Abstract
This paper proposes an age of information (AoI)-inspired secure transmissions strategy for secure transmission from the maritime wireless sensor network to the onshore base station (BS) with the assistance of the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS), in which eavesdroppers exist near the BS. In the proposed scheme, the secure transmission process is divided into the data collection period and the data upload period according to the time sequence to minimize the age of information (AoI) for the privacy information. In the data collection period, we design two scheduling schemes by selecting the sensor with the smallest current AoI or the largest difference in the adjacent AoI. In addition, we propose two heuristic algorithms by adopting the particle swarm optimization algorithm (PSO) and genetic algorithm (GA) to solve the above two problems. In the data uploading period, the uploading time minimization problem is converted to the secrecy rate maximization problem. We design an iterative optimization algorithm with auxiliary variables that are introduced to optimize the reflection coefficient of the RIS. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme can reduce the average AoI by about 10 s compared to the current methods.
1. Introduction
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) technologies have been widely adopted in emergency communications, natural disaster warning, intelligent transportation, etc. [1,2,3]. In WSNs, sensors are deployed for data collection, but they are usually unable to efficiently transmit the sensing data over long distances to ground nodes with communication range and energy limitations. Therefore, the UAV has attracted a great deal of attention from both academia and industry due to its superior flexibility and maneuverability, and in particular, UAV-assisted data collection and transmission has emerged as a promising research direction [4].
UAVs acting as relays with buffers have shown superior environmental adaptability compared to fixed or shipboard observation methods due to their flexibility in approaching sensors [5,6,7]. The authors in [8,9,10] considered UAV-aided scenarios where UAVs collected data from clustered machine-type communications networks, maritime Internet of Things (IoT) systems, and the distributed 3D urban IoT system. In addition, the problem of minimizing the energy consumed by a single UAV-assisted WSN was investigated in [11] by jointly optimizing the UAV trajectory and the sensor transmit power. The authors in [12] proposed a UAV trajectory design scheme for the WSN with multiple UAVs for the purpose of minimizing the parallel data collection time. In wireless networks, UAV–ground communication links have strong line-of-sight (LoS) characteristics, and the transmission information is susceptible to be eavesdropped, so how to provide physical layer security for mobile users has important theoretical and practical significance [13,14,15]. In [15], a UAV-assisted short packet data collection and secure transmission network was constructed, which simultaneously considered the collection and forwarding of sensed information. The authors maximized the energy efficiency (EE) in the data collection period while maximizing the secrecy rate in the data upload period with the threat of eavesdroppers. However, the above schemes have some problems ignored such as channel link damage and signal fading in real communications, which are further aggravated when the UAV is flying at a low altitude [16].
The concept of controlled wireless propagation has been proposed recently with the reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS), and it has been a promising direction to combine the RIS with the UAV for enhancing the performance of future communication networks [17]. The RIS consists of numerous adjustable reflecting elements that are able to optimize the signal propagation path and performance by dynamically adjusting the phase and amplitude of the signal through a control unit. The authors in [18,19] considered the single-antenna IoT WSN, where data need to be uploaded to the base station (BS) with the assistance of a fixed RIS deployed on the surface of fixed-height buildings and moving UAV–RIS, respectively. A growing number of researchers have also considered the presence of eavesdropping nodes and utilized the feature of the RIS to enhance the legitimate link and weaken the received signal strength of eavesdroppers for secure communication at the physical layer [20,21,22,23]. The authors in [21] derived closed-form expressions for the lower bound of the average secrecy rate for uniform linear arrays (ULAs) and uniform planar arrays (UPAs). In [22], the authors further classified users into high-rate security requirement users and energy-constrained users with low-rate requirements and simulated the security performance of the system with adaptive the genetic simulated annealing algorithm under nonorthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and orthogonal multiple access (OMA) schemes. A framework for UAV-assisted secure uplink communication was presented in [23], where the authors jointly optimized the uplink power allocation and UAV beamforming based on the successive convex approximation (SCA) method, and they optimized the UAV localization with a synergized bisection and coordinate descent algorithm.
In addition, various vertical application scenarios with the IoT have imposed more strict requirements on ultrareliable and low-latency communication networks with the explosive increase in the demand for data resources in the future. To quantify the data freshness, the age of information (AoI) was introduced [24]. Different from information delay, which focuses on the time and speed of data transmission, the AoI is defined as the time elapsed from the source with the latest information generation to the destination, and it focuses on the freshness and real-time quality of the information. Some research had been conducted with the goal of minimizing the AoI [25,26,27]. In [25], the UAV flew from the starting point to the destination while collecting information from the ground sensor nodes in the mission area, and the authors jointly optimized the UAV flight trajectory and energy scheduling strategy based on the deep Q network (DQN) scheme in order to minimize the AoI. Dynamic programming (DP) plus the genetic algorithm (GA) and multistep dueling double DQN methods were employed in [26,27], respectively.
Motivated by the above discussions, a wireless sensor information security transmission system assisted by the UAV and RIS is proposed in this paper to minimize the AoI based on the fact that UAVs can be deployed rapidly, and the RIS can reconfigure the signal propagation link. In this system, the UAV is set to fly from the start point to the endpoint to collect the latest data generated at the maritime sensor nodes in the mission area and then upload the information securely to the BS with the aid of the RIS under the threat of eavesdroppers. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first UAV–RIS-assisted WSN that considers information collection and uploading securely. Moreover, we consider a more realistic UPA rather than a ULA for the RIS. The contributions of this article are summarized as follows:
- For the proposed secure transmission system of the UAV and RIS-assisted wireless sensing information collection, we divide the collection process into a data collection period and a data upload period according to the time sequence, and we design a sensor scheduling principle (Scheme 2) that maximizes the difference in the AoI of adjacent time slots, with the goal of minimizing the average AoI of the sensor network. The simulation analysis provea the superiority of Scheme 2. Meanwhile, the system AoI is also minimized by optimizing the UAV flight trajectory and the reflection coefficient of the RIS to maximize the transmission rate.
