Abstract
In this work, a new generation of eNose systems particularly suited for exhaled breath gas analysis is presented. The developed analyzer system comprises a compact modular, low volume, temperature controlled sensing chamber explicitly tested for the detection of acetone, isoprene, pentane and isopropanol. The eNose system sensing chamber consists of three compartments, each of which can contain 8 analog Metal Oxide (MOX) sensors or 10 digital MOX sensors. Additional sensors within the digital compartment allow for pressure, humidity and temperature measurements. The presented eNose system contains a sensor array with up to 30 physical sensors and provides the ability to discriminate between low VOC concentrations under dry and humid conditions. The MOX sensor signals were analyzed by pattern recognition methods.
1. Introduction
The importance of exhaled breath gas analysis is increasing in medical diagnostics for early disease detection and therapy progress monitoring. [1,2,3,4] This is largely due to the fact that non- communicable diseases have become the leading cause of death worldwide. [5,6] Among them, gastrointestinal cancer is an increasing global health problem. Chemical sensors for breath analysis in medical point-of-care diagnosis have become an emerging field and many research groups are pushing forward the frontier of non-invasive, rapid, portable and potentially low cost medical diagnosis tests for different diseases [3,7].
In this work, a novel and compact eNose system (shown in Figure 1a) that contains a modular sensor system with three exchangeable compartments, capable of hosting up to 30 analog and/or digital commercial sensors is presented. This versatile modular sensor system (shown in Figure 1a,b) allows the combination of different sensor types or sensor technologies within one device.
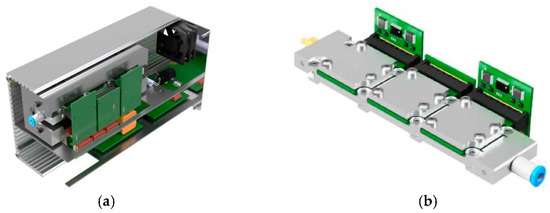
Figure 1.
(a) Novel modular eNose system based on commercial MOX sensors (completely assembled); (b) sensing chamber with three individual compartments, shown here as a combination of analog–digital–analog MOX sensor compartments.
2. Materials and Methods
The analog and digital sensor boards contain many of the most relevant sensors on the market. Each sensor board has a dedicated control board, providing accurate ADC measurements in the case of analog sensor boards and digital sensor communication in the case of digital sensor boards. The control boards also allow for the implementation of temperature modulation cycles. The device is designed to also enable the integration of a third chamber, where sensor prototypes may be connected. These sensors may be controlled and measured through the use of the analog control board.
On the digital sensor board, all sensors are connected via the I2C bus, with the control libraries and drivers implemented in the firmware. To build a small-sized sensing chamber with a volume of less than 3 mL, only Surface Mount Devices (SMD) sensors were selected. The detailed sensor array is shown in Figure 2a for the digital sensors and Figure 2b for the analog sensors. All sensors and the possible signals from each sensor are summarized in Table 1.
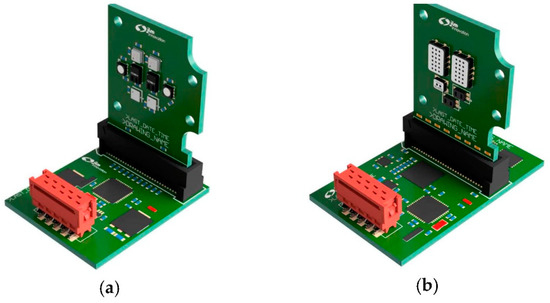
Figure 2.
(a) Digital sensors mounted on the digital sensor board (upper) connected to the digital control board (lower) (b) Analog sensors mounted on the analog sensor board (upper) connected to the analog control board (lower).

Table 1.
Total signals collected per second from a single device using one analog board and one digital board.
The firmware for the digital IDT sensors and the analog sensors allows for the implementation of temperature modulation, considering the maximum temperature from each manufacturer. The temperature and measuring cycle can be implemented in 16 steps, with the temperature set individually for each sensor. The eNose system is temperature controlled at 40 °C.
