Measuring Earthquake-Induced Deformation in the South of Halabjah (Sarpol-e-Zahab) Using Sentinel-1 Data on November 12, 2017 †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
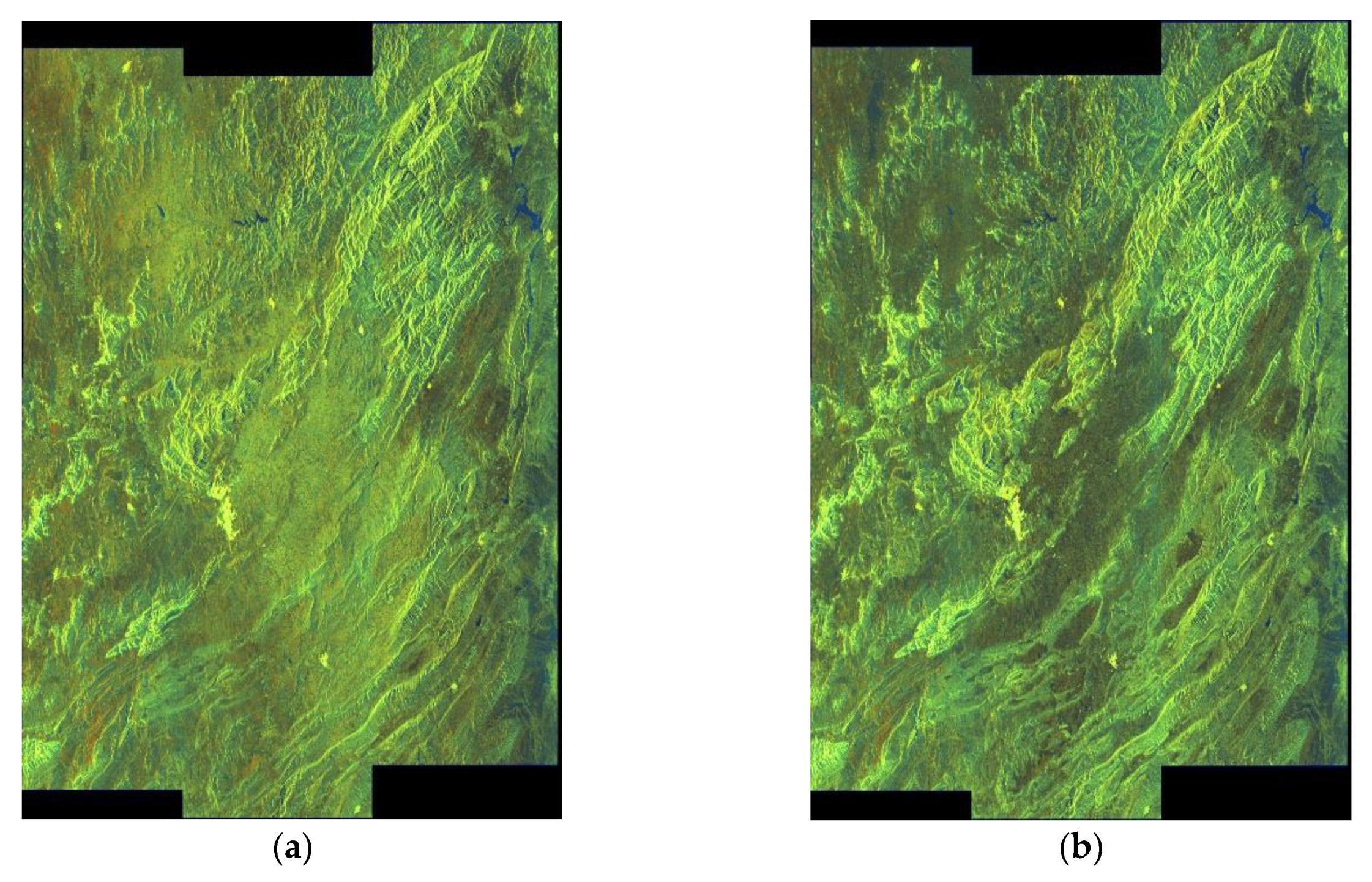
2. Study Area and Data Used
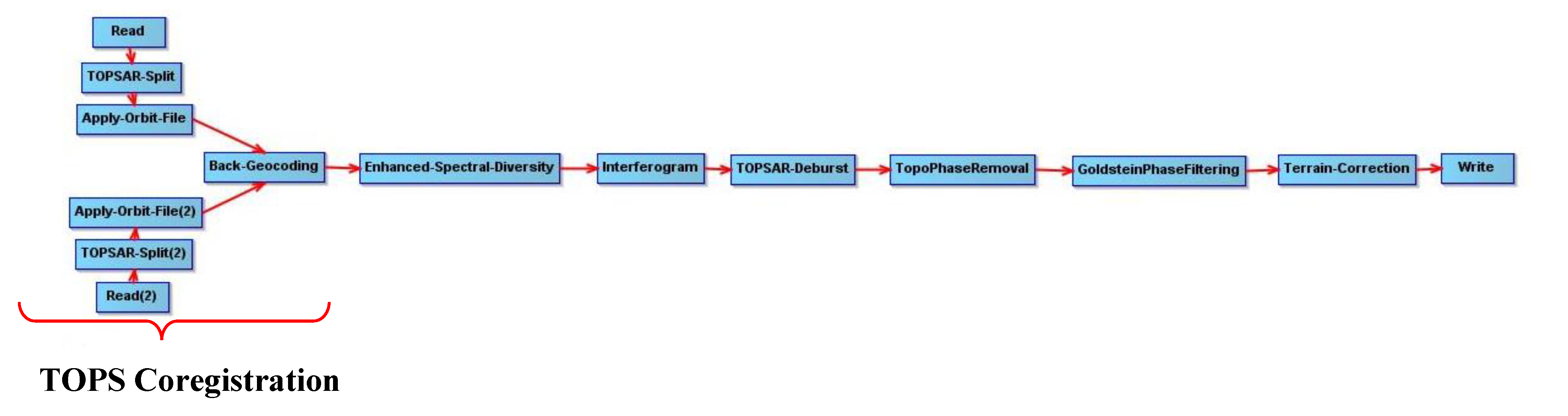
3. Methodology
3.1. Coregistration of the Datasets
3.2. InSAR Data Analysis
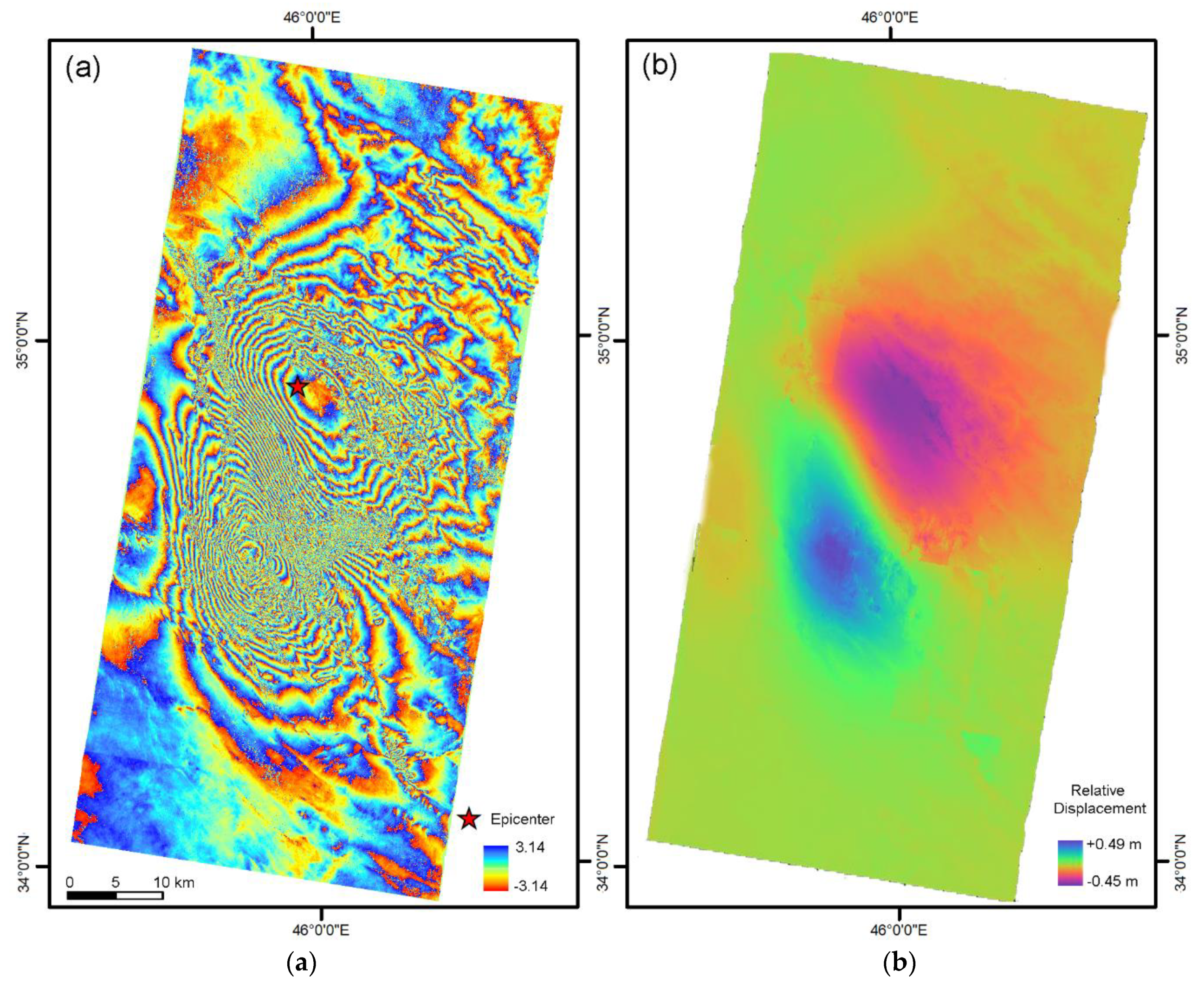
3.3. Phase Unwrapping
3.4. Displacement Measurements
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turker, M.; San, B.T. Detection of collapsed buildings caused by the 1999 Izmit, Turkey earthquake through digital analysis of post-event aerial photographs. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 4701–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turker, M.; San, B.T. SPOT HRV data analysis for detecting earthquake-induced changes in Izmit, Turkey. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, O.; Ordoqui, P.; Iglesias, R.; Blanco, P. Earthquake Rapid Mapping Using Ascending and Descending Sentinel-1 TOPSAR Interferograms. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 100, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- User Guides—Sentinel-1 SAR—Level-1 Single Look Complex—Sentinel Online. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/user-guides/sentinel-1-sar/resolutions/level-1-single-look-complex (accessed on 9 February 2018).