- In the data collection period, we adopt the realistic two-ray path loss channel instead of the commonly used air-to-ground LoS channel and optimize the UAV trajectory using the PSO algorithm with dynamic weights. In the data upload period, an auxiliary variable is introduced, and an iterative optimization method is developed to optimize the RIS reflection coefficients via relaxing the rank one constraints and Gaussian randomization.
- Scheduling the sensor with the smallest AoI of itself in the current time slot (Scheme 1) and the GA are introduced as comparison solutions. The simulation results demonstrate that the average AoI of the system is minimum using PSO with dynamic weights in conjunction with Scheme 2. More specifically, the average system AoI with the RIS optimization is reduced by nearly 10 s compared to the non-RIS scheme.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the models, including the network, channel model, and AoI model, and outlines the problem formulation. Section 3 is decomposed into UAV trajectory optimizations and sensor scheduling strategy problems in the data collection period, as well as RIS reflection coefficient optimization problems in the data upload period. The simulation results are provided in Section 4, followed by the conclusion in Section 5.
Notation: scalars are denoted by italic letters such as a and A. Vectors and matrices are denoted by bold letters and , respectively. ⊗ is the Kronecker product, and Tr denotes the trace operation of the square matrix. and denote the transpose and conjugate transpose, respectively. denotes the distribution of a circularly symmetric complex Gaussian (CSCG) random variable with a mean and a variance . and denote the terrestrial coordinate range and the statistical expectation, respectively. For a complex number a, arg represents its phase. denotes the complex matrix with M rows and N columns, and denotes an N-dimensional unit vector. means that matrix is positive semidefinite. denotes the modulus of a vector.
2. System Model and Problem Formulation
2.1. Network Model
We consider a UAV and RIS-assisted system, as shown in Figure 1, where maritime sensors need to upload the sensing information securely to a terrestrial BS. However, the sensor cannot transmit the information directly to the BS due to geographical factors or low transmission power. As a relay, the UAV assists in the data collection and forwarding. We divide the above process into the data collection period and data upload period according to the time sequence.
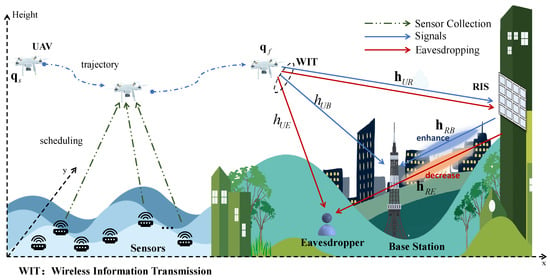
Figure 1.
The system model for sensing data collection and secure uploading from maritime WSN to the onshore BS.
In the data collection period, the UAV is set to fly from the starting point to the final point to collect the latest sensing data generated by sensors in the WSN. The sensor nodes (SNs) are denoted as , which are distributed in the area of assignment , and the coordinates at the time slot can be denoted as . The SNs adopt the generate-at-will model, where the sensing data can be generated at any time [28]. Specifically, each sensor follows a random sampling–replacement strategy, i.e., the new data generated overwrite the old data, and the packet sensing process obeys a Bernoulli process with mean value p. Each new data sensing is accompanied by a timestamp, which is important for calculating the AoI, and the buffer equipped with a sensor can only store one latest packet of size (The packet size collected by each sensor at any time slot is constant). Scheduling by the UAV is possible when there are information packets stored in the sensor buffer.
When the UAV successfully receives the information from sensor , it will take the step of discarding the old packet and storing the new packet information. To avoid interdevice interference, sensors are scheduled with the Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) protocol, i.e., only one sensor can be scheduled per time slot. Assuming that the UAV flies on a plane with a fixed height , the coordinates can be expressed as . The UAV moves at a speed of , which is a vector, and it satisfies , where denotes the maximum speed of the UAV. A circular area with a radius is defined near the final point , and the data upload period can start when the UAV enters the area, which is denoted as
The length of each time slot is denoted as , which is set to a small value such that the channel state remains constant at a single time slot and varies independently at different time slots. The total flight time can be calculated as the product of the total time slots N and the length of each time slot .
In the data upload period, the UAV, denoted as U, will hover in the fixed position and securely upload the collected sensing information to the onshore BS, denoted as B, with RIS assistance, which is denoted as R. Meanwhile, the information uploading process is threatened by an eavesdropper E. One antenna dedicated to receiving information from the UAV is employed at the BS, and single-antenna devices are used for both the UAV and the eavesdropper. With the number of elements , the RIS is able to improve the channel quality for legitimate users by reflecting the UAV signals, and the associated channel gains are denoted as , , and , which are the -dimensional channel gain arrays from the UAV to the RIS, from the RIS to the B, and from the RIS to the E, respectively. The channel gains from the UAV to the B and from the UAV to the E are scalar due to the single-antenna device used in the system, and they are denoted as and , respectively. The received signals at the B and E are given by
and
where , and . The transmit power of the U is denoted as , and is the source signal, which satisfies . The diagonal elements of can be represented as a vector:
and , where , and . denotes the matrix of the reflection coefficients consisting of as diagonal elements. and denote the amplitude factor and the phase shift factor of the element, respectively. Since each passive RIS amplitude reflection factor is expected to achieve full reflection, we set in the subsequent part of this paper.