3. Results
It is well known that stability, selectivity and reproducibility is critical for gas detection based on MOX sensors, especially for applications in the field of breath gas analysis. For this reason, in this work our device is tested for the detection of low concentration analytes under high humidity conditions, similar to breath samples. To conduct the laboratory experiments, synthetic air with known concentration of the target gases (acetone, isoprene, pentane and isopropanol) was used in conjunction with a humidity generator for measurements with high humidity content. The preliminary results of an experiment to discriminate ethanol and acetone are shown in Figure 3a, where one can observe the raw data collected for all the sensors every second. Then, we applied feature extraction [8] followed by Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for discrimination between both gases (Figure 3b). Furthermore, we computed calibration curves for low concentrations of acetone (from 80 ppb up to 1ppm) in dry conditions (Figure 4).
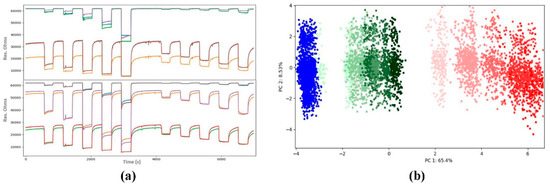
Figure 3.
(a) Raw data for increasing concentrations of ethanol and acetone (b) PCA scores plot for the discrimination of compounds and concentrations.
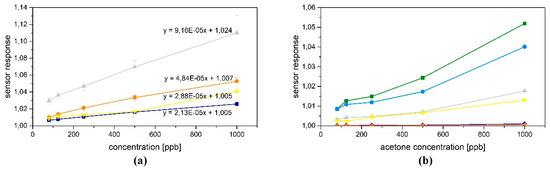
Figure 4.
(a) Calibration curves (acetone) of Sensirion SGP30 H2 (blue), Sensirion SGP30 EtH (orange), Bosch BME680 (grey), IDT ZMOD 4410 (yellow), (b) calibration curves of IDT ZMOD 4410 operated in temperature modulation mode (each line representing a temperature from 50 °C (orange) to 300 °C (green).
4. Conclusions and Outlook
An eNose system capable of measuring commercial analog and digital MOX sensors has been developed and tested under dry and humid conditions with several concentrations of VOCs. Commercial MOX sensors could be successfully integrated in a low volume sensing chamber with temperature modulation cycles. The core parts of the presented instrument are aimed to be used in a modular breath analyzer instrument as a point-of-care breath analysis platform with a specific breath sampling protocol, where the presented commercial gas sensors as well as other experimental sensors can be integrated. Exchangeable sensor chambers with three individual, modular compartments allows for the implementation of different sensors or sensor technologies within one device.
Author Contributions
C.J. and O.G. conceived and designed the experiments; C.J. and J.G. performed the experiments; O.G. and M.P. analyzed the data; J.G., L.T.H. and F.A. contributed infrastructure/materials/analysis tools; K.R. and B.M. proofread the article; C.J. and O.G. wrote the paper.
Acknowledgments
This project has received funding from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) under grant agreement No. GRK2203-PULMOSENS and from the Horizon 2020 Framework Programme of the European Union within the MSCA RISE Project TROPSENSE under project number 645758.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.K.; Noeldge-Schomburg, G.F.E. Diagnostic potential of breath analysis—Focus on volatile organic compounds. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 347, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musteata, F.M. Recent progress in in-vivo sampling and analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 45, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewski, B.; Kesy, M.; Ligor, T.; Amann, A. Human exhaled air analytics: Biomarkers of diseases. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Francesco, F.; Fuoco, R.; Trivella, M.G.; Ceccarini, A. Breath analysis: trends in techniques and clinical applications. Microchem. J. 2005, 79, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.-R.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, P.J. Analysis of volatile organic compounds in the exhaled breath for the diagnosis of lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Natale, C.; Davide, F.; D’Amico, A. Pattern recognition in gas sensing: Well-stated techniques and advances. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1995, 23, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).