E-Skin Pressure Sensors Made by Laser Engraved PDMS Molds †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
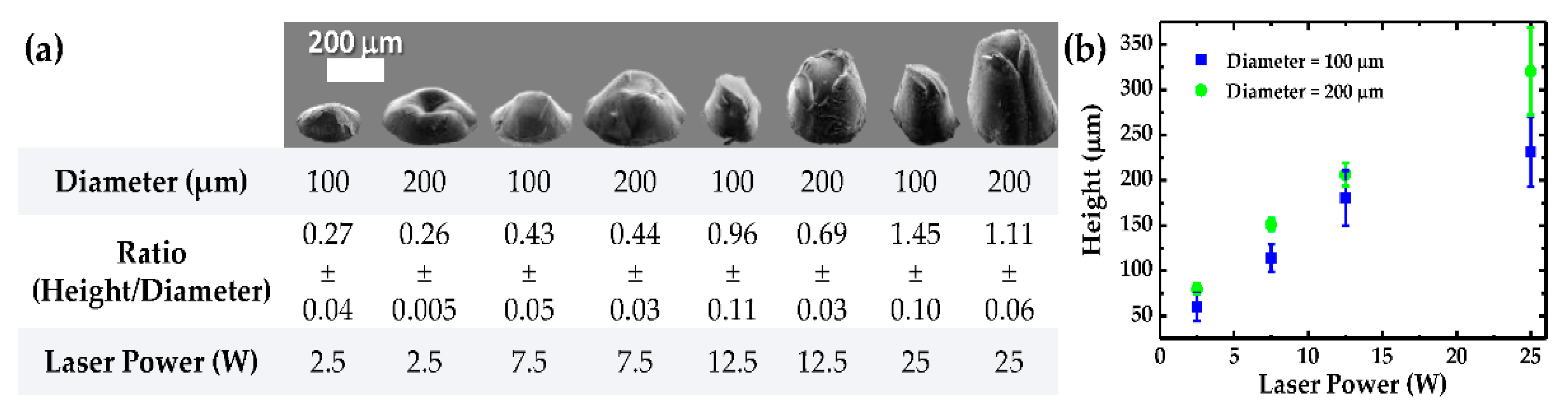
3.1. h-PDMS Patterning
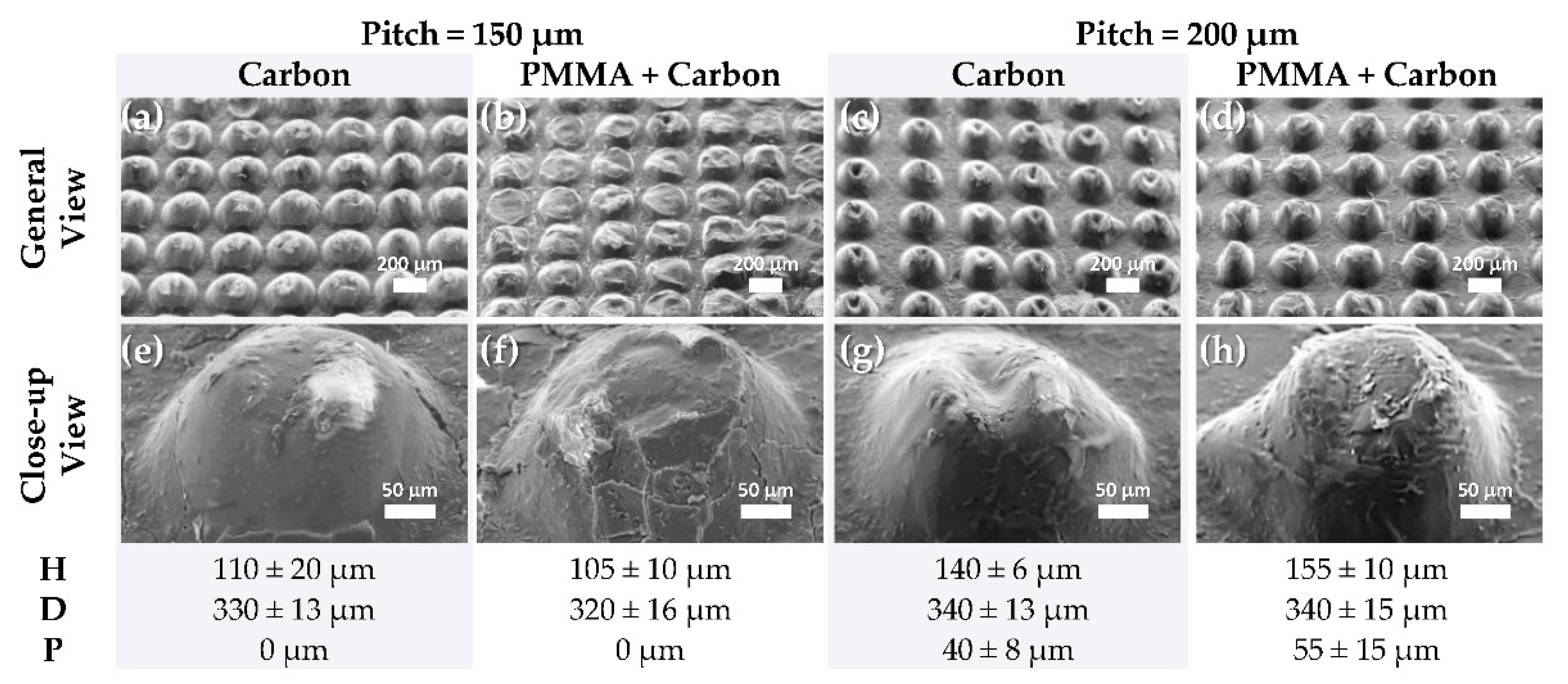
3.2. Characterization of Micro-Structured Films Peeled off from h-PDMS Molds
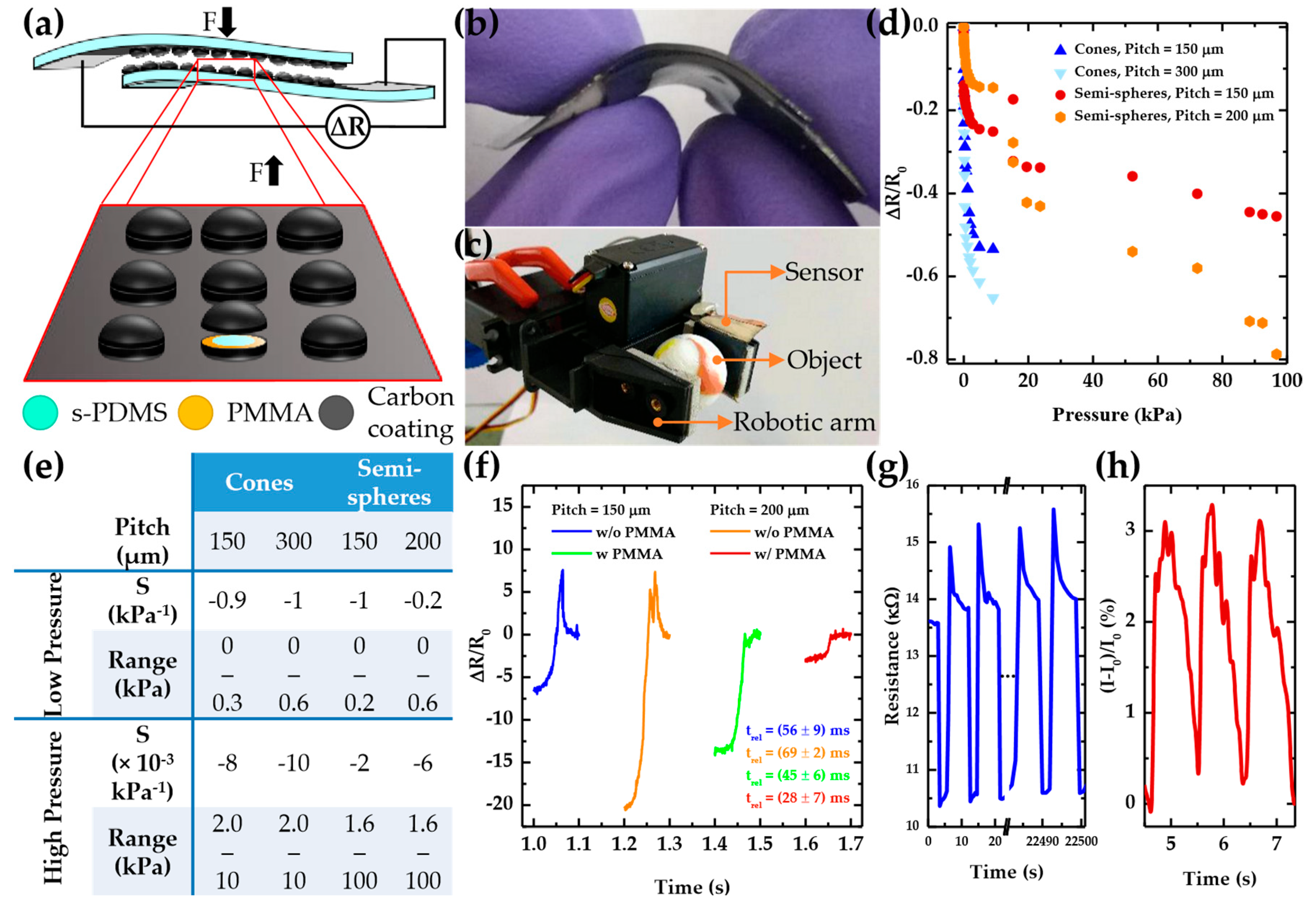
3.3. Electrical Characterization of Sensors
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hammock, M.L.; Chortos, A.; Tee, B.C.K.; Tok, J.B.H.; Bao, Z. 25th anniversary article: The evolution of electronic skin (E-Skin): A brief history, design considerations, and recent progress. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5997–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, G.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Mei, J.; Appleton, A.L.; Kim, D.H.; Wang, H.; Bao, Z. Flexible polymer transistors with high pressure sensitivity for application in electronic skin and health monitoring. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Someya, T.; Kato, Y.; Sekitani, T.; Iba, S.; Noguchi, Y.; Murase, Y.; Kawaguchi, H.; Sakurai, T. Conformable, flexible, large-area networks of pressure and thermal sensors with organic transistor active matrixes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12321–12325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerratt, A.P.; Michaud, H.O.; Lacour, S.P. Elastomeric Electronic Skin for Prosthetic Tactile Sensation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2287–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.P.; Lopes, P.A.; De Almeida, A.T.; Tavakoli, M.; Majudu, C. Fabrication and characterization of bending and pressure sensors for a soft prosthetic hand. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018, 28, 34001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannsfeld, S.C.B.