2.2. Channel Model
In the data collection period, for the air–sea channel between the UAV and the sensor, we modeled it as a more realistic two-ray path loss model, where the LoS and NLoS attenuation expressions are
and
respectively. and denote the attenuation coefficients of the LoS channel and NLoS channel, respectively. denotes the wavelength, and . denotes the Euclidean distance between the UAV and , which is calculated as
The total path loss of the air–sea channel can be expressed as
where and denote the probability of occurrence of air–sea LoS and NLoS channels, respectively. The values are related to the environmental parameters a and b, and the elevation angle of the communication link between the UAV and is calculated as
and
where . a and b are constants, which depend on the environment. Following Shannon’s formula, the transmission rate between the UAV and for each time slot can be calculated as
If the UAV can successfully collect information from in the current time slot, it needs to satisfy that the buffer of in the previous time slot is not empty, and the upload rate must be higher than the threshold , where . Moreover, B denotes the transmission bandwidth, and (It is worth noting that we set the transmit power of all sensors to be ) and denote the sensor transmit power and Gaussian white noise power, respectively. Figure 2 shows the three-dimensional schematic of the transmission rate with the UAV when the sensor is set at the center of the mission area in different frequency sets. As in Table 1, the parameters are set to default values, and it can be seen that different operating frequency affects and hence the transmission rate.
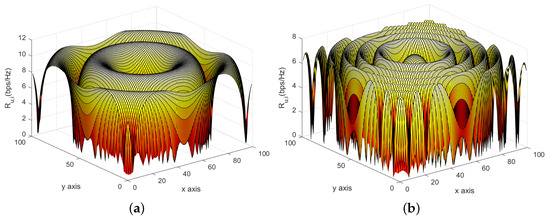
Figure 2.
Three-dimensional diagram of the transmission rate of a sensor with fixed position at different operating frequencies and positions of UAVs. (a) f:1.8 GHz; (b) f:5 GHz.

Table 1.
Default simulation parameters.
When the UAV has collected all the sensor data and reaches within the region , the UAV uploads the collected information to the BS at coordinates . In the data upload period, the coordinates of all nodes are fixed and are denoted as , , and for the the RIS, BS, and eavesdroppers. Since the RIS is deployed on the surface of a high-rise building, there are few obstacles between the UAV and the RIS, so the channel conditions are favorable. For the channel between the UAV and the RIS, we consider the LoS channel to be dominant as
where is the path loss at unit length, is the attenuation exponent, and the distance can be solved using the Euclidean distance formula. is the LoS component, and it expresses as an array response associated with the azimuth and elevation angles of the signals arriving at the RIS, which are calculated as
where . and denote the number of elements of the UPA-designed RIS in the direction of the coordinate axis, respectively, thus satisfying . More specifically, with the RIS array element interval , and are steering vectors (SVs) in the direction of the coordinate axes, and they are denoted as
and
To optimize the reflection and phase shift of the RIS, the signals change the path and arrive at the B and E (It is noted that the two-hop reflective link among the UAV–RIS–ground nodes can be completed in the single time slot). The transmission environment at this time is located in towns or cities with many buildings and high signal attenuation. Thus, we consider Rician fading as the channel model, which is denoted as
where , and is Rician factor. When is equal to 0, i.e., the LoS component is 0, the channel only consists of large-scale fading and the NLoS component, and we consider it as the direct channel between the hovering UAV and the B, as well as E. It can be given by
where . The NLoS component is modeled by a complex Gaussian fading with a zero mean and unit variance. Based on (19) and (20), the secure transmission rate for the data upload period can be calculated as
where denotes and
and
2.3. AoI Model
The AoI can measure the freshness of the sensor information uploaded to the BS, which is defined as the time that has occurred since the latest received packet is generated. The sensor samples the environmental information with a fixed probability p and replaces the old packets in the buffer; it then sends the newest packets to the UAV after being scheduled, and the UAV discards the previous packets.
New packet generation and scheduling by the UAV for are denoted as and , respectively. If sensor samples environmental information and generates a new packet at the time slot, then ; otherwise, . If is scheduled successfully at the time slot, i.e., , it needs to satisfy
where , which refers to the buffer length of .
We define the duration of the latest packet stored in as the survival period , which is denoted as
When is scheduled with and the information is successfully collected by the UAV, the buffer will be empty, i.e., the survival period is 0. When is not scheduled, but a new packet is generated with , this means that the new packet replaces the old one using the sample–replace strategy, and the survival period will be updated to 1. For other cases, the survival period increases linearly over the time slot.
Correspondingly, the AoI evolution of the captured packet at the UAV is given by
If is successfully scheduled, the AoI of the sensed information at the UAV is set to its survival period in the previous time slot plus one; otherwise, it is the AoI of the packet of the previously collected by the UAV plus one. Figure 3 depicts the survival period and the AoI evolution of , in which the generate point and the scheduling line are randomly generated.
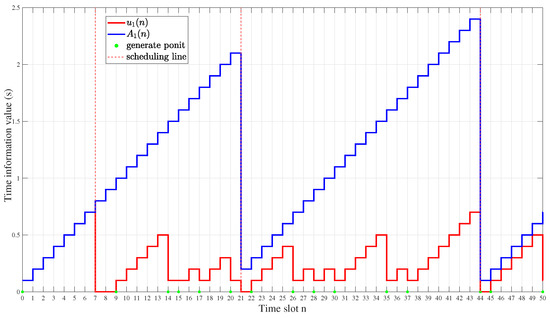
Figure 3.
