A Sonochemically-Synthesized Microporous Metal-Organic Framework for the Rapid and Efficient Ultrasonic-Assisted Removal of Mercury (II) Ions in a Water Solution and a Study of the Antibacterial Activity †
Abstract
:Highlights
- ▪
- Sonochemically microporous metal-organic framework (Zn2(oba)2(bpy)) (1) was synthesized;
- ▪
- Zn2(oba)2(bpy) (1) MOF showed the maximum absorption of Hg2+ ions at pH = 5;
- ▪
- The absorption kinetics was followed by the pseudo-second-order model;
- ▪
- The adsorption isotherm was followed by the Langmuir model;
- ▪
- The maximum absorption capacity for this framework was 338 mgg−1 for Zn2(oba)2(bpy) (1), which was achieved in less than 30 min;
- ▪
- The antibacterial activity study of Zn2(oba)2(bpy) (1).
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Measurements
2.2. Solvothermal Synthesis of Zn2(oba)2(bpy) (1)
2.3. Sonochemical Synthesis of Zn2(oba)2bpy (1)
2.4. Ultrasonic-Assisted Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Zn2(oba)2(bpy) (1)
3.2. Hg(II) Adsorption Studies
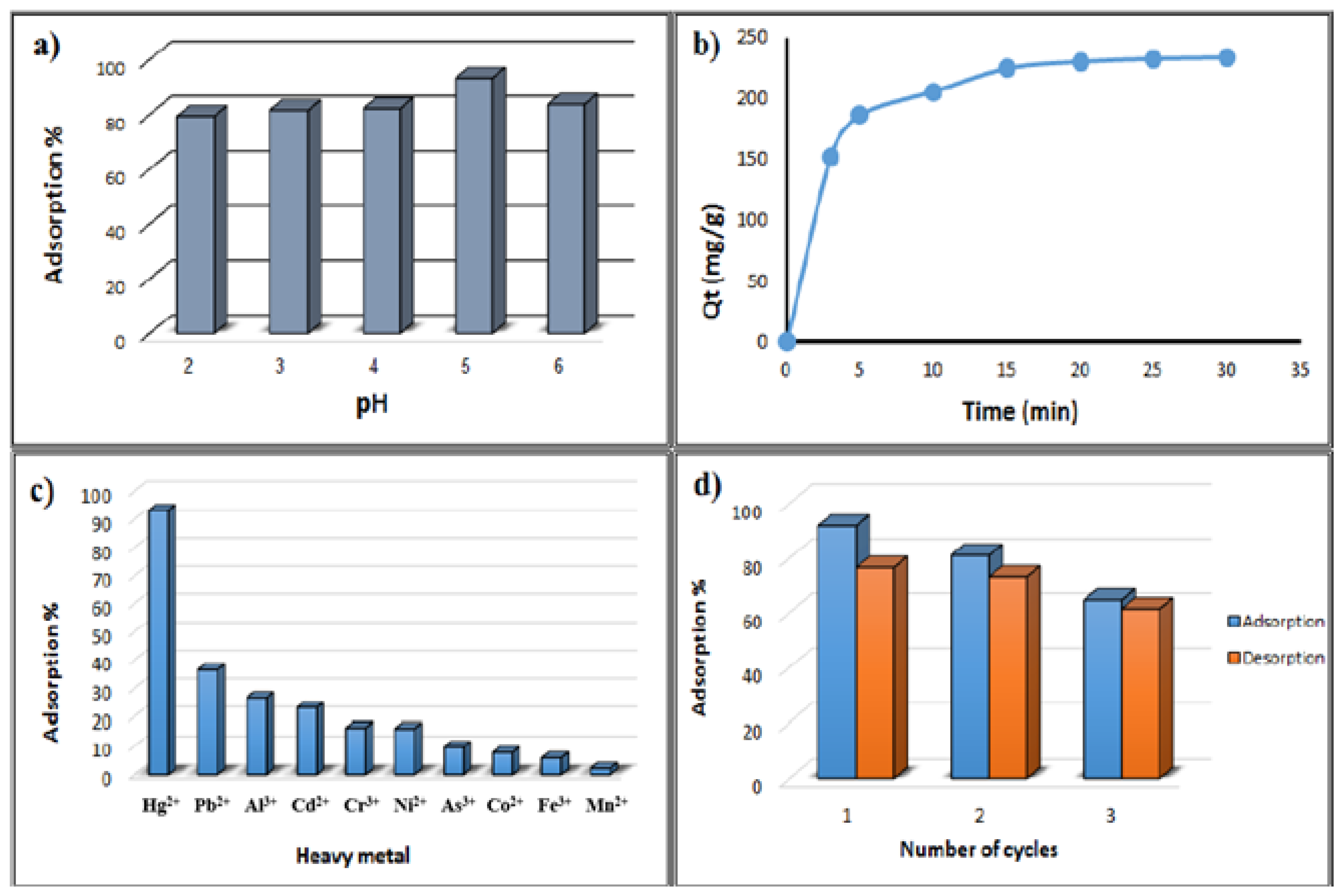
3.3. Effect of pH
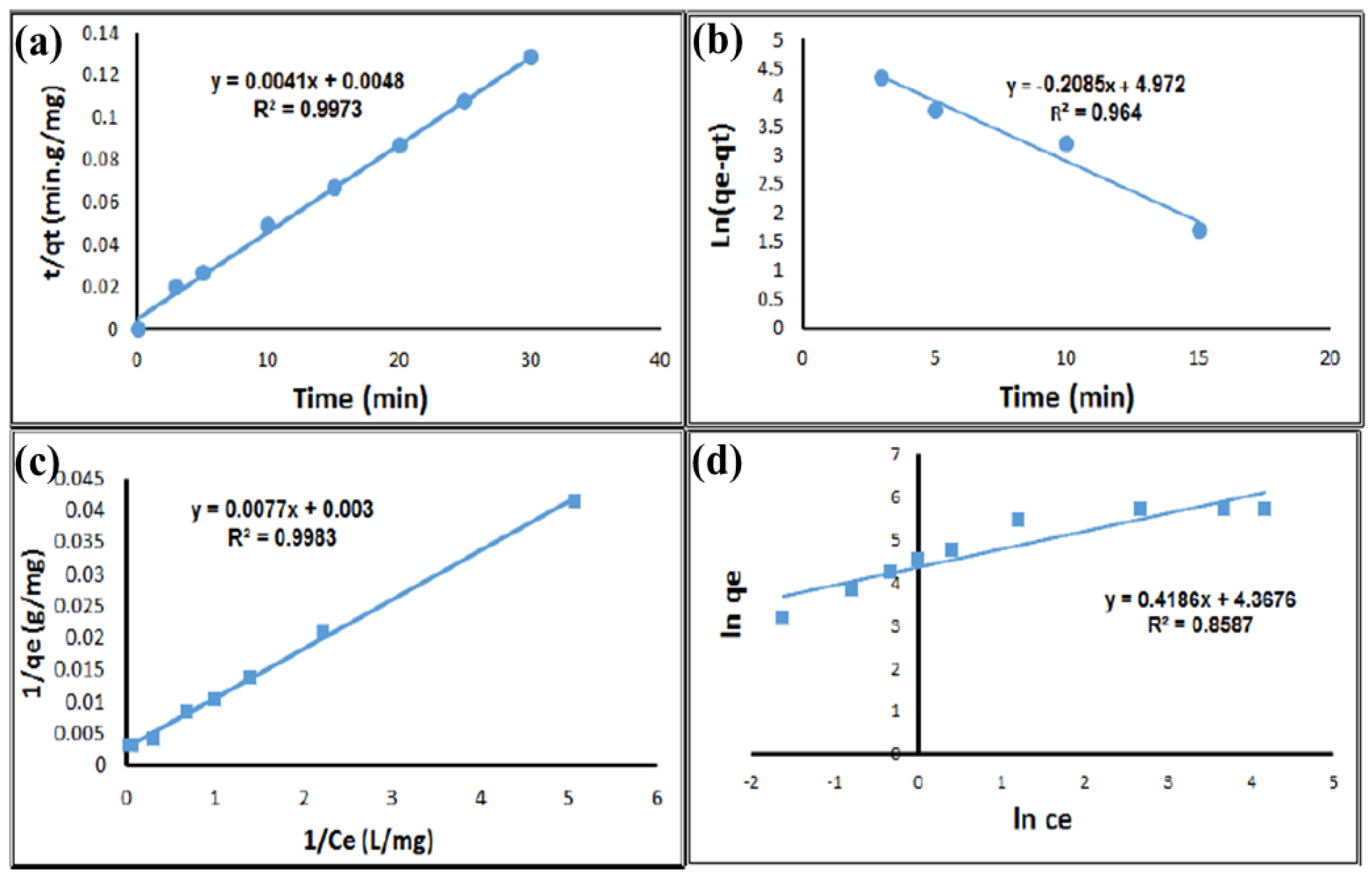
3.4. Study of Sorption Kinetics
3.5. Adsorption Isotherm
3.6. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
3.7. Investigation of Comparative Adsorption
3.8. Reusability Study
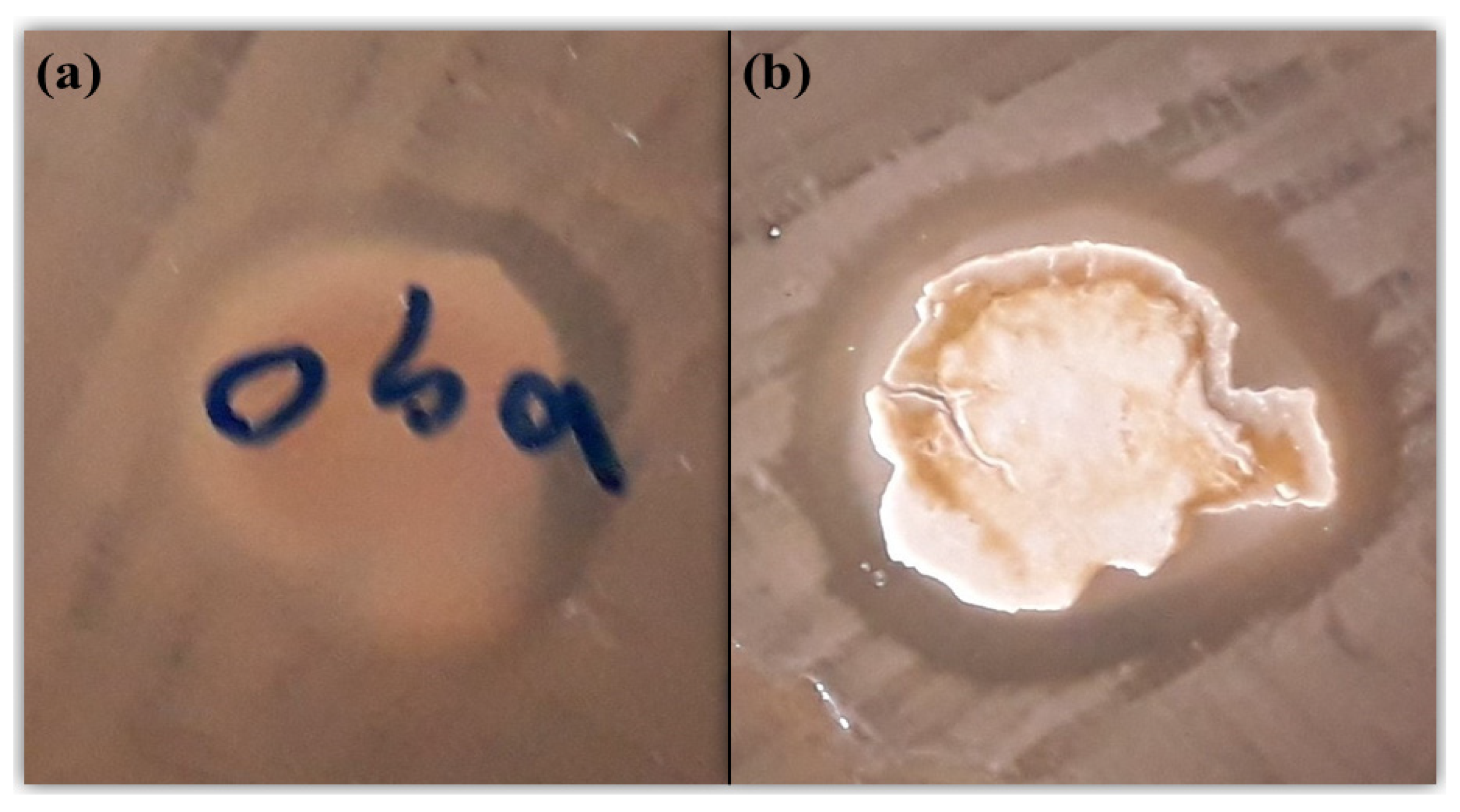
3.9. Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Zhang, X.; Xia, T.; Jiang, K.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qian, G. Highly sensitive and selective detection of mercury (II) based on a zirconium metal-organic framework in aqueous media. J. Solid State Chem. 2017, 253, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-Y.; Yan, B. Fabrication and application of a ratiometric and colorimetric fluorescent probe for Hg2+ based on dual-emissive metal-organic framework hybrids with carbon dots and Eu3+. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 1543–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, P.; Desai, A.V.; Sharma, S.; Chandra, P.; Ghosh, S.K. Selective Recognition of Hg2+ ion in Water by a Functionalized Metal−Organic Framework (MOF) Based Chemodosimeter. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 2360–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. Cadmium-Based Metal−Organic Framework as a Highly Selective and Sensitive Ratiometric Luminescent Sensor for Mercury(II). Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 11046–11048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, D.; Breynaert, E.; Bajpe, S.R.; Martens, J.A.; Kirschhock, C.E. Stability improvement of Cu3(BTC)2 metal-organic frameworks under steaming conditions by encapsulation of a Keggin polyoxometalate. Chem. Comm. 2011, 47, 8037–8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, M.S.; Zare-Dorabei, R. Highly efficient simultaneous ultrasonic-assisted adsorption of methylene blue and rhodamine B onto metal-organic framework MIL-68 (Al): Central composite design optimization. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 27416–27425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-J.; Liu, Y.-G.; Wang, H.; Zeng, G.-M.; Hu, X.; Guo, Y.-M.; Li, T.-T.; Chen, A.-W.; Jiang, L.-H.; Guo, F.-Y. Adsorption of copper by magnetic graphene oxide-supported β-cyclodextrin: Effects of pH, ionic strength, background electrolytes, and citric acid. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 93, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, M.S.; Zare-Dorabei, R. Competitive removal of hazardous dyes from aqueous solution by MIL-68 (Al): Derivative spectrophotometric method and response surface methodology approach. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2016, 160, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oubagaranadin, J.U.K.; Murthy, Z. Adsorption of divalent lead on a montmorillonite—Illite type of clay. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 10627–10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esrafili, L.; Safarifard, V.; Tahmasebi, E.; Esrafili, M.; Morsali, A. Functional group effect of isoreticular metal-organic frameworks on heavy metal ion adsorption. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 8864–8873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, E.; Masoomi, M.Y.; Yamini, Y.; Morsali, A. Application of mechanosynthesis azine-decorated zinc (II) metal-organic frameworks for highly efficient removal and extraction of some heavy metal ions from aqueous samples: A comparative study. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 54, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.Y.; Wu, H.Q.; Luo, F. The MOF+ Technique: A Potential Multifunctional Platform. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 13701–13705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.-G.; Zong, W.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.-B. Nanoscale zeolitic imidazole framework-90: Selective, sensitive and dual-excitation ratiometric fluorescent detection of hazardous Cr (VI) anions in aqueous media. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 12549–12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.-T.; Zhao, J.; Fang, Z.-W.; Li, M.-T.; Sun, C.-Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.-L.; Su, Z.-M. A luminescent metal-organic framework with high sensitivity for detecting and removing copper ions from simulated biological fluids. