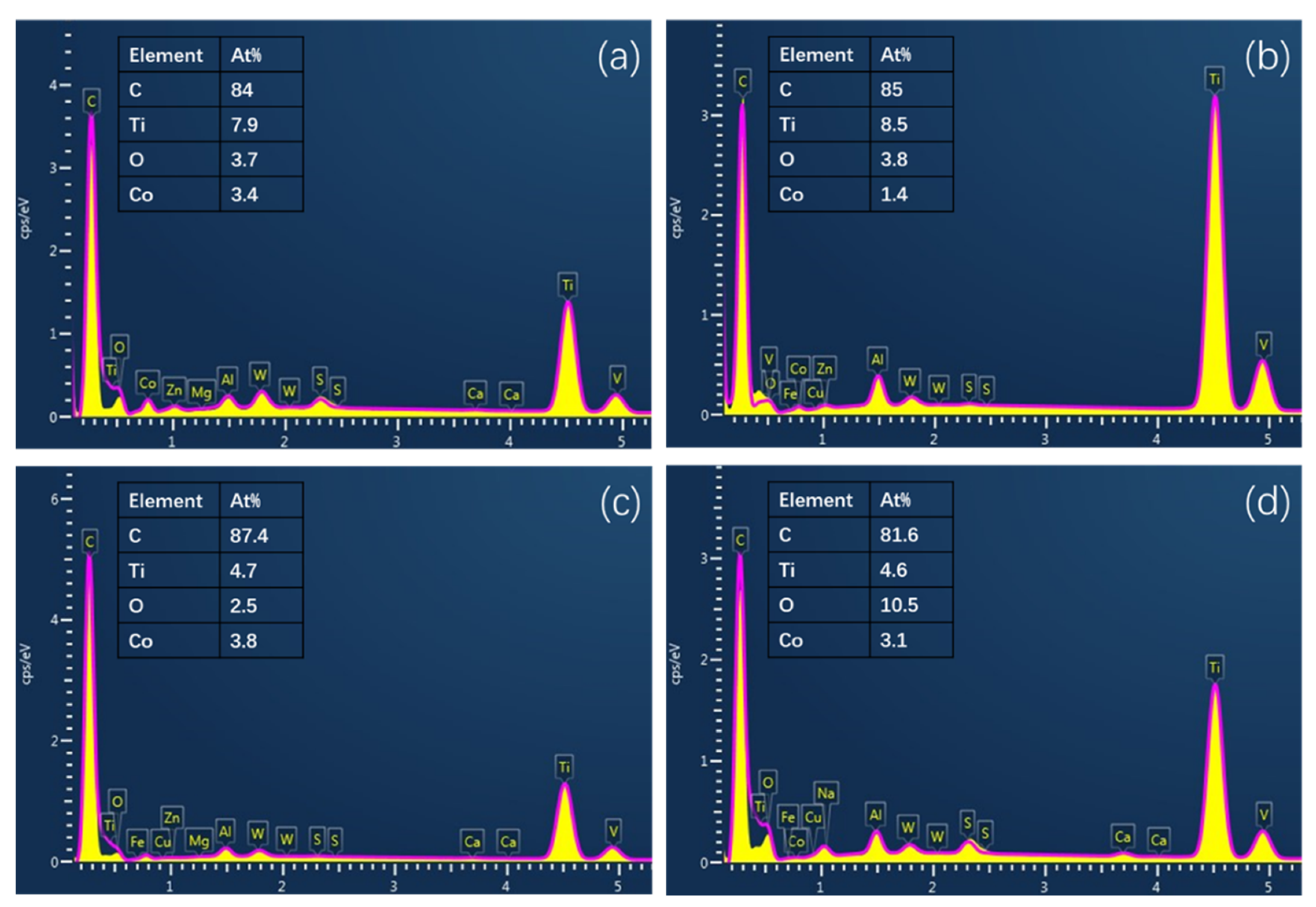
3.3. Analysis of the Residual Elements
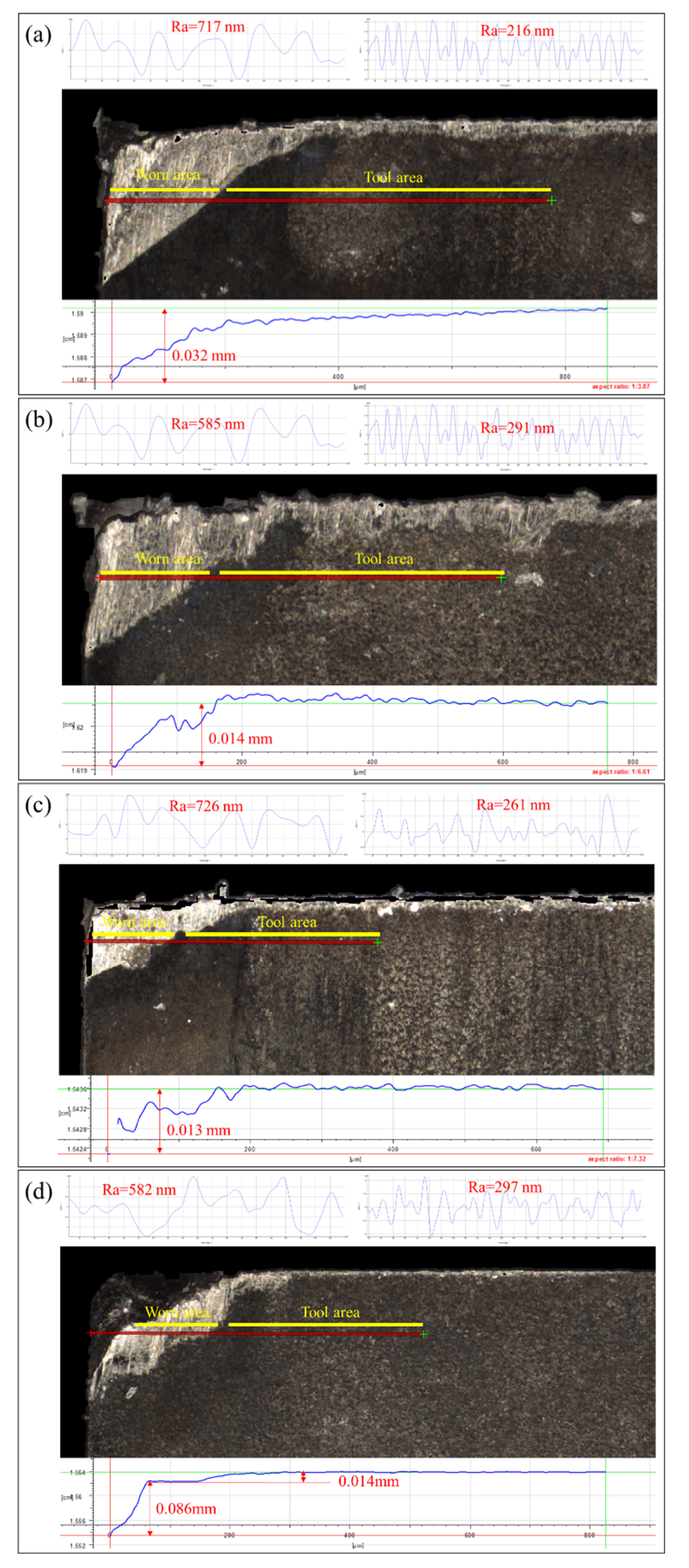
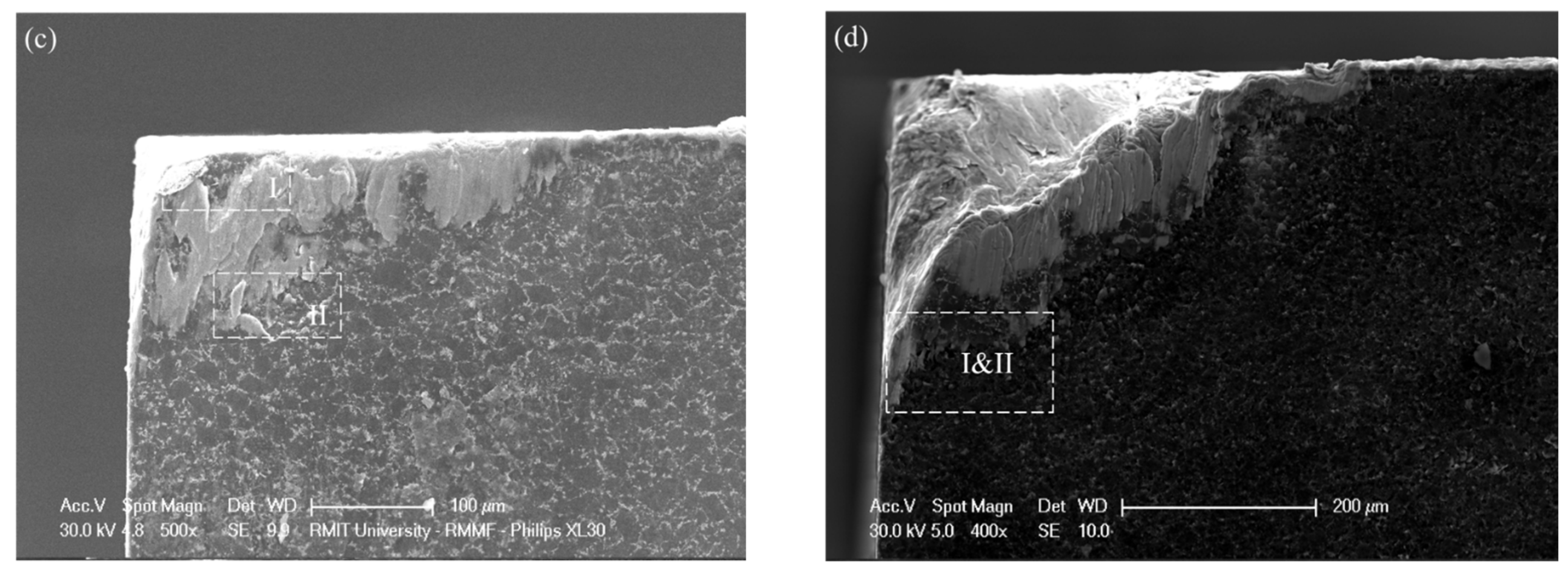
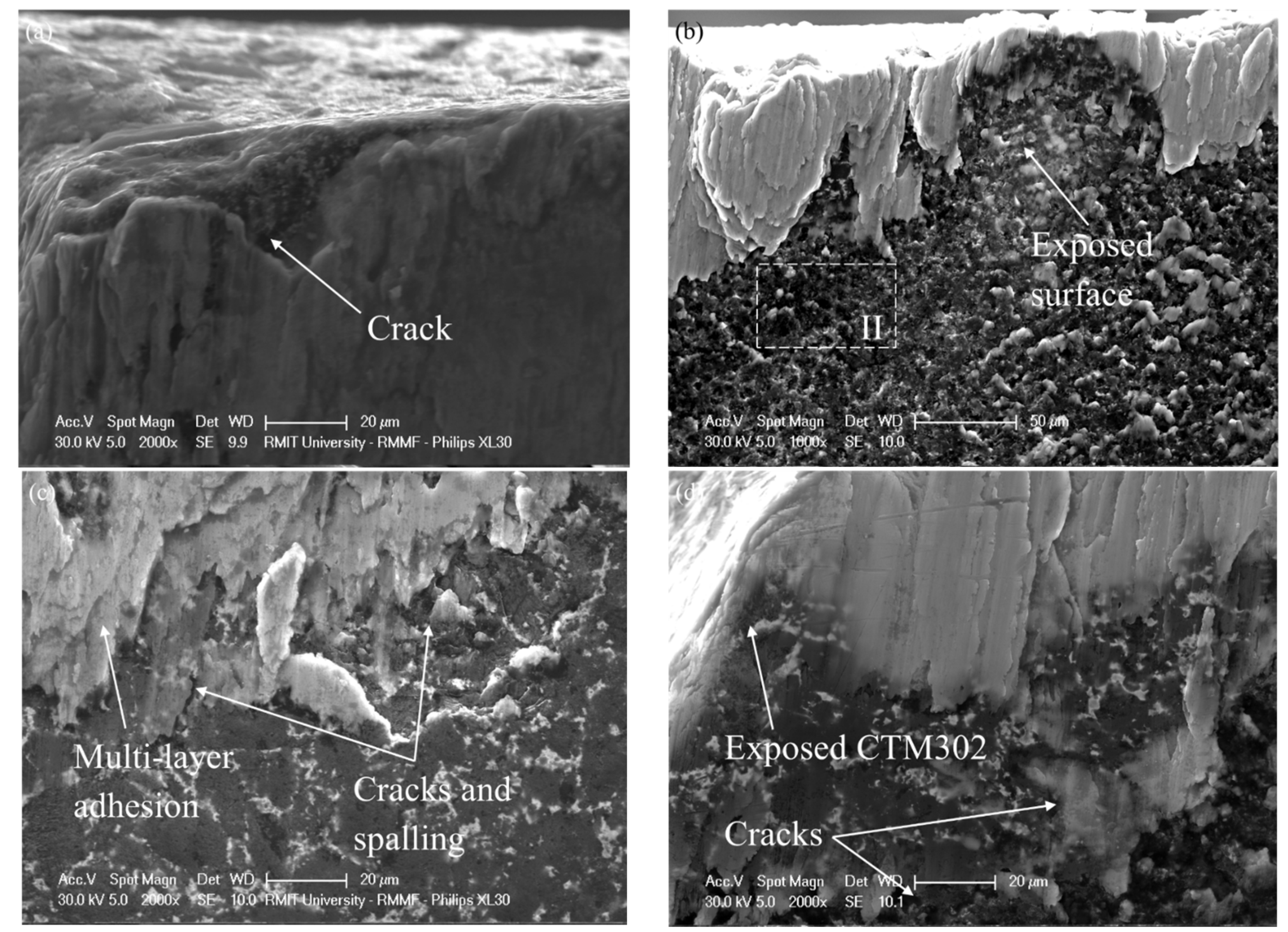
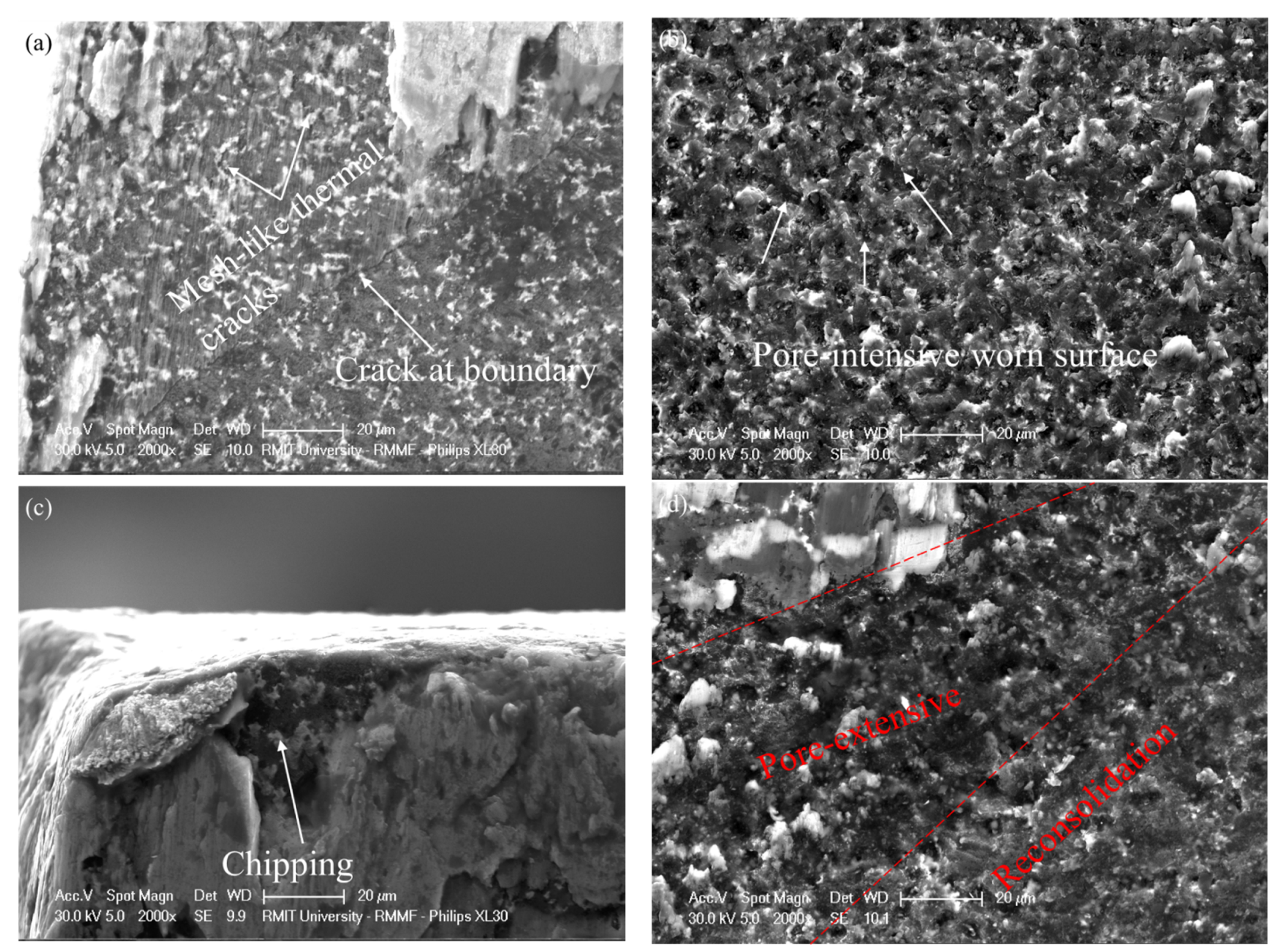
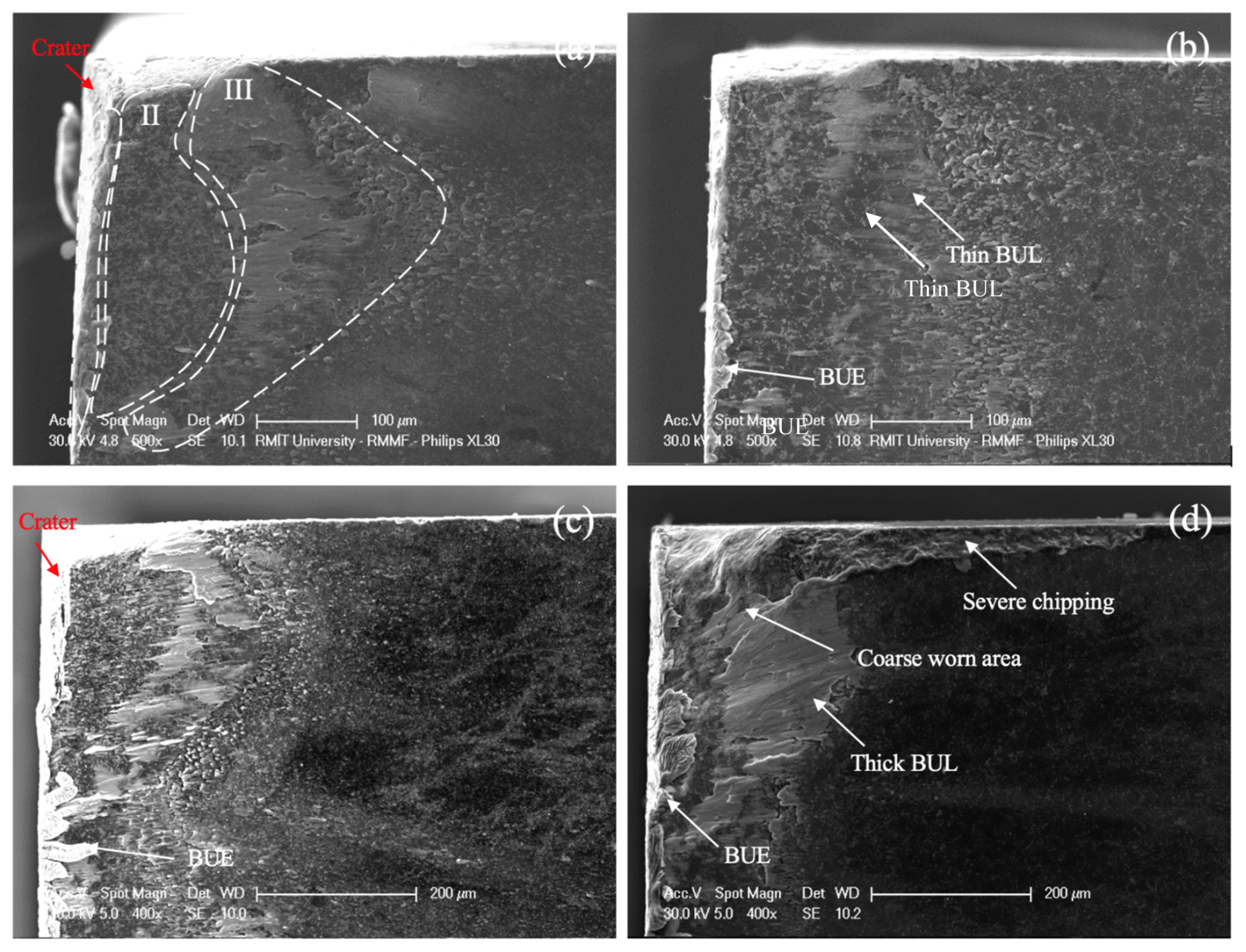
3.4. Crater Wear Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nath, C.; Rahman, M.; Neo, K. Machinability study of tungsten carbide using PCD tools under ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2009, 49, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wandi, S.; Ding, S.; Mo, J. An approach to evaluate delamination factor when drilling carbon fiber-reinforced plastics using different drill geometries: Experiment and finite element study. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 4043–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, N.; Wen, C.; Ding, S. Investigation and modeling of flank wear process of different PCD tools in cutting titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 95, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yi, S.; Li, N.; Pan, W.; Wen, C.; Ding, S. Quantitative analysis of cooling and lubricating effects of graphene oxide nanofluids in machining titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 271, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Yang, H.; Han, Z. Boundary-conformed machining of turbine blades. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2005, 219, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Mahdavian, S.; Aswin, D.; Ding, S. Experimental study of temperature and clamping force during Nd:YAG laser butt welding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2009, 41, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.; Deng, Z.; Chen, J. An experimental study on laser cutting mechanisms of polycrystalline diamond compacts. CIRP Ann. 2007, 56, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Rahim, M.; Pan, W.; Wen, C.; Ding, S. The manufacturing and the application of polycrystalline diamond tools—A comprehensive review. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 56, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulafif Rahim, M.; Ding, S.; Mo, J. Electrical discharge grinding of polycrystalline diamond-effect of wheel rotation. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2016, 20, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoczypiec, S.; Bizoń, W.; Żyra, A. Research on electrodischarge drilling of polycrystalline diamond with increased gap voltage. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: College Park, MD, USA, 2018; p. 100015. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, H.; Ye, P.; Wang, C. Research on Electronic Discharge Grinding of Polycrystalline Diamond Based on Response Surface Method. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 764, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, P.; Chong, C.; Rahim, M.; Lee, W.; Sia, C.; Ahmad, M. Intelligent approach for process modelling and optimization on electrical discharge machining of polycrystalline diamond. J. Intell. Manuf. 2018, 31, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.H.; Li, J.G.; Lu, X. Study on EDM machining technics of polycrystalline diamond cutting tool and PCD cutting tool’s life. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 268, 309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Chris, J.; Vallance, R.; Eric, R. Micro machining glass with polycrystalline diamond tools shaped by micro electro discharge machining. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, 1687. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.; Li, X.; Rahman, M. Study of the mechanism of groove wear of the diamond tool in nanoscale ductile mode cutting of monocrystalline silicon. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2007, 129, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Tu, G. Study of electrical discharge grinding using metal matrix composite electrodes. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2003, 43, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanasundaram, D.; Schmidt, A.; Shrotriya, P.; Molian, P. Understanding Thermo-Chemical Machining of Polycrystalline Diamond by Hybrid Laser/Waterjet System. Mechanics Guided Design of Hybrid Laser/Waterjet System for Machining Hard