Survival period and AoI evolution of . As can be seen from the figure, the red stair indicates the survival period curve , and the blue stair indicates the AoI of the corresponding sensed information at the UAV. With , generates a new data packet, and it is scheduled by UAV with ; stays at 0 between the and time slot as sensor information is scheduled, and there is no new generation. With , UAV reschedules the information of , at which point . It is notable that with the time slot , the sensor regenerates the information but is not scheduled, so becomes 1, but still continues to increase following the previous value.
The total time slot of the UAV flight is defined as , and the average AoI of the data collection period can be calculated as
In the data upload period, the UAV no longer receives new sensor information, and the AoI for this period can be expressed as the data transmission delay, which depends on the safe upload rate and packet size and is expressed as
Therefore, the total average AoI can be expressed as , which is also our optimization goal.
2.4. Problem Formulation
In the proposed system, our goal is to minimize the AoI received by the BS by optimizing the trajectory of the UAV, the scheduling strategy of sensors, and the phase shift of the RIS.
where (26b)–(26d) are the flight area constraints of the UAV, and (26c) and (26d) denote the starting and final points of the UAV as fixed coordinates and , respectively. The constraint (26e) indicates that only one sensor can be scheduled per time slot, and (26f) represents that all sensors must be scheduled at least once before the UAV reaches the . (26g) indicates that the diagonal elements of follow the unit modulus constraint, which is a nonconvex constraint.
3. AoI Minimization Optimization for Two Periods of Data Collection and Data Upload
3.1. General Description of Data Collection and Data Upload
In this section, we summarize the overall data collection and data upload period in Figure 4. First of all, we initialize the parameters such as the initial position of the UAV , the number of sensors I, etc. Then, in the data collection period, the UAV flies from to . When it reaches the area , the UAV hovers over and performs the data upload process until the transmission is complete. During this process, UAV can only schedule one sensor in each time slot, and the total collected data can be calculated as after the data collection period.
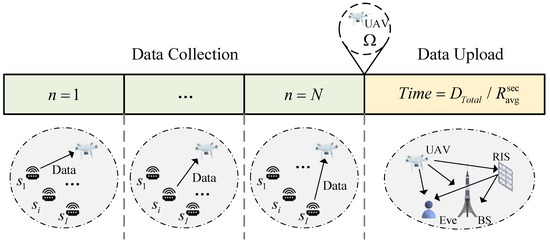
Figure 4.
The general description of data collection and data upload.
The target of the data collection period is to minimize the average AoI of the sensor network, and the scheduling selection of the sensors and the optimization of the UAV position are carried out per time slot to form the trajectory of the UAV. In the data upload period, we minimize the AoI by maximizing the secrecy rate, and the phase shift of the RIS is adjusted in each time slot, which can reconfigure the channel to enhance the legal signal strength and weaken the illegal channel. We can minimize the AoI during the data upload period by maximizing the secrecy rate at each time slot. More detailed information is provided in Section 3.2 and Section 3.3.
3.2. Data Collection Period
In this period, the UAV schedules a cluster of sensors over the sea surface with a total number of I. At most, one sensor can be scheduled per time slot, and when all sensors fail to meet the scheduling conditions, the scheduling flag satisfies . For scheduling principles, we consider the following two schemes:
- Scheme 1: Scheduling the sensor with the smallest AoI of itself in the current time slot, which is also the scheduling principle used in most of the research [23,24,25].
- Scheme 2: Scheduling the sensor with the largest AoI difference between the current time slot and the previous neighboring time slot, which has significant efficacy for the AoI reduction in a multiquantity sensor network.
With different scheduling principles, the optimization of the UAV position at each time slot varies. In this paper, we consider the PSO algorithm with dynamic inertial weights to optimize the trajectory of the UAV, and we also introduce the comparison algorithm GA in Section 3.2.2.
3.2.1. PSO with Dynamic Inertial Weights
This algorithm originates from the study of the flight of flocks of birds, where each bird is equivalent to a particle and has its own speed and position, and the food at the position corresponds to the current value of the optimization function. In this method, individuals are evaluated with fitness values, and the optimization search is guided by the group intelligence generated by cooperation and competition among particles.
The number and dimension of the particle swarm are and D, respectively. In K optimization iterations, the particle updates itself by monitoring two important “extreme values”: one is the best solution discovered by the particle itself—whose position is denoted as , where , which is a -dimensional vector—and the other corresponds to the optimal solution found by the entire particle swarm, whose position is represented by . The velocity and position update equations are
and
where denotes the position of the ith particle at the kth iteration. Obviously, (28) indicates that the update of the particle position depends on the position at the former moment and the velocity vector at the next moment.
In (27), the update of is influenced by three factors, namely the velocity inertia , where denotes the inertia weight, the memory capacity of individual particles , and the communication capacity among particles . and are the learning factors that represent the trend factors of particles approaching to their own historical best and group best positions, respectively. and are pseudorandom numbers, which obey the uniform distribution . is the optimal position of the ith particle recorded up to the kth iteration, and is the globally optimal position of all particles recorded up to the kth iteration.
Moreover, an adaptive adjustment strategy is adopted for the inertia weights , which is used to explore new directions and ensure global convergence performance. It is given by a linear variation equation
where and are the maximum and minimum inertia weights, respectively. k and K indicate the current iteration and the maximum iteration number, respectively. As k increases, decreases continuously, which gives the PSO algorithm a higher probability of converging to the globally optimal solution.