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 2456–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.Y.; Li, J.Q.; le Gong, L.; Feng, X.F.; Meng, L.N.; Zhang, L.; Meng, P.P.; Luo, M.B.; Luo, F. Using MOF-74 for Hg2+ removal from ultra-low concentration aqueous solution. J. Solid State Chem. 2017, 246, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppler, R.J.; Timmons, D.J.; Fang, Q.-R.; Li, J.-R.; Makal, T.A.; Young, M.D.; Yuan, D.; Zhao, D.; Zhuang, W.; Zhou, H.-C. Potential applications of metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 3042–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, S.; Safarifard, V. Carbon dioxide capture in MOFs: The effect of ligand functionalization. Polyhedron 2018, 154, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradia, E.; Rahimib, R.; Safarifardc, V. Sonochemical synthesis of fabrication nanoporous metal-organic framework base on tetrakis (4-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin (TCPP) linker. In Proceedings of the 21st International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1–30 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Eddaoudi, M.; Kim, J.; Rosi, N.; Vodak, D.; Wachter, J.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Systematic design of pore size and functionality in isoreticular MOFs and their application in methane storage. Science 2002, 295, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreno, L.E.; Leong, K.; Farha, O.K.; Allendorf, M.; van Duyne, R.P.; Hupp, J.T. Metal-organic framework materials as chemical sensors. Chem. Rev. 2011, 112, 1105–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezerloo, E.; Mousavi-khoshdel, S.M.; Safarifard, V. Sensitive and selective detection of metal ions and small molecules in aqueous media using a hydrolytically stable amide-functionalized metal-organic framework. Polyhedron 2019, 166, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanhaei, M.; Mahjoub, A.R.; Safarifard, V. Energy-efficient sonochemical approach for the preparation of nanohybrid composites from graphene oxide and metal-organic framework. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 102, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Seredych, M.; Zhong, Q.; Bandosz, T.J. Superior performance of copper-based MOF and aminated graphite oxide composites as CO2 adsorbents at room temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4951–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.A. Design and Synthesis of Novel Octacarboxy Porphyrinic Metal-Organic Frameworks. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, NE, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Horcajada, P.; Gref, R.; Baati, T.; Allan, P.K.; Maurin, G.; Couvreur, P.; Ferey, G.; Morris, R.E.; Serre, C. Metal-organic frameworks in biomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2011, 112, 1232–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoomi, M.Y.; Morsali, A. Applications of metal-organic coordination polymers as precursors for the preparation of nano-materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 2921–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, E.; Rahimi, R.; Safarifard, V. Sonochemically synthesized microporous metal-organic framework representing unique selectivity for detection of Fe3+ ions. Polyhedron 2019, 159, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, F.; Ghaedi, M.; Daneshfar, A. The headspace solid-phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental water samples using silica fiber modified by self-assembled gold nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 8086–8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosta, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Daneshfar, A.; Sahraei, R. Ultrasound-assisted microextraction-nano material solid-phase dispersion for extraction and determination of thymol and carvacrol in pharmaceutical samples: Experimental design methodology. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 975, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaram, A.; Ghaedi, M.; Hajati, S.; Goudarzi, A. Synthesis of magnetic γ-Fe2O3-based nanomaterial for ultrasonic-assisted dyes adsorption: Modeling and optimization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 32, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S.; Didenko, Y.; Fang, M.M.; Hyeon, T.; Kolbeck, K.J.; McNamara, W.B., III; Mdleleni, M.M.; Wong, M. Acoustic cavitation and its chemical consequences, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A: Mathematical. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1999, 357, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare-Dorabei, R.; Ferdowsi, S.M.; Barzin, A.; Tadjarodi, A. Highly efficient simultaneous ultrasonic-assisted adsorption of Pb (II), Cd (II), Ni (II) and Cu (II) ions from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide modified with 2, 2′-dipyridylamine: Central composite design optimization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 32, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashamiri, S.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K.; Rahimi, M.R.; Goudarzi, A.; Jannesar, R. Ultrasonic enhancement of the simultaneous removal of quaternary toxic organic dyes by CuO nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon: Central composite design, kinetic and isotherm study. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshidi, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K.; Hajati, S.; Bazrafshan, A. Sonochemical assisted the hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO: Cr nanoparticles loaded activated carbon for simultaneous ultrasound-assisted adsorption of ternary toxic organic dye: Derivative spectrophotometric, optimization, kinetic and isotherm study. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 32, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, F.N.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K.; Hajati, S.; Pezeshkpour, V. Ultrasonically assisted hydrothermal synthesis of activated carbon–HKUST-1-MOF hybrid for efficient simultaneous ultrasound-assisted removal of ternary organic dyes and antibacterial investigation: Taguchi optimization. Ultrason. Sonochem 2016, 31, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K.; Ghaedi, A.; Hajati, S.; Goudarzi, A.; Alipanahpour, E. Highly efficient simultaneous ultrasonic-assisted adsorption of brilliant green and eosin B onto ZnS nanoparticles loaded activated carbon: Artificial neural network modeling and central composite design optimization. Spectrochim. Acta A 2016, 153, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, 5th ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Pramanik, S.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, X.; Emge, T.J.; Li, J. New Microporous Metal−Organic Framework Demonstrating Unique Selectivity for Detection of High Explosives and Aromatic Compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4153–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, E.; Rahimi, R.; Davoudabadi Farahani, Y.; Safarifard, V. Porphyrinic zirconium-based MOF with exposed pyrrole Lewis base site as a luminescent sensor for highly selective sensing of Cd2+ and Br− ions and THF small molecule. J. Solid-State Chem. 2020, 822, 121103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yang, S.-T.; Choi, S.B.; Sim, J.; Kim, J.; Ahn, W.-S. Control of catenation in CuTATB-n metal–organic frameworks by sonochemical synthesis and its effect on CO2 adsorption. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3070–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, H.; Xiao, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, T.; Zuo, J.; Huang, W. A microporous luminescent europium metal–organic framework for nitroexplosive sensing. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 5718–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedanken, A. Using sonochemistry for the fabrication of nanomaterials. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2004, 11, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Chen, C.; Chai, Z.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Metal-organic framework-based materials: Superior adsorbents for the capture of toxic and radioactive metal ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2322–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Song, F.; Wei, G.