- Zuo, R.; Qu, C.; Shan, X.; Zhang, G.; Song, X. Coseismic deformation fields and a fault slip model for the Mw7.8 mainshock and Mw7.3 aftershock of the Gorkha-Nepal 2015 earthquake derived from Sentinel-1A SAR interferometry. Tectonophysics 2016, 686, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yague-Martinez, N.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Gonzalez, F.R.; Brcic, R.; Shau, R.; Geudtner, D.; Eineder, M.; Bamler, R. Interferometric Processing of Sentinel-1 TOPS Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2220–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M 7.3—29 km S of Halabjah, Iraq. Available online: https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/us2000bmcg#executive (accessed on 9 February 2018).
- Iran-Iraq Earthquake is Deadliest of 2017—CNN. Available online: https://edition.cnn.com/2017/11/12/middleeast/iraq-earthquake/index.html (accessed on 9 February 2018).
- Yekrangnia, M.; Eghbali, M.; Seyri, H.; Panahi, M.; Zanganeh, S.Y.; Beyti, M.; Hayatgheybi, D.S.V.; Nazarpour, M.; Amiri, G.G. A Preliminary Report on School Buildings Performance during M 7.3 Ezgeleh; Iran Earthquake of Participants Project Team Steering Committee Advisory Committee: Ezgeleh, Iran, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.-K.; Li, T.; Chen, J. Thrust faulting and 3D ground deformation of the 3 July 2015 Mw 6.4 Pishan, China earthquake from Sentinel-1A radar interferometry. Tectonophysics 2016, 683, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Li, Z.; Tomás, R.; Liu, G.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Chen, J.; Stockamp, J. Monitoring activity at the Daguangbao mega-landslide (China) using Sentinel-1 TOPS time series interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veci, L. Sentinel-1 Toolbox TOPS Interferometry Tutorial; ESA: Paris, France, 2016; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; Mazzanti, P.; Esposito, C.; Crosetto, M.; Scarascia Mugnozza, G. First insights on the potential of Sentinel-1 for landslides detection. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 7, 1874–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Lu, Y. Phase unwrapping algorithms for radar interferometr residue-cut least-squares, and synthesis algorithms. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1998, 15, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgmann, R.; Rosen, P.A.; Fielding, E.J. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry To Measure Earth’s Surface Topography and It’s Deformation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Volume 276, ISBN 0792369459. [Google Scholar]

| Master–Slave(yymmdd) | Orbit Direction | Track | Incidence (Degree) | Pixel Spacing in Slant Range (m) | Pixel Spacing in Azimuth (m) | Wavelength(cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20171107–20171119 | Descending | 6 | 41–46 | 2.3 | 13.9 | 5.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
GUNCE, H.B.; SAN, B.T. Measuring Earthquake-Induced Deformation in the South of Halabjah (Sarpol-e-Zahab) Using Sentinel-1 Data on November 12, 2017. Proceedings 2018, 2, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecrs-2-05159
GUNCE HB, SAN BT. Measuring Earthquake-Induced Deformation in the South of Halabjah (Sarpol-e-Zahab) Using Sentinel-1 Data on November 12, 2017. Proceedings. 2018; 2(7):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecrs-2-05159
Chicago/Turabian StyleGUNCE, Hamit Beran, and Bekir Taner SAN. 2018. "Measuring Earthquake-Induced Deformation in the South of Halabjah (Sarpol-e-Zahab) Using Sentinel-1 Data on November 12, 2017" Proceedings 2, no. 7: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecrs-2-05159
APA StyleGUNCE, H. B., & SAN, B. T. (2018). Measuring Earthquake-Induced Deformation in the South of Halabjah (Sarpol-e-Zahab) Using Sentinel-1 Data on November 12, 2017. Proceedings, 2(7), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecrs-2-05159