3.2.2. GA
Unlike PSO, which decides the search position based on velocity, the GA performs selection, crossover, mutation, and other operations to generate better individuals based on probability so as to find the optimal solution within the current scope Figure 5. It performs an adaptive global optimization search by imitating the genetic and evolutionary process of organisms in the natural environment, which is an efficient, practical, and robust optimization technique to solve nondeterministic polynomial (NP) problems. Specifically, we have the following:
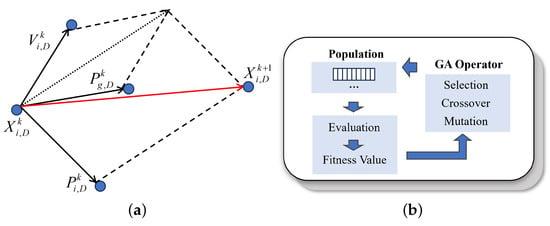
Figure 5.
Schematic of PSO and GA principles. (a) PSO: UAV position is optimized by utilizing dynamic weights to optimize speed and combining individual and population optimal positions. (b) GA: Selection, crossover, and mutation between parents and offspring are used to select better individuals.
- Selection: According to a certain rule or method, a strong individual is selected from the current population as the parent of the next generation based on the fitness of the individual. In this paper, the emperor scheme is introduced, i.e., the best-performing individual (“the emperor”) is selected in each iteration, and its chromosome is crossed with half of the individuals in the whole population, thus increasing the proportion of the emperor’s chromosome in the whole population.
- Crossover: Randomly matching selected individuals in the population to exchange some of the chromosomes between them with a crossover probability .
- Mutation: Randomly altering individual genes to maintain population diversity and prevent premature convergence. In this paper, we adopt the real-valued mutation method, which utilizes the set mutation probability to determine whether it mutates or not. If it is judged as a mutated individual, the corresponding gene value is replaced with a random value.
It is worth noting that during the data collection period, we designed two scheduling principles and combined them with two UAV positional trajectory algorithms for altogether four combined optimization analyses. Among them, the combination of the Scheme 2 and the PSO algorithm with dynamic weights yielded the greatest results, as illustrated in more detail in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 PSO Scheme 2 for Data Collection Period |
|
3.3. Data Upload Period
After the UAV flies to the final position and completes the data collection task, it needs to upload the collected sensing data to the BS. During the data uploading period, the direct channel conditions between the UAV and the BS are unfavorable due to the long distance and the presence of many obstacles. Meanwhile, the eavesdropping user located near the BS will receive signals from the UAV, thus affecting the safe uploading of information. In this regard, we incorporate the capability that the RIS can improve the channel environment by radiating reflected signals to enhance the signal strength received by legitimate users and weaken the influence of eavesdropping nodes, thus improving the secrecy rate of the data uploading and enhancing the speed.
In this period, the optimization problem can be expressed as
where represents the total time to securely upload the sensing data to the BS, which depends on the secrecy rate of each time slot and can be calculated as (31).
The reflection phase shift of each element of the RIS satisfies the unit modulus constraint (30b), which is nonconvex. For the nonlinear objective function (30a), we convert the minimization problem of transmission duration into a maximization problem of the transmission rate per time slot, which is denoted as
On this basis, we define , , and , which are -dimensional column vectors. It is notable that when (32a) is less than or equal to zero, it makes no sense to optimize the phase shift of the RIS. Therefore, we consider the case where the secrecy rate is positive within the single time slot. The optimization problem can be converted to
With the transformations based on the matrix trace, we have the following:
and
where , , and , which are -dimensional squares. Moreover, in conjunction with Lemma 1, we introduce the auxiliary variable y and can obtain
where we utilize the base changing formula for logarithms .
Lemma 1.
For any , introduce the function , and we can obtain
An upper bound for can be obtained, and is the optimal solution.
Proof.
Please see [29,30] for the detailed proof. □
Therefore, for the maximization problem (32a), we convert the original nonconvex objective function into the form of a convex function on or y. denotes the element in the row and column, and the optimal should satisfy to be a semipositive definite matrix with rank one. However, it remains a nonconvex problem attributed to rank one constraint (38c).
The optimal solution can be obtained directly from (39) and denoted as
For the optimization problem of V with a given y, it is nonconvex and can be denoted as
To make the whole problem tractable with standard convex optimization methods, i.e., the interior point method, we introduce the semipositive definite relaxation (SDR) technique, where we remove the rank one constraint and obtain the convex semidefinite programming (SDP) as
However, the relaxation problem may not yield an optimal rank one result, which implies that we need to take further steps to construct an approximate rank one solution from the obtained higher-order solutions, and the Gaussian randomization technique will be applied, and all this is described in detail in [31,32]. Based on the discussion above, we iteratively derive the optimal solutions and until convergence. The detailed steps are summarized in Algorithm 2. Furthermore, we combine the two periods to form the overall algorithm, as shown in Algorithm 3.
| Algorithm 2 Iterative Optimization for RIS Phase Shift |
|
| Algorithm 3 Overall Algorithm for Two Periods |
|
4. Simulation Results
The numerical results are presented in this section to evaluate the ability of our proposed algorithm to minimize the AoI in the system, where the RIS–UAV-assisted maritime sensing information is securely uploaded to the onshore BS. In the mission area, the positions of sensors were randomly generated, and each sensor followed the generate-at-will model with probability p. The UAV moved from the starting point to the final point ; the length of each time slot was s, and the maximum flight speed was 20 m/s. The transmission data amount of each sensor was bps , and the transmission minimum threshold was calculated to be 8 bps/s using the formula .
During the data collection period, a two-ray path loss channel was adopted, and we set the operating frequency to GHz, thus calculating the wavelength as m using the formula , where m/s denotes the speed of light. The probabilities of the LoS and NLoS channels were derived from (5) and (6), where the values of constants a and b were set as and [33], respectively. The attenuation coefficients and were set as 1 and 20, respectively.