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Stoltenberg, R.M.; Chen, C.V.H.-H.; Barman, S.; Muir, B.V.O.; Sokolov, A.N.; Reese, C.; Bao, Z. Highly sensitive flexible pressure sensors with microstructured rubber dielectric layers. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagdeviren, C.; Su, Y.; Joe, P.; Yona, R.; Liu, Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Huang, Y.Y.; Damadoran, A.R.; Xia, J.; Martin, L.W.; et al. Conformable amplified lead zirconate titanate sensors with enhanced piezoelectric response for cutaneous pressure monitoring. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Lin, L.; Zhu, G.; Wu, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Transparent Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Pressure Sensors based on Micropatterned Plastic Films. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, C.; Lee, G.-Y.; Kim, T.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, H.N.; Ahn, S.-H.; Suh, K.-Y. A flexible and highly sensitive strain-gauge sensor using reversible interlocking of nanofibres. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, T. Silk-molded flexible, ultrasensitive, and highly stable electronic skin for monitoring human physiological signals. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choong, C.-L.; Shim, M.-B.; Lee, B.-S.; Jeon, S.; Ko, D.-S.; Kang, T.-H.; Bae, J.; Lee, S.H.; Byun, K.-E.; Im, J.; et al. Highly stretchable resistive pressure sensors using a conductive elastomeric composite on a micropyramid array. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3451–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lee, Y.; Hong, J.; Ha, M.; Do Jung, Y.; Lim, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Ko, H. Giant Tunneling Piezoresistance of Composite Elastomers with Interlocked Microdome Arrays for Ultrasensitive and Multimodal Electronic Skins. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4689–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Cai, H.; Wu, Y.; Ding, H.; Pan, N.; Wang, X. Highly sensitive and skin-like pressure sensor based on asymmetric double-layered structures of reduced graphite oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.; Pinela, N.; Alves, P.; Santos, R.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Águas, H.; Igreja, R. Piezoresistive E-Skin Sensors Produced with Laser Engraved Molds. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 4, 1800182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, A.d.; Pinela, N.; Alves, P.; Santos, R.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Águas, H.; Igreja, R. E-Skin Pressure Sensors Made by Laser Engraved PDMS Molds. Proceedings 2018, 2, 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2131039
Santos Ad, Pinela N, Alves P, Santos R, Fortunato E, Martins R, Águas H, Igreja R. E-Skin Pressure Sensors Made by Laser Engraved PDMS Molds. Proceedings. 2018; 2(13):1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2131039
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Andreia dos, Nuno Pinela, Pedro Alves, Rodrigo Santos, Elvira Fortunato, Rodrigo Martins, Hugo Águas, and Rui Igreja. 2018. "E-Skin Pressure Sensors Made by Laser Engraved PDMS Molds" Proceedings 2, no. 13: 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2131039
APA StyleSantos, A. d., Pinela, N., Alves, P., Santos, R., Fortunato, E., Martins, R., Águas, H., & Igreja, R. (2018). E-Skin Pressure Sensors Made by Laser Engraved PDMS Molds. Proceedings, 2(13), 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2131039