and Brittle Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Rahim, M.; Ding, S.; Sun, S.; Mo, J. Experimental study on quality of PCD tools machined by different electric discharge grinding processes. Cogent Eng. 2016, 3, 1228234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Jain, V.K.; Dixit, P.M. Thermal stresses due to electrical discharge machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2002, 42, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Ding, S.; Mo, J. Thermal characteristics in milling Ti6Al4V with polycrystalline diamond tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 75, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, R.B.; Machado, Á.; Ezugwu, E.; Bonney, J.; Sales, W. Tool life and wear mechanisms in high speed machining of Ti–6Al–4V alloy with PCD tools under various coolant pressures. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, J.; Díaz-Álvarez, J.; Miguélez, M.; Marín, N. Analysis of tool wear patterns in finishing turning of Inconel 718. Wear 2013, 297, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhao, J.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Y. Failure mechanisms of a PCD tool in high-speed face milling of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 67, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Peng, L.; Yucan, F.; Jiuhua, X. Tool life and surface integrity in high-speed milling of titanium alloy TA15 with PCD/PCBN tools. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2012, 25, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.; Li, G.; Ding, S.; Mo, J.; Brandt, M. Electrical discharge grinding versus abrasive grinding in polycrystalline diamond machining—tool quality and performance analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 85, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Rahim, M.Z.B.; Yi, S.; Ding, S.; Sun, S.; Mo, J.; Rahman, M. Wear Mechanism of pcd tools of different grain sizes manufactured by conventionally abrasive grinding and electrical discharge grinding. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 5248–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Rahim, M.Z.; Ding, S.; Sun, S. Performance and wear analysis of polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools manufactured with different methods in turning titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 85, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yi, S.; Sun, S.; Ding, S. Wear mechanisms and performance of abrasively ground polycrystalline diamond tools of different diamond grains in machining titanium alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 29, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosthuizen, G.; Akdogan, G.; Dimitrov, D.; Treunicht, N. A review of the machinability of titanium alloys. R & D J. S. Afr. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2010, 26, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Arrazola, P.; Garay, A.; Iriarte, L.; Armendia, M.; Marya, S.; Maitre, F. Machinability of titanium alloys (Ti6Al4V and Ti555. 3). J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yi, S.; Wen, C.; Ding, S. Wear mechanism and modeling of tribological behavior of polycrystalline diamond tools when cutting Ti6Al4V. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2018, 140, 121011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, S.; Moro, L.; Ghiotti, A.; Bruschi, S. On the tool wear mechanisms in dry and cryogenic turning Additive Manufactured titanium alloys. Tribol. Int. 2017, 105, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, G.; Sutter, G.; Bouthiche, A. Cutting temperature prediction in high speed machining by numerical modelling of chip formation and its dependence with crater wear. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2012, 54, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Rahman, M.; Wong, Y. Tool wear characteristics of binderless CBN tools used in high-speed milling of titanium alloys. Wear 2005, 258, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Kou, Z.; Liu, T.; Yan, X.; Liu, F.; Ding, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; He, D. Submicron binderless polycrystalline diamond sintering under ultra-high pressure. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 77, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Material | CTB002 | CTB302 |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Size (µm) | 2 | 2 and 30 |
| Binder Material | cobalt | cobalt |
| Diamond Fraction (%) | 84.8 | 91.4 |
| Density (g/mm3) | 4.35 | 3.99 |
| Young’s Modulus (Gpa) | 883 | 901 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.1 | 0.11 |
| Hardness (Gpa) | 50 | 50 |
| Conventional Abrasive Grinding | Electrical Discharge Grinding |
|---|---|
| Machine tool: COBORN RG6-FE Feed rate: 0.2 mm/min Grinding speed: 20 m/s Total infeed: 100 μm | Machine tool: ANCA EDGe Electrode: Cu-Ni alloy Voltage: 120 V Current: 12 A, 1 A Time on/off: 40/20 ms, 1/4 ms Total infeed: 150 μm |
| Material | Density | Hardness | Elastic Modulus | Poisson’s Ratio | Thermal Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti6Al4V | 4.43 g/mm3 | 349 | 113.8 GPa | 0.342 | 6.7 W/m.K |
| Cutting Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | 240 m/min |
| Feed Rate | 0.15 mm/rev |
| Cutting Depth | 0.2 mm |
| Time Interval | 35 s |
| Cutting Paths | 6 |
| Coolant | 8 MPa |
| Label | PCD Material | Grinding Method | Sharpness (μm) | Roughness (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 002A | CTB002 | Abrasive grinding | 5.42 | 111 |
| 002E | CTB002 | EDG | 5.87 | 233 |
| 302A | CTM302 | Abrasive grinding | 6.48 | 129 |
| 302E | CTM302 | EDG | 7.11 | 227 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Wu, G.; Pan, W.; Rahman Rashid, R.A.; Palanisamy, S.; Ding, S. The Performance of Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) Tools Machined by Abrasive Grinding and Electrical Discharge Grinding (EDG) in High-Speed Turning. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5020034
Li G, Wu G, Pan W, Rahman Rashid RA, Palanisamy S, Ding S. The Performance of Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) Tools Machined by Abrasive Grinding and Electrical Discharge Grinding (EDG) in High-Speed Turning. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2021; 5(2):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5020034
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guangxian, Ge Wu, Wencheng Pan, Rizwan Abdul Rahman Rashid, Suresh Palanisamy, and Songlin Ding. 2021. "The Performance of Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) Tools Machined by Abrasive Grinding and Electrical Discharge Grinding (EDG) in High-Speed Turning" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 5, no. 2: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5020034
APA StyleLi, G., Wu, G., Pan, W., Rahman Rashid, R. A., Palanisamy, S., & Ding, S. (2021). The Performance of Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) Tools Machined by Abrasive Grinding and Electrical Discharge Grinding (EDG) in High-Speed Turning. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 5(2), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5020034