For the air–ground channels in the data upload period, we modeled them differently depending on the altitude and environment. Large-scale fading exists in all channels, and we set the path loss at unit length and attenuation exponent to be dB and 1 for channels associated with the RIS and the BS; we set dB and 4 for those associated with the eavesdropper. The reason is that the former was located at a higher altitude with fewer obstacles, and the path loss is naturally smaller. For small-scale fading, there are only LoS components between the UAV and the RIS, and there are only NLoS components in the direct link between the UAV, the BS and the eavesdropping user. Moreover, for the Rician channel between the RIS, the BS, and the eavesdropper, we set the Rician factor to . The LoS component depends on the SV of the RIS, with the UPA design and the NLoS component following complex Gaussian fading with a zero mean and unit variance. Where not specifically stated, the remaining parameters were set as in Table 1.
Figure 6 represents the trajectory of the UAVs with different schemes during the data collection period under the premise of 20 randomly generated sensors in the mission area. Figure 7 represents the real-time variation of the average AoI during the data collection period with the corresponding method of Figure 6. As can be seen from Figure 7, in terms of the AoI minimization, Scheme 2 which aims at maximizing the AoI difference, was superior to Scheme 1, which chooses the sensor with the minimum AoI. This indicates that Scheme 2 is more suitable for the reduction in the system average AoI. Meanwhile, during the flight of the UAV from to , the PSO scheme was used to reach faster in comparison to the GA algorithm. At the same time, compared to the essential PSO, the PSO with dynamic weights was able to realize a smaller system average AoI. It shows that the adaptive adjustment by adding inertia weights has a positive effect on the search for the global optimal solution.
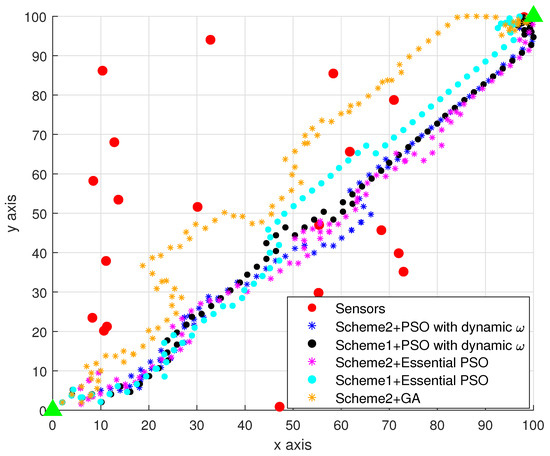
Figure 6.
The sensor distribution and UAV trajectory map. The red circles represent randomly generated sensors, the green triangles are the starting and final points, and the four curves are the UAV flight curves.
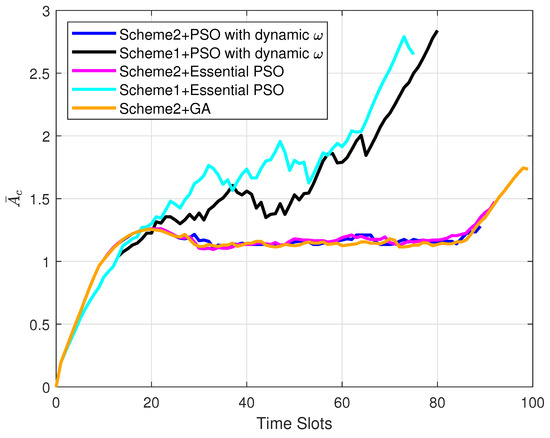
Figure 7.
The average AoI of the data collection period versus time slots.
Figure 8 shows the convergence curves of the fitness values for the optimization of the UAV position under a certain time slot with three methods mentioned in the article. It can be observed that the PSO algorithm with dynamic weights converged the fastest, while the basic PSO algorithm experienced double time compared to the former. The GA method converged in between, but the convergence value is larger than the previous two. This indicates that PSO with dynamic weights converges faster and has better convergence results, which is more suitable for the model we proposed.
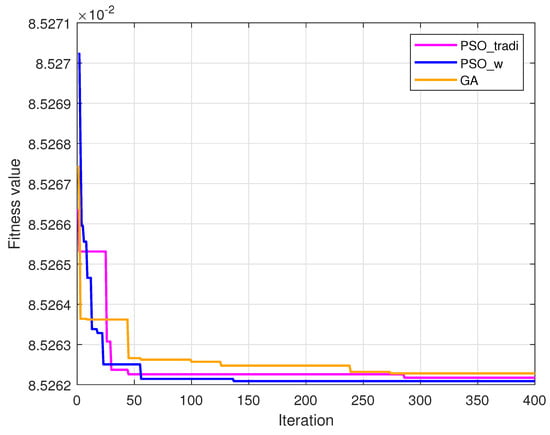
Figure 8.
Convergence curves when optimizing the position of the UAV at a certain time slot.
Figure 9 investigates the system average AoI histogram for the data collection period with different packet sizes and a number of maritime sensors I. It can be observed that the larger the packet size and the number of sensors, the larger the system average AoI was. The reason is that an increase in brings about a rise in the minimum requirement of rate, , and naturally, the sensor that can be scheduled by the UAV decreases; thus, the overall AoI of the system goes up. The average AoI of the system did not grow much when the went from Mbit to Mbit; this is because the transmittable area does not change much in this process. While in the process of 1 Mbit, the transmittable area decreased extremely rapidly, and the UAV could not schedule the sensor, so the average AoI of the system grew very quickly.