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, C. A highly selective and sensitive polymer-based OFF-ON fluorescent sensor for Hg2+ detection incorporating salen and perylenyl moieties. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yue, X.; Yang, Q.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. One-pot synthesis of multifunctional magnetic ferrite–MoS2–carbon dot nanohybrid adsorbent for efficient Pb (II) removal. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 3893–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singbumrung, K.; Motina, K.; Pisitsak, P.; Chitichotpanya, P.; Wongkasemjit, S.; Inprasit, T. Preparation of Cu-BTC/PVA Fibers with Antibacterial Applications. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabipour, H.; Soltani1, B.; Nasab, N.A. Gentamicin Loaded Zn2(bdc)2(dabco) Frameworks as Efficient Materials for Drug Delivery and Antibacterial Activity. J. Inorg. Organometal. Poly Mater. 2018, 28, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabipour, H.; Sadr, M.H.; Bardajee, G.R. Release behavior, kinetic and antimicrobial study of nalidixic acid from [Zn2(bdc)2(dabco)] metal-organic frameworks. J. Coord. Chem. 2017, 70, 2771–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moradi, E.; Rahimi, R.; Safarifard, V.; Azari, S. A Sonochemically-Synthesized Microporous Metal-Organic Framework for the Rapid and Efficient Ultrasonic-Assisted Removal of Mercury (II) Ions in a Water Solution and a Study of the Antibacterial Activity. Proceedings 2019, 41, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-23-06482
Moradi E, Rahimi R, Safarifard V, Azari S. A Sonochemically-Synthesized Microporous Metal-Organic Framework for the Rapid and Efficient Ultrasonic-Assisted Removal of Mercury (II) Ions in a Water Solution and a Study of the Antibacterial Activity. Proceedings. 2019; 41(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-23-06482
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoradi, Ehsan, Rahmatollah Rahimi, Vahid Safarifard, and Shahram Azari. 2019. "A Sonochemically-Synthesized Microporous Metal-Organic Framework for the Rapid and Efficient Ultrasonic-Assisted Removal of Mercury (II) Ions in a Water Solution and a Study of the Antibacterial Activity" Proceedings 41, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-23-06482
APA StyleMoradi, E., Rahimi, R., Safarifard, V., & Azari, S. (2019). A Sonochemically-Synthesized Microporous Metal-Organic Framework for the Rapid and Efficient Ultrasonic-Assisted Removal of Mercury (II) Ions in a Water Solution and a Study of the Antibacterial Activity. Proceedings, 41(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-23-06482