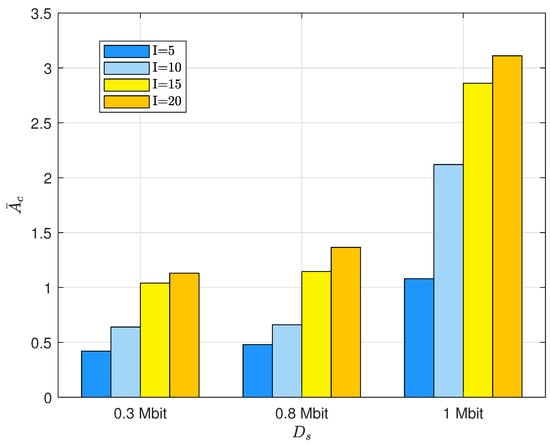
Figure 9.
Histogram of the system average AoI in the data collection period for different packet sizes and number of maritime sensors.
For the data upload period, the UAV is hovering around . Considering that the RIS was fixed on the surface of a tall building, as well as the fact that the height of the ground user was higher but lower than the BS, the coordinates of each node were denoted as , , and , where the BS and the eavesdropper were located close to each other, but the height of the BS was higher than that of the latter. Considering the height of the actual building, we set the RIS height to 60 m, which is equivalent to the RIS being equipped on the surface of a 20-floor-high building.
Figure 10 represents the variation of the secure upload rate of information with the number of RIS elements in the unit frequency band. To avoid the effect generated by the random channel fading coefficient, the experimental results depict the average secure rate under 300 cycles. It can be observed that the secure upload rate with the RIS aid was significantly larger than the case without the RIS, which is attributed to the fact that the RIS reflects signals from the UAV, thus enhancing the signals at the BS through the phase shift optimization and weakening the reception at the eavesdropping node, thus enhancing the overall secure rate. Without the RIS equipped, the secure transmission rate did not change with the number of RIS elements but only had a small up-and-down jitter with random channel conditions. Conversely, the security rate of the RIS-equipped system increased as rose, thus growing more rapidly when the number of elements was relatively small but leveling off as the number of elements continued to increase.
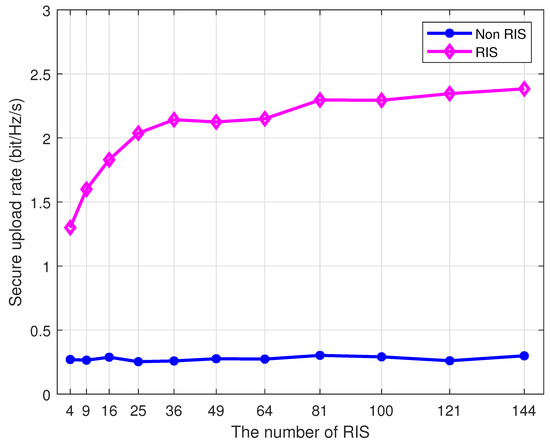
Figure 10.
Curves of secure upload rate with and without RIS for different .
The data upload time is given by (25), and it is related to the total packet size collected and the average security rate, which is shown in Figure 10. It can be easily observed that equipping the RIS could reduce the data upload time significantly based on what is shown in Figure 11. Compared to the case without the RIS, the transmission time during the data upload period was significantly reduced in the scenario with RIS optimization, which is attributed to the fact that the RIS increases the number of reflective links and enhances the reception strength at the base station, as well as weakens the signals received by the eavesdropping user. By comparing the curves for and , it can be observed that more information collected also extended the transmission time.
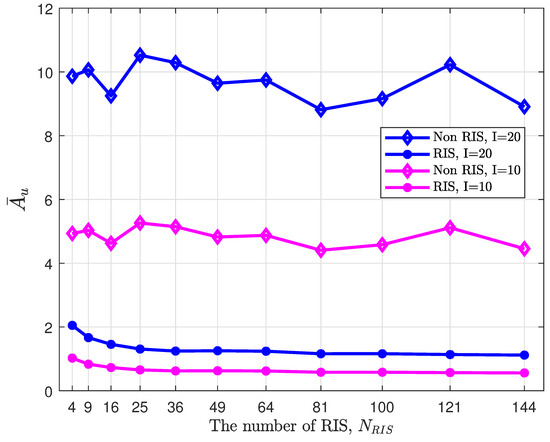
Figure 11.
Curves of data upload time with respect to the number of RIS elements for different numbers of sensors.
Connecting the two periods of data collection and upload, the average AoI of the information transmitted to the BS under different modes of transmission is shown in Table 2. The results show that using the difference maximum scheme and the PSO algorithm with dynamic weights in the data collection period, as well as adding the RIS to increase the secure rate with phase shift optimization in the data upload period, is optimal. Compared to the worst case, the optimal solution could reduce the AoI by about 10 s.

Table 2.
Average AoI of sensed data uploaded to the BS with default parameters.
5. Conclusions
In this work, we designed a secure transmission system for maritime wireless sensor data collection and upload to an onshore base station. We proposed two sensor scheduling schemes and optimized the UAV trajectory using heuristic algorithms such as PSO and the GA in the data collection period, and we introduced the RIS to change the wireless transmission environment in the data upload period to increase the transmission secrecy rate to thus reduce the average AoI of the sensor information. Simulation results show that our proposed scheme and algorithm can effectively reduce the average AoI of the system.
Author Contributions
D.W.: conceptualization, methodology, software, and writing—original draft preparation. L.Y.: conceptualization, software, and writing—review and editing. L.P.: resources, writing—review and editing, and funding acquisition. Q.X.: conceptualization, resources, writing—review and editing, supervision, and funding acquisition. Y.H.: conceptualization, resources, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62271399, in part by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant LQ24F010003, and in part by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant 2020YFB1807003.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Xie, J.; Fu, Q.; Jia, R.; Lin, F.; Li, M.; Zheng, Z. Optimal Energy and Delay Tradeoff in UAV-Enabled Wireless Sensor Networks. Drones 2023, 7, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Hong, Y.; Luo, C.; Li, D.; Chen, Z. Optimization Algorithms for UAV-and-MUV Cooperative Data Collection in Wireless Sensor Networks. Drones 2023, 7, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodu, O.A.; Nordin, R.; Jarray, C.; Bukar, U.A.; Raja Mahmood, R.A.; Othman, M. A Survey on the Design Aspects and Opportunities in Age-Aware UAV-Aided Data Collection for Sensor Networks and Internet of Things Applications. Drones 2023, 7, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, N.; Wang, L.; Zou, Y.; Meng, Z.; Wu, H.; Feng, Z. UAV-Assisted Data Collection for Internet of Things: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 15460–15483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L. UAV-Assisted Data Collection with Nonorthogonal Multiple Access. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, F.; Zhang, R.; Gu, X.; Pan, J. A V2I and V2V Collaboration Framework to Support Emergency Communications in ABS-Aided Internet of Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2023, 7, 2038–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, F.; Zhang, R.; Min, L. Aerial-Ground Integrated Vehicular Networks: A UAV-Vehicle Collaboration Perspective. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 5154–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, N.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Mu, X.; Cai, L. UAV-Enabled Data Collection over Clustered Machine-Type Communication Networks: AEM Modeling and Trajectory Planning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 10016–10032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Chu, Z.; Lin, B.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, N. Fast Trajectory Planning for UAV-Enabled Maritime IoT Systems: A Fermat-Point Based Approach. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, Z.; Guo, X. RIS-Assisted UAV for Fresh Data Collection in 3D Urban Environments: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 632–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Pan, C.; Wang, K.; Pan, Y. Joint Optimization of UAV Trajectory and Sensor Uploading Powers for UAV-Assisted Data Collection in Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 11214–11226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, G.; Ma, T.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, H.; Mumtaz, S.; Ding, Z. Coarse Closed-Loop Trajectory Design of Multiple UAVs for Parallel Data Collection. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 4026–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Mo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, N.; Wu, Y.; Nallanathan, A. Secure Transmission for Multi-UAV-Assisted Mobile Edge Computing Based on Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, G.; Gu, J. Offloading Optimization for Energy-Minimization Secure UAV-Edge-Computing Systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Nanjing, China, 29 March–1 April 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, N.; Chang, Z.; Hämäläinen, T.; Wang, X. UAV-Aided Secure Short-Packet Data Collection and Transmission. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 71, 2475–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, R. Fundamental Trade-offs in Communication and Trajectory Design for UAV-Enabled Wireless Network. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2019, 26, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Chen, M.Z.; Chen, X.; Dai, J.Y.; Han, Y.; Di Renzo, M.; Zeng, Y.; Jin, S.; Cheng, Q.; Cui, T.J. Wireless Communications with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface: Path Loss Modeling and Experimental Measurement. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Height-Fixed UAV Enabled Energy-Efficient Data Collection in RIS-Aided Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 7452–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrovolas, D.; Mekikis, P.-V.; Tegos, S.A.; Diamantoulakis, P.D.; Liaskos, C.K.; Karagiannidis, G.K. Energy-Aware Design of UAV-Mounted RIS Networks for IoT Data Collection. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 71, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, P.; Alipour-Fanid, A.; Jiao, L.; Zeng, K. Physical-Layer Security of 5G Wireless Networks for IoT: Challenges and Opportunities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 8169–8181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Yu, K.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, H.; Al-Dhahir, N.; Guizani, M.; Leung, V.C.M. Active Aerial Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Assisted Secure Communications: Integrating Sensing and Positioning. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yang, W.; Cai, Y. Secure Communication in NOMA-Assisted Millimeter-Wave SWIPT UAV Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 1884–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Cheng, N.; Song, Y.; Hui, Y.; Li, Y.; Luan, T.H.; Yu, S. UAV-Assisted Secure Uplink Communications in Satellite-Supported IoT: Secrecy Fairness Approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 6904–6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Xu, X.; Qin, X.; Zhang, P. AoI-Energy-Aware UAV-Assisted Data Collection for IoT Networks: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Method. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 17275–17289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiong, K.; Cao, J.; Lu, Y.; Fan, P.; Letaief, K.B. Average AoI Minimization in UAV-Assisted Data Collection with RF Wireless Power Transfer: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Scheme. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 5216–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Bai, B.; Dai, H. Age-optimal trajectory planning for UAV-assisted data collection. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2018—IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–19 April 2018; pp. 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Yang, C.; Song, Q.; Guan, Y.; Guo, L.; Jamalipour, A. Minimizing Age of Information for Hybrid UAV-RIS-Assisted Vehicular Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 17886–17895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tong, P.; Wang, X.; Bai, B.; Dai, H. UAV-Aided Data Collection for Information Freshness in Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 2368–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hong, M.; Wai, H.-T.; Liu, Y.-F.; Ma, W.-K.; Luo, Z.-Q. Transmit solutions for MIMO wiretap channels using alternating optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2023, 31, 1714–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Hou, W.; Mao, Y.; Tellambura, C. Artificial noise assisted secure transmission for uplink MIMO rate splitting healthcare systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2023, 27, 3176–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Kong, Z.; Shi, S.; Huang, H.; Ni, Y.; Gui, G.; Gacanin, H.; Sari, H.; Adachi, F. Air Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Enhanced Multiuser NOMA System. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, B.; Wang, X. Efficient DOA Estimation Method for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces Aided UAV Swarm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, F.; Li, B.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, H. Placement optimization of caching UAV-assisted mobile relay maritime communication. China Commun. 2020, 17, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).